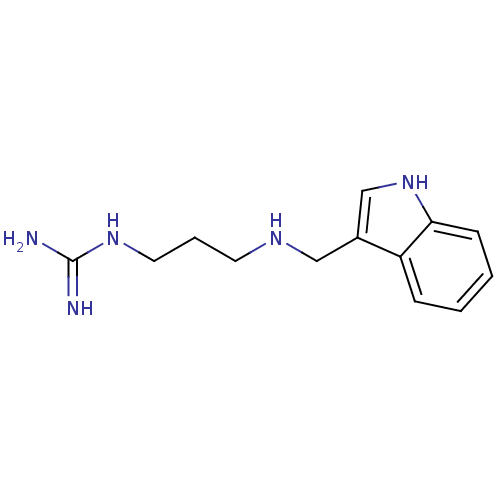
BDBM50111169 CHEMBL8742::N-{3-[(1H-Indol-3-ylmethyl)-amino]-propyl}-guanidine
SMILES NC(=N)NCCCNCc1c[nH]c2ccccc12
InChI Key InChIKey=MATURKKSYUGPNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Data 4 KI
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
 Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50111169
Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50111169
TargetMelanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor(Homo sapiens (Human))
Uppsala University
Curated by ChEMBL
Uppsala University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataKi: 1.20E+4nMAssay Description:Tested for its binding affinity towards human recombinant Melanocortin 1 receptor by using radioligand binding assayMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 4.50E+4nMAssay Description:Tested for its binding affinity towards human recombinant Melanocortin 3 receptor by using radioligand binding assayMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 4.70E+4nMAssay Description:Tested for its binding affinity towards human recombinant Melanocortin 5 receptor by using radioligand binding assayMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 1.07E+5nMAssay Description:Tested for its binding affinity towards human recombinant Melanocortin 4 receptor by using radioligand binding assayMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair