 CHEBI:28645 BDBM50249032 Levulose Dietade Dietary Foods Fructose
CHEBI:28645 BDBM50249032 Levulose Dietade Dietary Foods Fructose cid_16717706 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide BDBM88125 SMR000451233 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidino-6,7-dihydro-5H-1-pyrindine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide (R)-(+)-4-Pyrrolidinopyrindinyl(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iron MLS000766813 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide
cid_16717706 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide BDBM88125 SMR000451233 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidino-6,7-dihydro-5H-1-pyrindine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide (R)-(+)-4-Pyrrolidinopyrindinyl(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iron MLS000766813 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704187 US12139488, Example 524
Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704187 US12139488, Example 524 Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704269 US12139488, Example 665
Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704269 US12139488, Example 665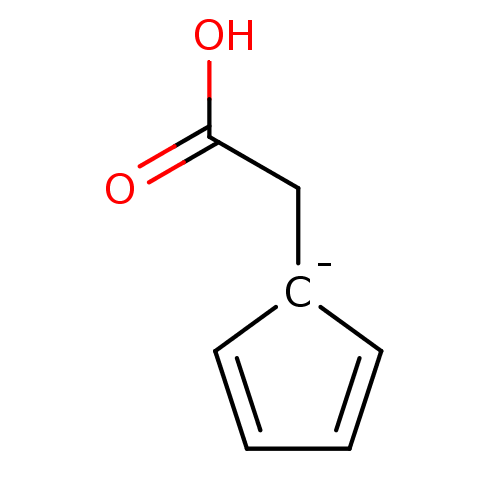 Ferrocene acetic acid BDBM16432 1-(carboxymethyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-ide cyclopentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaide iron
Ferrocene acetic acid BDBM16432 1-(carboxymethyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-ide cyclopentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaide iron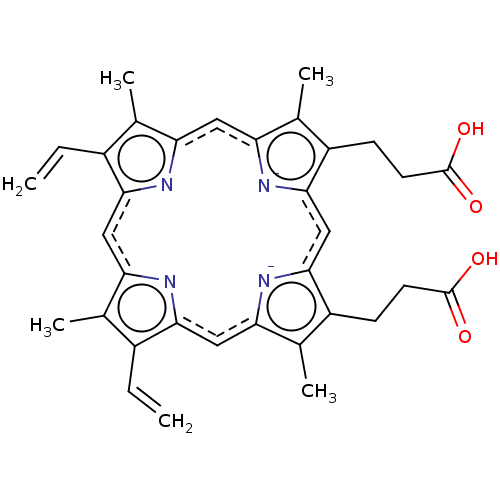 Haemin BDBM209868 Heme 3-[18-(2-carboxyethyl)-8,13-bis(ethenyl)-3,7,12,17-tetramethylporphyrin-21,24-diid-2-yl]propanoic acid;iron(2+)
Haemin BDBM209868 Heme 3-[18-(2-carboxyethyl)-8,13-bis(ethenyl)-3,7,12,17-tetramethylporphyrin-21,24-diid-2-yl]propanoic acid;iron(2+)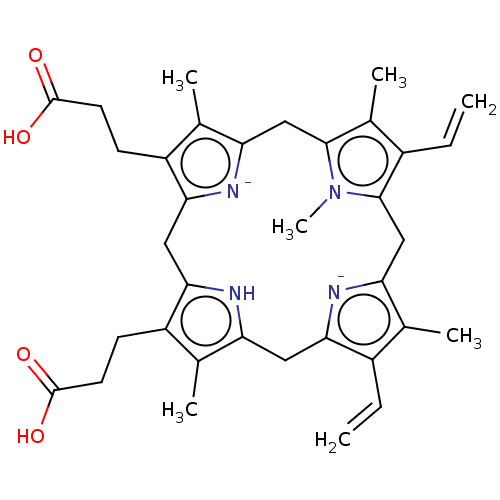 BDBM20 Hematin(iron protoporphyrin IX) 3-[5-(2-carboxyethyl)-15,20-diethenyl-22-hydroxy-4,10,14,19,24-pentamethyl-21,23,24,25-tetraaza-22-ferrahexacyclo[9.9.3.1^{3,6}.1^{13,16}.0^{8,23}.0^{18,21}]pentacosa-1(20),3,5,8,10,13,15,18-octaen-9-yl]propanoic acid
BDBM20 Hematin(iron protoporphyrin IX) 3-[5-(2-carboxyethyl)-15,20-diethenyl-22-hydroxy-4,10,14,19,24-pentamethyl-21,23,24,25-tetraaza-22-ferrahexacyclo[9.9.3.1^{3,6}.1^{13,16}.0^{8,23}.0^{18,21}]pentacosa-1(20),3,5,8,10,13,15,18-octaen-9-yl]propanoic acid
- van Breemen, RB Development of Safe and Effective Botanical Dietary Supplements. J Med Chem 58: 8360-72 (2015)
- Androutsopoulos, VP; Papakyriakou, A; Vourloumis, D; Spandidos, DA Comparative CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 substrate and inhibitor profile of dietary flavonoids. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 2842-9 (2011)
- Takasawa, R; Saeki, K; Tao, A; Yoshimori, A; Uchiro, H; Fujiwara, M; Tanuma, S Delphinidin, a dietary anthocyanidin in berry fruits, inhibits human glyoxalase I. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 7029-33 (2010)
- Whitley, AC; Sweet, DH; Walle, T The dietary polyphenol ellagic acid is a potent inhibitor of hOAT1. Drug Metab Dispos 33: 1097-100 (2005)
- Chen, W; Yuan, X; Li, Z; Lu, Z; Kong, S; Jiang, H; Du, H; Pan, X; Nandi, M; Kong, X; Brown, K; Liu, Z; Zhang, G; Hider, RC; Yu, Y CN128: A New Orally Active Hydroxypyridinone Iron Chelator. J Med Chem 63: 4215-4226 (2020)
- Chua, K; Fung, E; Micewicz, ED; Ganz, T; Nemeth, E; Ruchala, P Small cyclic agonists of iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 4961-9 (2015)
- Li, J; Mahdi, F; Du, L; Jekabsons, MB; Zhou, YD; Nagle, DG Semisynthetic studies identify mitochondria poisons from botanical dietary supplements--geranyloxycoumarins from Aegle marmelos. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 1795-803 (2013)
- Yang, Y; Xiang, K; Sun, D; Zheng, M; Song, Z; Li, M; Wang, X; Li, H; Chen, L Withanolides from dietary tomatillo suppress HT1080 cancer cell growth by targeting mutant IDH1. Bioorg Med Chem 36: (2021)
- Balunas, MJ; Su, B; Brueggemeier, RW; Kinghorn, AD Xanthones from the botanical dietary supplement mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) with aromatase inhibitory activity. J Nat Prod 71: 1161-6 (2008)
- Spear, KL; Brown, MS; Reinhard, EJ; McMahon, EG; Olins, GM; Palomo, MA; Patton, DR Conformational restriction of angiotensin II: cyclic analogues having high potency. J Med Chem 33: 1935-40 (1990)
- Nakhi, A; Wong, HL; Weldy, M; Khoruts, A; Sadowsky, MJ; Dosa, PI Structural modifications that increase gut restriction of bile acid derivatives. RSC Med Chem 12: 394-405 (2021)
- Jiang, X; Zhou, T; Bai, R; Xie, Y Hydroxypyridinone-Based Iron Chelators with Broad-Ranging Biological Activities. J Med Chem 63: 14470-14501 (2020)
- Ding, J; Shi, J; Cui, D; Xu, L; Duan, S; Guo, L; Fei, J Development of peptidic dopamine transporter inhibitors via aromatic modification-mediated conformational restriction. J Med Chem 49: 4048-51 (2006)
- Rerat, V; Laurent, S; Burtéa, C; Driesschaert, B; Pourcelle, V; Vander Elst, L; Muller, RN; Marchand-Brynaert, J Ultrasmall particle of iron oxide--RGD peptidomimetic conjugate: synthesis and characterisation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1861-5 (2010)
- Thaisrivongs, S; Pals, DT; Turner, SR; Kroll, LT Conformationally constrained renin inhibitory peptides: gamma-lactam-bridged dipeptide isostere as conformational restriction. J Med Chem 31: 1369-76 (1988)
- Liu, F; Cui, Y; Yang, F; Xu, Z; Da, LT; Zhang, Y Inhibition of polypeptide N-acetyl-α-galactosaminyltransferases is an underlying mechanism of dietary polyphenols preventing colorectal tumorigenesis. Bioorg Med Chem 27: 3372-3382 (2019)
- Leslie, EM; Mao, Q; Oleschuk, CJ; Deeley, RG; Cole, SP Modulation of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1) transport and atpase activities by interaction with dietary flavonoids. Mol Pharmacol 59: 1171-80 (2001)
- El Bakali, J; Muccioli, GG; Body-Malapel, M; Djouina, M; Klupsch, F; Ghinet, A; Barczyk, A; Renault, N; Chavatte, P; Desreumaux, P; Lambert, DM; Millet, R Conformational Restriction Leading to a Selective CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist Orally Active Against Colitis. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 198-203 (2015)
- Sang, Y; Han, S; Pannecouque, C; De Clercq, E; Zhuang, C; Chen, F Conformational restriction design of thiophene-biphenyl-DAPY HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 182: (2019)
- Miyahara, S; Miyakoshi, H; Yokogawa, T; Chong, KT; Taguchi, J; Muto, T; Endoh, K; Yano, W; Wakasa, T; Ueno, H; Takao, Y; Fujioka, A; Hashimoto, A; Itou, K; Yamamura, K; Nomura, M; Nagasawa, H; Shuto, S; Fukuoka, M Discovery of highly potent human deoxyuridine triphosphatase inhibitors based on the conformation restriction strategy. J Med Chem 55: 5483-96 (2012)
- Bit, RA; Davis, PD; Elliott, LH; Harris, W; Hill, CH; Keech, E; Kumar, H; Lawton, G; Maw, A; Nixon, JS Inhibitors of protein kinase C. 3. Potent and highly selective bisindolylmaleimides by conformational restriction. J Med Chem 36: 21-9 (1993)
- Davis, PD; Hallam, TJ; Harris, W; Hill, CH; Lawton, G; Nixon, JS; Smith, JL; Vesey, DR; Wilkinson, SE Bisindolylmaleimide inhibitors of protein kinase C. Further conformational restriction of a tertiary amine side chain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 1303-1308 (1994)
- Geyer, R; Nordemann, U; Strasser, A; Wittmann, HJ; Buschauer, A Conformational Restriction and Enantioseparation Increase Potency and Selectivity of Cyanoguanidine-Type Histamine H4 Receptor Agonists. J Med Chem 59: 3452-70 (2016)
- Scott, JS; Brocklehurst, KJ; Brown, HS; Clarke, DS; Coe, H; Groombridge, SD; Laber, D; MacFaul, PA; McKerrecher, D; Schofield, P Conformational restriction in a series of GPR119 agonists: differences in pharmacology between mouse and human. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 3175-9 (2013)
- Witschel, M Design, synthesis and herbicidal activity of new iron chelating motifs for HPPD-inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 4221-9 (2009)
- Zurawski, Jr., VR; Stout, DM; Nitz, TJ; Youdim, MB; Weinreb, O Neuroprotective and neuro-restorative iron chelators and monoamine oxidase inhibitors and uses thereof US Patent US9034303 (2015)
- Dickmann, LJ; VandenBrink, BM; Lin, YS In vitro hepatotoxicity and cytochrome P450 induction and inhibition characteristics of carnosic acid, a dietary supplement with antiadipogenic properties. Drug Metab Dispos 40: 1263-7 (2012)
- Borsari, C; Rageot, D; Dall'Asen, A; Bohnacker, T; Melone, A; Sele, AM; Jackson, E; Langlois, JB; Beaufils, F; Hebeisen, P; Fabbro, D; Hillmann, P; Wymann, MP A Conformational Restriction Strategy for the Identification of a Highly Selective Pyrimido-pyrrolo-oxazine mTOR Inhibitor. J Med Chem 62: 8609-8630 (2019)
- Heinzl, GA; Huang, W; Yu, W; Giardina, BJ; Zhou, Y; MacKerell, AD; Wilks, A; Xue, F Iminoguanidines as Allosteric Inhibitors of the Iron-Regulated Heme Oxygenase (HemO) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Chem 59: 6929-42 (2016)
- von Geldern, TW; Tasker, AS; Sorensen, BK; Winn, M; Szczepankiewicz, BG; Dixon, DB; Chiou, WJ; Wang, L; Wessale, JL; Adler, A; Marsh, KC; Nguyen, B; Opgenorth, TJ Pyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acids as endothelin antagonists. 4. Side chain conformational restriction leads to ET(B) selectivity. J Med Chem 42: 3668-78 (1999)
- Schiller, PW; Weltrowska, G; Nguyen, TM; Lemieux, C; Chung, NN; Marsden, BJ; Wilkes, BC Conformational restriction of the phenylalanine residue in a cyclic opioid peptide analogue: effects on receptor selectivity and stereospecificity. J Med Chem 34: 3125-32 (1991)
- Martínez González, S; Rodríguez-Arístegui, S; Hernández, AI; Varela, C; González Cantalapiedra, E; Álvarez, RM; Rodríguez Hergueta, A; Bischoff, JR; Albarrán, MI; Cebriá, A; Cendón, E; Cebrián, D; Alfonso, P; Pastor, J Generation of tricyclic imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazines as novel PI3K inhibitors by application of a conformational restriction strategy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 2536-2543 (2017)
- Watanabe, M; Hirokawa, T; Kobayashi, T; Yoshida, A; Ito, Y; Yamada, S; Orimoto, N; Yamasaki, Y; Arisawa, M; Shuto, S Investigation of the bioactive conformation of histamine H3 receptor antagonists by the cyclopropylic strain-based conformational restriction strategy. J Med Chem 53: 3585-93 (2010)
- Newton, E; Starcovic, SA; Menze, M; Konkle, ME; Long, TE; Hazlehurst, LA; Huber, JD; Robart, AR; Geldenhuys, WJ Development of a fluorescence screening assay for binding partners of the iron-sulfur mitochondrial protein mitoNEET. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 89: (2023)
- Bharti, SK; Sommers, JA; George, F; Kuper, J; Hamon, F; Shin-ya, K; Teulade-Fichou, MP; Kisker, C; Brosh, RM Specialization among iron-sulfur cluster helicases to resolve G-quadruplex DNA structures that threaten genomic stability. J Biol Chem 288: 28217-29 (2013)
- Yonezawa, S; Yamakawa, H; Muto, C; Hosono, M; Yamamoto, T; Hattori, K; Sakagami, M; Togame, H; Tanaka, Y; Nakano, T; Takemoto, H; Arisawa, M; Shuto, S Conformational restriction approach to BACE1 inhibitors II: SAR study of the isocytosine derivatives fixed with a cis-cyclopropane ring. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 2912-5 (2013)
- Yonezawa, S; Yamamoto, T; Yamakawa, H; Muto, C; Hosono, M; Hattori, K; Higashino, K; Yutsudo, T; Iwamoto, H; Kondo, Y; Sakagami, M; Togame, H; Tanaka, Y; Nakano, T; Takemoto, H; Arisawa, M; Shuto, S Conformational restriction approach toß-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors: effect of a cyclopropane ring to induce an alternative binding mode. J Med Chem 55: 8838-58 (2012)
- Banerjee, A; Velagaleti, R; Patil, S; Pawar, M; Yadav, P; Kadam, P; Qadri, MM; Chakraborti, S; Saini, JS; Behera, DB; Karanjai, K; Iyer, PS; Gharat, LA; Das, S Development of potent and selective Cathepsin C inhibitors free of aortic binding liability by application of a conformational restriction strategy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 47: (2021)
- Hayashi, Y; Katada, J; Harada, T; Tachiki, A; Iijima, K; Takiguchi, Y; Muramatsu, M; Miyazaki, H; Asari, T; Okazaki, T; Sato, Y; Yasuda, E; Yano, M; Uno, I; Ojima, I GPIIb/IIIa integrin antagonists with the new conformational restriction unit, trisubstituted beta-amino acid derivatives, and a substituted benzamidine structure. J Med Chem 41: 2345-60 (1998)
- Watanabe, M; Kazuta, Y; Hayashi, H; Yamada, S; Matsuda, A; Shuto, S Stereochemical diversity-oriented conformational restriction strategy. Development of potent histamine H3 and/or H4 receptor antagonists with an imidazolylcyclopropane structure. J Med Chem 49: 5587-96 (2006)
- Gu, Y; Lee, H; Hudson, RA Bis-catechol-substituted redox-reactive analogues of hexamethonium and decamethonium: stimulated affinity-dependent reactivity through iron peroxide catalysis. J Med Chem 37: 4417-20 (1995)
- Yu, MJ; McCowan, JR; Bertsch, B; Ho, PP; Phebus, LA; Ruterbories, KJ; Lindstrom, TD; Smallwood, JK; Simpson, PJ Phenothiazine and phenoxazine derivatives of nafazatrom. In vitro evaluation as 5-lipoxygenase and iron-dependent lipid peroxidation inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2: 59-62 (1992)
- Pirat, C; Dacquet, C; Leclerc, V; Hennuyer, N; Beucher-Gaudin, M; Zanirato, G; Géant, A; Staels, B; Ktorza, A; Farce, A; Caignard, DH; Berthelot, P; Lebegue, N Anti-diabetic activity of fused PPARγ-SIRT1 ligands with limited body-weight gain by mimicking calorie restriction and decreasing SGK1 expression. Eur J Med Chem 137: 310-326 (2017)
- Yin, W; Liu, L; Jiang, H; Wu, T; Cui, H; Zhang, Y; Gao, Z; Sun, Y; Qin, Q; Zhao, L; Su, X; Zhao, D; Cheng, M Design, synthesis, and evaluation of novel 3-thiophene derivatives as potent fungistatic and fungicidal reagents based on a conformational restriction strategy. Eur J Med Chem 233: (2022)
- Dong, X; Zhan, W; Zhao, M; Che, J; Dai, X; Wu, Y; Xu, L; Zhou, Y; Zhao, Y; Tian, T; Cheng, G; Jin, Z; Li, J; Shao, Y; He, Q; Yang, B; Weng, Q; Hu, Y Discovery of 3,4,6-Trisubstituted Piperidine Derivatives as Orally Active, Low hERG Blocking Akt Inhibitors via Conformational Restriction and Structure-Based Design. J Med Chem 62: 7264-7288 (2019)
- Nakada, K; Yoshikawa, M; Ide, S; Suemasa, A; Kawamura, S; Kobayashi, T; Masuda, E; Ito, Y; Hayakawa, W; Katayama, T; Yamada, S; Arisawa, M; Minami, M; Shuto, S Cyclopropane-based conformational restriction of GABA by a stereochemical diversity-oriented strategy: identification of an efficient lead for potent inhibitors of GABA transports. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 4938-50 (2013)
- Zhang, C; Yang, K; Yu, S; Su, J; Yuan, S; Han, J; Chen, Y; Gu, J; Zhou, T; Bai, R; Xie, Y Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of hydroxypyridinone-coumarin hybrids as multimodal monoamine oxidase B inhibitors and iron chelates against Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Med Chem 180: 367-382 (2019)
- Sakakibara, R; Sasaki, W; Onda, Y; Yamaguchi, M; Ushirogochi, H; Hiraga, Y; Sato, K; Nishio, M; Egi, Y; Takedomi, K; Shimizu, H; Ohbora, T; Akahoshi, F Discovery of Novel Pyrazole-Based Selective Aldosterone Synthase (CYP11B2) Inhibitors: A New Template to Coordinate the Heme-Iron Motif of CYP11B2. J Med Chem 61: 5594-5608 (2018)
- Jiang, X; Guo, J; Lv, Y; Yao, C; Zhang, C; Mi, Z; Shi, Y; Gu, J; Zhou, T; Bai, R; Xie, Y Rational design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel multitargeting anti-AD iron chelators with potent MAO-B inhibitory and antioxidant activity. Bioorg Med Chem 28: (2020)
- Gangjee, A; Zeng, Y; McGuire, JJ; Kisliuk, RL Effect of C9-methyl substitution and C8-C9 conformational restriction on antifolate and antitumor activity of classical 5-substituted 2,4-diaminofuro[2,3-d]pyrimidines. J Med Chem 43: 3125-33 (2000)
- Terauchi, M; Abe, H; Tovey, SC; Dedos, SG; Taylor, CW; Paul, M; Trusselle, M; Potter, BV; Matsuda, A; Shuto, S A systematic study of C-glucoside trisphosphates as myo-inositol trisphosphate receptor ligands. Synthesis of beta-C-glucoside trisphosphates based on the conformational restriction strategy. J Med Chem 49: 1900-9 (2006)
- Yonezawa, S; Fujiwara, K; Yamamoto, T; Hattori, K; Yamakawa, H; Muto, C; Hosono, M; Tanaka, Y; Nakano, T; Takemoto, H; Arisawa, M; Shuto, S Conformational restriction approach to β-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors III: effective investigation of the binding mode by combinational use of X-ray analysis, isothermal titration calorimetry and theoretical calculations. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 6506-22 (2013)
- Kazuta, Y; Hirano, K; Natsume, K; Yamada, S; Kimura, R; Matsumoto, S; Furuichi, K; Matsuda, A; Shuto, S Cyclopropane-based conformational restriction of histamine. (1S,2S)-2-(2-aminoethyl)-1-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)cyclopropane, a highly selective agonist for the histamine H3 receptor, having a cis-cyclopropane structure. J Med Chem 46: 1980-8 (2003)
- Ghosh, B; Antonio, T; Reith, ME; Dutta, AK Discovery of 4-(4-(2-((5-Hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl)(propyl)amino)ethyl)piperazin-1-yl)quinolin-8-ol and its analogues as highly potent dopamine D2/D3 agonists and as iron chelator: in vivo activity indicates potential application in symptomatic and neuroprotective therapy for Parkin J Med Chem 53: 2114-25 (2010)
- ChEMBL_2269290 Inhibition of human ALKBH2 demethylase activity by restriction endonuclease digestion assay
- ChEMBL_2269291 Inhibition of human ALKBH3 demethylase activity by restriction endonuclease digestion assay
- ChEMBL_51019 (CHEMBL664411) Aromatase inhibitor potency as iron-binding-related type II difference spectrum
- ChEMBL_51020 (CHEMBL664412) Aromatase inhibitor potency as iron-binding-related type II difference spectrum
- Enzyme Inhibition Assay The predication of no specific interaction between enzyme and iron-binding inhibitors but the Enzyme inhibition constants (IC50s)will change in parallel with the iron-binding constants.
- ChEMBL_154575 (CHEMBL761923) Inhibitory activity against isolated Escherichia coli peptidyl deformylase (PDF) enzyme containing iron.
- ChEMBL_451282 (CHEMBL901493) Inhibition of Escherichia coli methionine aminopeptidase in presence of 6 uM Iron
- ChEMBL_2269294 Inhibition of human ALKBH5 (66 to 292 residues) demethylase activity using 49 nt methylated ssDNA as substrate incubated for 2 hrs by GelRed staining based restriction endonuclease digestion assay
- ChEMBL_851772 (CHEMBL2156240) Activation of human HIF1alpha expressed in DFX-induced human U2OS cells incubated for 30 mins prior to DFX-induction measured after overnight incubation by luciferase reporter gene assay in presence of 50 uM iron
- Luminescence-based cell-based high throughput dose response assay for activators of the GAA850 frataxin (FXN) promoter Source (MLPCN Center Name): The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center (SRISMC) Center Affiliation: The Scripps Research Institute, TSRI Assay Provider: Marek Napierala, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Network: Molecular Library Probe Production Center Network (MLPCN) Grant Proposal Number: 11R21NS064827-01 Grant Proposal PI: Marek Napierala, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center External Assay ID: FXN-GAA850_ACT_LUMI_1536_3XEC50 DRUN Name: Luminescence-based cell-based high throughput dose response assay for activators of the GAA850 frataxin (FXN) promoter. Description: The most frequently inherited early-onset ataxia in Caucasians is Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA), a severe autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease. FRDA is associated with progressive neurological disability, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, increased risk of diabetes mellitus, severe disruption of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biosynthesis, mitochondrial iron overload coupled to
- Inhibition Tests on JAK-1, JAK-2 and JAK-3 Kinases In Kinase Reaction, JAK-1, JAK-2 or JAK-3 may transfer γ-phosphoric acid in ATP onto a single tyrosine residue of a peptide substrate; and there were JAK-1, JAK-2 or JAK-3 inhibitors in the system, γ-phosphoric acid groups on ATP would be not transferred onto the peptide substrate, thus resulting in the failure of phosphorylation. An evaluation experiment was designed based on the principle, a peptide substrate was designed with kinase phosphorylation sites, namely, protein restriction enzyme cutting sites; and both ends thereof were respectively connected with 2 fluorophores as a donor and a receptor respectively; if the kinase kept activity in the system, a γ-phosphonic acid group was transferred onto restriction enzyme cutting sites of the substrate, so that the γ-phosphonic acid group would not be cut and separated into two segments by a protease; moreover, under the stimulation of a laser having a specific wavelength, energy from a segment of fluorescence would be transferred onto another end of fluorophores, thus emitting energy. Otherwise, after kinase activity was inhibited, phosphoric acid groups would be not transferred, and restriction enzyme cutting sites in the substrate would be cut by a kinase in the system to separate the substrate into two segments, thereby no energy transfer of fluorescence occurred. Based on this, the activity of the kinase was evaluated. In this experiment, a 10 μl kinase reaction system was selected, firstly, 2.5 μl kinase (concentration: 1 nM), 2.5 μl peptide substrate (concentration: 2 μM), 2.5 μl ATP (concentration: 10 PM) and 2.5 μl compound were added to each system for reaction for 1 h at room temperature, and then a 5 μl test solution was added for reaction for 1 h at room temperature, then a 5 μl stop buffer was added. A microplate reader (Synergy H1, BioTek, USA) was used to measure fluorescence intensity (emission intensity of coumarin at 445 nm and emission intensity of fluorescein at 520 nm were detected under the stimulation of 400 nm).
- Fluorescence Polarization Assay The enzyme and the substrate were each diluted with a 50 mM tris-hydrochloric acid buffer (pH 7.5) containing 12.5 mM KCl, 3.75 mM MgCl2, 25 μM iron sulfate, 5 mM ascorbic acid, and 2.5 mM DTT, whereas each test compound was diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).A test compound and the substrate solution were preliminarily added onto 384-well plates and reaction was initiated by adding a human PHD2 enzyme solution (40 ng/well). After 20-min incubation at 30° C., an EDTA-containing quench solution was added and the amount of the proline residues hydroxylated via binding to an added HIF-OH antibody solution was quantified by fluorescence polarization.
- FBXL10 Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of FBXL10 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM FBXL10, 30 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64442), 0.2 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 uM sodium L-ascorbate, 5 uM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product is determined quantitatively by AlphaScreen detection after the addition of detection reagents anti-H3K36me1 antibody, AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads, and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA to final 10 ug/ml beads.
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 uM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 uM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.
- JMJD3 Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD3 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM JMJD3, 250 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64367), 1 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 uM sodium L-ascorbate, 5 uM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product is determined quantitatively by AlphaScreen detection after the addition of detection reagents anti-H3K27me1 antibody, 5 ug/ml AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads, and 5 ug/ml AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 10 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA.
- Jarid1B Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 uM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 uM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.
- Luminescence-based biochemical high throughput dose response assay for inhibitors of the interaction of the lipase co-activator protein, abhydrolase domain Source (MLPCN Center Name): The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center (SRIMSC) Affiliation: The Scripps Research Institute, TSRI Assay Provider: James Granneman, Wayne State University Network: Molecular Library Probe Production Centers Network (MLPCN) Grant Proposal Number: 1 R21 NS061634-01 Grant Proposal PI: James Granneman, Wayne State University External Assay ID: ABHD5-MLDP_INH_LUMI_1536_3XIC50 2K Name: Luminescence-based biochemical high throughput dose response assay for inhibitors of the interaction of the lipase co-activator protein, abhydrolase domain containing 5 (ABHD5) with perilipin-5 (MLDP; PLIN5) (2K validation set). Description: Adipocytes are important regulators of vertebrate energy stores, in part through the storage of dietary fat (triglyceride) that is mobilized via lipolysis during fasting states for use by tissues such as heart and skeletal muscle (1, 2). However, in chronic conditions of overnutrition, such as obesity and lipid storage diso
- Luminescence-based biochemical high throughput dose response assay for inhibitors of the interaction of the lipase co-activator protein, abhydrolase domain Source (MLPCN Center Name): The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center (SRIMSC) Affiliation: The Scripps Research Institute, TSRI Assay Provider: James Granneman, Wayne State University Network: Molecular Library Probe Production Centers Network (MLPCN) Grant Proposal Number: 1 R21 NS061634-01 Grant Proposal PI: James Granneman, Wayne State University External Assay ID: ABHD5-PLIN1_INH_LUMI_1536_3XIC50 2K Name: Luminescence-based biochemical high throughput dose response assay for inhibitors of the interaction of the lipase co-activator protein, abhydrolase domain containing 5 (ABHD5) with perilipin-1 (PLIN1) (2K validation set). Description: Adipocytes are important regulators of vertebrate energy stores, in part through the storage of dietary fat (triglyceride) that is mobilized via lipolysis during fasting states for use by tissues such as heart and skeletal muscle (1, 2). However, in chronic conditions of overnutrition, such as obesity and lipid storage disorders
- Spectral Titration of TCCYP51 As a cysteine-coordinated hemoprotein, sterol 14-alpha-demethylase responds spectrally to any perturbations in the area surrounding the heme iron. These spectral responses can be used to estimate the apparent dissociation constants (Kd) of the enzyme/ligand complexes. The titration experiments were carried out at in a cuvette containing TCCYP51 in the wavelength range 350-500 nm using a Shimadzu UV-2401PC spectrophotometer. The tested compounds were added in 1 ul aliquots to the test cuvette until the maximum in spectral response was reached. Equal volumes of DMSO were added to the reference cuvette. The apparent Kd values were determined from the equilibrium titration curves by plotting absorbance changes against the concentration of free ligand and fitting the data to a rectangular hyperbola using SigmaPlot Statistics.
- Inhibition Assay In the design of clinically safe and effective metalloenzyme inhibitors, use of the most appropriate metal-binding group for the particular target and clinical indication is critical. If a weakly binding metal-binding group is utilized, potency may be suboptimal. On the other hand, if a very tightly binding metal-binding group is utilized, selectivity for the target enzyme versus related metalloenzymes may be suboptimal. The lack of optimal selectivity can be a cause for clinical toxicity due to unintended inhibition of these off-target metalloenzymes. One example of such clinical toxicity is the unintended inhibition of human drug metabolizing enzymes such as CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 by the currently-available prostate anticancer agent ketoconazole. It is believed that this off-target inhibition is caused primarily by the indiscriminate binding of the currently utilized 1-imidazole to iron in the active site of CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4.
- In Vitro Assay Human recombinant PDE10A2 was expressed in Sf9 cells, using a recombinant baculovirus construct containing the full length sequence containing a 6 His sequence following the start Met to allow metal affinity purification of the recombinant protein. Cells were harvested and the phosphodiesterase protein was purified by metal chelate chromatography on Ni-sepharose 6FF.The affinity of the compounds of Formula (I) for phophodiesterases (PDE) was measured by a scintillation proximity assay (SPA). PDE Yttrium Silicate SPA beads allow PDE activity to be measured by direct binding of the primary phosphate groups of non-cyclic AMP or GMP to the beads via a complex iron chelation mechanism. The amount of bound tritiated product ([3H]-AMP) is measured by liquid scintillation counting.The compounds were dissolved and diluted in 100% DMSO in polystyrene plates to a concentration of 100-fold the final concentration in the assay. Human PDE10A enzyme solution (10 uL) was added.
- In Vitro Assay hPDE10a Human recombinant PDE10A2 was expressed in Sf9 cells, using a recombinant baculovirus construct containing the full length sequence containing a 6×His sequence following the start Met to allow metal affinity purification of the recombinant protein. Cells were harvested and the phosphodiesterase protein was purified by metal chelate chromatography on Ni-sepharose 6FF.The affinity of the compounds of Formula (I) for phophodiesterases (PDE) was measured by a scintillation proximity assay (SPA). PDE Yttrium Silicate SPA beads allow PDE activity to be measured by direct binding of the primary phosphate groups of non-cyclic AMP or GMP to the beads via a complex iron chelation mechanism. The amount of bound tritiated product ([3H]-AMP) is measured by liquid scintillation counting.The compounds were dissolved and diluted in 100% DMSO in polystyrene plates to a concentration of 100-fold the final concentration in the assay. Human PDE10A enzyme solution (10 uL) was added to 20 μL, of incub
- Enzymatic Assay The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction.
- Inhibition Assay Materials: PAD1, PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 were purchased from commercial sources. Assay buffer: 50 mM Tris pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM CaCl2, 5 mM DTT. Color reagent: 1 volume of reagent A (80 mM diacetyl monoxime, 2 mM thiosemicarbazide) and 3 volumes of reagent B (17.35% v/v H3PO4, 33.7% v/v H2SO4, and 0.765 mg/mL ammonium iron (III) sulfate). The assays were conducted at 37° C. in the presence of each inhibitor in the concentration range of 1 to 1000 μM of each inhibitor tested. The inhibitor (12.5 μL of stock) was mixed with appropriate amount of substrate (BAEE) stock solution and preincubated at 37° C. for a period in the range of 0-60 min. The reaction was initiated by the addition of the enzyme. The reaction samples were incubated for a period in the range of 0-60 min. Color reagent was added (in the range of 50-300 μL/sample) and the samples were boiled for a period in the range of 0-45 min in a water bath. Samples were cooled on ice, vortexed and centrifuged. 200 μL aliquots were transferred to the 96-well plate and the absorbance was measured at 530 nm and the remaining activity was computed.
- KDM2B TR-FRET Assay Full length KDM2B was cloned, expressed, and purified to homogeneity. Compound inhibition of KDM2B demethylase activity was assessed by monitoring the methylation status of a biotin-H3K36me2 peptide substrate (H2N-RKSAPATGGV(KMe2)KPHRYRPGTV-NTPEGBiot; New England Peptide) in the presence of α-keotglutarate (2-OG) and iron (Fe2+) using the TR-FRET assay technology (Cisbio). Specifically, in a 384 well ProxiPlate KDM2B (5 mM final), ascorbate (500 μM final) and DTT (2 mM final) were combined with the biotin-H3K36me2 peptide substrate (200 nM final), 2-OG (0.3 μM or 6 μM final; Sigma K2010) and Fe2+ (100 μM final; Sigma F1543) in 50 mM HEPES (pH 6.5) and 0.01% Triton-X 100 either in the presence of DMSO (final 0.25% DMSO) or compound dilution series in DMSO and mixed. After a two hour incubation at room temperature, a mixture of EU-anti-H3K36me1 antibody (2 nM final; Cisbio #64CUSKAZ), and Streptavidin-d2 (50 nM final; Cisbio #64CUS000) in 200 mM KF, 200 mM EDTA, 0.1% BSA and 50 mM HEPES (pH 6.5) was added. After 1 hour incubation, the plates were read on an Envision instrument, the readouts were transformed into % inhibition, and IC50 values were generated using a four parameter logistic model (XLFIT5).
- PHD1 Enzyme Assay The IC50 values for the PHD1 enzyme (residues 1-407) were determined by mixing increasing amounts of a compound of the invention with a fixed amount of the enzyme (20 nM final concentration) and peptide substrate (Asp-Leu-Asp-Leu-Glu-Ala-Leu-Ala-Pro-Tyr-Ile-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Asp-Phe-Gln-Leu, 1 μM final concentration) and 2-oxoglutarate (0.5 M final concentration) in an assay buffer comprising 30 mM 2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid pH 6.0, 2 mM sodium ascorbate, 100 μM dithiothreitol, 2 mg/ml bovine serum albumin, 60 μg/ml catalase enzyme and 1 μM iron (II) sulphate (FeSO4). The reaction was conducted by pre-incubating the PHD1 enzyme in the presence of a compound of the invention for 60 minutes at room temperature. The activity of the free enzyme was measured by adding the peptide, the 2-oxoglutarate and sodium ascorbate (see above for final concentrations). The assay was quenched by the addition of 30% v/v trichloroacetic acid (final concentration 5%). The amount of product released was measured using a UPLC-MS (Agilent 1290 with an ABSciex 4000qTrap Mass Spectrometer). Data were analysed using the classical isotherm equation for the determination of IC50.
- holoenzyme assay A diverse compound library from NCI Developmental Therapeutics Program (DTP) was subjected to a virtual screening process to identify potential RR inhibitors. The DTP library contains 2,000 different compounds. A novel ligand binding pocket on human RRM2 identified from the X-ray crystal structure (PDB 2UW2) was selected to identify potential inhibitor compounds that were in close proximity to the RRM1/RRM2 interface but distant from the dityrosyl-diiron center in order to avoid iron chelating side effects. This ligand binding pocket, which consists of 32 amino acid residues conserved among human and mouse RRM2 protein families, is in close proximity to the RRM1/RRM2 interface. The structure of the ligand binding pocket is set forth in FIG. 4. The pocket consists of helices α7, α8, and α10 at the C-terminal domain. The narrow interior end of the V-shaped pocket is lined up with hydrophobic residues near the back of dityrosyl diiron cluster center. Polar residues such as D271, R330, and E334 that are located near the open-end of the pocket may potentially interact with the flexible C-terminus. The pocket is lined mostly with interior hydrophobic residues with charged residues exposed to the surface.
