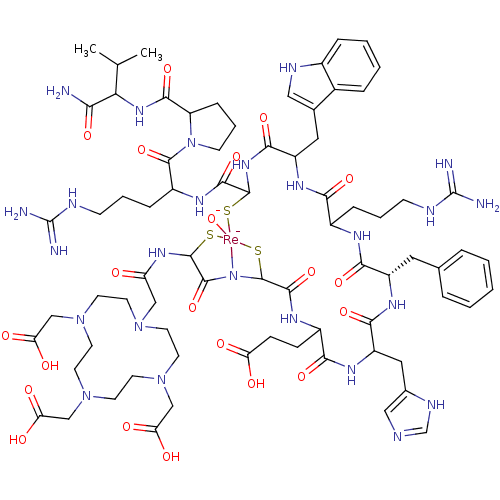
TargetMelanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor(Mus musculus)
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
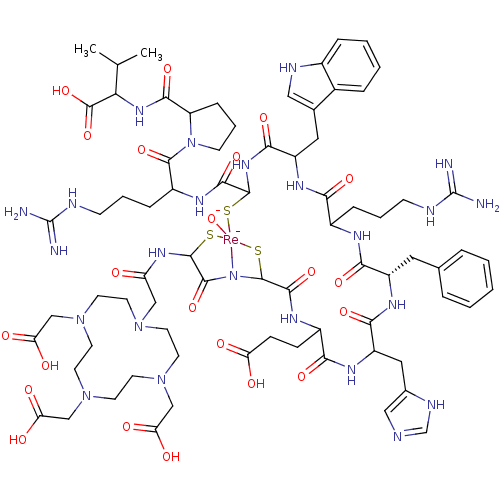
Affinity DataIC50: 0.160nMAssay Description:In vitro binding affinity for the melanoma receptor was determined in the murine melanoma B16/F1 cell lineMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
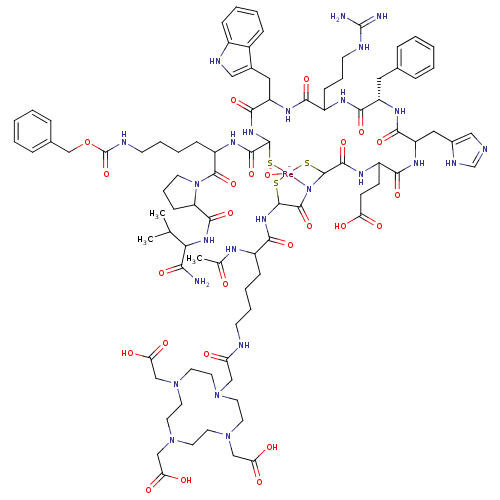
TargetMelanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor(Mus musculus)
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
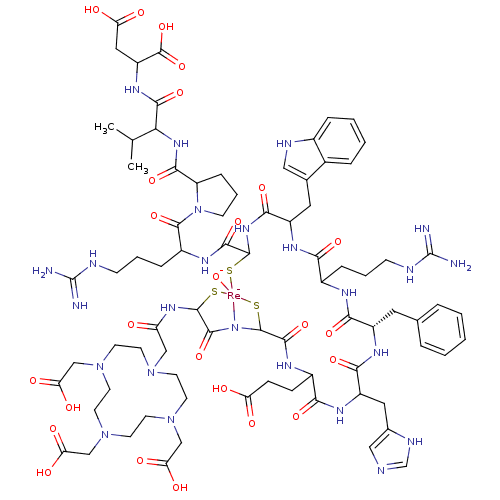
Affinity DataIC50: 0.790nMAssay Description:In vitro binding affinity for the melanoma receptor was determined in the murine melanoma B16/F1 cell lineMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetMelanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor(Mus musculus)
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
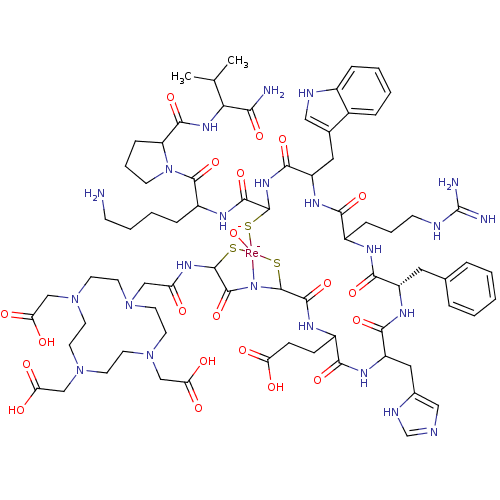
Affinity DataIC50: 1.20nMAssay Description:In vitro binding affinity for the melanoma receptor was determined in the murine melanoma B16/F1 cell lineMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetMelanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor(Mus musculus)
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 2.10nMAssay Description:In vitro binding affinity for the melanoma receptor was determined in the murine melanoma B16/F1 cell lineMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetMelanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor(Mus musculus)
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
University Of Missouri-Columbia
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 3.30nMAssay Description:In vitro binding affinity for the melanoma receptor was determined in the murine melanoma B16/F1 cell lineMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair