 DASATINIB BDBM31089
DASATINIB BDBM31089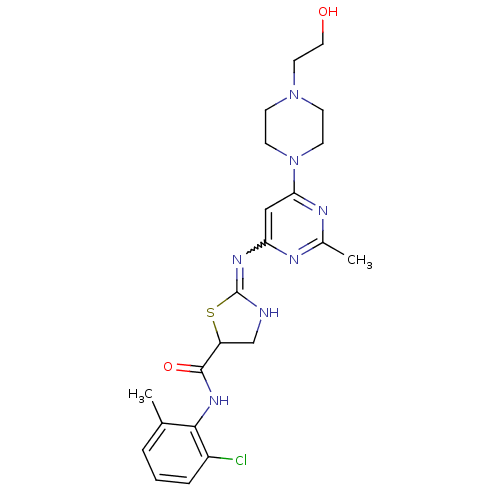 Dasatinib BDBM82130
Dasatinib BDBM82130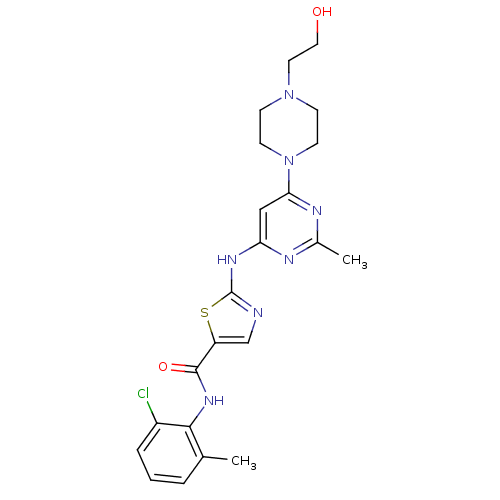 med.21724, Compound Dasatinib US20230348453, Compound A8 US10294227, Code Dasatinib BDBM13216 BMS-354825 CHEMBL1421 DASATINIB cid_3062316 N-(2-Chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-({6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl}amino)-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide
med.21724, Compound Dasatinib US20230348453, Compound A8 US10294227, Code Dasatinib BDBM13216 BMS-354825 CHEMBL1421 DASATINIB cid_3062316 N-(2-Chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-({6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl}amino)-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide
- Veach, DR; Namavari, M; Pillarsetty, N; Santos, EB; Beresten-Kochetkov, T; Lambek, C; Punzalan, BJ; Antczak, C; Smith-Jones, PM; Djaballah, H; Clarkson, B; Larson, SM Synthesis and biological evaluation of a fluorine-18 derivative of dasatinib. J Med Chem 50: 5853-7 (2007)
- Kwarcinski, FE; Brandvold, KR; Phadke, S; Beleh, OM; Johnson, TK; Meagher, JL; Seeliger, MA; Stuckey, JA; Soellner, MB Conformation-Selective Analogues of Dasatinib Reveal Insight into Kinase Inhibitor Binding and Selectivity. ACS Chem Biol 11: 1296-304 (2016)
- Li, HY; He, DD; Zhao, XJ; Sun, TY; Zhang, Q; Bai, CG; Chen, Y Design and synthesis of novel dasatinib derivatives as inhibitors of leukemia stem cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 700-706 (2018)
- Hantschel, O; Rix, U; Schmidt, U; Bürckstümmer, T; Kneidinger, M; Schütze, G; Colinge, J; Bennett, KL; Ellmeier, W; Valent, P; Superti-Furga, G The Btk tyrosine kinase is a major target of the Bcr-Abl inhibitor dasatinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 13283-8 (2007)
- Liu, L; Hussain, M; Luo, J; Duan, A; Chen, C; Tu, Z; Zhang, J Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel dasatinib analogues as potent DDR1 and DDR2 kinase inhibitors. Chem Biol Drug Des 89: 420-427 (2017)
- Das, J; Chen, P; Norris, D; Padmanabha, R; Lin, J; Moquin, RV; Shen, Z; Cook, LS; Doweyko, AM; Pitt, S; Pang, S; Shen, DR; Fang, Q; de Fex, HF; McIntyre, KW; Shuster, DJ; Gillooly, KM; Behnia, K; Schieven, GL; Wityak, J; Barrish, JC 2-aminothiazole as a novel kinase inhibitor template. Structure-activity relationship studies toward the discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1- piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide (dasatinib, BMS-354825) as a potent pan-Src kinase i J Med Chem 49: 6819-32 (2006)
- ChEMBL_2362669 Inhibition of wild type human BCR-ABL1 using Tyr2 peptide as substrate incubated for 1 hrs in presence of dasatinib by FRET based Z-LYTE assay
- Inhibition of SIK; Abl and Src Kinases by Other Kinase Inhibitor The IC50 for the inhibition of ABL1 by dasatinib, by C7 and by B3 is approximately 1.5 nM, 5.1 nM and 1.6 nM, and of SRC is 1.5 nM, 1.5 nM and 1.5 nM; each, respectively for dasatinib, C7 and by B3 (Table 3A). The compound C12 is also a strong inhibitor of SRC (<100 nM IC50), and is selective to SRC over ABL1. Briefly, a radiometric protein kinase assay (33PanQinase Activity Assay) was used for measuring the kinase activity of the five protein kinases. All kinase assays were performed in 96-well FlashPlates™ from PerkinElmer (Boston, MA, USA) in a 50 uL reaction volume. The reaction cocktail was pipetted in four steps in the following order:25 uL of assay buffer (standard buffer/[gamma-33P]-ATP)10 uL of ATP solution (in water)5 uL of test compound (in 10% DMSO)20 uL enzyme/substrate mix. The assay for all protein kinases contained 70 mM HEPES-NaOH pH7.5, 3 mM MgCl2, 3 mM MnCl2, 3 μM Na-orthovanadate, 1.2 mM DTT, ATP (variable concentrations, corresponding to the apparent ATP-Km of the respective kinase, see Table 2A), [gamma-33P]-ATP (approx. 8 105 cpm per well), protein kinase (variable amount, see Table 2A), and substrate (variable amounts, see Table 2A).
- End Point Fluorescence Assay Reaction volumes of 50 μL were used in 96-well plates. Buffer A (1×, 34 μL; 100 mM Tris, pH 8, 10 mM MgCl2) was added to a single row, followed by 15 μL ofenzyme (3.3× concentration) in buffer A with 3-fold dilutions (typically, 125 nM and 42, 14, 4.6, 1.5, 0.5, 0.17, 0.06, 0.02, 0.01, and 0 μM final well concentrations in buffer A). Then, 1 μL of a 500 nM stock of the appropriate dasatinib analogue BODIPY probe in DMSO was added (2% DMSO final). Wells were incubated at rt for 30 min prior to end point read (ex/em 485/535 nm). Reactions had final concentrations of 10 nM BODIPY-probe, 100 mM Tris buffer (pH 8),and 10 mM MgCl2.
- Cell-Based Assays of c-Kit Mutant Kinase Activity The c-Kit mutant D816V inhibitors were assessed using an engineered BaF3-FL KIT D816V or BaF3-FL KIT V560G/D816V cell line. The BaF3-FL KIT D816V cell lines were created by introduction of KIT mutant (D816V) full length constructs that render the cells dependent on the introduced kinase for growth. Inhibitors of c-Kit mutant D816V kinase reduce or eliminate the mediated c-kit mutant D816V kinase activation, resulting in reduced cell proliferation of the BaF3-FL Kit mutant D816V cells. This inhibition is measured by the effect of compound concentration on cell growth to assess IC50 values. BaF3-FL KIT D816V cells were seeded at 1×104 cells per well of a 96 well cell culture plate in 50 μl of cell culture medium of RPMI Medium 1× (Invitrogen #11875-093) supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen #10438), 1% Non Essential Amino Acids (Invitrogen #11140), 1% Penicillin Streptomycin (Invitrogen #15140), 1% L-Glutamine (Invitrogen #25030-081). Compounds were dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 5 mM and were serially diluted 1:3 for a total of eight points and added to the cells to a final maximum concentration of 10 μM in 100 μl cell culture medium (final concentration 0.2% DMSO). Cells were also treated with Dasatinib as a positive control. The cells were incubated at 37° C., 5% CO2 for three days. ATPlite Buffer (Perkin Elmer #6016739) and substrate were equilibrated to room temperature, and enzyme/substrate Recombinant Firefly Luciferase/D-Luciferin was reconstituted. The cell plates were equilibrated to room temperature for 30 minutes, then lysed by addition of 25 uL per well of the ATPlite Reagent. The plate was mixed for 5 minutes on a plate shaker to lyse the cells. The plates were read on a Tecan Safire using Luminescence protocol modified to read 0.1s per well. The luminescence reading assesses the ATP content, which correlates directly with cell number such that the reading as a function of compound concentration is used to determine the IC50 value.
 DASATINIB BDBM31089
DASATINIB BDBM31089 Dasatinib BDBM82130
Dasatinib BDBM82130 med.21724, Compound Dasatinib US20230348453, Compound A8 US10294227, Code Dasatinib BDBM13216 BMS-354825 CHEMBL1421 DASATINIB cid_3062316 N-(2-Chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-({6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl}amino)-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide
med.21724, Compound Dasatinib US20230348453, Compound A8 US10294227, Code Dasatinib BDBM13216 BMS-354825 CHEMBL1421 DASATINIB cid_3062316 N-(2-Chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-({6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl}amino)-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide