- nmda
- glutamate-nmda-mk801
- glun1/glun2b nmda receptor
- glutamate nmda receptor; grin1/grin2a
- glutamate nmda receptor; grin1/grin2b
- glutamate nmda receptor; grin1/grin2c
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 2a
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 2b
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 2c
- glutamate (nmda) receptor subunit zeta 1
- glutamate [nmda] receptor associated protein 1
- glutamate [nmda] receptor subunit epsilon 1
- glutamate [nmda] receptor subunit epsilon 2
- glutamate [nmda] receptor subunit epsilon 3
- glutamate [nmda] receptor subunit epsilon 4
- glutamate [nmda] receptor subunit epsilon-1
- glutamate [nmda] receptor subunit epsilon-2
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 1/2b
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 1/2c
- ionotropic glutamate receptor nmda 1/2c
- ionotropic glutamate receptor nmda 1/2d
- nmda receptor subunit 3a-1 (glun3a)
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 1/2c/3b
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 1 [f484a,t518l]/3a
- glutamate receptor ionotropic, nmda 1 [f484a,t518l]/3b
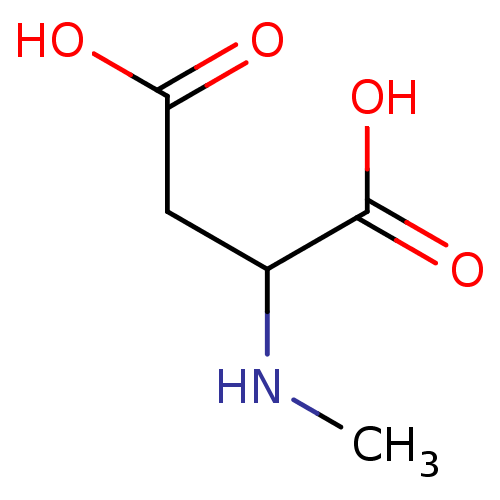 BDBM50002343 CHEMBL275325 NMDA 2-Methylamino-succinic acid
BDBM50002343 CHEMBL275325 NMDA 2-Methylamino-succinic acid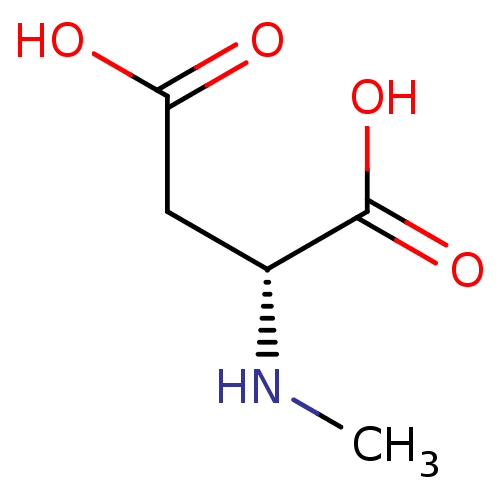 BDBM50013876 CHEMBL291278 N-Methyl-D-aspartate US9182402, 16 NMDA N-Methyl aspartic acid N-Methylaspartate N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid Methyl aspartic acid
BDBM50013876 CHEMBL291278 N-Methyl-D-aspartate US9182402, 16 NMDA N-Methyl aspartic acid N-Methylaspartate N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid Methyl aspartic acid
- Kilburn, JP; Ascic, E; Marigo, M; David, L Modulators of the NMDA receptor US Patent US11466027 (2022)
- Liotta, DC; Snyder, JP; Traynelis, SF; Wilson, L; Mosley, C; Dingledine, RJ; Myers, S; Tahirovic, YA NMDA receptor antagonists for neuroprotection US Patent US9079852 (2015)
- Bresink, I; Danysz, W; Parsons, CG; Mutschler, E Different binding affinities of NMDA receptor channel blockers in various brain regions--indication of NMDA receptor heterogeneity. Neuropharmacology 34: 533-40 (1995)
- Shapiro, G Difluoroethylpyridine derivatives as NR2B NMDA receptor antagonists US Patent US10030026 (2018)
- Cohen-Kaminsky, S; Humbert, M; Dumas, S; Bru-Mercier, G; Messaoudi, S; Brion, J; Alami, M; Galvani, G Dizocilpine derivatives as peripheral NMDA receptor antagonists US Patent US11944616 (2024)
- Traynelis, SF; Mullasseril, P; Garnier, EC; Liotta, DC; Zimmerman, S NMDA receptor modulators and uses related thereto US Patent US9737522 (2017)
- Claiborne, CF; McCauley, JA; Libby, BE; Curtis, NR; Diggle, HJ; Kulagowski, JJ; Michelson, SR; Anderson, KD; Claremon, DA; Freidinger, RM; Bednar, RA; Mosser, SD; Gaul, SL; Connolly, TM; Condra, CL; Bednar, B; Stump, GL; Lynch, JJ; Macaulay, A; Wafford, KA; Koblan, KS; Liverton, NJ Orally efficacious NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 697-700 (2003)
- Chenard, BL; Butler, TW; Shalaby, IA; Prochniak, MA; Koe, BK; Fox, CB Oxindole N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) antagonists Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 91-94 (1993)
- Kilburn, JP; Ascic, E; Marigo, M; David, L Prodrugs of modulators of the NMDA receptor US Patent US11358971 (2022)
- Rosse, G Pyrazole Inhibitors of GluN2B NMDA Receptor Subunit. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 1018-1019 (2016)
- Shapiro, G Pyrrolopyrimidine derivatives as NR2B NMDA receptor antagonists US Patent US9567341 (2017)
- Barta-Szalai, G; Borza, I; Bozó, E; Kiss, C; Agai, B; Proszenyák, A; Keseru, GM; Gere, A; Kolok, S; Galgóczy, K; Horváth, C; Farkas, S; Domány, G Oxamides as novel NR2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 3953-6 (2004)
- Lowe, III, JA; Khan, MA Spiro-lactam NMDA receptor modulators and uses thereof US Patent US12167998 (2024)
- Chen, G; Chrovian, CC; Coate, HR; Dvorak, CA; Gelin, CF; Hiscox, A; Letavic, MA; Rech, JC; Soyode-Johnson, A; Stenne, B; Wall, JL; Zhang, W Substituted 1,2,3-triazoles as NR2B-selective NMDA modulators US Patent US10071988 (2018)
- Shapiro, G 3,3-difluoro-piperidine derivatives as NR2B NMDA receptor antagonists US Patent US10221182 (2019)
- Lütnant, I; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B Benzimidazolone bioisosteres of potent GluN2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Eur J Med Chem 116: 136-146 (2016)
- Banerjee, A; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B Synthesis and NMDA receptor affinity of fluorinated dioxadrol analogues. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 4095-102 (2010)
- Shapiro, G 3,3-difluoropiperidine carbamate heterocyclic compounds as NR2B NMDA receptor antagonists US Patent US10584127 (2020)
- Davies, DJ; Crowe, M; Lucas, N; Quinn, J; Miller, DD; Pritchard, S; Grose, D; Bettini, E; Calcinaghi, N; Virginio, C; Abberley, L; Goldsmith, P; Michel, AD; Chessell, IP; Kew, JN; Miller, ND; Gunthorpe, MJ A novel series of benzimidazole NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 2620-3 (2012)
- Borza, I; Kolok, S; Gere, A; Nagy, J; Fodor, L; Galgóczy, K; Fetter, J; Bertha, F; Agai, B; Horváth, C; Farkas, S; Domány, G Benzimidazole-2-carboxamides as novel NR2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 4638-40 (2006)
- Nguyen, KT; Claiborne, CF; McCauley, JA; Libby, BE; Claremon, DA; Bednar, RA; Mosser, SD; Gaul, SL; Connolly, TM; Condra, CL; Bednar, B; Stump, GL; Lynch, JJ; Koblan, KS; Liverton, NJ Cyclic benzamidines as orally efficacious NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 3997-4000 (2007)
- Gitto, R; De Luca, L; Ferro, S; Scala, A; Ronsisvalle, S; Parenti, C; Prezzavento, O; Buemi, MR; Chimirri, A From NMDA receptor antagonists to discovery of selectives2 receptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem 22: 393-7 (2013)
- Borza, I; Kolok, S; Gere, A; Agai-Csongor, E; Agai, B; Tárkányi, G; Horváth, C; Barta-Szalai, G; Bozó, E; Kiss, C; Bielik, A; Nagy, J; Farkas, S; Domány, G Indole-2-carboxamides as novel NR2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 3859-61 (2003)
- Zarantonello, P; Bettini, E; Paio, A; Simoncelli, C; Terreni, S; Cardullo, F Novel analogues of ketamine and phencyclidine as NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 2059-63 (2011)
- Katzman, BM; Perszyk, RE; Yuan, H; Tahirovic, YA; Sotimehin, AE; Traynelis, SF; Liotta, DC A novel class of negative allosteric modulators of NMDA receptor function. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 5583-8 (2015)
- Nirogi, R; Shinde, AK; Jayarajan, P; Bhyrapuneni, G; Kambhampati, R; Jasti, V Combination of pure 5-HT6 receptor antagonists with NMDA receptor antagonist US Patent US11116764 (2021)
- Köhler, J; Bergander, K; Fabian, J; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B Enantiomerically pure 1,3-dioxanes as highly selective NMDA ands1 receptor ligands. J Med Chem 55: 8953-7 (2012)
- Madsen, U; Ferkany, JW; Jones, BE; Ebert, B; Johansen, TN; Holm, T; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P NMDA receptor agonists derived from ibotenic acid. Preparation, neuroexcitation and neurotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol 189: 381-91 (1990)
- Curtis, NR; Diggle, HJ; Kulagowski, JJ; London, C; Grimwood, S; Hutson, PH; Murray, F; Richards, P; Macaulay, A; Wafford, KA Novel N1-(benzyl)cinnamamidine derived NR2B subtype-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 693-6 (2003)
- Gregory, TF; Wright, JL; Wise, LD; Meltzer, LT; Serpa, KA; Konkoy, CS; Whittemore, ER; Woodward, RM Parallel synthesis of a series of subtype-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 527-9 (2000)
- Kornberg, BE; Nikam, SS; Wright, JL; Kesten, SR; Meltzer, LT; Coughenour, L; Barr, B; Serpa, KA; McCormick, J Subtype selective NMDA receptor antagonists: evaluation of some novel alkynyl analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 1213-6 (2004)
- Traynelis, SF; Liotta, DC; Santangelo, RM; Garnier, EC Subunit selective NMDA receptor potentiators for the treatment of neurological conditions US Patent US10273214 (2019)
- Thum, S; Schepmann, D; Ayet, E; Pujol, M; Nieto, FR; Ametamey, SM; Wünsch, B Tetrahydro-3-benzazepines with fluorinated side chains as NMDA and σ Eur J Med Chem 177: 47-62 (2019)
- Rowley, M; Leeson, P; Grimwood, S; Marshall, G; Saywell, K 5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroquinolones as antagonists at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5: 2089-2092 (1995)
- Kumamoto, T; Nakajima, M; Uga, R; Ihayazaka, N; Kashihara, H; Katakawa, K; Ishikawa, T; Saiki, R; Nishimura, K; Igarashi, K Design, synthesis, and evaluation of polyamine-memantine hybrids as NMDA channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 603-608 (2018)
- Gitto, R; De Luca, L; Ferro, S; Citraro, R; De Sarro, G; Costa, L; Ciranna, L; Chimirri, A Development of 3-substituted-1H-indole derivatives as NR2B/NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 1640-7 (2009)
- Alarcon, K; Martz, A; Mony, L; Neyton, J; Paoletti, P; Goeldner, M; Foucaud, B Reactive derivatives for affinity labeling in the ifenprodil site of NMDA receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 2765-70 (2008)
- Höfner, G; Hoesl, CE; Parsons, C; Quack, G; Wanner, KT NMDA-NR2B subtype selectivity of stereoisomeric 2-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-isoquinolyl)ethanol derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 2231-4 (2005)
- Utech, T; Köhler, J; Wünsch, B Synthesis of 4-(aminoalkyl) substituted 1,3-dioxanes as potent NMDA ands receptor antagonists. Eur J Med Chem 46: 2157-69 (2011)
- Leeson, PD; Iversen, LL The glycine site on the NMDA receptor: structure-activity relationships and therapeutic potential. J Med Chem 37: 4053-67 (1995)
- Schwarthoff, S; Tischer, N; Sager, H; Schätz, B; Rohrbach, MM; Raztsou, I; Robaa, D; Gaube, F; Arndt, HD; Winckler, T Evaluation of γ-carboline-phenothiazine conjugates as simultaneous NMDA receptor blockers and cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 46: (2021)
- Temme, L; Frehland, B; Schepmann, D; Robaa, D; Sippl, W; Wünsch, B Hydroxymethyl bioisosteres of phenolic GluN2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists: Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation. Eur J Med Chem 144: 672-681 (2018)
- Mony, L; Triballeau, N; Paoletti, P; Acher, FC; Bertrand, HO Identification of a novel NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist using a virtual screening approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 5552-8 (2010)
- Lüken, J; Goerges, G; Ritter, N; Disse, P; Schreiber, JA; Schmidt, J; Frehland, B; Schepmann, D; Seebohm, G; Wünsch, B Indazole as a Phenol Bioisostere: Structure-Affinity Relationships of GluN2B-Selective NMDA Receptor Antagonists. J Med Chem 66: 11573-11588 (2023)
- Franchini, S; Linciano, P; Puja, G; Tait, A; Borsari, C; Denora, N; Iacobazzi, RM; Brasili, L; Sorbi, C Novel Dithiolane-Based Ligands Combining Sigma and NMDA Receptor Interactions as Potential Neuroprotective Agents. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1028-1034 (2020)
- Baskin, II; Tikhonova, IG; Palyulin, VA; Zefirov, NS Selectivity fields: comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) of the glycine/NMDA and AMPA receptors. J Med Chem 46: 4063-9 (2003)
- Nirogi, R; Shinde, AK; Jayarajan, P; Bhyrapuneni, G; Kambhampati, R; Jasti, V Triple combination of pure 5-HT6 receptor antagonists, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonist US Patent US11253514 (2022)
- Whitten, JP; Baron, BM; Muench, D; Miller, F; White, HS; McDonald, IA (R)-4-oxo-5-phosphononorvaline: a new competitive glutamate antagonist at the NMDA receptor complex. J Med Chem 33: 2961-3 (1990)
- Salituro, FG; Tomlinson, RC; Baron, BM; Demeter, DA; Weintraub, HJ; McDonald, IA Design, synthesis and molecular modeling of 3-acylamino-2- Carboxyindole NMDA receptor glycine-site antagonists Bioorg Med Chem Lett 1: 455-460 (1991)
- Takayama, H; Yaegashi, Y; Kitajima, M; Han, X; Nishimura, K; Okuyama, S; Igarashi, K Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of tricyclic heterocycle-tetraamine conjugates as potent NMDA channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 4729-32 (2007)
- Saiki, R; Yoshizawa, Y; Minarini, A; Milelli, A; Marchetti, C; Tumiatti, V; Toida, T; Kashiwagi, K; Igarashi, K In vitro and in vivo evaluation of polymethylene tetraamine derivatives as NMDA receptor channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 3901-4 (2013)
- Irvine, MW; Costa, BM; Dlaboga, D; Culley, GR; Hulse, R; Scholefield, CL; Atlason, P; Fang, G; Eaves, R; Morley, R; Mayo-Martin, MB; Amici, M; Bortolotto, ZA; Donaldson, L; Collingridge, GL; Molnár, E; Monaghan, DT; Jane, DE Piperazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid derivatives as dual antagonists of NMDA and GluK1-containing kainate receptors. J Med Chem 55: 327-41 (2012)
- Zscherp, R; Baumeister, S; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B Pyridine bioisosteres of potent GluN2B subunit containing NMDA receptor antagonists with benzo[7]annulene scaffold. Eur J Med Chem 157: 397-404 (2018)
- Dey, S; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B Role of the phenolic OH moiety of GluN2B-selective NMDA antagonists with 3-benzazepine scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 889-93 (2016)
- Tamiz, AP; Cai, SX; Zhou, ZL; Yuen, PW; Schelkun, RM; Whittemore, ER; Weber, E; Woodward, RM; Keana, JF Structure-activity relationship of N-(phenylalkyl)cinnamides as novel NR2B subtype-selective NMDA receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 42: 3412-20 (1999)
- Banerjee, A; Schepmann, D; Köhler, J; Würthwein, EU; Wünsch, B Synthesis and SAR studies of chiral non-racemic dexoxadrol analogues as uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 7855-67 (2010)
- Müller, SL; Schreiber, JA; Schepmann, D; Strutz-Seebohm, N; Seebohm, G; Wünsch, B Systematic variation of the benzenesulfonamide part of the GluN2A selective NMDA receptor antagonist TCN-201. Eur J Med Chem 129: 124-134 (2017)
- Pérez-Areales, FJ; Turcu, AL; Barniol-Xicota, M; Pont, C; Pivetta, D; Espargaró, A; Bartolini, M; De Simone, A; Andrisano, V; Pérez, B; Sabate, R; Sureda, FX; Vázquez, S; Muñoz-Torrero, D A novel class of multitarget anti-Alzheimer benzohomoadamantane‒chlorotacrine hybrids modulating cholinesterases and glutamate NMDA receptors. Eur J Med Chem 180: 613-626 (2019)
- Summer, SL; Kell, SA; Zhu, Z; Moore, R; Liotta, DC; Myers, SJ; Koszalka, GW; Traynelis, SF; Menaldino, DS Di-aryl Sulfonamide Motif Adds π-Stacking Bulk in Negative Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 248-254 (2019)
- Beinat, C; Banister, SD; Hoban, J; Tsanaktsidis, J; Metaxas, A; Windhorst, AD; Kassiou, M Structure-activity relationships of N-substituted 4-(trifluoromethoxy)benzamidines with affinity for GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 828-30 (2014)
- McIntyre, CJ; McCauley, JA; Bednar, B; Bednar, RA; Butcher, JW; Claremon, DA; Cunningham, ME; Freidinger, RM; Gaul, SL; Homnick, CF; Koblan, KS; Mosser, SD; Romano, JJ; Liverton, NJ Synthesis and evaluation of novel tricyclic benzo[4.5]cyclohepta[1.2]pyridine derivatives as NMDA/NR2B antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 5132-5 (2009)
- Hamilton, G; Bednar, D; Borosky, S; Huang, Z; Zubrowski, R; Ferkany, J; Karbon, E Synthesis and glutamate antagonist activity of 4-phosphonoalkylquinoline derivatives: A novel class of non-NMDA antagonist Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 2035-2040 (1994)
- Morley, RM; Tse, HW; Feng, B; Miller, JC; Monaghan, DT; Jane, DE Synthesis and pharmacology of N1-substituted piperazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid derivatives acting as NMDA receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 48: 2627-37 (2005)
- Dey, S; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B 2-Methyltetrahydro-3-benzazepin-1-ols - The missing link in SAR of GluN2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 501-508 (2018)
- Leeson, PD; Carling, RW; Moore, KW; Moseley, AM; Smith, JD; Stevenson, G; Chan, T; Baker, R; Foster, AC; Grimwood, S 4-Amido-2-carboxytetrahydroquinolines. Structure-activity relationships for antagonism at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor. J Med Chem 35: 1954-68 (1992)
- Volgraf, M; Sellers, BD; Jiang, Y; Wu, G; Ly, CQ; Villemure, E; Pastor, RM; Yuen, PW; Lu, A; Luo, X; Liu, M; Zhang, S; Sun, L; Fu, Y; Lupardus, PJ; Wallweber, HJ; Liederer, BM; Deshmukh, G; Plise, E; Tay, S; Reynen, P; Herrington, J; Gustafson, A; Liu, Y; Dirksen, A; Dietz, MG; Liu, Y; Wang, TM; Hanson, JE; Hackos, D; Scearce-Levie, K; Schwarz, JB Discovery of GluN2A-Selective NMDA Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulators (PAMs): Tuning Deactivation Kinetics via Structure-Based Design. J Med Chem 59: 2760-79 (2016)
- Pabel, J; Höfner, G; Wanner, KT Synthesis and resolution of racemic eliprodil and evaluation of the enantiomers of eliprodil as NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 1377-80 (2000)
- Grauert, M; Bechtel, WD; Ensinger, HA; Merz, H; Carter, AJ Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 6,7-benzomorphan derivatives as antagonists of the NMDA receptor-channel complex. J Med Chem 40: 2922-30 (1997)
- Brown, DG; Maier, DL; Sylvester, MA; Hoerter, TN; Menhaji-Klotz, E; Lasota, CC; Hirata, LT; Wilkins, DE; Scott, CW; Trivedi, S; Chen, T; McCarthy, DJ; Maciag, CM; Sutton, EJ; Cumberledge, J; Mathisen, D; Roberts, J; Gupta, A; Liu, F; Elmore, CS; Alhambra, C; Krumrine, JR; Wang, X; Ciaccio, PJ; Wood, MW; Campbell, JB; Johansson, MJ; Xia, J; Wen, X; Jiang, J; Wang, X; Peng, Z; Hu, T; Wang, J 2,6-Disubstituted pyrazines and related analogs as NR2B site antagonists of the NMDA receptor with anti-depressant activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 3399-403 (2011)
- Rowley, M; Leeson, PD; Grimwood, S; Foster, A; Saywell, K 2-carboxy indolines and indoles as potential glycine/NMDA antagonists: effect of five-membered ring conformation on affinity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2: 1627-1630 (1992)
- Nguyen, KT; Luethi, E; Syed, S; Urwyler, S; Bertrand, S; Bertrand, D; Reymond, JL 3-(aminomethyl)piperazine-2,5-dione as a novel NMDA glycine site inhibitor from the chemical universe database GDB. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 3832-5 (2009)
- Colotta, V; Catarzi, D; Varano, F; Calabri, FR; Filacchioni, G; Costagli, C; Galli, A 3-hydroxy-quinazoline-2,4-dione as a useful scaffold to obtain selective Gly/NMDA and AMPA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 2345-9 (2004)
- Acklin, P; Allgeier, H; Auberson, YP; Bischoff, S; Ofner, S; Sauer, D; Schmutz, M 5-Aminomethylquinoxaline-2,3-diones, Part III: Arylamide derivatives as highly potent and selective glycine-site NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8: 493-8 (1999)
- Gawaskar, S; Schepmann, D; Bonifazi, A; Robaa, D; Sippl, W; Wünsch, B Benzo[7]annulene-based GluN2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists: Surprising effect of a nitro group in 2-position. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 5748-51 (2015)
- Wright, JL; Gregory, TF; Boxer, PA; Meltzer, LT; Serpa, KA; Wise, LD Discovery of subtype-selective NMDA receptor ligands: 4-benzyl-1-piperidinylalkynylpyrroles, pyrazoles and imidazoles as NR1A/2B antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 2815-8 (1999)
- Linciano, P; Sorbi, C; Rossino, G; Rossi, D; Marsala, A; Denora, N; Bedeschi, M; Marino, N; Miserocchi, G; Dondio, G; Peviani, M; Tesei, A; Collina, S; Franchini, S Novel S1R agonists counteracting NMDA excitotoxicity and oxidative stress: A step forward in the discovery of neuroprotective agents. Eur J Med Chem 249: (2023)
- Fuchigami, T; Yamaguchi, H; Ogawa, M; Biao, L; Nakayama, M; Haratake, M; Magata, Y Synthesis and biological evaluation of radio-iodinated benzimidazoles as SPECT imaging agents for NR2B subtype of NMDA receptor. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 7497-506 (2010)
- Büttelmann, B; Alanine, A; Bourson, A; Gill, R; Heitz, MP; Mutel, V; Pinard, E; Trube, G; Wyler, R 2-(3,4-Dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2yl)-pyridines as a novel class of NR1/2B subtype selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 829-32 (2003)
- Anan, K; Masui, M; Hara, S; Ohara, M; Kume, M; Yamamoto, S; Shinohara, S; Tsuji, H; Shimada, S; Yagi, S; Hasebe, N; Kai, H Discovery of orally bioavailable cyclohexanol-based NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonists with analgesic activity utilizing a scaffold hopping approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4194-4198 (2017)
- Padmanabhan, S; Perlman, ME; Zhang, L; Moore, D; Zhou, D; Fischer, JB; Durant, GJ; McBurney, RN Identification and characterization of a potential ischemia-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor ion-channel blocker, CNS 5788. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 501-4 (2001)
- Temme, L; Bechthold, E; Schreiber, JA; Gawaskar, S; Schepmann, D; Robaa, D; Sippl, W; Seebohm, G; Wünsch, B Negative allosteric modulators of the GluN2B NMDA receptor with phenylethylamine structure embedded in ring-expanded and ring-contracted scaffolds. Eur J Med Chem 190: (2020)
- Bonifazi, A; Del Bello, F; Mammoli, V; Piergentili, A; Petrelli, R; Cimarelli, C; Pellei, M; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B; Barocelli, E; Bertoni, S; Flammini, L; Amantini, C; Nabissi, M; Santoni, G; Vistoli, G; Quaglia, W Novel Potent N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonists ors1 Receptor Ligands Based on Properly Substituted 1,4-Dioxane Ring. J Med Chem 58: 8601-15 (2015)
- Burnell, ES; Irvine, M; Fang, G; Sapkota, K; Jane, DE; Monaghan, DT Positive and Negative Allosteric Modulators of N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptors: Structure-Activity Relationships and Mechanisms of Action. J Med Chem 62: 3-23 (2019)
- Nagata, R; Ae, N; Tanno, N Structure-activity relationships of tricyclic quinoxalinediones as potent antagonists for the glycine binding site of the NMDA receptor 1 Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5: 1527-1532 (1995)
- Nagata, R; Kodo, T; Yamaguchi, H; Tanno, N Structure-activity relationships of tricyclic quinoxalinediones as potent antagonists for the glycine binding site of the NMDA receptor 2 Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5: 1533-1536 (1995)
- Baumeister, S; Schepmann, D; Wünsch, B Thiophene bioisosteres of GluN2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists: Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of [7]annuleno[b]thiophen-6-amines. Bioorg Med Chem 28: (2020)
- Alanine, A; Bourson, A; Büttelmann, B; Gill, R; Heitz, MP; Mutel, V; Pinard, E; Trube, G; Wyler, R 1-Benzyloxy-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl-amines, a novel class of NR1/2B subtype selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 3155-9 (2003)
- Tewes, B; Frehland, B; Schepmann, D; Schmidtke, KU; Winckler, T; Wünsch, B Conformationally constrained NR2B selective NMDA receptor antagonists derived from ifenprodil: Synthesis and biological evaluation of tetrahydro-3-benzazepine-1,7-diols. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 8005-15 (2010)
- Leeson, PD; Williams, BJ; Rowley, M; Moore, KW; Baker, R; Kemp, JA; Priestley, T; Foster, AC; Donald, AE Derivatives of 1-hydroxy-3-aminopyrrolidin-2-one (HA-966). Partial agonists at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 71-76 (1993)
- Rosini, M; Simoni, E; Caporaso, R; Basagni, F; Catanzaro, M; Abu, IF; Fagiani, F; Fusco, F; Masuzzo, S; Albani, D; Lanni, C; Mellor, IR; Minarini, A Merging memantine and ferulic acid to probe connections between NMDA receptors, oxidative stress and amyloid-β peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Med Chem 180: 111-120 (2019)
- de Candia, M; Zaetta, G; Denora, N; Tricarico, D; Majellaro, M; Cellamare, S; Altomare, CD New azepino[4,3-b]indole derivatives as nanomolar selective inhibitors of human butyrylcholinesterase showing protective effects against NMDA-induced neurotoxicity. Eur J Med Chem 125: 288-298 (2017)
- Catarzi, D; Colotta, V; Varano, F; Cecchi, L; Filacchioni, G; Galli, A; Costagli, C 4,5-Dihydro-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]quinoxalin-4-ones: excitatory amino acid antagonists with combined glycine/NMDA and AMPA receptor affinity. J Med Chem 42: 2478-84 (1999)
- Zhou, ZL; Cai, SX; Whittemore, ER; Konkoy, CS; Espitia, SA; Tran, M; Rock, DM; Coughenour, LL; Hawkinson, JE; Boxer, PA; Bigge, CF; Wise, LD; Weber, E; Woodward, RM; Keana, JF 4-Hydroxy-1-[2-(4-hydroxyphenoxy)ethyl]-4-(4-methylbenzyl)piperidine: a novel, potent, and selective NR1/2B NMDA receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 42: 2993-3000 (1999)
- Auberson, YP; Allgeier, H; Bischoff, S; Lingenhoehl, K; Moretti, R; Schmutz, M 5-Phosphonomethylquinoxalinediones as competitive NMDA receptor antagonists with a preference for the human 1A/2A, rather than 1A/2B receptor composition. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 1099-102 (2002)
- Kvist, T; Steffensen, TB; Greenwood, JR; Mehrzad Tabrizi, F; Hansen, KB; Gajhede, M; Pickering, DS; Traynelis, SF; Kastrup, JS; Bräuner-Osborne, H Crystal structure and pharmacological characterization of a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist at the GluN1 glycine binding site. J Biol Chem 288: 33124-35 (2013)
- Dey, S; Temme, L; Schreiber, JA; Schepmann, D; Frehland, B; Lehmkuhl, K; Strutz-Seebohm, N; Seebohm, G; Wünsch, B Deconstruction - reconstruction approach to analyze the essential structural elements of tetrahydro-3-benzazepine-based antagonists of GluN2B subunit containing NMDA receptors. Eur J Med Chem 138: 552-564 (2017)
- Kawai, M; Nakamura, H; Sakurada, I; Shimokawa, H; Tanaka, H; Matsumizu, M; Ando, K; Hattori, K; Ohta, A; Nukui, S; Omura, A; Kawamura, M Discovery of novel and orally active NR2B-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists, pyridinol derivatives with reduced HERG binding affinity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 5533-6 (2007)
- Jansen, M; Potschka, H; Brandt, C; Löscher, W; Dannhardt, G Hydantoin-substituted 4,6-dichloroindole-2-carboxylic acids as ligands with high affinity for the glycine binding site of the NMDA receptor. J Med Chem 46: 64-73 (2002)
- Katayama, S; Ae, N; Kodo, T; Masumoto, S; Hourai, S; Tamamura, C; Tanaka, H; Nagata, R Tricyclic indole-2-carboxylic acids: highly in vivo active and selective antagonists for the glycine binding site of the NMDA receptor. J Med Chem 46: 691-701 (2003)
- Gynther, M; Proietti Silvestri, I; Hansen, JC; Hansen, KB; Malm, T; Ishchenko, Y; Larsen, Y; Han, L; Kayser, S; Auriola, S; Petsalo, A; Nielsen, B; Pickering, DS; Bunch, L Augmentation of Anticancer Drug Efficacy in Murine Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by a Peripherally Acting Competitive N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Antagonist. J Med Chem 60: 9885-9904 (2017)
- Kreimeyer, A; Laube, B; Sturgess, M; Goeldner, M; Foucaud, B Evaluation and biological properties of reactive ligands for the mapping of the glycine site on the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. J Med Chem 42: 4394-404 (1999)
- Cai, SX; Zhou, ZL; Huang, JC; Whittemore, ER; Egbuwoku, ZO; Lü, Y; Hawkinson, JE; Woodward, RM; Weber, E; Keana, JF Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-2,3,4-trione 3-oximes: novel and highly potent antagonists for NMDA receptor glycine site. J Med Chem 39: 3248-55 (1996)
- Kulagowski, JJ; Baker, R; Curtis, NR; Leeson, PD; Mawer, IM; Moseley, AM; Ridgill, MP; Rowley, M; Stansfield, I; Foster, AC 3'-(Arylmethyl)- and 3'-(aryloxy)-3-phenyl-4-hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-ones: orally active antagonists of the glycine site on the NMDA receptor. J Med Chem 37: 1402-5 (1994)
- Cai, SX; Huang, JC; Espitia, SA; Tran, M; Ilyin, VI; Hawkinson, JE; Woodward, RM; Weber, E; Keana, JF 5-(N-oxyaza)-7-substituted-1,4-dihydroquinoxaline-2,3-diones: novel, systemically active and broad spectrum antagonists for NMDA/glycine, AMPA, and kainate receptors. J Med Chem 40: 3679-86 (1997)
- Mutel, V; Buchy, D; Klingelschmidt, A; Messer, J; Bleuel, Z; Kemp, JA; Richards, JG In vitro binding properties in rat brain of [3H]Ro 25-6981, a potent and selective antagonist of NMDA receptors containing NR2B subunits. J Neurochem 70: 2147-55 (1998)
- Rosini, M; Simoni, E; Bartolini, M; Cavalli, A; Ceccarini, L; Pascu, N; McClymont, DW; Tarozzi, A; Bolognesi, ML; Minarini, A; Tumiatti, V; Andrisano, V; Mellor, IR; Melchiorre, C Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, beta-amyloid aggregation, and NMDA receptors in Alzheimer's disease: a promising direction for the multi-target-directed ligands gold rush. J Med Chem 51: 4381-4 (2008)
- Buchstaller, HP; Siebert, CD; Steinmetz, R; Frank, I; Berger, ML; Gottschlich, R; Leibrock, J; Krug, M; Steinhilber, D; Noe, CR Synthesis of thieno[2,3-b]pyridinones acting as cytoprotectants and as inhibitors of [3H]glycine binding to the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. J Med Chem 49: 864-71 (2006)
- Ametamey, SM; Kokic, M; Carrey-Rémy, N; Bläuenstein, P; Willmann, M; Bischoff, S; Schmutz, M; Schubiger, PA; Auberson, YP Synthesis, radiolabelling and biological characterization of (D)-7-iodo-N-(1-phosphonoethyl)-5-aminomethylquinoxaline-2,3-dione, a glycine-binding site antagonist of NMDA receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 75-8 (2000)
- Büttelmann, B; Alanine, A; Bourson, A; Gill, R; Heitz, MP; Mutel, V; Pinard, E; Trube, G; Wyler, R 4-(3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2yl)-pyridines and 4-(3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl)-quinolines as potent NR1/2B subtype selective NMDA receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 1759-62 (2003)
- Cai, SX; Kher, SM; Zhou, ZL; Ilyin, V; Espitia, SA; Tran, M; Hawkinson, JE; Woodward, RM; Weber, E; Keana, JF Structure-activity relationships of alkyl- and alkoxy-substituted 1,4-dihydroquinoxaline-2,3-diones: potent and systemically active antagonists for the glycine site of the NMDA receptor. J Med Chem 40: 730-8 (1997)
- Reddy, NL; Hu, LY; Cotter, RE; Fischer, JB; Wong, WJ; McBurney, RN; Weber, E; Holmes, DL; Wong, ST; Prasad, R Synthesis and structure-activity studies of N,N'-diarylguanidine derivatives. N-(1-naphthyl)-N'-(3-ethylphenyl)-N'-methylguanidine: a new, selective noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 37: 260-7 (1994)
- Labas, R; Gilbert, G; Nicole, O; Dhilly, M; Abbas, A; Tirel, O; Buisson, A; Henry, J; Barré, L; Debruyne, D; Sobrio, F Synthesis, evaluation and metabolic studies of radiotracers containing a 4-(4-[18F]-fluorobenzyl)piperidin-1-yl moiety for the PET imaging of NR2B NMDA receptors. Eur J Med Chem 46: 2295-309 (2011)
- Yang, L; Liu, H; Wang, E; Liu, H; Liu, H; Zhou, L; Deng, T; Pan, X; Hu, Z; Yang, X Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel 1-phenyl-pyrrolo[1,2-b]isoquinolin-3-one derivatives as antagonists for the glycine binding site of the NMDA receptor. Eur J Med Chem 258:
- Guzikowski, AP; Tamiz, AP; Acosta-Burruel, M; Hong-Bae, S; Cai, SX; Hawkinson, JE; Keana, JF; Kesten, SR; Shipp, CT; Tran, M; Whittemore, ER; Woodward, RM; Wright, JL; Zhou, ZL Synthesis of N-substituted 4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)piperidines, 4-(4-hydroxybenzyl)piperidines, and (+/-)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)pyrrolidines: selective antagonists at the 1A/2B NMDA receptor subtype. J Med Chem 43: 984-94 (2000)
- Pinard, E; Alanine, A; Bourson, A; Büttelmann, B; Gill, R; Heitz, M; Jaeschke, G; Mutel, V; Trube, G; Wyler, R Discovery of (R)-1-[2-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-propyl]-4-(4-methyl-benzyl)-piperidin-4-ol: a novel NR1/2B subtype selective NMDA receptor antagonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 2173-6 (2001)
- Tamiz, AP; Whittemore, ER; Woodward, RM; Upasani, RB; Keana, JF Structure-activity relationship for a series of 2-substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indoles: potent subtype-selective inhibitors of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 1619-24 (1999)
- Carling, RW; Leeson, PD; Moore, KW; Smith, JD; Moyes, CR; Mawer, IM; Thomas, S; Chan, T; Baker, R; Foster, AC 3-Nitro-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolones. Excitatory amino acid antagonists acting at glycine-site NMDA and (RS)-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors. J Med Chem 36: 3397-408 (1993)
- Monn, JA; Thurkauf, A; Mattson, MV; Jacobson, AE; Rice, KC Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of C5-substituted analogues of (+-)-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5,10-imine [(+-)-desmethyl-MK801]: ligands for the NMDA receptor-coupled phencyclidine binding site. J Med Chem 33: 1069-76 (1990)
- Guzikowski, AP; Hawkinson, J; Weber, E; Keana, JF 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3-hydroxy-1H-1-benzazepine-2,5-diones via a diels-alder reaction:antagonists with a non-planar hydrophobic region for NMDA receptor glycine sites Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5: 2747-2748 (1995)
- Shuto, S; Ono, S; Imoto, H; Yoshii, K; Matsuda, A Synthesis and biological activity of conformationally restricted analogues of milnacipran: (1S, 2R)-1-phenyl-2-[(R)-1-amino-2-propynyl]-N,N- diethylcyclopropanecarboxamide is a novel class of NMDA receptor channel blocker. J Med Chem 41: 3507-14 (1998)
- Guzikowski, AP; Whittemore, ER; Woodward, RM; Weber, E; Keana, JF Synthesis of racemic 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-3-hydroxy-1H-1-benzazepine-2,5-diones as antagonists of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptors. J Med Chem 40: 2424-9 (1997)
- Kawai, M; Ando, K; Matsumoto, Y; Sakurada, I; Hirota, M; Nakamura, H; Ohta, A; Sudo, M; Hattori, K; Takashima, T; Hizue, M; Watanabe, S; Fujita, I; Mizutani, M; Kawamura, M Discovery of (-)-6-[2-[4-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-hydroxy-1-piperidinyl]-1-hydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone--a potent NR2B-selective N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist for the treatment of pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 5558-62 (2007)
- Butler, TW; Blake, JF; Bordner, J; Butler, P; Chenard, BL; Collins, MA; DeCosta, D; Ducat, MJ; Eisenhard, ME; Menniti, FS; Pagnozzi, MJ; Sands, SB; Segelstein, BE; Volberg, W; White, WF; Zhao, D (3R,4S)-3-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-hydroxypiperidin-1-yl]chroman-4,7-diol: a conformationally restricted analogue of the NR2B subtype-selective NMDA antagonist (1S,2S)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-4-phenylpiperidino)- 1-propanol. J Med Chem 41: 1172-84 (1998)
- Linders, JT; Monn, JA; Mattson, MV; George, C; Jacobson, AE; Rice, KC Synthesis and binding properties of MK-801 isothiocyanates; (+)-3-isothiocyanato-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten- 5,10-imine hydrochloride: a new, potent and selective electrophilic affinity ligand for the NMDA receptor-coupled phencyclidine binding site. J Med Chem 36: 2499-507 (1993)
- ChEMBL_2201483 (CHEMBL5114191) Displacement of [3H]NMDA from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201496 (CHEMBL5114204) Antagonist activity at NMDA receptor (unknown origin) assessed as NMDA-induced depolarizations
- ChEBML_1526086 Binding affinity to NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1852469 (CHEMBL4353093) Inhibition of NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1884187 (CHEMBL4385769) Inhibition of NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2215305 (CHEMBL5128437) Inhibition of NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_455780 (CHEMBL887786) Binding affinity to NMDA NR2B receptor
- ChEMBL_141157 (CHEMBL749675) Displacement of NMDA receptor-specific [3H]ifenprodil binding to recombinant human NMDA receptor, NR2B subtype expressed in L cells
- ChEBML_140490 Ability to displace [3H]glycine from NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_1526086 (CHEMBL3636333) Binding affinity to NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1899851 (CHEMBL4401966) Binding affinity to NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1912591 (CHEMBL4415174) Modulator activity at NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201505 (CHEMBL5114213) Binding affinity to NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2260007 (CHEMBL5215018) Binding affinity to NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2275503 Inhibition of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2497329 Antagonist activity at GluN2A NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_456499 (CHEMBL887322) Antagonist activity at human NMDA NR1 receptor
- ChEMBL_983632 (CHEMBL2427287) Inhibition of NMDA GluN2D receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2260017 (CHEMBL5215028) Binding affinity to TCP-stimulated NMDA (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2284556 Displacement of [3H]MDL from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2294019 Displacement of [3H]ifenprodyl from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2294721 Antagonist activity at NMDA receptor NR2B subunit (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_428114 (CHEMBL914283) Antagonist activity at NR2B NMDA receptor in Wistar rat neocortical cells assessed as inhibition of NMDA-evoked elevation of intracellular calcium concentration
- ChEMBL_154227 (CHEMBL763473) Inhibition of MK 801 binding to NMDA, PCP receptor
- ChEMBL_2201475 (CHEMBL5114183) Displacement of [3H]glycine from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201476 (CHEMBL5114184) Displacement of [3H]DCKA from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201480 (CHEMBL5114188) Displacement of [3H]AMPA from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201481 (CHEMBL5114189) Displacement of [3H]MDL from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_70971 (CHEMBL857373) Inhibition of MDL 105519 binding to NMDA, glycine receptor
- ChEBML_140542 Displacement of [3H]glycine from glycine site on the NMDA receptor.
- ChEBML_142510 Binding affinity at glycine co-agonist site of rat NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_1884189 (CHEMBL4385771) Displacement of [3H]MK-801 from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201478 (CHEMBL5114186) Displacement of [3H]CGP-39653 from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201479 (CHEMBL5114187) Displacement of [3H]kainic acid from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201482 (CHEMBL5114190) Displacement of [3H]L-689560 from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2201494 (CHEMBL5114202) Displacement of [3H]MK-801 from NMDA receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2294014 Displacement of [3H]ifenprodyl from NMDA receptor NR2B subunit (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2294015 Displacement of [3H]MK801 from NMDA receptor NR2B subunit (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2303221 Antagonist activity at NMDA receptor (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_455781 (CHEMBL887787) Antagonist activity at NMDA NR2B receptor assessed as calcium flux
- ChEMBL_489454 (CHEMBL982936) Inhibition of NMDA NR1/NR2B receptor expressed in xenopus oocytes assessed as inhibition of NMDA and glycine-induced current response by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEBML_140304 In vitro inhibitory activity to inhibit [3H]glycine binding to NMDA receptor
- ChEBML_143320 Inhibition of NMDA response at NR1A/2B receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140328 (CHEMBL858425) In vitro binding affinity for glycine site on the NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_2302902 Inhibition of GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells
- ChEMBL_533724 (CHEMBL974277) Inhibition of rat NMDA NR2D receptor expressed in xenopus oocytes coexpressing NMDA NR13b assessed as effect on glycine-induced current response at -70 mV by voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_533730 (CHEMBL974283) Inhibition of rat NMDA NR2A receptor expressed in xenopus oocytes coexpressing NMDA NR13b assessed as effect on glycine-induced current response at -70 mV by voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_533731 (CHEMBL974284) Inhibition of rat NMDA NR2B receptor expressed in xenopus oocytes coexpressing NMDA NR13b assessed as effect on glycine-induced current response at -70 mV by voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_533732 (CHEMBL974285) Inhibition of rat NMDA NR2C receptor expressed in xenopus oocytes coexpressing NMDA NR13b assessed as effect on glycine-induced current response at -70 mV by voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_140401 (CHEMBL746727) Inhibition of [3H]- glycine binding to NMDA receptor from rat cortical membranes.
- ChEMBL_140403 (CHEMBL746729) Inhibition of [3H]- DCKA binding to NMDA receptor of rat brain membranes
- ChEMBL_140473 (CHEMBL747064) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of oocytes at NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_141949 (CHEMBL749586) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of oocytes at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_428115 (CHEMBL914284) Displacement of [3H]Ro 25,6981 from NR2B NMDA receptor in rat forebrain
- ChEBML_1690438 Inhibition of calpain-1 in rat hippocampal slices assessed as prevention of NMDA-induced spectrin cleavage preincubated for 30 mins followed by NMDA addition measured after 5 hrs by Western blot analysis
- ChEBML_140310 Tested for the inhibition of [3H]5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid (DCKA) binding to NMDA receptor
- ChEBML_140337 The binding affinity was measured on NMDA receptor using [3H]- CGS-19755 as radioligand.
- ChEBML_142501 Binding affinity towards NMDA receptor to displace [3H]L-689,560 from rat cortical membranes
- ChEMBL_140464 (CHEMBL750516) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of [3H]TCP at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_140465 (CHEMBL750517) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of cortical slice at NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_140471 (CHEMBL747062) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of cortical slice at NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_140474 (CHEMBL747065) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of spinal cord at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_140491 (CHEMBL747081) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of cortical neuron at NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_141147 (CHEMBL749665) Percentage inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor produced by oocytes
- ChEMBL_1852494 (CHEMBL4353118) Displacement of [3H]-ifenprodil from NMDA receptor (unknown origin) by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2497328 Antagonist activity at GluN2B NMDA receptor (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of channel current
- ChEMBL_306468 (CHEMBL828708) Inhibition of NMDA-evoked increased intracellular [Ca2+] in cells expressing NR1/NR2B receptor
- ChEMBL_395467 (CHEMBL909221) Displacement of [3H]Ro25-6981 from NR2B NMDA receptor in rat forebrain membrane
- ChEMBL_1283718 (CHEMBL3108298) Displacement of [3H]Ifenprodil from NMDA receptor GluN2B subunit in Wistar rat cerebral cortex
- ChEMBL_140330 (CHEMBL749576) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of binding of [3H]glycine to NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_140337 (CHEMBL749581) The binding affinity was measured on NMDA receptor using [3H]- CGS-19755 as radioligand.
- ChEMBL_140463 (CHEMBL884513) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of [3H]-GABA release at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_140469 (CHEMBL747060) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of [3H]L-689,560 at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_140470 (CHEMBL747061) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of cGMP cerebellar slice at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_140472 (CHEMBL747063) Compound was evaluated for in vitro inhibition of cortical slice release at NMDA receptor.
- ChEMBL_141918 (CHEMBL750561) Inhibitory activity against Xenopus laevis oocyte expressing 1A/2A heteromeric human NMDA (hNMDA) receptor
- ChEMBL_141935 (CHEMBL746993) Inhibitory activity against Xenopus laevis oocyte expressing 1A/2B heteromeric human NMDA (hNMDA) receptor
- ChEMBL_142507 (CHEMBL748575) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of binding of [3H]glycine to NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_143317 (CHEMBL753019) In vitro inhibition of NMDA responses at NR1A/2A receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143326 (CHEMBL752244) In vitro inhibition of NMDA responses at NR1A/2B receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143335 (CHEMBL752252) In vitro inhibition of NMDA responses at NR1A/2C receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_1852493 (CHEMBL4353117) Displacement of [3H]-MK-801 from NMDA receptor (unknown origin) by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_540808 (CHEMBL1034049) Displacement of [3H]ifenprodil from NMDA NR2B receptor in Wistar rat cerebral cortex membrane
- ChEMBL_57 (CHEMBL615180) Functional antagonism by electrical assays in Xenopus oocytes expressing 1A/2A NMDA receptor subtype
- ChEMBL_58 (CHEMBL615181) Functional antagonism by electrical assays in Xenopus oocytes expressing the 1A/2B NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_59 (CHEMBL615182) Functional antagonism by electrical assays in Xenopus oocytes expressing the 1A/2C NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_950641 (CHEMBL2352644) Displacement of [3H]MK-801 from NMDA receptor complex (unknown origin) after 40 mins
- ChEBML_141035 Inhibition of the response to NMDA glutamate/glycine receptor NR2A subtype was determined using FLIPR assay
- ChEBML_142504 Inhibition of [3H]L-689,560 binding to Glycine site of NMDA receptor of rat cortical membranes
- ChEMBL_141146 (CHEMBL749664) Concentration required to inhibit of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor produced by oocytes
- ChEMBL_143324 (CHEMBL752242) In vitro inhibitory concentration against NMDA responses at NR1A/2B receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143333 (CHEMBL752250) In vitro inhibitory concentration against NMDA responses at NR1A/2C receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_451962 (CHEMBL901120) Blockade of L-glutamate/glycine-activated rat NR1/NR2A NMDA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEBML_140325 Affinity measured by using [3H]5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid (DCKA) for the glycine binding site of NMDA receptor
- ChEBML_141936 Antagonist activity against rat 1A/2B subtype of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in xenopus oocytes.
- ChEMBL_140478 (CHEMBL747069) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2A NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140482 (CHEMBL747072) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2AB NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140483 (CHEMBL747073) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2B NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140485 (CHEMBL747075) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2C NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_141036 (CHEMBL749390) Inhibition of the response to NMDA glutamate/glycine receptor NR2B subtype was determined using FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_141803 (CHEMBL748701) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2A NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_141911 (CHEMBL751529) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2AB NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_141912 (CHEMBL751530) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2C NMDA expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143314 (CHEMBL753016) In vitro inhibitory concentration against NMDA responses at cloned NR1A/2A receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143321 (CHEMBL750404) The compound was tested in vitro for activity against NR1A/2B sub type of NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_143332 (CHEMBL752249) The compound was tested in vitro for activity against NR1A/2C sub type of NMDA receptor
- ChEBML_140302 In vitro binding assay for the displacement of [3H]MDL-105519 from the glycine-site of NMDA receptors
- ChEBML_140492 Compound was tested for binding affinity against glycine site of NMDA receptor using [3H]glycine as a radioligand.
- ChEBML_140852 Inhibition of specific binding of [3H]glycine to NMDA receptors, in rat cortical membranes at 32 uM conc.
- ChEBML_142502 Binding affinity towards glycine binding site of NMDA receptor to rat cortical membrane using [3H]glycine as radioligand
- ChEMBL_140325 (CHEMBL748576) Affinity measured by using [3H]5,7-dichlorokynurenic acid (DCKA) for the glycine binding site of NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_140405 (CHEMBL746731) Inhibition of [3H]-3 binding to the glycine site on the NMDA receptor in Rat cortical slices
- ChEMBL_140872 (CHEMBL752503) Binding selectivity towards N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor 1 was determined by using [3H]- glycine/NMDA
- ChEMBL_877721 (CHEMBL2186401) Displacement of [3H]ifenprodil from NMDA receptor GluN2B subunit in Wistar rat cerebral cortex after 120 mins
- ChEBML_140308 Tested for in vitro binding affinity against glycine-bining site of NMDA receptor using [3H]MDL-105519 binding assay
- ChEBML_140321 Affinity for the glycine binding site of the NMDA receptor using [3H]- 5,7- dichloro -kynurenic acid as radio-ligand
- ChEBML_140336 Tested for the ability to displace [3H]CGS-19,755 (10 nM) binding in rat forebrain membranes for NMDA receptor
- ChEBML_140475 Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity towards strychnine - insensitive glycine site of NMDA in presence of [3H]- CPP
- ChEBML_143313 Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2A receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEBML_143329 Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2C receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140550 (CHEMBL747256) Binding affinity towards N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor (NMDA) determined electrophysically using the rat cortical wedge model.
- ChEMBL_305335 (CHEMBL833556) Mean inhibitory concentration against rat N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor 1a/2A expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_305336 (CHEMBL833557) Mean inhibitory concentration against rat N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor 1a/2B expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_305337 (CHEMBL833558) Mean inhibitory concentration against rat N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor 1a/2C expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_756410 (CHEMBL1803132) Antagonist activity against NR1/NR2B receptor expressed in xenopus oocytes assessed as inhibition of NMDA induced Ca2+ influx
- ChEMBL_799740 (CHEMBL1941446) Displacement of [3H]ifenprodil from GluN2B/NMDA in Wistar rat cerebral cortex after 120 mins by scintillation counting
- ChEBML_140322 Binding affinity for glycine site-NMDA receptor was determined by the ability to displace [3H]glycine in rat cortical membranes
- ChEBML_142506 Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity towards strychnine - insensitive glycine site of NMDA receptor in presence of [3H]- Gly
- ChEMBL_140336 (CHEMBL749580) Tested for the ability to displace [3H]CGS-19,755 (10 nM) binding in rat forebrain membranes for NMDA receptor
- ChEMBL_143311 (CHEMBL753013) Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2A receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143312 (CHEMBL753014) Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2A receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143313 (CHEMBL753015) Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2A receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143330 (CHEMBL883551) Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2C receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_143331 (CHEMBL752248) Compound was tested in vitro for inhibition of NMDA response at cloned NR1A/2C receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_756313 (CHEMBL1805126) Antagonist activity against NR1a/NR2B receptor transfected in human HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of NMDA-induced Ca2+ influx
- ChEMBL_140477 (CHEMBL747068) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2A N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140480 (CHEMBL747071) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2AB N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140481 (CHEMBL872726) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2AB N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_140484 (CHEMBL747074) Concentration required for 50% Inhibition of responses at cloned NR1A/2C N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) expressed in Xenopus oocytes
- ChEMBL_440415 (CHEMBL890729) Agonist activity at rat recombinant NMDA NR2A receptor expressed in xenopus laevis oocyte assessed as inhibition of glycine-stimulated current
- ChEBML_142498 Ability of compound to compete with [3H]glycine for the strychnine-insensitive NMDA receptor glycine binding sites on rat cortical and hippocampus
- ChEMBL_1281790 (CHEMBL3100693) Displacement of [3H]ifenprodil from Wistar rat cerebral cortex glutamate NMDA receptor GluN2B subunit after 120 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_140406 (CHEMBL746732) Inhibition of [3H]-MK-801 binding to a N-methyl-D-aspartic acid(NMDA) receptor in glycine-sensitive rat cortical membranes.
- ChEMBL_140617 (CHEMBL752265) Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor-evoked increase of intracellular Ca+ in cells expressing NMDA glutamate receptor 1/2B
- ChEMBL_141004 (CHEMBL747012) The compound was tested for its binding affinity towards Glycine/NMDA receptor in rat cortical membranes using [3H]glycine as radioligand
- ChEMBL_2501953 Inhibition of NMDA/glycine-activated rat GluN1/Glu2A expressed in xenopus laevis oocytes at -75 mV holding potential by voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_2501954 Inhibition of NMDA/glycine-activated rat GluN1/Glu2B expressed in xenopus laevis oocytes at -75 mV holding potential by voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_440414 (CHEMBL890728) Agonist activity at rat recombinant NMDA NR1 receptor expressed in xenopus laevis oocyte assessed as inhibition of L-glutamate-stimulated current
- ChEBML_140329 In vitro affinity of compound for the glycinergic site associated with NMDA receptor was assessed by inhibition of the binding of [3H]glycine
- ChEMBL_2494849 Binding affinity to C-terminal GFP-tagged Grin1 NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293F cells assessed as dissociation constant by MST assay
- ChEBML_140488 Tested for the NMDA antagonist activity using a functional assay, by protection of cultured hippocampus neurons from the toxic effects of extracellularly applied glutamate
- ChEMBL_140541 (CHEMBL748769) Binding affinity towards glycine binding site on NMDA receptor was determined in rat whole brain membrane using strychnine-insensitive [3H]Gly as radioligand
- ChEMBL_1507833 (CHEMBL3598769) Displacement of [3H]-(+)-MK-801 from phencyclidine binding site of NMDA receptor in human frontal cortex after 22 hrs by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_2494850 Binding affinity to C-terminal GFP-tagged NMDA Grin1.M mutant (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293F cells assessed as dissociation constant by MST assay
- ChEMBL_877712 (CHEMBL2185923) Inhibition of rat NMDA receptor NR1F/NR2B subunit expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes after 2 days by two-electrode voltage-clamp electrophysiological assay
- ChEMBL_877713 (CHEMBL2186393) Inhibition of rat NMDA receptor NR1C/NR2B subunit expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes after 2 days by two-electrode voltage-clamp electrophysiological assay
- ChEBML_140324 Tested for the ability to displace [3H]glycine, by greater than 50%, from NMDA receptor of rat cortical membranes at a dose of 10 uM
- ChEMBL_2185020 (CHEMBL5097102) Inhibition of GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in xenopus laevis oocytes with holding potential of -70 mV by two-electrode voltage-clamp assay
- ChEMBL_140711 (CHEMBL751881) Functional antagonism at the NMDA receptor-ion channel complex was demonstarted by the ability to inhibit the binding of the channel-blocking agent [3H](+)-MK-801
- ChEMBL_140848 (CHEMBL752332) In vitro ability to displace [3H]L-689,560 binding to glycine site on the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor 1 from rat cortical membranes
- ChEMBL_2156480 (CHEMBL5041140) Agonist activity at rat GluN1/GluN2A NMDA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes measured after 4 days in presence of L-glutamte by two-electrode voltage-clamp recording assay
- ChEMBL_2156481 (CHEMBL5041141) Agonist activity at rat GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes measured after 4 days in presence of L-glutamte by two-electrode voltage-clamp recording assay
- ChEMBL_2156482 (CHEMBL5041142) Agonist activity at rat GluN1/GluN2C NMDA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes measured after 4 days in presence of L-glutamte by two-electrode voltage-clamp recording assay
- ChEMBL_2156483 (CHEMBL5041143) Agonist activity at rat GluN1/GluN2D NMDA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes measured after 4 days in presence of L-glutamte by two-electrode voltage-clamp recording assay
- ChEMBL_2283603 Positive allosteric modulator activity at GluN2A NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO cells co-expressing GluN1a in the presence of L-glutamate and glycine by Ca2+ influx assay
- ChEMBL_2283608 Positive allosteric modulator activity at GluN2B NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO cells co-expressing GluN1a in the presence of L-glutamate and glycine by Ca2+ influx assay
- ChEMBL_2283610 Positive allosteric modulator activity at GluN2C NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO cells co-expressing GluN1a in the presence of L-glutamate and glycine by Ca2+ influx assay
- ChEMBL_2283612 Positive allosteric modulator activity at GluN2D NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO cells co-expressing GluN1a in the presence of L-glutamate and glycine by Ca2+ influx assay
- ChEMBL_2207452 (CHEMBL5120160) Displacement of [3H]ifenprodil from recombinant human GluN2B NMDA receptor (unknown origin) expressed in dexamethasone-induced mouse L-M(TK-) cell after 120 mins by microbeta scintillation counting method
- Receptor Binding Assay In vitro binding assays for the phencyclidine site of NMDA-type glutamate receptors, and for sigma-1 receptors, both of which are known to be bound by DM, were conducted by Sekisui Medical Co., Ltd. of Ibaraki, Japan. In these assays, DM acts as an antagonist at NMDA receptors, which are excitatory in their effects, thereby allowing DM to reduce, calm, and modulate unwanted neuronal activity in neuronal networks that are activated by glutamate agonist activity at NMDA receptors. DM acts as an agonist at sigma-1 receptors, which are inhibitory receptors, thereby allowing DM to reduce unwanted neuronal activity by a second mechanism.
- NMDA receptor FLIPR assay NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 149 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, and 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (149 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2, 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC80 (standard assay) or EC40 (HTS assay) is used to maximize the assay's signal window or the ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators, respectively. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- Receptor Binding Assay Affinities of various compounds were measured in vitro using competitive radioligand binding assays. Serial dilutions of test compounds were incubated with membranes prepared from CHO-K1 cells expressing the mu opioid receptor (MOR; for opioid receptor binding) or rat forebrain membranes (for NMDA receptor binding). 2 nM [3H] Naloxone (MOR) or 0.2 nM [3H] MK801 (NMDA) were used as the specific, competitive radioligands. 10 uM Naloxone (MOR), or 10 uM MK801 (NMDA) was used to determine non-specific binding. Bound radioactivity was measured using a scintillation counter & IC50 values for test compounds were determined by non-linear regression analysis using a one-site competition model (Graph Pad Prizm). Due to each test compound being solubilized in a buffered system for the assay, the results presented herein reflect the free base activity.
- Biological Assay (HTS) NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device. Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2), 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (150 mM, 3 mM, 2 mM CaCl2), 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC40 is used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- Biological Assay (standard) NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2), 0.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2), 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to ~EC40 used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- NR2B standard assay NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 149 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, and 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (149 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2, 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC80 (standard assay) or EC40 (HTS assay) is used to maximize the assay's signal window or the ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators, respectively. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- ChEMBL_1659838 (CHEMBL4009450) Negative allosteric modulation of eGFP-fused human GluN2A receptor expressed in HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of NMDA-induced channel current at -60 mV holding potential measured for 5 secs every 60 secs in presence of glycine by whole cell patch clamp method
- ChEMBL_1759312 (CHEMBL4194320) Modulation of recombinant human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptor expressed in mammalian cells assessed as inhibition of glutamate/glycine-induced intracellular calcium flux pretreated for 5 mins followed by glutamate/glycine addition measured after 5 mins by calcium 5 dye based FLIPR assay
- Effect of Compounds of Formula (I) on Cloned Human GluN1/GluN2B Ion Channels Expressed in Mammalian Cells NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2 (standard assay) or 1.5 mM MgCl2 (HTS assay), 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2, 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC40 (standard assay) or EC40 (HTS assay) is used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- Effects of Test Articles on Cloned Human NR1/GuN2B Ion Channels Expressed in Mammalian Cells NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty-four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed, and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2 (standard assay) or 1.5 mM MgCl2 (HTS assay), 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2), 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC40 (standard assay) or EC40 (HTS assay) is used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- HTS cell-based calcium flux assay NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2 (standard assay) or 1.5 mM MgCl2 (HTS assay), 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2, 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC40 (HTS assay) is used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- Standard cell-based calcium flux assay NMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2 (standard assay) or 1.5 mM MgCl2 (HTS assay), 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2, 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC40 (standard assay) is used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- Scintillation Proximity Assay (SPA) To determine the affinity of the compounds of the present invention a SPA is used. The assay is run in a 384-plate format (OptiPlate-384) where each well contains a mix of 5 μL of test compound, 5 μL NR1s1s2 (ligand binding domains of the NMDA receptor, MW 35.6 kDa, 0.075 ug/well final), 5 μL [3H]-MDL-105,519 (radiolabelled, high affinity N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor antagonist at the glycine site obtained fromSigma Aldrich, final concentration 5 nM, Kd=1.3 nM), 5 μL streptavidin coated imaging beads (Perkin Elmer cat. No.: RPNQ0273, 8 ug/well). The assay buffer contains 100 mM HEPES-NaOH, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 10% glycerol at pH 7.4 in ultra-pure water. Non-specific binding is defined by inclusion of 10 μM L-689,560 (highly potent NMDA antagonist) and total binding by 1% DMSO. Following 30 minutes incubation in the dark (shaker, Multi-microplate Genie), the SPA beads are allowed to settle for 3 h after which the signal is read on a Viewlux instrument (Perkin Elmer). Normalized data are used to calculate IC50 and Ki values.
- Scintillation Proximity Assay To determine the affinity of the compounds of the present invention a SPA is used. The assay is run in a 384-plate format (OptiPlate-384) where each well contains a mix of 5 μL of test compound, 5 μL NR1s1s2 (ligand binding domains of the NMDA receptor, MW 35.6 kDa, 0.075 ug/well final), 5 μL [3H]-MDL-105,519 (radiolabelled, high affinity N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptor antagonist at the glycine site, final concentration 5 nM, Kd=1.3 nM), 5 μL streptavidin coated imaging beads (Perkin Elmer cat. No.: RPNQ0273, 8 ug/well). The assay buffer contains 100 mM HEPES-NaOH, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 10% glycerol at pH 7.4 in ultra-pure water. Non-specific binding is defined by inclusion of 10 μM L-689,560 (highly potent NMDA antagonist) and total binding by 1% DMSO. Following 30 minutes incubation in the dark (shaker, Multi-microplate Genie), the SPA beads are allowed to settle for 3 hours after which the signal is read on a Viewlux instrument (Perkin Elmer). Normalized data are used to calculate Ki values.
- Inhibition of Specific Binding to the Rat NR1/NR2B Receptor The assay depends on the binding of a tracer to the GluN2B subunit-containing NMDA receptors and the ability of the test compounds to displace such binding. 3-[3H] 1-(azetidin-1-yl)-2-[6-(4-fluoro-3-methyl-phenyl)pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-1-yl]ethanone is a high-affinity GluN2B-selective antagonist, which binds to the Ifenprodil binding site located at the interphase between GluN1 and GluN2B subunits. Alternatively, The assay measures binding affinity for ligands that compete for the Ifenprodil binding site in the native NMDA receptors from adult rat cortical membranes.In brief, rat adult cortex is homogenized in the assay buffer (50 mM Tris; pH 7.4). The resulting cortical membranes containing native NMDA receptors are purified by centrifugation and extensively washed, then re-suspended in the assay buffer. The test compounds, tracer and membranes are mixed together and incubated with shaking for 2 hours at room temperature to reach binding equilibrium. Non-specific binding of the tracer is determined by pre-incubation of brain membranes with 10 μM of CP 101,606. Following the incubation, the bound and unbound tracer is separated by filtration with cell harvester and GF/B filter plates (PerkinElmer) soaked with polyethylenimine.The extent of binding is measured by counting [3H] radioactivity retained on the filters plates with liquid scintillator counter. Binding affinity (equilibrium dissociation constant Ki) for the test compounds is determined by fitting experimental data with the following model log EC50=log(10^ log Ki*(1+[Radioligand]/HotKd)) and Y=Bottom+(Top-Bottom)/(1+10^(X-Log EC50)) where [Radioligand] is the concentration of the tracer, HotKdNM is the equilibrium dissociation constant of the tracer, Top and Bottom are the curve plateaus in the units of Y axis.HNR2BC: Effects of Test Articles on Cloned Human NR1/NR2B Ion Channels Expressed in Mammalian CellsNMDA receptors are ion channels that are highly permeable to Ca2+ ions, rendering it possible to monitor NMDA receptor function using cell-based calcium flux assay. In this assay, co-agonists glutamate and glycine are added to cells heterologously expressing human GluN1/GluN2B NMDA receptors to initiate cellular Ca2+ influx. The time course of the changes in intracellular calcium is measured using a fluorescent dye and a FLIPR (Fluorometric Imaging Plate Reader) device.Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity. Next, co-agonists, glutamate and glycine are added for another 5 minutes. The concentration of glutamate corresponding to EC80 is used to maximize the assay's signal window and ability to detect NMDA receptor antagonists and negative allosteric modulators. A saturating concentration (10 μM) of glycine is also present in the assay. A non-selective NMDA receptor antagonist, (+)MK-801 is used as a positive control for antagonist activity. The fluorescent signal in the presence of test compounds is quantified and normalized to the signal defined by the appropriate control wells.
- Cell-Based Assay The assay involves using a cell line that expresses the NR1 subunit together with either NR2C or NR2D. These cell lines can be prepared by transfecting a cell line with an appropriate vector that includes the DNA encoding the NR2C or NR2D receptors. One suitable cell line is BHK-1 (Syrian hamster kidney BHK-21 is a subclone (clone 13) of the parental line established from the kidneys of five unsexed, one-day-old hamsters in 1961).The NR2D receptor cDNA has also been cloned, for example, in 293T cells (Glover et al., Interaction of the N-Methyl-D-Aspartic Acid Receptor NR2D Subunit with the c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase*, J. Biol. Chem., Vol. 275, Issue 17, 12725-12729, Apr. 28, 2000). The cDNA for NR2D is also described in this reference.An NR2D cDNA (clone designation pNR2D422) is also disclosed in Arvanian, et al., Viral Delivery of NR2D Subunits Reduces Mg2+ Block of NMDA Receptor and Restores NT-3-Induced Potentiation of AMPA-Kainate Responses in Maturing Rat Motoneurons, J Neurophysiol 92: 2394-2404, 2004.The cDNA for the NR2C is described, for example, in Lin, Y. J., Bovetto, S, Carver, J. M., and Giordano, T., Cloning of the cDNA for the human NMDA receptor NR2C subunit and its expression in the central nervous system and periphery, Molecular Brain Research, 1996, vol. 43, no 1-2, pp. 57-64 (41 ref.). Lin et al. describe several overlapping cDNA clones containing 3995 nucleotides of the human 2C NMDA receptor subunit (NR2C) that were isolated from human hippocampal and cerebellar cDNA libraries. The predicted protein sequence is 1233 amino acids long. Lin et al. noted that readily detectable levels of NR2C are present in the hippocampus, amygdala, caudate nucleus, corpus callosum, subthalamic nuclei and thalamus, as well as the heart, skeletal muscle and pancreas, demonstrating a widespread expression pattern of the NR2C gene, both in the CNS and in the periphery.In one embodiment, the high throughput bioassay uses commercially-available BHK-21 cell lines expressing NR1 under control of the Tet-On system (Clontech) (Hansen et al (2008), and which constitutively express either NR2C or NR2D. FIG. 4A illustrates vector design for the NR2D cell line. A similar strategy can be used for the NR2C cell line, except that the NR2C cDNA is used in place of NR2D cDNA.Stable expression of NMDA receptor subunits is cytotoxic. To avoid this toxicity, the culture media can be supplemented with NMDA receptor antagonists, for example, DL-APV and 7Cl-kynurenate. Functional NR1 expression can be induced by doxycyclin before the assay.
- Biological Assay Twenty four hours before measurements, the expression of the NMDA receptors in the stable cell line is induced with Tet-On inducible system in the presence of a non-selective NMDA receptor blocker. On the day of the experiment, cell culture media is carefully washed and the cells are loaded with Calcium 5 Dye Kit (Molecular Devices) in dye loading buffer containing 137 mM NaCl, 4 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2), 0.5 mM MgCl2(standard assay) or 1.5 mM MgCl2 (HTS assay), 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4. After 1 h incubation at the room temperature, the dye is washed away with the assay buffer (137 mM NaCl (standard assay) or 150 mM (HTS assay), 4 mM KCl (standard assay) or 3 mM (HTS assay), 2 mM CaCl2), 0.01 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES and 5 mM D-glucose; pH 7.4) In the FLIPR TETRA reader, various concentrations of the test compounds are added to the cells for 5 min while fluorescence is monitored to detect potential agonist activity.
- Automated Patch-Clamp System (OPatch HTX) Cells are transferred as suspension in serum-free medium to the QPatch HTX system and kept in the cell storage tank/stirrer during experiments. All solutions applied to cells including the intracellular solution will be maintained at room temperature (19° C. to 30° C.).During the sealing process standard bath solution described above will be used. All solutions applied to cells including the pipette solution will be maintained at room temperature (19° C. to 30° C.). After formation of a Gigaohm seal between the patch electrodes and transfected individual HEK293 cells only Mg-free bath solution will be perfused and the cell membrane will be ruptured to assure electrical access to the cell interior (whole-cell patch-configuration). Inward currents will be measured upon application of 300 μM NMDA (and 8.0 μM Glycine) to patch-clamped cells for 5 sec. During the entire experiment the cells will be voltage-clamped at a holding potential of −80 mV.
- Inhibition Assay Two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings were made from Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing recombinant rat GluN1/GluN2A, GluN1/GluN2B, GluN1/GluN2C, GluN1/GluN2D, GluA1, or GluK2 receptors following injection of 5-10 ng of cRNA synthesized according to manufacturers' protocols (Ambin, mMessage, mMachine). cDNAs used were rat GluN1-1a (GenBank accession numbers U11418 and U08261; hereafter GluN1), GluN2A (D13211), GluN2B (U11419), GluN2C (M91563), GluN2D (L31611), GluA1 (X17184), GluK2 (Z11548). The current under voltage-clamp was recorded during perfusion with recording solution containing (in mM) 90 NaCl, 1.0 KCl, 0.5 BaCl2, 0.005 EDTA, and 10 HEPES at pH 7.4 (23° C.). Glass micropipettes had resistances of 0.3-1.0 MS2 and were filled with 3.0 M KCl. The membrane potential was clamped at −40 mV during the experiment. Recordings were digitized at 10 Hz and analyzed off line. 20 mM stock solutions of test compounds in 100% DMSO were made and diluted to obtain the final concentration; final DMSO content was 0.05-0.5% (vol/vol). Oocytes expressing GluK2 homomeric receptors were first treated with 10 μM concanavalin A (10 minutes). NMDA receptor responses were obtained by challenging oocytes with 100 μM glutamate plus 30 μM glycine; GluA1 and GluK2 receptors responses were recorded during application of 100 μM glutamate. We recorded the response to 5-7 concentrations of test drug co-applied with glutamate and glycine in 5 or more oocytes obtained from two different frogs.
- Radioligand Binding Assay Binding experiments to determine binding to NR2B-subtype NMDA receptors were performed on forebrains of 8-10 weeks old male Sprague Dawley rats (Harlan, Netherlands) using 3H Ro 25-6981 (Mutel V; Buchy D; Klingelschmidt A; Messer J; Bleuel Z; Kemp J A; Richards J G. Journal of Neurochemistry, 1998, 70(5):2147-2155. Rats were decapitated without anesthesia using a Guillotine (approved by animal ethics committee) and the harvested brains were snap-frozen and stored at −80° C. for 3-6 months for membrane preparation.For membrane preparation, rat forebrains were thawed on ice for 20 minutes in homogenization buffer composed of 50 mM KH2PO4 (pH adjusted to 7.4 with KOH), 1 mM EDTA, 0.005% Triton X 100 and protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma Aldrich). Thawed brains were homogenized using a Dounce homogenizer and centrifuged at 48000×g for 20 min. The pellet was resuspended in cold buffer and homogenized again using a Dounce homogenizer. Subsequently, the homogenate was aliquoted, snap-frozen and stored at −80° C. for not more than 3-4 months.To perform the competition binding assay, thawed membrane homogenate was added to each well of a 96-well plate (20 μg/well). The experimental compounds were serially diluted in 100% DMSO and added to each row of the assay plate to achieve desired compound concentrations, keeping the DMSO concentration in the assay plate at 1.33% of the final reaction volume. Next, 3H Ro 25-6981 (4 nM) was added to the assay plate. After incubation for 1 hr at room temperature, the membrane bound radioligand was harvested on to GF/B filter plates (treated with 0.5% PEI for 1 hr at room temperature). The filter plates were dried at 50° C. for 20 mins, incubated with microscint 20 for 10 minutes and finally, the counts were read on TopCount (Perkin Elmer).
- NR2B Antagonist Activity HEK293 cell lines stably expressing cloned human NR1/NR2B and NR1/NR2A, respectively, were established according to standard previously described methods (Hansen et al. Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 2008, 11:304-315). Activation of the NR2A or NR2B subtype of NMDA receptor with glutamate as an agonist and glycine co-agonist on these cells results in calcium influx, which can be monitored with fluorescent indicator Fluo-4. A cell-based assay has been implemented to evaluate the effect of a compound on NR2A and NR2B receptors by measuring the fluorescent changes (Hansen et al. Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 2008, 11:304-315).HEK293 cells stably expressing NR2A or NR2B receptors were cultured at 37 ° C. in a humidified CO2 incubator in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone), 10 M MK801 (Sigma-Aldrich) and 50 M AP-5 (Tocris). For experiments, the cells were seeded onto poly-D-lysine-coated 96-well black plates with clear bottom (Corning) at a density of 50,000 cells/well. After overnight culture, the growth medium was removed from the wells and the cells were incubated at 37 ° C. for 60 minutes in Hanks buffer containing 4 M fluo-4-AM (Invitrogen) and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). After dye-loading, the cells were washed three times with Hanks buffer and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature with various concentrations of test compounds prepared in Hanks buffer with 0.1% BSA. The cell plates were placed onto an FDSS Cell fluorescence reader (Hamamatsu). After 20 seconds of reading background fluorescence, agonist glutamate at final 100 M and co-agonist glycine at final 50 M were added to the cells to activate the receptor, and the resulting fluorescence changes were recorded and quantified. Based on the changes in fluorescence intensity, the pharmacological effect of test compounds was analyzed and the IC50 values derived from a non-linear least squares fitting of the concentration-dependent response to a standard logistic equation using Prism (Graphpad Software, Inc.):Amplitude=Max Amplitude/(1+(IC50/[antagonist])n).
- NR2B Antagonist Activity HEK293 cell lines stably expressing cloned human NR1/NR2B and NR1/NR2A, respectively, were established according to standard previously described methods (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008). Activation of the NR2A or NR2B subtype of NMDA receptor with glutamate as an agonist and glycine co-agonist on these cells results in calcium influx, which can be monitored with fluorescent indicator Fluo-4. A cell based assay has been implemented to evaluate the effect of a compound on NR2A and NR2B receptors by measuring the fluorescent changes (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008).HEK293 cells stably expressing NR2A or NR2B receptors were cultured at 37° C. in a humidified CO2 incubator in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone), 10 μM MK801 (Sigma-Aldrich) and 50 μM AP-5 (Tocris). For experiments, the cells were seeded onto poly-D-lysine-coated 96-well black plates with clear bottom (Corning) at a density of 50,000 cells/well. After overnight culture, the growth medium was removed from the wells and the cells were incubated at 37° C. for 60 min in Hanks buffer containing 4 μM fluo-4-AM (Invitrogen) and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). After dye-loading, the cells were washed three times with Hanks buffer and incubated for 10 min at room temperature with various concentrations of test compounds prepared in Hanks buffer with 0.1% BSA. The cell plates were placed onto FDSS μCell fluorescence reader (Hamamatsu). After 20 sec reading of background fluorescence, agonist glutamate at final 100 μM and co-agonist glycine at final 50 μM were added to the cells to activate the receptor, and the resulting fluorescence changes were recorded and quantified. Based on the changes in fluorescence intensity, the pharmacological effect of test compounds were analyzed and the IC50 values derived from a non-linear least squares fitting of the concentration-dependent response to a standard logistic equation using Prism (Graphpad, Inc): Amplitude=Max Amplitude/(1+(IC50/[antagonist])n).
- NR2B Antagonist Activity HEK293 cell lines stably expressing cloned human NR1/NR2B and NR1/NR2A, respectively, were established according to standard previously described methods (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008). Activation of the NR2A or NR2B subtype of NMDA receptor with glutamate as an agonist and glycine co-agonist on these cells results in calcium influx, which can be monitored with fluorescent indicator Fluo-4. A cell based assay has been implemented to evaluate the effect of a compound on NR2A and NR2B receptors by measuring the fluorescent changes (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008).HEK293 cells stably expressing NR2A or NR2B receptors were cultured at 37° C. in a humidified CO2 incubator in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone), 10 μM MK801 (Sigma-Aldrich) and 50 μM AP-5 (Tocris). For experiments, the cells were seeded onto poly-D-lysine-coated 96-well black plates with clear bottom (Corning) at a density of 50,000 cells/well. After overnight culture, the growth medium was removed from the wells and the cells were incubated at 37° C. for 60 min in Hanks buffer containing 4 μM fluo-4-AM (Invitrogen) and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). After dye-loading, the cells were washed three times with Hanks buffer and incubated for 10 min at room temperature with various concentrations of test compounds prepared in Hanks buffer with 0.1% BSA. The cell plates were placed onto FDSS μCell fluorescence reader (Hamamatsu). After 20 sec reading of background fluorescence, agonist glutamate at final 100 μM and co-agonist glycine at final 50 μM were added to the cells to activate the receptor, and the resulting fluorescence changes were recorded and quantified. Based on the changes in fluorescence intensity, the pharmacological effect of test compounds were analyzed and the IC50 values derived from a non-linear least squares fitting of the concentration-dependent response to a standard logistic equation using Prism (Graphpad, Inc):Amplitude=Max Amplitude/(1+(IC 50/[antagonist])n).
- NR2B Antagonist Activity HEK293 cell lines stably expressing cloned human NR1/NR2B and NR1/NR2A, respectively, were established according to standard previously described methods (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008). Activation of the NR2A or NR2B subtype of NMDA receptor with glutamate as an agonist and glycine co-agonist on these cells results in calcium influx, which can be monitored with fluorescent indicator Fluo-4. A cell based assay has been implemented to evaluate the effect of a compound on NR2A and NR2B receptors by measuring the fluorescent changes (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008).HEK293 cells stably expressing NR2A or NR2B receptors were cultured at 37° C. in a humidified CO2 incubator in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone), 10 μM MK801 (Sigma-Aldrich) and 50 μM AP-5 (Tocris). For experiments, the cells were seeded onto poly-D-lysine-coated 96-well black plates with clear bottom (Corning) at a density of 50,000 cells/well. After overnight culture, the growth medium was removed from the wells and the cells were incubated at 37° C. for 60 min in Hanks buffer containing 4 μM fluo-4-AM (Invitrogen) and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). After dye-loading, the cells were washed three times with Hanks buffer and incubated for 10 min at room temperature with various concentrations of test compounds prepared in Hanks buffer with 0.1% BSA. The cell plates were placed onto FDSS μCell fluorescence reader (Hamamatsu). After 20 sec reading of background fluorescence, agonist glutamate at final 100 μM and co-agonist glycine at final 50 μM were added to the cells to activate the receptor, and the resulting fluorescence changes were recorded and quantified. Based on the changes in fluorescence intensity, the pharmacological effect of test compounds were analyzed and the IC50 values derived from a non-linear least squares fitting of the concentration-dependent response to a standard logistic equation using Prism (Graphpad, Inc):Amplitude=Max Amplitude/(1+(IC50/[antagonist])n).
- NR2B Antagonist Activity HEK293 cell lines stably expressing cloned human NR1/NR2B and NR1/NR2A, respectively, were established according to standard previously described methods (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008). Activation of the NR2A or NR2B subtype of NMDA receptor with glutamate as an agonist and glycine co-agonist on these cells results in calcium influx, which can be monitored with fluorescent indicator Fluo-4. A cell based assay has been implemented to evaluate the effect of a compound on NR2A and NR2B receptors by measuring the fluorescent changes (Hansen et al., Comb. Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:304, 2008).HEK293 cells stably expressing NR2A or NR2B receptors were cultured at 37° C. in a humidified CO2 incubator in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone), 10 μM MK801 (Sigma-Aldrich) and 50 μM AP-5 (Tocris). For experiments, the cells were seeded onto poly-D-lysine-coated 96-well black plates with clear bottom (Corning) at a density of 50,000 cells/well. After overnight culture, the growth medium was removed from the wells and the cells were incubated at 37° C. for 60 min in Hanks buffer containing 4 μM fluo-4-AM (Invitrogen) and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA). After dye-loading, the cells were washed three times with Hanks buffer and incubated for 10 min at room temperature with various concentrations of test compounds prepared in Hanks buffer with 0.1% BSA. The cell plates were placed onto FDSS pCell fluorescence reader (Hamamatsu). After 20 sec reading of background fluorescence, agonist glutamate at final 100 μM and co-agonist glycine at final 50 μM were added to the cells to activate the receptor, and the resulting fluorescence changes were recorded and quantified. Based on the changes in fluorescence intensity, the pharmacological effect of test compounds were analyzed and the IC50 values derived from a non-linear least squares fitting of the concentration-dependent response to a standard logistic equation using Prism (Graphpad, Inc): Amplitude=Max Amplitude/(1+(IC50/[antagonist])n).

