BDBM60438 US9067937, 28
SMILES CN(C)C[C@H]1CC[C@@H](CC1)Nc1c(cnc2ccc(nc12)-c1cc(Cl)c(O)c(Cl)c1)C(C)=O
InChI Key InChIKey=DKZYXHCYPUVGAF-JCNLHEQBSA-N
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
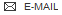 Found 4 hits for monomerid = 60438
Found 4 hits for monomerid = 60438
Affinity DataIC50: 0.400nMpH: 7.4 T: 2°CAssay Description:MELK activity was determined in the presence or absence of compounds using fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled (FITC-labeled) histone H3 peptide as a ...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetDual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A(Homo sapiens (Human))
Stanford University
Curated by ChEMBL
Stanford University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataEC50: 5nMAssay Description:Inhibition of human DYRK1A transfected in HEK293T cells co-transfected with Renilla plasmid, pGL3-NFAT and NFATc1 assessed as derepression of NFAT-de...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKd: 15nMAssay Description:Binding affinity to wild-type human full length MELK (M1 to V651 residues) expressed in bacterial expression system by Kinomescan methodMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
TargetDual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A(Homo sapiens (Human))
Stanford University
Curated by ChEMBL
Stanford University
Curated by ChEMBL
Affinity DataKd: 0.120nMAssay Description:Binding affinity to wild-type human partial length DYRK1A (H129 to S509 residues) expressed in mammalian expression system by Kinomescan methodMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
 3D Structure (crystal)
3D Structure (crystal)