 BDBM50129950 EBSELEN
BDBM50129950 EBSELEN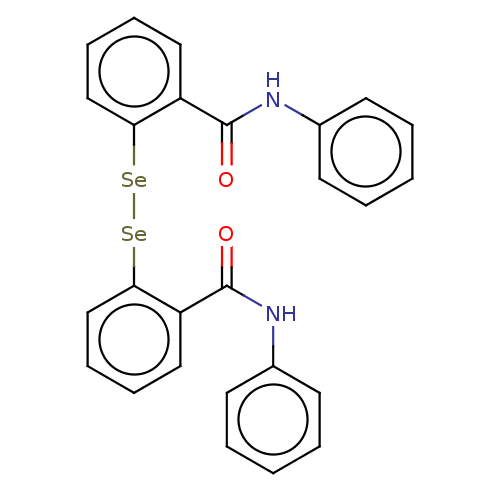 Ebselen Diselenide BDBM50197347
Ebselen Diselenide BDBM50197347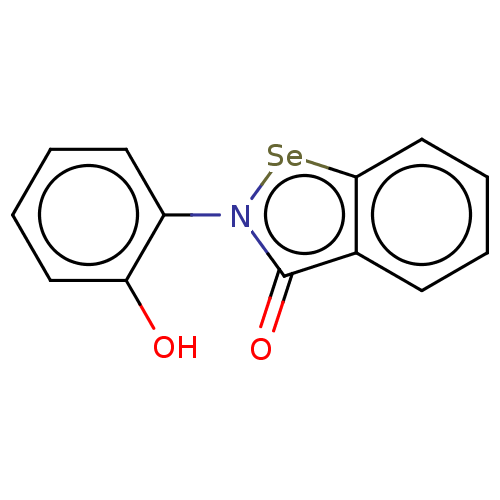 CHEMBL3922662 ebselen derivative 1d BDBM50197301
CHEMBL3922662 ebselen derivative 1d BDBM50197301 ebselen derivative 1e BDBM50197349 CHEMBL3983492
ebselen derivative 1e BDBM50197349 CHEMBL3983492 ebselen derivative 2d CHEMBL3928799 BDBM50197297
ebselen derivative 2d CHEMBL3928799 BDBM50197297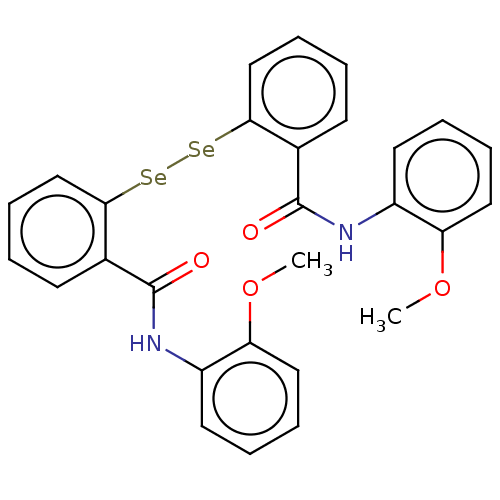 ebselen derivative 2e CHEMBL3912164 BDBM50197300
ebselen derivative 2e CHEMBL3912164 BDBM50197300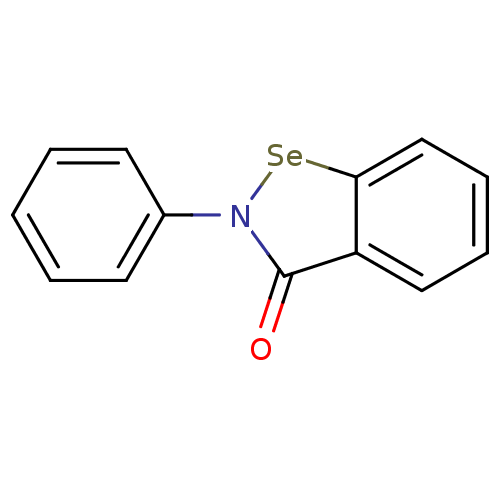 Ebselen (C5) cid_3194 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one MLS000028488 CHEMBL51085 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one 2-phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one med.21724, Compound 153 SMR000058445 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one(Ebselen) BDBM34233 EBSELEN 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselazol-3(2H)-one
Ebselen (C5) cid_3194 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one MLS000028488 CHEMBL51085 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one 2-phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one med.21724, Compound 153 SMR000058445 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one(Ebselen) BDBM34233 EBSELEN 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselazol-3(2H)-one
- Crocetti, L; Catarzi, F; Giovannoni, MP; Vergelli, C; Bartolucci, G; Pallecchi, M; Paoli, P; Rossi, P; Lippi, M; Schepetkin, IA; Quinn, MT; Guerrini, G Ebselen analogues with dual human neutrophil elastase (HNE) inhibitory and antiradical activity. RSC Med Chem 15: 1247-1257 (2024)
- Macegoniuk, K; Tabor, W; Mazzei, L; Cianci, M; Giurg, M; Olech, K; Burda-Grabowska, M; Kaleta, R; Grabowiecka, A; Mucha, A; Ciurli, S; Berlicki, Ł Optimized Ebselen-Based Inhibitors of Bacterial Ureases with Nontypical Mode of Action. J Med Chem 66: 2054-2063 (2023)
- Design, synthesis and antibacterial activity evaluation of ebselen derivatives in NDM-1 producing bacteria.
- Mao, F; Chen, J; Zhou, Q; Luo, Z; Huang, L; Li, X Novel tacrine-ebselen hybrids with improved cholinesterase inhibitory, hydrogen peroxide and peroxynitrite scavenging activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 6737-42 (2013)
- Mukherjee, S; Weiner, WS; Schroeder, CE; Simpson, DS; Hanson, AM; Sweeney, NL; Marvin, RK; Ndjomou, J; Kolli, R; Isailovic, D; Schoenen, FJ; Frick, DN Ebselen Inhibits Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Helicase Binding to Nucleic Acid and Prevents Viral Replication ACS Chem Biol 9: 2393-2403 (2014)
- Leroux, F; Bosc, D; Beghyn, T; Hermant, P; Warenghem, S; Landry, V; Pottiez, V; Guillaume, V; Charton, J; Herledan, A; Urata, S; Liang, W; Sheng, L; Tang, WJ; Deprez, B; Deprez-Poulain, R Identification of ebselen as a potent inhibitor of insulin degrading enzyme by a drug repurposing screening. Eur J Med Chem 179: 557-566 (2019)
- Luo, Z; Sheng, J; Sun, Y; Lu, C; Yan, J; Liu, A; Luo, HB; Huang, L; Li, X Synthesis and evaluation of multi-target-directed ligands against Alzheimer's disease based on the fusion of donepezil and ebselen. J Med Chem 56: 9089-99 (2013)
- Zhang, H; Li, J; Toth, K; Tollefson, AE; Jing, L; Gao, S; Liu, X; Zhan, P Identification of Ebselen derivatives as novel SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors: Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and structure-activity relationships exploration. Bioorg Med Chem 96: (2023)
- Luo, Z; Liang, L; Sheng, J; Pang, Y; Li, J; Huang, L; Li, X Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new series of ebselen derivatives as glutathione peroxidase (GPx) mimics and cholinesterase inhibitors against Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg Med Chem 22: 1355-61 (2014)
- Weglarz-Tomczak, E; Burda-Grabowska, M; Giurg, M; Mucha, A Identification of methionine aminopeptidase 2 as a molecular target of the organoselenium drug ebselen and its derivatives/analogues: Synthesis, inhibitory activity and molecular modeling study. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 5254-5259 (2016)
- EMSA Binding assays containing 25 mM MOPS pH 7.5, 1.25 mM MgCl2, 20 nM Cy5-dT15, and 200 nM NS3h_1b were incubated 5 min at RT. Following addition of indicated concentrations of ebselen, the binding reactions were incubated another 5 min at 23 C.
- Antiviral activity assay To further substantiate the enzymatic inhibition results in vitro, we evaluated whether these compounds could prevent viral replication in cell-based assays. As shown in Fig. 4a, quantitative real-time RT PCR (qRT PCR) demonstrated that, among these compounds, ebselen and N3 showed the strongest antiviral effects at a concentration of 10 μM treatment in SARS-CoV-2-infected Vero cells. We performed a plaque-reduction assay (Extended Data Fig. 8) to further assess the efficacy of these two compounds in protecting cells. Ebselen and N3 displayed inhibition against SARS-CoV-2 with individual half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) values of 4.67 μM and 16.77 μM, respectively (Fig. 4b, c). The dose response curves suggest that both of these compounds may be able to penetrate the cellular membrane to access their targets. Ebselen is an organoselenium compound with anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and cytoprotective properties. This compound has previously been investigated for the treatment of multiple diseases, including bipolar disorders26 and hearing loss27,28. Ebselen has extremely low cytotoxicity (the median lethal dose in rats is >4,600 mg kg−1, when taken orally)29, and its safety in humans has been evaluated in a number of clinical trials27,28,30. These data strongly suggest the clinical potential of ebselen for the treatment of coronaviruses. It is also interesting to note that cinanserin displayed moderate inhibition against SARS-CoV-2 with an EC50 value of 20.61 μM, as shown from qRT PCR analysis (Extended Data Fig. 4). This value is superior to that in the enzymatic inhibition assay, which suggests that cinanserin might have multidrug targets in preventing viral infection. In further studies, the selection and characterization of drug-resistant mutants will help to clarify the mode of action of cinanserin.
 BDBM50129950 EBSELEN
BDBM50129950 EBSELEN Ebselen Diselenide BDBM50197347
Ebselen Diselenide BDBM50197347 CHEMBL3922662 ebselen derivative 1d BDBM50197301
CHEMBL3922662 ebselen derivative 1d BDBM50197301 ebselen derivative 1e BDBM50197349 CHEMBL3983492
ebselen derivative 1e BDBM50197349 CHEMBL3983492 ebselen derivative 2d CHEMBL3928799 BDBM50197297
ebselen derivative 2d CHEMBL3928799 BDBM50197297 ebselen derivative 2e CHEMBL3912164 BDBM50197300
ebselen derivative 2e CHEMBL3912164 BDBM50197300 Ebselen (C5) cid_3194 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one MLS000028488 CHEMBL51085 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one 2-phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one med.21724, Compound 153 SMR000058445 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one(Ebselen) BDBM34233 EBSELEN 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselazol-3(2H)-one
Ebselen (C5) cid_3194 2-phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3-one MLS000028488 CHEMBL51085 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one 2-phenylbenzo[d][1,2]selenazol-3(2H)-one med.21724, Compound 153 SMR000058445 2-Phenyl-benzo[d]isoselenazol-3-one(Ebselen) BDBM34233 EBSELEN 2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselazol-3(2H)-one