- Biochemical Evaluation Proteins used as transcription factors (POLRMT: NP_005026.3, TFAM: NP_003192.1, TFB2M: NP_071761.1) are diluted from their stocks to working concentrations of 1 μM, 20 μM and 4 μM respectively, in a dilution buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, 10% (v/v) glycerol, 1 mM Dithiothreitol (DTT), 0.5 mM EDTA.DNA template is a pUC18 plasmid with the mitochondrial light strand promotor sequence (1-477) cloned between HindIII and BamHI sites. The DNA template is restriction linearized proximal to the promotor 3′-end (pUC-LSP). The reaction mixture (10 uL) containing 7.5 nM POLRMT, 15 nM of TFB2M, 30 nM of TFAM, 0.5 nM of DNA template and 500 μM nucleotide triphosphate mix (NTPs) in a reaction buffer (containing 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 40 mM NaCl, 10 mM DTT, 0.005% (w/v) Tween-20, 160 units/ml Rnase inhibitor and 0.1 mg/mL BSA) are dispensed to compounds in microplates, using a Thermo Multidrop® dispenser, and incubated at 37° C. in a VWR INCU-Line incubator for 60 minutes after mixing. No nucleotide triphosphate mix is added to negative control samples. Microplates with compounds to be tested in the assay are prepared from 10 mM compound stocks in 100% DMSO, equal amounts of DMSO without any compound are added to positive control and negative control samples.
- KDM2B TR-FRET Assay Full length KDM2B was cloned, expressed, and purified to homogeneity. Compound inhibition of KDM2B demethylase activity was assessed by monitoring the methylation status of a biotin-H3K36me2 peptide substrate (H2N-RKSAPATGGV(KMe2)KPHRYRPGTV-NTPEGBiot; New England Peptide) in the presence of α-keotglutarate (2-OG) and iron (Fe2+) using the TR-FRET assay technology (Cisbio). Specifically, in a 384 well ProxiPlate KDM2B (5 mM final), ascorbate (500 μM final) and DTT (2 mM final) were combined with the biotin-H3K36me2 peptide substrate (200 nM final), 2-OG (0.3 μM or 6 μM final; Sigma K2010) and Fe2+ (100 μM final; Sigma F1543) in 50 mM HEPES (pH 6.5) and 0.01% Triton-X 100 either in the presence of DMSO (final 0.25% DMSO) or compound dilution series in DMSO and mixed. After a two hour incubation at room temperature, a mixture of EU-anti-H3K36mel antibody (2 nM final; Cisbio #64CUSKAZ), and Streptavidin-d2 (50 nM final; Cisbio #64CUS000) in 200 mM KF, 200 mM EDTA, 0.1% BSA and 50 mM HEPES (pH 6.5) was added. After 1 hour incubation, the plates were read on an Envision instrument, the readouts were transformed into % inhibition, and IC50 values were generated using a four parameter logistic model (XLFIT5). The KDM2B TR-FRET Assay described above represents an additional embodiment of the invention.
- Enzymatic Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody.
- Human ACMSD-1 Inhibitor Assay A solution of 7.8 μg/ml 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase (3-HAO) with protein dilution buffer (50 mM 4-Morpholineethanesulfonic acid MES pH 6.0) and a solution of 6 μg/ml Human 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate-6-semialdehyde decarboxylase (human ACMSD) with protein dilution buffer (50 mM MES pH 6.0) were prepared separately. A serial 2-fold dilution of test compounds, from 512 nM until 0.5 nM were prepared. To a 96-well plate was added 50 μl of 7.8 μg/ml 3-HAO and 50 μl of 2× working solution (50 μM 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (Sigma 148776), 2 mM ammonium iron(II) sulfate hexahydrate (Sigma V900031), in 50 mM MES pH 6.0) to start the reaction. The plate was placed into a SpectraMax Plus 384 Microplate Reader, Molecular Devices with the temperature set to 28° C. The absorbance at 360 nm for 10 min with 10 seconds interval was monitored and recorded. To a 96-well plate was added 50 μl of 6 μg/ml human ACMSD with series concentrations of the test compound. The absorbance was recorded at 360 nm for 10 min with 10 seconds interval. The data was analyzed in GraphPad Prism 6. A four-parameter dose-response curve was fitted. “Hill Slope” was constrained between −0.5 and −3, and such constrains was indicated when applied.
- ROR gamma t 5xRORE Assay in Jurkat Cells (Assay 2) Compounds of the present invention were tested for ROR gamma inverse agonist activity in a cell-based, transcriptional activity assay. Secreted Nanoluc luciferase was used as a reporter for transcriptional activity of the full-length ROR gamma t in Jurkat cells (ATCC, Cat. # TIB-152). A reporter plasmid was constructed by inserting 5 repeats of the ROR Response Element (RORE) AAAGTAGGTCA (SEQ ID NO:1) into a commercially available promoterless plasmid pNL1.3[secNluc] (Promega, Cat. # N1021) using KpnI and HindIII restriction sites. The expression plasmid for ROR gamma t was purchased (Geneocopoeia, Cat. # EX-T6988-M02). Jurkat cells (30 million cells) were transfected with 11 μg of EX-T6988-M02 and 26 μg of the reporter plasmid in OptiMEM media using Lipofectamine LTX and Plus reagents (Life Technologies, Cat. #15338-100). After 5-6 hrs of incubation at 37° C./5% CO2, the cells were collected, resuspended in phenol-red free RPMI media containing 10% (v/v) delipidated FBS (Hyclone, Cat. # SH30855.03) and dispensed into 96-well clear bottom tissue culture plates (CoStar, Cat. #3603), at 80,000 cells per well. Tested compounds were added to the cells in the same media (final concentration of DMSO was 0.1% (v/v)), and the plates were incubated at 37° C./5% CO2 for 16-18 hrs. Luciferase activity in the conditioned supernatants was determined with NanoGlo assay reagents (Promega, Cat.# N1130). Percent inhibition values were calculated based on the fully inhibited and non-inhibited (DMSO) controls, and the values were regressed against concentrations of the tested compounds to derive IC50 values using a four-parameter non-linear fitting model.
- RORgammat 5xRORE Assay in Jurkat Cells (Assay 2) Compounds of the present invention were tested for RORγ inverse agonist activity in a cell-based, transcriptional activity assay. Secreted Nanoluc luciferase was used as a reporter for transcriptional activity of the full-length RORγt in Jurkat cells (ATCC, Cat. # TIB-152). A reporter plasmid was constructed by inserting 5 repeats of the ROR Response Element (RORE) AAAGTAGGTCA (SEQ ID NO:1) into a commercially available promoterless plasmid pNL1.3[secNluc] (Promega, Cat. # N1021) using KpnI and HindIII restriction sites. The expression plasmid for RORyt was purchased (Geneocopoeia, Cat. # EX-T6988-M02). Jurkat cells (30 million cells) were transfected with 11 μg of EX-T6988-M02 and 26 μg of the reporter plasmid in OptiMEM media using Lipofectamine LTX and Plus reagents (Life Technologies, Cat. #15338-100). After 5-6 hrs of incubation at 37° C./5% CO2, the cells were collected, resuspended in phenol-red free RPMI media containing 10% (v/v) delipidated FBS (Hyclone, Cat. # SH30855.03) and dispensed into 96-well clear bottom tissue culture plates (CoStar, Cat. #3603), at 80,000 cells per well. Tested compounds were added to the cells in the same media (final concentration of DMSO was 0.1% (v/v)), and the plates were incubated at 37° C./5% CO2 for 16-18 hrs. Luciferase activity in the conditioned supernatants was determined with NanoGlo assay reagents (Promega, Cat. # N1130). Percent inhibition values were calculated based on the fully inhibited and non-inhibited (DMSO) controls, and the values were regressed against concentrations of the tested compounds to derive IC50 values using a four-parameter non-linear fitting model.
- RORgammat 5xRORE Assay in Jurkat Cells (Assay 2) Compounds described herein were tested for RORγ inverse agonist activity in a cell-based, transcriptional activity assay. Secreted Nanoluc luciferase was used as a reporter for transcriptional activity of the full-length RORγt in Jurkat cells (ATCC, Cat. # TIB-152). A reporter plasmid was constructed by inserting 5 repeats of the ROR Response Element (RORE) AAAGTAGGTCA (SEQ ID NO: 1) into a commercially available promoterless plasmid pNL1.3[secNluc] (Promega, Cat. # N1021) using KpnI and HindIII restriction sites. The expression plasmid for RORγt was purchased (Geneocopoeia, Cat. # EX-T6988-M02). Jurkat cells (30 million cells) were transfected with 11 μg of EX-T6988-MO2 and 26 μg of the reporter plasmid in OptiMEM media using Lipofectamine LTX and Plus reagents (Life Technologies, Cat. #15338-100). After 5-6 hrs of incubation at 37° C./5% CO2, the cells were collected, resuspended in phenol-red free RPMI media containing 10% (v/v) delipidated FBS (Hyclone, Cat. # SH30855.03) and dispensed into 96-well clear bottom tissue culture plates (CoStar, Cat. #3603), at 80,000 cells per well. Tested compounds were added to the cells in the same media (final concentration of DMSO was 0.1% (v/v)), and the plates were incubated at 37° C./5% CO2 for 16-18 hrs. Luciferase activity in the conditioned supernatants was determined with NanoGlo assay reagents (Promega, Cat.# N1130). Percent inhibition values were calculated based on the fully inhibited and non-inhibited (DMSO) controls, and the values were regressed against concentrations of the tested compounds to derive IC50 values using a four-parameter non-linear fitting model.
- Enzymatic Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 2 nM JMJD2A, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 6 nM JMJD2A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature.
- Enzymatic Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature.
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay JMJD2C: The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT.
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay Jarid1b: The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-H3K4me or -H3K4me2 antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me/H3K4me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT.
- Enzymatic Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- FBXL11 Assay PHF8 Assay: The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of PHF8 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 3 nM PHF8, 200 nM H3K9me1-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64358), 0.5 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 uM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 uM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-unmodified-histone H3 lysine 9/lysine27 (H3K9/K27) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 0.5 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 ul of the mixture of 600 nM H3K9me1-biotin labeled peptide and 1.5 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 ul of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 ul of 9 nM PHF8 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 ul of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 1 nM Europium-anti-unmodified H3K9/K27 antibody. Plates were read by EnVision Multilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay JMJD3: The enzymatic assay of JMJD3 activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD3 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 5 nM JMJD3, 250 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64367), 0.4 to 2 μM o-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 750 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide and 1.2 to 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μL of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 15 nM JMJD3 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μL of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT.
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2A was determined in 38-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 2 nM JMJD2A, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 6 nM JMJD2A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μL of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μL of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μL of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay for Jarid1B Activity The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-H3K4me or -H3K4me2 antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively. The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me/H3K4me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2A Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 2 nM JMJD2A, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 6 nM JMJD2A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively. The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at rt. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD2C Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate-format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1B Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384 well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono-or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at rt for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at rt. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1B Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-H3K4me or -H3K4me2 antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me/H3K4me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- PHF8 Assay PHF8 Assay: The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of PHF8 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 3 nM PHF8, 200 nM H3K9me1-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64358), 0.5 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 uM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 uM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-unmodified-histone H3 lysine 9/lysine27 (H3K9/K27) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 0.5 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 ul of the mixture of 600 nM H3K9me1-biotin labeled peptide and 1.5 uM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 ul of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 ul of 9 nM PHF8 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 ul of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 1 nM Europium-anti-unmodified H3K9/K27 antibody. Plates were read by EnVision Multilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- BCA Protein Assay Escherichia coli BL21*DE3 pET30a-Ec yeaWX #1 (Ec YeaWX) strain was generated as described below. The contiguous Escherichia coli coding sequence yeaW (equivalent to uniprot ID P0ABR7.1 (YeaW) (SEQ ID NO: 2)) and yeaX (equivalent to uniprot ID P76254.1 (YeaX) (SEQ ID NO: 3)) were PCR amplified from Escherichia coli strain K-12 substr. BW25113 genomic DNA. PCR primers (YeaW_Nde I_fwd2-SEQ ID NO: 4; YeaX_rev2-SEQ ID NO: 5) were designed to create a 5′ NdeI restriction site including the ATG start codon of yeaW and create a PstI restriction site just 3′ of the yeaX TAG stop codon.The bacteria were grown aerobically in 50 mL LB broth (Difco #244620; 10 g/L Tryptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, 10 g/L NaCl, 50 μg/mL kanamycin), in a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask. The cultures were inoculated from glycerol stock of BL21*DE3 pET30a-Ec yeaWX #1 strain. Strains were cultured all day at 37° C. with 250 rpm shaking. Two 300 mL Minimal M9 Medium (6 g/L Na2HPO4, 3 g/L KH2PO4, 0.5 g/L NaCl, 1 g/L NH4Cl, 0.1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgSO4, 0.2% Dextrose, 1 mg/L Thiamine, 50 μg/mL kanamycin), in 1 L Erlenmeyer flasks, were inoculated with 5 mL of the LB broth day culture and cultured overnight at 37° C. with 250 rpm shaking. The overnight cultures were used to inoculate twelve 1 L cultures of Minimal M9 media in 2.8 L fluted Erlenmeyer flasks to an OD 600 nm of 0.05 (typically approximately 28 mLs), which were grown at 37° C. with 250 rpm shaking until an OD600 of approximately 0.4 was reached. Expression of YeaWX was induced with 1 mM IPTG and the induced cultures were further grown overnight at 37° C. with 250 rpm shaking. The biomass was pelleted by centrifugation at 6000×g for 12 minutes at 4° C. The cell pellet was suspended in 240 mL of ice-cold 1× Phosphate Buffered Saline (Ca2+ and Mg2+ free). Ninety micrograms of Lysozyme (Sigma #L6876 Lot #SLBG8654V; Sigma-Aldrich Corp., St. Louis, Mo.) was added and incubated with 320 rpm shaking for 30 minutes at 4° C. Lysis was achieved via French press with a 4° C. prechilled 1″ diameter chamber at 1000 psi (high ratio; internal PSI equivalent 16000). The lysate was centrifuged at 6,000×g for 12 minutes at 4° C. to pellet extra debris. Glycerol was added to the centrifuged lysate supernatant at a final concentration of 15% A protein concentration of the centrifuged lysate supernatant was determined by a BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce #23225), typically in the 2.5 to 4.5 mg/ml range. The centrifuged Ec YeaWX lysate supernatant was aliquoted into 20 mL volumes and stored frozen at −80° C.Ec YeaWX lysate was diluted to 2.0 mg/mL protein with 1× Dulbecco's phosphate buffered saline (DPBS) plus 15% glycerol. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) was added to 250 μM. One hundred and fifty microliters of Ec YeaWX lysate was dispensed into a deep-well plate (polypropylene, 2 mL volume, Corning Axygen catalogue #P-DW-20-C). Candidate IC50 compounds from TABLE 1 and vehicle control (respective vehicle control of DMSO or water), or control compounds (IC50 control, 8-Quinolinol hemisulfate salt (Sigma Catalog #55100)) were added at a 1:100 dilution (e.g., 1.5 μL per well). The plates were agitated on a plate shaker for 1 minute. d9-carnitine chloride (1.5 μL of 5 mM) was added to all wells to reach a final d9-carnitine chloride concentration of 50 μM.
- Enzymatic Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Enzymatic Assay The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay for JMJD2C Activity The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min,and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay for JMJD3 Activity The enzymatic assay of JMJD3 activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD3 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 5 nM JMJD3, 250 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64367), 0.4 to 2 μM α-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 750 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide and 1.2 to 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μL of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 15 nM JMJD3 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μL of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT. A ratio from the readout of 665/615 was calculated for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD3 Assay The enzymatic assay of JMJD3 activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD3 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 5 nM JMJD3, 250 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64367), 0.4 to 2 μM α-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μM of the mixture of 750 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide and 1.2 to 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μL of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 15 nM JMJD3 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at RT for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μL of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at RT. A ratio from the readout of 665/615 was calculated for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- JMJD3 Assay The enzymatic assay of JMJD3 activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD3 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 5 nM JMJD3, 250 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64367), 0.4 to 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 750 nM H3K27me3-biotin labeled peptide and 1.2 to 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μL of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 15 nM JMJD3 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μL of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K27me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio from the readout of 665/615 was calculated for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1A Assay The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono-or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at rt for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at rt. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1A Assay The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1A Assay The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1B Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at room temp. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Jarid1B Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- PHF8 Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of PHF8 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 3 nM PHF8, 200 nM H3K9me1-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64358), 0.5 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-unmodified-histone H3 lysine 9/lysine27 (H3K9/K27) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 0.5 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 600 nM H3K9me1-biotin labeled peptide and 1.5 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 9 nM PHF8 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 1 nM Europium-anti-unmodified H3K9/K27 antibody. Plates were read by EnVision Multilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hour incubation at room temperature. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) JMJD2C: The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of JMJD2C was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM JMJD2C, 300 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64360), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-di-methylated histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 50 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K9me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 0.9 nM JMJD2C to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 100 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K9me2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at rt. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) Jarid1A: The enzymatic assay of Jarid1A activity is based upon Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) detection. The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1A was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 1 nM Jarid1A, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 3 nM Jarid1A to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at rt for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at rt. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- Time Resolved-Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (TR-FRET) Jarid1B: The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of Jarid1B was determined in 384 well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.8 nM Jarid1B, 300 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64357), 2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 2 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by TR-FRET after the addition of detection reagent Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin (Prozyme) and Europium-anti-mono- or di-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1-2) antibody (PerkinElmer) in the presence of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer (PerkinElmer) at a final concentration of 25 nM and 1 nM, respectively.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 2 μl of the mixture of 900 nM H3K4me3-biotin labeled peptide and 6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 2 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO was added to each well of the plate, followed by the addition of 2 μl of 2.4 nM Jarid1B to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at rt for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 6 μl of 5 mM EDTA in LANCE detection buffer containing 50 nM Phycolink Streptavidin-allophycocyanin and 2 nM Europium-anti-H3K4me1-2 antibody. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in TR-FRET mode (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 615 nm and 665 nm) after 1 hr incubation at rt. A ratio was calculated (665/615) for each well and fitted to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- FBXL10 Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of FBXL10 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM FBXL10, 30 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64442), 0.2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product is determined quantitatively by AlphaScreen detection after the addition of detection reagents anti-H3K36me1 antibody, AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads, and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA to final 10 μg/ml beads.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 3 μl of the mixture of 90 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide and 0.6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 3 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO are added to each well of 384 well Proxiplate (Perkin Elmer), followed by the addition of 3 μl of 0.9 nM FBXL10 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture is incubated at room temperature for 1 hour, and terminated by the addition of 3 μl of appropriate dilution of anti H3K36me1 antibody in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA. Plates will then incubated at room temperature for 40 minutes, followed by addition of 3 ul of 50 μg/ml AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA. Plates will then be read by EnVision Multilabel Reader in AlphaScreen mode after minimum 2 hour incubation at room temperature. The AlphaScreen signal for each well is used to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- FBXL10 Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of FBXL10 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM FBXL10, 30 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64442), 0.2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by AlphaScreen detection after the addition of detection reagents anti-H3K36me1 antibody, AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads, and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA to final 10 μg/ml beads.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 3 μl of the mixture of 90 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide and 0.6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 3 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of 384 well Proxiplate (Perkin Elmer), followed by the addition of 3 μl of 0.9 nM FBXL10 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, and terminated by the addition of 3 μl of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA containing appropriate dilution of anti H3K36me1 antibody. Plates were incubated at room temperature for 40 minutes, followed by addition of 3 μl of 50 μg/ml AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in AlphaScreen mode after a minimum of 2 hour or up to overnight incubation at room temperature. The AlphaScreen signal for each well was used to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- FBXL11 Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of FBXL11 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.15 nM FBXL11, 30 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64442), 0.2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product is determined quantitatively by AlphaScreen detection after the addition of detection reagents anti-H3K36me1 antibody, AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads, and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA to final 10 μg/ml beads.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 3 μl of the mixture of 90 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide and 0.6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 3 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO are added to each well of 384 well Proxiplate (Perkin Elmer), followed by the addition of 3 μl of 0.45 nM FBXL11 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture is incubated at room temperature for 1 hour, and terminated by the addition of 3 μl of appropriate dilution of anti H3K36me1 antibody in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA. Plates will then incubated at room temperature for 40 minutes, followed by addition of 3 ul of 50 μg/ml AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA. Plates will then be read by EnVision Multilabel Reader in AlphaScreen mode after minimum 2 hour incubation at room temperature. The AlphaScreen signal for each well is used to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Assay The ability of test compounds to inhibit the activity of FBXL10 was determined in 384-well plate format under the following reaction conditions: 0.3 nM FBXL10, 30 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide (Anaspec cat #64442), 0.2 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid in assay buffer of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 0.005% Brij35, 0.5 mM TCEP, 0.2 mg/ml BSA, 50 μM sodium L-ascorbate, and 5 μM ammonium iron(II) sulfate. Reaction product was determined quantitatively by AlphaScreen detection after the addition of detection reagents anti-H3K36me1 antibody, AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads, and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA to final 10 μg/ml beads.The assay reaction was initiated by the following: 3 μl of the mixture of 90 nM H3K36me2-biotin labeled peptide and 0.6 μM alpha-ketoglutaric acid with 3 μl of 11-point serial diluted inhibitor in 3% DMSO were added to each well of 384 well Proxiplate (Perkin Elmer), followed by the addition of 3 μl of 0.9 nM FBXL10 to initiate the reaction. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temp for 30 min, and terminated by the addition of 3 μl of 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA containing appropriate dilution of anti H3K36me1 antibody. Plates were incubated at room temp for 40 min, followed by addition of 3 μl of 50 μg/ml AlphaScreen Streptavidin-coated Donor beads and AlphaScreen Protein A Acceptor beads in 50 mM HEPES, pH7.3, 10 mM NaCl, 0.005% Brij35, 5 mM EDTA, 2 mg/ml BSA. Plates were read by EnVisionMultilabel Reader in AlphaScreen mode after a minimum of 2 hr or up to overnight incubation at room temp. The AlphaScreen signal for each well was used to determine inhibition constant (IC50).
- LOX Activity in Cysts Assay Cell Culture and TransfectionAll cell lines used in this study was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Mycoplasma contamination was routinely monitored by PCR. Cells used were not found to be Mycoplasma positive. MDCK cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% Penicillin Streptomycin solution (Pen Strep). For GFP constructs transfection in MDCK cells, lipofectamine 3000 was used according to manufactures protocols. Cells were either selected with G418 (Life Technologies) at 5 mg/ml. All cell culture reagents were purchased from Life Technologies.To produce MDCK cysts, cells were cultured on Matrigel (Corning) with 2% Matrigel supplemented in DMEM with 10% FBS. Cysts were allowed to form for 10 days before subsequent studies.Cloning of LOX Expression ConstructsMouse LOX cDNA was purchased from OriGene. Full length LOX cDNA was then PCR cloned into pEGFP-N1 (Clonetech), or biosensor vector proGFP2-N1 (Hanson, 2004) using the following primers, GAGAGAGCTAGCATGCGTTTCGCCTGGG (SEQ. ID NO. 1) (forward primer) and TCTCTCCTCGAGATACGGTGAAATTGTGCAGCC (SEQ. ID NO. 2) (reverse primer). For the insertion into pEGFP-N1 or proGFP2-N1, Nhel and Xhol restriction sites were added to forward and reverse primers accordingly. Mutant LOX constructs were made using QuickChange II site-directed mutagenesis kit (Agilent Technologies) following manufacture's protocol using LOX-GFP as template. To generate, roGFP2 versions of LOX mutant constructs, LOX mutant cDNA was transferred from pEGFP-N1 to proGFP2-N1 using Nhel and Xhol.Confocal Imaging and Imaging AnalysisAll photomicrographs were taken with a Leica TCS SP8 X confocal system. For LOX biosensor imaging, live MDCK cysts were used. The oxidised biosensor was excited using a 405 nm laser, while the reduced biosensor was excited with a 488 nm laser. Emission of the biosensor was recorded at 500 nm˜530 nm range using sequential scans. Ratio images were generated following a published protocol {Kardash, 2011 #376}. Note, while the published protocol generates YFP/CFP ratio images, we used it to generate Oxidised/Reduced (roGFP2 ratio) ratio images. The roGFP2 ratio at the basal surface of MDCK cysts was used to indicate LOX inhibition. LOX inhibitors were added 30min prior to imaging at 20 uM.
- TR-FRET Assay The ability of some compounds of the present invention to inhibit POLRMT were determined in a homogeneous TR-FRET Assay using high-throughput screening in a 384-well plate format. This method is used to monitor the activity of mitochondrial transcription through measurement of its product, a 407 bp long RNA transcript. Detection of the product is facilitated by hybridization of two DNA-oligonucleotide probes to specific and adjacent sequences within the RNA product sequence. Upon annealing of the probes, two fluorophores are coupled directly to an acceptor nucleotide probe (ATTO647, 5′), or introduced via a coupled streptavidin with a biotinylated donor nucleotide probe (Europium cryptate) that is brought into sufficient proximity to serve as a fluorescence-donor-acceptor pair. Thus, a FRET signal at 665 nm is generated upon excitation at 340 nm.Proteins used as transcription factors (POLRMT: NP_005026.3, TFAM: NP_003192.1, TFB2M: NP_071761.1) are diluted from their stocks to working concentrations of 1 μM, 20 μM and 4 μM respectively, in a dilution buffer containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, 10% (v/v) glycerol, 1 mM Dithiothreitol (DTT), 0.5 mM EDTA.DNA template is a pUC18 plasmid with the mitochondrial light strand promotor sequence (1-477) cloned between HindIII and BamHI sites. The DNA template is restriction linearized proximal to the promotor 3′-end (pUC-LSP).The reaction mixture (10 uL) containing 7.5 nM POLRMT, 15 nM of TFB2M, 30 nM of TFAM, 0.5 nM of DNA template and 500 μM nucleotide triphosphate mix (NTPs) in a reaction buffer (containing 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 40 mM NaCl, 10 mM DTT, 0.005% (w/v) Tween-20, 160 units/ml Rnase inhibitor and 0.1 mg/mL BSA) are dispensed to compounds in microplates, using a Thermo Multidrop® dispenser, and incubated at 37° C. in a VWR INCU-Line incubator for 60 minutes after mixing. No nucleotide triphosphate mix is added to negative control samples. Microplates with compounds to be tested in the assay are prepared from 10 mM compound stocks in 100% DMSO, equal amounts of DMSO without any compound are added to positive control and negative control samples.
- Expression and Purification of Active Kinases Full length CDPK1 was PCR amplified from a T. gondii RH cDNA library generated using the SMART cDNA synthesis kit (Clontech). The primers contained restriction sites that were used to directionally clone the PCR product, NdeI to XhoI, into the pET-22b(+) vector, in frame with a C-terminal hexahistidine tag. Single mutation of the codon corresponding to glycine 128 was achieved using the QuikChange II Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (Agilent Technologies), with specific primers designed according to manufacturer instructions. Plasmids were transformed into BL21(DE3)V2RpAcYc-LIC+LamP E. coli, which express the LamP phosphatase, as described previously. Following overnight growth in Terrific Broth at 37° C., cells were diluted 1:50 in fresh medium and cultured for 3 h at 37° C., then cooled to 15° C., induced by addition of 1 mM IPTG, and cultured overnight. Cells were lysed in CelLyticB solution (Sigma Aldrich), and proteins purified using HIS-select Nickel Affinity Gel following manufacturers instructions (Sigma-Aldrich). Purified proteins were dialyzed (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.125% Chelex 100) and stored in 20% glycerol at −80° C. Protein purity and concentration were determined by SDS-PAGE followed by staining with SYPRO Ruby (Invitrogen).Kinase assays were conducted using a peptide-based ELISA based on the syntide-2 peptide (Calbiochem). Syntide-2 peptide (10 mg/ml) was used to coat 96-well plates by overnight incubation in carbonate coating buffer (pH 9.6) at 4° C. Following washing in Tris tween (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.2% Tween20), plates were blocked with 3% BSA in Tris-tween for 2 h at room temperature, and further washing steps were conducted with Tris-tween. Kinase reactions were conducted at 30° C. for 20 min in kinase buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.005% Tween20) containing appropriate amounts of ATP (Km for each enzyme) and enzyme dilutions (see below). Phosphorylated syntide peptides were detected with mAb MS-6E6 (MBL Intl. Corp.), followed by peroxidase-conjugated goat-anti-mouse IgG, developed with the substrate 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) and detected by absorbance at 450 nm. The activity of human calmodulin dependent kinase II alpha (aCaMKII) was tested using the CaM Kinase II Assay CycLex kit (MBL Intl. Corp.).
- Measurement of TRPA1 Antagonist Activity Human TRPA1 Expression PlasmidUsing cDNA encoding human TRPA1 (GenBank accession No. NM_007332) (manufactured by Kazusa DNA Research Institute, item No. FHC07217) as a template, primer 1 (SEQ ID NO: 1) and primer 2 (SEQ ID NO: 2), PCR by PfuUltra High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (Stratagene) was performed, and full-length human TRPA1 gene was amplified.primer 1: (SEQ ID NO: 1) 5′-AACTTTTAGTAAGCTTCGATCGCCATGAAG-3′ primer 2: (SEQ ID NO: 2) 5′-GTACCGATCTAGAATTCGTTTTACTAAGGCTCAAG-3′A recognition site (underlined) of restriction enzyme HindIII was added to the 5′ end of human TRPA1 gene, and XbaI site (underlined) was added to the 3′ end of human TRPA1 gene, and GTT of the template sequence was changed to termination codon TAG (bold). The obtained double stranded DNA was enzyme-digested with HindIII and XbaI, and introduced into a multicloning site of expression plasmid pcDNA3.1/zeo(+) (manufactured by Invitrogen) to give a human TRPA1 expression plasmid.Cell PreparationHuman embryonic kidney-derived 293T cells were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 10 unit penicillin, and 10 μg streptomycin. One day before assay, 3×106 of 293T cells were plated on a petri dish having a diameter of 10 cm, and cultured in a CO2 incubator for 24 hr. OPTI-MEM I Reduced Serum Media (Invitrogen) (600 μL), Mirus TransIT-293 (Mirus Bio) (18 μL), and human TRPA1 expression plasmid (6 μg) were mixed, the total amount of the mixture was added to the cells on the petri dish to allow for gene transfer. The cells were recovered about for 8 hr later, plated on a poly-D-lysine coated 384 well black/clear bottom plate at 12,000 cells/well, and cultured overnight.Measurement of Intracellular Calcium IncreaseThe medium was removed from the 384 well plate, calcium indicator (Molecular Device, trade name: FLIPR Calcium4 Assay Kit) dissolved in HBSS (Thermo Fisher Scientific) (pH 7.2) containing 20 mM HEPES was added (38 μL/well), and the cells were stained in a CO2 incubator for 1 hr. The 384 well plate was stood at room temperature for not less than 15 min, set on FDSS7000 (Hamamatsu Photonics K.K.), and a test substance solution was added at 10 μL/well. After 10 min, allylisothiocyanate solution (12 μL/well) was added, the relative fluorescence intensity was measured for 5 min after addition of the allylisothiocyanate solution.Test Substance PreparationPreparation of Test Substance Solution and Allylisothiocyanate SolutionA test substance solution was prepared to have a composition of HBSS (Thermo Fisher Scientific) (pH 7.2) containing 0.48% dimethyl sulfoxide, a test substance at 4.8-fold concentration of the evaluation concentration, 0.1% bovine serum albumin and 20 mM HEPES. An allylisothiocyanate solution was prepared to have a composition of HBSS (Thermo Fisher Scientific) (pH 7.2) containing 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide, 100 μM allylisothiocyanate, 0.1% bovine serum albumin and 20 mM HEPES.Calculation of Antagonist ActivityThe activity rate of a test substance at each concentration was calculated, wherein the relative fluorescence intensity change of a well free of a test substance and containing allylisothiocyanate is 100% activity rate, and the relative fluorescence intensity change of a well free of a test substance and allylisothiocyanate is 0% activity rate. The inhibitory rate of a test substance at each concentration was calculated by subtracting the activity rate of the test substance from 100% activity rate, and the concentration of a test substance showing 50% inhibitory rate was calculated as IC50 from the sigmoid approximate curve by XLfit (idbs).
- PI(4)K enzymatic Assay Baculovirus expression and purification of C. parvum phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase: The full-length coding sequence of C. parvum PI(4)K (cgd8_4500, 1114 amino acids) was codon-optimized for baculovirus expression, synthesized and cloned into pFastBac-HTb (Invitrogen 10584-027) in frame with the amino-terminal polyhistidine tag using the BamHI and HindIII restriction sites. Recombinant pFastBacHTb-CpPI(4)K bacmid clones were generated by site-specific transposition in E. coli DH10Bac (Invitrogen 10361-012). The bacmid sequence was confirmed by direct DNA sequencing to confirm a lack of mutations across the whole gene. The subsequent steps for bacmid isolation, transfection and selection of the recombinant viruses were performed according to the manufacturer s protocol (Bac-to-Bac system # 10359, Invitrogen).SF9 cells, cultured in SF-900 III serum-free medium, were transfected with recombinant baculovirus at 1/200 (v/v) and incubated at 27^°C for 72^h. The pellets were collected after centrifugation and re-suspended in cell lysis buffer (20^mM Tris-HCl, pH^7.5, 300^mM NaCl, 1mM DTT, 20mM imidazole, 0.01% Triton X-100 and 1×^complete protease inhibitor cocktail without EDTA (Roche Diagnostics 04693116001)). The cell suspension was lysed by sonication and the clarified supernatant was loaded onto a 1^ml HisTrap affinity column (GE Healthcare) pre-equilibrated with buffer A (20^mM Tris-HCl, pH^7.5, 300^mM NaCl, 1mM DTT, 20mM Imidazole, and 1×^complete protease inhibitor cocktail without EDTA). The column was washed with buffer B (buffer A containing 45 mM imidazole) and the bound protein of interest was eluted with buffer C (buffer A with 90^mM imidazole). The fractions containing CpPI(4)K were pooled, concentrated using Amicon Ultra-15 and purified by a gel-filtration column (Hi-Load 26/60 Superdex 200, GE Healthcare) equilibrated with 20^mM Tris, pH^7.5, 300^mM NaCl, 1^mM DTT and 1×^protease inhibitor cocktail without EDTA. The concentrations of the purified protein (Mw 132.39 kda) was determined by using the protein molar extinction coefficient (ε280^nm = 133,810^M−1^cm−1). Aliquots were flash frozen in liquid nitrogen and immediately stored at −80^°C.PI(4)K enzymatic Assay: The CpPI(4)K enzymatic assay was performed as described earlier with a some modifications (McNamara et al., 2013). Briefly, L-α-phosphatidylinositol (Avanti Polar Lipid 840046), dissolved in 3% n-octylglucoside (Roche Diagnostics 10634425001), was used as the lipid substrate for the PI(4)K activity assay. CpPI(4)K was assayed using Transcreener ADP2 FP detection kit (BellBrook 3010) in a black, solid 384-well plate (Corning 3575). The final assay volume was 10^μl and contained 3^nM of the respective CpPI(4)K construct in 10^mM Tris, pH^7.5, 1^mM DTT, 3^μM ATP, 5^mM Mn2+, 0.05% Triton X-100 and 10^μM phosphatidylinositol/octylglucoside. The enzyme reaction was performed for 50 minutes at room temperature and was stopped by adding 10^μl of detection mix containing 1×^stop buffer (50mM HEPES, pH7.5, 400mM NaCl, 20mM EDTA, and 0.02% Brij-35), 2^nM AMP Alexa Fluor 633 tracer, and 20^μg^ml−1 ADP antibody. Fluorescence polarization measurements were performed on the Infinite M1000 plate reader (Tecan) with λex = 635^nm and λem = 680^nm (20-nm bandwidth). IC50 values were calculated using Graphpad Prism software.
 CHEBI:28645 BDBM50249032 Levulose Dietade Dietary Foods Fructose
CHEBI:28645 BDBM50249032 Levulose Dietade Dietary Foods Fructose cid_16717706 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide BDBM88125 SMR000451233 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidino-6,7-dihydro-5H-1-pyrindine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide (R)-(+)-4-Pyrrolidinopyrindinyl(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iron MLS000766813 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide
cid_16717706 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidin-1-yl-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide BDBM88125 SMR000451233 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-pyrrolidino-6,7-dihydro-5H-1-pyrindine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide (R)-(+)-4-Pyrrolidinopyrindinyl(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iron MLS000766813 iron;1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopenta-1,3-diene;4-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-6,7-dihydro-5H-cyclopenta[b]pyridine-4a,5,6,7,7a-pentaide Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704187 US12139488, Example 524
Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704187 US12139488, Example 524 Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704269 US12139488, Example 665
Example 524 (Iron Metal as Reducing Agent for Step 2) BDBM704269 US12139488, Example 665 Ferrocene acetic acid BDBM16432 1-(carboxymethyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-ide cyclopentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaide iron
Ferrocene acetic acid BDBM16432 1-(carboxymethyl)cyclopenta-2,4-dien-1-ide cyclopentane-1,2,3,4,5-pentaide iron Haemin BDBM209868 Heme 3-[18-(2-carboxyethyl)-8,13-bis(ethenyl)-3,7,12,17-tetramethylporphyrin-21,24-diid-2-yl]propanoic acid;iron(2+)
Haemin BDBM209868 Heme 3-[18-(2-carboxyethyl)-8,13-bis(ethenyl)-3,7,12,17-tetramethylporphyrin-21,24-diid-2-yl]propanoic acid;iron(2+) BDBM20 Hematin(iron protoporphyrin IX) 3-[5-(2-carboxyethyl)-15,20-diethenyl-22-hydroxy-4,10,14,19,24-pentamethyl-21,23,24,25-tetraaza-22-ferrahexacyclo[9.9.3.1^{3,6}.1^{13,16}.0^{8,23}.0^{18,21}]pentacosa-1(20),3,5,8,10,13,15,18-octaen-9-yl]propanoic acid
BDBM20 Hematin(iron protoporphyrin IX) 3-[5-(2-carboxyethyl)-15,20-diethenyl-22-hydroxy-4,10,14,19,24-pentamethyl-21,23,24,25-tetraaza-22-ferrahexacyclo[9.9.3.1^{3,6}.1^{13,16}.0^{8,23}.0^{18,21}]pentacosa-1(20),3,5,8,10,13,15,18-octaen-9-yl]propanoic acid