 BDBM50448927 US20250129055, Control Dapagliflozin CHEMBL3125318
BDBM50448927 US20250129055, Control Dapagliflozin CHEMBL3125318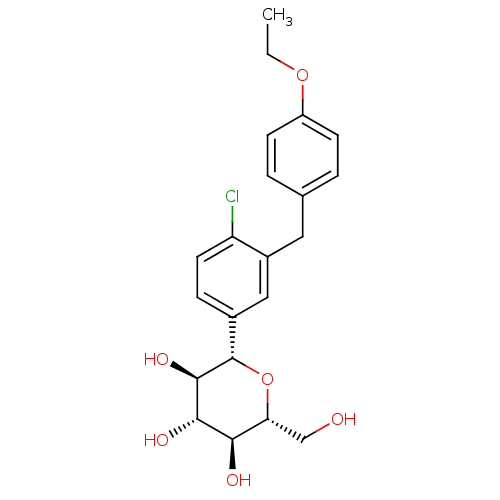 Dapagliflozin BDBM20880 CHEMBL429910 (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-{4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol C-aryl glucoside, 6 BMS-512148
Dapagliflozin BDBM20880 CHEMBL429910 (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-{4-chloro-3-[(4-ethoxyphenyl)methyl]phenyl}-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol C-aryl glucoside, 6 BMS-512148
- Li, Z; Xu, X; Deng, L; Liao, R; Liang, R; Zhang, B; Zhang, L Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of nitric oxide releasing derivatives of dapagliflozin as potential anti-diabetic and anti-thrombotic agents. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 3947-3952 (2018)
- Meng, W; Ellsworth, BA; Nirschl, AA; McCann, PJ; Patel, M; Girotra, RN; Wu, G; Sher, PM; Morrison, EP; Biller, SA; Zahler, R; Deshpande, PP; Pullockaran, A; Hagan, DL; Morgan, N; Taylor, JR; Obermeier, MT; Humphreys, WG; Khanna, A; Discenza, L; Robertson, JG; Wang, A; Han, S; Wetterau, JR; Janovitz, EB; Flint, OP; Whaley, JM; Washburn, WN Discovery of Dapagliflozin: A Potent, Selective Renal Sodium-Dependent Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J Med Chem 51: 1145-9 (2008)
- ChEMBL_739866 (CHEMBL1762926) Displacement of [3H]dapagliflozin from human SGLT2 expressed in CHO cells after 60 mins by scintillation counting
- In Vitro SGLT2 Inhibitory Activity Assay 1. Materials and methods(1) MaterialsThe humanized SGLT2 overexpression cells (CHO-SGLT2) constructed from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells were cultured in 1640 medium (Gibco) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, 10270), subcultured at a ratio of 1:3, and replaced with new culture medium 3 times every week. Fluorescence detection cell culture plates and other culture flasks were purchased from Corning Company. Dapagliflozin was used as a positive control, and the test compounds were compound 2 and compound 3. Appropriate amounts of all compounds were weighed, prepared into 100 mM stock solutions with DMSO, and stored at 4° C. in the dark.(2) Main reagentsPreparation of choline buffer: 140 mM choline chloride, 5 mM KCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgSO4, 1 mM KH2PO4, 10 mM HEPES, pH adjusted to 7.4 with Tris base. The filtration was conducted with a 0.22 m membrane.Preparation of Na+ sodium buffer: 140 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgSO4, 1 mM KH2PO4, 10 mM HEPES, pH adjusted to 7.4 with Tris basePreparation of neutral lysate: 1% Nonidet P-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 40 mM KCl, pH adjusted to 20 mM Tris base.(3) InstrumentsMultifunctional microplate reader Biotek Synergy2(4) Detection of uptake of NBDG by cells:Before the 1-NBDG uptake test, CHO-SGLT2 cells were digested and seeded in a 96-well cell culture plate with a cell number of 40,000/well. After the cells were cultured for 48 h, the medium was discarded, and 100 μl of choline buffer was added to each well. After the cells were starved at 37° C. for 30 min, the choline buffer was discarded and 100 μl of the newly prepared Na+ sodium buffer containing 100 M 1-NBDG and the test compounds (Compound) was added. The solvent DMSO was used as the negative control (Control) for the test compounds.The Na+ sodium buffer without 1-NBDG was used as the blank control (Blank). After 1 h of culture, the incubation solution was discarded. The cells were washed with choline buffer solution 3 times, and then 50 μl of neutral lysate was added to each well to lyse the cells on ice for 10 min. The fluorescence value of each well was detected using a multi-functional microplate reader at Em=485/20 nm and Ex=528/20 nm.(5) Calculation and statistical methodsAt least 3 experimental replicates were set for each compound at indicated concentrations, and the data were expressed as mean±SEM. Uptake amount of 1-NBDG by cells=fluorescence value1-NBDG-fluorescence valueBlank. Inhibition rate on uptake amount of SGLT2 glucose (%)=(uptake amountcontrol−uptake amountcompound)/uptake amountcontrol×100%. Concentration-inhibition rate curves were plotted using Graphpad Prism software, and IC50 values were calculated accordingly.

