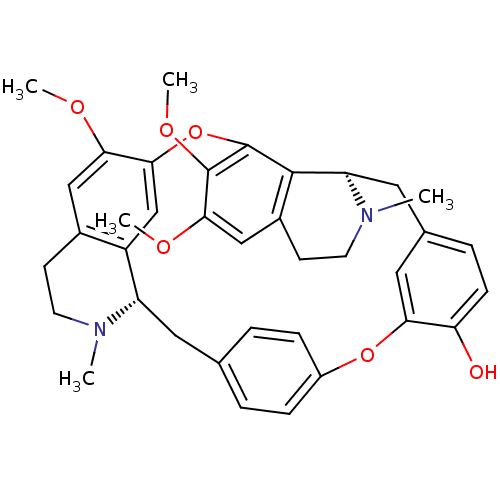
 CHEMBL504323 (+)-berbamine Berbamine BDBM50241654
CHEMBL504323 (+)-berbamine Berbamine BDBM50241654 O-(4-Ethoxybutyl)berbamine BDBM50293304 CHEMBL454806 O-(4-ethoxybutyl)-berbamine
O-(4-Ethoxybutyl)berbamine BDBM50293304 CHEMBL454806 O-(4-ethoxybutyl)-berbamine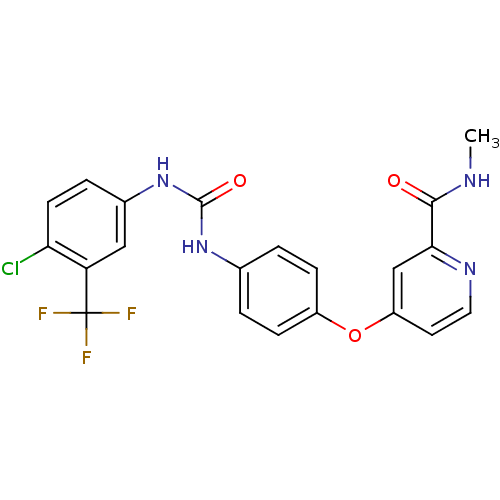 US10183928, Sorafenib US9902709, Comparative example 1 US10980809, Example Sorafenib US11505527, Compound Sorafenib BAY 439006 US10227329, Compound Sorafenib US10774070, Compound Sorafenib Xarelto CHEMBL1336 BAY439006 Sorafenib, 4 BDBM16673 Hit compound, 8 US10584114, Compound Sorafenib US11279688, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]phenoxy]-N-methyl-picolinamide;tosylic acid US11912663, Compound Sorafenib US9469639, Sorafenib US10202365, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)phenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide US20250129067, Compound Sorafenib BAY 43-9006 Nexavar Sorafenib cid_216239 US9029401, Sorafenib
US10183928, Sorafenib US9902709, Comparative example 1 US10980809, Example Sorafenib US11505527, Compound Sorafenib BAY 439006 US10227329, Compound Sorafenib US10774070, Compound Sorafenib Xarelto CHEMBL1336 BAY439006 Sorafenib, 4 BDBM16673 Hit compound, 8 US10584114, Compound Sorafenib US11279688, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]phenoxy]-N-methyl-picolinamide;tosylic acid US11912663, Compound Sorafenib US9469639, Sorafenib US10202365, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)phenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide US20250129067, Compound Sorafenib BAY 43-9006 Nexavar Sorafenib cid_216239 US9029401, Sorafenib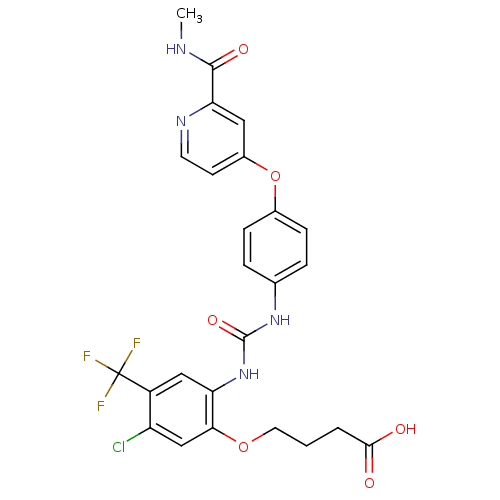 BDBM92353 Sorafenib derivative, 16
BDBM92353 Sorafenib derivative, 16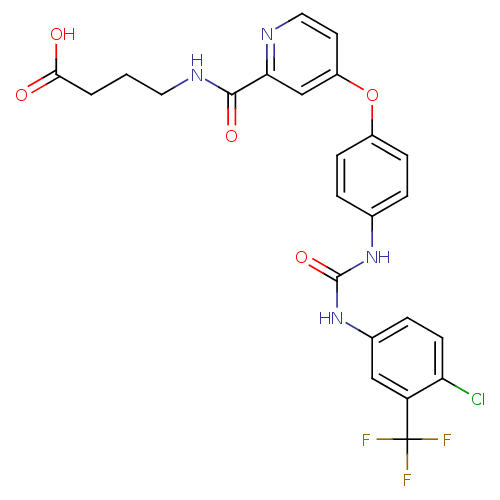 Sorafenib derivative, 17 BDBM92354
Sorafenib derivative, 17 BDBM92354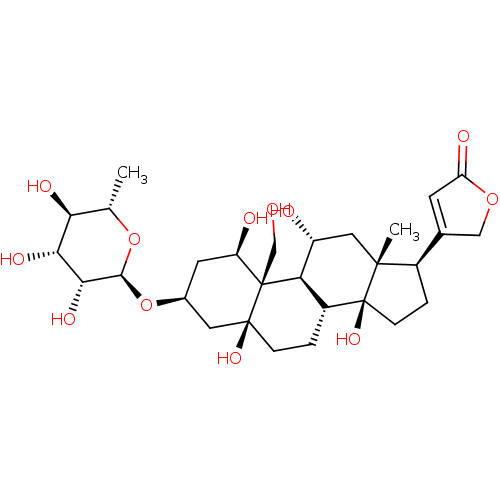 4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[(1R,3S,5S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one Ouabain4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one(Ouabain) Ouabain CHEMBL222863 4-[(R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one cid_439501 BDBM50286739 NSC-25485
4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[(1R,3S,5S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one Ouabain4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one(Ouabain) Ouabain CHEMBL222863 4-[(R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one cid_439501 BDBM50286739 NSC-25485
- Hammock, BD; Hwang, SH; Wecksler, AT; Morisseau, C Sorafenib derivatives as sEH inhibitors US Patent US9029401 (2015)
- Xie, Z; Shapiro, JI; Si, S; Zhang, Z Na/K-ATPase ligands, ouabain antagonists, assays and uses thereof US Patent US9114126 (2015)
- Vitello, R; Taouba, H; Derand, M; Liégeois, JF The Bis(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline) Alkaloids Cepharanthine and Berbamine Are Ligands of SK Channels. ACS Med Chem Lett 15: 215-220 (2024)
- Chen, F; Fang, Y; Zhao, R; Le, J; Zhang, B; Huang, R; Chen, Z; Shao, J Evolution in medicinal chemistry of sorafenib derivatives for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Med Chem 179: 916-935 (2019)
- Wang, W; Wu, C; Wang, J; Luo, R; Wang, C; Liu, X; Li, J; Zhu, W; Zheng, P Synthesis, activity and docking studies of phenylpyrimidine-carboxamide Sorafenib derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem 24: 6166-6173 (2016)
- Wang, M; Xu, S; Wu, C; Liu, X; Tao, H; Huang, Y; Liu, Y; Zheng, P; Zhu, W Design, synthesis and activity of novel sorafenib analogues bearing chalcone unit. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 5450-5454 (2016)
- Hwang, SH; Wecksler, AT; Zhang, G; Morisseau, C; Nguyen, LV; Fu, SH; Hammock, BD Synthesis and biological evaluation of sorafenib- and regorafenib-like sEH inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 3732-7 (2013)
- Wang, M; Xu, S; Lei, H; Wang, C; Xiao, Z; Jia, S; Zhi, J; Zheng, P; Zhu, W Design, synthesis and antitumor activity of Novel Sorafenib derivatives bearing pyrazole scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem 25: 5754-5763 (2017)
- Xie, Y; Fan, S; Ni, D; Wan, W; Xu, P; Ding, Y; Zhang, R; Lu, J; Zhang, N; Zhang, Y; Xiao, W; Zhao, K; Luo, C An ATG4B inhibitor blocks autophagy and sensitizes Sorafenib inhibition activities in HCC tumor cells. Bioorg Med Chem 84: (2023)
- Lin, X; Huang, XP; Chen, G; Whaley, R; Peng, S; Wang, Y; Zhang, G; Wang, SX; Wang, S; Roth, BL; Huang, N Life beyond kinases: structure-based discovery of sorafenib as nanomolar antagonist of 5-HT receptors. J Med Chem 55: 5749-59 (2012)
- Bozdag, M; Ferraroni, M; Ward, C; Carta, F; Bua, S; Angeli, A; Langdon, SP; Kunkler, IH; Al-Tamimi, AS; Supuran, CT Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors based on sorafenib scaffold: Design, synthesis, crystallographic investigation and effects on primary breast cancer cells. Eur J Med Chem 182: (2019)
- Sun, S; He, Z; Huang, M; Wang, N; He, Z; Kong, X; Yao, J Design and discovery of thioether and nicotinamide containing sorafenib analogues as multikinase inhibitors targeting B-Raf, B-Raf Bioorg Med Chem 26: 2381-2391 (2018)
- Syeda, SS; Sánchez, G; Hong, KH; Hawkinson, JE; Georg, GI; Blanco, G Design, Synthesis, and in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Ouabain Analogues as Potent and Selective Na,K-ATPaseα4 Isoform Inhibitors for Male Contraception. J Med Chem 61: 1800-1820 (2018)
- Jiao, Y; Xin, BT; Zhang, Y; Wu, J; Lu, X; Zheng, Y; Tang, W; Zhou, X Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel 2-(1H-imidazol-2-yl) pyridine Sorafenib derivatives as potential BRAF inhibitors and anti-tumor agents. Eur J Med Chem 90: 170-83 (2015)
- Sbenati, RM; Zaraei, SO; El-Gamal, MI; Anbar, HS; Tarazi, H; Zoghbor, MM; Mohamood, NA; Khakpour, MM; Zaher, DM; Omar, HA; Alach, NN; Shehata, MK; El-Gamal, R Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and modeling studies of novel conformationally-restricted analogues of sorafenib as selective kinase-inhibitory antiproliferative agents against hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur J Med Chem 210: (2021)
- ChEMBL_2263475 Activation of PKM2 (unknown origin) in presence of sorafenib
- ChEMBL_54059 (CHEMBL669632) Inhibition of [3H]ouabain binding to Digitalis receptor in dog heart microsomes
- ChEMBL_1838867 (CHEMBL4339000) Inhibition of human CYP3A4 using sorafenib as substrate by LC/MS/MS analysis
- ChEMBL_144101 (CHEMBL751505) Compound was evaluated for its ability to inhibit the specific [3H]-ouabain binding to dog kidney Na+/K+ ATPase
- ChEMBL_1571199 (CHEMBL3795960) Inhibition of rat ROMK assessed as thallium flux after 30 mins in presence of ouabain by cell based FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_2069798 (CHEMBL4725051) Inhibition of human liver microsome CYP3A4 using sorafenib as substrate incubated for 20 mins by LC-MS/MS with HPLC analysis
- ChEMBL_2248038 (CHEMBL5162248) Inhibition of CYP3A4 in human liver microsomes using sorafenib as cocktail probe substrate preincubated for 5 mins followed by NADPH addition and measured after 30 mins by HPLC-MS/MS analysis
- Na,K-ATPase Activity Assay Na,K-ATPase activity was assayed in vitro by measuring the release of 32P-ATP, as described previously (see Ferrandi M. et al., Hypertension 1996; 28(6):1018-25). Increasing concentrations of the standard ouabain, or tested compound, were incubated with 0.3 μg of purified dog kidney enzyme for 10 min at 37° C. in 120 μl final volume of a medium containing 140 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 50 mM Hepes-Tris, 3 mM ATP at a pH 7.5. Then, 10 μl of incubation solution containing 10 mM KCl and 20 nCi of 32P-ATP (3-10 Ci/mmol, Perkin Elmer) was added, and the reaction was continued for 15 min at 37° C. The reaction was then stopped by acidification with 20% v/v ice-cold perchloric acid. 32P was separated by centrifugation with activated Charcoal (Norit A, Serva) and the radioactivity was measured. The inhibitory activity was expressed as percent of the control samples carried out in the absence of ouabain or tested compound. The concentration of compound causing 50% inhibition of the Na,K-ATPase activity (IC50) was calculated by using a multiple parameter non-linear regression best fitting program (Kaleidagraph™, Sinergy Software).
- Biological Assay The Inhibitory Activity of the Present Compounds on Human ROMK and Rat ROMK ChannelsThe method described hereafter was used for determining the inhibitory activity of the present compounds on human ROMK and rat ROMK channels.1. Materials and Instruments(1) FluxOR potassium ion channel assay (F10016, Invitrogen)(2) Ouabain (O3125-1G, Sigma)(3) FlexStation3 microplate reader (Molecular Devices)(4) Human ROMK/HEK293 cell: HEK293 cell line stably expressing the ROMK channel transfected by human ROMK cDNA (NCBI SEQ ID NO. NM-000220.4)(5) Rat ROMK/HEK293 cell: HEK293 cell line transfected by rat ROMK cDNA (NCBI SEQ ID NO. NM-017023.1) stably expressing the ROMK channel(6) HEK293 cell line: Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences, GNHu432. Experimental ProcedureExcept for ddH2O and Ouabain, all of the experimental reagents are from FluxOR Potassium Ion Channel Assay Kit and the formulation methods also refer to the kit instructions. (1) Human ROMK/HEK293 cell was seeded on PDL (Poly-D-lysine) coated plates at 20000 cells/well on the previous day; (2) After overnight culture, the plate medium was discarded; then according to the Fluxor Potassium Ion Channel Assay Kit instructions, the dye was added at 100 μL/hole, and then incubated for 90 mins at room temperature; (3) The dye was then decanted and 1004, of assay buffer containing ouabain (30004) and probenecid were added in each well; (4) 1 μL of compound or DMSO was added to the corresponding wells, shocked for 30 seconds, and incubated for 30 mins at room temperature; (5) The plates were placed in a FlexStation3 microplate reader, and then added with stimulation buffer (K2SO4: Tl2SO4: 1×FluxOR Chloride-free Buffer: ddH2O=3:12:40:125) at 25 μL/well, then the value was read continuously for 5 mins at EX/EM of 490/525 nm immediately; and (6) The IC50 of the present compounds on human ROMK channel was obtained by data processing software Graphpad.
- Inhibitory Activity Assay human ROMK and rat ROMK: 1. Materials and Instruments (1) FluxOR potassium ion channel assay (F10016, Invitrogen) (2) Ouabain (03125-1G, Sigma) (3) FlexStation3 microplate reader (Molecular Devices) (4) Human ROMK/HEK293 cell: HEK293 cell line stably expressing the ROMK channel transfected by human ROMK cDNA (NCBI SEQ ID NO. NM-000220.4) (5) Rat ROMK/HEK293 cell: HEK293 cell line transfected by rat ROMK cDNA (NCBI SEQ ID NO. NM-017023.1) stably expressing the ROMK channel (6) HEK293 cell line: Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences, GNHu43 2. Experimental Procedure - Human ROMK/HEK293 cell was seeded on PDL(Poly-D-lysine) coated plates at 20000 cells/well on the previous day; After overnight culture, the plate medium was discarded; then according to the Fluxor Potassium Ion Channel Assay Kit instructions, the dye was added at 100 μL/hole, and then incubated for 90 mins at room temperature; The dye was then decanted and 100 μL of assay buffer containing ouabain (300 μM) and probenecid were added in each well;1 μL of compound or DMSO was added to the corresponding wells, shocked for 30 seconds, and incubated for 30 mins at room temperature; The plates were placed in a FlexStation3 microplate reader, and then added with stimulation buffer (K2SO4:Tl2SO4:1XFluxOR Chloride-free Buffer:ddH2O=3:12:40:125) at 25 μL/well, then the value was read continuously for 5 mins at EX/EM of 490/525 nm immediately; and The IC50 of the present compounds on human ROMK channel was obtained by data processing software Graphpad.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Experimental Procedures(1) Kinase reaction substrate Poly(Glu, Tyr, 4:1) was diluted to 20 g/ml with potassium ion-free PBS, and enzyme labeled plate was coated by the substrate, reacted at 37° C. for 12-16 h, and then the liquid in holes was removed.(2) Enzyme labeled plate was washed with T-PBS for three times, 10 min each time.(3) Enzyme labeled plate was dried at 37° C. in a dryer.(4) The tested samples were added into holes of the coated enzyme labeled plate:The tested samples were firstly formulated to be a 10 2 M stock solution with DMSO, and then diluted to required concentration with reaction buffer before use, added into the experiment holes to reach corresponding final concentration in a 100 uL reaction system. Meanwhile, positive control holes were created, and compound Sorafenib was added. The rest of the stock solutions was storaged at 20° C. after subpackage.
- Test of Small Molecule Compounds for Inhibiting the Activity of C-RAF and B-RAF Kinases 1. Preparation of test compounds: according to the molecular weight of the compounds, an appropriate volume of DMSO was directly added to dissolve the test compounds. For storing the compound, the concentration of DMSO is 100%, and the final concentration of DMSO in the experimental system is 1%. The compounds were 3-fold serially diluted with DMSO to obtain a total of 8 dilutions, with a maximum concentration of 1000 nM and a minimum concentration of 0.46 nM.2. Preparation of the sorafenib positive control: sorafenib, a selective inhibitor of BRAF and RAF1, was used as the positive control of this experiment, and the dilution method thereof was the same as that of the above test compounds.3. Test Conditions:Enzyme: B-RAF: 0.1 ng/l (the final concentration in the reaction system); C-RAF: 0.1 ng/μl (the final concentration in the reaction system)Substrate and ATP: inactive MEKI: 2 ng/μl (the final concentration in the reaction system); ATP: 35 μM (the final concentration in the reaction system)HPE: the reaction without enzyme (1% DMSO)ZPE: the reaction with enzyme but without compound (1% DMSO)4. Test procedure:a) 1 ul of 10-fold diluted compound or 10% DMSO was added to a 384-well assay plate,b) 4 ul enzyme solution or assay buffer was added to the wells of the assay plate,c) the plate was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 1 minute to homogeneous,d) 5 ul of ATP-substrate mixture was added to the wells of the assay plate,e) the plate was shaked for mixing for 2 minutes,f) the plate was incubated at 30° C. for 1 hour,g) 10 ul of ADP-Glo reagent was added to the wells of the assay plate, and the plate was incubated for 40 minutes at 27° C.,h) 20 ul of kinase assay solution was added to the wells of the plate, and the plate was incubated for 30 minutes at 27° C.,i) the chemiluminescent signal was read with Envision.5. Analysis of the results: calculation of the compound inhibition rate:Inhibition rate (%)=(control measurement without compound−sample measurement)/(control measurement without compound−control measurement without enzyme)*100%The IC50 values of the positive control compound and the test compounds were calculated using the Prism software according to the variable slope of the curve.
- Inhibition Assay Human HEK293 cells over-expressing human IK are grown in culture medium (DMEM supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum), in polystyrene culture flasks (175 mm2) in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air, at 37° C. Cell confluence should be 80-90% on day of plating. Cells are rinsed with 4 mL of PBS (phosphate buffered saline) and incubated 2 min with 1 mL of Trypsin-EDTA. After addition of 25 mL of culture medium cells are re-suspended by trituration with a 25 mL pipette.The cells are seeded at a density of 3×106 cells/mL (25 μL/well) in black-walled, clear bottom, 384-well plates pre-treated with 0.01 g/L poly-D-lysin (20 μL/well for ≧30 min). Plated cells were allowed to proliferate for 24 h before loading with dye.BTC-AM (50 mg, Invitrogen) is added 25.5 μl DMSO. The BTC-AM stock solution (2 mM) is diluted to a final concentration of 2 μM in Cl+ free assay buffer (in mM: 140 Na+-gluconate, 2.5 K+-gluconate, 6 Ca2+-gluconate, 1 Mg2+ gluconate, 5 glucose, 10 HEPES, pH 7.3) containing 2 μM ouabain, 2 mM amaranth and 1 mM tartrazine.The culture medium is aspirated from the wells, and 25 μl of the BTC-AM loading solution are added to each well. The cells are incubated at 37° C. for 60 min.After the loading period, the Tl+-sensitive BTC fluorescence signal is measured over time using a FLIPR.
- Selective Inhibition Assays of Isolated Na,K-ATPase To screen for isoform selectivity of the digoxin derivatives we compared inhibition of Na,K-ATPase activity of purified detergent-soluble human isoform complexes α1β1FXYD1, α2β1FXYD1, α2β2FXTD1 and α2β3FXYD1. Although all the preparations and assays were conducted with FXYD1 in order to stabilize the complexes, the FXYD1 suffix is omitted in naming of isoform complexes for simplicity.Na,K-ATPase activity of α/βPFXYD1 complexes was measured over one hour at 37° C. in a medium containing 130 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 25 mM Histidine, pH 7.4 and 1 mM ATP using the PiColor Lock gold malachite green assay (Inova Biosciences).The Na,K-ATPase activities were α1β1, 21.5±5.3 μmoles/min/mg; α2β1, 18.7±1.8 μmoles/min/mg, and α2β3, 10.7±1.9 μmoles/min/mg protein. As discussed below, an important kinetic property in relation to inhibition by cardiac glycosides is K0.5 for activation by K: α1β1-1.25±0.05 mM, α2β1-2.7±0.14 mM and α2β3 6.4±0.50 mM, respectively.Selectivity of the compounds for various isolated isoforms of human Na,K-ATPase was determined essentially as described before [Katz, A. et al., J Biol Chem., 2010, 285(25), pp. 19582-19592].ATPase activity assays as well as titrations with NaCl, KCl and vanadate were performed as described in Lifshitz-2007 and Loayza-1998 using PiColorLock malachite green assay (Inova Bioscience). Inhibitor assays were performed as described in Katz-2010. [3H]ouabain binding and K+-[3H]digoxin displacement assays were performed as described in Katz-2010.The percent inhibition VCG/V0 was calculated and Ki values were obtained by fitting the data to the function VCG/V0=Ki/([CG]+Ki)+c (CG stands for cardiac glycoside). Inhibition was estimated in 3-5 separate experiments and average Ki values±standard error of the mean (SEM) were calculated. The ratios Ki α1β1/α2β1, α1β1/α2β2 and α1β1/α2β3 was calculated for each compound.
- LanthaScreen Eu Kinase Binding Assay Binding of an Alexa Fluor™ conjugate or “tracer” to a kinase is detected by addition of an Eu-labeled anti-tag antibody. Binding of the tracer and antibody to a kinase result in a high degree of FRET, whereas displacement of the tracer with a kinase inhibitor results in a loss of FRET. This assay is carried out by mixing the compound tested with the reagents and reading, no development step is required. Life Technologies' Kinase Tracers are based on ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors, making them suitable for detection of any compounds that bind to the ATP site. Inhibitors that bind the ATP site include both Type I kinase inhibitors, which bind solely to the ATP site, and Type II inhibitors (e.g., Gleevec /Imatinib, Sorafenib, BIRB-796), which bind to both the ATP site and a second site often referred to as the allosteric site. The following protocol is used to carry out this assay: The Test Compounds are screened in 1% DMSO (final) in the well. For 10-point titrations, 3-fold serial dilutions are conducted from the starting concentration. All Kinase/Antibody Mixtures are diluted to a 2× working concentration in the specified kinase buffer. The 4× AlexaFluor labeled Tracer is prepared in Kinase Buffer. Assay Protocol Bar-coded, low volume, white 384-well plate (Greiner Cat. #784207) 1. 160 nL100× Test Compound in 100% DMSO 2. 3.84 μL—Kinase Buffer 3. 8.0 μL2× Kinase/Antibody Mixture 4. 4.0 μL—4× Tracer 5. 30-second plate shake 6. 60-minute incubation at room temperature7. Read on fluorescence plate reader and analyze the data. The following controls are made for each individual kinase and are located on the same plate as the kinase:0% Displacement Control: the maximum Emission Ratio is established by the 0% Displacement Control wells, which do not contain known inhibitor in the reaction and therefore exhibits no displacement of the tracer. 100% Displacement Control: the minimum Emission Ratio is established by the 100% Displacement Control wells, which contain the highest concentration of the known inhibitor used in that assay. Known Inhibitor Control Protocol: a known inhibitor control standard curve, 10-point titration, is run for each individual kinase on the same plate as the kinase to ensure the inhibitor is displaced within an expected IC50 range previously determined.
- Thallium Flux Assay Solutions and reagents: Thallium flux assay was performed using FluxOR kit (F10017, Life Technologies). Loading buffer, assay buffer and stimulus buffer were prepared using kit components. HBSS (Hank's balanced salt solution, Cat #14025-092) was purchased separately from Life Technologies.To prepare 10 ml of loading buffer: 10 μl of FluxOR dye (reconstituted in DMSO) was first added to 100 μl of powerload concentrate and this mix along with 100 μl of Probenicid (100×) was then added to 9.79 ml of HBSS. Assay buffer (10 ml) was prepared by addition of 2 ml of FluxOR chloride free buffer (5×), 100 μl of Probenicid (100×), and 0.2 ml of Ouabain (13.77 mM) to 7.7 ml of deionized water. Stimulus buffer was composed of 15 mM Tl2SO4, 0.75 mM K2SO4 in FluxOR chloride free buffer (diluted to 1× using deionized water). The final concentration of Tl2SO4 and K2SO4 in the assay plate was 3 mM and 0.15 mM, respectively.Plating and induction of cells: The CHO T-Rex hROMK (human Kir1.1) stable cell line was maintained in Ham's F12 media supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin, 500 μg/ml Zeocin and 10 μg/ml Blasticidin at 37° C. in a 5% CO2 incubator. One day before the experiment, the cells were dissociated by incubation with Versene solution (15040-066, Life Technologies) for 10 minutes at 37° C. followed by addition of growth media. The cell suspension was centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 min. After discarding the supernatant, the cells were resuspended in fresh growth media and cell concentration was determined using a hemocytometer. Next, 0.5 μg/ml of Doxycycline was added to the cell suspension to induce hROMK channel expression and 50 μl (10,000 cells/well) of cell suspension was added to each well of a poly-D lysine coated 384 well black, optically clear bottom plate (6007718, Perkin Elmer). The assay plate was kept at 37° C. in a 5% CO2 incubator.Assay protocol: On the day of experiment, media was removed and loading buffer was added (30 μl/well) to the assay plate. The cells were incubated in the loading buffer for 30 minutes at 37° C. The loading buffer was then replaced by assay buffer (30 μl/well) followed by addition of test compounds or controls. The cells were incubated with compounds for 30 minutes and the plate was then mounted on FlexStation (Molecular Devices) for fluorescence read out with excitation and emission wavelengths at 488 and 525 nm, respectively. Each well was read for 90 sec at 2 sec interval and the stimulus buffer was added after 20 seconds of baseline recording. The final DMSO concentration was either 0.5 or 1% in the assay plate. Positive and negative controls were defined by addition of DMSO or 3 μM of a standard ROMK inhibitor, respectively, to the wells instead of a test compound.Data analysis: The slope (over a period of 15 seconds) of fluorescence increase after stimulus buffer addition was exported from SoftMax Pro into a custom made software where it was converted to % inhibition. A 10-point concentration response curve was used to estimate the IC50 value of test compounds.
- Biochemical Assay for mTOR TR-FRET assays for protein kinases uses a long-lifetime lanthanide Terbium or Europium chelates as the donor species which overcome interference by compound autofluorescence or light scatter from precipitated compounds, by introducing a delay after excitation by a flashlamp excitation source. Results are often expressed as a ratio of the intensities of the acceptor and donor fluorophores. The ratiometric nature of such a value corrects for differences in assay volumes between wells, as well as corrects for quenching effects due to colored compounds.Binding Assays are based on the binding and displacement of an Alexa Fluor 647-labeled, ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors to the kinase of interest. Invitrogen's “Kinase Tracers” have been developed to address a wide range of kinase targets and are based on ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors, making them suitable for detection of any compounds that bind to the ATP site or to an allosteric site altering the conformation of the ATP site. Inhibitors that bind the ATP site include both Type I kinase inhibitors, which bind solely to the ATP site, and Type II inhibitors (e.g., Gleevec/Imatinib, Sorafenib, BIRB-796), which bind to both the ATP site and a hydrophobic site exposed in the DFG-out (non-active) conformation. Type III inhibitors are compounds that do not compete with ATP are loosely referred to as allosteric inhibitors. A study of 15 diverse Type III inhibitors demonstrated that all but one compound was detected in the binding assay with equivalent potency to activity assays. The sole exception was a substrate-competitive compound, and thus not a true allosteric inhibitor.In contrast to most fluorescence-based kinase activity assays, LanthaScreen Eu3+ Kinase Binding Assays can be read continuously, which facilitates evaluation of compounds with slow binding kinetics. Also, unlike most activity assays, binding assays can be performed using either active or non-activated kinase preparations, which enables characterization of compounds that bind preferentially to non-activated kinases, such as Gleevec /imatinib and some allosteric inhibitors.In the Lanthascreen™ kinase binding assay, the donor (Eu3+-anti-GST antibody) is excited at 340 nm and will transfer its energy to the acceptor (Alexa Fluor 647-labeled ATP-competitive kinase inhibitor=Tracer-314). The emission from the Tracer-314 (Alexa Fluor 647 inhibitor) can be monitored with a filter centered at 665 nm because it is located between the emission peaks of the donor, which is measured at 615/620 nm. The binding of both, the Tracer-314 and Eu3+-anti-GST antibody, to the kinase results in a high degree of FRET from the Eu3+-donor fluorophore to the Alexa-Fluor 647-acceptor fluorophore on the Tracer-314. Binding of an inhibitor to the kinase competes for binding with the tracer, resulting in a loss of FRET.50 nL of compound dilutions were dispensed onto white 384-well small volume polystyrene plate as described in section 2.2. Then 5 μL of GST-mTOR and Europium-anti-GST antibody followed by 5 μL of tracer-314 (final assay volume 10 μL) are incubated at RT. The standard reaction buffer for the Lanthascreen™ kinase binding assay contained 50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 0.01% Pluronic F-127. Plates are read 60 mins later in a Synergy2 reader using an integration time of 0.2 microseconds and a delay of 0.1 microseconds.To calculate the emission ratio, the signal emitted at 665 nm from the acceptor (Alexa Fluor 647-labeled Tracer-314) is divided by the signal emitted at 620 nm from the donor (Eu3+ anti-GST antibody)Control for the 0% inhibition was given by the solvent vehicle of the compounds (90% DMSO in H2O). Control for the relative 100% inhibition was performed by adding 10 μM in the mix containing GST-mTOR and Europium anti-GST antibody. An additional control for the absolute 0% inhibition is given by Eu3+ anti-GST antibody without GST-mTOR.
 CHEMBL504323 (+)-berbamine Berbamine BDBM50241654
CHEMBL504323 (+)-berbamine Berbamine BDBM50241654 O-(4-Ethoxybutyl)berbamine BDBM50293304 CHEMBL454806 O-(4-ethoxybutyl)-berbamine
O-(4-Ethoxybutyl)berbamine BDBM50293304 CHEMBL454806 O-(4-ethoxybutyl)-berbamine US10183928, Sorafenib US9902709, Comparative example 1 US10980809, Example Sorafenib US11505527, Compound Sorafenib BAY 439006 US10227329, Compound Sorafenib US10774070, Compound Sorafenib Xarelto CHEMBL1336 BAY439006 Sorafenib, 4 BDBM16673 Hit compound, 8 US10584114, Compound Sorafenib US11279688, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]phenoxy]-N-methyl-picolinamide;tosylic acid US11912663, Compound Sorafenib US9469639, Sorafenib US10202365, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)phenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide US20250129067, Compound Sorafenib BAY 43-9006 Nexavar Sorafenib cid_216239 US9029401, Sorafenib
US10183928, Sorafenib US9902709, Comparative example 1 US10980809, Example Sorafenib US11505527, Compound Sorafenib BAY 439006 US10227329, Compound Sorafenib US10774070, Compound Sorafenib Xarelto CHEMBL1336 BAY439006 Sorafenib, 4 BDBM16673 Hit compound, 8 US10584114, Compound Sorafenib US11279688, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoylamino]phenoxy]-N-methyl-picolinamide;tosylic acid US11912663, Compound Sorafenib US9469639, Sorafenib US10202365, Compound Sorafenib 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}amino)phenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide US20250129067, Compound Sorafenib BAY 43-9006 Nexavar Sorafenib cid_216239 US9029401, Sorafenib BDBM92353 Sorafenib derivative, 16
BDBM92353 Sorafenib derivative, 16 Sorafenib derivative, 17 BDBM92354
Sorafenib derivative, 17 BDBM92354 4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[(1R,3S,5S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one Ouabain4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one(Ouabain) Ouabain CHEMBL222863 4-[(R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one cid_439501 BDBM50286739 NSC-25485
4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,9S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[(1R,3S,5S,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one Ouabain4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-((1R,3S,5S,8R,10R,11R,13R,14S,17R)-1,5,11,14-tetrahydroxy-10-(hydroxymethyl)-13-methyl-3-((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)furan-2(5H)-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one(Ouabain) Ouabain CHEMBL222863 4-[(R)-1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one 4-[1,5,11,14-Tetrahydroxy-10-hydroxymethyl-13-methyl-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-yloxy)-hexadecahydro-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-5H-furan-2-one cid_439501 BDBM50286739 NSC-25485