Target (2)
Compound (3)
Assay (80)
ChEMBL_521101 (CHEMBL960362) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease assessed as ammonia production by indophenol method ChEMBL_1274834 (CHEMBL3090408) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as ammonia production after 30 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1508769 (CHEMBL3603108) Inhibition of jack bean Urease assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1885469 (CHEMBL4387051) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production by Berthelot colorimetric method ChEMBL_684536 (CHEMBL1285239) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_774847 (CHEMBL1913189) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as ammonia production after 30 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1508397 (CHEMBL3602335) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori urease assessed as ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol method ChEMBL_986745 (CHEMBL2438166) Inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins ChEMBL_2214302 (CHEMBL5127434) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori urease assessed as measuring ammonia production incubated for 1.5 hr by indophenol method ChEMBL_605129 (CHEMBL1064672) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease assessed as ammonia production after 3 hrs by indophenol method ChEMBL_829354 (CHEMBL2060145) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori urease assessed as ammonia production preincubated for 3 hrs measured by indophenol method ChEMBL_956072 (CHEMBL2379097) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease-mediated ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol method ChEMBL_980091 (CHEMBL2423528) Inhibition of Jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as production of ammonia after 15 mins ChEMBL_1809971 (CHEMBL4309431) Inhibition of mouse kidney glutaminase assessed as ammonia formation using glutamine as substrate by Nessler's reagent based assay ChEMBL_1929320 (CHEMBL4432496) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease assessed as amount of ammonia after 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_931029 (CHEMBL3070477) Inhibition of Canavalia ensiformis (jack bean) urease assessed as release of ammonia after 30 min by indophenol method ChEMBL_1293004 (CHEMBL3122983) Inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1508665 (CHEMBL3602820) Inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by Weatherburn assay ChEMBL_1929068 (CHEMBL4432244) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 50 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_923491 (CHEMBL3054040) Inhibition of Canavalia ensiformis (jack bean) urease assessed as inhibition of ammonia production after 15 min by indophenol method ChEMBL_1523760 (CHEMBL3631998) Inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production incubated for 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1434171 (CHEMBL3383979) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production incubated at 30 degC for 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1590361 (CHEMBL3830509) Inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as reduction in ammonia production after 30 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1740612 (CHEMBL4156362) Inhibition of urease in Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as reduction in ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol method ChEMBL_1747806 (CHEMBL4182316) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production using urea as substrate after 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1921930 (CHEMBL4424775) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production using urea as substrate after 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_1921931 (CHEMBL4424776) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production using urea as substrate after 30 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_981464 (CHEMBL2428642) Inhibition of urease extracted from Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol-based method ChEMBL_1505977 (CHEMBL3595645) Inhibition of urease in Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as ammonia production incubated for 1.5 hrs prior to testing by indophenol method ChEMBL_2014729 (CHEMBL4668307) Inhibition of jack bean urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production using urea as substrate incubated for 15 mins by indophenol method ChEMBL_2467420 Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori urease using urea as substrate assessed as decrease in ammonia production incubated for 0.5 hrs by indole phenol method ChEMBL_684016 (CHEMBL1286287) Inhibition of cell free Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production by indophenol based Berthelot color reaction method ChEMBL_684017 (CHEMBL1286288) Inhibition of urease in intact Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as reduction in ammonia production by indophenol based Berthelot color reaction method ChEMBL_981463 (CHEMBL2428641) Inhibition of urease in Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 intact cell assessed as ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol-based method ChEMBL_1293003 (CHEMBL3122982) Competitive inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by Lineweaver-Burk/Dixon plot analysis ChEMBL_1505976 (CHEMBL3595644) Inhibition of urease isolated from Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as ammonia production incubated for 1.5 hrs prior to testing by indophenol method ChEMBL_1736059 (CHEMBL4151595) Activation of ATPase activity of ABCG2 (unknown origin) expressed in High Five insect cell membranes by ascorbic acid ammonia molybdate reaction based colorimetry ChEMBL_1875742 (CHEMBL4377136) Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum ADA assessed as reduction in formation of ammonia using adenosine as substrate incubated for 15 mins by spectrophotometric analysis ChEMBL_1293002 (CHEMBL3122981) Non-competitive inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by Lineweaver-Burk/Dixon plot analysis ChEMBL_1293005 (CHEMBL3122984) Mixed-type inhibition of jack bean urease using urea as substrate assessed as ammonia production after 15 mins by Lineweaver-Burk/Dixon plot analysis ChEMBL_1665912 (CHEMBL4015708) Activation of ABCG2 (unknown origin) ATPase activity expressed in baculovirus infected high five cell membranes by ascorbic acid/ammonia molybdate reaction-based colorimetric analysis ChEMBL_1665915 (CHEMBL4015711) Inhibition of ABCG2 (unknown origin) ATPase activity expressed in baculovirus infected high five cell membranes by ascorbic acid/ammonia molybdate reaction-based colorimetric analysis ChEMBL_1740613 (CHEMBL4156363) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs under cell free condition by indophenol method ChEMBL_1809973 (CHEMBL4309433) Inhibition of mouse kidney glutaminase assessed as ammonia formation at 0.1 uM using glutamine as substrate by Nessler's reagent based assay relative to control ChEMBL_1740616 (CHEMBL4156366) Mixed type non-competitive inhibition of urease in Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as reduction in ammonia production preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol method ChEMBL_1776582 (CHEMBL4233574) Inhibition of urease in Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 assessed as reduction in ammonia production using urea as substrate preincubated for 1.5 hrs by indophenol method Enzyme-coupled Assay Enzyme-coupled assay using oleamide as substrate where stoichiometic quantites of NAD are formed upon the generation of ammonia from oleamide by FAAH hydrolysis. ChEMBL_1717975 (CHEMBL4132975) Activation of ABCG2 ATPase activity (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected high5 cell membranes after 20 mins by ascorbic acid ammonia molybdate reaction based colorimetric assay ChEMBL_1717978 (CHEMBL4132978) Inhibition of ABCG2 ATPase activity (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected high5 cell membranes after 20 mins by ascorbic acid ammonia molybdate reaction based colorimetric assay ChEMBL_851318 (CHEMBL2156025) Inhibition of human recombinant ASNS expressed in Sf9 cells assessed as assessed as initial inhibition constant for ammonia dependent production of inorganic pyrophosphate by spectrophotometry analysis ChEMBL_851327 (CHEMBL2156034) Inhibition of human recombinant ASNS expressed in Sf9 cells assessed as assessed as overall inhibition constant for ammonia dependent production of inorganic pyrophosphate by spectrophotometry analysis ChEBML_1697859 Activation of recombinant human ABCG2 ATPase activity expressed in baculovirus infected High five insect cell membranes after 20 mins by ascorbic acid ammonia molybdate reaction-based colorimetric method ChEMBL_1520796 (CHEMBL3625950) Inhibition of jack beans urease assessed as hydrolysis of urea into ammonia preincubated for 10 mins followed by urea addition measured after 10 mins by Berthelot assay GDH-Coupled Nicotinamidase Assay Nicotinamidase activity was monitored by coupling the production of ammonia with the consumption of NAD(P)H by the enzyme bovine glutamate dehydrogenase from Sigma. ChEMBL_1697859 (CHEMBL4048749) Activation of recombinant human ABCG2 ATPase activity expressed in baculovirus infected High five insect cell membranes after 20 mins by ascorbic acid ammonia molybdate reaction-based colorimetric method ChEMBL_1776581 (CHEMBL4233573) Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 43504 urease assessed as reduction in ammonia production using urea as substrate preincubated for 1.5 hrs under cell free condition by indophenol method ChEMBL_1515820 (CHEMBL3614582) Inhibition of recombinant human DAAO expressed in HEK cells using D-serine as substrate assessed as formation of alpha-keto acid, ammonia, hydrogen peroxidase after 20 mins by horseradish peroxidase/o-phenylenediamine-based assay FAAH Inhibition Assay (15 min Preincubation) FAAH activity was measured by following the production of ammonia generated from the hydrolysis of oleamide by FAAH. GDH catalyzes the condensation of ammonia and alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamate with a concomitant conversion of NADH to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidized form (NAD+), which is spectrophotometrically measured at 340 nm. Test compounds were preincubated with FAAH at room temperature for 15 min. The reaction was initiated with the addition of substrate oleamide. The absorbance at 340 nm was collected over a period of 30 min with reading taken in 10-s intervals using a spectrophotometer. FAAH Inhibition Assay (30 min Preincubation) FAAH activity was measured by following the production of ammonia generated from the hydrolysis of oleamide by FAAH. GDH catalyzes the condensation of ammonia and alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamate with a concomitant conversion of NADH to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidized form (NAD+), which is spectrophotometrically measured at 340 nm. Test compounds were preincubated with FAAH at room temperature for 30 min. The reaction was initiated with the addition of substrate oleamide. The absorbance at 340 nm was collected over a period of 30 min with reading taken in 10-s intervals using a spectrophotometer. FAAH Inhibition Assay (5 min Preincubation) FAAH activity was measured by following the production of ammonia generated from the hydrolysis of oleamide by FAAH. GDH catalyzes the condensation of ammonia and alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamate with a concomitant conversion of NADH to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidized form (NAD+), which is spectrophotometrically measured at 340 nm. Test compounds were preincubated with FAAH at room temperature for 5 min. The reaction was initiated with the addition of substrate oleamide. The absorbance at 340 nm was collected over a period of 30 min with reading taken in 10-s intervals using a spectrophotometer. FAAH Inhibition Assay (60 min Preincubation) FAAH activity was measured by following the production of ammonia generated from the hydrolysis of oleamide by FAAH. GDH catalyzes the condensation of ammonia and alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamate with a concomitant conversion of NADH to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, oxidized form (NAD+), which is spectrophotometrically measured at 340 nm. Test compounds were preincubated with FAAH at room temperature for 60 min. The reaction was initiated with the addition of substrate oleamide. The absorbance at 340 nm was collected over a period of 30 min with reading taken in 10-s intervals using a spectrophotometer. In vitro D-Amino Acid Oxidase Assay D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) was assayed in a 96-well plate format. D-serine was oxidatively deaminated by porcine D-amino acid oxidase in the presence of molecular oxygen and flavin adenosine dinucleotide (FAD) to yield the corresponding alpha-keto acid, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. The resulting hydrogen peroxide was quantified using horseradish peroxidase and o-phenylenediamine, which displays a defined yellow absorbance at 411 nm when it becomes oxidized. Carbonic Anhydrase II Kinetic Assay Kinetic studies were performed by using different concentration of inhibitors over different concentrations of substrate (4-NPA) such as 0.175, 0.35, 0.70 and 1.40 mM. The enzyme 0.2 mg/mL concentration for each well was used after dissolving in de-ionized water. HEPES-tris ammonia was used as buffer at pH of 7.4. The change in absorbance was measured by keeping the 96-well flat bottom plate in ELISA reader (Spectra max 384, Molecular Devices USA) after addition of substrate for a period of 30 min at 25 °C with 1 min interval. Urease Inhibition Assay Reaction mixtures comprising one unit of urease enzyme (B. pasteurii) solution and 55 uL of buffers containing 100 mMol urea were incubated with 5 uL of test compounds (1 mMol concentration) at 30° C for 15 min in 96-well plates. Urease activity was determined by measuring ammonia production using the indophenol'smethod. Momentarily, 45 uL each of phenol reagent and 70 uL of alkali reagent were added to each well. The increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured after 50 min, using a micro-plate reader (Molecular Devices, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 uL. The results (change in absorbance per min.) were processed by using the Soft-Max Pro s4.5.Software (Molecular Devices, USA). Biochemical Assay Citrullination assay was detected via ammonia release. PAD4 was diluted to 120 nM in assay buffer (100 mM HEPES, 50 mM NaCl, 2 mM DDT, 0.6 mg/mL BSA, pH 7.4) added to wells containing various concentration of compound or DMSO vehicle (1% final) in black 384 well plate. Following a 60-min preincubation at RT, the reaction was initiated by the addition of substrate (1.5 mM BAEE in 200 mM HEPES, 50 mM NaCl, 350 uM CaCl2, 2 mM, pH 7.4). The reaction was stopped after 60 min by addition of stop/detection buffer containing 50 mM EDTA, 2.6 mM of o-phthaladehyde and 2.6 mM DTT. Assay was incubated at RT for 90 min before measuring fluorescence's (λex 405/λem 460 nm) on Tecan reader. Urease Inhibition Assay Reaction mixtures comprising 25 μL of enzyme (jack bean urease) solution and 55 μL of buffers containing 100 mM urea were incubated with 5 μL of test compounds (0.5 mM concentration) at 30°C for 15 min in 96-well plates. Urease activity was determined by measuring ammonia production using the indophenol method as described by weather burn14. Briefly, 45 μL each phenol reagent (1% w/v phenol and 0.005% w/v sodium nitroprusside) and 70 μL of alkali reagent (0.5% w/v NaOH and0.1% active chloride NaOCl) were added to each well. The increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured after 50 min, using a microplate reader (Molecular Device). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 μL. Inhibition Assay Reaction mixtures consisting of 25 μL (1 unit/well) of Jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) urease, 55 μL of buffer at pH 6.8, 100 mM of urea, and 5 μL of various concentrations of test compounds were incubated at 30° C. for 15 min in 96-well plates. Subsequently 45 μL phenol reagents (1% w/v phenol and 0.005% w/v sodium nitroprussside), and 70 μL of alkali reagent (0.5% w/v NaOH and 0.1% w/v NaOCl) were added to each well. Urease activity through indophenols method was confirmed by the production of ammonia, as described by Weatherburn [12]. After 50 min, the increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured in a microplate reader SpectraMax M2 (Molecular Devices, CA, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 μL. Urease Inhibition Assay The urease inhibitory activity of synthesized sulfonamides (3a-j) was determined by measuring the amount of ammonia produced by the indophenols method described byWeatherburn (27,28). The reaction mixtures, comprising 20 µL of enzyme (Jack bean urease, 5 U/mL) and 20 µL of test compounds in 50 µL buffer (100 mM urea, 0.01 MK2HPO4, 1 mM EDTA and 0.01 M LiCl2, pH 8.2), were incubated for 10 min at 37 °C in 96-well plate. Briefly, 40 µL each of phenol reagents (1%, w/v phenol and0.005%, w/v sodium nitroprusside) and 70 µL of alkali reagent (0.5%, w/v NaOH and 0.1% active chloride NaOCl) were added to each well. The absorbance at 625 nm was measured after 30 min, using a microplate reader (OPTIMax, Tunable). All reactions were performed in triplicate. In Vitro Assay A reliable 96-well plate D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) assay was developed based on previously published reports (J. Biol. Chem. 277: 27782 (2002)). Briefly, D-serine (5 mM) was oxidatively deaminated by human recombinant D-amino acid oxidase in the presence of molecular oxygen and flavin adenosine dinucleotide (FAD, 1 μM), to yield the corresponding α-keto acid, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide. The resulting hydrogen peroxide was quantified using horseradish peroxidase (0.01 mg/mL) and o-phenylenediamine (180 μg/mL), which displays a defined yellow absorbance at 411 nm when it becomes oxidized. All reactions were carried out for 20 min at room temperature in a 100-μL volume in Tris buffer (50 mM, pH 8.5). Additionally, stock solutions and serial dilutions of potential DAO inhibitors were made in 10:90 DMSO:buffer with a final assay DMSO concentration of 1%. Urease Inhibition Assay Mixture of 25 μL of urease enzyme (Jack bean) solution containing 1 unit of enzyme (1 unit = 0.02 mg of enzyme) was dissolved in phosphate buffer of pH 6.8, 55 μL of buffer containing 100 mM urea, and 5 μL of test compounds (0.5 mM concentration) was incubated at 30°C for 15 min in 96-well plates. Urease activity was determined by measuring ammonia production using the iodophenol method38. Briefly, 45 μL each of phenol reagent and 70 μL of alkali reagent were added to each well. The increase in absorbance at 630 nm was measured after 50 min, using a microplate reader (Molecular Device, CA, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 μL. The results (change in absorbance per min) were processed using Soft-Max Pro software (Molecular Device, CA, USA). Spectrophotometric Assay This novel assay was used to determine the kinetic parameters for most of the QC substrates. QC activity was analyzed spectrophotometrically using a continuous method, that was derived by adapting a previous discontinuous assay (Bateman, R. C. J. 1989 J Neurosci Methods 30, 23-28) utilizing glutamate dehydrogenase as auxiliary enzyme. Samples consisted of the respective QC substrate, 0.3 mM NADH, 14 mM α-Ketoglutaric acid and 30 U/ml glutamate dehydrogenase in a final volume of 250 μl. Reactions were started by addition of QC and persued by monitoring of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm for 8-15 min.The initial velocities were evaluated and the enzymatic activity was determined from a standard curve of ammonia under assay conditions. All samples were measured at 30° C., using either the SPECTRAFluor Plus or the Sunrise (both from TECAN) reader for microplates. Kinetic data was evaluated using GraFit software. Spectrophotometric Assay This novel assay was used to determine the kinetic parameters for most of the QC substrates. QC activity was analyzed spectrophotometrically using a continuous method, that was derived by adapting a previous discontinuous assay (Bateman, R. C. J. 1989 J Neurosci Methods 30, 23-28) utilizing glutamate dehydrogenase as auxiliary enzyme. Samples consisted of the respective QC substrate, 0.3 mM NADH, 14 mM α-Ketoglutaric acid and 30 U/ml glutamate dehydrogenase in a final volume of 250 ul. Reactions were started by addition of QC and perused by monitoring of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm for 8-15 min.The initial velocities were evaluated and the enzymatic activity was determined from a standard curve of ammonia under assay conditions. All samples were measured at 30° C., using either the SPECTRAFluor Plus or the Sunrise (both from TECAN) reader for microplates. Kinetic data was evaluated using GraFit software. Spectrophotometric Assay This novel assay was used to determine the kinetic parameters for most of the QC substrates. QC activity was analyzed spectrophotometrically using a continuous method, that was derived by adapting a previous discontinuous assay (Bateman, R. C. J. 1989 J Neurosci Methods 30, 23-28) utilizing glutamate dehydrogenase as auxiliary enzyme. Samples consisted of the respective QC substrate, 0.3 mM NADH, 14 mM alpha-Ketoglutaric acid and 30 U/ml glutamate dehydrogenase in a final volume of 250 ul. Reactions were started by addition of QC and persued by monitoring of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm for 8-15 min. The initial velocities were evaluated and the enzymatic activity was determined from a standard curve of ammonia under assay conditions. All samples were measured at 30 C., using either the SPECTRAFluor Plus or the Sunrise (both from TECAN) reader for microplates. Kinetic data was evaluated using GraFit software. Urease Inhibition Assay Reaction mixture consisting of 25 µL of Jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) urease (1 unit/well), 55 µL of 100 mM urea dissolved in phosphate buffer (4 mM concentration of 6.80 pH, and 5 µL of various concentrations of test compound (from 0.5 to 0.00625 mM) were incubated at 30 °C for 15 min in 96-well plates.In kinetic experiments, various concentrations of both substrate and test compounds were used. Subsequently 45 µL phenol reagents (1% w/v phenol and 0.005% w/v sodium nitroprusside), and 70 µL of alkali reagent (0.5% w/v NaOH and 0.1% w/v NaOCl) were added to each well. Urease activity was measured through Weatherburn indophenols method by the production of ammonia [21]. After 50 min duration, the increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured in a microplate reader (SpectraMax M2, Molecular Devices, CA, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 lL. Thiourea was used as the standard inhibitor of urease [15]. Urease Inhibition Assay Reaction mixtures comprising 25 μL of enzyme (jack bean urease) solution and 55 μL of buffer containing 100 mM urea were incubated with 5 μL of test compound (0.5 mM) at 30°C for 15 min in 96-well plates. Urease activity was determined by measuring the ammonia production using the indophenol method, as described by Weatherburn11. Briefly, 45 μL of each phenol reagent (1% (w/v) phenol and 0.005% (w/v) sodium nitroprussside) and 70 μL of alkali reagent (0.5% (w/v) NaOH and 0.1% active chloride, NaOCl) were added to each well. The increasing absorbanceat 630 nm was measured after 50 min, using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 μL. The results (change in absorbance per min) were processed using SoftMax Pro software (Molecular Devices). The entire assay was performed at pH 6.8. Urease Inhibition Assay This assay was modified from Berthelot assay and was employed for the determination of urease activity. The assay is based on the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia which reacts with phenol-hypochlorite to form light blue colored complex measured at 625 nm. A total volume of 85 µl assay mixture contained 10 µl of 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, 10 µl of sample solution and 25 µl of Bacillus pasteurii urease (Sigma) solution (0.015 units). The contents were pre-incubated at 37 °C for 10 min. Then, 40 µl of urea stock solution (20 mM) was added to each well and incubation continued at 37 °C for further 10 min and preread at 625 nm using the 96-well plate reader Synergy HT (Biotek Inc.). Phenol hypochlorite (115 µl) reagent was added in each well (freshly prepared by mixing 45 µl phenol reagent with 70 µl of alkali reagent). For color development, incubation was done at 37 °C for another 10 min. Absorbance was again measured at 625 nm. Enzymatic Activity Assay The inhibition of purified recombinant human GAC by varying concentrations of inhibitors is assessed via a dual-coupled enzymatic assay. The glutamate produced by the glutaminase reaction is used by glutamate oxidase to produce α-ketoglutarate, ammonia, and hydrogen peroxide, with this hydrogen peroxide subsequently being used by horseradish peroxidase to produce resorufin in the presence of Amplex UltraRed. The assay buffer consisted of 50 mM Hepes (pH 7.4), 0.25 mM EDTA and 0.1 mM Triton X-100. GAC was incubated with potassium phosphate (10 minutes at room temperature) prior to incubation with inhibitor (10 minutes at room temperature). The final reaction conditions were as follows: 2 nM GAC, 50 mM potassium phosphate, 100 mU/mL glutamate oxidase (Sigma), 1 mM glutamine (Sigma), 100 mU/mL horseradish peroxidase (Sigma), 75 μM Amplex UltraRed (Life Technologies), and 1% (v/v) DMSO. The production of resorufin was monitored on a Perkin Elmer Envision plate reader (excitation 530 nm, emission 590 nm) either in a kinetics or endpoint mode (at 20 minutes). IC50 values were calculated using a four-parameter logistic curve fit. Urease Inhibition Assay The inhibition studies of soybean urease were initiated with boric acid and boronic acids (butylboronic acid, 4-bromophenylboronic acid, and phenylboronic acid). Also, heavy metal ions (HgCl2, AgCl, and Cu(CH3COO)2) and sodium salts of mineral acids (NaF, NaCl, NaNO3, and Na2SO4) were investigated for their inhibitory effects. Stock solutions of inhibitors, except for 4-bromophenylboronicacid, were prepared in 0.05 M Tris-acetate buffer, pH 7.0, and were suitably diluted for experiments, whereas a stock solution of 4-bromophenylboronic acid was prepared in absolute ethanol and subsequently diluted in respective buffer. The activity assay was carried out at standard conditions as described earlier in the presence of varying concentrations of inhibitors. The yellow-orange colored solution was measured at 405 nm on a Unicam UV-2 spectrophotometer. The amount of NH3 liberated in the reaction mixture was estimated by calibrating Nessler's reagent with standard NH4Cl solution. One enzyme unit is defined as the amount of urease required to liberate 1 μmol of ammonia per minute under our test conditions (0.1 M urea, 0.05 M Trisacetatebuffer, pH 7.0, 37°C). In Vitro PAD4 BAEE Biochemical Assay One hundred nanoliters of test compounds dissolved in DMSO at various concentrations were dispensed into a 384-well black OptiPlate using a Labcyte Echo instrument. Ten microliters of a solution of recombinant PAD4 and calcium chloride diluted in PAD4 assay buffer (50 mM MOPS [3-(N-morpholino) propanesulfonic acid], pH 7.6; 50 mM sodium chloride; 0.05% Tween-20; 2 mM dithiothreitol) was added to the compound-containing plate and was incubated for 30 minutes at 25° C. Ten microliters of a solution of BAEE (Sigma-Aldrich #B4500) diluted in PAD4 assay buffer was then added to start the reaction. Final concentrations were 5 nM PAD4, 2 mM calcium chloride, and 3 mM BAEE. The reaction mixture was incubated at 25° C. for 2 hours and was stopped with the addition of 10 microliters of a solution of 75 mM EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) in PAD4 assay buffer. Thirty microliters of detection solution (5 mM o-phthalaldehyde, 50 mM MOPS [3-(N-morpholino) propanesulfonic acid], pH 7.6; 50 mM sodium chloride; 0.05% Tween-20; 5 mM dithiothreitol) was then added and the reaction was incubated for 1 hour at 25° C. The level of fluorescent thiol-substituted isoindole resulting from the reaction of ammonia, o-phthalaldehyde, and dithiothreitol was measured on an Envision plate reader (PerkinElmer) with 405 nm excitation and 535 nm emission. Urease Inhibition Assay To understand the binding modes of the compounds given in Table 1, all ligands were docked into the binding site of Urease enzyme. The top ranked conformations of each ligand were saved in a separate database for further evaluation. The docking results well correlated with the experimental results. The reaction mixtures, comprising 25 uL of enzyme (jack bean urease, Sigma aldrich) solution and 55 uL of buffers containing 100 mM urea, were incubated with 5 uL of the test compounds (0.5 mM concentration) at 30 °C for 15 min in 96-well plates. For the kinetics assessment the urea concentrations were changed from 2 to 24 mM. Urease activity was determined by measuring ammonia production using the indophenol method as described by Weatherburn. Briefly, 45 uL of phenol reagent (1% w/v phenol and 0.005% w/v sodium nitroprusside (Sigma Aldrich)) and, 70 uL of alkali reagent (0.5% w/v NaOH (Sigma Aldrich) and 0.1% active chloride NaOCl (Sigma Aldrich)) were added to each well. The increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured after 50 min, using a microplate reader (Molecular Device, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 uL. The results (change in absorbance per min) were processed by using SoftMax-Pro software (molecular Device, USA). The entire assays were performed at pH 6.8.
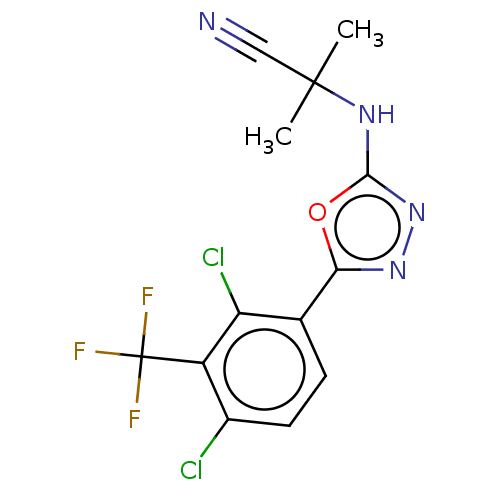 BDBM600986 US11634391, Compound 246 N-(5-(2,4-dichloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)cyanamide, Ammonia Salt
BDBM600986 US11634391, Compound 246 N-(5-(2,4-dichloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)cyanamide, Ammonia Salt (11Z)-4-chloro-3-ethyl-14-methyl-1-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-7-{3-[(naphthalen-1-yl)oxy]propyl}-10,13,14,15-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3′,4′:8,9][1,6]diazacycloundecino[10,11,1-hi]indole-8-carboxylic Acid-Ammonia Salt (Enantiomer 2) BDBM572191 US11447504, Example 44
(11Z)-4-chloro-3-ethyl-14-methyl-1-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-7-{3-[(naphthalen-1-yl)oxy]propyl}-10,13,14,15-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3′,4′:8,9][1,6]diazacycloundecino[10,11,1-hi]indole-8-carboxylic Acid-Ammonia Salt (Enantiomer 2) BDBM572191 US11447504, Example 44 BDBM572190 US11447504, Example 43 (11Z)-4-chloro-3-ethyl-14-methyl-1-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-7-{3-[(naphthalen-1-yl)oxy]propyl}-10,13,14,15-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3′,4′:8,9][1,6]diazacycloundecino[10,11,1-hi]indole-8-carboxylic Acid-Ammonia Salt (Enantiomer 1)
BDBM572190 US11447504, Example 43 (11Z)-4-chloro-3-ethyl-14-methyl-1-[2-(morpholin-4-yl)ethyl]-7-{3-[(naphthalen-1-yl)oxy]propyl}-10,13,14,15-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3′,4′:8,9][1,6]diazacycloundecino[10,11,1-hi]indole-8-carboxylic Acid-Ammonia Salt (Enantiomer 1)