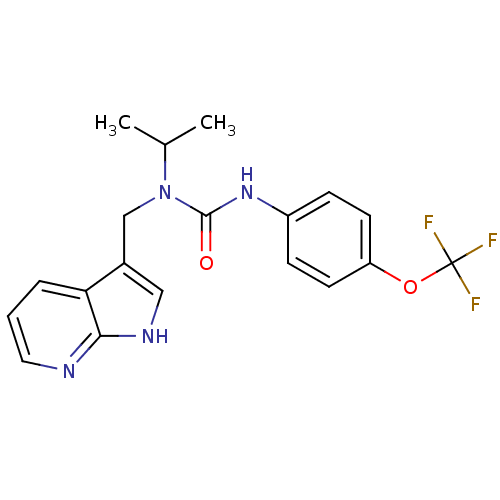
BDBM50446392 CHEMBL3109645::US9181261, 2
SMILES CC(C)N(Cc1c[nH]c2ncccc12)C(=O)Nc1ccc(OC(F)(F)F)cc1
InChI Key InChIKey=GKLLTYZVZSJZPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
 Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50446392
Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50446392
Affinity DataEC50: 11.3nMT: 2°CAssay Description:TrkA kinase activity was measured as the ability of the enzyme to phosphorylate a fluorescently labeled peptide substrate. Buffer salts, reagents, an...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataEC50: 11nMAssay Description:Inhibition of TrkA (unknown origin) using fluorescently labeled peptide substrate after 3 hrsMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human TrkA expressed in human U2OS cells assessed as inhibition of NGF-induced maximum response after 1 hr by beta-galactosidase assayMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 11nMAssay Description:Inhibition of phsophorylated TrkA (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of fluorescently-labelled substrate phosphorylation by CALIPER enzymatic as...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair