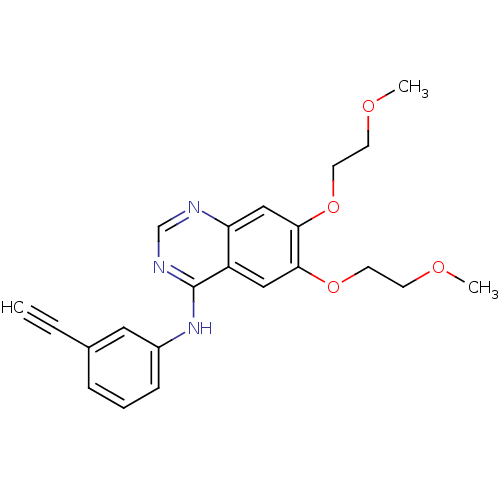
 ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE US9730934, Erlotinib US9409845, Table 1, Compound 22: erlotinib OSI-774 US10189853, erlotinib WO2022090481, Example erlotinib BDBM5446 Erotinib CHEMBL553 US11524945, Compound Erlotinib N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine US10507209, Compound Erlotinib Erlotinib Tarceva N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine Monohydrochloride cid_176870
ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE US9730934, Erlotinib US9409845, Table 1, Compound 22: erlotinib OSI-774 US10189853, erlotinib WO2022090481, Example erlotinib BDBM5446 Erotinib CHEMBL553 US11524945, Compound Erlotinib N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine US10507209, Compound Erlotinib Erlotinib Tarceva N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine Monohydrochloride cid_176870 ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE Erlotinib OSI-774 CP-358774-01 BDBM50311470 CHEMBL1079742
ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE Erlotinib OSI-774 CP-358774-01 BDBM50311470 CHEMBL1079742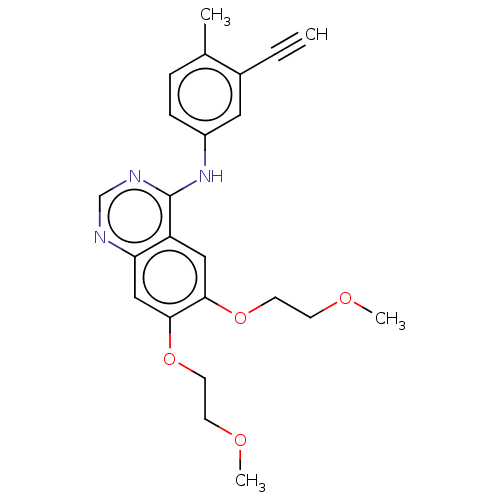 US11524945, Compound Erlotinib-4-methylphenyl analog (E4ME) BDBM582529
US11524945, Compound Erlotinib-4-methylphenyl analog (E4ME) BDBM582529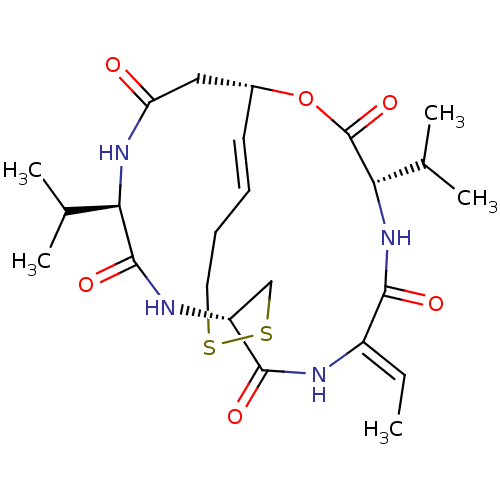 Depsipeptide Antibiotic FR 901228 (1S,4S,7Z,10S,16E,21R)-7-ethylidene-4,21-bis(propan-2-yl)-2-oxa-12,13-dithia-5,8,20,23-tetraazabicyclo[8.7.6]tricos-16-ene-3,6,9,19,22-pentone CHEMBL343448 BDBM19151 Romidepsin FK228
Depsipeptide Antibiotic FR 901228 (1S,4S,7Z,10S,16E,21R)-7-ethylidene-4,21-bis(propan-2-yl)-2-oxa-12,13-dithia-5,8,20,23-tetraazabicyclo[8.7.6]tricos-16-ene-3,6,9,19,22-pentone CHEMBL343448 BDBM19151 Romidepsin FK228
- Peoples, AJ; Hughes, D; Ling, LL; Millett, W; Nitti, A; Spoering, A; Steadman, VA; Chiva, JC; Lazarides, L; Jones, MK; Poullennec, KG; Lewis, K; Epstein, S Depsipeptide and uses thereof US Patent US9402878 (2016)
- Hegde, VR; Dai, P; Patel, M; Das, PR; Wang, S; Puar, MS A depsipeptide fungal metabolite inhibitor of cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8: 1277-80 (1999)
- Li, Z; Xu, M; Xing, S; Ho, WT; Ishii, T; Li, Q; Fu, X; Zhao, ZJ Erlotinib effectively inhibits JAK2V617F activity and polycythemia vera cell growth. J Biol Chem 282: 3428-32 (2007)
- Smith, AN; Blackwell, DJ; Knollmann, BC; Johnston, JN Ring Size as an Independent Variable in Cyclooligomeric Depsipeptide Antiarrhythmic Activity. ACS Med Chem Lett 12: 1942-1947 (2021)
- Igarashi, Y; Yamamoto, K; Fukuda, T; Shojima, A; Nakayama, J; Carro, L; Trujillo, ME Arthroamide, a Cyclic Depsipeptide with Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Activity from Arthrobacter sp. J Nat Prod 78: 2827-31 (2015)
- Gunasekera, SP; Miller, MW; Kwan, JC; Luesch, H; Paul, VJ Molassamide, a depsipeptide serine protease inhibitor from the marine cyanobacterium Dichothrix utahensis. J Nat Prod 73: 459-62 (2010)
- Chen, KF; Pao, KC; Su, JC; Chou, YC; Liu, CY; Chen, HJ; Huang, JW; Kim, I; Shiau, CW Development of erlotinib derivatives as CIP2A-ablating agents independent of EGFR activity. Bioorg Med Chem 20: 6144-53 (2012)
- Yurek-George, A; Cecil, AR; Mo, AH; Wen, S; Rogers, H; Habens, F; Maeda, S; Yoshida, M; Packham, G; Ganesan, A The First Biologically Active Synthetic Analogues of FK228, the Depsipeptide Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. J Med Chem 50: 5720-5726 (2007)
- Zhang, Y; Tortorella, MD; Liao, J; Qin, X; Chen, T; Luo, J; Guan, J; Talley, JJ; Tu, Z Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel Erlotinib-NSAID Conjugates as More Comprehensive Anticancer Agents. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 1086-90 (2015)
- Yang, X; Hou, Z; Wang, D; Mou, Y; Guo, C Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel heptamethine cyanine dye-erlotinib conjugates as antitumor agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30: (2020)
- Chen, X; Du, Y; Sun, H; Wang, F; Kong, L; Sun, M Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel tricyclic oxazine and oxazepine fused quinazolines. Part 1: erlotinib analogs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 884-7 (2014)
- Almaliti, J; Al-Hamashi, AA; Negmeldin, AT; Hanigan, CL; Perera, L; Pflum, MK; Casero, RA; Tillekeratne, LM Largazole Analogues Embodying Radical Changes in the Depsipeptide Ring: Development of a More Selective and Highly Potent Analogue. J Med Chem 59: 10642-10660 (2016)
- Biochemical Assay Thus, while these compounds were extensively used in studying ILK-mediated cellular and disease processes, their reported inhibitory effects are probably due to unknown artifacts or indirect binding events. Next, we turned our attention to previously reported studies on kinase profiling and quantitative chemical proteomics. These studies suggested that a widely known lung cancer drug erlotinib, which targets EGFR, might also bind to ILK as an off target. By performing a robust fluorescence-based binding assay, we found that the FDA approved drug Erlotinib (TARCEVA) indeed binds potently to purified recombinant ILK at KD 0.43M, which is very close to the affinity of Erlotinib to EGFR measured at the same experimental conditions (KD 0.31 μM). Another erlotinib-like EGFR inhibitor Gefitinib exhibited 10-fold weaker binding affinity to ILK (KD 4.51 μM) yet 3-fold stronger affinity to EGFR (KD 0.11 μM) than erlotinib.
- ChEMBL_1538415 (CHEMBL3737962) Inhibition of EGFR T790M/del (746 to 750) deletion mutant phosphorylation in erlotinib-resistant human PC9 cells preincubated for 1 hr followed by stimulation with EGF for 8 mins by electrochemiluminescent immunoassay
- Enzymatic Assay The aim of this in vitro assay was to measure the inhibition of HCV NS3/4A protease complexes by the compounds of the present invention. This assay provides an indication of how effective compounds of the present invention would be in inhibiting HCV NS3/4A proteolytic activity. The inhibition of full-length hepatitis C NS3 protease enzyme was measured essentially as described in Poliakov, 2002 Prot Expression & Purification 25 363 371. Briefly, the hydrolysis of a depsipeptide substrate, Ac-DED(Edans)EEAbu [COO]ASK(Dabcyl)-NH2 (AnaSpec, San Jose, USA), was measured spectrofluorometrically in the presence of a peptide cofactor, KKGSVVIVGRIVLSGK ( ke Engstrom, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala University, Sweden). [Landro, 1997 #Biochem 36 9340-9348].
- Inhibition Assay The inhibition of full-length hepatitis C NS3 protease enzyme was measured essentially as described in Poliakov, 2002 Prot Expression & Purification 25 363 371. Briefly, the hydrolysis of a depsipeptide substrate, Ac-DED(Edans)EEAbu[COO]ASK(Dabcyl)-NH2 (AnaSpec, San Jose, USA), was measured spectrofluorometrically in the presence of a peptide cofactor, KKGSVVIVGRIVLSGK (Ake Engstrom, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala University, Sweden). [Landro, 1997 #Biochem 36 9340-9348]. The enzyme (1 nM) was incubated in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mM DTT, 40% glycerol, 0.1% n-octyl-D-glucoside, with 25 μM NS4A cofactor and inhibitor at 30 C. for 10 min, whereupon the reaction was initiated by addition of 0.5 μM substrate. Inhibitors were dissolved in DMSO, sonicated for 30 sec. and vortexed.
- Kinase Inhibition Assay Reagents and Materials:WT EGFR (Carna, Cat. No. 08-115), EGFR [L858R] (Carna, Cat. No. 08-502), EGFR [L858R/T790M] (Carna, Cat. No. 08-510), ATP (Sigma, Cat. No. A7699-1G), DMSO (Sigma, Cat. No. D2650), 96-well plate (Corning, Cat. No. 3365), 384-well plate (Greiner, Cat. No. 784076), HTRF Kinase TK Kit (Cisbio, Cat. No. 62TK0PEJ), Erlotinib (Selleckchem, Cat. No. S7787), EGFR [d746-750] (Life Technologies, Cat. No. PV6178), 5× Kinase Buffer A (Life Technologies, Cat. No. PV3186), Kinase Tracer 199 (Life Technologies, Cat. No. PV5830), LanthaScreen Eu-anti-GST antibody (Life Technologies, Cat. No. PV5594).Specific Experimental Protocol:Compound preparation: the test compound was dissolved in DMSO to make a 20 mM stock solution. Then, it was diluted in DMSO with a 3-fold series gradient dilution for 10 times. The dilutions were diluted 10 fold with buffer when dosing.WT EGFR and EGFR [L858R/T790M] kinase assay: WT EGFR or EGFR [L858R/T790M] kinase was mixed with different concentrations of pre-diluted compounds for 10 minutes in 5× Kinase Buffer A in duplicate. The corresponding substrate and ATP were added and reacted at room temperature for 20 minutes (in which a negative and a positive control were set: the negative control is blank and the positive control is erlotinib). After the reaction, the detection reagent (the reagent in the HTRF Kinase TK kit) was added, and after incubation at room temperature for 30 minutes, the enzyme activity in the presence of the compounds of the present disclosure at each concentration was measured by an Evnvision microplate reader, and the inhibition of the enzyme by the compound at each concentrations were calculated. The inhibitions of the enzyme activity by the compounds at different concentrations were then fitted using Graphpad 5.0 software according to the four-parameter equation, and the IC50 values were calculated.
- Inhibition Assay The inhibition of full-length hepatitis C NS3 protease enzyme was measured essentially as described in Poliakov, 2002 Prot Expression & Purification 25 363 371. Briefly, the hydrolysis of a depsipeptide substrate, Ac-DED(Edans)EEAbuψ[COO]ASK(Dabcyl)-NH2 (AnaSpec, San Jos , USA), was measured spectrofluorometrically in the presence of a peptide cofactor, KKGSVVIVGRIVLSGK (Åke Engstr m, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala University, Sweden) (Landro, 1997 Biochem 36 9340-9348). The enzyme (1 nM) was incubated in 50 mM HEPES (4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) pH 7.5, 10 mM dithiothreitol, 40% glycerol, 0.1% n-octyl-D-glucoside, with 25 μM NS4A cofactor and inhibitor at 30° C. for 10 min, whereupon the reaction was initiated by addition of 0.5 μM substrate. Inhibitors were dissolved in DMSO, sonicated for 30 sec and vortexed. The solutions were stored at −20° C. between measurements.
- Enzymatic assay The aim of this in vitro assay was to measure the inhibition of HCV NS3/4A protease complexes by the compounds of the present invention. This assay provides an indication of how effective compounds of the present invention would be in inhibiting HCV NS3/4A proteolytic activity. The inhibition of full-length hepatitis C NS3 protease enzyme was measured essentially as described in Poliakov, 2002 Prot Expression & Purification 25 363 371. Briefly, the hydrolysis of a depsipeptide substrate, Ac-DED(Edans)EEAbu-y-[COO]ASK(Dabcyl)-NH2 (AnaSpec, San Jose, USA), was measured spectrofluorometrically in the presence of a peptide cofactor, KKGSVVIVGRIVLSGK (Ake Engstrom, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala University, Sweden). [Landro, 1997 #Biochem 36 9340-9348]. The enzyme (1 nM) was incubated in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mM DTT, 40% glycerol, 0.1% n-octyl-D-glucoside, with 25 uM NS4A cofactor and inhibitor at 30 C. for 10 min.
- Kinase Assay JAK2 and JAK2 [V617F] Kinase Assay: In 5× Kinase Buffer A, JAK2 or JAK2 [V617F] kinase was mixed with pre-diluted compounds at different concentrations in duplicate for 10 minutes. The corresponding substrate and ATP were added and reacted at room temperature for 20 minutes (in which negative and positive controls were set: the negative control was a blank control and the positive control was erlotinib). After the reaction was completed, a detection reagent (the reagent in the HTRF Kinase TK kit) was added. After incubation at room temperature for 30 minutes, the enzyme activities in the presence of the compounds disclosed herein at each concentration were measured by an Evnvision microplate reader, and inhibitory activities of compounds at different concentrations on the enzyme activity were calculated. The inhibitory activities of compounds at different concentrations on enzyme activity were then fitted according to the four-parameter equation using Graphpad 5.0 software, and the IC50 values were calculated.
- Kinase Inhibition Assay WT EGFR and EGFR[L858R/T790M] kinase detection: In 5× kinase buffer A, WT EGFR or EGFR[L858R/T790M] kinase was mixed with different concentrations of compounds prepared by pre-dilution for 10 minutes. Each concentration was tested in duplicate. The corresponding substrate and ATP were added, and reaction was performed at room temperature for 20 minutes (negative and positive controls were provided: the negative control was a blank control, and the positive control was erlotinib). After completion of the reaction, detection reagents (reagents in the HTRF Kinase TK kit) were added. After incubating for 30 minutes at room temperature, enzyme activity in the presence of various concentrations of the compounds of the present disclosure was determined by Evnvision microplate reader, and inhibitory activity of different concentrations of the compounds on enzyme activity was calculated. The inhibitory activity of different concentrations of the compounds on enzyme activity was then fitted by Graphpad 5.0 software according to the four-parameter equation, and the IC50 value was calculated.
- Ki Determination for Genotypes 1b and 3a NS3 Protease Purified NS3 protease domain (amino acids 1-181) of the genotype 1b and 3a virus were generated as above. The internally quenched fluorogenic depsipeptide substrate Ac-DED(Edans)-EEAbuΨ[COO]ASK(Dabcyl)-NH2 and a synthetic peptide containing the hydrophobic core residues of the NS4A protein cofactor (KKGSVVIVGRIILSGRKK; NS4A peptide) were obtained from Anaspec, Inc. (San Jose, Calif.). Other chemicals and biochemicals were of reagent grade or better and were purchased from standard suppliers.Reactions were run at room temperature in buffer consisting of 50 mM HEPES, 40% glycerol, 0.05% Triton X-100, 10 mM DTT, and 10% DMSO. The final assay solutions contained 50 pM NS3 genotype 1 b protease or 200 pM genotype 3a protease, 20 μM NS4A peptide, and 4 μM substrate (genotype 1b) or 2 μM substrate (genotype 3a). Inhibitor concentrations varied from 100 nM to 5 pM in 3-fold dilutions, and no-inhibitor controls were included.Compound dilutions were made in DMSO at 20× final concentration. Reaction mixtures were prepared in 96-well assay plates. A solution of enzyme and NS4A peptide in assay buffer (25 μL volume with both reagents at 4× final concentration) was mixed with 45 μL assay buffer and 5 μL of either inhibitor or DMSO, and pre-incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. The reaction was started by addition of 25 μL substrate solution at 4× final concentration. Plates were mixed vigorously for 5-10 seconds and reactions were allowed to proceed for 90 minutes, fluorescence was measured every 30 s between 90 and 120 minutes reaction time using a Tecan InfiniTe M1000 or PerkinElmer Envision multimode plate reader with an excitation wavelength of 340 nm and an emission wavelength of 490 nm.Rates were calculated from the progress curves at steady state, in the time frame of 90-120 minutes after addition of substrate. To determine the Ki, rates were plotted as a function of inhibitor concentration, and the data were fit with equation 1 (Morrison, J. F., Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1969, 185, 269-286) to calculate Ki app using GraphPad Prism 5. Active fraction of enzyme was determined by active site titration with known potent inhibitors. Ki was calculated from Ki app/(1+[[S]/Km]).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibitory Activity Samples:Controls: Gefitinib, erlotinib hydrochloride, purchased from Anqing worldchem Co., LTD.; lapatinib ditosylate, purchased from Taizhou Xingcheng Chempharm Co., Ltd.; CI-1033 hydrochloride, purchased from Shanghai hanxiangchem, Co., Ltd.; andThe present compounds: lab-made, their chemical names and structural formulae are shown in the preparation examples.Assay Procedures:The abbreviations used in the following assay have the following meanings:HEPES: hydroxyethyl piperazine ethanesulfonic acid;Brij-35: polyoxyethylene lauryl ether;DTT: dithiothreitol;Coating Reagent #3: #3 coating agent;EDTA: ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, purchased from Sigma Co. Ltd.;FAM labeled peptide: fluorescein labeled peptide 22 (GL Biochem);ATP: adenosine triphosphate (Sigma);DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide;EGFR: human epidermal growth factor receptor (Carna);HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Carna);HER4: human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (Carna).1. Formulating the agents to be used in the assay(1) 1.25-fold MnCl2-free kinase buffer (62.5 mM HEPES, PH 7.5, 0.001875% Brij-35, 12.5 mM MgCl2, 2.5 mM DTT);(2) 1.25-fold MnCl2-containing kinase buffer (62.5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 0.001875% Brij-35, 12.5 mM MgCl2, 12.5 mM MnCl2, 2.5 mM DTT);(3) Stop buffer (100 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 0.015% Brij-35, 0.2% Coating Reagent #3, 50 mM EDTA);(4) 2.5-fold kinase solutions (to the 1.25-fold kinase buffers were added the corresponding kinases to formulate 2.5-fold EGFR, HER2, HER4 kinase solutions);(5) 2.5-fold peptide solutions (to the 1.25-fold kinase buffers were added FAM labeled peptide and ATP to formulate the peptide solutions);(6) 5-fold compound solutions (using 100% DMSO to formulate 50-fold compound solutions having different concentration gradients, and diluting with water by 10 times to obtain 5-fold compound solutions having different concentration gradients);2. Adding 5 μL of a 5-fold compound solution to a 384-well plate;3. Adding 10 μL of a 2.5-fold kinase solution to incubate for 10 min;4. Then adding 10 μL of a 2.5-fold peptide solution, and reacting at 28° C. for 1 h; and5. Finally, adding 25 μL of stop buffer to terminate the reaction, and reading the data with Caliper.6. Curve fitting to obtain an IC50 value.The calculated inhibition ratio (%)=(the maximum conversion rate−the conversion rate)/(the maximum conversion rate−the minimum conversion rate)×100The curve fitting was conducted with the Xlfit software to obtain IC50 values.
 ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE US9730934, Erlotinib US9409845, Table 1, Compound 22: erlotinib OSI-774 US10189853, erlotinib WO2022090481, Example erlotinib BDBM5446 Erotinib CHEMBL553 US11524945, Compound Erlotinib N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine US10507209, Compound Erlotinib Erlotinib Tarceva N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine Monohydrochloride cid_176870
ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE US9730934, Erlotinib US9409845, Table 1, Compound 22: erlotinib OSI-774 US10189853, erlotinib WO2022090481, Example erlotinib BDBM5446 Erotinib CHEMBL553 US11524945, Compound Erlotinib N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine US10507209, Compound Erlotinib Erlotinib Tarceva N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine Monohydrochloride cid_176870 ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE Erlotinib OSI-774 CP-358774-01 BDBM50311470 CHEMBL1079742
ERLOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE Erlotinib OSI-774 CP-358774-01 BDBM50311470 CHEMBL1079742 US11524945, Compound Erlotinib-4-methylphenyl analog (E4ME) BDBM582529
US11524945, Compound Erlotinib-4-methylphenyl analog (E4ME) BDBM582529 Depsipeptide Antibiotic FR 901228 (1S,4S,7Z,10S,16E,21R)-7-ethylidene-4,21-bis(propan-2-yl)-2-oxa-12,13-dithia-5,8,20,23-tetraazabicyclo[8.7.6]tricos-16-ene-3,6,9,19,22-pentone CHEMBL343448 BDBM19151 Romidepsin FK228
Depsipeptide Antibiotic FR 901228 (1S,4S,7Z,10S,16E,21R)-7-ethylidene-4,21-bis(propan-2-yl)-2-oxa-12,13-dithia-5,8,20,23-tetraazabicyclo[8.7.6]tricos-16-ene-3,6,9,19,22-pentone CHEMBL343448 BDBM19151 Romidepsin FK228