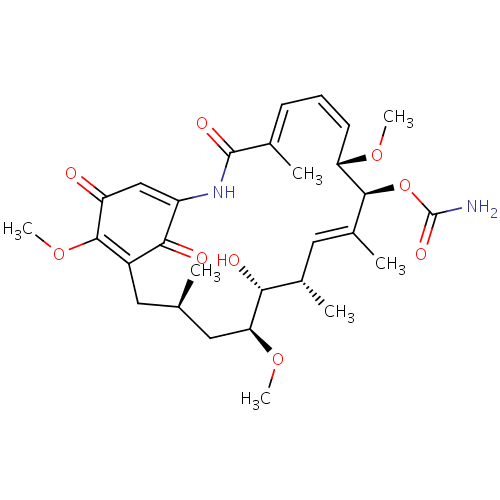
 BDBM20740 Geldanamycin
BDBM20740 Geldanamycin BDBM50008059 GELDANAMYCIN CHEBI:5292
BDBM50008059 GELDANAMYCIN CHEBI:5292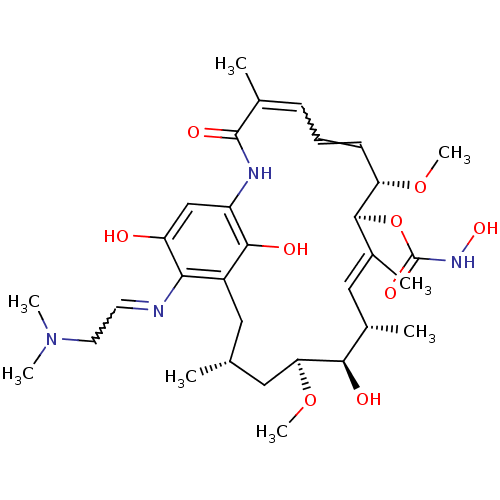 BDBM50173901 Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370404
BDBM50173901 Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370404 BDBM50173911 CHEMBL198417 Geldanamycin derivative
BDBM50173911 CHEMBL198417 Geldanamycin derivative Geldanamycin derivative BDBM50173898 CHEMBL371539
Geldanamycin derivative BDBM50173898 CHEMBL371539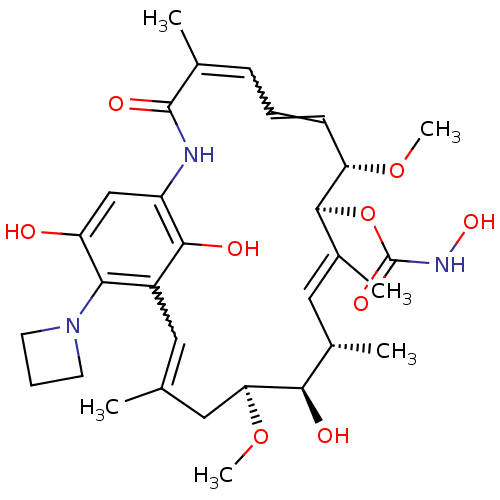 Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370418 BDBM50173905
Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370418 BDBM50173905 (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14,19-trimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate GM-BODIPY BDBM20732 CHEMBL278315 Geldanamycin geldanomycin BODIPY-labeled Geldanamycin
(4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14,19-trimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate GM-BODIPY BDBM20732 CHEMBL278315 Geldanamycin geldanomycin BODIPY-labeled Geldanamycin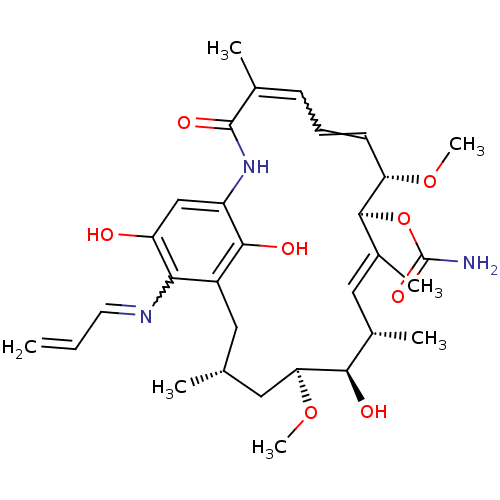 Tanespimycin BDBM15359 GLD-36 17-AAG (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14-dimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-19-(prop-2-en-1-ylamino)-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate 17-(Allylamino)geldanamycin CHEMBL109480 17AAG
Tanespimycin BDBM15359 GLD-36 17-AAG (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14-dimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-19-(prop-2-en-1-ylamino)-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate 17-(Allylamino)geldanamycin CHEMBL109480 17AAG
- Tian, ZQ; Wang, Z; MacMillan, KS; Zhou, Y; Carreras, CW; Mueller, T; Myles, DC; Liu, Y Potent cytotoxic C-11 modified geldanamycin analogues. J Med Chem 52: 3265-73 (2009)
- Kuduk, SD; Zheng, FF; Sepp-Lorenzino, L; Rosen, N; Danishefsky, SJ Synthesis and evaluation of geldanamycin-estradiol hybrids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 1233-8 (1999)
- Rastelli, G; Tian, ZQ; Wang, Z; Myles, D; Liu, Y Structure-based design of 7-carbamate analogs of geldanamycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 5016-21 (2005)
- Chiosis, G; Rosen, N; Sepp-Lorenzino, L LY294002-geldanamycin heterodimers as selective inhibitors of the PI3K and PI3K-related family. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 909-13 (2001)
- Skrzypczak, N; Buczkowski, A; Bohusz, W; Nowak, E; Tokarska, K; Leśniewska, A; Alzebari, AM; Ruszkowski, P; Gdaniec, M; Bartl, F; Przybylski, P Modifications of geldanamycin via CuAAC altering affinity to chaperone protein Hsp90 and cytotoxicity. Eur J Med Chem 256: (2023)
- Roe, SM; Prodromou, C; O'Brien, R; Ladbury, JE; Piper, PW; Pearl, LH Structural basis for inhibition of the Hsp90 molecular chaperone by the antitumor antibiotics radicicol and geldanamycin. J Med Chem 42: 260-6 (1999)
- Le Brazidec, JY; Kamal, A; Busch, D; Thao, L; Zhang, L; Timony, G; Grecko, R; Trent, K; Lough, R; Salazar, T; Khan, S; Burrows, F; Boehm, MF Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new class of geldanamycin derivatives as potent inhibitors of Hsp90. J Med Chem 47: 3865-73 (2004)
- ChEMBL_1871320 (CHEMBL4372487) Displacement of biotin-labeled geldanamycin from His-tagged HSP90alpha NTD (unknown origin) preincubated for 2 hrs followed by biotin-labeled geldanamycin addition and measured after 1 hr by AlphaScreen assay
- ChEMBL_1631535 (CHEMBL3874241) Inhibition of FITC-labeled geldanamycin binding to human Hsp90alpha by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_883046 (CHEMBL2210690) Displacement of biotinylated geldanamycin from human His-tagged Hsp90 by TR-FRET assay
- ChEMBL_1901439 (CHEMBL4403661) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to recombinant human HSP90alpha expressed in Escherichia coli preincubated for 2 hrs followed by Geldanamycin-FITC addition and measured after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_1901440 (CHEMBL4403662) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to recombinant human HSP90beta expressed in Escherichia coli preincubated for 2 hrs followed by Geldanamycin-FITC addition and measured after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_1770412 (CHEMBL4222524) Inhibition of geldanamycin-based probe binding to HSP90 (unknown origin) by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_862684 (CHEMBL2174232) Inhibition of human HSP90 using BODIPY labelled geldanamycin as substrate by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1335736 (CHEMBL3239735) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from HSP90 (unknown origin) after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1901443 (CHEMBL4403665) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 24 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1901444 (CHEMBL4403666) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from HSP90beta (unknown origin) after 24 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1901445 (CHEMBL4403667) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from GRP94 (unknown origin) after 24 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1901446 (CHEMBL4403668) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1901447 (CHEMBL4403669) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from GRP94 (unknown origin) after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2035398 (CHEMBL4689556) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from GRP94 (unknown origin) after 24 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2035399 (CHEMBL4689557) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 24 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1901441 (CHEMBL4403663) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to N-terminal His-tagged recombinant human GRP94 expressed in Escherichia coli preincubated for 2 hrs followed by Geldanamycin-FITC addition and measured after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_1336948 (CHEMBL3242256) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from recombinant HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1336949 (CHEMBL3242257) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from recombinant HSP90beta (unknown origin) after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1336950 (CHEMBL3242258) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from recombinant GRP94 (unknown origin) after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1336951 (CHEMBL3242259) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from recombinant TRAP1 (unknown origin) after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1743107 (CHEMBL4158857) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to canine GRP94 incubated for 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1774365 (CHEMBL4231357) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 3 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_770130 (CHEMBL1832709) Displacement of FITC-labeled geldanamycin from human recombinant HSP90alpha after 24 hrs by fluorescence displacement assay
- ChEMBL_1708207 (CHEMBL4059440) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from human HSP90alpha at 277 K after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1714080 (CHEMBL4124129) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to recombinant human HSP90alpha expressed in Escherichia coli by fluorescence anisotropy method
- ChEMBL_1743108 (CHEMBL4158858) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to HSP90alpha (unknown origin) incubated for 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_535423 (CHEMBL984452) Inhibition of Hsp90 in human SKBR3 cells assessed as interaction with Cy3b-conjugated geldanamycin by FP assay
- ChEMBL_647264 (CHEMBL1217470) Displacement of biotin-labeled geldanamycin from N-terminal His-tagged human recombinant HSP90alpha expressed in Escherichia coli
- ChEMBL_1901442 (CHEMBL4403664) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to N-terminal His-tagged recombinant human TRAP1 (60 to 704 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli preincubated for 2 hrs followed by Geldanamycin-FITC addition and measured after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay
- ChEBML_1691111 Inhibition of fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled geldanamycin binding to recombinant Hsp90alpha (unknown origin) after 1 hr by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1738230 (CHEMBL4153980) Inhibition of FITC-labeled geldanamycin binding to recombinant HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 1 hr by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_487670 (CHEMBL1009438) Inhibition of Hsp90 in human MCF7 cell lysates assessed as interaction with Cy3b-conjugated geldanamycin by FP assay
- ChEMBL_944926 (CHEMBL2343965) Inhibition of biotinylated geldanamycin binding to human recombinant Hsp90 ATP binding domain after 60 mins by fluorescence assay
- ChEMBL_1708206 (CHEMBL4059439) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from full length dog GRP94 at 277 K after 5 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2015035 (CHEMBL4668613) Displacement of biotin-labelled geldanamycin from human HSP90 (D9 to E236 residues) incubated for 3 hrs by FRET assay
- ChEMBL_2051997 (CHEMBL4706998) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from N-terminal HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_2052002 (CHEMBL4707003) Displacement of FITC-geldanamycin from N-terminal GRP94 (unknown origin) after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_2110128 (CHEMBL4818803) Inhibition of HSP90 (unknown origin) assessed as competition of fluorescently labelled geldanamycin binding after 2 hrs by microplate reader analysis
- ChEMBL_1781423 (CHEMBL4252940) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to N-terminal domain of recombinant full-length HSP90alpha (unknown origin) after 16 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_757006 (CHEMBL1803755) Binding affinity to human Hsp90 N-terminal domain (1 to 241) expressed in insect Sf9 cells by SPR analysis in presence of 20 uM geldanamycin
- ChEMBL_1875120 (CHEMBL4376409) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSP90alpha expressed in Escherichia coli after 3 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1714076 (CHEMBL4124125) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to recombinant human N-terminal His6-tagged TRAP1 (60 to 704 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21-CodonPlus-RIL by fluorescence anisotropy method
- ChEMBL_1635598 (CHEMBL3878496) Inhibition of fluorescein isothiocyanate labeled geldanamycin binding to N-terminal domain of full length human recombinant Hsp90alpha expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) after 14 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1743073 (CHEMBL4158823) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to human His-tagged HSP90alpha N-terminal domain (1 to 236 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21star (DE3) after 4 hrs by FP assay relative to control
- ChEMBL_1840545 (CHEMBL4340844) Inhibition of FITC-geldanamycin binding to recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSP90alpha N-terminal domain (1 to 732 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli after 1 hr by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2091213 (CHEMBL4772476) Inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal Hsi-tagged HSP90alpha (1 to 732 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli measured after 2 to 3 hrs by FITC-labeled geldanamycin probe based fluorescence polarization assay
- FP-based equilibrium competition assay EC50 values were determined by FP-based equilibrium competition assay performed in 384-well format using whole cell lysates prepared from C. neoformans (a) and C. albicans (c) and serial compound dilutions. All determinations were performed in duplicate. To calculate fold-selectivity (b), the EC50 value determined in human HepG2 cell lysate was divided by the EC50 value determined in fungal cell lysate. The resulting ratio was then normalized to values determined in the same assay for the non-selective inhibitor geldanamycin using lysate of each cell type. Results for key selective compounds were confirmed by repeat assay.
- Inhibition Assay Hsp90 protein is obtained from Stressgen (Cat#SPP-770). Assay buffer: 100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2. Malachite green (0.0812% w/v) (M9636) and polyviny alcohol USP (2.32% w/v) (P1097) are obtained from Sigma. A Malachite Green Assay (see Methods Mol Med, 2003, 85:149 for method details) is used for examination of ATPase activity of Hsp90 protein. Briefly, Hsp90 protein in assay buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2) is mixed with ATP alone (negative control) or in the presence of Geldanamycin (a positive control) or a compound of the invention in a 96-well plate. Malachite green reagent is added to the reaction. The mixtures are incubated at 37 C. for 4 hours and sodium citrate buffer (34% w/v sodium citrate) is added to the reaction.
- AlphaScreen Competitive Assay HSP90-binding activity was determined by an AlphaScreen competitive assay system. The purified HSP90 solution was diluted with a binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% Triton-X 100, 1 mM DTT, 0.1% BSA) and added to a 384-well plate (#3673, Corning Inc.) containing test substances. After reaction at room temperature for 2 hours, biotinylated geldanamycin was added thereto at a concentration of 40 nM/well and further reacted for 1 hour. Detection mix (20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5), 0.5% BSA, 0.04 mg/mL Nickel Chelate Acceptor beads, 0.04 mg/mL Streptavidin-coated Donor beads) (#6760619C, PerkinElmer, Inc.) was added to each well in an amount equal to the amount of the reaction solution and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour in the dark. Then, fluorescence intensity was measured using Multilabel Plate Reader EnVision (PerkinElmer, Inc.).
- AlphaScreen Competitive Assay The HSP90-binding activity was measured by an AlphaScreen competitive assay system. The purified HSP90 solution was diluted with a binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% Triton-X100, 1 mM DTT, 0.1% BSA) and added to a 384-well plate (No. 3673, Corning Incorporated) containing test substances. After reaction at room temperature for 2 hours, biotin-labeled geldanamycin was added to each reaction solution in an amount of 40 nM, followed by reaction for further 1 hour. Detection mix (20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5), 0.5% BSA, 0.04 mg/mL Nickel Chelate Acceptor beads, 0.04 mg/mL Streptavidin-coated Donor beads) (No. 6760619C, Perkin Elmer, Inc.) was added to each well in the same amount as that of the reaction solution. After reaction in a dark place at room temperature for 1 hour, the fluorescence intensity in each well was measured with a multilabel plate reader, EnVision (Perkin Elmer, Inc.).
- AlphaScreen Competitive Assay The HSP90-binding activity was measured by an AlphaScreen competitive assay system. The purified HSP90 solution was diluted with a binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% Triton-X100, 1 mM DTT, 0.1% BSA) and added to a 384-well plate (No. 3673, Corning Incorporated) containing test substances. After reaction at room temperature for 2 hr, biotin-labeled geldanamycin was added to each reaction solution in an amount of 40 nM, followed by reaction for further 1 hr. Detection mix (20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.5), 0.5% BSA, 0.04 mg/mL Nickel Chelate Acceptor beads, 0.04 mg/mL Streptavidin-coated Donor beads) (No. 6760619C, Perkin Elmer, Inc.) was added to each well in the same amount as that of the reaction solution. After reaction in a dark place at room temperature for 1 hr, the fluorescence intensity in each well was measured with a multilabel plate reader, EnVision (Perkin Elmer, Inc.).
- Fluorescence Polarization Assay An in vitro competition fluorescence polarization assay in which a test compound competes with a fluorescent probe for binding to the binding domain of human recombinant HSP90. The reaction can be followed kinetically using fluorescence (excitation lamda==485 nm; emission lamda==538 nm). The binding affinity of the test compound to HSP90 is determined by the changes in the polarized fluorescence; the intensity of the polarized fluorescence is proportional to the fraction of bound probe. To each test well, an aliquot of buffer, 2 ul of test compound in 10% DMSO, 4 ul of 6.25 nM of TSD FP probe, 4 ul of 12.5 nM of purified HSP90a protein were added. For positive control, 1 uM geldanamycin (GM) was used instead of the test compound (GM is a natural benzoquinone ansamycin that is known to bind to the N-terminal ATP-binding pocket of HSP90 and inhibits ATP binding and ATP-dependent chaperone activities). For negative control, no inhibitor was added.
- Inhibition Assay Hsp90 protein is obtained from Stressgen (Cat#SPP-770). Assay buffer: 100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2. Malachite green (0.0812% w/v) (M9636) and polyvinyl alcohol USP (2.32% w/v) (P1097) are obtained from Sigma. A Malachite Green Assay (see Methods Mol Med, 2003, 85:149 for method details) is used for examination of ATPase activity of Hsp90 protein. Briefly, Hsp90 protein in assay buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2) is mixed with ATP alone (negative control) or in the presence of Geldanamycin (a positive control) or a compound of the invention in a 96-well plate. Malachite green reagent is added to the reaction. The mixtures are incubated at 37° C. for 4 hours and sodium citrate buffer (34% w/v sodium citrate) is added to the reaction. The plate is read by an ELISA reader with an absorbance at 620 nm.
- Inhibition Assay Hsp90 protein is obtained from Stressgen (Cat#SPP-770). Assay buffer: 100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2. Malachite green (0.0812% w/v) (M9636) and polyvinyl alcohol USP (2.32% w/v) (P1097) are obtained from Sigma. A Malachite Green Assay (see Methods Mol Med, 2003, 85:149 for method details) is used for examination of ATPase activity of Hsp90 protein. Briefly, Hsp90 protein in assay buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2) is mixed with ATP alone (negative control) or in the presence of Geldanamycin (a positive control) or a compound of the invention in a 96-well plate. Malachite green reagent is added to the reaction. The mixtures are incubated at 37° C. for 4 hours and sodium citrate buffer (34% w/v sodium citrate) is added to the reaction. The plate is read by an ELISA reader with an absorbance at 620 nm.
- Malachite Green Assay Hsp90 protein is obtained from Stressgen (Cat#SPP-770). Assay buffer: 100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2. Malachite green (0.0812% w/v) (M9636) and polyvinyl alcohol USP (2.32% w/v) (P1097) are obtained from Sigma. A Malachite Green Assay (see Methods Mol Med, 2003, 85:149 for method details) is used for examination of ATPase activity of Hsp90 protein. Briefly, Hsp90 protein in assay buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, Ph7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2) is mixed with ATP alone (negative control) or in the presence of Geldanamycin (a positive control) or a compound of the invention in a 96-well plate. Malachite green reagent is added to the reaction. The mixtures are incubated at 37° C. for 4 hours and sodium citrate buffer (34% w/v sodium citrate) is added to the reaction. The plate is read by an ELISA reader with an absorbance at 620 nm.
- fluorescence polarization assay The fluorescent labeled small molecule used in the present invention was VER-00051001 (synthesized by reference to the synthetic method described in JMC, 2008, 51, 196-218). The reaction was carried out in a 384-well black plate, using the reaction hydrophobic protein HFB buffer: 100 mM Tris.Cl pH 7.4, 20 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2, 5 μg/mL BSA, 25 nM full-length Hsp90U, 10 nM VER-51001. The volume of the reaction system was 50 mL, containing 5 nM GM-BODIPY (geldanamycin), 30 nM HSP90 and the test small molecular compound or DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), wherein the DMSO content was 2% o. Additional two group wells were established, wherein the wells only added with HFB buffer were used as blank controls, and the wells further added with 5 nM GM-BODIPY were used as negative controls. The reaction was carried out at 4° C. for 12-16 hours. The mP value was measured by Biotek microplate reader at 485 nm of excitation wavelength and 535 nm of emission wavelength. The inhibition rate was calculated using the following equation:(Compound-free mP−Compound mP)/(Compound-free mP−negative control mP)×100%After the inhibitory rates of the compound at different concentrations were calculated, the IC50 of the compound can be calculated.
- Tumor Hsp90 Inhibitors Dose Response Confirmation A fluorescence polarization based HTS assay has been developed and optimized for the identification of Hsp90 inhibitors by using tumor cell lysate Hsp90 and fluorescently (Cy3B) labeled geldanamycin (cy3B-GM) in 384-well black assay plate format. Fluorescence polarization in mP is measured at room temperature with an Analyst HT reader. An excitation filter at 545nm and an emission filter at 610 to 675nm are used with a dichroic mirror of 565nm. Assay data are analyzed using BioAssay software from CambridgeSoft. Percentage of inhibition is calculated by the equation based on per plate: % of Inhibition = 100 - ((mPc - mPf)/(mPb - mPf)) * 100 Where mPc is the recorded mP from compound wells; mPf is average recorded mP from cy3B-GM only wells; mPb is average recorded mP from wells containing cy3B-GM and NCI-N417 lysate. For each compound, a 4 parameter sigmoidal dose-response curve was fitted using BioAssay software from CambridgeSoft. The reported IC50 values were generated from fitted curves by solving for X-intercept at the 50% level of Y-intercept. When the highest concentration tested (50 micromolar) did not result in greater than 50% inhibition, the IC50 is reported as greater than 50 micromolar. Similarly, when the lowest concentration tested (1.5625 micromolar) resulted in greater than 50% inhibition, the IC50 is reported as less than 1.5625 micromolar. Compounds with IC50 values of greater than 30 micromolar were considered inactive.
 BDBM20740 Geldanamycin
BDBM20740 Geldanamycin BDBM50008059 GELDANAMYCIN CHEBI:5292
BDBM50008059 GELDANAMYCIN CHEBI:5292 BDBM50173901 Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370404
BDBM50173901 Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370404 BDBM50173911 CHEMBL198417 Geldanamycin derivative
BDBM50173911 CHEMBL198417 Geldanamycin derivative Geldanamycin derivative BDBM50173898 CHEMBL371539
Geldanamycin derivative BDBM50173898 CHEMBL371539 Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370418 BDBM50173905
Geldanamycin derivative CHEMBL370418 BDBM50173905 (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14,19-trimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate GM-BODIPY BDBM20732 CHEMBL278315 Geldanamycin geldanomycin BODIPY-labeled Geldanamycin
(4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14,19-trimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate GM-BODIPY BDBM20732 CHEMBL278315 Geldanamycin geldanomycin BODIPY-labeled Geldanamycin Tanespimycin BDBM15359 GLD-36 17-AAG (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14-dimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-19-(prop-2-en-1-ylamino)-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate 17-(Allylamino)geldanamycin CHEMBL109480 17AAG
Tanespimycin BDBM15359 GLD-36 17-AAG (4E,6Z,8S,9S,10E,12S,13R,14S,16R)-13-hydroxy-8,14-dimethoxy-4,10,12,16-tetramethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-19-(prop-2-en-1-ylamino)-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate 17-(Allylamino)geldanamycin CHEMBL109480 17AAG