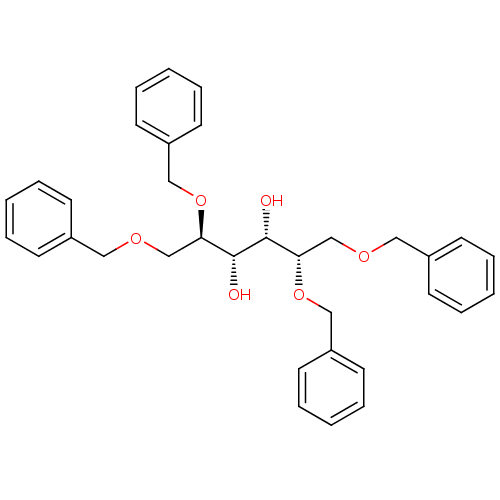
 BDBM9566 1,2,5,6-tetra-O-benzyl-D-sorbitol 5 (2R,3S,4S,5S)-1,2,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)hexane-3,4-diol
BDBM9566 1,2,5,6-tetra-O-benzyl-D-sorbitol 5 (2R,3S,4S,5S)-1,2,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)hexane-3,4-diol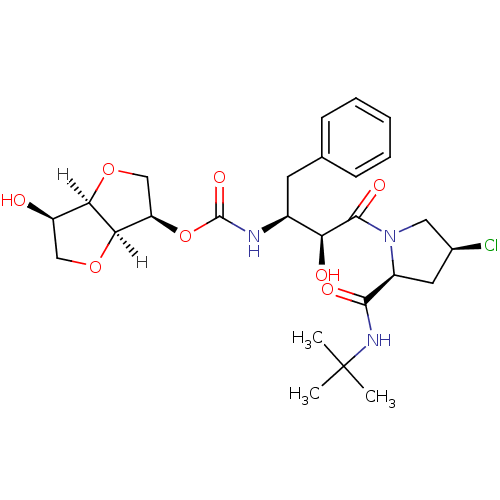 (3R,3aR,6R,6aR)-6-hydroxy-hexahydrofuro[3,2-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2S,3S)-4-[(2S,4S)-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-4-chloropyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-hydroxy-4-oxo-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate BDBM4242 AHPBA 11 (1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol)carbonyl-(2S,3S)-AHPBA-4(S)-Cl-Pro-NH-t-Bu
(3R,3aR,6R,6aR)-6-hydroxy-hexahydrofuro[3,2-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2S,3S)-4-[(2S,4S)-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-4-chloropyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-hydroxy-4-oxo-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate BDBM4242 AHPBA 11 (1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol)carbonyl-(2S,3S)-AHPBA-4(S)-Cl-Pro-NH-t-Bu
- Chu-Moyer, MY; Ballinger, WE; Beebe, DA; Coutcher, JB; Day, WW; Li, J; Oates, PJ; Weekly, RM SAR and species/stereo-selective metabolism of the sorbitol dehydrogenase inhibitor, CP-470,711. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 1477-80 (2002)
- Darmanin, C; El-Kabbani, O Modelling studies of the active site of human sorbitol dehydrogenase: an approach to structure-based inhibitor design of the enzyme. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 3133-6 (2001)
- Chu-Moyer, MY; Ballinger, WE; Beebe, DA; Berger, R; Coutcher, JB; Day, WW; Li, J; Mylari, BL; Oates, PJ; Weekly, RM Orally-effective, long-acting sorbitol dehydrogenase inhibitors: synthesis, structure-activity relationships, and in vivo evaluations of novel heterocycle-substituted piperazino-pyrimidines. J Med Chem 45: 511-28 (2002)
- Mylari, BL; Oates, PJ; Beebe, DA; Brackett, NS; Coutcher, JB; Dina, MS; Zembrowski, WJ Sorbitol dehydrogenase inhibitors (SDIs): a new potent, enantiomeric SDI, 4-[2-1R-hydroxy-ethyl)-pyrimidin-4-yl]piperazine-1-sulfonic acid dimethylamide. J Med Chem 44: 2695-700 (2001)
- Mylari, BL; Oates, PJ; Zembrowski, WJ; Beebe, DA; Conn, EL; Coutcher, JB; O'Gorman, MT; Linhares, MC; Withbroe, GJ A sorbitol dehydrogenase inhibitor of exceptional in vivo potency with a long duration of action: 1-(R)-[4-[4-(4,6-dimethyl[1,3,5]triazin-2-yl)- 2R,6S-dimethylpiperazin-1-yl]pyrimidin-2- yl]ethanol. J Med Chem 45: 4398-401 (2002)
- Iqbal, Z; Morahan, G; Arooj, M; Sobolev, AN; Hameed, S Synthesis of new arylsulfonylspiroimidazolidine-2',4'-diones and study of their effect on stimulation of insulin release from MIN6 cell line, inhibition of human aldose reductase, sorbitol accumulations in various tissues and oxidative stress. Eur J Med Chem 168: 154-175 (2019)
- ChEBML_201006 Inhibition of recombinant rat Sorbitol dehydrogenase
- ChEMBL_201007 (CHEMBL801928) Inhibition of recombinant rat sorbitol dehydrogenase
- ChEMBL_664732 (CHEMBL1260799) Inhibition sorbitol dehydrogenase by spectrophotometric analysis
- ChEBML_201005 In vitro inhibition against human recombinant sorbitol dehydrogenase
- ChEMBL_201005 (CHEMBL801255) In vitro inhibition against human recombinant sorbitol dehydrogenase
- ChEBML_223912 Concentration required for inhibitory activity against human sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH)
- ChEMBL_32101 (CHEMBL644302) Percent inhibition of sorbitol accumulation in rat lens was measured
- ChEMBL_958225 (CHEMBL2384568) Inhibition of ERK5 phosphorylation in sorbitol-stimulated human HeLa cells
- ChEMBL_201011 (CHEMBL803972) In vitro inhibitory activity against sorbitol dehydrogenase (SD) from sheep liver
- ChEMBL_201008 (CHEMBL803029) Inhibition of sorbitol dehydrogenase from sheep liver (40 U/mg of protein)
- ChEMBL_223911 (CHEMBL844303) Concentration required for 50% in vitro activity against human SDH (sorbitol dehydrogenase)
- ChEMBL_223914 (CHEMBL846060) Concentration required for 50% in vitro activity against rat SDH (sorbitol dehydrogenase)
- ChEMBL_223917 (CHEMBL846063) Concentration required for 50% in vitro activity against rat SDH (sorbitol dehydrogenase)
- ChEMBL_223910 (CHEMBL844302) Concentration required for 50% for in vitro activity against human SDH (sorbitol dehydrogenase)
- ChEMBL_201003 (CHEMBL801253) Concentration required for 50% in vitro inhibition of recombinant human sorbitol dehydrogenase (h-SDH)
- ChEMBL_201010 (CHEMBL882165) Concentration required for 50% in vitro inhibition in sheep liver sorbitol dehydrogenase (s-SDH)
- ChEBML_1690564 Allosteric inhibition of WNK1 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing flag-OSR1 assessed as reduction in sorbitol-stimulated OSR1 phosphorylation preincubated with compound for 2.5 hrs followed co-administration with sorbitol measured after 1 hr by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_1690564 (CHEMBL4041134) Allosteric inhibition of WNK1 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing flag-OSR1 assessed as reduction in sorbitol-stimulated OSR1 phosphorylation preincubated with compound for 2.5 hrs followed co-administration with sorbitol measured after 1 hr by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_1886417 (CHEMBL4388094) Inhibition of ALR2 in rat sciatic nerve assessed as reduction in sorbitol accumulation incubated for 3 hrs in presence of 28 mM glucose by gas chromatographic analysis
- ChEMBL_1886412 (CHEMBL4388089) Inhibition of ALR2 in rat erythrocytes assessed as reduction in sorbitol accumulation incubated for 3 hrs in presence of 28 mM glucose by gas chromatographic analysis relative to control
- ChEMBL_1886422 (CHEMBL4388099) Inhibition of ALR2 in rat lens assessed as reduction in sorbitol accumulation incubated for 3 hrs in presence of 28 mM glucose by gas chromatographic analysis relative to control
- beta-lactamase assay Expression and Purification of Beta-Lactamases. For his tag KPC-2 beta-lactamase, bacteria were grown overnight at 30 C with shaking in 50 mL LB broth supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin. Two liters of LB broth supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin, 200 mM sorbitol, and 5 mM betaine were each inoculated with 10 mL of overnight bacterial culture. Cultures were then grown at 37 C until an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.6-0.7. Protein expression was then initiated by the addition of IPTG (final concentration 0.5 mM), followed by growth for 16 hr at 20 C. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation and stored at −80 C until further use. The his tag KPC-2 beta-lactamase was purified by nickel affinity chromatography and gel filtration. Briefly, the cell pellets were thawed and re-suspended in 40 mL of buffer A (20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole) with one complete protease inhibitor cocktail tablet (Roche) and disrupted by sonication, followed by ultracentrifugation to clarify the lysate. After ultracentrifugation, the supernatant was passed through a 0.22 μm filter before loading onto a 5 mL HisTrap HP affinity column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, USA) pre-equilibrated with buffer A. His tag KPC-2 was eluted by a linear imidazole gradient (20 mM to 500 mM). Fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Fractions containing his tag KPC-2 were concentrated using a 10 k NMWL Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Unit. Concentrated his tag KPC-2 was then loaded onto a superdex 75 gel filtration column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) pre-equilibrated with 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 300 mM NaCl. Protein concentration was determined by absorbance at 280 using an extinction coefficient of 39,545. SDS-PAGE analysis indicated that the eluted protein was more than 95% pure.For sumo tag NDM-1 metallo-beta-lactamase, bacteria were grown overnight at 30 C with shaking in 50 mL LB broth supplemented with 100 μg/mL ampicillin. Two liters of LB broth supplemented with 100 μg/mL ampicillin were each inoculated with 10 mL of overnight bacterial culture. Cultures were then grown at 37 C until an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.6-0.7. Protein expression was then initiated by the addition of IPTG (final concentration 0.5 mM), followed by growth for 16 hr at 20 C. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation and stored at −80 C until further use. The sumo tag NDM-1 beta-lactamase was purified by nickel affinity chromatography and gel filtration. Briefly, the cell pellets were thawed and re-suspended in 40 mL of buffer A (20 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 0.5 M NaCl, 20 mM imidazole) with one complete protease inhibitor cocktail tablet (Roche) and disrupted by sonication, followed by ultracentrifugation to clarify the lysate. After ultracentrifugation, the supernatant was passed through a 0.22 μm filter before loading onto a 5 mL HisTrap HP affinity column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, USA) pre-equilibrated with buffer A. Sumo tag NDM-1 was eluted by a linear imidazole gradient (20 mM to 500 mM). Fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Fractions containing sumo tag NDM-1 were buffer exchanged into 20 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 100 mM NaCl. Cleavage of the sumo tag was then carried out with ULP1 protease overnight at room temperature and then concentrated using a 10 k NMWL Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Unit. The sample was then loaded back onto a nickel affinity column and the flow through was collected, containing the untag NDM-1. NDM-1 was concentrated and loaded onto a gel filtration column (GE Healthcare Life Sciences) pre-equilibrated with 20 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 100 mM NaCl. Protein concentration was determined by absorbance at 280 using an extinction coefficient of 27,960. SDS-PAGE analysis indicated that the eluted protein was more than 95% pure.Steady-State Kinetic Analysis. Steady-state kinetic parameters were determined by using a Biotek Cytation Multi-Mode Reader. For KPC-2, each assay was performed in 100 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.0,
 BDBM9566 1,2,5,6-tetra-O-benzyl-D-sorbitol 5 (2R,3S,4S,5S)-1,2,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)hexane-3,4-diol
BDBM9566 1,2,5,6-tetra-O-benzyl-D-sorbitol 5 (2R,3S,4S,5S)-1,2,5,6-tetrakis(benzyloxy)hexane-3,4-diol (3R,3aR,6R,6aR)-6-hydroxy-hexahydrofuro[3,2-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2S,3S)-4-[(2S,4S)-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-4-chloropyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-hydroxy-4-oxo-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate BDBM4242 AHPBA 11 (1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol)carbonyl-(2S,3S)-AHPBA-4(S)-Cl-Pro-NH-t-Bu
(3R,3aR,6R,6aR)-6-hydroxy-hexahydrofuro[3,2-b]furan-3-yl N-[(2S,3S)-4-[(2S,4S)-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-4-chloropyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-hydroxy-4-oxo-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate BDBM4242 AHPBA 11 (1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol)carbonyl-(2S,3S)-AHPBA-4(S)-Cl-Pro-NH-t-Bu