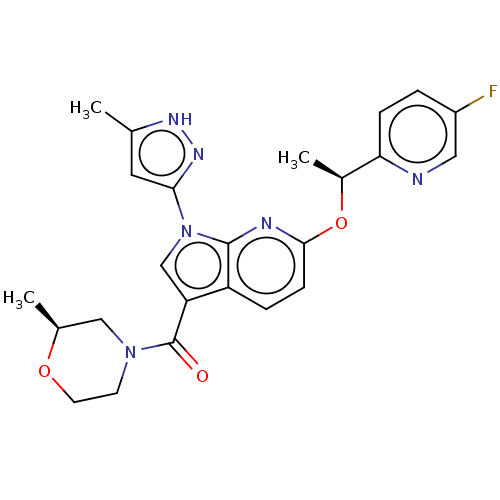
BDBM50524979 CHEMBL4440381
SMILES C[C@H](Oc1ccc2c(cn(-c3cc(C)[nH]n3)c2n1)C(=O)N1CCO[C@@H](C)C1)c1ccc(F)cn1
InChI Key InChIKey=UTDAGOYVDYQGFI-HOTGVXAUSA-N
Data 4 IC50
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
 Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50524979
Found 4 hits for monomerid = 50524979
Affinity DataIC50: 25nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human FAK kinase domain (411 to 686 residues) expressed in baculovirus expression system using biotin-poly-GT as substrate pre-incubate...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetHigh affinity nerve growth factor receptor(Homo sapiens (Human))
Takeda Pharmaceutical
Curated by ChEMBL
Takeda Pharmaceutical
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataIC50: 2.60E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of N-terminal GST-tagged human TrkA kinase domain (436 to 790 residues) expressed in baculovirus expression system using biotin-poly-GT as...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 2.90nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human ALK kinase domain (1058 to 1620 residues) expressed in baculovirus expression system using biotin-poly-GT as substrate pre-incuba...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 27nMAssay Description:Inhibition of recombinant human ALK expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in ALK autophosphorylation at Tyr1604 residue incubated for 60 mi...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair