Simple Search Results
Query String: B12
Compound (30)
Assay (2)
SPR Binding Assay All binding assays were performed on a ProteOn XPR36 SPR Protein Interaction Array System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The instrument temperature was set at 25° C. for all kinetic analyses. ProteOn GLH sensor chips were preconditioned with two short pulses each (10 s) of 50 mM NaOH, 100 mM HCl, and 0.5% sodium dodecyl sulfide. Then the system was equilibrated with running buffer (1×PBS pH 7.4, 3% DMSO and 0.005% polysorbate 20). The surface of a GLH sensor chip was activated with a 1:100 dilution of a 1:1 mixture of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (0.2 M) and sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimide (0.05 M). Immediately after chip activation, the HIV-1 CA protein constructs were prepared at a concentration of 10 μg/mL in 10 mM sodium acetate, pH 5.5, and injected across ligand flow channels for 5 min at a flow rate of 30 μL/min. Then, after unreacted protein had been washed out, excess active ester groups on the sensor surface were capped by a 5 min injection of 1M ethanolamine HCl (pH 8.0) at a flow rate of 5 μL/min. A reference surface was similarly created by immobilizing a nonspecific protein (IgG b12 anti-HIV-1 gp120; was obtained through the NIH AIDS Reagent Program, Division of AIDS, NIAID, NIH: Anti-HIV-1 gp120 Monoclonal (IgG1 b12) from Dr. Dennis Burton and Carlos Barbas) and was used as a background to correct nonspecific binding. Serial dilutions of hACSS-2 inhibitors were then prepared in the running buffer and injected at a flow rate of 100 μL/min, for a 50 s association phase, followed by up to a 5 min dissociation phase using the “one-shot kinetics” capability of the ProteOn instrument. Data were analyzed using the ProteOn Manager Software version 3.0 (Bio-Rad). The responses from the reference flow cell were subtracted to account for the nonspecific binding and injection artifacts. Experimental data were fitted to a simple 1:1 binding model. Experiments were performed in triplicate to detect kinetic and equilibrium dissociation constants (KD). Fluorescence Polarization Assay 1) Costar 96-well black assay plate. Assay buffer of (a) 100 mM Tris pH7.4; (b) 20 mM KCl; (c) 6 mM MgCl2. Stored at room temperature.3) BSA (bovine serum albumen) 10 mg/ml (New England Biolabs # B9001S)4) 20 mM probe in 100% DMSO stock concentration. Stored in the dark at RT. Working concentration is 200 nM diluted in AR water and stored at 4 ° C. Final concentration in assay 80 nM.5) E. coli expressed human full-length HSP90 protein, purified>95% (see, e.g., Panaretou et al., 1998) and stored in 50 uL aliquots at C. Protocol: 1) Add 100 ul buffer to wells 11A and 12A (=FP BLNK)2) Prepare assay reagents are kept on ice with a lid on the bucket as the probe is light-sensitive. i. Final Conc Hsp90 FP Buffer 10 ml 1xBSA 10 mg/ml (NEB) 5.0 ul 5 ug/ml Probe 200 uM 4.0 ul 80 nM Human full-length Hsp90 6.25 ul 200 nM 3) Aliquot 100 ul assay mix to all other wells 4) Seal plate and leave in dark at room temp for 20 minutes to equilibrate. Compound Dilution Plate 1x3 Dilution Series1) In a clear 96-well v-bottom plate {# VWR 007/008/257} add 10 ul 100% DMSO to wells B1 to H112) To wells A1 to A11 add 17.5 ul 100% DMSO 3) Add 2.5 ul cpd to A1. This gives 2.5 mM {50x} stock cpd assuming cpds 20 mM. 4) Repeat for wells A2 to A10. Control in columns 11 and 12.5) Transfer 5 ul from row A to row B-not column 12. Mix well.6) Transfer 5 ul from row B to row C. Mix well.7) Repeat to row G. 8) Do not add any compound to row H-this is the 0 row. 9) This produces a 1x3 dilution series from 50 uM to 0.07 uM.10) In well B12 prepare 20 ul of 100 uM standard compound. 11) After first incubation the assay plate is read on a Fusion a-FP plate reader. 12) After the first read, 2 ul of diluted compound is added to each well for columns 1 to 10. In column 11 {provides standard curve} only add compound B11-H11. Add 2 ul of 100 mM standard cpd to wells B12-H12 {is positive control} 13) The Z factor is calculated from zero controls and positive wells. It typically gives a value of 0.7-0.9.
 US9539260, B12 BDBM203347 US9763952, Example B12
US9539260, B12 BDBM203347 US9763952, Example B12 BDBM512999 Vitamin B12
BDBM512999 Vitamin B12 US8987314, B12 BDBM151221
US8987314, B12 BDBM151221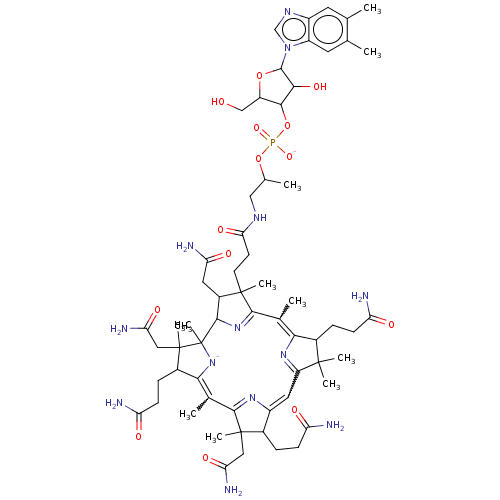 Vitamin B12 BDBM420313
Vitamin B12 BDBM420313 BDBM365689 US9868748, I-B12
BDBM365689 US9868748, I-B12 BDBM423377 US10501466, Example B12
BDBM423377 US10501466, Example B12 BDBM468879 US10807959, Example B12
BDBM468879 US10807959, Example B12 BDBM567266 US11420968, Example B12
BDBM567266 US11420968, Example B12 BDBM621490 US11773085, Compound B12
BDBM621490 US11773085, Compound B12 BDBM676815 US20240166660, Compound B12
BDBM676815 US20240166660, Compound B12 BDBM726072 US20250074919, Example B12
BDBM726072 US20250074919, Example B12 BDBM763872 US12384776, Compound B12
BDBM763872 US12384776, Compound B12 US10919869, No. B12 BDBM482845
US10919869, No. B12 BDBM482845 US11116757, No. B12 BDBM519025
US11116757, No. B12 BDBM519025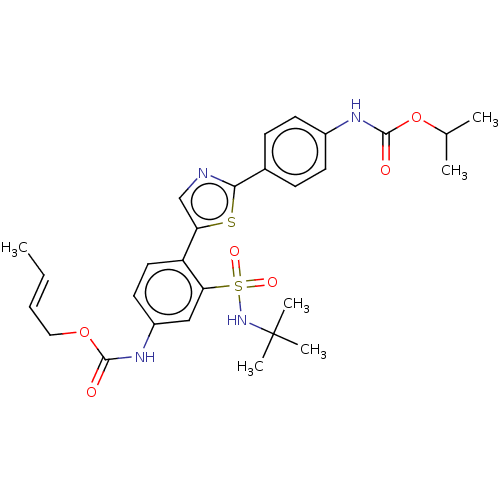 US11291655, No B12 BDBM546355
US11291655, No B12 BDBM546355 US11352330, Example B12 BDBM556574
US11352330, Example B12 BDBM556574 US12269819, Example B12 BDBM731645
US12269819, Example B12 BDBM731645 US20240368109, Example B12 BDBM703473
US20240368109, Example B12 BDBM703473 US20250188030, Compound B12 BDBM748397
US20250188030, Compound B12 BDBM748397 BDBM705343 US12145923, Compound (S)-B12
BDBM705343 US12145923, Compound (S)-B12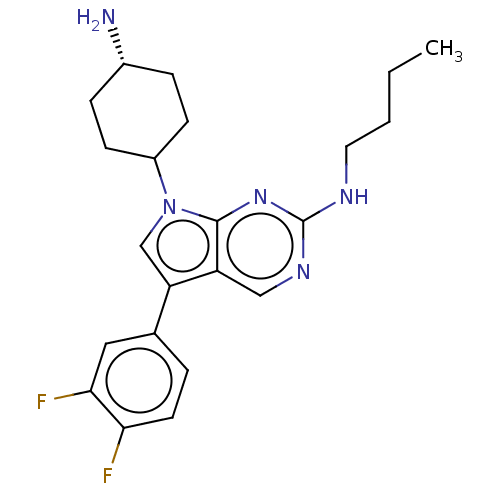 UNC2125A BDBM350853 US9795606, B12 US10004755, Compound UNC2125A
UNC2125A BDBM350853 US9795606, B12 US10004755, Compound UNC2125A US9303033, B12, Table 23A, Compound 88 BDBM219131
US9303033, B12, Table 23A, Compound 88 BDBM219131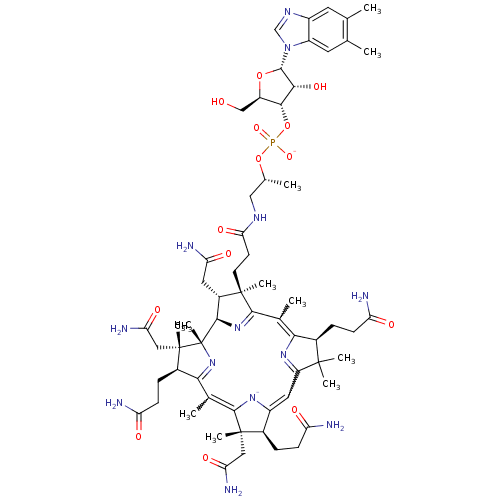 CYANOCOBALAMIN Cobalamin SMR001233181 RUVITE MLS002153809 vitamin B12 cid_25102581 BDBM83973
CYANOCOBALAMIN Cobalamin SMR001233181 RUVITE MLS002153809 vitamin B12 cid_25102581 BDBM83973 BDBM676814 US20240166660, Compound B13 US20240166660, Compound B11 US20240166660, Compound B12
BDBM676814 US20240166660, Compound B13 US20240166660, Compound B11 US20240166660, Compound B12 hydroxamate deriv. B12 BDBM11766 2-{[(2-chlorophenyl)methyl](4-iodobenzene)sulfonamido}-N-hydroxypropanamide
hydroxamate deriv. B12 BDBM11766 2-{[(2-chlorophenyl)methyl](4-iodobenzene)sulfonamido}-N-hydroxypropanamide BDBM106771 2‐(pyridin‐3‐yl)‐1‐(pyridin‐3‐ylmethyl)‐1,3‐ benzodiazole (B12)
BDBM106771 2‐(pyridin‐3‐yl)‐1‐(pyridin‐3‐ylmethyl)‐1,3‐ benzodiazole (B12) US20240059711, Compound B12 (S)-3-((S)-2- ((benzyloxy)methyl)-6-oxo- 2,3,6,8-tetrahydro-7H- [1,4]dioxino[2,3-f]isoindol-7- yl)piperidine-2,6-dione BDBM653571
US20240059711, Compound B12 (S)-3-((S)-2- ((benzyloxy)methyl)-6-oxo- 2,3,6,8-tetrahydro-7H- [1,4]dioxino[2,3-f]isoindol-7- yl)piperidine-2,6-dione BDBM653571 methyl 2-((3aR, 7aS)-6-(2-(2H-1,2,3-triazol-2- yl)benzoyl)octahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3- c]pyridin-1-yl)-5-methylthiazole-4- carboxylate BDBM387117 US9938276, B12
methyl 2-((3aR, 7aS)-6-(2-(2H-1,2,3-triazol-2- yl)benzoyl)octahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3- c]pyridin-1-yl)-5-methylthiazole-4- carboxylate BDBM387117 US9938276, B12 (S)-3-(1'-(3-(1-(methyl-d3)-1H- pyrazol-4-yl)benzyl)-6-oxo-6,8- dihydro-2H,7H-spiro[furo[2,3- e]isoindole-3,4'-piperidin]-7- yl)piperidine-2,6-dione US20250215012, Example B12 BDBM756530
(S)-3-(1'-(3-(1-(methyl-d3)-1H- pyrazol-4-yl)benzyl)-6-oxo-6,8- dihydro-2H,7H-spiro[furo[2,3- e]isoindole-3,4'-piperidin]-7- yl)piperidine-2,6-dione US20250215012, Example B12 BDBM756530 Synthesis of N ((S)-1-((3R,5R,8R,9R,10S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-3,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethyl)benzamide (B11) & N ((R)-1-((3R,5R,8R,9R,10S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-3,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethyl)benzamide (B12) BDBM625637 US20230322846, Example 23
Synthesis of N ((S)-1-((3R,5R,8R,9R,10S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-3,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethyl)benzamide (B11) & N ((R)-1-((3R,5R,8R,9R,10S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-3,13-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl)ethyl)benzamide (B12) BDBM625637 US20230322846, Example 23