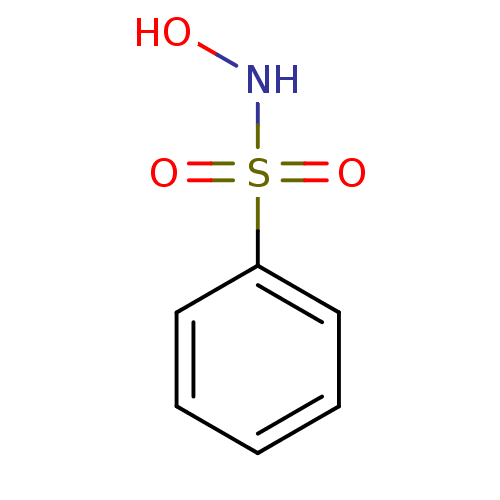
BDBM11372 CHEMBL55310::Hydroxysulfonamide 53::N-hydroxybenzenesulfonamide
SMILES c1ccc(cc1)S(=O)(=O)NO
InChI Key InChIKey=BRMDATNYMUMZLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
 Found 9 hits for monomerid = 11372
Found 9 hits for monomerid = 11372
Affinity DataKi: 26nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 74nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 1.80E+4nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 4.80E+4nMAssay Description:In vitro inhibition against yeast Alcohol dehydrogenaseMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 7.00E+4nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 7.40E+4nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 7.80E+4nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 7.90E+4nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 8.30E+4nMAssay Description:Initial rates of 4-nitrophenyl acetate hydrolysis catalyzed by different CA isozymes were monitored spectrophotometrically at 400 nm. A molar absorpt...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair