Target (31)
Compound (43)
Article Title (688)
Article Author (6)
Assay (167)
Judge, RA; Zhu, H; Upadhyay, AK; Bodelle, PM; Hutchins, CW; Torrent, M; Marin, VL; Yu, W; Vedadi, M; Li, F; Brown, PJ; Pappano, WN; Sun, C; Petros, AM Turning a Substrate Peptide into a Potent Inhibitor for the Histone Methyltransferase SETD8. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 1102 -1106 (2016) Wu, L; Yin, J; Wang, C; Xiao, Z; Li, J; Chen, S Benzopyrazole compound used as RHO kinase inhibitor US Patent US11345678 (2022) Yang, X; Zhong, J; Zhang, Q; Qian, J; Song, K; Ruan, C; Xu, J; Ding, K; Zhang, J Rational Design and Structure Validation of a Novel Peptide Inhibitor of the Adenomatous-Polyposis-Coli (APC)-Rho-Guanine-Nucleotide-Exchange-Factor-4 (Asef) Interaction. J Med Chem 61: 8017 -8028 (2018) Knütter, I; Theis, S; Hartrodt, B; Born, I; Brandsch, M; Daniel, H; Neubert, K A novel inhibitor of the mammalian peptide transporter PEPT1. Biochemistry 40: 4454 -8 (2001) Lampe, JW; Watson, PS; Slade, DJ Bridged bicyclic RHO kinase inhibitor compounds, composition and use US Patent US8476295 (2013) Lampe, JW; Watson, PS; Slade, DJ; Peterson, WM; Crean, CS; Vittitow, JL; DeCamp, JB; Pelz, NF Cytoskeletal active rho kinase inhibitor compounds, composition and use US Patent US8604218 (2013) Guan, R; Xu, X; Chen, M; Hu, H; Ge, H; Wen, S; Zhou, S; Pi, R Advances in the studies of roles of Rho/Rho-kinase in diseases and the development of its inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 70: 613 -22 (2013) Bendzunas, NG; Dörfler, S; Autenrieth, K; Bertinetti, D; Machal, EMF; Kennedy, EJ; Herberg, FW Investigating PKA-RII specificity using analogs of the PKA:AKAP peptide inhibitor STAD-2. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 1174 -1178 (2018) Chen, HH; Namil, A; Severns, B; Ward, J; Kelly, C; Drace, C; McLaughlin, MA; Yacoub, S; Li, B; Patil, R; Sharif, N; Hellberg, MR; Rusinko, A; Pang, IH; Combrink, KD In vivo optimization of 2,3-diaminopyrazine Rho Kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glaucoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 1875 -9 (2014) Abdel-Magid, AF Rho kinase inhibitors: potentially versatile therapy for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and more. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 371 -2 (2015) Rosen, KM; Abbinanti, MD; Ruschel, J; McKerracher, L; Bond Moritz, L Rho kinase inhibitor BA-1049 (R) and active metabolites thereof US Patent US11198680 (2021) Zhang, Y; Li, G; Zhao, Y Advances in the development of Rho GTPase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 90: (2023) Zhao, Y; Wang, H; Li, G; Jiang, Y; Li, X; Zhou, L; Liu, Y Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, as well as preparation method and use thereof US Patent US10323023 (2019) Hu, X; Nguyen, KT; Verlinde, CL; Hol, WG; Pei, D Structure-based design of a macrocyclic inhibitor for peptide deformylase. J Med Chem 46: 3771 -4 (2003) Evelyn, CR; Bell, JL; Ryu, JG; Wade, SM; Kocab, A; Harzdorf, NL; Showalter, HD; Neubig, RR; Larsen, SD Design, synthesis and prostate cancer cell-based studies of analogs of the Rho/MKL1 transcriptional pathway inhibitor, CCG-1423. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 665 -72 (2010) Luo, Q; Ma, Y; Liang, H; Feng, Y; Liu, N; Lian, C; Zhu, L; Ye, Y; Liu, Z; Hou, Z; Chen, S; Wang, Y; Dai, C; Song, C; Zhang, M; He, Z; Xing, Y; Zhong, W; Li, S; Wu, J; Lu, F; Yin, F; Li, Z Covalent Peptide LSD1 Inhibitor Specifically Recognizes Cys360 in the Enzyme-Active Region. J Med Chem 66: 15409 -15423 (2023) Smith, HK; Beckett, RP; Clements, JM; Doel, S; East, SP; Launchbury, SB; Pratt, LM; Spavold, ZM; Thomas, W; Todd, RS; Whittaker, M Structure-activity relationships of the peptide deformylase inhibitor BB-3497: modification of the metal binding group. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 3595 -9 (2002) Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, pharmaceutical composition comprising same, and use thereof Bonn, S; Herrero, S; Breitenlechner, CB; Erlbruch, A; Lehmann, W; Engh, RA; Gassel, M; Bossemeyer, D Structural analysis of protein kinase A mutants with Rho-kinase inhibitor specificity. J Biol Chem 281: 24818 -30 (2006) Peptide-Drug Conjugates: An Emerging Direction for the Next Generation of Peptide Therapeutics. Moinet, C; Contour-Galcéra, MO; Poitout, L; Morgan, B; Gordon, T; Rouber, P; Thurieau, C Novel non-peptide ligands for the somatostatin sst3 receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 991 -5 (2001) Leurs, U; Clausen, RP; Kristensen, JL; Lohse, B Inhibitor scaffold for the histone lysine demethylase KDM4C (JMJD2C). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 5811 -3 (2012) San Juan, AA Towards predictive inhibitor design for the EGFR autophosphorylation activity. Eur J Med Chem 43: 781 -91 (2008) Aicher, TD; Padilla, F; Toogood, PL; Chen, S Indazolyl thiadiazolamines and related compounds for inhibition of Rho-associated protein kinase and the treatment of disease US Patent US10112935 (2018) Mezo, AR; McDonnell, KA; Castro, A; Fraley, C Structure-activity relationships of a peptide inhibitor of the human FcRn:human IgG interaction. Bioorg Med Chem 16: 6394 -405 (2008) Pilla, E; Kilisch, M; Lenz, C; Urlaub, H; Geiss-Friedlander, R The SUMO1-E67 interacting loop peptide is an allosteric inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidases 8 and 9. J Biol Chem 288: 32787 -96 (2013) Brandsch, M; Thunecke, F; Küllertz, G; Schutkowski, M; Fischer, G; Neubert, K Evidence for the absolute conformational specificity of the intestinal H+/peptide symporter, PEPT1. J Biol Chem 273: 3861 -4 (1998) Davies, SJ; Ayscough, AP; Beckett, RP; Bragg, RA; Clements, JM; Doel, S; Grew, C; Launchbury, SB; Perkins, GM; Pratt, LM; Smith, HK; Spavold, ZM; Thomas, SW; Todd, RS; Whittaker, M Structure-activity relationships of the peptide deformylase inhibitor BB-3497: modification of the methylene spacer and the P1' side chain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 2709 -13 (2003) Sturdivant, JM; Royalty, SM; Lin, CW; Moore, LA; Yingling, JD; Laethem, CL; Sherman, B; Heintzelman, GR; Kopczynski, CC; deLong, MA Discovery of the ROCK inhibitor netarsudil for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 2475 -80 (2016) Houghten, RA; Dooley, CT The use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for the determination of peptide ligands in radio-receptor assays: Opioid peptides Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 405 -412 (1993) Development of an Imidazopyridazine-Based MNK1/2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Lymphoma. Knudsen, LB; Kiel, D; Teng, M; Behrens, C; Bhumralkar, D; Kodra, JT; Holst, JJ; Jeppesen, CB; Johnson, MD; de Jong, JC; Jorgensen, AS; Kercher, T; Kostrowicki, J; Madsen, P; Olesen, PH; Petersen, JS; Poulsen, F; Sidelmann, UG; Sturis, J; Truesdale, L; May, J; Lau, J Small-molecule agonists for the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 937 -42 (2007) Lumangtad, LA; Bell, TW The signal peptide as a new target for drug design. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30: (2020) Silvestri, AP; Zhang, Q; Ping, Y; Muir, EW; Zhao, J; Chakka, SK; Wang, G; Bray, WM; Chen, W; Fribourgh, JL; Tripathi, S; He, Y; Rubin, SM; Satz, AL; Pye, CR; Kuai, L; Su, W; Schwochert, JA DNA-Encoded Macrocyclic Peptide Libraries Enable the Discovery of a Neutral MDM2-p53 Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 14: 820 -826 (2023) Duncan, KE; Dempsey, BR; Killip, LE; Adams, J; Bailey, ML; Lajoie, GA; Litchfield, DW; Brandl, CJ; Shaw, GS; Shilton, BH Discovery and characterization of a nonphosphorylated cyclic peptide inhibitor of the peptidylprolyl isomerase, Pin1. J Med Chem 54: 3854 -65 (2011) Davies, SJ; Ayscough, AP; Beckett, RP; Clements, JM; Doel, S; Pratt, LM; Spavold, ZM; Thomas, SW; Whittaker, M Structure--activity relationships of the peptide deformylase inhibitor BB-3497: modification of the P2' and P3' side chains. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 2715 -8 (2003) He, Y; Guo, X; Yu, ZH; Wu, L; Gunawan, AM; Zhang, Y; Dixon, JE; Zhang, ZY A potent and selective inhibitor for the UBLCP1 proteasome phosphatase. Bioorg Med Chem 23: 2798 -809 (2015) Rew, Y Benzoic acid derivative MDM2 inhibitor for the treatment of cancer US Patent US8952036 (2015) Zhou, J; Qiao, L; Weng, L Process for the synthesis of a phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor US Patent US9732097 (2017) Suzuki, R; Brown, GA; Christopher, JA; Scully, CCG; Congreve, M Recent Developments in Therapeutic Peptides for the Glucagon-like Peptide 1 and 2 Receptors. J Med Chem 63: 905 -927 (2020) Karlberg, T; Markova, N; Johansson, I; Hammarström, M; Schütz, P; Weigelt, J; Schüler, H Structural basis for the interaction between tankyrase-2 and a potent Wnt-signaling inhibitor. J Med Chem 53: 5352 -5 (2010) Cook, BN; Kowalski, JA; Li, X; Marshall, DR; Schlyer, S; Sibley, R; Smith-Keenan, LL; Soleymanzadeh, F; Sorcek, RJ; Young, ER; Zhang, Y Rho kinase inhibitors US Patent US8697911 (2014) de Veer, SJ; Li, CY; Swedberg, JE; Schroeder, CI; Craik, DJ Engineering potent mesotrypsin inhibitors based on the plant-derived cyclic peptide, sunflower trypsin inhibitor-1. Eur J Med Chem 155: 695 -704 (2018) Pepanian, A; Binbay, FA; Roy, S; Nubbemeyer, B; Koley, A; Rhodes, CA; Ammer, H; Pei, D; Ghosh, P; Imhof, D Bicyclic Peptide Library Screening for the Identification of Gαi Protein Modulators. J Med Chem 66: 12396 -12406 (2023) Kok, ZY; Stoddart, LA; Mistry, SJ; Mocking, TAM; Vischer, HF; Leurs, R; Hill, SJ; Mistry, SN; Kellam, B Optimization of Peptide Linker-Based Fluorescent Ligands for the Histamine H J Med Chem 65: 8258 -8288 (2022) Lawhorn, BG; Philp, J; Graves, AP; Shewchuk, L; Holt, DA; Gatto, GJ; Kallander, LS GSK114: A selective inhibitor for elucidating the biological role of TNNI3K. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 3355 -3358 (2016) Miyano, N; Kinoshita, T; Nakai, R; Kirii, Y; Yokota, K; Tada, T Structural basis for the inhibitor recognition of human Lyn kinase domain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 6557 -60 (2009) Furuya, N; Momose, T; Katsuno, K; Fushimi, N; Muranaka, H; Handa, C; Ozawa, T; Kinoshita, T The juxtamembrane region of TrkA kinase is critical for inhibitor selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 1233 -1236 (2017) Lücking, U; Kosemund, D; Böhnke, N; Lienau, P; Siemeister, G; Denner, K; Bohlmann, R; Briem, H; Terebesi, I; Bömer, U; Schäfer, M; Ince, S; Mumberg, D; Scholz, A; Izumi, R; Hwang, S; von Nussbaum, F Changing for the Better: Discovery of the Highly Potent and Selective CDK9 Inhibitor VIP152 Suitable for Once Weekly Intravenous Dosing for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 64: 11651 -11674 (2021) Asari, T; Takayama, K; Nakamura, A; Shimada, T; Taguchi, A; Hayashi, Y Structural Basis for the Effective Myostatin Inhibition of the Mouse Myostatin Prodomain-Derived Minimum Peptide. ACS Med Chem Lett 8: 113 -117 (2017) Huang, A; Jayaraman, L; Fura, A; Vite, GD; Trainor, GL; Gottardis, MM; Spires, TE; Spires, VM; Rizzo, CA; Obermeier, MT; Elzinga, PA; Todderud, G; Fan, Y; Newitt, JA; Beyer, SM; Zhu, Y; Warrack, BM; Goodenough, AK; Tebben, AJ; Doweyko, AM; Gold, DL; Balog, A Discovery of the Selective CYP17A1 Lyase Inhibitor BMS-351 for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 40 -5 (2016) Zhao, Y; Wang, H; Li, G; Jiang, Y; Li, X; Liu, B; Zhong, W; Liu, K; Li, F; Zhou, L; Liu, Y Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, pharmaceutical composition comprising same, and preparation method and use thereof US Patent US11390609 (2022) Xia, M; Sreedharan, SP; Bolin, DR; Gaufo, GO; Goetzl, EJ Novel cyclic peptide agonist of high potency and selectivity for the type II vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281: 629 -33 (1997) Owen, DR; Allerton, CM; Anderson, AS; Aschenbrenner, L; Avery, M; Berritt, S; Boras, B; Cardin, RD; Carlo, A; Coffman, KJ; Dantonio, A; Di, L; Eng, H; Ferre, R; Gajiwala, KS; Gibson, SA; Greasley, SE; Hurst, BL; Kadar, EP; Kalgutkar, AS; Lee, JC; Lee, JS; Liu, W; Mason, SW; Noell, S; Novak, JJ; Obach, RS; Ogilvie, K; Patel, NC; Pettersson, M; Rai, DK; Reese, MR; Sammons, MF; Sathish, JG; Singh, RS; Steppan, CM; Stewart, AE; Tuttle, JB; Updyke, L; Verhoest, PR; Wei, LQ; Yang, QY; Zhu, Y An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19 Science 374: 1 -13 (2021) Gerstenberger, BS; Ambler, C; Arnold, EP; Banker, ME; Brown, MF; Clark, JD; Dermenci, A; Dowty, ME; Fensome, A; Fish, S; Hayward, MM; Hegen, M; Hollingshead, BD; Knafels, JD; Lin, DW; Lin, TH; Owen, DR; Saiah, E; Sharma, R; Vajdos, FF; Xing, L; Yang, X; Yang, X; Wright, SW Discovery of Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2) Inhibitor (PF-06826647) for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases. J Med Chem 63: 13561 -13577 (2020) Tombling, BJ; Lammi, C; Lawrence, N; Gilding, EK; Grazioso, G; Craik, DJ; Wang, CK Bioactive Cyclization Optimizes the Affinity of a Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) Peptide Inhibitor. J Med Chem 64: 2523 -2533 (2021) Igarashi, H; Ito, T; Pradhan, TK; Mantey, SA; Hou, W; Coy, DH; Jensen, RT Elucidation of the vasoactive intestinal peptide pharmacophore for VPAC(2) receptors in human and rat and comparison to the pharmacophore for VPAC(1) receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303: 445 -60 (2002) Röver, S; Adam, G; Cesura, AM; Galley, G; Jenck, F; Monsma, FJ; Wichmann, J; Dautzenberg, FM High-affinity, non-peptide agonists for the ORL1 (orphanin FQ/nociceptin) receptor. J Med Chem 43: 1329 -38 (2001) Horwell, DC; Howson, W; Ratcliffe, GS; Rees, DC The design of a dipeptide library for screening at peptide receptor sites Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 799 -802 (1993) Gomez-Monterrey, I; Sala, M; Rusciano, MR; Monaco, S; Maione, AS; Iaccarino, G; Tortorella, P; D'Ursi, AM; Scrima, M; Carotenuto, A; De Rosa, G; Bertamino, A; Vernieri, E; Grieco, P; Novellino, E; Illario, M; Campiglia, P Characterization of a selective CaMKII peptide inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem 62: 425 -34 (2013) Pan, X; Iyer, KA; Liu, H; Sweet, DH; Dukat, M A new chemotype inhibitor for the human organic cation transporter 3 (hOCT3). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4440 -4445 (2017) Perry, MWD; Björhall, K; Bold, P; Brűlls, M; Börjesson, U; Carlsson, J; Chang, HA; Chen, Y; Eriksson, A; Fihn, BM; Fransson, R; Fredlund, L; Ge, H; Huang, H; Karabelas, K; Lamm Bergström, E; Lever, S; Lindmark, H; Mogemark, M; Nikitidis, A; Palmgren, AP; Pemberton, N; Petersen, J; Rodrigo Blomqvist, M; Smith, RW; Thomas, MJ; Ullah, V; Tyrchan, C; Wennberg, T; Westin Eriksson, A; Yang, W; Zhao, S; Öster, L Discovery of AZD8154, a Dual PI3Kγδ Inhibitor for the Treatment of Asthma. J Med Chem 64: 8053 -8075 (2021) LaMarche, MJ; Acker, M; Argintaru, A; Bauer, D; Boisclair, J; Chan, H; Chen, CH; Chen, YN; Chen, Z; Deng, Z; Dore, M; Dunstan, D; Fan, J; Fekkes, P; Firestone, B; Fodor, M; Garcia-Fortanet, J; Fortin, PD; Fridrich, C; Giraldes, J; Glick, M; Grunenfelder, D; Hao, HX; Hentemann, M; Ho, S; Jouk, A; Kang, ZB; Karki, R; Kato, M; Keen, N; Koenig, R; LaBonte, LR; Larrow, J; Liu, G; Liu, S; Majumdar, D; Mathieu, S; Meyer, MJ; Mohseni, M; Ntaganda, R; Palermo, M; Perez, L; Pu, M; Ramsey, T; Reilly, J; Sarver, P; Sellers, WR; Sendzik, M; Shultz, MD; Slisz, J; Slocum, K; Smith, T; Spence, S; Stams, T; Straub, C; Tamez, V; Toure, BB; Towler, C; Wang, P; Wang, H; Williams, SL; Yang, F; Yu, B; Zhang, JH; Zhu, S Identification of TNO155, an Allosteric SHP2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 63: 13578 -13594 (2020) Ung, PM; Song, W; Cheng, L; Zhao, X; Hu, H; Chen, L; Schlessinger, A Inhibitor Discovery for the Human GLUT1 from Homology Modeling and Virtual Screening. ACS Chem Biol 11: 1908 -16 (2016) Geanes, AR; Cho, HP; Nance, KD; McGowan, KM; Conn, PJ; Jones, CK; Meiler, J; Lindsley, CW Ligand-based virtual screen for the discovery of novel M5 inhibitor chemotypes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 4487 -4491 (2016) Ahn, Y; Kim, JW; Bang, KC; Park, BW; Kim, SY; Lee, K; Lee, K; Ko, M; Kim, HK; Kim, YH; Kim, MS; Lee, GS Quinazoline derivatives as a multiplex inhibitor and method for the preparation thereof US Patent US8846699 (2014) He, LJ; Zhu, YB; Fan, QZ; Miao, DD; Zhang, SP; Liu, XP; Zhang, C Shape-based virtual screen for the discovery of novel CDK8 inhibitor chemotypes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 549 -555 (2019) Zhang, L; Fan, C; Guo, Z; Li, Y; Zhao, S; Yang, S; Yang, Y; Zhu, J; Lin, D Discovery of a potent dual EGFR/HER-2 inhibitor L-2 (selatinib) for the treatment of cancer. Eur J Med Chem 69: 833 -41 (2013) Yang, W; Glunz, PW; Bhide, RS; Thiyagarajan, K Tricyclic rho kinase inhibitors US Patent US10654860 (2020) Wang, Z; Yin, L; Xiong, Z; Huang, F; Yang, N; Jiang, F; Li, H; Cui, Y; Ren, J; Cheng, Z; Jia, K; Lu, T; Zhu, J; Hu, Q; Chen, Y Discovery of a Bromodomain and Extra Terminal Domain (BET) Inhibitor with the Selectivity for the Second Bromodomain (BD2) and the Capacity for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. J Med Chem 66: 10824 -10848 (2023) Wang, Jx; Bray, AM; DiPasquale, AJ; Maeji, N; Geysen, H Application of the multipin peptide synthesis technique for peptide receptor binding studies: Substance P as A model system Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 447 -450 (1993) Shu, C; Ge, H; Song, M; Chen, JH; Zhou, H; Qi, Q; Wang, F; Ma, X; Yang, X; Zhang, G; Ding, Y; Zhou, D; Peng, P; Shih, CK; Xu, J; Wu, F Discovery of Imigliptin, a Novel Selective DPP-4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. ACS Med Chem Lett 5: 921 -6 (2014) Yan, VC; Pham, CD; Ballato, ES; Yang, KL; Arthur, K; Khadka, S; Barekatain, Y; Shrestha, P; Tran, T; Poral, AH; Washington, M; Raghavan, S; Czako, B; Pisaneschi, F; Lin, YH; Satani, N; Hammoudi, N; Ackroyd, JJ; Georgiou, DK; Millward, SW; Muller, FL Prodrugs of a 1-Hydroxy-2-oxopiperidin-3-yl Phosphonate Enolase Inhibitor for the Treatment of J Med Chem 65: 13813 -13832 (2022) Durek, T; Cromm, PM; White, AM; Schroeder, CI; Kaas, Q; Weidmann, J; Ahmad Fuaad, A; Cheneval, O; Harvey, PJ; Daly, NL; Zhou, Y; Dellsén, A; Österlund, T; Larsson, N; Knerr, L; Bauer, U; Kessler, H; Cai, M; Hruby, VJ; Plowright, AT; Craik, DJ Development of Novel Melanocortin Receptor Agonists Based on the Cyclic Peptide Framework of Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor-1. J Med Chem 61: 3674 -3684 (2018) Bell, IM; Gallicchio, SN; Stump, CA; Bruno, JG; Fan, H; Gantert, LT; Hostetler, ED; Kemmerer, AL; McWherter, M; Moore, EL; Mosser, SD; Purcell, ML; Riffel, K; Salvatore, CA; Sanabria-Bohórquez, S; Staas, DD; White, RB; Williams, M; Zartman, CB; Cook, JJ; Hargreaves, RJ; Kane, SA; Graham, SL; Selnick, HG [(11)C]MK-4232: The First Positron Emission Tomography Tracer for the Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 863 -8 (2013) Yarravarapu, N; Geffert, L; Surratt, CK; Cascio, M; Lapinsky, DJ Clickable photoaffinity ligands for the human serotonin transporter based on the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (S)-citalopram. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 3431 -3435 (2018) The Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitor A-366 Uncovers a Role for G9a/GLP in the Epigenetics of Leukemia. Wrobleski, ST; Moslin, R; Lin, S; Zhang, Y; Spergel, S; Kempson, J; Tokarski, JS; Strnad, J; Zupa-Fernandez, A; Cheng, L; Shuster, D; Gillooly, K; Yang, X; Heimrich, E; McIntyre, KW; Chaudhry, C; Khan, J; Ruzanov, M; Tredup, J; Mulligan, D; Xie, D; Sun, H; Huang, C; D'Arienzo, C; Aranibar, N; Chiney, M; Chimalakonda, A; Pitts, WJ; Lombardo, L; Carter, PH; Burke, JR; Weinstein, DS Highly Selective Inhibition of Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2) for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases: Discovery of the Allosteric Inhibitor BMS-986165. J Med Chem 62: 8973 -8995 (2019) Takayama, K; Noguchi, Y; Aoki, S; Takayama, S; Yoshida, M; Asari, T; Yakushiji, F; Nishimatsu, S; Ohsawa, Y; Itoh, F; Negishi, Y; Sunada, Y; Hayashi, Y Identification of the minimum peptide from mouse myostatin prodomain for human myostatin inhibition. J Med Chem 58: 1544 -9 (2015) Duprez, W; Premkumar, L; Halili, MA; Lindahl, F; Reid, RC; Fairlie, DP; Martin, JL Peptide inhibitors of the Escherichia coli DsbA oxidative machinery essential for bacterial virulence. J Med Chem 58: 577 -87 (2015) Terada, T; Sawada, K; Irie, M; Saito, H; Hashimoto, Y; Inui, K Structural requirements for determining the substrate affinity of peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2. Pflugers Arch 440: 679 -84 (2000) Ganapathy, ME; Huang, W; Wang, H; Ganapathy, V; Leibach, FH Valacyclovir: a substrate for the intestinal and renal peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 246: 470 -5 (1998) Juettner, NE; Bogen, JP; Bauer, TA; Knapp, S; Pfeifer, F; Huettenhain, SH; Meusinger, R; Kraemer, A; Fuchsbauer, HL Decoding the Papain Inhibitor from J Nat Prod 83: 2983 -2995 (2020) Showell, GA; Barnes, MJ; Daiss, JO; Mills, JS; Montana, JG; Tacke, R; Warneck, JB (R)-sila-venlafaxine: a selective noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor for the treatment of emesis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 2555 -8 (2006) Zhang, Y; Seigal, BA; Terrett, NK; Talbott, RL; Fargnoli, J; Naglich, JG; Chaudhry, C; Posy, SL; Vuppugalla, R; Cornelius, G; Lei, M; Wang, C; Zhang, Y; Schmidt, RJ; Wei, DD; Miller, MM; Allen, MP; Li, L; Carter, PH; Vite, GD; Borzilleri, RM Dimeric Macrocyclic Antagonists of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins for the Treatment of Cancer. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 770 -5 (2015) Thoma, G; Duthaler, RO; Waelchli, R; Hauchard, A; Bruno, S; Strittmatter-Keller, U; Orjuela Leon, A; Viebrock, S; Aichholz, R; Beltz, K; Grove, K; Hoque, S; Rudewicz, PJ; Zerwes, HG Discovery and Characterization of the Topical Soft JAK Inhibitor CEE321 for Atopic Dermatitis. J Med Chem 66: 2161 -2168 (2023) Jadhav, PK; Schiffler, MA; Gavardinas, K; Kim, EJ; Matthews, DP; Staszak, MA; Coffey, DS; Shaw, BW; Cassidy, KC; Brier, RA; Zhang, Y; Christie, RM; Matter, WF; Qing, K; Durbin, JD; Wang, Y; Deng, GG Discovery of Cathepsin S Inhibitor LY3000328 for the Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. ACS Med Chem Lett 5: 1138 -42 (2014) Erra, M; Taltavull, J; Bernal, FJ; Caturla, JF; Carrascal, M; Pagès, L; Mir, M; Espinosa, S; Gràcia, J; Domínguez, M; Sabaté, M; Paris, S; Maldonado, M; Hernández, B; Bravo, M; Calama, E; Miralpeix, M; Lehner, MD; Calbet, M Discovery of a Novel Inhaled PI3Kδ Inhibitor for the Treatment of Respiratory Diseases. J Med Chem 61: 9551 -9567 (2018) Lee, CA; Jones, JP; Katayama, J; Kaspera, R; Jiang, Y; Freiwald, S; Smith, E; Walker, GS; Totah, RA Identifying a selective substrate and inhibitor pair for the evaluation of CYP2J2 activity. Drug Metab Dispos 40: 943 -51 (2012) Pacritinib (SB1518), a JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Santos, JA; Kondo, MY; Freitas, RF; dos Santos, MH; Ramalho, TC; Assis, DM; Juliano, L; Juliano, MA; Puzer, L The natural flavone fukugetin as a mixed-type inhibitor for human tissue kallikreins. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 1485 -9 (2016) Coleman, DR; Ren, Z; Mandal, PK; Cameron, AG; Dyer, GA; Muranjan, S; Campbell, M; Chen, X; McMurray, JS Investigation of the binding determinants of phosphopeptides targeted to the SRC homology 2 domain of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Development of a high-affinity peptide inhibitor. J Med Chem 48: 6661 -70 (2005) Ren, H; Bakas, NA; Vamos, M; Chaikuad, A; Limpert, AS; Wimer, CD; Brun, SN; Lambert, LJ; Tautz, L; Celeridad, M; Sheffler, DJ; Knapp, S; Shaw, RJ; Cosford, NDP Design, Synthesis, and Characterization of an Orally Active Dual-Specific ULK1/2 Autophagy Inhibitor that Synergizes with the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Med Chem 63: 14609 -14625 (2020) Borner, T; Tinsley, IC; Milliken, BT; Doebley, SA; Najjar, NR; Kerwood, DJ; De Jonghe, BC; Hayes, MR; Doyle, RP Creation of a Peptide Antagonist of the GFRAL-RET Receptor Complex for the Treatment of GDF15-Induced Malaise. J Med Chem 66: 11237 -11249 (2023) Peptide Inhibitor Targeting the Extraterminal Domain in BRD4 Potently Suppresses Breast Cancer Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Levesque, C; Fugère, M; Kwiatkowska, A; Couture, F; Desjardins, R; Routhier, S; Moussette, P; Prahl, A; Lammek, B; Appel, JR; Houghten, RA; D'Anjou, F; Dory, YL; Neugebauer, W; Day, R The Multi-Leu peptide inhibitor discriminates between PACE4 and furin and exhibits antiproliferative effects on prostate cancer cells. J Med Chem 55: 10501 -11 (2012) Discovery of GLPG3667, a Selective ATP Competitive Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases. Smith, CR; Aranda, R; Bobinski, TP; Briere, DM; Burns, AC; Christensen, JG; Clarine, J; Engstrom, LD; Gunn, RJ; Ivetac, A; Jean-Baptiste, R; Ketcham, JM; Kobayashi, M; Kuehler, J; Kulyk, S; Lawson, JD; Moya, K; Olson, P; Rahbaek, L; Thomas, NC; Wang, X; Waters, LM; Marx, MA Fragment-Based Discovery of MRTX1719, a Synthetic Lethal Inhibitor of the PRMT5•MTA Complex for the Treatment of J Med Chem 65: 1749 -1766 (2022) Zhang, X; He, Y; Liu, S; Yu, Z; Jiang, ZX; Yang, Z; Dong, Y; Nabinger, SC; Wu, L; Gunawan, AM; Wang, L; Chan, RJ; Zhang, ZY Salicylic acid based small molecule inhibitor for the oncogenic Src homology-2 domain containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP2). J Med Chem 53: 2482 -93 (2010) Boteju, LW; Zalewska, T; Yamamura, HI; Hruby, VJ Tryptophan-norleucine 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles as cis peptide bond mimics: Investigation of the bioactive conformation of a potent and selective peptide for the cholecystokinin-B receptor Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 2011 -2016 (1993) Sawada, Y; Kayakiri, H; Abe, Y; Mizutani, T; Inamura, N; Asano, M; Hatori, C; Aramori, I; Oku, T; Tanaka, H Discovery of the first non-peptide full agonists for the human bradykinin B(2) receptor incorporating 4-(2-picolyloxy)quinoline and 1-(2-picolyl)benzimidazole frameworks. J Med Chem 47: 2853 -63 (2004) Lavrador, K; Murphy, B; Saunders, J; Struthers, S; Wang, X; Williams, J A screening library for peptide activated G-protein coupled receptors. 1. The test set. J Med Chem 47: 6864 -74 (2004) Howson, W; Hodgson, J; Richardson, R; Walton, L; Guard, S; Watling, K An SAR study for the non-peptide substance P receptor (NK1) antagonist, CP-96,345. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2: 559 -564 (1992) Hu, X; Nguyen, KT; Jiang, VC; Lofland, D; Moser, HE; Pei, D Macrocyclic inhibitors for peptide deformylase: a structure-activity relationship study of the ring size. J Med Chem 47: 4941 -9 (2004) Jenkins, RJ; Heslip, KA; Meagher, JL; Stuckey, JA; Dotson, GD Structural basis for the recognition of peptide RJPXD33 by acyltransferases in lipid A biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 289: 15527 -35 (2014) Gao, Y; Voigt, J; Zhao, H; Pais, GC; Zhang, X; Wu, L; Zhang, ZY; Burke, TR Utilization of a peptide lead for the discovery of a novel PTP1B-binding motif. J Med Chem 44: 2869 -78 (2001) El-Kabbani, O; Carbone, V; Darmanin, C; Oka, M; Mitschler, A; Podjarny, A; Schulze-Briese, C; Chung, RP Structure of aldehyde reductase holoenzyme in complex with the potent aldose reductase inhibitor fidarestat: implications for inhibitor binding and selectivity. J Med Chem 48: 5536 -42 (2005) Penning, TD; Zhu, GD; Gandhi, VB; Gong, J; Liu, X; Shi, Y; Klinghofer, V; Johnson, EF; Donawho, CK; Frost, DJ; Bontcheva-Diaz, V; Bouska, JJ; Osterling, DJ; Olson, AM; Marsh, KC; Luo, Y; Giranda, VL Discovery of the Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor 2-[(R)-2-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide (ABT-888) for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 52: 514 -23 (2009) Hanessian, S; Raghavan, S Design and synthesis of a prototypical non-peptidic inhibitor model for the enzme renin Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 1697 -1702 (1994) Rezende Miranda, R; Fu, Y; Chen, X; Perino, J; Cao, P; Carpten, J; Chen, Y; Zhang, C Development of a Potent and Specific FGFR4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Med Chem 63: 11484 -11497 (2020) Discovery of JNJ-74856665: A Novel Isoquinolinone DHODH Inhibitor for the Treatment of AML. Freeman-Cook, KD; Hoffman, RL; Behenna, DC; Boras, B; Carelli, J; Diehl, W; Ferre, RA; He, YA; Hui, A; Huang, B; Huser, N; Jones, R; Kephart, SE; Lapek, J; McTigue, M; Miller, N; Murray, BW; Nagata, A; Nguyen, L; Niessen, S; Ninkovic, S; O'Doherty, I; Ornelas, MA; Solowiej, J; Sutton, SC; Tran, K; Tseng, E; Visswanathan, R; Xu, M; Zehnder, L; Zhang, Q; Zhang, C; Dann, S Discovery of PF-06873600, a CDK2/4/6 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 64: 9056 -9077 (2021) Li, Y; Liu, Y; Zhang, Y; Wu, Y; Xing, Z; Wang, J; Fan, GH Discovery of a First-in-Class CD38 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Mitochondrial Myopathy. J Med Chem 66: 12762 -12775 (2023) Leonard, KA; Madge, LA; Krawczuk, PJ; Wang, A; Kreutter, KD; Bacani, GM; Chai, W; Smith, RC; Tichenor, MS; Harris, MC; Malaviya, R; Seierstad, M; Johnson, ME; Venable, JD; Kim, S; Hirst, GC; Mathur, AS; Rao, TS; Edwards, JP; Rizzolio, MC; Koudriakova, T Discovery of a Gut-Restricted JAK Inhibitor for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Med Chem 63: 2915 -2929 (2020) He, G; Wan, S; Wu, Y; Chu, Z; Shen, H; Zhang, S; Chen, L; Bao, Z; Gu, S; Huang, J; Huang, L; Gong, G; Zou, Y; Zhu, Q; Xu, Y Discovery of the First Selective IDO2 Inhibitor As Novel Immunotherapeutic Avenues for Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Med Chem 65: 14348 -14365 (2022) Porter, NJ; Shen, S; Barinka, C; Kozikowski, AP; Christianson, DW Molecular Basis for the Selective Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 6 by a Mercaptoacetamide Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 1301 -1305 (2018) Kuhnert, M; Steuber, H; Diederich, WE Structural basis for HTLV-1 protease inhibition by the HIV-1 protease inhibitor indinavir. J Med Chem 57: 6266 -72 (2014) Bromberg, KD; Mitchell, TR; Upadhyay, AK; Jakob, CG; Jhala, MA; Comess, KM; Lasko, LM; Li, C; Tuzon, CT; Dai, Y; Li, F; Eram, MS; Nuber, A; Soni, NB; Manaves, V; Algire, MA; Sweis, RF; Torrent, M; Schotta, G; Sun, C; Michaelides, MR; Shoemaker, AR; Arrowsmith, CH; Brown, PJ; Santhakumar, V; Martin, A; Rice, JC; Chiang, GG; Vedadi, M; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D; Pappano, WN The SUV4-20 inhibitor A-196 verifies a role for epigenetics in genomic integrity. Nat Chem Biol 13: 317 -324 (2017) Griffith, DA; Kung, DW; Esler, WP; Amor, PA; Bagley, SW; Beysen, C; Carvajal-Gonzalez, S; Doran, SD; Limberakis, C; Mathiowetz, AM; McPherson, K; Price, DA; Ravussin, E; Sonnenberg, GE; Southers, JA; Sweet, LJ; Turner, SM; Vajdos, FF Decreasing the rate of metabolic ketone reduction in the discovery of a clinical acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibitor for the treatment of diabetes. J Med Chem 57: 10512 -26 (2014) Kumar, V; Yarravarapu, N; Lapinsky, DJ; Perley, D; Felts, B; Tomlinson, MJ; Vaughan, RA; Henry, LK; Lever, JR; Newman, AH Novel Azido-Iodo Photoaffinity Ligands for the Human Serotonin Transporter Based on the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (S)-Citalopram. J Med Chem 58: 5609 -19 (2015) Li, J; Sheng, H; Wang, Y; Lai, Z; Wang, Y; Cui, S Scaffold Hybrid of the Natural Product Tanshinone I with Piperidine for the Discovery of a Potent NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor. J Med Chem 66: 2946 -2963 (2023) Skerratt, SE; Andrews, M; Bagal, SK; Bilsland, J; Brown, D; Bungay, PJ; Cole, S; Gibson, KR; Jones, R; Morao, I; Nedderman, A; Omoto, K; Robinson, C; Ryckmans, T; Skinner, K; Stupple, P; Waldron, G The Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Peripherally Restricted Pan-Trk Inhibitor (PF-06273340) for the Treatment of Pain. J Med Chem 59: 10084 -10099 (2016) Rawson, DJ; Ballard, S; Barber, C; Barker, L; Beaumont, K; Bunnage, M; Cole, S; Corless, M; Denton, S; Ellis, D; Floc'h, M; Foster, L; Gosset, J; Holmwood, F; Lane, C; Leahy, D; Mathias, J; Maw, G; Million, W; Poinsard, C; Price, J; Russel, R; Street, S; Watson, L The discovery of UK-369003, a novel PDE5 inhibitor with the potential for oral bioavailability and dose-proportional pharmacokinetics. Bioorg Med Chem 20: 498 -509 (2011) Baeriswyl, V; Calzavarini, S; Gerschheimer, C; Diderich, P; Angelillo-Scherrer, A; Heinis, C Development of a selective peptide macrocycle inhibitor of coagulation factor XII toward the generation of a safe antithrombotic therapy. J Med Chem 56: 3742 -6 (2013) A Second-Generation Oral SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of COVID-19. Hutchinson, JH; Rowbottom, MW; Lonergan, D; Darlington, J; Prodanovich, P; King, CD; Evans, JF; Bain, G Small Molecule Lysyl Oxidase-like 2 (LOXL2) Inhibitors: The Identification of an Inhibitor Selective for LOXL2 over LOX. ACS Med Chem Lett 8: 423 -427 (2017) WANG, L; WU, H; MI, Y; LIU, Y; FU, X; WANG, M; SHI, H; GUO, J PRMT5 INHIBITOR AND THE USE THEREOF US Patent US20240376126 (2024) Yamamoto, T; Nair, P; Jacobsen, NE; Davis, P; Ma, SW; Navratilova, E; Moye, S; Lai, J; Yamamura, HI; Vanderah, TW; Porreca, F; Hruby, VJ The importance of micelle-bound states for the bioactivities of bifunctional peptide derivatives for delta/mu opioid receptor agonists and neurokinin 1 receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 51: 6334 -47 (2008) Osher, EL; Castillo, F; Elumalai, N; Waring, MJ; Pairaudeau, G; Tavassoli, A A genetically selected cyclic peptide inhibitor of BCL6 homodimerization. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 3034 -3038 (2018) Dziadulewicz, EK; Ritchie, TJ; Hallett, A; Snell, CR; Ko, SY; Wrigglesworth, R; Hughes, GA; Dunstan, AR; Bloomfield, GC; Drake, GS; Brown, MC; Lee, W; Burgess, GM; Davis, C; Yaqoob, M; Perkins, MN; Campbell, EA; Davis, AJ; Rang, HP 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)thiosemicarbazides: a novel class of potent, orally active non-peptide antagonist for the bradykinin B(2) receptor. J Med Chem 43: 769 -71 (2000) Protasevich, II; Brouillette, CG; Snow, ME; Dunham, S; Rubin, JR; Gogliotti, R; Siegel, K Role of inhibitor aliphatic chain in the thermodynamics of inhibitor binding to Escherichia coli enoyl-ACP reductase and the Phe203Leu mutant: a proposed mechanism for drug resistance. Biochemistry 43: 13380 -9 (2004) Kong, YK; Song, KS; Jung, ME; Kang, M; Kim, HJ; Kim, MJ Discovery of GCC5694A: A potent and selective sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 56: (2022) Morwick, T; Büttner, FH; Cywin, CL; Dahmann, G; Hickey, E; Jakes, S; Kaplita, P; Kashem, MA; Kerr, S; Kugler, S; Mao, W; Marshall, D; Paw, Z; Shih, CK; Wu, F; Young, E Hit to lead account of the discovery of bisbenzamide and related ureidobenzamide inhibitors of Rho kinase. J Med Chem 53: 759 -77 (2010) Exploiting high-energy hydration sites for the discovery of potent peptide aldehyde inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease with cellular antiviral activity. Ettari, R; Previti, S; Maiorana, S; Amendola, G; Wagner, A; Cosconati, S; Schirmeister, T; Hellmich, UA; Zappalà, M Optimization Strategy of Novel Peptide-Based Michael Acceptors for the Treatment of Human African Trypanosomiasis. J Med Chem 62: 10617 -10629 (2019) Hruby, VJ Peptide science: exploring the use of chemical principles and interdisciplinary collaboration for understanding life processes. J Med Chem 46: 4215 -31 (2003) Murage, EN; Schroeder, JC; Beinborn, M; Ahn, JM Search for alpha-helical propensity in the receptor-bound conformation of glucagon-like peptide-1. Bioorg Med Chem 16: 10106 -12 (2008) Horwell, DC; Morrell, AI; Roberts, E The design and synthesis of non-peptide ligands with affinity and selectivity for tachykinin receptors Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 165 -166 (1996) Coombs, GS; Hazzard, J; Corey, DR Kinetic characterization of a peptide inhibitor of trypsin isolated from a synthetic peptide combinatorial library Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5: 611 -614 (1995) Biegel, A; Gebauer, S; Brandsch, M; Neubert, K; Thondorf, I Structural requirements for the substrates of the H+/peptide cotransporter PEPT2 determined by three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis. J Med Chem 49: 4286 -96 (2006) Henderson, AJ; Hadden, M; Guo, C; Douglas, N; Decornez, H; Hellberg, MR; Rusinko, A; McLaughlin, M; Sharif, N; Drace, C; Patil, R 2,3-Diaminopyrazines as rho kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1137 -40 (2010) Ghosh, AK; Dawson, ZL; Mitsuya, H Darunavir, a conceptually new HIV-1 protease inhibitor for the treatment of drug-resistant HIV. Bioorg Med Chem 15: 7576 -80 (2007) Bendele, AM; Neelagiri, M; Neelagiri, V; Sucholeiki, I Development of a selective matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13) inhibitor for the treatment of Osteoarthritis. Eur J Med Chem 224: (2021) Boiteau, JG; Ouvry, G; Arlabosse, JM; Astri, S; Beillard, A; Bhurruth-Alcor, Y; Bonnary, L; Bouix-Peter, C; Bouquet, K; Bourotte, M; Cardinaud, I; Comino, C; Deprez, B; Duvert, D; Féret, A; Hacini-Rachinel, F; Harris, CS; Luzy, AP; Mathieu, A; Millois, C; Orsini, N; Pascau, J; Pinto, A; Piwnica, D; Polge, G; Reitz, A; Reversé, K; Rodeville, N; Rossio, P; Spiesse, D; Tabet, S; Taquet, N; Tomas, L; Vial, E; Hennequin, LF Discovery and process development of a novel TACE inhibitor for the topical treatment of psoriasis. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 945 -956 (2018) Discovery of 4-benzylpiperazinequinoline BChE inhibitor that suppresses neuroinflammation for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Ogoshi, Y; Matsui, T; Mitani, I; Yokota, M; Terashita, M; Motoda, D; Ueyama, K; Hotta, T; Ito, T; Hase, Y; Fukui, K; Deai, K; Yoshiuchi, H; Ito, S; Abe, H Discovery of JTZ-951: A HIF Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Renal Anemia. ACS Med Chem Lett 8: 1320 -1325 (2017) Williams, TE; Subramanian, S; Verhagen, J; McBride, CM; Costales, A; Sung, L; Antonios-McCrea, W; McKenna, M; Louie, AK; Ramurthy, S; Levine, B; Shafer, CM; Machajewski, T; Renhowe, PA; Appleton, BA; Amiri, P; Chou, J; Stuart, D; Aardalen, K; Poon, D Discovery of RAF265: A Potent mut-B-RAF Inhibitor for the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 961 -5 (2015) Wan, H; Schroeder, GM; Hart, AC; Inghrim, J; Grebinski, J; Tokarski, JS; Lorenzi, MV; You, D; Mcdevitt, T; Penhallow, B; Vuppugalla, R; Zhang, Y; Gu, X; Iyer, R; Lombardo, LJ; Trainor, GL; Ruepp, S; Lippy, J; Blat, Y; Sack, JS; Khan, JA; Stefanski, K; Sleczka, B; Mathur, A; Sun, JH; Wong, MK; Wu, DR; Li, P; Gupta, A; Arunachalam, PN; Pragalathan, B; Narayanan, S; K C, N; Kuppusamy, P; Purandare, AV Discovery of a Highly Selective JAK2 Inhibitor, BMS-911543, for the Treatment of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 850 -5 (2015) Chen, N; Bürli, RW; Neira, S; Hungate, R; Zhang, D; Yu, V; Nguyen, Y; Tudor, Y; Plant, M; Flynn, S; Meagher, KL; Lee, MR; Zhang, X; Itano, A; Schrag, M; Xu, Y; Ng, GY; Hu, E Discovery of a potent and selective c-Kit inhibitor for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 4137 -41 (2008) Dorsey, BD; Iqbal, M; Chatterjee, S; Menta, E; Bernardini, R; Bernareggi, A; Cassarà, PG; D'Arasmo, G; Ferretti, E; De Munari, S; Oliva, A; Pezzoni, G; Allievi, C; Strepponi, I; Ruggeri, B; Ator, MA; Williams, M; Mallamo, JP Discovery of a potent, selective, and orally active proteasome inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 51: 1068 -72 (2008) Picaud, S; Fedorov, O; Thanasopoulou, A; Leonards, K; Jones, K; Meier, J; Olzscha, H; Monteiro, O; Martin, S; Philpott, M; Tumber, A; Filippakopoulos, P; Yapp, C; Wells, C; Che, KH; Bannister, A; Robson, S; Kumar, U; Parr, N; Lee, K; Lugo, D; Jeffrey, P; Taylor, S; Vecellio, ML; Bountra, C; Brennan, PE; O'Mahony, A; Velichko, S; Müller, S; Hay, D; Daniels, DL; Urh, M; La Thangue, NB; Kouzarides, T; Prinjha, R; Schwaller, J; Knapp, S Generation of a Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of the CBP/p300 Bromodomain for Leukemia Therapy. Cancer Res 75: 5106 -5119 (2015) Katragadda, M; Magotti, P; Sfyroera, G; Lambris, JD Hydrophobic effect and hydrogen bonds account for the improved activity of a complement inhibitor, compstatin. J Med Chem 49: 4616 -22 (2006) Harris, PA; Marinis, JM; Lich, JD; Berger, SB; Chirala, A; Cox, JA; Eidam, PM; Finger, JN; Gough, PJ; Jeong, JU; Kang, J; Kasparcova, V; Leister, LK; Mahajan, MK; Miller, G; Nagilla, R; Ouellette, MT; Reilly, MA; Rendina, AR; Rivera, EJ; Sun, HH; Thorpe, JH; Totoritis, RD; Wang, W; Wu, D; Zhang, D; Bertin, J; Marquis, RW Identification of a RIP1 Kinase Inhibitor Clinical Candidate (GSK3145095) for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 857 -862 (2019) Kokkonda, S; Deng, X; White, KL; El Mazouni, F; White, J; Shackleford, DM; Katneni, K; Chiu, FCK; Barker, H; McLaren, J; Crighton, E; Chen, G; Angulo-Barturen, I; Jimenez-Diaz, MB; Ferrer, S; Huertas-Valentin, L; Martinez-Martinez, MS; Lafuente-Monasterio, MJ; Chittimalla, R; Shahi, SP; Wittlin, S; Waterson, D; Burrows, JN; Matthews, D; Tomchick, D; Rathod, PK; Palmer, MJ; Charman, SA; Phillips, MA Lead Optimization of a Pyrrole-Based Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitor Series for the Treatment of Malaria. J Med Chem 63: 4929 -4956 (2020) Preclinical characterization of GLPG0634, a selective inhibitor of JAK1, for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Kargbo, RB Selective DYRK1A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Alzheimer, Parkinson, Huntington, and Down Syndrome. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1795 -1796 (2020) Targeting the mitotic checkpoint for cancer therapy with NMS-P715, an inhibitor of MPS1 kinase. Rotella, DP; McFarlane, GR; Greenfield, A; Grosanu, C; Robichaud, AJ; Denny, RA; Feenstra, RW; Núñez-García, S; Reinders, JH; Neut, Mv; McCreary, A; Kruse, CG; Sullivan, K; Pruthi, F; Lai, M; Zhang, J; Kowal, DM; Carrick, T; Grauer, SM; Navarra, RL; Graf, R; Brennan, J; Marquis, KL; Pausch, MH Tetrahydrocarbazole-based serotonin reuptake inhibitor/dopamine D2 partial agonists for the potential treatment of schizophrenia. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 5552 -5 (2009) Jones, CD; Andrews, DM; Barker, AJ; Blades, K; Daunt, P; East, S; Geh, C; Graham, MA; Johnson, KM; Loddick, SA; McFarland, HM; McGregor, A; Moss, L; Rudge, DA; Simpson, PB; Swain, ML; Tam, KY; Tucker, JA; Walker, M The discovery of AZD5597, a potent imidazole pyrimidine amide CDK inhibitor suitable for intravenous dosing. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 6369 -73 (2008) Huang, Y; Sendzik, M; Zhang, J; Gao, Z; Sun, Y; Wang, L; Gu, J; Zhao, K; Yu, Z; Zhang, L; Zhang, Q; Blanz, J; Chen, Z; Dubost, V; Fang, D; Feng, L; Fu, X; Kiffe, M; Li, L; Luo, F; Luo, X; Mi, Y; Mistry, P; Pearson, D; Piaia, A; Scheufler, C; Terranova, R; Weiss, A; Zeng, J; Zhang, H; Zhang, J; Zhao, M; Dillon, MP; Jeay, S; Qi, W; Moggs, J; Pissot-Soldermann, C; Li, E; Atadja, P; Lingel, A; Oyang, C Discovery of the Clinical Candidate MAK683: An EED-Directed, Allosteric, and Selective PRC2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Advanced Malignancies. J Med Chem 65: 5317 -5333 (2022) Padmakar Darne, C; Velaparthi, U; Saulnier, M; Frennesson, D; Liu, P; Huang, A; Tokarski, J; Fura, A; Spires, T; Newitt, J; Spires, VM; Obermeier, MT; Elzinga, PA; Gottardis, MM; Jayaraman, L; Vite, GD; Balog, A The discovery of BMS-737 as a potent, CYP17 lyase-selective inhibitor for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 75: (2022) Angus, D; Bingham, M; Buchanan, D; Dunbar, N; Gibson, L; Goodwin, R; Haunsø, A; Houghton, A; Huggett, M; Morphy, R; Napier, S; Nimz, O; Passmore, J; Walker, G The identification, and optimisation of hERG selectivity, of a mixed NET/SERT re-uptake inhibitor for the treatment of pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 271 -5 (2010) Cha, MY; Lee, KO; Kim, JW; Lee, CG; Song, JY; Kim, YH; Lee, GS; Park, SB; Kim, MS Discovery of a novel Her-1/Her-2 dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of Her-1 selective inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. J Med Chem 52: 6880 -8 (2009) Lu, MC; Jiao, Q; Liu, T; Tan, SJ; Zhou, HS; You, QD; Jiang, ZY Discovery of a head-to-tail cyclic peptide as the Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction inhibitor with high cell potency. Eur J Med Chem 143: 1578 -1589 (2018) Kumaran, D; Adler, M; Levit, M; Krebs, M; Sweeney, R; Swaminathan, S Interactions of a potent cyclic peptide inhibitor with the light chain of botulinum neurotoxin A: Insights from X-ray crystallography. Bioorg Med Chem 23: 7264 -73 (2015) Kim, HJ; Kwak, WY; Min, JP; Lee, JY; Yoon, TH; Kim, HD; Shin, CY; Kim, MK; Choi, SH; Kim, HS; Yang, EK; Cheong, YH; Chae, YN; Park, KJ; Jang, JM; Choi, SJ; Son, MH; Kim, SH; Yoo, M; Lee, BJ Discovery of DA-1229: a potent, long acting dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 3809 -12 (2011) Mattei, P; Boehringer, M; Di Giorgio, P; Fischer, H; Hennig, M; Huwyler, J; Koçer, B; Kuhn, B; Loeffler, BM; Macdonald, A; Narquizian, R; Rauber, E; Sebokova, E; Sprecher, U Discovery of carmegliptin: a potent and long-acting dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1109 -13 (2010) Wang, L; Coric, P; Broussy, S; Di Stasi, R; Zhou, L; D'Andrea, LD; Ji, L; Vidal, M; Bouaziz, S; Liu, WQ Structural studies of the binding of an antagonistic cyclic peptide to the VEGFR1 domain 2. Eur J Med Chem 169: 65 -75 (2019) Meng, W; Ellsworth, BA; Nirschl, AA; McCann, PJ; Patel, M; Girotra, RN; Wu, G; Sher, PM; Morrison, EP; Biller, SA; Zahler, R; Deshpande, PP; Pullockaran, A; Hagan, DL; Morgan, N; Taylor, JR; Obermeier, MT; Humphreys, WG; Khanna, A; Discenza, L; Robertson, JG; Wang, A; Han, S; Wetterau, JR; Janovitz, EB; Flint, OP; Whaley, JM; Washburn, WN Discovery of Dapagliflozin: A Potent, Selective Renal Sodium-Dependent Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J Med Chem 51: 1145 -9 (2008) Li, Y; Shi, Z; Chen, L; Zheng, S; Li, S; Xu, B; Liu, Z; Liu, J; Deng, C; Ye, F Discovery of a Potent, Selective Renal Sodium-Dependent Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor (HSK0935) for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes. J Med Chem 60: 4173 -4184 (2017) Pratt, LM; Beckett, RP; Davies, SJ; Launchbury, SB; Miller, A; Spavold, ZM; Todd, RS; Whittaker, M Asymmetric synthesis of BB-3497--a potent peptide deformylase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 2585 -8 (2001) Okawa, T; Aramaki, Y; Yamamoto, M; Kobayashi, T; Fukumoto, S; Toyoda, Y; Henta, T; Hata, A; Ikeda, S; Kaneko, M; Hoffman, ID; Sang, BC; Zou, H; Kawamoto, T Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of the Highly Selective and Potent G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 (GRK2) Inhibitor for the Potential Treatment of Heart Failure. J Med Chem 60: 6942 -6990 (2017) Cunha, MR; Bhardwaj, R; Lindinger, S; Butorac, C; Romanin, C; Hediger, MA; Reymond, JL Photoswitchable Inhibitor of the Calcium Channel TRPV6. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1341 -1345 (2019) Kargbo, RB Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Oncogenic KRAS ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 767 -769 (2022) Rose, NR; Ng, SS; Mecinovic;, J; Liénard, MR; Bello, SH; Sun, Z; McDonough, MA; Oppermann, U; Schofield, CJ Inhibitor Scaffolds for 2-Oxoglutarate-Dependent Histone Lysine Demethylases. J Med Chem 51: 7053 -6 (2008) The formyl peptide receptors FPR1 and FPR2 as targets for inflammatory disorders: recent advances in the development of small-molecule agonists. Yang, C; Xu, C; Li, Z; Chen, Y; Wu, T; Hong, H; Lu, M; Jia, Y; Yang, Y; Liu, X; Deng, M; Chen, Z; Li, Q; Ling, Y; Zhou, Y Bioisosteric replacements of the indole moiety for the development of a potent and selective PI3Kδ inhibitor: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Eur J Med Chem 223: (2021) Goodwin, NC; Ding, ZM; Harrison, BA; Strobel, ED; Harris, AL; Smith, M; Thompson, AY; Xiong, W; Mseeh, F; Bruce, DJ; Diaz, D; Gopinathan, S; Li, L; O'Neill, E; Thiel, M; Wilson, AG; Carson, KG; Powell, DR; Rawlins, DB Discovery of LX2761, a Sodium-Dependent Glucose Cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) Inhibitor Restricted to the Intestinal Lumen, for the Treatment of Diabetes. J Med Chem 60: 710 -721 (2017) Identification and Validation of PKR as a Direct Target for the Novel Sulfonamide-Substituted Tetrahydroquinoline Nonselective Inhibitor of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Danvy, D; Monteil, T; Plaquevent, JC; Duhamel, L; Duhamel, P; Gros, C; Noël, N; Schwartz, JC; Lecomte, JM Studies on the structural feature of S'1 subsite of neprilysin (EC.3.4.24.11): Stereochemical requirement for the enzyme-inhibitor docking process Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 2437 -2440 (1996) Sigal, GB; Whitesides, GM Benzenesulfonamide-peptide conjugates as probes for secondary binding sites near the active site of carbonic anhydrase Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 559 -564 (1996) Olson, EJ; Lechtenberg, BC; Zhao, C; Rubio de la Torre, E; Lamberto, I; Riedl, SJ; Dawson, PE; Pasquale, EB Modifications of a Nanomolar Cyclic Peptide Antagonist for the EphA4 Receptor To Achieve High Plasma Stability. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 841 -6 (2016) Shahripour, A; Plummer, MS; Lunney, EA; Para, KS; Stankovic, CJ; Rubin, JR; Humblet, C; Fergus, JH; Marks, JS; Herrera, R; Hubbell, SE; Saltiel, AR; Sawyer, TK Novel phosphotyrosine mimetics in the design of peptide ligands for pp60src SH2 domain Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 1209 -1214 (1996) Du, W; Ai, C; Li, Y; Wen, K; Lv, H; Ren, W; He, J; Qin, D; Li, X; Chen, Y Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor, the preparative method and the use thereof US Patent US11447477 (2022) Bebbington, D; Binch, H; Charrier, JD; Everitt, S; Fraysse, D; Golec, J; Kay, D; Knegtel, R; Mak, C; Mazzei, F; Miller, A; Mortimore, M; O'Donnell, M; Patel, S; Pierard, F; Pinder, J; Pollard, J; Ramaya, S; Robinson, D; Rutherford, A; Studley, J; Westcott, J The discovery of the potent aurora inhibitor MK-0457 (VX-680). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 3586 -92 (2009) Borsari, C; Rageot, D; Dall'Asen, A; Bohnacker, T; Melone, A; Sele, AM; Jackson, E; Langlois, JB; Beaufils, F; Hebeisen, P; Fabbro, D; Hillmann, P; Wymann, MP A Conformational Restriction Strategy for the Identification of a Highly Selective Pyrimido-pyrrolo-oxazine mTOR Inhibitor. J Med Chem 62: 8609 -8630 (2019) Fray, MJ; Dickinson, RP; Huggins, JP; Occleston, NL A potent, selective inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-3 for the topical treatment of chronic dermal ulcers. J Med Chem 46: 3514 -25 (2003) Zhang, K; Huang, L; Lai, F; Lin, S; Tian, H; Wu, D; Chen, X; Xu, H Bioevaluation of a dual PI3K/HDAC inhibitor for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 71: (2022) Discovery of Darovasertib (NVP-LXS196), a Pan-PKC Inhibitor for the Treatment of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Layton, ME; Kern, JC; Hartingh, TJ; Shipe, WD; Raheem, I; Kandebo, M; Hayes, RP; Huszar, S; Eddins, D; Ma, B; Fuerst, J; Wollenberg, GK; Li, J; Fritzen, J; McGaughey, GB; Uslaner, JM; Smith, SM; Coleman, PJ; Cox, CD Discovery of MK-8189, a Highly Potent and Selective PDE10A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. J Med Chem 66: 1157 -1171 (2023) Lakkaniga, NR; Zhang, L; Belachew, B; Gunaganti, N; Frett, B; Li, HY Discovery of SP-96, the first non-ATP-competitive Aurora Kinase B inhibitor, for reduced myelosuppression. Eur J Med Chem 203: (2020) Lampe, JW; Alford, JS; Boriak-Sjodin, PA; Brach, D; Cosmopoulos, K; Duncan, KW; Eckley, ST; Foley, MA; Harvey, DM; Motwani, V; Munchhof, MJ; Raimondi, A; Riera, TV; Tang, C; Thomenius, MJ; Totman, J; Farrow, NA Discovery of a First-in-Class Inhibitor of the Histone Methyltransferase SETD2 Suitable for Preclinical Studies. ACS Med Chem Lett 12: 1539 -1545 (2021) Erra, M; Taltavull, J; Gréco, A; Bernal, FJ; Caturla, JF; Gràcia, J; Domínguez, M; Sabaté, M; Paris, S; Soria, S; Hernández, B; Armengol, C; Cabedo, J; Bravo, M; Calama, E; Miralpeix, M; Lehner, MD Discovery of a Potent, Selective, and Orally Available PI3Kd Inhibitor for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases. ACS Med Chem Lett 8: 118 -123 (2017) Mayer, SC; Kreft, AF; Harrison, B; Abou-Gharbia, M; Antane, M; Aschmies, S; Atchison, K; Chlenov, M; Cole, DC; Comery, T; Diamantidis, G; Ellingboe, J; Fan, K; Galante, R; Gonzales, C; Ho, DM; Hoke, ME; Hu, Y; Huryn, D; Jain, U; Jin, M; Kremer, K; Kubrak, D; Lin, M; Lu, P; Magolda, R; Martone, R; Moore, W; Oganesian, A; Pangalos, MN; Porte, A; Reinhart, P; Resnick, L; Riddell, DR; Sonnenberg-Reines, J; Stock, JR; Sun, SC; Wagner, E; Wang, T; Woller, K; Xu, Z; Zaleska, MM; Zeldis, J; Zhang, M; Zhou, H; Jacobsen, JS Discovery of begacestat, a Notch-1-sparing gamma-secretase inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J Med Chem 51: 7348 -51 (2008) Gu, H; Yan, W; Wang, Y; Xu, W; Huang, L; Yang, J; Zhai, B; Wang, H; Su, Y; Zhu, Q; Liu, B; Hao, H; Zou, Y; Xu, Y Discovery of the Potent and Highly Selective PARP7 Inhibitor as a Novel Immunotherapeutic Agent for Tumors. J Med Chem 66: 473 -490 (2023) Browne, LJ; Gude, C; Rodriguez, H; Steele, RE; Bhatnager, A Fadrozole hydrochloride: a potent, selective, nonsteroidal inhibitor of aromatase for the treatment of estrogen-dependent disease. J Med Chem 34: 725 -36 (1991) Bao, Q; Zhang, L; Wang, N; Gabet, B; Yang, W; Gao, X; You, Q; Jiang, Z Hydrogen Peroxide Inducible JAK3 Covalent Inhibitor: Prodrug for the Treatment of RA with Enhanced Safety Profile. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 2182 -2189 (2020) Taylor, AM; Williams, BR; Giordanetto, F; Kelley, EH; Lescarbeau, A; Shortsleeves, K; Tang, Y; Walters, WP; Arrazate, A; Bowman, C; Brophy, E; Chan, EW; Deshmukh, G; Greisman, JB; Hunsaker, TL; Kipp, DR; Saenz Lopez-Larrocha, P; Maddalo, D; Martin, IJ; Maragakis, P; Merchant, M; Murcko, M; Nisonoff, H; Nguyen, V; Nguyen, V; Orozco, O; Owen, C; Pierce, L; Schmidt, M; Shaw, DE; Smith, S; Therrien, E; Tran, JC; Watters, J; Waters, NJ; Wilbur, J; Willmore, L Identification of GDC-1971 (RLY-1971), a SHP2 Inhibitor Designed for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. J Med Chem 66: 13384 -13399 (2023) Zhou, S; Mao, W; Su, Y; Zheng, X; Qian, W; Shen, M; Shan, N; Li, Y; Wang, D; Wu, S; Sun, T; Mu, L Identification of TUL01101: A Novel Potent and Selective JAK1 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Med Chem 65: 16716 -16740 (2022) Izumikawa, M; Hashimoto, J; Hirokawa, T; Sugimoto, S; Kato, T; Takagi, M; Shin-Ya, K JBIR-22, an inhibitor for protein-protein interaction of the homodimer of proteasome assembly factor 3. J Nat Prod 73: 628 -31 (2010) Zificsak, CA; Gingrich, DE; Breslin, HJ; Dunn, DD; Milkiewicz, KL; Theroff, JP; Thieu, TV; Underiner, TL; Weinberg, LR; Aimone, LD; Albom, MS; Mason, JL; Saville, L; Husten, J; Angeles, TS; Finn, JP; Jan, M; O'Kane, TM; Dobrzanski, P; Dorsey, BD Optimization of a novel kinase inhibitor scaffold for the dual inhibition of JAK2 and FAK kinases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 133 -7 (2011) SB1518, a novel macrocyclic pyrimidine-based JAK2 inhibitor for the treatment of myeloid and lymphoid malignancies. Liu, YA; Jin, Q; Zou, Y; Ding, Q; Yan, S; Wang, Z; Hao, X; Nguyen, B; Zhang, X; Pan, J; Mo, T; Jacobsen, K; Lam, T; Wu, TY; Petrassi, HM; Bursulaya, B; DiDonato, M; Gordon, WP; Liu, B; Baaten, J; Hill, R; Nguyen-Tran, V; Qiu, M; Zhang, YQ; Kamireddy, A; Espinola, S; Deaton, L; Ha, S; Harb, G; Jia, Y; Li, J; Shen, W; Schumacher, AM; Colman, K; Glynne, R; Pan, S; McNamara, P; Laffitte, B; Meeusen, S; Molteni, V; Loren, J Selective DYRK1A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes: Discovery of 6-Azaindole Derivative GNF2133. J Med Chem 63: 2958 -2973 (2020) Long, A; Zhao, H; Huang, X Structural basis for the interaction between casein kinase 1 delta and a potent and selective inhibitor. J Med Chem 55: 956 -60 (2012) Xiong, Y; Wiltsie, J; Woods, A; Guo, J; Pivnichny, JV; Tang, W; Bansal, A; Cummings, RT; Cunningham, BR; Friedlander, AM; Douglas, CM; Salowe, SP; Zaller, DM; Scolnick, EM; Schmatz, DM; Bartizal, K; Hermes, JD; MacCoss, M; Chapman, KT The discovery of a potent and selective lethal factor inhibitor for adjunct therapy of anthrax infection. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 964 -8 (2006) Heidary, DK; Huang, G; Boucher, D; Ma, J; Forster, C; Grey, R; Xu, J; Arnost, M; Choquette, D; Chen, G; Zhou, JH; Yao, YM; Ball, ED; Namchuk, M; Davies, RJ; Henkel, G VX-322: a novel dual receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia. J Med Chem 55: 725 -34 (2012) Previti, S; Ettari, R; Cosconati, S; Amendola, G; Chouchene, K; Wagner, A; Hellmich, UA; Ulrich, K; Krauth-Siegel, RL; Wich, PR; Schmid, I; Schirmeister, T; Gut, J; Rosenthal, PJ; Grasso, S; Zappalà, M Development of Novel Peptide-Based Michael Acceptors Targeting Rhodesain and Falcipain-2 for the Treatment of Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs). J Med Chem 60: 6911 -6923 (2017) Stepniewski, TM; Filipek, S Non-peptide ligand binding to the formyl peptide receptor FPR2--A comparison to peptide ligand binding modes. Bioorg Med Chem 23: 4072 -81 (2015) Fotsch, C; Smith, DM; Adams, JA; Cheetham, J; Croghan, M; Doherty, EM; Hale, C; Jarosinski, MA; Kelly, MG; Norman, MH; Tamayo, NA; Xi, N; Baumgartner, JW Design of a new peptidomimetic agonist for the melanocortin receptors based on the solution structure of the peptide ligand, Ac-Nle-cyclo[Asp-Pro-DPhe-Arg-Trp-Lys]-NH(2). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 2337 -40 (2003) Isaacs, RC; Solinsky, MG; Cutrona, KJ; Newton, CL; Naylor-Olsen, AM; McMasters, DR; Krueger, JA; Lewis, SD; Lucas, BJ; Kuo, LC; Yan, Y; Lynch, JJ; Lyle, EA Structure-based design of novel groups for use in the P1 position of thrombin inhibitor scaffolds. Part 2: N-acetamidoimidazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 2062 -6 (2008) Blackie, JA; Bloomer, JC; Brown, MJ; Cheng, HY; Elliott, RL; Hammond, B; Hickey, DM; Ife, RJ; Leach, CA; Lewis, VA; Macphee, CH; Milliner, KJ; Moores, KE; Pinto, IL; Smith, SA; Stansfield, IG; Stanway, SJ; Taylor, MA; Theobald, CJ; Whittaker, CM The discovery of SB-435495. A potent, orally active inhibitor of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) for evaluation in man. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 2603 -6 (2002) Breinlinger, E; Van Epps, S; Friedman, M; Argiriadi, M; Chien, E; Chhor, G; Cowart, M; Dunstan, T; Graff, C; Hardee, D; Herold, JM; Little, A; McCarthy, R; Parmentier, J; Perham, M; Qiu, W; Schrimpf, M; Vargo, T; Webster, MP; Wu, F; Bennett, D; Edmunds, J Targeting the Tyrosine Kinase 2 (TYK2) Pseudokinase Domain: Discovery of the Selective TYK2 Inhibitor ABBV-712. J Med Chem 66: 14335 -14356 (2023) Lawrence, NJ; Sebti, SM; Pireddu, R Rho kinase inhibitors and methods of use US Patent US9616064 (2017) Ganellin, CR; Bishop, PB; Bambal, RB; Chan, SM; Law, JK; Marabout, B; Luthra, PM; Moore, AN; Peschard, O; Bourgeat, P; Rose, C; Vargas, F; Schwartz, JC Inhibitors of tripeptidyl peptidase II. 2. Generation of the first novel lead inhibitor of cholecystokinin-8-inactivating peptidase: a strategy for the design of peptidase inhibitors. J Med Chem 43: 664 -74 (2000) Pickett, JE; Nagakura, K; Pasternak, AR; Grinnell, SG; Majumdar, S; Lewis, JS; Pasternak, GW Sandmeyer reaction repurposed for the site-selective, non-oxidizing radioiodination of fully-deprotected peptides: studies on the endogenous opioid peptide α-neoendorphin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 4347 -50 (2013) PubChem, PC Dose-response biochemical assay of inhibitors of Rho kinase 2 (Rock2) PubChem Bioassay (2007) Ladduwahetty, T; Lee, MR; Maillard, MC; Cachope, R; Todd, D; Barnes, M; Beaumont, V; Chauhan, A; Gallati, C; Haughan, AF; Kempf, G; Luckhurst, CA; Matthews, K; McAllister, G; Mitchell, P; Patel, H; Rose, M; Saville-Stones, E; Steinbacher, S; Stott, AJ; Thatcher, E; Tierney, J; Urbonas, L; Munoz-Sanjuan, I; Dominguez, C Identification of a Potent, Selective, and Brain-Penetrant Rho Kinase Inhibitor and its Activity in a Mouse Model of Huntington's Disease. J Med Chem 65: 9819 -9845 (2022) Futatsugi, K; Smith, AC; Tu, M; Raymer, B; Ahn, K; Coffey, SB; Dowling, MS; Fernando, DP; Gutierrez, JA; Huard, K; Jasti, J; Kalgutkar, AS; Knafels, JD; Pandit, J; Parris, KD; Perez, S; Pfefferkorn, JA; Price, DA; Ryder, T; Shavnya, A; Stock, IA; Tsai, AS; Tesz, GJ; Thuma, BA; Weng, Y; Wisniewska, HM; Xing, G; Zhou, J; Magee, TV Discovery of PF-06835919: A Potent Inhibitor of Ketohexokinase (KHK) for the Treatment of Metabolic Disorders Driven by the Overconsumption of Fructose. J Med Chem 63: 13546 -13560 (2020) Identification of the Clinical Candidate PF-07284890 (ARRY-461), a Highly Potent and Brain Penetrant BRAF Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. Yim, V; Noisier, AFM; Hung, KY; Bartsch, JW; Schlomann, U; Brimble, MA Synthesis and biological evaluation of analogues of the potent ADAM8 inhibitor cyclo(RLsKDK) for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer metastasis. Bioorg Med Chem 24: 4032 -4037 (2016) Domínguez, JL; Gossas, T; Carmen Villaverde, M; Helena Danielson, U; Sussman, F Experimental and 'in silico' analysis of the effect of pH on HIV-1 protease inhibitor affinity: implications for the charge state of the protein ionogenic groups. Bioorg Med Chem 20: 4838 -47 (2012) Skalova, T; Dohnalek, J; Duskova, J; Petrokova, H; Hradílek, M; Soucek, M; Konvalinka, J; Hasek, J HIV-1 protease mutations and inhibitor modifications monitored on a series of complexes. Structural basis for the effect of the A71V mutation on the active site. J Med Chem 49: 5777 -84 (2006) Sánchez-Morales, A; Biçer, A; Panagiotopoulos, V; Crecente-Garcia, S; Benaiges, C; Bayod, S; Luís Hernández, J; Busqué, F; Matsoukas, MT; Pérez-Riba, M; Alibés, R Design and synthesis of a novel non peptide CN-NFATc signaling inhibitor for tumor suppression in triple negative breast cancer. Eur J Med Chem 238: (2022) Inoue, Y; Omodani, T; Shiratake, R; Okazaki, H; Kuromiya, A; Kubo, T; Sato, F Development of a highly water-soluble peptide-based human neutrophil elastase inhibitor; AE-3763 for treatment of acute organ injury. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 7477 -86 (2009) Ja, WW; West, AP; Delker, SL; Bjorkman, PJ; Benzer, S; Roberts, RW Extension of Drosophila melanogaster life span with a GPCR peptide inhibitor. Nat Chem Biol 3: 415 -9 (2007) Yoo, JS; Zheng, CJ; Lee, S; Kwak, JH; Kim, WG Macrolactin N, a new peptide deformylase inhibitor produced by Bacillus subtilis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 4889 -92 (2006) Iben, LG; Olson, RE; Balanda, LA; Jayachandra, S; Robertson, BJ; Hay, V; Corradi, J; Prasad, CV; Zaczek, R; Albright, CF; Toyn, JH Signal peptide peptidase and gamma-secretase share equivalent inhibitor binding pharmacology. J Biol Chem 282: 36829 -36 (2007) Harms, M; Fabech Hansson, R; Gilg, A; Almeida-Hernández, Y; Löffler, J; Rodríguez-Alfonso, A; Habib, MMW; Albers, D; Ahmed, NS; Abadi, AH; Winter, G; Rasche, V; Beer, AJ; Weidinger, G; Preising, N; Ständker, L; Wiese, S; Sanchez-Garcia, E; Zelikin, AN; Münch, J Development of N-Terminally Modified Variants of the CXCR4-Antagonistic Peptide EPI-X4 for Enhanced Plasma Stability. J Med Chem 66: 15189 -15204 (2023) Long-Residence Time Peptide Antagonist for the Vasopressin V2 Receptor to Treat Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Teufel, DP; Bennett, G; Harrison, H; van Rietschoten, K; Pavan, S; Stace, C; Le Floch, F; Van Bergen, T; Vermassen, E; Barbeaux, P; Hu, TT; Feyen, JHM; Vanhove, M Stable and Long-Lasting, Novel Bicyclic Peptide Plasma Kallikrein Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema. J Med Chem 61: 2823 -2836 (2018) Shanbhag, C; Saraogi, I Bacterial GTPases as druggable targets to tackle antimicrobial resistance. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 87: (2023) Gendaszewska-Darmach, E; Garstka, MA; Błażewska, KM Targeting Small GTPases and Their Prenylation in Diabetes Mellitus. J Med Chem 64: 9677 -9710 (2021) He, Y; Selvaraju, S; Curtin, ML; Jakob, CG; Zhu, H; Comess, KM; Shaw, B; The, J; Lima-Fernandes, E; Szewczyk, MM; Cheng, D; Klinge, KL; Li, HQ; Pliushchev, M; Algire, MA; Maag, D; Guo, J; Dietrich, J; Panchal, SC; Petros, AM; Sweis, RF; Torrent, M; Bigelow, LJ; Senisterra, G; Li, F; Kennedy, S; Wu, Q; Osterling, DJ; Lindley, DJ; Gao, W; Galasinski, S; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D; Vedadi, M; Buchanan, FG; Arrowsmith, CH; Chiang, GG; Sun, C; Pappano, WN The EED protein-protein interaction inhibitor A-395 inactivates the PRC2 complex. Nat Chem Biol 13: 389 -395 (2017) Giardina, GA; Sarau, HM; Farina, C; Medhurst, AD; Grugni, M; Foley, JJ; Raveglia, LF; Schmidt, DB; Rigolio, R; Vassallo, M; Vecchietti, V; Hay, DW 2-Phenyl-4-quinolinecarboxamides: a novel class of potent and selective non-peptide competitive antagonists for the human neurokinin-3 receptor. J Med Chem 39: 2281 -4 (1996) Asahina, Y; Wurtz, NR; Arakawa, K; Carson, N; Fujii, K; Fukuchi, K; Garcia, R; Hsu, MY; Ishiyama, J; Ito, B; Kick, E; Lupisella, J; Matsushima, S; Ohata, K; Ostrowski, J; Saito, Y; Tsuda, K; Villarreal, F; Yamada, H; Yamaoka, T; Wexler, R; Gordon, D; Kohno, Y Discovery of BMS-986235/LAR-1219: A Potent Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 (FPR2) Selective Agonist for the Prevention of Heart Failure. J Med Chem 63: 9003 -9019 (2020) Velcicky, J; Bodendorf, U; Rigollier, P; Epple, R; Beisner, DR; Guerini, D; Smith, P; Liu, B; Feifel, R; Wipfli, P; Aichholz, R; Couttet, P; Dix, I; Widmer, T; Wen, B; Brandl, T Discovery of the First Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Signal Peptide Peptidase-Like 2a (SPPL2a) Inhibitor Displaying Pronounced Immunomodulatory Effects In Vivo. J Med Chem 61: 865 -880 (2018) De Roos, J; Uitdehaag, JC; De Man, AP; Buijsman, RC; Zaman, GJ Prognostic biomarkers for TTK inhibitor chemotherapy US Patent US11208696 (2021) Kim, DH; Li, ZH Stereochemical approach for enzyme inhibitor design Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 2297 -2302 (1994) Lavecchia, A; Cosconati, S; Novellino, E Architecture of the human urotensin II receptor: comparison of the binding domains of peptide and non-peptide urotensin II agonists. J Med Chem 48: 2480 -92 (2005) Mochizuki, A; Nagata, T; Kanno, H; Suzuki, M; Ohta, T 2-aminomethylphenylamine as a novel scaffold for factor Xa inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 1623 -42 (2011) Yeh, TK; Kang, IJ; Hsu, TA; Lee, YC; Lee, CC; Hsu, SJ; Tian, YW; Yang, HY; Chen, CT; Chao, YS; Yueh, A; Chern, JH A novel, potent, and orally bioavailable thiazole HCV NS5A inhibitor for the treatment of hepatitis C virus. Eur J Med Chem 167: 245 -268 (2019) Jesudason, CD; Baker, JE; Bryant, RD; Fisher, JW; Gaich, GA; He, MM; Kahl, SD; Kriauciunas, AV; Heiman, ML; Peters, MA; Rito, CJ; Satterwhite, JH; Tinsley, FC; Trankle, WG; Shuker, AJ Combination of a Beta adrenoceptor modulator and a norepinephrine-serotonin uptake inhibitor for the treatment of obesity. ACS Med Chem Lett 2: 583 -586 (2011) Demonstration of a genetic therapeutic index for tumors expressing oncogenic BRAF by the kinase inhibitor SB-590885. Shirai, F; Mizutani, A; Yashiroda, Y; Tsumura, T; Kano, Y; Muramatsu, Y; Chikada, T; Yuki, H; Niwa, H; Sato, S; Washizuka, K; Koda, Y; Mazaki, Y; Jang, MK; Yoshida, H; Nagamori, A; Okue, M; Watanabe, T; Kitamura, K; Shitara, E; Honma, T; Umehara, T; Shirouzu, M; Fukami, T; Seimiya, H; Yoshida, M; Koyama, H Design and Discovery of an Orally Efficacious Spiroindolinone-Based Tankyrase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Colon Cancer. J Med Chem 63: 4183 -4204 (2020) Purushothaman, B; Arumugam, P; Kulsi, G; Song, JM Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel catecholopyrimidine based PDE4 inhibitor for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Eur J Med Chem 145: 673 -690 (2018) Harrison, BA; Almstead, ZY; Burgoon, H; Gardyan, M; Goodwin, NC; Healy, J; Liu, Y; Mabon, R; Marinelli, B; Samala, L; Zhang, Y; Stouch, TR; Whitlock, NA; Gopinathan, S; McKnight, B; Wang, S; Patel, N; Wilson, AG; Hamman, BD; Rice, DS; Rawlins, DB Discovery and Development of LX7101, a Dual LIM-Kinase and ROCK Inhibitor for the Treatment of Glaucoma. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 84 -8 (2015) Hopkins, BT; Bame, E; Bajrami, B; Black, C; Bohnert, T; Boiselle, C; Burdette, D; Burns, JC; Delva, L; Donaldson, D; Grater, R; Gu, C; Hoemberger, M; Johnson, J; Kapadnis, S; King, K; Lulla, M; Ma, B; Marx, I; Magee, T; Meissner, R; Metrick, CM; Mingueneau, M; Murugan, P; Otipoby, KL; Polack, E; Poreci, U; Prince, R; Roach, AM; Rowbottom, C; Santoro, JC; Schroeder, P; Tang, H; Tien, E; Zhang, F; Lyssikatos, J Discovery and Preclinical Characterization of BIIB091, a Reversible, Selective BTK Inhibitor for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. J Med Chem 65: 1206 -1224 (2022) Scutt, PJ; Chu, ML; Sloane, DA; Cherry, M; Bignell, CR; Williams, DH; Eyers, PA Discovery and exploitation of inhibitor-resistant aurora and polo kinase mutants for the analysis of mitotic networks. J Biol Chem 284: 15880 -93 (2009) Chuang, C; Collibee, S; Ashcraft, L; Wang, W; Vander Wal, M; Wang, X; Hwee, DT; Wu, Y; Wang, J; Chin, ER; Cremin, P; Zamora, J; Hartman, J; Schaletzky, J; Wehri, E; Robertson, LA; Malik, FI; Morgan, BP Discovery of Aficamten (CK-274), a Next-Generation Cardiac Myosin Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J Med Chem 64: 14142 -14152 (2021) Discovery of BMS-986308: A Renal Outer Medullary Potassium Channel Inhibitor for the Treatment of Heart Failure. Discovery of DS44470011: An oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for the treatment of renal anemia. Chobanian, HR; Guo, Y; Liu, P; Chioda, MD; Fung, S; Lanza, TJ; Chang, L; Bakshi, RK; Dellureficio, JP; Hong, Q; McLaughlin, M; Belyk, KM; Krska, SW; Makarewicz, AK; Martel, EJ; Leone, JF; Frey, L; Karanam, B; Madeira, M; Alvaro, R; Shuman, J; Salituro, G; Terebetski, JL; Jochnowitz, N; Mistry, S; McGowan, E; Hajdu, R; Rosenbach, M; Abbadie, C; Alexander, JP; Shiao, LL; Sullivan, KM; Nargund, RP; Wyvratt, MJ; Lin, LS; DeVita, RJ Discovery of MK-4409, a Novel Oxazole FAAH Inhibitor for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. ACS Med Chem Lett 5: 717 -21 (2014) Wu, WL; Domalski, M; Burnett, DA; Josien, H; Bara, T; Rajagopalan, M; Xu, R; Clader, J; Greenlee, WJ; Brunskill, A; Hyde, LA; Del Vecchio, RA; Cohen-Williams, ME; Song, L; Lee, J; Terracina, G; Zhang, Q; Nomeir, A; Parker, EM; Zhang, L Discovery of SCH 900229, a Potent Presenilin 1 Selective ¿-Secretase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. ACS Med Chem Lett 3: 892 -896 (2012) Dong, Q; Dougan, DR; Gong, X; Halkowycz, P; Jin, B; Kanouni, T; O'Connell, SM; Scorah, N; Shi, L; Wallace, MB; Zhou, F Discovery of TAK-733, a potent and selective MEK allosteric site inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 1315 -9 (2011) Discovery of TYRA-300: First Oral Selective FGFR3 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Urothelial Cancers and Achondroplasia. Zhang, Q; Chen, X; Cao, J; Yang, W; Wan, G; Feng, Q; Zhou, S; Yang, H; Wang, N; Liu, Z; Xiao, H; Zhu, Y; Yu, L Discovery of a Novel Covalent EZH2 Inhibitor Based on Tazemetostat Scaffold for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. J Med Chem 66: 1725 -1741 (2023) Liu, JJ; Higgins, B; Ju, G; Kolinsky, K; Luk, KC; Packman, K; Pizzolato, G; Ren, Y; Thakkar, K; Tovar, C; Zhang, Z; Wovkulich, PM Discovery of a highly potent, orally active mitosis/angiogenesis inhibitor r1530 for the treatment of solid tumors. ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 259 -63 (2013) Bartolomé-Nebreda, JM; Delgado, F; Martín-Martín, ML; Martínez-Viturro, CM; Pastor, J; Tong, HM; Iturrino, L; Macdonald, GJ; Sanderson, W; Megens, A; Langlois, X; Somers, M; Vanhoof, G; Conde-Ceide, S Discovery of a potent, selective, and orally active phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor for the potential treatment of schizophrenia. J Med Chem 57: 4196 -212 (2014) Ma, Y; Ma, Y; Luo, Q; Luo, Q; Fu, J; Fu, J; Che, Y; Che, Y; Guo, F; Guo, F; Mei, L; Mei, L; Zhang, Q; Zhang, Q; Li, Y; Li, Y; Yang, H; Yang, H Discovery of an Inhibitor for the TREK-1 Channel Targeting an Intermediate Transition State of Channel Gating. J Med Chem 63: 10972 -10983 (2020) Bunnage, ME; Blagg, J; Steele, J; Owen, DR; Allerton, C; McElroy, AB; Miller, D; Ringer, T; Butcher, K; Beaumont, K; Evans, K; Gray, AJ; Holland, SJ; Feeder, N; Moore, RS; Brown, DG Discovery of potent& selective inhibitors of activated thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor for the treatment of thrombosis. J Med Chem 50: 6095 -103 (2007) Cavalli, A; Prati, F; Bottegoni, G; Favia, AD; Pizzirani, D; Scarpelli, R; Bolognesi, ML Dual inhibitor compounds for use in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and alzheimer''s disease US Patent US9975861 (2018) Park, E; Park, S; Lee, SJ; Jeong, D; Jin, H; Moon, H; Cha, B; Kim, D; Ma, S; Seo, W; Han, SH; Lee, YS; Kang, S Identification and Biological Evaluation of a Potent and Selective JAK1 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis. J Med Chem 66: 16342 -16363 (2023) Ugolev, Y; Segal, T; Yaffe, D; Gros, Y; Schuldiner, S Identification of conformationally sensitive residues essential for inhibition of vesicular monoamine transport by the noncompetitive inhibitor tetrabenazine. J Biol Chem 288: 32160 -71 (2013) De Pascale, M; Bissegger, L; Tarantelli, C; Beaufils, F; Prescimone, A; Mohamed Seid Hedad, H; Kayali, O; Orbegozo, C; Raguž, L; Schaefer, T; Hebeisen, P; Bertoni, F; Wymann, MP; Borsari, C Investigation of morpholine isosters for the development of a potent, selective and metabolically stable mTOR kinase inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem 248: (2023) Vidovic, D; Schürer, SC Knowledge-based characterization of similarity relationships in the human protein-tyrosine phosphatase family for rational inhibitor design. J Med Chem 52: 6649 -59 (2009) Jones, P; Wilcoxen, K; Rowley, M; Toniatti, C Niraparib: A Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Tumors with Defective Homologous Recombination. J Med Chem 58: 3302 -14 (2015) Małuch, I; Levesque, C; Kwiatkowska, A; Couture, F; Ly, K; Desjardins, R; Neugebauer, WA; Prahl, A; Day, R Positional Scanning Identifies the Molecular Determinants of a High Affinity Multi-Leucine Inhibitor for Furin and PACE4. J Med Chem 60: 2732 -2744 (2017) Smart, BP; Oslund, RC; Walsh, LA; Gelb, MH The first potent inhibitor of mammalian group X secreted phospholipase A2: elucidation of sites for enhanced binding. J Med Chem 49: 2858 -60 (2006) Futatsugi, K; Cabral, S; Kung, DW; Huard, K; Lee, E; Boehm, M; Bauman, J; Clark, RW; Coffey, SB; Crowley, C; Dechert-Schmitt, AM; Dowling, MS; Dullea, R; Gosset, JR; Kalgutkar, AS; Kou, K; Li, Q; Lian, Y; Loria, PM; Londregan, AT; Niosi, M; Orozco, C; Pettersen, JC; Pfefferkorn, JA; Polivkova, J; Ross, TT; Sharma, R; Stock, IA; Tesz, G; Wisniewska, H; Goodwin, B; Price, DA Discovery of Ervogastat (PF-06865571): A Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 2 for the Treatment of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. J Med Chem 65: 15000 -15013 (2022) Wu, Y; Qi, Z; Wang, B; Wang, J; Liu, Q; Wang, A; Shi, C; Zhou, B; Liang, Q; Wang, W; Zou, F; Qi, S; Wang, Z; Wang, L; Wang, W; Liu, J; Liu, Q Discovery of IHMT-MST1-58 as a Novel, Potent, and Selective MST1 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Type 1/2 Diabetes. J Med Chem 65: 11818 -11839 (2022) Kuroda, S; Kobashi, Y; Oi, T; Amada, H; Okumura-Kitajima, L; Io, F; Yamamto, K; Kakinuma, H Discovery of a potent, low-absorbable sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) inhibitor (TP0438836) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 3534 -3539 (2018) Yao, W; Zhuo, J; Burns, DM; Xu, M; Zhang, C; Li, YL; Qian, DQ; He, C; Weng, L; Shi, E; Lin, Q; Agrios, C; Burn, TC; Caulder, E; Covington, MB; Fridman, JS; Friedman, S; Katiyar, K; Hollis, G; Li, Y; Liu, C; Liu, X; Marando, CA; Newton, R; Pan, M; Scherle, P; Taylor, N; Vaddi, K; Wasserman, ZR; Wynn, R; Yeleswaram, S; Jalluri, R; Bower, M; Zhou, BB; Metcalf, B Discovery of a potent, selective, and orally active human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 sheddase inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 50: 603 -6 (2007) Gambacorti-Passerini, C; Mologni, L; Scapozza, L; Bisson, W; Goekjian, P; D Attoma, J 2-acylaminothiazoles for the treatment of cancer US Patent US9708279 (2017) Barril, X; Beswick, MC; Collier, A; Drysdale, MJ; Dymock, BW; Fink, A; Grant, K; Howes, R; Jordan, AM; Massey, A; Surgenor, A; Wayne, J; Workman, P; Wright, L 4-Amino derivatives of the Hsp90 inhibitor CCT018159. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 2543 -8 (2006) Vanderpool, D; Johnson, TO; Ping, C; Bergqvist, S; Alton, G; Phonephaly, S; Rui, E; Luo, C; Deng, YL; Grant, S; Quenzer, T; Margosiak, S; Register, J; Brown, E; Ermolieff, J Characterization of the CHK1 allosteric inhibitor binding site. Biochemistry 48: 9823 -30 (2009) Schirmer, H Inhibitor of the mutated isocitrate dehydrogenase IDH1 R132H US Patent US10344004 (2019) Kryštof, V; Rárová, L; Liebl, J; Zahler, S; Jorda, R; Voller, J; Cankar, P The selective P-TEFb inhibitor CAN508 targets angiogenesis. Eur J Med Chem 46: 4289 -94 (2011) Ashwood, V; Brownhill, V; Higginbottom, M; Horwell, DC; Hughes, J; Lewthwaite, RA; McKnight, AT; Pinnock, RD; Pritchard, MC; Suman-Chauhan, N; Webb, C; Williams, SC PD 176252--the first high affinity non-peptide gastrin-releasing peptide (BB2) receptor antagonist. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8: 2589 -94 (1999) Giardina, GA; Sarau, HM; Farina, C; Medhurst, AD; Grugni, M; Raveglia, LF; Schmidt, DB; Rigolio, R; Luttmann, M; Vecchietti, V; Hay, DW Discovery of a novel class of selective non-peptide antagonists for the human neurokinin-3 receptor. 1. Identification of the 4-quinolinecarboxamide framework. J Med Chem 40: 1794 -807 (1997) Gourlet, P; Woussen-Colle, MC; Robberecht, P; de Neef, P; Cauvin, A; Vandermeers-Piret, MC; Vandermeers, A; Christophe, J Structural requirements for the binding of the pituitary adenylate-cyclase-activating peptide to receptors and adenylate-cyclase activation in pancreatic and neuronal membranes. Eur J Biochem 195: 535 -41 (1991) Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway for the Treatment of Melanoma--Application of LY2090314, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3. Yuthavong, Y; Vilaivan, T; Chareonsethakul, N; Kamchonwongpaisan, S; Sirawaraporn, W; Quarrell, R; Lowe, G Development of a lead inhibitor for the A16V+S108T mutant of dihydrofolate reductase from the cycloguanil-resistant strain (T9/94) of Plasmodium falciparum. J Med Chem 43: 2738 -44 (2000) Discovery of a brain-permeable bromodomain and extra terminal domain (BET) inhibitor with selectivity for BD1 for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Ginn, JD; Bosanac, T; Chen, R; Cywin, C; Hickey, E; Kashem, M; Kerr, S; Kugler, S; Li, X; Prokopowicz, A; Schlyer, S; Smith, JD; Turner, MR; Wu, F; Young, ER Substituted 2H-isoquinolin-1-ones as potent Rho-kinase inhibitors: part 2, optimization for blood pressure reduction in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 5153 -6 (2010) Blobaum, AL; Uddin, MJ; Felts, AS; Crews, BC; Rouzer, CA; Marnett, LJ The 2'-Trifluoromethyl Analogue of Indomethacin Is a Potent and Selective COX-2 Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 486 -490 (2013) Itoh, T; Yoshimoto, N; Hirano, Y; Yamamoto, K Structural basis for the selective inhibition of activated thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFIa) by a selenium-containing inhibitor with chloro-aminopyridine as a basic group. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 2256 -2260 (2018) Bell, JL; Haak, AJ; Wade, SM; Kirchhoff, PD; Neubig, RR; Larsen, SD Optimization of novel nipecotic bis(amide) inhibitors of the Rho/MKL1/SRF transcriptional pathway as potential anti-metastasis agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 3826 -32 (2013) Emonds-Alt, X; Bichon, D; Ducoux, JP; Heaulme, M; Miloux, B; Poncelet, M; Proietto, V; Van Broeck, D; Vilain, P; Neliat, G SR 142801, the first potent non-peptide antagonist of the tachykinin NK3 receptor. Life Sci 56: -32 (1995) Sessions, EH; Yin, Y; Bannister, TD; Weiser, A; Griffin, E; Pocas, J; Cameron, MD; Ruiz, C; Lin, L; Schürer, SC; Schröter, T; LoGrasso, P; Feng, Y Benzimidazole- and benzoxazole-based inhibitors of Rho kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 6390 -3 (2008) Yin, Y; Lin, L; Ruiz, C; Cameron, MD; Pocas, J; Grant, W; Schröter, T; Chen, W; Duckett, D; Schürer, S; Lograsso, P; Feng, Y Benzothiazoles as Rho-associated kinase (ROCK-II) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 6686 -90 (2009) Chen, YT; Bannister, TD; Weiser, A; Griffin, E; Lin, L; Ruiz, C; Cameron, MD; Schürer, S; Duckett, D; Schröter, T; LoGrasso, P; Feng, Y Chroman-3-amides as potent Rho kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 6406 -9 (2008) Iwakubo, M; Takami, A; Okada, Y; Kawata, T; Tagami, Y; Ohashi, H; Sato, M; Sugiyama, T; Fukushima, K; Iijima, H Design and synthesis of Rho kinase inhibitors (II). Bioorg Med Chem 15: 350 -64 (2006) Iwakubo, M; Takami, A; Okada, Y; Kawata, T; Tagami, Y; Sato, M; Sugiyama, T; Fukushima, K; Taya, S; Amano, M; Kaibuchi, K; Iijima, H Design and synthesis of rho kinase inhibitors (III). Bioorg Med Chem 15: 1022 -33 (2006) Feng, Y; LoGrasso, PV; Defert, O; Li, R Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibitors and Their Therapeutic Potential. J Med Chem 59: 2269 -300 (2016) Long, YQ; Lee, SL; Lin, CY; Enyedy, IJ; Wang, S; Li, P; Dickson, RB; Roller, PP Synthesis and evaluation of the sunflower derived trypsin inhibitor as a potent inhibitor of the type II transmembrane serine protease, matriptase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 2515 -9 (2001) Kratzel, M; Hiessböck, R; Bernkop-Schnürch, A Auxiliary agents for the peroral administration of peptide and protein drugs: synthesis and evaluation of novel pepstatin analogues. J Med Chem 41: 2339 -44 (1998) Han, HK; Rhie, JK; Oh, DM; Saito, G; Hsu, CP; Stewart, BH; Amidon, GL CHO/hPEPT1 cells overexpressing the human peptide transporter (hPEPT1) as an alternative in vitro model for peptidomimetic drugs. J Pharm Sci 88: 347 -50 (1999) Ying, J; Gu, X; Cai, M; Dedek, M; Vagner, J; Trivedi, DB; Hruby, VJ Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of new cyclic melanotropin peptide analogues selective for the human melanocortin-4 receptor. J Med Chem 49: 6888 -96 (2006) Replacement of the hydroxamic acid group in the selective HDAC8 inhibitor PCI-34051. Yurek-George, A; Cecil, AR; Mo, AH; Wen, S; Rogers, H; Habens, F; Maeda, S; Yoshida, M; Packham, G; Ganesan, A The First Biologically Active Synthetic Analogues of FK228, the Depsipeptide Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. J Med Chem 50: 5720 -5726 (2007) Peel, MR; Sternbach, DD The synthesis and evaluation of flexible analogues of the topoisomerase I inhibitor, camptothecin Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 2753 -2758 (1994) Exploring the structural activity relationship of the Osimertinib: A covalent inhibitor of double mutant EGFRL858R/T790M tyrosine kinase for the treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Discovery of the Clinical Candidate Sonrotoclax (BGB-11417), a Highly Potent and Selective Inhibitor for Both WT and G101V Mutant Bcl-2. Gorczynski, MJ; Smitherman, PK; Akiyama, TE; Wood, HB; Berger, JP; King, SB; Morrow, CS Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) by nitroalkene fatty acids: importance of nitration position and degree of unsaturation. J Med Chem 52: 4631 -9 (2009) Xiu, ZM; Wang, LP; Fu, J; Xu, J; Liu, L 1-Acetyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-ylacetate: An aldose reductase inhibitor for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4482 -4487 (2017) Zarrinkar, PP; Gunawardane, RN; Cramer, MD; Gardner, MF; Brigham, D; Belli, B; Karaman, MW; Pratz, KW; Pallares, G; Chao, Q; Sprankle, KG; Patel, HK; Levis, M; Armstrong, RC; James, J; Bhagwat, SS AC220 is a uniquely potent and selective inhibitor of FLT3 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 114: 2984 -92 (2009) Coburn, CA; Young, MB; Hungate, RW; Isaacs, RC; Vacca, JP; Huff, JR Aromatic P1 replacements for the highly potent HIV-1 protease inhibitor CRIXIVAN® Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 1937 -1940 (1996) CI-1033, an irreversible pan-erbB receptor inhibitor and its potential application for the treatment of breast cancer. Holson, E; Nacht, M Combination of a selective histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) inhibitor and an immunotherapy agent for the treatment of cancer US Patent US12128018 (2024) Musella, S; D'Avino, D; Peltner, LK; Di Sarno, V; Cerqua, I; Merciai, F; Vestuto, V; Ciaglia, T; Smaldone, G; Di Matteo, F; Di Micco, S; Napolitano, V; Bifulco, G; Pepe, G; Sommella, EM; Basilicata, MG; Aquino, G; Gomez-Monterrey, IM; Campiglia, P; Ostacolo, C; Roviezzo, F; Werz, O; Rossi, A; Bertamino, A Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Characterization of a Potent Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis. J Med Chem 66: 9201 -9222 (2023) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel DCLK1 inhibitor containing purine skeleton for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nagle, A; Biggart, A; Be, C; Srinivas, H; Hein, A; Caridha, D; Sciotti, RJ; Pybus, B; Kreishman-Deitrick, M; Bursulaya, B; Lai, YH; Gao, MY; Liang, F; Mathison, CJN; Liu, X; Yeh, V; Smith, J; Lerario, I; Xie, Y; Chianelli, D; Gibney, M; Berman, A; Chen, YL; Jiricek, J; Davis, LC; Liu, X; Ballard, J; Khare, S; Eggimann, FK; Luneau, A; Groessl, T; Shapiro, M; Richmond, W; Johnson, K; Rudewicz, PJ; Rao, SPS; Thompson, C; Tuntland, T; Spraggon, G; Glynne, RJ; Supek, F; Wiesmann, C; Molteni, V Discovery and Characterization of Clinical Candidate LXE408 as a Kinetoplastid-Selective Proteasome Inhibitor for the Treatment of Leishmaniases. J Med Chem 63: 10773 -10781 (2020) Liu, J; Huang, J; Wang, K; Li, Y; Li, C; Zhu, Y; He, X; Zhang, Y; Zhao, Y; Hu, C; Xi, Z; Tong, M; Li, Z; Gong, P; Hou, Y Discovery and optimization of dihydropteridone derivatives as novel PLK1 and BRD4 dual inhibitor for the treatment of cancer. Bioorg Med Chem 101: (2024) Konteatis, Z; Travins, J; Gross, S; Marjon, K; Barnett, A; Mandley, E; Nicolay, B; Nagaraja, R; Chen, Y; Sun, Y; Liu, Z; Yu, J; Ye, Z; Jiang, F; Wei, W; Fang, C; Gao, Y; Kalev, P; Hyer, ML; DeLaBarre, B; Jin, L; Padyana, AK; Dang, L; Murtie, J; Biller, SA; Sui, Z; Marks, KM Discovery of AG-270, a First-in-Class Oral MAT2A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Tumors with Homozygous J Med Chem 64: 4430 -4449 (2021) Irie, T; Asami, T; Sawa, A; Uno, Y; Taniyama, C; Funakoshi, Y; Masai, H; Sawa, M Discovery of AS-0141, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of CDC7 Kinase for the Treatment of Solid Cancers. J Med Chem 64: 14153 -14164 (2021) Discovery of BIO-8169─A Highly Potent, Selective, and Brain-Penetrant IRAK4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Neuroinflammation. Ma, C; Ma, C; Wu, J; Wu, J; Wang, L; Wang, L; Ji, X; Ji, X; Wu, Y; Wu, Y; Miao, L; Miao, L; Chen, D; Chen, D; Zhang, L; Zhang, L; Wu, Y; Wu, Y; Feng, H; Feng, H; Tang, Y; Tang, Y; Zhou, Q; Zhou, Q; Pei, J; Pei, J; Yang, X; Yang, X; Xu, D; Xu, D; You, Q; You, Q; Xie, Y; Xie, Y Discovery of Clinical Candidate NTQ1062 as a Potent and Bioavailable Akt Inhibitor for the Treatment of Human Tumors. J Med Chem 65: 8144 -8168 (2022) Brebion, F; Gosmini, R; Deprez, P; Varin, M; Peixoto, C; Alvey, L; Jary, H; Bienvenu, N; Triballeau, N; Blanque, R; Cottereaux, C; Christophe, T; Vandervoort, N; Mollat, P; Touitou, R; Leonard, P; De Ceuninck, F; Botez, I; Monjardet, A; van der Aar, E; Amantini, D Discovery of GLPG1972/S201086, a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable ADAMTS-5 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J Med Chem 64: 2937 -2952 (2021) Tang, H; Zhu, Y; Teumelsan, N; Walsh, SP; Shahripour, A; Priest, BT; Swensen, AM; Felix, JP; Brochu, RM; Bailey, T; Thomas-Fowlkes, B; Pai, LY; Hampton, C; Corona, A; Hernandez, M; Metzger, J; Forrest, M; Zhou, X; Owens, K; Tong, V; Parmee, E; Roy, S; Kaczorowski, GJ; Yang, L; Alonso-Galicia, M; Garcia, ML; Pasternak, A Discovery of MK-7145, an Oral Small Molecule ROMK Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hypertension and Heart Failure. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 697 -701 (2016) Burnett, GL; Yang, YC; Aggen, JB; Pitzen, J; Gliedt, MK; Semko, CM; Marquez, A; Evans, JW; Wang, G; Won, WS; Tomlinson, ACA; Kiss, G; Tzitzilonis, C; Thottumkara, AP; Cregg, J; Mellem, KT; Choi, JS; Lee, JC; Zhao, Y; Lee, BJ; Meyerowitz, JG; Knox, JE; Jiang, J; Wang, Z; Wildes, D; Wang, Z; Singh, M; Smith, JAM; Gill, AL Discovery of RMC-5552, a Selective Bi-Steric Inhibitor of mTORC1, for the Treatment of mTORC1-Activated Tumors. J Med Chem 66: 149 -169 (2023) Langston, SP; Grossman, S; England, D; Afroze, R; Bence, N; Bowman, D; Bump, N; Chau, R; Chuang, BC; Claiborne, C; Cohen, L; Connolly, K; Duffey, M; Durvasula, N; Freeze, S; Gallery, M; Galvin, K; Gaulin, J; Gershman, R; Greenspan, P; Grieves, J; Guo, J; Gulavita, N; Hailu, S; He, X; Hoar, K; Hu, Y; Hu, Z; Ito, M; Kim, MS; Lane, SW; Lok, D; Lublinsky, A; Mallender, W; McIntyre, C; Minissale, J; Mizutani, H; Mizutani, M; Molchinova, N; Ono, K; Patil, A; Qian, M; Riceberg, J; Shindi, V; Sintchak, MD; Song, K; Soucy, T; Wang, Y; Xu, H; Yang, X; Zawadzka, A; Zhang, J; Pulukuri, SM Discovery of TAK-981, a First-in-Class Inhibitor of SUMO-Activating Enzyme for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 64: 2501 -2520 (2021) Bonazzi, S; Goold, CP; Gray, A; Thomsen, NM; Nunez, J; Karki, RG; Gorde, A; Biag, JD; Malik, HA; Sun, Y; Liang, G; Lubicka, D; Salas, S; Labbe-Giguere, N; Keaney, EP; McTighe, S; Liu, S; Deng, L; Piizzi, G; Lombardo, F; Burdette, D; Dodart, JC; Wilson, CJ; Peukert, S; Curtis, D; Hamann, LG; Murphy, LO Discovery of a Brain-Penetrant ATP-Competitive Inhibitor of the Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) for CNS Disorders. J Med Chem 63: 1068 -1083 (2020) Sun, Y; Xu, L; Shao, H; Quan, D; Mo, Z; Wang, J; Zhang, W; Yu, J; Zhuang, C; Xu, K Discovery of a Trifluoromethoxy Cyclopentanone Benzothiazole Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 1 Inhibitor as the Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease. J Med Chem 65: 14957 -14969 (2022) Cai, H; Liu, Z; Sun, P; Zhou, Y; Yan, Y; Luo, Y; Zhang, X; Wu, R; Liang, X; Wu, D; Hu, W; Yang, Z Discovery of a dual-acting inhibitor of interleukin-1β and STATs for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. RSC Med Chem 15: 193 -206 (2024) Zhang, B; Zhu, C; Chan, ASC; Lu, G Discovery of a first-in-class Aurora A covalent inhibitor for the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Eur J Med Chem 256: (2023) Luo, R; Fu, W; Shao, J; Ma, L; Shuai, S; Xu, Y; Jiang, Z; Ye, Z; Zheng, L; Zheng, L; Yu, J; Zhang, Y; Yin, L; Tu, L; Lv, X; Li, J; Liang, G; Chen, L Discovery of a potent and selective allosteric inhibitor targeting the SHP2 tunnel site for RTK-driven cancer treatment. Eur J Med Chem 253: (2023) Ye, YL; Zhou, Z; Zou, HJ; Shen, Y; Xu, TF; Tang, J; Yin, HZ; Chen, ML; Leng, Y; Shen, JH Discovery of novel dual functional agent as PPARgamma agonist and 11beta-HSD1 inhibitor for the treatment of diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 5722 -32 (2009) Summa, V; Petrocchi, A; Bonelli, F; Crescenzi, B; Donghi, M; Ferrara, M; Fiore, F; Gardelli, C; Gonzalez Paz, O; Hazuda, DJ; Jones, P; Kinzel, O; Laufer, R; Monteagudo, E; Muraglia, E; Nizi, E; Orvieto, F; Pace, P; Pescatore, G; Scarpelli, R; Stillmock, K; Witmer, MV; Rowley, M Discovery of raltegravir, a potent, selective orally bioavailable HIV-integrase inhibitor for the treatment of HIV-AIDS infection. J Med Chem 51: 5843 -55 (2008) Discovery of the Selective and Orally Available Galectin-1 Inhibitor GB1908 as a Potential Treatment for Lung Cancer. Lin, WH; Wu, SY; Yeh, TK; Chen, CT; Song, JS; Shiao, HY; Kuo, CC; Hsu, T; Lu, CT; Wang, PC; Wu, TS; Peng, YH; Lin, HY; Chen, CP; Weng, YL; Kung, FC; Wu, MH; Su, YC; Huang, KW; Chou, LH; Hsueh, CC; Yen, KJ; Kuo, PC; Huang, CL; Chen, LT; Shih, C; Tsai, HJ; Jiaang, WT Identification of a Multitargeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Med Chem 62: 11135 -11150 (2019) Identification of a Novel Selective CDK9 Inhibitor for the Treatment of CRC: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity Evaluation. Liu, Q; Shi, Q; Marcoux, D; Batt, DG; Cornelius, L; Qin, LY; Ruan, Z; Neels, J; Beaudoin-Bertrand, M; Srivastava, AS; Li, L; Cherney, RJ; Gong, H; Watterson, SH; Weigelt, C; Gillooly, KM; McIntyre, KW; Xie, JH; Obermeier, MT; Fura, A; Sleczka, B; Stefanski, K; Fancher, RM; Padmanabhan, S; Rp, T; Kundu, I; Rajareddy, K; Smith, R; Hennan, JK; Xing, D; Fan, J; Levesque, PC; Ruan, Q; Pitt, S; Zhang, R; Pedicord, D; Pan, J; Yarde, M; Lu, H; Lippy, J; Goldstine, C; Skala, S; Rampulla, RA; Mathur, A; Gupta, A; Arunachalam, PN; Sack, JS; Muckelbauer, JK; Cvijic, ME; Salter-Cid, LM; Bhide, RS; Poss, MA; Hynes, J; Carter, PH; Macor, JE; Ruepp, S; Schieven, GL; Tino, JA Identification of a Potent, Selective, and Efficacious Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinaseδ (PI3Kδ) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Immunological Disorders. J Med Chem 60: 5193 -5208 (2017) Chi, G; Manos-Turvey, A; O'Connor, PD; Johnston, JM; Evans, GL; Baker, EN; Payne, RJ; Lott, JS; Bulloch, EM Implications of binding mode and active site flexibility for inhibitor potency against the salicylate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry 51: 4868 -79 (2012) Divakaran, A; Talluri, SK; Ayoub, AM; Mishra, NK; Cui, H; Widen, JC; Berndt, N; Zhu, JY; Carlson, AS; Topczewski, JJ; Schonbrunn, EK; Harki, DA; Pomerantz, WCK Molecular Basis for the N-Terminal Bromodomain-and-Extra-Terminal-Family Selectivity of a Dual Kinase-Bromodomain Inhibitor. J Med Chem 61: 9316 -9334 (2018) Cuozzo, JW; Clark, MA; Keefe, AD; Kohlmann, A; Mulvihill, M; Ni, H; Renzetti, LM; Resnicow, DI; Ruebsam, F; Sigel, EA; Thomson, HA; Wang, C; Xie, Z; Zhang, Y Novel Autotaxin Inhibitor for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Clinical Candidate Discovered Using DNA-Encoded Chemistry. J Med Chem 63: 7840 -7856 (2020) Palomo, V; Perez, DI; Roca, C; Anderson, C; Rodríguez-Muela, N; Perez, C; Morales-Garcia, JA; Reyes, JA; Campillo, NE; Perez-Castillo, AM; Rubin, LL; Timchenko, L; Gil, C; Martinez, A Subtly Modulating Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β: Allosteric Inhibitor Development and Their Potential for the Treatment of Chronic Diseases. J Med Chem 60: 4983 -5001 (2017) Muratspahić, E; Tomašević, N; Koehbach, J; Duerrauer, L; Hadžić, S; Castro, J; Schober, G; Sideromenos, S; Clark, RJ; Brierley, SM; Craik, DJ; Gruber, CW Design of a Stable Cyclic Peptide Analgesic Derived from Sunflower Seeds that Targets the κ-Opioid Receptor for the Treatment of Chronic Abdominal Pain. J Med Chem 64: 9042 -9055 (2021) PubChem, PC Dose-response biochemical assay for antagonists of the interaction between the Eph receptor B4 (EphB4) and its ligand ephrin-B2 via TNYL-RAW peptide PubChem Bioassay (2007) Wurtz, NR; Johnson, JA; Viet, A; Shirude, PS; Baligar, V; Madduri, S; Cheney, DL; Park, H; Lupisella, JA; Hsu, MY; Abousleiman, M; Galella, MA; Aulakh, D; Dierks, EA; Garcia, RA; Ostrowski, J; Kick, EK; Wexler, RR Discovery of Heteroaryl Urea Isosteres for Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 Agonists. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 943 -948 (2022) Leblanc, Y; Roy, P; Boyce, S; Brideau, C; Chan, CC; Charleson, S; Gordon, R; Grimm, E; Guay, J; Léger, S; Li, CS; Riendeau, D; Visco, D; Wang, Z; Webb, J; Xu, LJ; Prasit, P SAR in the alkoxy lactone series: the discovery of DFP, a potent and orally active COX-2 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 2207 -12 (1999) Araki, Y; Miyawaki, A; Miyashita, T; Mizutani, M; Hirai, N; Todoroki, Y A new non-azole inhibitor of ABA 8'-hydroxylase: effect of the hydroxyl group substituted for geminal methyl groups in the six-membered ring. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 3302 -5 (2006) A M Subbaiah, M; Mandlekar, S; Desikan, S; Ramar, T; Subramani, L; Annadurai, M; Desai, SD; Sinha, S; Jenkins, SM; Krystal, MR; Subramanian, M; Sridhar, S; Padmanabhan, S; Bhutani, P; Arla, R; Singh, S; Sinha, J; Thakur, M; Kadow, JF; Meanwell, NA Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Phosphate and Amino Acid Ester Prodrugs for Improving the Oral Bioavailability of the HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Atazanavir. J Med Chem 62: 3553 -3574 (2019) Horikawa, M; Kato, Y; Tyson, CA; Sugiyama, Y The potential for an interaction between MRP2 (ABCC2) and various therapeutic agents: probenecid as a candidate inhibitor of the biliary excretion of irinotecan metabolites. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 17: 23 -33 (2002) Meiring, L; Petzer, JP; Legoabe, LJ; Petzer, A The evaluation of N-propargylamine-2-aminotetralin as an inhibitor of monoamine oxidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 67: (2022) Jones, P; Storer, RI; Sabnis, YA; Wakenhut, FM; Whitlock, GA; England, KS; Mukaiyama, T; Dehnhardt, CM; Coe, JW; Kortum, SW; Chrencik, JE; Brown, DG; Jones, RM; Murphy, JR; Yeoh, T; Morgan, P; Kilty, I Design and Synthesis of a Pan-Janus Kinase Inhibitor Clinical Candidate (PF-06263276) Suitable for Inhaled and Topical Delivery for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases of the Lungs and Skin. J Med Chem 60: 767 -786 (2017) Wang, E; Casciano, CN; Clement, RP; Johnson, WW The farnesyl protein transferase inhibitor SCH66336 is a potent inhibitor of MDR1 product P-glycoprotein. Cancer Res 61: 7525 -9 (2001) Sootome, H Therapeutic agent for FGFR inhibitor-resistant cancer US Patent US10124003 (2018) Qiao, Y; Zhou, B; Zhang, M; Liu, W; Han, Z; Song, C; Yu, W; Yang, Q; Wang, R; Wang, S; Shi, S; Zhao, R; Chai, J; Chang, J A Novel Inhibitor of the Obesity-Related Protein FTO. Biochemistry 55: 1516 -22 (2016) Kodani, S; Ishida, K; Murakami, M Dehydroradiosumin, a trypsin inhibitor from the cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica. J Nat Prod 61: 854 -6 (1998) Hadden, MK; Galam, L; Gestwicki, JE; Matts, RL; Blagg, BS Derrubone, an inhibitor of the Hsp90 protein folding machinery. J Nat Prod 70: 2014 -8 (2007) Perez, C; Li, J; Parlati, F; Rouffet, M; Ma, Y; Mackinnon, AL; Chou, TF; Deshaies, RJ; Cohen, SM Discovery of an Inhibitor of the Proteasome Subunit Rpn11. J Med Chem 60: 1343 -1361 (2017) Munck Af Rosenschöld, M; Johannesson, P; Nikitidis, A; Tyrchan, C; Chang, HF; Rönn, R; Chapman, D; Ullah, V; Nikitidis, G; Glader, P; Käck, H; Bonn, B; Wågberg, F; Björkstrand, E; Andersson, U; Swedin, L; Rohman, M; Andreasson, T; Bergström, EL; Jiang, F; Zhou, XH; Lundqvist, AJ; Malmberg, A; Ek, M; Gordon, E; Pettersen, A; Ripa, L; Davis, AM Discovery of the Oral Leukotriene C4 Synthase Inhibitor (1 J Med Chem 62: 7769 -7787 (2019) Nagy, MA; Hilgraf, R; Mortensen, DS; Elsner, J; Norris, S; Tikhe, J; Yoon, W; Paisner, D; Delgado, M; Erdman, P; Haelewyn, J; Khambatta, G; Xu, L; Romanow, WJ; Condroski, K; Bahmanyar, S; McCarrick, M; Benish, B; Blease, K; LeBrun, L; Moghaddam, MF; Apuy, J; Canan, SS; Bennett, BL; Satoh, Y Discovery of the c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitor J Med Chem 64: 18193 -18208 (2021) Robarge, KD; Brunton, SA; Castanedo, GM; Cui, Y; Dina, MS; Goldsmith, R; Gould, SE; Guichert, O; Gunzner, JL; Halladay, J; Jia, W; Khojasteh, C; Koehler, MF; Kotkow, K; La, H; Lalonde, RL; Lau, K; Lee, L; Marshall, D; Marsters, JC; Murray, LJ; Qian, C; Rubin, LL; Salphati, L; Stanley, MS; Stibbard, JH; Sutherlin, DP; Ubhayaker, S; Wang, S; Wong, S; Xie, M GDC-0449-a potent inhibitor of the hedgehog pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 5576 -81 (2009) Zhang, R; Wu, M; Cao, T; Luo, K; Huang, F; Zhang, R; Huang, Z; Zhou, J; Wang, Y; Zhu, S Identification of the gossypol derivatives as androgen receptor inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 75: (2022) Weinstabl, H; Treu, M; Rinnenthal, J; Zahn, SK; Ettmayer, P; Bader, G; Dahmann, G; Kessler, D; Rumpel, K; Mischerikow, N; Savarese, F; Gerstberger, T; Mayer, M; Zoephel, A; Schnitzer, R; Sommergruber, W; Martinelli, P; Arnhof, H; Peric-Simov, B; Hofbauer, KS; Garavel, G; Scherbantin, Y; Mitzner, S; Fett, TN; Scholz, G; Bruchhaus, J; Burkard, M; Kousek, R; Ciftci, T; Sharps, B; Schrenk, A; Harrer, C; Haering, D; Wolkerstorfer, B; Zhang, X; Lv, X; Du, A; Li, D; Li, Y; Quant, J; Pearson, M; McConnell, DB Intracellular Trapping of the Selective Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase (PHGDH) Inhibitor J Med Chem 62: 7976 -7997 (2019) Kaneko, A; Tsukada, M; Fukai, M; Suzuki, T; Nishio, K; Miki, K; Kinoshita, K; Takahashi, K; Koyama, K KDR Kinase Inhibitor Isolated from the Mushroom Boletopsis leucomelas. J Nat Prod 73: 1002 -4 (2010) Schadt, O; Esdar, C; Schultz-Fademrecht, C; Eickhoff, J Quinoline inhibitor of the macrophage stimulating 1 receptor MSTR1 US Patent US9481668 (2016) Sehon, CA; Wang, GZ; Viet, AQ; Goodman, KB; Dowdell, SE; Elkins, PA; Semus, SF; Evans, C; Jolivette, LJ; Kirkpatrick, RB; Dul, E; Khandekar, SS; Yi, T; Wright, LL; Smith, GK; Behm, DJ; Bentley, R; Doe, CP; Hu, E; Lee, D Potent, selective and orally bioavailable dihydropyrimidine inhibitors of Rho kinase (ROCK1) as potential therapeutic agents for cardiovascular diseases. J Med Chem 51: 6631 -4 (2008) Nomura, S; Sakamaki, S; Hongu, M; Kawanishi, E; Koga, Y; Sakamoto, T; Yamamoto, Y; Ueta, K; Kimata, H; Nakayama, K; Tsuda-Tsukimoto, M Discovery of canagliflozin, a novel C-glucoside with thiophene ring, as sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Med Chem 53: 6355 -60 (2010) Fehrenbach, T; Cui, Y; Faulstich, H; Keppler, D Characterization of the transport of the bicyclic peptide phalloidin by human hepatic transport proteins. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 368: 415 -20 (2003) Bernad, N; Burgaud, BG; Horwell, DC; Lewthwaite, RA; Martinez, J; Pritchard, MC The design and synthesis of the high efficacy, non-peptide CCK1 receptor agonist PD170292. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 1245 -8 (2000) Mogil, JS; Pasternak, GW The molecular and behavioral pharmacology of the orphanin FQ/nociceptin peptide and receptor family. Pharmacol Rev 53: 381 -415 (2001) Miller, MJ; Anderson, KS; Braccolino, DS; Cleary, DG; Gruys, KJ; Han, CY; Lin, KC; Pansegrau, PD; Ream, JE; Sammons, RD; Sikorski, JA EPSP synthase inhibitor design II. The importance of the 3-phosphate group for ligand binding at the shikimate-3-phosphate site & the identification of 3-malonate ethers as novel 3-phosphate mimics. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 1435 -1440 (1993) Carroll, FI; Gao, Y; Abraham, P; Lewin, AH; Lew, R; Patel, A; Boja, JW; Kuhar, MJ Probes for the cocaine receptor. Potentially irreversible ligands for the dopamine transporter. J Med Chem 35: 1813 -7 (1992) Boeglin, D; Hamdan, FF; Melendez, RE; Cluzeau, J; Laperriere, A; Héroux, M; Bouvier, M; Lubell, WD Calcitonin gene-related peptide analogues with aza and indolizidinone amino acid residues reveal conformational requirements for antagonist activity at the human calcitonin gene-related peptide 1 receptor. J Med Chem 50: 1401 -8 (2007) Rishton, GM; Retz, DM; Tempest, PA; Novotny, J; Kahn, S; Treanor, JJ; Lile, JD; Citron, M Fenchylamine sulfonamide inhibitors of amyloid beta peptide production by the gamma-secretase proteolytic pathway: potential small-molecule therapeutic agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J Med Chem 43: 2297 -9 (2000) Discovery of CZL-046 with an (S)-3-Fluoropyrrolidin-2-one Scaffold as a p300 Bromodomain Inhibitor for the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma. Burgess, K; Lim, D; Mousa, SA Synthesis and solution conformation of cyclo[RGDRGD]: a cyclic peptide with selectivity for the alpha V beta 3 receptor. J Med Chem 39: 4520 -6 (1996) Shrimp, JH; Sorum, AW; Garlick, JM; Guasch, L; Nicklaus, MC; Meier, JL Characterizing the Covalent Targets of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Lysine Acetyltransferase P300. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 151 -5 (2016) Mai, A; Massa, S; Rotili, D; Pezzi, R; Bottoni, P; Scatena, R; Meraner, J; Brosch, G Exploring the connection unit in the HDAC inhibitor pharmacophore model: novel uracil-based hydroxamates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 4656 -61 (2005) Dhar, TG; Nakanishi, H; Borden, LA; Gluchowski, C On the bioactive conformation of the gaba uptake inhibitor SK&F 89976-A Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 1535 -1540 (1996) Wu, X; Xu, G; Li, X; Xu, W; Li, Q; Liu, W; Kirby, KA; Loh, ML; Li, J; Sarafianos, SG; Qu, CK Small Molecule Inhibitor that Stabilizes the Autoinhibited Conformation of the Oncogenic Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP2. J Med Chem 62: 1125 -1137 (2019) Hantschel, O; Rix, U; Schmidt, U; Bürckstümmer, T; Kneidinger, M; Schütze, G; Colinge, J; Bennett, KL; Ellmeier, W; Valent, P; Superti-Furga, G The Btk tyrosine kinase is a major target of the Bcr-Abl inhibitor dasatinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 13283 -8 (2007) Pireddu, R; Forinash, KD; Sun, NN; Martin, MP; Sung, SS; Alexander, B; Zhu, JY; Guida, WC; Schönbrunn, E; Sebti, SM; Lawrence, NJ Pyridylthiazole-based ureas as inhibitors of Rho associated protein kinases (ROCK1 and 2). Medchemcomm 3: 699 -709 (2012) Freezing the Bioactive Conformation to Boost Potency: The Identification of BAY 85-8501, a Selective and Potent Inhibitor of Human Neutrophil Elastase for Pulmonary Diseases. Sakamoto, T; Koga, Y; Hikota, M; Matsuki, K; Murakami, M; Kikkawa, K; Fujishige, K; Kotera, J; Omori, K; Morimoto, H; Yamada, K The discovery of avanafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: a novel pyrimidine-5-carboxamide derivative as a potent and highly selective phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 5460 -5 (2015) Valentine, JJ; Nakanishi, S; Hageman, DL; Snider, R; Spencer, RW; Vinick, FJ CP-70,030 and CP-75,998: The first non-peptide antagonists of bombesin and gastrin releasing peptide Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2: 333 -338 (1992) Slaymaker, IM; Bracey, M; Mileni, M; Garfunkle, J; Cravatt, BF; Boger, DL; Stevens, RC Correlation of inhibitor effects on enzyme activity and thermal stability for the integral membrane protein fatty acid amide hydrolase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 5847 -50 (2008) Hattori, K; Kohchi, Y; Oikawa, N; Suda, H; Ura, M; Ishikawa, T; Miwa, M; Endoh, M; Eda, H; Tanimura, H; Kawashima, A; Horii, I; Ishitsuka, H; Shimma, N Design and synthesis of the tumor-activated prodrug of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) inhibitor, RO0094889 for combination therapy with capecitabine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 867 -72 (2003) Huang, N; Liao, P; Zuo, Y; Zhang, L; Jiang, R Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of a Potent Dual EZH2-BRD4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Some Solid Tumors. J Med Chem 66: 2646 -2662 (2023) Blake, JF; Xu, R; Bencsik, JR; Xiao, D; Kallan, NC; Schlachter, S; Mitchell, IS; Spencer, KL; Banka, AL; Wallace, EM; Gloor, SL; Martinson, M; Woessner, RD; Vigers, GP; Brandhuber, BJ; Liang, J; Safina, BS; Li, J; Zhang, B; Chabot, C; Do, S; Lee, L; Oeh, J; Sampath, D; Lee, BB; Lin, K; Liederer, BM; Skelton, NJ Discovery and preclinical pharmacology of a selective ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor (GDC-0068) for the treatment of human tumors. J Med Chem 55: 8110 -27 (2012) Popovici-Muller, J; Lemieux, RM; Artin, E; Saunders, JO; Salituro, FG; Travins, J; Cianchetta, G; Cai, Z; Zhou, D; Cui, D; Chen, P; Straley, K; Tobin, E; Wang, F; David, MD; Penard-Lacronique, V; Quivoron, C; Saada, V; de Botton, S; Gross, S; Dang, L; Yang, H; Utley, L; Chen, Y; Kim, H; Jin, S; Gu, Z; Yao, G; Luo, Z; Lv, X; Fang, C; Yan, L; Olaharski, A; Silverman, L; Biller, S; Su, SM; Yen, K Discovery of AG-120 (Ivosidenib): A First-in-Class Mutant IDH1 Inhibitor for the Treatment of IDH1 Mutant Cancers. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 300 -305 (2018) Lu, B; Shen, X; Zhang, L; Liu, D; Zhang, C; Cao, J; Shen, R; Zhang, J; Wang, D; Wan, H; Xu, Z; Ho, MH; Zhang, M; Zhang, L; He, F; Tao, W Discovery of EBI-2511: A Highly Potent and Orally Active EZH2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 98 -102 (2018) Discovery of MT-1207: A Novel, Potent Multitarget Inhibitor as a Promising Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of Hypertension. Machauer, R; Lueoend, R; Hurth, K; Veenstra, SJ; Rueeger, H; Voegtle, M; Tintelnot-Blomley, M; Rondeau, JM; Jacobson, LH; Laue, G; Beltz, K; Neumann, U Discovery of Umibecestat (CNP520): A Potent, Selective, and Efficacious β-Secretase (BACE1) Inhibitor for the Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease. J Med Chem 64: 15262 -15279 (2021) Gu, H; Zhang, T; Guan, T; Wu, M; Li, S; Li, Y; Guo, M; Zhang, L; Peng, Y; Mi, D; Liu, M; Yi, Z; Chen, Y Discovery of a Highly Potent and Selective MYOF Inhibitor with Improved Water Solubility for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. J Med Chem 66: 16917 -16938 (2023) Discovery of a Novel and Potent Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 8/19 (CDK8/19) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Cancer. Wang, Z; Zhang, M; Quereda, V; Frydman, SM; Ming, Q; Luca, VC; Duckett, DR; Ji, H Discovery of an Orally Bioavailable Small-Molecule Inhibitor for the β-Catenin/B-Cell Lymphoma 9 Protein-Protein Interaction. J Med Chem 64: 12109 -12131 (2021) Discovery of novel, potent, selective and orally bioavailable HPK1 inhibitor for enhancing the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 antibody. Day, JP; Lindsay, B; Riddell, T; Jiang, Z; Allcock, RW; Abraham, A; Sookup, S; Christian, F; Bogum, J; Martin, EK; Rae, RL; Anthony, D; Rosair, GM; Houslay, DM; Huston, E; Baillie, GS; Klussmann, E; Houslay, MD; Adams, DR Elucidation of a structural basis for the inhibitor-driven, p62 (SQSTM1)-dependent intracellular redistribution of cAMP phosphodiesterase-4A4 (PDE4A4). J Med Chem 54: 3331 -47 (2011) Giannetti, AM; Wong, H; Dijkgraaf, GJ; Dueber, EC; Ortwine, DF; Bravo, BJ; Gould, SE; Plise, EG; Lum, BL; Malhi, V; Graham, RA Identification, characterization, and implications of species-dependent plasma protein binding for the oral Hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449). J Med Chem 54: 2592 -601 (2011) Kapková, P; Heller, E; Unger, M; Folkers, G; Holzgrabe, U Random chemistry as a new tool for the generation of small compound libraries: development of a new acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. J Med Chem 48: 7496 -9 (2005) Lund, BA; Christopeit, T; Guttormsen, Y; Bayer, A; Leiros, HK Screening and Design of Inhibitor Scaffolds for the Antibiotic Resistance Oxacillinase-48 (OXA-48) through Surface Plasmon Resonance Screening. J Med Chem 59: 5542 -54 (2016) Fiorito, J; Saeed, F; Zhang, H; Staniszewski, A; Feng, Y; Francis, YI; Rao, S; Thakkar, DM; Deng, SX; Landry, DW; Arancio, O Synthesis of quinoline derivatives: discovery of a potent and selective phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Med Chem 60: 285 -94 (2013) Hammock, BD; McReynolds, CB; Wagner, K; Buckpitt, A; Cortes-Puch, I; Croston, G; Lee, KSS; Yang, J; Schmidt, WK; Hwang, SH Movement to the Clinic of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor EC5026 as an Analgesic for Neuropathic Pain and for Use as a Nonaddictive Opioid Alternative. J Med Chem 64: 1856 -1872 (2021) Qian, WJ; Park, JE; Lee, KS; Burke, TR Non-proteinogenic amino acids in the pThr-2 position of a pentamer peptide that confer high binding affinity for the polo box domain (PBD) of polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 7306 -8 (2012) Skucas, E; Liu, KG; Kim, J; Poyurovsky, MV; Mo, R Inhibitors of RHO associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase US Patent US11613531 (2023) Skucas, E; Liu, KG; Kim, J; Poyurovsky, MV; Mo, R; Zhang, J Inhibitors of Rho associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase US Patent US11479533 (2022) Suzuki, T; Asaba, T; Imai, E; Tsumoto, H; Nakagawa, H; Miyata, N Identification of a cell-active non-peptide sirtuin inhibitor containing N-thioacetyl lysine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 5670 -2 (2009) Passioura, T; Bhushan, B; Tumber, A; Kawamura, A; Suga, H Structure-activity studies of a macrocyclic peptide inhibitor of histone lysine demethylase 4A. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 1225 -1231 (2018) Viswanath, V; Beard, RL; Donello, JE; Hsia, E Use of agonists of formyl peptide receptor 2 for treating dermatological diseases US Patent US10799518 (2020) Di Micco, S; Rahimova, R; Sala, M; Scala, MC; Vivenzio, G; Musella, S; Andrei, G; Remans, K; Mammri, L; Snoeck, R; Bifulco, G; Di Matteo, F; Vestuto, V; Campiglia, P; Márquez, JA; Fasano, A Rational design of the zonulin inhibitor AT1001 derivatives as potential anti SARS-CoV-2. Eur J Med Chem 244: (2022) Dickinson, RP; Dack, KN; Steele, J; Tute, MS Thromboxane modulating agents. 2. Thromboxane receptor antagonists derived from the thromboxane synthase inhibitor dazmegrel. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 6: 1691 -1696 (1996) Proulx, C; Picard, É; Boeglin, D; Pohankova, P; Chemtob, S; Ong, H; Lubell, WD Azapeptide analogues of the growth hormone releasing peptide 6 as cluster of differentiation 36 receptor ligands with reduced affinity for the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a. J Med Chem 55: 6502 -11 (2012) Jacobsson, E; Peigneur, S; Andersson, HS; Laborde, Q; Strand, M; Tytgat, J; Göransson, U Functional Characterization of the Nemertide α Family of Peptide Toxins. J Nat Prod 84: 2121 -2128 (2021) Lynagh, T; Kiontke, S; Meyhoff-Madsen, M; Gless, BH; Johannesen, J; Kattelmann, S; Christiansen, A; Dufva, M; Laustsen, AH; Devkota, K; Olsen, CA; Kümmel, D; Pless, SA; Lohse, B Peptide Inhibitors of the α-Cobratoxin-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Interaction. J Med Chem 63: 13709 -13718 (2020) Einsiedel, J; Hübner, H; Hervet, M; Härterich, S; Koschatzky, S; Gmeiner, P Peptide backbone modifications on the C-terminal hexapeptide of neurotensin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 2013 -8 (2008) Llinàs-Brunet, M; Bailey, M; Fazal, G; Goulet, S; Halmos, T; Laplante, S; Maurice, R; Poirier, M; Poupart, MA; Thibeault, D; Wernic, D; Lamarre, D Peptide-based inhibitors of the hepatitis C virus serine protease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8: 1713 -8 (1999) Steel, RJ; O'Connell, MA; Searcey, M Perfluoroarene-based peptide macrocycles that inhibit the Nrf2/Keap1 interaction. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 2728 -2731 (2018) Sgrignani, J; Cecchinato, V; Fassi, EMA; D'Agostino, G; Garofalo, M; Danelon, G; Pedotti, M; Simonelli, L; Varani, L; Grazioso, G; Uguccioni, M; Cavalli, A Systematic Development of Peptide Inhibitors Targeting the CXCL12/HMGB1 Interaction. J Med Chem 64: 13439 -13450 (2021) Chen, C; Li, H; Long, YQ GPR40 agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: The biological characteristics and the chemical space. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 5603 -5612 (2016) Expanding the ligand spaces for E3 ligases for the design of protein degraders. Li, X; Craven, TW; Levine, PM Cyclic Peptide Screening Methods for Preclinical Drug Discovery. J Med Chem 65: 11913 -11926 (2022) Dziadulewicz, EK; Brown, MC; Dunstan, AR; Lee, W; Said, NB; Garratt, PJ The design of non-peptide human bradykinin B2 receptor antagonists employing the benzodiazepine peptidomimetic scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 463 -8 (1999) Riggs, JR; Nagy, M; Elsner, J; Erdman, P; Cashion, D; Robinson, D; Harris, R; Huang, D; Tehrani, L; Deyanat-Yazdi, G; Narla, RK; Peng, X; Tran, T; Barnes, L; Miller, T; Katz, J; Tang, Y; Chen, M; Moghaddam, MF; Bahmanyar, S; Pagarigan, B; Delker, S; LeBrun, L; Chamberlain, PP; Calabrese, A; Canan, SS; Leftheris, K; Zhu, D; Boylan, JF The Discovery of a Dual TTK Protein Kinase/CDC2-Like Kinase (CLK2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Initiated from a Phenotypic Screen. J Med Chem 60: 8989 -9002 (2017) Smil, DV; Souza, FE; Fallis, AG A general carbometalation, three component coupling strategy for the synthesis of alpha,beta-unsaturated gamma-sultines including thio-rofecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 2057 -60 (2005) Sato, T; Ashizawa, N; Matsumoto, K; Iwanaga, T; Nakamura, H; Inoue, T; Nagata, O Discovery of 3-(2-cyano-4-pyridyl)-5-(4-pyridyl)-1,2,4-triazole, FYX-051 - a xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor for the treatment of hyperuricemia [corrected] Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 6225 -9 (2009) Zhou, B; Liang, X; Mei, H; Qi, S; Jiang, Z; Wang, A; Zou, F; Liu, Q; Liu, J; Wang, W; Hu, C; Chen, Y; Wang, Z; Wang, B; Wang, L; Liu, J; Liu, Q Discovery of IHMT-EZH2-115 as a Potent and Selective Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) Inhibitor for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphomas. J Med Chem 64: 15170 -15188 (2021) Zhou, Z; Zalutsky, MR; Chitneni, SK Stapled peptides as scaffolds for developing radiotracers for intracellular targets: Preliminary evaluation of a radioiodinated MDM2-binding stapled peptide in the SJSA-1 osteosarcoma model. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 66: (2022) DeRatt, LG; Christine Pietsch, E; Tanner, A; Shaffer, P; Jacoby, E; Wang, W; Kazmi, F; Zhang, X; Attar, RM; Edwards, JP; Kuduk, SD A carboxylic acid isostere screen of the DHODH inhibitor Brequinar. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30: (2020) BAY-9835: Discovery of the First Orally Bioavailable ADAMTS7 Inhibitor. CRYSTALLINE FORMS OF AN INHIBITOR OF THE MENIN/MLL INTERACTION Ferguson, FM; Doctor, ZM; Chaikuad, A; Sim, T; Kim, ND; Knapp, S; Gray, NS Characterization of a highly selective inhibitor of the Aurora kinases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4405 -4408 (2017) Girnys, EA; Porter, VR; Mosberg, HI Conformationally restricted analogs of the direct thrombin inhibitor FM 19. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 7425 -34 (2011) Vaz, RJ; Li, Y; Metz, M; Yang, D; Shen, H; Munson, M Decreasing the CYP2D6 contribution to metabolism of a CK1ε inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 3681 -3684 (2018) Werner, S; Mesch, S; Hillig, RC; Ter Laak, A; Klint, J; Neagoe, I; Laux-Biehlmann, A; Dahllöf, H; Bräuer, N; Puetter, V; Nubbemeyer, R; Schulz, S; Bairlein, M; Zollner, TM; Steinmeyer, A Discovery and Characterization of the Potent and Selective P2X4 Inhibitor J Med Chem 62: 11194 -11217 (2019) Chowdhury, SF; Joseph, L; Kumar, S; Tulsidas, SR; Bhat, S; Ziomek, E; Ménard, R; Sivaraman, J; Purisima, EO Exploring inhibitor binding at the s' subsites of cathepsin L. J Med Chem 51: 1361 -8 (2008) Abbott, BM; Thompson, PE PDE2 inhibition by the PI3 kinase inhibitor LY294002 and analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 2847 -51 (2004) Bedingfield, PT; Cowen, D; Acklam, P; Cunningham, F; Parsons, MR; McConkey, GA; Fishwick, CW; Johnson, AP Factors influencing the specificity of inhibitor binding to the human and malaria parasite dihydroorotate dehydrogenases. J Med Chem 55: 5841 -50 (2012) Gademann, K; Portmann, C; Blom, JF; Zeder, M; Jüttner, F Multiple toxin production in the cyanobacterium microcystis: isolation of the toxic protease inhibitor cyanopeptolin 1020. J Nat Prod 73: 980 -4 (2010) Jorda, R; Krajčovičová, S; Králová, P; Soural, M; Kryštof, V Scaffold hopping of the SYK inhibitor entospletinib leads to broader targeting of the BCR signalosome. Eur J Med Chem 204: (2020) Schrøder, TJ; Christensen, S; Lindberg, S; Langgård, M; David, L; Maltas, PJ; Eskildsen, J; Jacobsen, J; Tagmose, L; Simonsen, KB; Biilmann Rønn, LC; de Jong, IE; Malik, IJ; Karlsson, JJ; Bundgaard, C; Egebjerg, J; Stavenhagen, JB; Strandbygård, D; Thirup, S; Andersen, JL; Uppalanchi, S; Pervaram, S; Kasturi, SP; Eradi, P; Sakumudi, DR; Watson, SP The identification of AF38469: an orally bioavailable inhibitor of the VPS10P family sorting receptor Sortilin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 177 -80 (2013) Heyl, DL; Dandabathula, M; Kurtz, KR; Mousigian, C Opioid receptor binding requirements for the delta-selective peptide deltorphin. I: Phe3 replacement with ring-substituted and heterocyclic amino acids. J Med Chem 38: 1242 -6 (1995) Selvaraj, R; Liu, S; Hassink, M; Huang, CW; Yap, LP; Park, R; Fox, JM; Li, Z; Conti, PS Tetrazine-trans-cyclooctene ligation for the rapid construction of integrinavß3 targeted PET tracer based on a cyclic RGD peptide. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 5011 -4 (2011) Miranda, LP; Holder, JR; Shi, L; Bennett, B; Aral, J; Gegg, CV; Wright, M; Walker, K; Doellgast, G; Rogers, R; Li, H; Valladares, V; Salyers, K; Johnson, E; Wild, K Identification of potent, selective, and metabolically stable peptide antagonists to the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor. J Med Chem 51: 7889 -97 (2008) Gebauer, S; Knütter, I; Hartrodt, B; Brandsch, M; Neubert, K; Thondorf, I Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analyses of peptide substrates of the mammalian H+/peptide cotransporter PEPT1. J Med Chem 46: 5725 -34 (2003) Ochiiwa, H; Hirai, H Antitumor drug for intermittent administration of FGFR inhibitor US Patent US10894048 (2021) Assadieskandar, A; Yu, C; Maisonneuve, P; Kurinov, I; Sicheri, F; Zhang, C Rigidification Dramatically Improves Inhibitor Selectivity for RAF Kinases. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1074 -1080 (2019) Nichols, RJ; Goldsmith, MA; Schulze, C; Smith, J; Wildes, DE; Kelsey, S; Singh, M SHP2 inhibitor compositions and methods for treating cancer US Patent US11596633 (2023) Yang, LL; Wang, HL; Yan, YH; Liu, S; Yu, ZJ; Huang, MY; Luo, Y; Zheng, X; Yu, Y; Li, GB Sensitive fluorogenic substrates for sirtuin deacylase inhibitor discovery. Eur J Med Chem 192: (2020) Thomsen, AE; Friedrichsen, GM; Sørensen, AH; Andersen, R; Nielsen, CU; Brodin, B; Begtrup, M; Frokjaer, S; Steffansen, B Prodrugs of purine and pyrimidine analogues for the intestinal di/tri-peptide transporter PepT1: affinity for hPepT1 in Caco-2 cells, drug release in aqueous media and in vitro metabolism. J Control Release 86: 279 -92 (2003) He, Y; Liu, S; Menon, A; Stanford, S; Oppong, E; Gunawan, AM; Wu, L; Wu, DJ; Barrios, AM; Bottini, N; Cato, AC; Zhang, ZY A potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor for the lymphoid-specific tyrosine phosphatase (LYP), a target associated with autoimmune diseases. J Med Chem 56: 4990 -5008 (2013) Donnell, AF; Michoud, C; Rupert, KC; Han, X; Aguilar, D; Frank, KB; Fretland, AJ; Gao, L; Goggin, B; Hogg, JH; Hong, K; Janson, CA; Kester, RF; Kong, N; Le, K; Li, S; Liang, W; Lombardo, LJ; Lou, Y; Lukacs, CM; Mischke, S; Moliterni, JA; Polonskaia, A; Schutt, AD; Solis, DS; Specian, A; Taylor, RT; Weisel, M; Remiszewski, SW Benzazepinones and benzoxazepinones as antagonists of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) selective for the second baculovirus IAP repeat (BIR2) domain. J Med Chem 56: 7772 -87 (2013) Discovery and Preclinical Characterization of BIIB129, a Covalent, Selective, and Brain-Penetrant BTK Inhibitor for the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Hu, Y; Sun, F; Yuan, Q; Du, J; Hu, L; Gu, Z; Zhou, Q; Du, X; He, S; Sun, Y; Wang, Q; Fan, L; Wang, L; Qin, S; Chen, S; Li, J; Wu, W; Mao, J; Zhou, Y; Zhou, Q; Zhang, G; Ding, CZ Discovery and preclinical evaluations of GST-HG131, a novel HBV antigen inhibitor for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 75: (2022) Li, Z; Wang, X; Eksterowicz, J; Gribble, MW; Alba, GQ; Ayres, M; Carlson, TJ; Chen, A; Chen, X; Cho, R; Connors, RV; DeGraffenreid, M; Deignan, JT; Duquette, J; Fan, P; Fisher, B; Fu, J; Huard, JN; Kaizerman, J; Keegan, KS; Li, C; Li, K; Li, Y; Liang, L; Liu, W; Lively, SE; Lo, MC; Ma, J; McMinn, DL; Mihalic, JT; Modi, K; Ngo, R; Pattabiraman, K; Piper, DE; Queva, C; Ragains, ML; Suchomel, J; Thibault, S; Walker, N; Wang, X; Wang, Z; Wanska, M; Wehn, PM; Weidner, MF; Zhang, AJ; Zhao, X; Kamb, A; Wickramasinghe, D; Dai, K; McGee, LR; Medina, JC Discovery of AMG 925, a FLT3 and CDK4 dual kinase inhibitor with preferential affinity for the activated state of FLT3. J Med Chem 57: 3430 -49 (2014) Gallant, M; Aspiotis, R; Day, S; Dias, R; Dubé, D; Dubé, L; Friesen, RW; Girard, M; Guay, D; Hamel, P; Huang, Z; Lacombe, P; Laliberté, S; Lévesque, JF; Liu, S; Macdonald, D; Mancini, J; Nicholson, DW; Styhler, A; Townson, K; Waters, K; Young, RN; Girard, Y Discovery of MK-0952, a selective PDE4 inhibitor for the treatment of long-term memory loss and mild cognitive impairment. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 6387 -93 (2010) Kattar, SD; Gulati, A; Margrey, KA; Keylor, MH; Ardolino, M; Yan, X; Johnson, R; Palte, RL; McMinn, SE; Nogle, L; Su, J; Xiao, D; Piesvaux, J; Lee, S; Hegde, LG; Woodhouse, JD; Faltus, R; Moy, LY; Xiong, T; Ciaccio, PJ; Pearson, K; Patel, M; Otte, KM; Leyns, CEG; Kennedy, ME; Bennett, DJ; DiMauro, EF; Fell, MJ; Fuller, PH Discovery of MK-1468: A Potent, Kinome-Selective, Brain-Penetrant Amidoisoquinoline LRRK2 Inhibitor for the Potential Treatment of Parkinson's Disease. J Med Chem 66: 14912 -14927 (2023) Schenck Eidam, H; Russell, J; Raha, K; DeMartino, M; Qin, D; Guan, HA; Zhang, Z; Zhen, G; Yu, H; Wu, C; Pan, Y; Joberty, G; Zinn, N; Laquerre, S; Robinson, S; White, A; Giddings, A; Mohammadi, E; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B; Oliff, A; Kumar, S; Cheung, M Discovery of a First-in-Class Gut-Restricted RET Kinase Inhibitor as a Clinical Candidate for the Treatment of IBS. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 623 -628 (2018) Boras, B; Jones, RM; Anson, BJ; Arenson, D; Aschenbrenner, L; Bakowski, MA; Beutler, N; Binder, J; Chen, E; Eng, H; Hammond, J; Hoffman, R; Kadar, EP; Kania, R; Kimoto, E; Kirkpatrick, MG; Lanyon, L; Lendy, EK; Lillis, JR; Luthra, SA; Ma, C; Noell, S; Obach, RS; O Brien, MN; O Connor, R; Ogilvie, K; Owen, D; Pettersson, M; Reese, MR; Rogers, T; Rossulek, MI; Sathish, JG; Steppan, C; Ticehurst, M; Updyke, LW; Zhu, Y; Wang, J; Chatterjee, AK; Mesecar, AD; Anderson, AS; Allerton, C Discovery of a Novel Inhibitor of Coronavirus 3CL Protease as a Clinical Candidate for the Potential Treatment of COVID-19. bioRxiv (2020) Zhu, G; Li, J; Lin, X; Zhang, Z; Hu, T; Huo, S; Li, Y Discovery of a Novel Ketohexokinase Inhibitor with Improved Drug Distribution in Target Tissue for the Treatment of Fructose Metabolic Disease. J Med Chem 66: 13501 -13515 (2023) Zimmermann, TJ; Niesen, FH; Pilka, ES; Knapp, S; Oppermann, U; Maier, ME Discovery of a potent and selective inhibitor for human carbonyl reductase 1 from propionate scanning applied to the macrolide zearalenone. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 530 -6 (2009) Shiraga, T; Yajima, K; Suzuki, K; Suzuki, K; Hashimoto, T; Iwatsubo, T; Miyashita, A; Usui, T Identification of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases responsible for the glucuronidation of darexaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor, in human liver and intestine. Drug Metab Dispos 40: 276 -82 (2012) Chakraborty, S; Shah, NH; Fishbein, JC; Hosmane, RS Investigations into specificity of azepinomycin for inhibition of guanase: discrimination between the natural heterocyclic inhibitor and its synthetic nucleoside analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 7214 -8 (2012) Boyle, CD; Xu, R; Asberom, T; Chackalamannil, S; Clader, JW; Greenlee, WJ; Guzik, H; Hu, Y; Hu, Z; Lankin, CM; Pissarnitski, DA; Stamford, AW; Wang, Y; Skell, J; Kurowski, S; Vemulapalli, S; Palamanda, J; Chintala, M; Wu, P; Myers, J; Wang, P Optimization of purine based PDE1/PDE5 inhibitors to a potent and selective PDE5 inhibitor for the treatment of male ED. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 2365 -9 (2005) Research progress on small molecule inhibitors targeting KRAS G12C with acrylamide structure and the strategies for solving KRAS inhibitor resistance. Pissarnitski, DA; Asberom, T; Boyle, CD; Chackalamannil, S; Chintala, M; Clader, JW; Greenlee, WJ; Hu, Y; Kurowski, S; Myers, J; Palamanda, J; Stamford, AW; Vemulapalli, S; Wang, Y; Wang, P; Wu, P; Xu, R SAR development of polycyclic guanine derivatives targeted to the discovery of a selective PDE5 inhibitor for treatment of erectile dysfunction. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 1291 -4 (2004) Turdi, H; Chao, H; Hangeland, JJ; Ahmad, S; Meng, W; Brigance, R; Zhao, G; Wang, W; Moore, F; Ye, XY; Mathur, A; Hou, X; Kempson, J; Wu, DR; Li, YX; Azzara, AV; Ma, Z; Chu, CH; Chen, L; Cullen, MJ; Rooney, S; Harvey, S; Kopcho, L; Panemangelor, R; Abell, L; O'Malley, K; Keim, WJ; Dierks, E; Chang, S; Foster, K; Apedo, A; Harden, D; Dabros, M; Gao, Q; Pelleymounter, MA; Whaley, JM; Robl, JA; Cheng, D; Lawrence, RM; Devasthale, P Screening Hit to Clinical Candidate: Discovery of BMS-963272, a Potent, Selective MGAT2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Metabolic Disorders. J Med Chem 64: 14773 -14792 (2021) Oh, C; Kim, H; Kang, JS; Yun, J; Sim, J; Kim, HM; Han, G Synthetic strategy for increasing solubility of potential FLT3 inhibitor thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine derivatives through structural modifications at the C Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 496 -500 (2017) Pooput, C; Rosemond, E; Karpiak, J; Deflorian, F; Vilar, S; Costanzi, S; Wess, J; Kirk, KL Structural basis of the selectivity of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor for fluorinated catecholamines. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 7987 -92 (2009) Abdel-Magid, AF Targeting the Inhibition of B-Cell Lymphoma 2 Protein for the Treatment of Cancer. ACS Med Chem Lett 14: 1320 -1322 (2023) Ma, BB; Montgomery, AP; Chen, B; Kassiou, M; Danon, JJ Strategies for targeting the P2Y Bioorg Med Chem Lett 71: (2022) Canzoneri, JC; Chen, PC; Oyelere, AK Design and synthesis of novel histone deacetylase inhibitor derived from nuclear localization signal peptide. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 6588 -90 (2009) Hines, AC; Cole, PA Design, synthesis, and characterization of an ATP-peptide conjugate inhibitor of protein kinase A. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 2951 -4 (2004) Egbertson, M; Naylor, A; Hartman, G; Cook, J; Gould, R; Holahan, M; Lynch, J; Lynch, R; Stranieri, M; Vassallo, L Non-peptide fibrinogen receptor antagonists. 3. design and discovery of a centrally constrained inhibitor Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 1835 -1840 (1994) Middendorp, SJ; Wilbs, J; Quarroz, C; Calzavarini, S; Angelillo-Scherrer, A; Heinis, C Peptide Macrocycle Inhibitor of Coagulation Factor XII with Subnanomolar Affinity and High Target Selectivity. J Med Chem 60: 1151 -1158 (2017) Goodman, KB; Cui, H; Dowdell, SE; Gaitanopoulos, DE; Ivy, RL; Sehon, CA; Stavenger, RA; Wang, GZ; Viet, AQ; Xu, W; Ye, G; Semus, SF; Evans, C; Fries, HE; Jolivette, LJ; Kirkpatrick, RB; Dul, E; Khandekar, SS; Yi, T; Jung, DK; Wright, LL; Smith, GK; Behm, DJ; Bentley, R; Doe, CP; Hu, E; Lee, D Development of dihydropyridone indazole amides as selective rho-kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem 50: 6 -9 (2007) Kesar, S; Paliwal, S; Mishra, P; Madan, K; Chauhan, M; Chauhan, N; Verma, K; Sharma, S Identification of Novel Rho-Kinase-II Inhibitors with Vasodilatory Activity. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1694 -1703 (2020) Doe, C; Bentley, R; Behm, DJ; Lafferty, R; Stavenger, R; Jung, D; Bamford, M; Panchal, T; Grygielko, E; Wright, LL; Smith, GK; Chen, Z; Webb, C; Khandekar, S; Yi, T; Kirkpatrick, R; Dul, E; Jolivette, L; Marino, JP; Willette, R; Lee, D; Hu, E Novel Rho kinase inhibitors with anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory activities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320: 89 -98 (2006) Fang, X; Yin, Y; Chen, YT; Yao, L; Wang, B; Cameron, MD; Lin, L; Khan, S; Ruiz, C; Schröter, T; Grant, W; Weiser, A; Pocas, J; Pachori, A; Schürer, S; Lograsso, P; Feng, Y Tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives as highly selective and potent Rho kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem 53: 5727 -37 (2010) Beard, RL; Donello, JE; Viswanath, V Use of agonists of formyl peptide receptor 2 for treating ocular inflammatory diseases US Patent US10208071 (2019) Robinson, DA; Stewart, KA; Price, NC; Chalk, PA; Coggins, JR; Lapthorn, AJ Crystal structures of Helicobacter pylori type II dehydroquinase inhibitor complexes: new directions for inhibitor design. J Med Chem 49: 1282 -90 (2006) Pratt, DJ; Bentley, J; Jewsbury, P; Boyle, FT; Endicott, JA; Noble, ME Dissecting the determinants of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor selectivity. J Med Chem 49: 5470 -7 (2006) Cheng, XR; Zhou, JW; Zhou, Y; Cheng, JP; Yang, RF; Zhou, WX; Zhang, YX; Yun, LH The green tea polyphenol (2)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is not aß-secretase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 1408 -14 (2012) Katzman, BM; Cox, BD; Prosser, AR; Alcaraz, AA; Murat, B; Héroux, M; Tebben, A; Zhang, Y; Schroeder, GM; Snyder, JP; Wilson, LJ; Liotta, DC Tetrahydroisoquinoline CXCR4 Antagonists Adopt a Hybrid Binding Mode within the Peptide Subpocket of the CXCR4 Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 67 -73 (2019) Qiu, W; Zhou, M; Mazumdar, M; Azzi, A; Ghanmi, D; Luu-The, V; Labrie, F; Lin, SX Structure-based inhibitor design for an enzyme that binds different steroids: a potent inhibitor for human type 5 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 282: 8368 -79 (2007) Xu, P; Xu, M; Jiang, L; Yang, Q; Luo, Z; Dauter, Z; Huang, M; Andreasen, PA Design of Specific Serine Protease Inhibitors Based on a Versatile Peptide Scaffold: Conversion of a Urokinase Inhibitor to a Plasma Kallikrein Inhibitor. J Med Chem 58: 8868 -76 (2015) Pak, VV; Koo, M; Kwon, DY; Shakhidoyatov, KM; Yun, L Peptide fragmentation as an approach in modeling of an active peptide and designing a competitive inhibitory peptide for HMG-CoA reductase. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 4300 -9 (2010) Azuma, M; Inoue, M; Nishida, A; Akahane, H; Kitajima, M; Natani, S; Chimori, R; Yoshimori, A; Mano, Y; Uchiro, H; Tanuma, SI; Takasawa, R Addition of hydrophobic side chains improve the apoptosis inducibility of the human glyoxalase I inhibitor, TLSC702. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 40: (2021) Lefas, G; Chaconas, G High-throughput screening identifies three inhibitor classes of the telomere resolvase from the lyme disease spirochete. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53: 4441 -9 (2009) Jarvest, RL; Breen, AL; Edge, CM; Chaikin, MA; Jennings, LJ; Truneh, A; Sweet, RW; Hertzberg, RP Structure-directed discovery of an inhibitor of the binding of HIV GP120 to the CD4 receptor Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 2851 -2856 (1993) Sham, HL; Betebenner, DA; Herrin, T; Kumar, G; Saldivar, A; Vasavanonda, S; Molla, A; Kempf, DJ; Plattner, JJ; Norbeck, DW Synthesis and antiviral activities of the major metabolites of the HIV protease inhibitor ABT-378 (Lopinavir). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1351 -3 (2001) de Lera Ruiz, M; Favuzza, P; Guo, Z; Zhao, L; Hu, B; Lei, Z; Zhan, D; Murgolo, N; Boyce, CW; Vavrek, M; Thompson, J; Ngo, A; Jarman, KE; Robbins, J; Boddey, J; Sleebs, BE; Lowes, KN; Cowman, AF; Olsen, DB; McCauley, JA The Invention of WM382, a Highly Potent PMIX/X Dual Inhibitor toward the Treatment of Malaria. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 1745 -1754 (2022) Xue, H; Guo, Y; Wang, Z BCL-2 Inhibitor US Patent US20240376097 (2024) Aeed, PA; Young, CL; Nagiec, MM; Elhammer, AP Inhibition of inositol phosphorylceramide synthase by the cyclic peptide aureobasidin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53: 496 -504 (2009) Giuliani, G; Cappelli, A; Matarrese, M; Masiello, V; Turolla, EA; Monterisi, C; Fazio, F; Anzini, M; Pericot Mohr, G; Riitano, D; Finetti, F; Morbidelli, L; Ziche, M; Giorgi, G; Vomero, S Non-peptide NK1 receptor ligands based on the 4-phenylpyridine moiety. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 2242 -51 (2011) Talma, M; Maślanka, M; Mucha, A Recent developments in the synthesis and applications of phosphinic peptide analogs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 1031 -1042 (2019) Joshi, AA; Murray, TF; Aldrich, JV Structure-Activity Relationships of the Peptide Kappa Opioid Receptor Antagonist Zyklophin. J Med Chem 58: 8783 -95 (2015) Neve, J; Leone, PA; Carroll, AR; Moni, RW; Paczkowski, NJ; Pierens, G; Björquist, P; Deinum, J; Ehnebom, J; Inghardt, T; Guymer, G; Grimshaw, P; Quinn, RJ Sideroxylonal C, a new inhibitor of human plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1, from the flowers of Eucalyptus albens. J Nat Prod 62: 324 -6 (1999) Small molecule inhibitor screen identifies synergistic activity of the bromodomain inhibitor CPI203 and bortezomib in drug resistant myeloma. Luz, JG; Antonysamy, S; Kuklish, SL; Condon, B; Lee, MR; Allison, D; Yu, XP; Chandrasekhar, S; Backer, R; Zhang, A; Russell, M; Chang, SS; Harvey, A; Sloan, AV; Fisher, MJ Crystal Structures of mPGES-1 Inhibitor Complexes Form a Basis for the Rational Design of Potent Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutics. J Med Chem 58: 4727 -37 (2015) Ardecky, RJ; Welsh, K; Finlay, D; Lee, PS; González-López, M; Ganji, SR; Ravanan, P; Mace, PD; Riedl, SJ; Vuori, K; Reed, JC; Cosford, ND Design, synthesis and evaluation of inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) antagonists that are highly selective for the BIR2 domain of XIAP. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 4253 -7 (2013) Arhancet, GB; Walker, DP; Metz, S; Fobian, YM; Heasley, SE; Carter, JS; Springer, JR; Jones, DE; Hayes, MJ; Shaffer, AF; Jerome, GM; Baratta, MT; Zweifel, B; Moore, WM; Masferrer, JL; Vazquez, ML Discovery and SAR of PF-4693627, a potent, selective and orally bioavailable mPGES-1 inhibitor for the potential treatment of inflammation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 1114 -9 (2013) Sun, LQ; Mull, E; D'Andrea, S; Zheng, B; Hiebert, S; Gillis, E; Bowsher, M; Kandhasamy, S; Baratam, VR; Puttaswamy, S; Pulicharla, N; Vishwakrishnan, S; Reddy, S; Trivedi, R; Sinha, S; Sivaprasad, S; Rao, A; Desai, S; Ghosh, K; Anumula, R; Kumar, A; Rajamani, R; Wang, YK; Fang, H; Mathur, A; Rampulla, R; Zvyaga, TA; Mosure, K; Jenkins, S; Falk, P; Tagore, DM; Chen, C; Rendunchintala, K; Loy, J; Meanwell, NA; McPhee, F; Scola, PM Discovery of BMS-986144, a Third-Generation, Pan-Genotype NS3/4A Protease Inhibitor for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. J Med Chem 63: 14740 -14760 (2020) Peixoto, C; Joncour, A; Temal-Laib, T; Tirera, A; Dos Santos, A; Jary, H; Bucher, D; Laenen, W; Pereira Fernandes, A; Lavazais, S; Delachaume, C; Merciris, D; Saccomani, C; Drennan, M; López-Ramos, M; Wakselman, E; Dupont, S; Borgonovi, M; Roca Magadan, C; Monjardet, A; Brys, R; De Vos, S; Andrews, M; Jimenez, JM; Amantini, D; Desroy, N Discovery of Clinical Candidate GLPG3970: A Potent and Selective Dual SIK2/SIK3 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. J Med Chem 67: 5233 -5258 (2024) Caldwell, RD; Qiu, H; Askew, BC; Bender, AT; Brugger, N; Camps, M; Dhanabal, M; Dutt, V; Eichhorn, T; Gardberg, AS; Goutopoulos, A; Grenningloh, R; Head, J; Healey, B; Hodous, BL; Huck, BR; Johnson, TL; Jones, C; Jones, RC; Mochalkin, I; Morandi, F; Nguyen, N; Meyring, M; Potnick, JR; Santos, DC; Schmidt, R; Sherer, B; Shutes, A; Urbahns, K; Follis, AV; Wegener, AA; Zimmerli, SC; Liu-Bujalski, L Discovery of Evobrutinib: An Oral, Potent, and Highly Selective, Covalent Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Immunological Diseases. J Med Chem 62: 7643 -7655 (2019) Discovery of Preclinical Candidate AD1058 as a Highly Potent, Selective, and Brain-Penetrant ATR Inhibitor for the Treatment of Advanced Malignancies. Huang, PQ; Boren, BC; Hegde, SG; Liu, H; Unni, AK; Abraham, S; Hopkins, CD; Paliwal, S; Samatar, AA; Li, J; Bunker, KD Discovery of ZN-c3, a Highly Potent and Selective Wee1 Inhibitor Undergoing Evaluation in Clinical Trials for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 64: 13004 -13024 (2021) Ha, HJ; Kang, DW; Kim, HM; Kang, JM; Ann, J; Hyun, HJ; Lee, JH; Kim, SH; Kim, H; Choi, K; Hong, HS; Kim, Y; Jo, DG; Lee, J; Lee, J Discovery of an Orally Bioavailable Benzofuran Analogue That Serves as aβ-Amyloid Aggregation Inhibitor for the Potential Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. J Med Chem 61: 396 -402 (2018) Mikami, S; Sasaki, S; Asano, Y; Ujikawa, O; Fukumoto, S; Nakashima, K; Oki, H; Kamiguchi, N; Imada, H; Iwashita, H; Taniguchi, T Discovery of an Orally Bioavailable, Brain-Penetrating, in Vivo Active Phosphodiesterase 2A Inhibitor Lead Series for the Treatment of Cognitive Disorders. J Med Chem 60: 7658 -7676 (2017) Gabr, MT; Brogi, S MicroRNA-Based Multitarget Approach for Alzheimer's Disease: Discovery of the First-In-Class Dual Inhibitor of Acetylcholinesterase and MicroRNA-15b Biogenesis. J Med Chem 63: 9695 -9704 (2020) Bagley, MC; Davis, T; Dix, MC; Murziani, PG; Rokicki, MJ; Kipling, D Microwave-assisted synthesis of 5-aminopyrazol-4-yl ketones and the p38(MAPK) inhibitor RO3201195 for study in Werner syndrome cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 3745 -8 (2008) Isaacs, RC; Solinsky, MG; Cutrona, KJ; Newton, CL; Naylor-Olsen, AM; Krueger, JA; Lewis, SD; Lucas, BJ Structure-based design of novel groups for use in the P1 position of thrombin inhibitor scaffolds. Part 1: Weakly basic azoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 338 -42 (2005) Tilley, AJ; Zanatta, SD; Qin, CX; Kim, IK; Seok, YM; Stewart, A; Woodman, OL; Williams, SJ 2-Morpholinoisoflav-3-enes as flexible intermediates in the synthesis of phenoxodiol, isophenoxodiol, equol and analogues: vasorelaxant properties, estrogen receptor binding and Rho/RhoA kinase pathway inhibition. Bioorg Med Chem 20: 2353 -61 (2012) Ullrich, T; Arista, L; Weiler, S; Teixeira-Fouchard, S; Broennimann, V; Stiefl, N; Head, V; Kramer, I; Guth, S Discovery of a novel 2-aminopyrazine-3-carboxamide as a potent and selective inhibitor of Activin Receptor-Like Kinase-2 (ALK2) for the treatment of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 64: (2022) Vankadara, S; Dawson, MD; Fong, JY; Oh, QY; Ang, QA; Liu, B; Chang, HY; Koh, J; Koh, X; Tan, QW; Joy, J; Chia, CSB A Warhead Substitution Study on the Coronavirus Main Protease Inhibitor Nirmatrelvir. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 1345 -1350 (2022) A selective jumonji H3K27 demethylase inhibitor modulates the proinflammatory macrophage response. Kodani, S; Ishida, K; Murakami, M Aeruginosin 103-A, a thrombin inhibitor from the cyanobacterium Microcystis viridis. J Nat Prod 61: 1046 -8 (1998) Qi, W; Zhao, K; Gu, J; Huang, Y; Wang, Y; Zhang, H; Zhang, M; Zhang, J; Yu, Z; Li, L; Teng, L; Chuai, S; Zhang, C; Zhao, M; Chan, H; Chen, Z; Fang, D; Fei, Q; Feng, L; Feng, L; Gao, Y; Ge, H; Ge, X; Li, G; Lingel, A; Lin, Y; Liu, Y; Luo, F; Shi, M; Wang, L; Wang, Z; Yu, Y; Zeng, J; Zeng, C; Zhang, L; Zhang, Q; Zhou, S; Oyang, C; Atadja, P; Li, E An allosteric PRC2 inhibitor targeting the H3K27me3 binding pocket of EED. Nat Chem Biol 13: 381 -388 (2017) Sabat, M; Dougan, DR; Knight, B; Lawson, JD; Scorah, N; Smith, CR; Taylor, ER; Vu, P; Wyrick, C; Wang, H; Balakrishna, D; Hixon, M; Madakamutil, L; McConn, D Discovery of the Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Clinical Candidate TAK-020 ( J Med Chem 64: 12893 -12902 (2021) Bhatia, S; Krieger, V; Groll, M; Osko, JD; Reßing, N; Ahlert, H; Borkhardt, A; Kurz, T; Christianson, DW; Hauer, J; Hansen, FK Discovery of the First-in-Class Dual Histone Deacetylase-Proteasome Inhibitor. J Med Chem 61: 10299 -10309 (2018) Discovery of the Potent and Selective ATR Inhibitor Camonsertib (RP-3500). Mori, M; Moraca, F; Deodato, D; Ferraris, DM; Selchow, P; Sander, P; Rizzi, M; Botta, M Discovery of the first potent and selective Mycobacterium tuberculosis Zmp1 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 2508 -11 (2014) Shi, J; Van de Water, R; Hong, K; Lamer, RB; Weichert, KW; Sandoval, CM; Kasibhatla, SR; Boehm, MF; Chao, J; Lundgren, K; Timple, N; Lough, R; Ibanez, G; Boykin, C; Burrows, FJ; Kehry, MR; Yun, TJ; Harning, EK; Ambrose, C; Thompson, J; Bixler, SA; Dunah, A; Snodgrass-Belt, P; Arndt, J; Enyedy, IJ; Li, P; Hong, VS; McKenzie, A; Biamonte, MA EC144 is a potent inhibitor of the heat shock protein 90. J Med Chem 55: 7786 -95 (2012) McCullough, BS; Wang, H; Barrios, AM Inhibitor Screen Identifies Covalent Inhibitors of the Protein Histidine Phosphatase PHPT1. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 1198 -1201 (2022) Firestine, SM; Wu, W; Youn, H; Davisson, VJ Interrogating the mechanism of a tight binding inhibitor of AIR carboxylase. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 794 -803 (2009) Kaiser, N; Corkery, D; Wu, Y; Laraia, L; Waldmann, H Modulation of autophagy by the novel mitochondrial complex I inhibitor Authipyrin. Bioorg Med Chem 27: 2444 -2448 (2019) Hsiao, CC; Rombouts, F; Gijsen, HJM New evolutions in the BACE1 inhibitor field from 2014 to 2018. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 761 -777 (2019) Son, IH; Chung, IM; Lee, SI; Yang, HD; Moon, HI Pomiferin, histone deacetylase inhibitor isolated from the fruits of Maclura pomifera. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 4753 -5 (2007) Andersen, OA; Nathubhai, A; Dixon, MJ; Eggleston, IM; van Aalten, DM Structure-based dissection of the natural product cyclopentapeptide chitinase inhibitor argifin. Chem Biol 15: 295 -301 (2008) Rajendran, V; Saxena, A; Doctor, BP; Kozikowski, AP Synthesis of more potent analogues of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, huperzine B. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 1521 -3 (2002) Sarges, R; Bordner, J; Dominy, BW; Peterson, MJ; Whipple, EB Synthesis, absolute configuration, and conformation of the aldose reductase inhibitor sorbinil. J Med Chem 28: 1716 -20 (1985) Williams, LK; Zhang, X; Caner, S; Tysoe, C; Nguyen, NT; Wicki, J; Williams, DE; Coleman, J; McNeill, JH; Yuen, V; Andersen, RJ; Withers, SG; Brayer, GD The amylase inhibitor montbretin A reveals a new glycosidase inhibition motif. Nat Chem Biol 11: 691 -6 (2015) Whitley, AC; Sweet, DH; Walle, T The dietary polyphenol ellagic acid is a potent inhibitor of hOAT1. Drug Metab Dispos 33: 1097 -100 (2005) Isabel, E; Bateman, KP; Chauret, N; Cromlish, W; Desmarais, S; Duong, le T; Falgueyret, JP; Gauthier, JY; Lamontagne, S; Lau, CK; Léger, S; LeRiche, T; Lévesque, JF; Li, CS; Massé, F; McKay, DJ; Mellon, C; Nicoll-Griffith, DA; Oballa, RM; Percival, MD; Riendeau, D; Robichaud, J; Rodan, GA; Rodan, SB; Seto, C; Thérien, M; Truong, VL; Wesolowski, G; Young, RN; Zamboni, R; Black, WC The discovery of MK-0674, an orally bioavailable cathepsin K inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 887 -92 (2010) Andersen, PH The dopamine inhibitor GBR 12909: selectivity and molecular mechanism of action. Eur J Pharmacol 166: 493 -504 (1989) Queffélec, C; Bailly, F; Mbemba, G; Mouscadet, JF; Debyser, Z; Witvrouw, M; Cotelle, P The total synthesis of fukiic acid, an HIV-1 integrase inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem 43: 2268 -71 (2008) Bruno, F; Spaziano, G; Liparulo, A; Roviezzo, F; Nabavi, SM; Sureda, A; Filosa, R; D'Agostino, B Recent advances in the search for novel 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors for the treatment of asthma. Eur J Med Chem 153: 65 -72 (2018) Zhang, B; Liu, F; Yang, MF; Xu, J; Wang, Z; Zhang, J; Wang, R; Yang, X A cell-based fluorescent assay for FAP inhibitor discovery. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 30: (2020) Fernández, D; Avilés, FX; Vendrell, J Aromatic organic compounds as scaffolds for metallocarboxypeptidase inhibitor design. Chem Biol Drug Des 73: 75 -82 (2009) HE, Q; WENG, Q; CHEN, B; YAN, F; MO, J; WU, C; JIN, R; YAN, L COMPOUND FOR EGFR KINASE INHIBITOR, COMPOSITION, AND USE THEREOF US Patent US20250101052 (2025) Kim, KY; Lee, H; Yoo, SE; Kim, SH; Kang, NS Discovery of new inhibitor for PDE3 by virtual screening. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 1617 -20 (2011) Naylor-Olsen, AM; Ponticello, GS; Lewis, SD; Mulichak, AM; Chen, Z; Habecker, CN; Phillips, BT; Sanders, WM; Tucker, TJ; Shafer, JA; Vacca, JP Identification and SAR for a selective, nonpeptidyl thrombin inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8: 1697 -702 (1999) Fatheree, PR; Jacobsen, JR; Brandt, GE; Fleury, M; Jiang, L; Smith, C; Sullivan, SD; Van Orden, LJ; Beausoleil, A JAK kinase inhibitor compounds for treatment of respiratory disease US Patent US11299492 (2022) Kammasud, N; Boonyarat, C; Tsunoda, S; Sakurai, H; Saiki, I; Grierson, DS; Vajragupta, O Novel inhibitor for fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 4812 -8 (2007) Jeong, LS; Kim, HO; Jacobson, KA; Choe, SA Adenosine derivatives, method for the synthesis thereof, and the pharmaceutical compositions for the prevention and treatment of the inflammatory diseases containing the same as an active ingredient US Patent US9018371 (2015) Rodriguez, M; Lignon, MF; Galas, MC; Fulcrand, P; Mendre, C; Aumelas, A; Laur, J; Martinez, J Synthesis and biological activities of pseudopeptide analogues of the C-terminal heptapeptide of cholecystokinin. On the importance of the peptide bonds. J Med Chem 30: 1366 -73 (1987) Augeri, DJ; Robl, JA; Betebenner, DA; Magnin, DR; Khanna, A; Robertson, JG; Wang, A; Simpkins, LM; Taunk, P; Huang, Q; Han, SP; Abboa-Offei, B; Cap, M; Xin, L; Tao, L; Tozzo, E; Welzel, GE; Egan, DM; Marcinkeviciene, J; Chang, SY; Biller, SA; Kirby, MS; Parker, RA; Hamann, LG Discovery and preclinical profile of Saxagliptin (BMS-477118): a highly potent, long-acting, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Med Chem 48: 5025 -37 (2005) Xu, P; Feng, X; Luan, H; Wang, J; Ge, R; Li, Z; Bian, J Current knowledge on the nucleotide agonists for the P2Y2 receptor. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 366 -375 (2018) Chauret, N; Yergey, JA; Brideau, C; Friesen, RW; Mancini, J; Riendeau, D; Silva, J; Styhler, A; Trimble, LA; Nicoll-Griffith, DA In vitro metabolism considerations, including activity testing of metabolites, in the discovery and selection of the COX-2 inhibitor etoricoxib (MK-0663). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1059 -62 (2001) Vig, BS; Zheng, MQ; Murray, TF; Aldrich, JV Effects of the substitution of Phe4 in the opioid peptide [D-Ala8]dynorphin A-(1-11)NH2. J Med Chem 46: 4002 -8 (2003) Xie, X; He, J Multivalent peptide dendrimers inhibit the fusion of viral-cellular membranes and the cellular NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur J Med Chem 230: (2022) Ganapathy, ME; Prasad, PD; Mackenzie, B; Ganapathy, V; Leibach, FH Interaction of anionic cephalosporins with the intestinal and renal peptide transporters PEPT 1 and PEPT 2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1324: 296 -308 (1997) Blackburn, BK; Lee, A; Baier, M; Kohl, B; Olivero, AG; Matamoros, R; Robarge, KD; McDowell, RS From peptide to non-peptide. 3. Atropisomeric GPIIbIIIa antagonists containing the 3,4-dihydro-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-dione nucleus. J Med Chem 40: 717 -29 (1997) Conformational control inhibition of the BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase, including the gatekeeper T315I mutant, by the switch-control inhibitor DCC-2036. Zhou, HJ; Aujay, MA; Bennett, MK; Dajee, M; Demo, SD; Fang, Y; Ho, MN; Jiang, J; Kirk, CJ; Laidig, GJ; Lewis, ER; Lu, Y; Muchamuel, T; Parlati, F; Ring, E; Shenk, KD; Shields, J; Shwonek, PJ; Stanton, T; Sun, CM; Sylvain, C; Woo, TM; Yang, J Design and synthesis of an orally bioavailable and selective peptide epoxyketone proteasome inhibitor (PR-047). J Med Chem 52: 3028 -38 (2009) Sviripa, VM; Zhang, W; Balia, AG; Tsodikov, OV; Nickell, JR; Gizard, F; Yu, T; Lee, EY; Dwoskin, LP; Liu, C; Watt, DS 2',6'-Dihalostyrylanilines, pyridines, and pyrimidines for the inhibition of the catalytic subunit of methionine S-adenosyltransferase-2. J Med Chem 57: 6083 -91 (2014) Lee, J; Han, Y; Kim, Y; Min, J; Bae, M; Kim, D; Jin, S; Kyung, J 1,3,4-oxadiazole sulfamide derivative compounds as histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor, and the pharmaceutical composition comprising the same US Patent US10464911 (2019) Kukimoto-Niino, M; Yoshikawa, S; Takagi, T; Ohsawa, N; Tomabechi, Y; Terada, T; Shirouzu, M; Suzuki, A; Lee, S; Yamauchi, T; Okada-Iwabu, M; Iwabu, M; Kadowaki, T; Minokoshi, Y; Yokoyama, S Crystal structure of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase in complex with the inhibitor STO-609. J Biol Chem 286: 22570 -9 (2011) Brai, A; Boccuto, A; Monti, M; Marchi, S; Vicenti, I; Saladini, F; Trivisani, CI; Pollutri, A; Trombetta, CM; Montomoli, E; Riva, V; Garbelli, A; Nola, EM; Zazzi, M; Maga, G; Dreassi, E; Botta, M Exploring the Implication of DDX3X in DENV Infection: Discovery of the First-in-Class DDX3X Fluorescent Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 956 -962 (2020) Preston, A; Atkinson, SJ; Bamborough, P; Chung, CW; Gordon, LJ; Grandi, P; Gray, JRJ; Harrison, LA; Lewis, AJ; Lugo, D; Messenger, C; Michon, AM; Mitchell, DJ; Prinjha, RK; Rioja, I; Seal, J; Taylor, S; Thesmar, P; Wall, ID; Watson, RJ; Woolven, JM; Demont, EH GSK973 Is an Inhibitor of the Second Bromodomains (BD2s) of the Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Family. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1581 -1587 (2020) Jacobs, MT; Zhang, YW; Campbell, SD; Rudnick, G Ibogaine, a noncompetitive inhibitor of serotonin transport, acts by stabilizing the cytoplasm-facing state of the transporter. J Biol Chem 282: 29441 -7 (2007) Identification of the exosomal PD-L1 inhibitor to promote the PD-1 targeting therapy of gastric cancer. Arya, T; Reddi, R; Kishor, C; Ganji, RJ; Bhukya, S; Gumpena, R; McGowan, S; Drag, M; Addlagatta, A Identification of the molecular basis of inhibitor selectivity between the human and streptococcal type I methionine aminopeptidases. J Med Chem 58: 2350 -7 (2015) Wilding, B; Pasqua, AE; E A Chessum, N; Pierrat, OA; Hahner, T; Tomlin, K; Shehu, E; Burke, R; Richards, GM; Whitton, B; Arwert, EN; Thapaliya, A; Salimraj, R; van Montfort, R; Skawinska, A; Hayes, A; Raynaud, F; Chopra, R; Jones, K; Newton, G; Cheeseman, MD Investigating the phosphinic acid tripeptide mimetic DG013A as a tool compound inhibitor of the M1-aminopeptidase ERAP1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 42: (2021) Adler, M; Davey, DD; Phillips, GB; Kim, SH; Jancarik, J; Rumennik, G; Light, DR; Whitlow, M Preparation, characterization, and the crystal structure of the inhibitor ZK-807834 (CI-1031) complexed with factor Xa. Biochemistry 39: 12534 -42 (2000) Antitumor activity of HKI-272, an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase. Dreyer, MK; Borcherding, DR; Dumont, JA; Peet, NP; Tsay, JT; Wright, PS; Bitonti, AJ; Shen, J; Kim, SH Crystal structure of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 in complex with the adenine-derived inhibitor H717. J Med Chem 44: 524 -30 (2001) Christopeit, T; Leiros, HK Fragment-based discovery of inhibitor scaffolds targeting the metallo-ß-lactamases NDM-1 and VIM-2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 1973 -7 (2016) Tesmer, JJ; Tesmer, VM; Lodowski, DT; Steinhagen, H; Huber, J Structure of human G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in complex with the kinase inhibitor balanol. J Med Chem 53: 1867 -70 (2010) Ju, Z; Shang, Z; Mahmud, T; Fang, J; Liu, Y; Pan, Q; Lin, X; Chen, F Synthesis and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Natural Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitor Axinelline A and Its Analogues. J Nat Prod 86: 958 -965 (2023) Nicoll-Griffith, DA; Yergey, JA; Trimble, LA; Silva, JM; Li, C; Chauret, N; Gauthier, JY; Grimm, E; Léger, S; Roy, P; Thérien, M; Wang, Z; Prasit, P; Zamboni, R; Young, RN; Brideau, C; Chan, CC; Mancini, J; Riendeau, D Synthesis, characterization, and activity of metabolites derived from the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor rofecoxib (MK-0966, Vioxx). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 2683 -6 (2000) Decara, JM; Vázquez-Villa, H; Brea, J; Alonso, M; Srivastava, RK; Orio, L; Alén, F; Suárez, J; Baixeras, E; García-Cárceles, J; Escobar-Peña, A; Lutz, B; Rodríguez, R; Codesido, E; Garcia-Ladona, FJ; Bennett, TA; Ballesteros, JA; Cruces, J; Loza, MI; Benhamú, B; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F; López-Rodríguez, ML Discovery of V-0219: A Small-Molecule Positive Allosteric Modulator of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor toward Oral Treatment for "Diabesity". J Med Chem 65: 5449 -5461 (2022) Wang, H; Wang, J; Zhao, X; Ye, R; Sun, L; Wang, J; Li, L; Liang, H; Wang, S; Lu, Y Discovery of an Anti-TNF-α 9-mer Peptide from a T7 Phage Display Library for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Med Chem 66: 6981 -6993 (2023) Blankley, CJ; Hodges, JC; Klutchko, SR; Himmelsbach, RJ; Chucholowski, A; Connolly, CJ; Neergaard, SJ; Van Nieuwenhze, MS; Sebastian, A; Quin, J Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a novel series of non-peptide angiotensin II receptor binding inhibitors specific for the AT2 subtype. J Med Chem 34: 3248 -60 (1991) Hamada, Y; Ishiura, S; Kiso, Y BACE1 Inhibitor Peptides: Can an Infinitely Small k cat Value Turn the Substrate of an Enzyme into Its Inhibitor? ACS Med Chem Lett 3: 193 -197 (2012) Dhagat, U; Endo, S; Sumii, R; Hara, A; El-Kabbani, O Selectivity determinants of inhibitor binding to human 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: crystal structure of the enzyme in ternary complex with coenzyme and the potent inhibitor 3,5-dichlorosalicylic acid. J Med Chem 51: 4844 -8 (2008) Biftu, T; Feng, D; Qian, X; Liang, GB; Kieczykowski, G; Eiermann, G; He, H; Leiting, B; Lyons, K; Petrov, A; Sinha-Roy, R; Zhang, B; Scapin, G; Patel, S; Gao, YD; Singh, S; Wu, J; Zhang, X; Thornberry, NA; Weber, AE (3R)-4-[(3R)-3-Amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butanoyl]-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-1,4-diazepan-2-one, a selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 49 -52 (2007) Schonbrunn, E; Li, R; Sebti, SM Inhibitors of rho associated protein kinases (ROCK) and methods of use US Patent US9409868 (2016) Fang, X; Chen, YT; Sessions, EH; Chowdhury, S; Vojkovsky, T; Yin, Y; Pocas, JR; Grant, W; Schröter, T; Lin, L; Ruiz, C; Cameron, MD; LoGrasso, P; Bannister, TD; Feng, Y Synthesis and biological evaluation of 4-quinazolinones as Rho kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 1844 -8 (2011) DW71177: A novel [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxaline-based potent and BD1-Selective BET inhibitor for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Roehrig, S; Ackerstaff, J; Jiménez Núñez, E; Teller, H; Ellerbrock, P; Meier, K; Heitmeier, S; Tersteegen, A; Stampfuss, J; Lang, D; Schlemmer, KH; Schaefer, M; Gericke, KM; Kinzel, T; Meibom, D; Schmidt, M; Gerdes, C; Follmann, M; Hillisch, A Design and Preclinical Characterization Program toward Asundexian (BAY 2433334), an Oral Factor XIa Inhibitor for the Prevention and Treatment of Thromboembolic Disorders. J Med Chem 66: 12203 -12224 (2023) Ding, H; Pei, Y; Li, Y; Xu, W; Mei, L; Hou, Z; Guang, Y; Cao, L; Li, P; Cao, H; Bian, J; Chen, K; Luo, C; Zhou, B; Zhang, T; Li, Z; Yang, Y Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel spiro oxazolidinedione as potent p300/CBP HAT inhibitor for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Bioorg Med Chem 52: (2021) Flanagan, ME; Blumenkopf, TA; Brissette, WH; Brown, MF; Casavant, JM; Shang-Poa, C; Doty, JL; Elliott, EA; Fisher, MB; Hines, M; Kent, C; Kudlacz, EM; Lillie, BM; Magnuson, KS; McCurdy, SP; Munchhof, MJ; Perry, BD; Sawyer, PS; Strelevitz, TJ; Subramanyam, C; Sun, J; Whipple, DA; Changelian, PS Discovery of CP-690,550: a potent and selective Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and organ transplant rejection. J Med Chem 53: 8468 -84 (2010) Sun, Y; Xue, Y; Liu, H; Mu, S; Sun, P; Sun, Y; Wang, L; Wang, H; Wang, J; Wu, T; Yin, W; Qin, Q; Sun, Y; Yang, H; Zhao, D; Cheng, M Discovery of CZS-241: A Potent, Selective, and Orally Available Polo-Like Kinase 4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. J Med Chem 66: 2396 -2421 (2023) Lu, B; Cao, H; Cao, J; Huang, S; Hu, Q; Liu, D; Shen, R; Shen, X; Tao, W; Wan, H; Wang, D; Yan, Y; Yang, L; Zhang, J; Zhang, L; Zhang, L; Zhang, M Discovery of EBI-907: A highly potent and orally active B-Raf(V600E) inhibitor for the treatment of melanoma and associated cancers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 819 -23 (2016) Albrecht, BK; Gehling, VS; Hewitt, MC; Vaswani, RG; Côté, A; Leblanc, Y; Nasveschuk, CG; Bellon, S; Bergeron, L; Campbell, R; Cantone, N; Cooper, MR; Cummings, RT; Jayaram, H; Joshi, S; Mertz, JA; Neiss, A; Normant, E; O'Meara, M; Pardo, E; Poy, F; Sandy, P; Supko, J; Sims, RJ; Harmange, JC; Taylor, AM; Audia, JE Identification of a Benzoisoxazoloazepine Inhibitor (CPI-0610) of the Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Family as a Candidate for Human Clinical Trials. J Med Chem 59: 1330 -9 (2016) Fu, C; Liu, C; Chen, Y; Tu, C; Hung, C Beta-amino acid derivative, kinase inhibitor and pharmaceutical composition containing the same, and method for performing an in vivo related application that benefits from the inhibition of a kinase US Patent US11608319 (2023) Palle, VP; Elzein, EO; Gothe, SA; Li, Z; Gao, Z; Meyer, S; Blackburn, B; Zablocki, JA Structure-affinity relationships of the affinity of 2-pyrazolyl adenosine analogues for the adenosine A2A receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 2935 -9 (2002) Zhu, G; Wang, K; Shi, J; Zhang, P; Yang, D; Fan, X; Zhang, Z; Liu, W; Sang, Z The development of 2-acetylphenol-donepezil hybrids as multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: (2019) Deaton, DN; Gao, EN; Graham, KP; Gross, JW; Miller, AB; Strelow, JM Thiol-based angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitors: P1 modifications for the exploration of the S1 subsite. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 732 -7 (2008) Deaton, DN; Graham, KP; Gross, JW; Miller, AB Thiol-based angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inhibitors: P1' modifications for the exploration of the S1' subsite. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 1681 -7 (2008) Lefrançois, M; Lefebvre, MR; Saint-Onge, G; Boulais, PE; Lamothe, S; Leduc, R; Lavigne, P; Heveker, N; Escher, E Agonists for the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4. ACS Med Chem Lett 2: 597 -602 (2011) Zavoronkovs, A; Aliper, A; Aladinskiy, V; Kukharenko, A Analogs for the treatment of disease US Patent US11530197 (2022) Ghosh, AK; Mitsuya, H; Mesecar, A COMPOUNDS FOR THE TREATMENT OF SARS US Patent US20240043417 (2024) Ghosh, AK; Mitsuya, H; Mesecar, A; Shahabi, D Compounds for the treatment of SARS US Patent US11795159 (2023) Cannizzaro, CE; Graupe, M; Guerrero, JA; Lu, Y; Strickley, RG; Venkataramani, C; Zablocki, J Compounds for the treatment of addiction US Patent US10507215 (2019) Wynn, TA; Alvarez, JC; Moustakas, DT; Haeberlein, M; Pennington, LD Compounds for the treatment of pain US Patent US10604489 (2020) Zaręba, P; Jaśkowska, J; Śliwa, P; Satała, G New dual ligands for the D Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 2236 -2242 (2019) Sugase, K; Oyama, Y; Kitano, K; Akutsu, H; Ishiguro, M Structure-activity relationships for mini atrial natriuretic peptide by proline-scanning mutagenesis and shortening of peptide backbone. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 1245 -7 (2002) Camps, P; Gómez, E; Muñoz-Torrero, D; Badia, A; Clos, MV; Curutchet, C; Muñoz-Muriedas, J; Luque, FJ Binding of 13-amidohuprines to acetylcholinesterase: exploring the ligand-induced conformational change of the gly117-gly118 peptide bond in the oxyanion hole. J Med Chem 49: 6833 -40 (2006) Teague, SJ; Stocks, MJ The affinity of the excised binding domain of FK-506 for the immunophilin FKBP12. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 3: 1947 -1950 (1993) Ryu, S; Imai, YN; Oiki, S The synergic modeling for the binding of fluoroquinolone antibiotics to the hERG potassium channel. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 3848 -51 (2013) Lange, G; Lesuisse, D; Deprez, P; Schoot, B; Loenze, P; Benard, D; Marquette, JP; Broto, P; Sarubbi, E; Mandine, E Requirements for specific binding of low affinity inhibitor fragments to the SH2 domain of (pp60)Src are identical to those for high affinity binding of full length inhibitors. J Med Chem 46: 5184 -95 (2003) Oliveira, BL; Morais, M; Mendes, F; Moreira, IS; Cordeiro, C; Fernandes, PA; Ramos, MJ; Alberto, R; Santos, I; Correia, JD Re(I) and Tc(I) complexes for targeting nitric oxide synthase: influence of the chelator in the affinity for the enzyme. Chem Biol Drug Des 86: 1072 -86 (2015) Porter, RA; Chan, WN; Coulton, S; Johns, A; Hadley, MS; Widdowson, K; Jerman, JC; Brough, SJ; Coldwell, M; Smart, D; Jewitt, F; Jeffrey, P; Austin, N 1,3-Biarylureas as selective non-peptide antagonists of the orexin-1 receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1907 -10 (2001) Mollica, A; Pinnen, F; Costante, R; Locatelli, M; Stefanucci, A; Pieretti, S; Davis, P; Lai, J; Rankin, D; Porreca, F; Hruby, VJ Biological active analogues of the opioid peptide biphalin: mixeda/ß(3)-peptides. J Med Chem 56: 3419 -23 (2013) Hossain, MA; Bathgate, RAD Challenges in the design of insulin and relaxin/insulin-like peptide mimetics. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 2827 -2841 (2018) Thakkar, R; Upreti, D; Ishiguro, S; Tamura, M; Comer, J Computational design of a cyclic peptide that inhibits the CTLA4 immune checkpoint. RSC Med Chem 14: 658 -670 (2023) Duggineni, S; Mitra, S; Lamberto, I; Han, X; Xu, Y; An, J; Pasquale, EB; Huang, Z Design and Synthesis of Potent Bivalent Peptide Agonists Targeting the EphA2 Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 344 -8 (2013) Evans, BE; Bock, MG; Rittle, KE; DiPardo, RM; Whitter, WL; Veber, DF; Anderson, PS; Freidinger, RM Design of potent, orally effective, nonpeptidal antagonists of the peptide hormone cholecystokinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83: 4918 -22 (1986) Bursavich, MG; Rich, DH Designing non-peptide peptidomimetics in the 21st century: inhibitors targeting conformational ensembles. J Med Chem 45: 541 -58 (2002) Harrison, RES; Zewde, NT; Narkhede, YB; Hsu, RV; Morikis, D; Vullev, VI; Palermo, G Factor H-Inspired Design of Peptide Biomarkers of the Complement C3d Protein. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1054 -1059 (2020) Herrero, S; Suarez-Gea, M; Gonzalez-Muniz, R; Garcia-Lopez, M; Herranz, R; Ballaz, S; Barber, A; Fortuno, A; Del Rio, J Pseudopeptide CCK-4 analogues incorporating the [CH(CN)NH] peptide bond surrogate Bioorg Med Chem Lett 7: 855 -860 (1997) Ulysse, LG; Chmielewski, J Restricting the flexibility of crosslinked, interfacial peptide inhibitors of HIV-1 protease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8: 3281 -6 (1999) Zhou, J; Li, Y; Huang, W; Shi, W; Qian, H Source and exploration of the peptides used to construct peptide-drug conjugates. Eur J Med Chem 224: (2021) Penning, TD; Zhu, GD; Gandhi, VB; Gong, J; Thomas, S; Lubisch, W; Grandel, R; Wernet, W; Park, CH; Fry, EH; Liu, X; Shi, Y; Klinghofer, V; Johnson, EF; Donawho, CK; Frost, DJ; Bontcheva-Diaz, V; Bouska, JJ; Olson, AM; Marsh, KC; Luo, Y; Rosenberg, SH; Giranda, VL Discovery and SAR of 2-(1-propylpiperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide: A potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) for the treatment of cancer. Bioorg Med Chem 16: 6965 -75 (2008) Stuart, BG; Coxon, JM; Morton, JD; Abell, AD; McDonald, DQ; Aitken, SG; Jones, MA; Bickerstaffe, R Molecular modeling: a search for a calpain inhibitor as a new treatment for cataractogenesis. J Med Chem 54: 7503 -22 (2011) Harrison, TJ; Bauer, D; Berdichevsky, A; Chen, X; Duvadie, R; Hoogheem, B; Hatsis, P; Liu, Q; Mao, J; Miduturu, V; Rocheford, E; Zecri, F; Zessis, R; Zheng, R; Zhu, Q; Streeper, R; Patel, SJ Successful Strategies for Mitigation of a Preclinical Signal for Phototoxicity in a DGAT1 Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1128 -1133 (2019) Monfardini, I; Huang, JW; Beck, B; Cellitti, JF; Pellecchia, M; Dömling, A Screening multicomponent reactions for X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis protein repeats domain binder. J Med Chem 54: 890 -900 (2012) Gademann, K; Kimmerlin, T; Hoyer, D; Seebach, D Peptide folding induces high and selective affinity of a linear and small beta-peptide to the human somatostatin receptor 4. J Med Chem 44: 2460 -8 (2001) Wessels, M; König, GM; Wright, AD A new tyrosine kinase inhibitor from the marine brown alga Stypopodium zonale. J Nat Prod 62: 927 -30 (1999) Préville, P; He, JX; Tarazi, M; Siddiqui, MA; Cody, WL; Doherty, AM An efficient preparation of the potent and selective pseudopeptide thrombin inhibitor, inogatran Bioorg Med Chem Lett 7: 1563 -1566 (1997) Hilinski, MK; Mrozowski, RM; Clark, DE; Lannigan, DA Analogs of the RSK inhibitor SL0101: optimization of in vitro biological stability. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 3244 -7 (2012) JI, Q; YU, C; WANG, C; SUN, H BRIDGED COMPOUNDS AS KRAS G12D INHIBITOR AND DEGRADER AND THE USE THEREOF US Patent US20240092803 (2024) M Serafim, RA; da Silva Santiago, A; Schwalm, MP; Hu, Z; Dos Reis, CV; Takarada, JE; Mezzomo, P; Massirer, KB; Kudolo, M; Gerstenecker, S; Chaikuad, A; Zender, L; Knapp, S; Laufer, S; Couñago, RM; Gehringer, M Development of the First Covalent Monopolar Spindle Kinase 1 (MPS1/TTK) Inhibitor. J Med Chem 65: 3173 -3192 (2022) Kettle, JG; Bagal, SK; Bickerton, S; Bodnarchuk, MS; Boyd, S; Breed, J; Carbajo, RJ; Cassar, DJ; Chakraborty, A; Cosulich, S; Cumming, I; Davies, M; Davies, NL; Eatherton, A; Evans, L; Feron, L; Fillery, S; Gleave, ES; Goldberg, FW; Hanson, L; Harlfinger, S; Howard, M; Howells, R; Jackson, A; Kemmitt, P; Lamont, G; Lamont, S; Lewis, HJ; Liu, L; Niedbala, MJ; Phillips, C; Polanski, R; Raubo, P; Robb, G; Robinson, DM; Ross, S; Sanders, MG; Tonge, M; Whiteley, R; Wilkinson, S; Yang, J; Zhang, W Discovery of AZD4625, a Covalent Allosteric Inhibitor of the Mutant GTPase KRAS J Med Chem 65: 6940 -6952 (2022) Ito, S; Otsuki, S; Ohsawa, H; Hirano, A; Kazuno, H; Yamashita, S; Egami, K; Shibata, Y; Yamamiya, I; Yamashita, F; Kodama, Y; Funabashi, K; Kazuno, H; Komori, T; Suzuki, S; Sootome, H; Hirai, H; Sagara, T Discovery of Futibatinib: The First Covalent FGFR Kinase Inhibitor in Clinical Use. ACS Med Chem Lett 14: 396 -404 (2023) Xie, Y; Liu, Y; Gong, G; Rinderspacher, A; Deng, SX; Smith, DH; Toebben, U; Tzilianos, E; Branden, L; Vidovic, D; Chung, C; Schürer, S; Tautz, L; Landry, DW Discovery of a novel submicromolar inhibitor of the lymphoid specific tyrosine phosphatase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 2840 -4 (2008) Ma, A; Yu, W; Li, F; Bleich, RM; Herold, JM; Butler, KV; Norris, JL; Korboukh, V; Tripathy, A; Janzen, WP; Arrowsmith, CH; Frye, SV; Vedadi, M; Brown, PJ; Jin, J Discovery of a selective, substrate-competitive inhibitor of the lysine methyltransferase SETD8. J Med Chem 57: 6822 -33 (2014) Papa, P; Whitefield, B; Mortensen, DS; Cashion, D; Huang, D; Torres, E; Parnes, J; Sapienza, J; Hansen, J; Correa, M; Delgado, M; Harris, R; Hegde, S; Norris, S; Bahmanyar, S; Plantevin-Krenitsky, V; Liu, Z; Leftheris, K; Kulkarni, A; Bennett, B; Hur, EM; Ringheim, G; Khambatta, G; Chan, H; Muir, J; Blease, K; Burnett, K; LeBrun, L; Morrison, L; Celeridad, M; Khattri, R; Cathers, BE Discovery of the Selective Protein Kinase C-θ Kinase Inhibitor, CC-90005. J Med Chem 64: 11886 -11903 (2021) Dötsch, L; Davies, C; Hennes, E; Schönfeld, J; Kumar, A; Guita, CDCL; Ehrler, JHM; Hiesinger, K; Thavam, S; Janning, P; Sievers, S; Knapp, S; Proschak, E; Ziegler, S; Waldmann, H Discovery of the sEH Inhibitor Epoxykynin as a Potent Kynurenine Pathway Modulator. J Med Chem 67: 4691 -4706 (2024) Bordeleau, ME; Mori, A; Oberer, M; Lindqvist, L; Chard, LS; Higa, T; Belsham, GJ; Wagner, G; Tanaka, J; Pelletier, J Functional characterization of IRESes by an inhibitor of the RNA helicase eIF4A. Nat Chem Biol 2: 213 -20 (2006) Identification and Optimization of the First Highly Selective GLUT1 Inhibitor BAY-876. Stebbins, JL; De, SK; Machleidt, T; Becattini, B; Vazquez, J; Kuntzen, C; Chen, LH; Cellitti, JF; Riel-Mehan, M; Emdadi, A; Solinas, G; Karin, M; Pellecchia, M Identification of a new JNK inhibitor targeting the JNK-JIP interaction site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 16809 -13 (2008) Horton, JR; Liu, X; Wu, L; Zhang, K; Shanks, J; Zhang, X; Rai, G; Mott, BT; Jansen, DJ; Kales, SC; Henderson, MJ; Pohida, K; Fang, Y; Hu, X; Jadhav, A; Maloney, DJ; Hall, MD; Simeonov, A; Fu, H; Vertino, PM; Yan, Q; Cheng, X Insights into the Action of Inhibitor Enantiomers against Histone Lysine Demethylase 5A. J Med Chem 61: 3193 -3208 (2018) Clark, PG; Vieira, LC; Tallant, C; Fedorov, O; Singleton, DC; Rogers, CM; Monteiro, OP; Bennett, JM; Baronio, R; Müller, S; Daniels, DL; Méndez, J; Knapp, S; Brennan, PE; Dixon, DJ LP99: Discovery and Synthesis of the First Selective BRD7/9 Bromodomain Inhibitor. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54: 6217 -21 (2015) Gao, Y; Voigt, J; Wu, JX; Yang, D; Burke, TR Macrocyclization in the design of a conformationally constrained Grb2 SH2 domain inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1889 -92 (2001) Perez, C; Barkley-Levenson, AM; Dick, BL; Glatt, PF; Martinez, Y; Siegel, D; Momper, JD; Palmer, AA; Cohen, SM Metal-Binding Pharmacophore Library Yields the Discovery of a Glyoxalase 1 Inhibitor. J Med Chem 62: 1609 -1625 (2019) Gunasekera, SP; Miller, MW; Kwan, JC; Luesch, H; Paul, VJ Molassamide, a depsipeptide serine protease inhibitor from the marine cyanobacterium Dichothrix utahensis. J Nat Prod 73: 459 -62 (2010) Baumann, HI; Keller, S; Wolter, FE; Nicholson, GJ; Jung, G; Süssmuth, RD; Jüttner, F Planktocyclin, a cyclooctapeptide protease inhibitor produced by the freshwater cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens. J Nat Prod 70: 1611 -5 (2007) Karim, RM; Chan, A; Zhu, JY; Schönbrunn, E Structural Basis of Inhibitor Selectivity in the BRD7/9 Subfamily of Bromodomains. J Med Chem 63: 3227 -3237 (2020) Lei, Y; An, Q; Shen, XF; Sui, M; Li, C; Jia, D; Luo, Y; Sun, Q Structure-Guided Design of the First Noncovalent Small-Molecule Inhibitor of CRM1. J Med Chem 64: 6596 -6607 (2021) Colis, LC; Herzon, SB Synergistic potentiation of (-)-lomaiviticin A cytotoxicity by the ATR inhibitor VE-821. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 3122 -6 (2016) Hanessian, S; Rogel, O Synthesis of a phostone glycomimetic of the endothelin converting enzyme inhibitor phosphoramidon. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 2441 -6 (1999) Kato, H; El-Desoky, AH; Takeishi, Y; Nehira, T; Angkouw, ED; Mangindaan, REP; de Voogd, NJ; Tsukamoto, S Tetradehydrohalicyclamine B, a new proteasome inhibitor from the marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 8 -10 (2019) Regueiro-Ren, A; Sit, SY; Chen, Y; Chen, J; Swidorski, JJ; Liu, Z; Venables, BL; Sin, N; Hartz, RA; Protack, T; Lin, Z; Zhang, S; Li, Z; Wu, DR; Li, P; Kempson, J; Hou, X; Gupta, A; Rampulla, R; Mathur, A; Park, H; Sarjeant, A; Benitex, Y; Rahematpura, S; Parker, D; Phillips, T; Haskell, R; Jenkins, S; Santone, KS; Cockett, M; Hanumegowda, U; Dicker, I; Meanwell, NA; Krystal, M The Discovery of GSK3640254, a Next-Generation Inhibitor of HIV-1 Maturation. J Med Chem 65: 11927 -11948 (2022) Duffy, JP; Harrington, EM; Salituro, FG; Cochran, JE; Green, J; Gao, H; Bemis, GW; Evindar, G; Galullo, VP; Ford, PJ; Germann, UA; Wilson, KP; Bellon, SF; Chen, G; Taslimi, P; Jones, P; Huang, C; Pazhanisamy, S; Wang, YM; Murcko, MA; Su, MS The Discovery of VX-745: A Novel and Selective p38a Kinase Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 2: 758 -763 (2011) Gauthier, JY; Chauret, N; Cromlish, W; Desmarais, S; Duong, le T; Falgueyret, JP; Kimmel, DB; Lamontagne, S; Léger, S; LeRiche, T; Li, CS; Massé, F; McKay, DJ; Nicoll-Griffith, DA; Oballa, RM; Palmer, JT; Percival, MD; Riendeau, D; Robichaud, J; Rodan, GA; Rodan, SB; Seto, C; Thérien, M; Truong, VL; Venuti, MC; Wesolowski, G; Young, RN; Zamboni, R; Black, WC The discovery of odanacatib (MK-0822), a selective inhibitor of cathepsin K. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 923 -8 (2008) de Veer, SJ; Wang, CK; Harris, JM; Craik, DJ; Swedberg, JE Improving the Selectivity of Engineered Protease Inhibitors: Optimizing the P2 Prime Residue Using a Versatile Cyclic Peptide Library. J Med Chem 58: 8257 -68 (2015) Ovadia, O; Linde, Y; Haskell-Luevano, C; Dirain, ML; Sheynis, T; Jelinek, R; Gilon, C; Hoffman, A The effect of backbone cyclization on PK/PD properties of bioactive peptide-peptoid hybrids: the melanocortin agonist paradigm. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 580 -9 (2010) El-Kabbani, O; Darmanin, C; Oka, M; Schulze-Briese, C; Tomizaki, T; Hazemann, I; Mitschler, A; Podjarny, A High-resolution structures of human aldose reductase holoenzyme in complex with stereoisomers of the potent inhibitor Fidarestat: stereospecific interaction between the enzyme and a cyclic imide type inhibitor. J Med Chem 47: 4530 -7 (2004) Fuselier, JA; Sun, L; Woltering, SN; Murphy, WA; Vasilevich, N; Coy, DH An adjustable release rate linking strategy for cytotoxin-peptide conjugates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 799 -803 (2003) Brain-Permeable Immunoproteasome-Targeting Macrocyclic Peptide Epoxyketones for Alzheimer's Disease. Evans, BE; Rittle, KE; Bock, MG; DiPardo, RM; Freidinger, RM; Whitter, WL; Gould, NP; Lundell, GF; Homnick, CF; Veber, DF Design of nonpeptidal ligands for a peptide receptor: cholecystokinin antagonists. J Med Chem 30: 1229 -39 (1987) Iqbal, M; Messina, PA; Freed, B; Das, M; Chatterjee, S; Tripathy, R; Tao, M; Josef, KA; Dembofsky, B; Dunn, D; Griffith, E; Siman, R; Senadhi, SE; Biazzo, W; Bozyczko-Coyne, D; Meyer, SL; Ator, MA; Bihovsky, R Subsite requirements for peptide aldehyde inhibitors of human calpain I Bioorg Med Chem Lett 7: 539 -544 (1997) Brameld, KA; Owens, TD; Verner, E; Venetsanakos, E; Bradshaw, JM; Phan, VT; Tam, D; Leung, K; Shu, J; LaStant, J; Loughhead, DG; Ton, T; Karr, DE; Gerritsen, ME; Goldstein, DM; Funk, JO Discovery of the Irreversible Covalent FGFR Inhibitor 8-(3-(4-Acryloylpiperazin-1-yl)propyl)-6-(2,6-dichloro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(methylamino)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7(8H)-one (PRN1371) for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. J Med Chem 60: 6516 -6527 (2017) Rosse, G Modulators of the GPR119 Receptor for the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 8 -9 (2013) Saha, D; Kharbanda, A; Yan, W; Lakkaniga, NR; Frett, B; Li, HY The Exploration of Chirality for Improved Druggability within the Human Kinome. J Med Chem 63: 441 -469 (2020) Scapin, G; Patel, SB; Becker, JW; Wang, Q; Desponts, C; Waddleton, D; Skorey, K; Cromlish, W; Bayly, C; Therien, M; Gauthier, JY; Li, CS; Lau, CK; Ramachandran, C; Kennedy, BP; Asante-Appiah, E The structural basis for the selectivity of benzotriazole inhibitors of PTP1B. Biochemistry 42: 11451 -9 (2003) Henke, BR; Drewry, DH; Jones, SA; Stewart, EL; Weaver, SL; Wiethe, RW 2-Amino-4,6-diarylpyridines as novel ligands for the estrogen receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1939 -42 (2001) Suto, MJ; Mathew, B; Cowell, R; Augelli-Szafran, CE 2-aminoaryl-5-aryloxazole analogs for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases US Patent US11905258 (2024) Blobaum, AL; Marnett, LJ Molecular determinants for the selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by lumiracoxib. J Biol Chem 282: 16379 -90 (2007) Gunera, J; Baker, JG; van Hilten, N; Rosenbaum, DM; Kolb, P Structure-Based Discovery of Novel Ligands for the Orexin 2 Receptor. J Med Chem 63: 11045 -11053 (2020) Newman, AH; Zou, MF; Ferrer, JV; Javitch, JA [3H]MFZ 2-12: a novel radioligand for the dopamine transporter. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1659 -61 (2001) Dossetter, AG; Beeley, H; Bowyer, J; Cook, CR; Crawford, JJ; Finlayson, JE; Heron, NM; Heyes, C; Highton, AJ; Hudson, JA; Jestel, A; Kenny, PW; Krapp, S; Martin, S; MacFaul, PA; McGuire, TM; Gutierrez, PM; Morley, AD; Morris, JJ; Page, KM; Ribeiro, LR; Sawney, H; Steinbacher, S; Smith, C; Vickers, M (1R,2R)-N-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-2-(6-methoxy-1,3,4,5-tetrahydropyrido[4,3-b]indole-2-carbonyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide (AZD4996): a potent and highly selective cathepsin K inhibitor for the treatment of osteoarthritis. J Med Chem 55: 6363 -74 (2012) Xu, G; Lv, B; Roberge, JY; Xu, B; Du, J; Dong, J; Chen, Y; Peng, K; Zhang, L; Tang, X; Feng, Y; Xu, M; Fu, W; Zhang, W; Zhu, L; Deng, Z; Sheng, Z; Welihinda, A; Sun, X Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of deuterated C-aryl glycoside as a potent and long-acting renal sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Med Chem 57: 1236 -51 (2014) Chen, X; Shu, C; Li, W; Hou, Q; Luo, G; Yang, K; Wu, X Discovery of a Novel Src Homology-2 Domain Containing Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase-2 (SHP2) and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 (CDK4) Dual Inhibitor for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Med Chem 65: 6729 -6747 (2022) Ohtake, Y; Sato, T; Kobayashi, T; Nishimoto, M; Taka, N; Takano, K; Yamamoto, K; Ohmori, M; Yamaguchi, M; Takami, K; Yeu, SY; Ahn, KH; Matsuoka, H; Morikawa, K; Suzuki, M; Hagita, H; Ozawa, K; Yamaguchi, K; Kato, M; Ikeda, S Discovery of tofogliflozin, a novel C-arylglucoside with an O-spiroketal ring system, as a highly selective sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Med Chem 55: 7828 -40 (2012) Zhao, H; Palencia, A; Seiradake, E; Ghaemi, Z; Cusack, S; Luthey-Schulten, Z; Martinis, S Analysis of the Resistance Mechanism of a Benzoxaborole Inhibitor Reveals Insight into the Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase Editing Mechanism. ACS Chem Biol 10: 2277 -85 (2015) End, DW; Smets, G; Todd, AV; Applegate, TL; Fuery, CJ; Angibaud, P; Venet, M; Sanz, G; Poignet, H; Skrzat, S; Devine, A; Wouters, W; Bowden, C Characterization of the antitumor effects of the selective farnesyl protein transferase inhibitor R115777 in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res 61: 131 -7 (2001) Watson, RJ; Bamborough, P; Barnett, H; Chung, CW; Davis, R; Gordon, L; Grandi, P; Petretich, M; Phillipou, A; Prinjha, RK; Rioja, I; Soden, P; Werner, T; Demont, EH GSK789: A Selective Inhibitor of the First Bromodomains (BD1) of the Bromo and Extra Terminal Domain (BET) Proteins. J Med Chem 63: 9045 -9069 (2020) Carroll, AR; Ngo, A; Quinn, RJ; Redburn, J; Hooper, JN Petrosamine B, an inhibitor of the Helicobacter pylori enzyme aspartyl semialdehyde dehydrogenase from the Australian sponge Oceanapia sp. J Nat Prod 68: 804 -6 (2005) Wielert-Badt, S; Lin, JT; Lorenz, M; Fritz, S; Kinne, RK Probing the conformation of the sugar transport inhibitor phlorizin by 2D-NMR, molecular dynamics studies, and pharmacophore analysis. J Med Chem 43: 1692 -8 (2000) Park, JK; Kim, S; Han, YJ; Kim, SH; Kang, NS; Lee, H; Park, S The discovery and the structural basis of an imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-based p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 2580 -3 (2016) Wang, H; Chi, L; Yu, F; Dai, H; Si, X; Gao, C; Wang, Z; Liu, L; Zheng, J; Ke, Y; Liu, H; Zhang, Q The overview of Mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK)-based dual inhibitor in the treatment of cancers. Bioorg Med Chem 70: (2022) Košak, U; Brus, B; Knez, D; Žakelj, S; Trontelj, J; Pišlar, A; Šink, R; Jukič, M; Živin, M; Podkowa, A; Nachon, F; Brazzolotto, X; Stojan, J; Kos, J; Coquelle, N; Sałat, K; Colletier, JP; Gobec, S The Magic of Crystal Structure-Based Inhibitor Optimization: Development of a Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity and in Vivo Activity. J Med Chem 61: 119 -139 (2018) Pierre, F; Chua, PC; O'Brien, SE; Siddiqui-Jain, A; Bourbon, P; Haddach, M; Michaux, J; Nagasawa, J; Schwaebe, MK; Stefan, E; Vialettes, A; Whitten, JP; Chen, TK; Darjania, L; Stansfield, R; Anderes, K; Bliesath, J; Drygin, D; Ho, C; Omori, M; Proffitt, C; Streiner, N; Trent, K; Rice, WG; Ryckman, DM Discovery and SAR of 5-(3-chlorophenylamino)benzo[c][2,6]naphthyridine-8-carboxylic acid (CX-4945), the first clinical stage inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 for the treatment of cancer. J Med Chem 54: 635 -54 (2011) M'Kadmi, C; Cabral, A; Barrile, F; Giribaldi, J; Cantel, S; Damian, M; Mary, S; Denoyelle, S; Dutertre, S; Péraldi-Roux, S; Neasta, J; Oiry, C; Banères, JL; Marie, J; Perello, M; Fehrentz, JA N-Terminal Liver-Expressed Antimicrobial Peptide 2 (LEAP2) Region Exhibits Inverse Agonist Activity toward the Ghrelin Receptor. J Med Chem 62: 965 -973 (2019) Wang, Z; Song, T; Guo, Z; Cao, K; Chen, C; Feng, Y; Wang, H; Yin, F; Zhou, S; Dai, J; Zhang, Z Targeting the Allosteric Pathway That Interconnects the Core-Functional Scaffold and the Distal Phosphorylation Sites for Specific Dephosphorylation of Bcl-2. J Med Chem 63: 13733 -13744 (2020) Bishop, AC; Blair, ER A gatekeeper residue for inhibitor sensitization of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 4002 -6 (2006) Warstat, R; Pervaiz, M; Regenass, P; Amann, M; Schmidtkunz, K; Einsle, O; Jung, M; Breit, B; Hügle, M; Günther, S A novel pan-selective bromodomain inhibitor for epigenetic drug design. Eur J Med Chem 249: (2023) Bronner, SM; Merrick, KA; Murray, J; Salphati, L; Moffat, JG; Pang, J; Sneeringer, CJ; Dompe, N; Cyr, P; Purkey, H; Boenig, GL; Li, J; Kolesnikov, A; Larouche-Gauthier, R; Lai, KW; Shen, X; Aubert-Nicol, S; Chen, YC; Cheong, J; Crawford, JJ; Hafner, M; Haghshenas, P; Jakalian, A; Leclerc, JP; Lim, NK; O'Brien, T; Plise, EG; Shalan, H; Sturino, C; Wai, J; Xiao, Y; Yin, J; Zhao, L; Gould, S; Olivero, A; Heffron, TP Design of a brain-penetrant CDK4/6 inhibitor for glioblastoma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 2294 -2301 (2019) Liu, F; Zhang, X; Weisberg, E; Chen, S; Hur, W; Wu, H; Zhao, Z; Wang, W; Mao, M; Cai, C; Simon, NI; Sanda, T; Wang, J; Look, AT; Griffin, JD; Balk, SP; Liu, Q; Gray, NS Discovery of a Selective Irreversible BMX Inhibitor for Prostate Cancer. ACS Chem Biol 8: 1423 -8 (2013) Zhang, R; Mayhood, T; Lipari, P; Wang, Y; Durkin, J; Syto, R; Gesell, J; McNemar, C; Windsor, W Fluorescence polarization assay and inhibitor design for MDM2/p53 interaction. Anal Biochem 331: 138 -46 (2004) Slusher, BS; Le, A; Tsukamoto, T Glutaminase inhibitor discovery and nanoparticle-enhanced delivery for cancer therapy US Patent US11191732 (2021) Zhang, X; Song, Z; Bao, J Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor, method for preparation and use thereof US Patent US11214554 (2022) Padilla-Coley, S; Rudebeck, EE; Smith, BD; Pfeffer, FM Intracellular fluorescence competition assay for inhibitor engagement of histone deacetylase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 47: (2021) Zahler, S; Tietze, S; Totzke, F; Kubbutat, M; Meijer, L; Vollmar, AM; Apostolakis, J Inverse in silico screening for identification of kinase inhibitor targets. Chem Biol 14: 1207 -14 (2007) Hao, X; Gong, S; Shen, D; Du, X SMALL MOLECULE INHIBITOR FOR CATHEPSIN C AND MEDICINAL USE THEREOF US Patent US20240083888 (2024) Surmiak, E; Ząber, J; Plewka, J; Wojtanowicz, G; Kocik-Krol, J; Kruc, O; Muszak, D; Rodríguez, I; Musielak, B; Viviano, M; Castellano, S; Skalniak, L; Magiera-Mularz, K; Holak, TA; Kalinowska-Tłuścik, J Solubilizer Tag Effect on PD-L1/Inhibitor Binding Properties for ACS Med Chem Lett 15: 36 -44 (2024) Kargbo, RB Targeting KRAS Mutant Protein Inhibitor for Potential Treatment in Cancer. ACS Med Chem Lett 12: 1633 -1634 (2021) Xiang, Q; Zhang, Y; Li, J; Xue, X; Wang, C; Song, M; Zhang, C; Wang, R; Li, C; Wu, C; Zhou, Y; Yang, X; Li, G; Ding, K; Xu, Y Y08060: A Selective BET Inhibitor for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 262 -267 (2018) Harbeson, SL; Shatzer, SA; Le, TB; Buck, SH A new class of high affinity ligands for the neurokinin A NK2 receptor: psi (CH2NR) reduced peptide bond analogues of neurokinin A4-10. J Med Chem 35: 3949 -55 (1992) Zheng, G; Zhang, Z; Dowell, C; Wala, E; Dwoskin, LP; Holtman, JR; McIntosh, JM; Crooks, PA Discovery of non-peptide, small molecule antagonists ofa9a10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as novel analgesics for the treatment of neuropathic and tonic inflammatory pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 2476 -9 (2011) Amano, Y; Umezawa, N; Sato, S; Watanabe, H; Umehara, T; Higuchi, T Activation of lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitor peptide by redox-controlled cleavage of a traceless linker. Bioorg Med Chem 25: 1227 -1234 (2017) Nitta, A; Fujii, H; Sakami, S; Nishimura, Y; Ohyama, T; Satoh, M; Nakaki, J; Satoh, S; Inada, C; Kozono, H; Kumagai, H; Shimamura, M; Fukazawa, T; Kawai, H (3R)-3-amino-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)-N-{4-[6-(2-methoxyethoxy)benzothiazol-2-yl]tetrahydropyran-4-yl}butanamide as a potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 5435 -8 (2008)
Choi, H; Hwang, H; Chin, J; Kim, E; Lee, J; Nam, SJ; Lee, BC; Rho, BJ; Kang, H J Nat Prod 74: 90 -4 (2011) Ahn, SM; Rho, HS; Baek, HS; Joo, YH; Hong, YD; Shin, SS; Park, YH; Park, SN Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 7466 -9 (2011) Kim, S; Lee, S; Rajesh, R; Kang, DH; Ryu, HC; Kim, J; Lee, S; Kim, KC; Rho, JK; Lee, JC US Patent US11248003 (2022) Shin, J; Seo, Y; Rho, JR; Cho, KW J Nat Prod 59: 679 -682 (1996) Ryu, YB; Jeong, HJ; Kim, JH; Kim, YM; Park, JY; Kim, D; Nguyen, TT; Park, SJ; Chang, JS; Park, KH; Rho, MC; Lee, WS Bioorg Med Chem 18: 7940 -7 (2010) Dunbar, PG; Durant, GJ; Rho, T; Ojo, B; Huzl, JJ; Smith, DA; el-Assadi, AA; Sbeih, S; Ngur, DO; Periyasamy, S J Med Chem 37: 2774 -82 (1994)
ChEMBL_66880 (CHEMBL676071) Dissociation constant for peptide inhibitor binding to HER2 receptor Fluorescence Assays for Determination of Binding Affinity. Binding was detected as a change in the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of the PI3K upon the addition of inhibitor. The inhibitor was incubated with the protein for at least 15 min before the fluorescence intensity was measured. Fluorescence data were acquired for 30 s and averaged for each concentration of inhibitor. The background fluorescence of a solution without inhibitor was subtracted from each measurement. Data were then fitted to a binding equation to obtain dissociation constants. ChEMBL_158026 (CHEMBL768619) Association rate constant for the interaction between inhibitor and HIV-1 protease Inhibition assay The inhibitor was screened against recombinant PLproSARS and PLproCoV2 at 37°Cin the assay buffer as described above. For steady state measurement the enzymes were incubated for 60min at 37°C with an inhibitor before adding the substrate to the wells. Eight different inhibitor concentrations were used. Value of the concentration of the inhibitor that achieved 50% inhibition (IC50) was taken from the dependence ofthe hydrolysis velocity on the logarithm of the inhibitor concentration [I]. Inhibition Assay Inhibition of Rho kinase 2 and Rho kinase 1 activity was determined using the IMAP™ Screening Express Kit (Molecular Devices product number #8073). Rho kinase 2 enzyme (Upstate/Chemicon #14-451), Rho kinase 1 (Upstate/Chemicon #14-601) and Flourescein tagged substrate peptide F1-AKRRRLSSLRA (Molecular Devices product number R7184) was pre-incubated with a test compound for 5 minutes in buffer containing 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, and 0.1% BSA. Following the pre-incubation, 10 μM ATP was added to initiate the reaction. After 60 minutes at room temperature, Molecular Devices IMAP™ binding solution was added to bind phosphorylated substrate. After 30 minutes of incubation in the presence of the IMAP™ beads, the fluorescence polarization was read and the ratio was reported as mP. ChEMBL_2274027 Inhibition of human USP7 using ubiquitin-Rho as substrate incubated for 1 hrs ChEMBL_98402 (CHEMBL706599) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Leucine aminopeptidase and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor ChEMBL_98520 (CHEMBL856600) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Leucine aminopeptidase and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor ChEMBL_98521 (CHEMBL706541) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Leucine aminopeptidase and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor ChEMBL_2437004 Inhibition of LPO (unknown origin)-mediated L-tyrosine nitration incubated for 20 mins in presence of H2O2 and sodium nitrite by RP-HPLC analysis Inhibition Potency Measurements The inhibition potency (IC50) was measured by fluorescent enzymatic assays. The compounds were evaluated for their ability to inhibit the hydrolysis of fluorescence-quenched peptide substrate. The enzyme was incubated with increasing concentration of inhibitor and the fluorescence (ex=328 nm; em=393 nm) was measured for 3 min after the addition of the substrate using a Varian Eclipse fluorimeter. Fitting of hydrolysis rate as a function of inhibitor concentration provided IC50. ChEMBL_432047 (CHEMBL918244) Inhibition of Rho kinase ChEMBL_432392 (CHEMBL915970) Inhibition of Rho kinase ChEBML_1703653 Inhibition of Rho-associated protein kinase 2 (unknown origin) ChEBML_157702 Compound was tested for the inhibition of HIV-1 protease by assaying the cleavage of a fluorescent peptide using HPLC In Vitro Assessment of Peptide Substrate Cleavage by BoNTA-LC Reactions between recombinant BoNTA-LC and fluorescent peptide substrate were carried out in 96-well microplates. Reaction progress was measured continuously by increase in fluorescence at Ex =398 nm, Em=485 nm as the cleavage of the substrate relieved the quenching of DACIA fluorescence by the 2,4-dinitrophenyl-lysine. The initial velocity values for enzymatic cleavage of peptide substrate were plotted against inhibitor concentration. The points were fit by non-linear regression analysis using the graphing program Prism (GraphPad). IC50 is the inhibitor concentration that achieves half-maximal enzyme inhibition. In Vitro Assay The IC50 of the compounds for inhibiting the interaction of a fluorescent NRF2 peptide and the Kelch domain of KEAP1 was determined using fluorescence anisotropy. Kinase assays for IC50 determinations Kinase activity was assayed in reaction buffer containing substrate peptide, enzyme, and inhibitor compound in the presence ATP/[gamma-33P] ATP. 33P incorporation was measured using a Perkin-Elmer Trilux scintillation counter. The IC50 is the inhibitor concentration, which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from 33P labeled ATP to the substrate. ChEMBL_35363 (CHEMBL874110) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Aminopeptidase M (AP-M) and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor ChEMBL_197036 (CHEMBL806275) compound was evaluated for the inhibitor constant against human S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase ChEMBL_461 (CHEMBL615691) The ability of the peptide to inhibit the binding of 50 pM [125I]gastrin releasing peptide to intact S-3T3 cells Enzyme Inhibition Assay IC50 is the concentration of inhibitor that decreases the velocity of the standard assay by 50%. The enzyme, NADPH, and varying concentrations of inhibitor were preincubated for 2 min, and the reaction was initiated by the addition of dihydrofolic acid. Steady state velocities were measured, and IC50 values were calculated from a linear regression plot of the percentage inhibition vs the logarithm of inhibitor concentration. Inhibitor Assay For inhibitor assays, IC50 was determined, in the presence of 1 mM NAD and 4 mM ATP (for LmNADK1) or 2 mM ATP (for SaNADK). Dixon plots were used to determine KI in the presence of 4 mM ATP (for LmNADK11) or 2 mM ATP (for Sa NADK) and three NAD concentrations (0.2, 0.5 and 1 mM). It was also checked that the inhibitors had no effect on the coupling enzyme activity. PKA assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from [gamma-32P] labeled ATP to a protein or peptide substrate. PKC assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from [gamma-32P] labeled ATP to a protein or peptide substrate. ChEMBL_98403 (CHEMBL706600) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Leucine aminopeptidase from porcine kidney and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor Protease Inhibition Assay The IC50 value is the inhibitor concentration that results in 50% of HIV-1 protease activity measured by a spectrophotometric assay using a chromophoric peptide. Dose-response biochemical assay of inhibitors of Rho kinase 2 (Rock2) Source (MLSCN Center Name): The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center Center Affiliation: The Scripps Research Institute, TSRI Assay Provider: Scripps Florida Network: Molecular Library Screening Center Network (MLSCN) Proposal Number: None External Assay ID: Rock2_INH_ LUMI_1536_ IC50 Name: Dose-response biochemical assay of inhibitors of Rho kinase 2 (Rock2) Description: Rho-Kinase is a serine/threonine kinase involved in the regulation of smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of nonmuscle cells (1). Its inhibition is known to promote the smooth muscle relaxation. Thus, small-molecule inhibitors of Rho-Kinase may be effective probes for treatment of cerebral vasospasm (2) and potentially effective for treatment of angina (3), hypertension (4), arteriosclerosis (5), and erectile dysfunction (6). References: [1] Trauger JW, Lin FF, Turner MS, Stephens J, LoGrasso PV. Kinetic mechanism for human Rho-Kinase II (ROCK-II).Biochemistry. 2002 J ChEMBL_197028 (CHEMBL803859) Compound was evaluated for the inhibitor constant against Escherichia coli S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase ChEMBL_197029 (CHEMBL803860) compound was evaluated for the inhibitor constant against Escherichia coli S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase PKA Inhibition Assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration, which inhibits 50% of PKA activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from [gamma-32P] labeled ATP to a synthetic kemptide peptide substrate. Phosphorylase Kinasse Assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from [gamma-32P] labeled ATP to a protein or peptide substrate. Inhibitor Assay The testing for the inhibition activities of imidazole derivatives and cacodylate on gQC and sQC was evaluated at 25 C using the fluorescent substrate L-glutaminyl 2-naphthylamide (Gln-BNA). Enzyme Assay and Determination of the Inhibition Constants. Ki values were obtained from human purified enzyme. All assays were run in microtiter plates. Plates were read for 30 min at 405 nm. Rates were determined for the controls (no inhibitor) and for the inhibitors. Percent enzyme activity was determined from these rates and used in the following formula to determine Ki: Ki=(1000)(inhibitor concentration)/{[(Km + S) - (S)(ACT)]/[(ACT)(Km)] -1}, where S is the substrate concentration and ACT is the % enzyme activity for inhibitor. Enzyme Assay and Determination of the Inhibition Constants. Ki values were obtained from purified enzyme. All assays were run in microtiter plates. Plates were read for 30 min at 405 nm. Rates were determined for the controls (no inhibitor) and for the inhibitors. Percent enzyme activity was determined from these rates and used in the following formula to determine Ki: Ki=(1000)(inhibitor concentration)/{[(Km + S) - (S)(ACT)]/[(ACT)(Km)] -1}, where S is the substrate concentration and ACT is the % enzyme activity for inhibitor. Biological Activity Assay For the measurement of CDK2/cyclinE activity, enzyme (0.22 nM) was incubated with 100 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for one hour. For the measurement of CDK4/CyclinD activity, enzyme (0.85 nM) was incubated with 200 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for three hours. Potential inhibitor compounds (as HCl salts) were tested using 12-point dose response curves in single point at the Km for ATP. The IC50 of each compound was determined using GraphPad Prism. Results from the IC50 values demonstrate 200 and 100 fold selectivity for compounds Compound 1 and Compound 3 for Cdk4/CycD1 over Cdk2/CycE respectively. Competitive Displacement Binding Assay The dissociation constant of the hCA and inhibitor complex was determined by competitive displacement of a fixed concentration of dansylamide by increasing concentrations of the inhibitor using Perkin-Elmer lambda 50-B spectrofluorometer. The excitation and emission wavelengths were maintained at 330 and 448 nm. Since the binding of the inhibitor competitively displaced dansylamide from the enzyme site, the fluorescence intensity at 448 nm decreased. The dissociation constant of the enzyme-inhibitor complex was determined by monitoring the decrease in the fluorescence of the enzyme-dansylamide complex as a function of the increasing concentration of the inhibitor. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from [gamma-32P] labeled ATP to a protein or peptide substrate. ChEMBL_35358 (CHEMBL647940) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Aminopeptidase M (AP-M) from porcine kidney and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor Kinase assay toxicity For nonspecific toxicity, the EC100 represents the concentration when 100% of the treated embryos exhibit either early lethality within hours of compound addition, variable embryonic defects, or developmental delay. For comparison, the effects of the known KDR inhibitor SU5416 are shown at the bottom. ChEBML_49250 Inhibition constant (KI) for the mmf chitin synthetase assay performed at constant inhibitor and varying substrate concentrations ChEMBL_4192 (CHEMBL619994) The compound was tested for inhibitory activity against 5-lipoxygenase translocation inhibitor in RBL-2H3 cells Direct Competition Assay The Ki for each inhibitor was determined by direct competition assays under steady-state conditions. The initial velocity was measured in the presence of a constant concentration of enzyme (3 nM for VIM-2 and 4 nM for VIM-24) with increasing concentrations of inhibitor (5−60 μM) against a fixed concentration (5KM) of the indicator substrate, NCF, as previously described. The reactionswere started by addition of VIM-2 or VIM-24 to substrate or to mixtures of substrate and inhibitor. ChEMBL_35364 (CHEMBL647945) Compound was evaluated for the inhibition of Aminopeptidase M (AP-M) and the inhibition constant was determined after preincubating the enzyme and inhibitor Value in the parentheses is IC50 (uM). Inhibition Activity Xanthine oxidase originated from bovine milk was incubated for 3 min with test compounds, and the initial velocity of uric acid formation was determined by adding the substrate xanthine. The initial velocity of test compound at each concentration was converted to % inhibition rate on the basis of the initial velocity under the absence of the inhibitor, thereby the inhibitor concentration needed for 50% inhibition was calculated as IC50 values. Biological Activity Kinase enzymatic reactions were performed in 384-well microplates using a 12-channel Caliper LabChip instrument as a detection device. The enzymatic phosphorylation of a peptide results in a change in net charge, enabling electrophoretic separation of product from substrate. As substrate and product are separated, two peaks of fluorescence are observed. Change in the relative fluorescence intensity of the substrate and product peaks is the parameter measured, reflecting enzyme activity. In the presence of an inhibitor, the ratio between product and substrate is altered. The signal of the product decreases, while the signal of the substrate increases.For the measurement of CDK2/cyclinE activity, enzyme (0.22 nM) was incubated with 100 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for one hour. For the measurement of CDK4/CyclinD activity, enzyme (0.85 nM) was incubated with 200 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for three hours. Potential inhibitor compounds (as HCl salts) were tested using 12-point dose response curves in single point at the Km for ATP. The IC50 of each compound was determined using GraphPad Prism. Src Inhibition Assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration, which inhibits 50% of pp60c-src activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from [gamma-32P] labeled ATP to a synthetic gastrin-based peptide substrate. LSD1 Assays Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of at least eight 3-fold serial dilutions of the respective inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 75 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in duplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, KM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 30 minutes at 37° C. in the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 5 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 μM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure level of H2O2 produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor. The maximum demethylase activity of LSD1 was obtained in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of LSD1. The IC50 value of each inhibitor was calculated with GraphPad Prism Software. The results presented in Table 1 below show the results of the LSD1 inhibition studies for a number of the Example compounds. In Table 2 the IC50 values for all examples tested in this assay are shown. Parnate (tranylcypromine; i.e., 2-trans phenylcyclopropylamine) was found to have a IC50 value of 35±10 micromolar. The studies show that the compounds of the invention have unexpectedly potent LSD1 inhibition. Oxadiazole SAR compounds tested by Multiplex dose response to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases specifically Cdc42 activated mutant University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Target Team Leader for the Center: Larry Sklar (lsklar@salud.unm.edu) Chemistry: University of Kansas Specialized Chemistry Center Target Team Leader for Chemistry: Jennifer Golden Dose Response Assay Background and Significance: Ras and related small molecular weight GTPases function in the regulation of signaling and cell growth, and collectively serve to control cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [Tekai et al. 2001; Wennerberg et al. 2005]. The Ras-related GTPases are divided into four subfamilies with the Rab proteins regulating membrane transport, Rho proteins (including Rac and Cdc 42) regulating cytoskeletal r Formaldehyde Dehydrogenase-Coupled Demethylase (FDH) Assay For inhibition assays, powders of inhibitor compounds were dissolved in 100% (v/v) DMSO to give a 20 or 50 mM concentration and stored at -20 °C until needed. Various compounds with the concentrations ranging from 1.25 mM to 5 nM in a half-log serial dilution were pre-incubated with the reaction mixture for 15 min (0.5 mM enzyme [E], 15 mM peptide [S], 50 mM (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2, 0.1 mM αKG, and variable inhibitor [I] in the KDM5 reaction buffer with 10% DMSO). The addition of peptide and APAD+ initiated the reaction for 15 min at room temperature. Formaldehyde Dehydrogenase-Coupled Demethylase (FDH) Assay For inhibition assays, powders of inhibitor compounds were dissolved in 100% (v/v) DMSO to give a 20 or 50 mM concentration and stored at -20 °C until needed. Various compounds with the concentrations ranging from 1.25 mM to 5 nM in a half-log serial dilution were pre-incubated with the reaction mixture for 15 min (0.5 mM enzyme [E], 15 mM peptide [S], 50 mM (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2, 1 mM αKG, and variable inhibitor [I] in the KDM5 reaction buffer with 10% DMSO). The addition of peptide and APAD+ initiated the reaction for 15 min at room temperature. Biochemical Assay A generalized procedure for a standard biochemical Btk Kinase Assay that can be used to test Formula I compounds. Alternatively, the Lanthascreen assay can be used to evaluate Btk activity through quantification of its phosphorylated peptide product. The FRET (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) that occurs between the fluorescein on the peptide product and the terbium on the detection antibody decreases with the addition of inhibitors of Btk that reduce the phosphorylation of the peptide. Biological Activity Assay Kinase enzymatic reactions were performed in 384-well microplates using a 12-channel Caliper LabChip instrument as a detection device. The enzymatic phosphorylation of a peptide results in a change in net charge, enabling electrophoretic separation of product from substrate. As substrate and product are separated, two peaks of fluorescence are observed. Change in the relative fluorescence intensity of the substrate and product peaks is the parameter measured, reflecting enzyme activity. In the presence of an inhibitor, the ratio between product and substrate is altered. The signal of the product decreases, while the signal of the substrate increases.For the measurement of CDK2/cyclinE activity, enzyme (0.22 nM) was incubated with 100 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for one hour. For the measurement of CDK4/CyclinD activity, enzyme (0.85 nM) was incubated with 200 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for three hours. Potential inhibitor compounds (as HCl salts) were tested using 12-point dose response curves in single point at the Km for ATP. Kinase Enzymatic Assay Kinase enzymatic reactions were performed in 384-well microplates using a 12-channel Caliper LabChip instrument as a detection device. The enzymatic phosphorylation of a peptide results in a change in net charge, enabling electrophoretic separation of product from substrate. As substrate and product are separated, two peaks of fluorescence are observed. Change in the relative fluorescence intensity of the substrate and product peaks is the parameter measured, reflecting enzyme activity. In the presence of an inhibitor, the ratio between product and substrate is altered. The signal of the product decreases, while the signal of the substrate increases.For the measurement of CDK2/cyclinE activity, enzyme (0.22 nM) was incubated with 100 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for one hour. For the measurement of CDK4/CyclinD activity, enzyme (0.85 nM) was incubated with 200 mM ATP and the phosphoacceptor substrate peptide (1 mM) for three hours. Potential inhibitor compounds (as HCl salts) were tested using 12-point dose response curves in single point at the Km for ATP. ChEBML_106803 Ability to inhibit the matrix metalloprotease-2 by method of Knight et al using the fluorogenic peptide substrate. ChEBML_45241 The equilibrium dissociation constant of the inhibitor-enzyme complex of human carbonic anhydrase Dissociation Constants (KD) Measurements and Enzyme Inhibition Assay (IC50) The NMR experiments were performed to determine the binding affinity (KD) for the MMP-12 catalytic domain. The alteration of the chemical shifts induced on 2D 1H-15N HSQC upon the titration with the test compound was analyzed. The fit of the experimental data as a function of ligand concentration provided dissociation constant. The inhibition potency (IC50) was measured by fluorescent enzymatic assays. The compounds were evaluated for their ability to inhibit the hydrolysis of fluorescence-quenched peptide substrate. The enzyme was incubated with increasing concentration of inhibitor and the fluorescence (ex=328 nm; em=393 nm) was measured for 3 min after the addition of the substrate using a Varian Eclipse fluorimeter. Fitting of hydrolysis rate as a function of inhibitor concentration provided IC50. ChEMBL_4193 (CHEMBL619995) The compound was tested for inhibitory activity against 5-lipoxygenase translocation inhibitor in rat RBL-2H3 cells ChEMBL_49250 (CHEMBL660670) Inhibition constant (KI) for the mmf chitin synthetase assay performed at constant inhibitor and varying substrate concentrations ChEMBL_88707 (CHEMBL873223) The compound was tested for it's in vitro inhibitor potency against inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase II (IMPDH II) BRD4 Fluorescence Polarization (FP) The assay used a Cy5 dye-labeled BRD inhibitor PFI-411FP. The synthesis of the probe and the procedure for the assay was reported recently (Hett et al.,2015; Wu et al., 2014). Inhibition Assay The IC50 values for the PHD2 enzyme (residues 181-417) were determined by mixing increasing amounts of inhibitor with a fixed amount of enzyme (5 nM, final concentration) and Biotin labeled peptide (Biotin-Asp-Leu-Glu-Met-Leu-Ala-Pro-Tyr-Ile-Pro-Met-Asp-Asp-Asp-Phe-Gln-Leu, 1 uM final concentration) and 2-Oxyglutarate (2 uM final concentration) in 50 mM HEPES, 50 mM KCl, 0.5 mM TCEP, 2 uM FeCl2, 0.1 mg/ml BSA, at pH 7.3. The reaction was conducted by pre-incubating the enzyme in the presence of inhibitor for 60 min at room temperature. The activity of the free enzyme was measured by adding the peptide, the 2-Oxoglutarate (see above for final concentrations), and Ascorbic Acid (1 mM final concentration). The enzymatic activity was quenched after 60 min by adding an excess of a tight binding inhibitor to the assay mixture. The amount of product released was measured by using a LC/MS system (Agilent HPLC with Applied Biosystems API3000 Mass Spectrometer). Metalloenzyme Activity V79-4 cells expressing recombinant andrenodoxin and andrenodoxin reductase with either recombinant human CYP11B2 or CYP11B1 were prepared according to methods previously described (LaSala et al 2009 Anal Bioch 394:56-61). An enzyme enriched microsomal fraction was prepared from cellular lysates and subsequently used as the enzyme source for determining inhibitor IC50s. The substrate Km values were experimentally determined for 11-deoxycorticosterone (CYP11B2 substrate) and 11-deoxycortisol (CYP11B1 substrate). Enzyme assays for inhibitor screening employed CYP11B2 and CYP11B1 enzyme enriched microsomes and were run at the Km of the respective substrates. Products of the enzyme reactions, aldosterone for CYP11B2 or cortisol for CYP11B1, were measured by LC-MS. Assays were run under conditions of less than 20% substrate turnover. Inhibitor IC50s were generated by determining the product formation in the absence or presence of inhibitor at various concentrations. In the absence of the test compound, the product formed (Pt) in each data set was defined as 100% activity. In the absence of enzyme, the product formed (Pb) in each data set was defined as 0% activity. The percent activity in the presence of each inhibitor was calculated according to the following equation: % activity=(P−Pb)/(Pt−Pb), where P=the product formed in the presence of the inhibitor. The IC50 value was defined as the inhibitor concentration causing a 50% decrease in activity relative to the no inhibitor control reaction. Enzyme Assay Enzyme assays for inhibitor screening employed CYP11B2 and CYP11B1 enzyme enriched microsomes and were run at the Km of the respective substrates. Products of the enzyme reactions, aldosterone for CYP11B2 or cortisol for CYP11B1, were measured by LC-MS. Assays were run under conditions of less than 20% substrate turnover. Inhibitor IC50s were generated by determining the product formation in the absence or presence of inhibitor at various concentrations. In the absence of the test compound, the product formed (Pt) in each data set was defined as 100% activity. In the absence of enzyme, the product formed (Pb) in each data set was defined as 0% activity. Amplex Red Peroxide/Peroxidase-Coupled Assay The compounds of the invention can be tested for their ability to inhibit LSD1. The ability of the compounds of the invention to inhibit LSD1 can be tested as follows. Human recombinant LSD1 protein was purchased from BPS Bioscience Inc. In order to monitor LSD1 enzymatic activity and/or its inhibition rate by our inhibitor(s) of interest, di-methylated H3-K4 peptide (Millipore) was chosen as a substrate. The demethylase activity was estimated, under aerobic conditions, by measuring the release of H2O2 produced during the catalytic process, using the Amplex Red peroxide/peroxidase-coupled assay kit (Invitrogen).Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of various concentrations of inhibitor (from 0 to 75 uM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in triplicate. ChEMBL_46665 (CHEMBL658626) Evaluated for the dissociation constant for the inhibition of caspase-3 Determination of the Inhibition Type and Constant (Ki) The Km and Kappm for the amino acid substrate were first calculated from Lineweaver-Burk plots. The Ki values were calculated from the Kappm vs [I] plot. The Ki values for the inhibitors with respect for the amino acid substrates were determined by measuring the apparent Km for the amino acid in the presence of saturating concentrations of both ATP and tRNA, and of various fixed concentrations of the inhibitor. Curve-fitting of these data using the theoretical functions for vi/v0 for various types of inhibition was made with the software Kaleidagraph (version 4.0) and was used to identify the types of inhibition and the Ki values. AdoMetDC Inhibition Assay The C-terminal his-tagged AdoMetDC was assayed by measuring the release of 14CO2 from S-adenosyl-L-[carboxy-14C]methionine (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech). For determination of the abilities of compounds to inhibit AdoMetDC, the enzyme activity was determined in the presence of no inhibitor and at least five concentrations of each potential inhibitor. The IC50 values were determined from curve fitting to plots of the inhibitor concentration versus the % inhibition of AdoMetDC. ChEMBL_45241 (CHEMBL658944) The equilibrium dissociation constant of the inhibitor-enzyme complex of human carbonic anhydrase ChEMBL_2299659 Inhibition of SRPK1 (unknown origin) using RS peptide as substrate incubated for 120 mins in the presence 33P-ATP ChEBML_160728 Tested for the inhibition of HIV-2 protease Chk1 Enzymatic Assay Chk1 kinase activity was assayed in reaction buffer containing substrate peptide, enzyme, and inhibitor in the presence of 100uM ATP/[gamma-33P] ATP. 33P incorporation was measured using a Perkin-Elmer Trilux scintillation counter. The IC50 is the inhibitor concentration, which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from 33P labeled ATP to the substrate. CA Inhibition Assay An applied photophysics stopped-flow instrument has been used for assaying the CA catalyzed CO2 hydration activity. Phenol red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM) has been used as indicator, working at the absorbance maximum of 557 nm, with 20mMHepes (pH 7.5) as buffer, and 20mM Na2SO4 (for maintaining constant the ionic strength), following the initial rates of the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 10-100 s. The CO2 concentrations ranged from 1.7 to 17mM for the determination of the kinetic parameters and inhibition constants. For each inhibitor at least six traces of the initial 5-10% of the reaction have been used for determining the initial velocity. The uncatalyzed rates were determined in the same manner and subtracted from the total observed rates. Stock solutions of inhibitor (0.1mM) were prepared in distilled-deionized water and dilutions up to 0.01nM were done thereafter with distilled deionized water. Inhibitor and enzyme solutions were preincubated together for 15 min to 72 h at room temperature (15 min) or 4 °C (all other incubation times) prior to assay, in order to allow for the formation of the E-I complex or for the eventual active site mediated hydrolysis of the inhibitor. Fluorescence Polarization Assay In the fluorescence polarization assay, the Bcl-XL protein is incubated with a fluorescein-tagged Bak-BH3 peptide. The Bcl-XL:Bak-BH3 peptide complex is then titrated with the test compounds, and the displacement of the Bak-BH3 peptide is measured as a function of decreasing polarized fluorescence. The fluorescence polarization values were determined using a Tecan GeniosPro plate reader using the excitation/emission wavelengths 485/535 nm. The binding affinities are reported as the inhibitory concentration of the titrant required to displace 50% of the Bak-BH3 peptide (IC50). Inhibitory Effect on HER2-Phosphorylating Activity (In Vitro) For setting the conditions for the method for measuring the in vitro inhibitory activity of a compound against HER2-phosphorylating activity, ProfilerPro Peptide 22 from PerkinElmer Inc. was used as a substrate on the basis of the report (PLoS One, 6 (7), e21487, 2011) on HER2 kinase reaction using, as a substrate, a peptide having the same sequence (5-FAM-EEPLYWSFPAKKK-CONH2) as that of ProfilerPro Peptide 22. The purified recombinant human HER2 protein used in the test was purchased from Carna Biosciences, Inc.For the inhibitory activity measurement of each compound, the synthesis example compound was first serially diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Next, the HER2 protein, the substrate peptide (final concentration: 0.5 μM), manganese chloride (final concentration: 10 mM), ATP (final concentration: 6 μM), and the solution of the synthesis example compound in DMSO (final concentration of DMSO: 5%) were added into a buffer solution for kinase reaction (15 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 2 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.01% Tween 20), and the mixture was incubated at 25° C. for 40 minutes for kinase reaction. The reaction was terminated by adding EDTA (final concentration: 30 mM) thereto. Finally, the unphosphorylated substrate peptide (S) and the phosphorylated peptide (P) were separated and detected by microcapillary electrophoresis using LabChip EZ Reader II (PerkinElmer Inc.). Biochemical Assay Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of various concentrations of inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 75 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in triplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, 12.5 μM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 1 hour at 37° C. in the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 30 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 μM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure level of H2O2 produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor. Human EGFR LanthaScreen Selectivity Assay TR-FRET LanthaScreen assays were performed by incubating a dilution series of inhibitor concentrations with 20 μM ATP, 100 nM peptide substrate (FITC-C6-KKAEEEEYFELVAKK-NH2 (SEQ ID NO.: 2, American Peptide, #333778) and 600 μM of human EGFR kinase domain (Invitrogen). The assays were performed with and without pre-incubating the inhibitors with the enzyme for 60 minutes before starting the kinase reaction by adding ATP and the peptide substrate. Samples containing enzyme but no inhibitor were included to determine the maximal extent of reaction. Samples containing no enzyme served as the negative control. The kinase reaction mixtures were incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes before stopping the kinase activity by the addition of 15 mM EDTA. The extent of peptide phosphorylation by EGFR was detected using a Terbium-conjugated anti-phospho-Tyrosine antibody (Tb-PT66 antibody, invitrogen # PV3557). Phosphorylation of peptide substrate was measured by determining the ratio of 520/495 nm on an Envision Multi-label Reader (Perkin Elmer) and IC50 values were calculated by fitting the data to a four-parameter equation using XLFIt4 (IDBS). TR-FRET LanthaScreen Assay EGFR: TR-FRET LanthaScreen assays were performed by incubating a dilution series of inhibitor concentrations with 20 μM ATP, 100 nM peptide substrate (FITC-C6-KKAEEEEYFELVAKK-NH2 (SEQ ID NO.: 2, American Peptide, #333778) and 600 pM of human EGFR kinase domain (Invitrogen). The assays were performed with and without pre-incubating the inhibitors with the enzyme for 60 minutes before starting the kinase reaction by adding ATP and the peptide substrate. Samples containing enzyme but no inhibitor were included to determine the maximal extent of reaction. Samples containing no enzyme served as the negative control. The kinase reaction mixtures were incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes before stopping the kinase activity by the addition of 15 mM EDTA. The extent of peptide phosphorylation by EGFR was detected using a Terbium-conjugated anti-phospho-Tyrosine antibody (Tb-PT66 antibody, Invitrogen # PV3557). Phosphorylation of peptide substrate was measured by determining the ratio of 520/495 nm on an Envision Multi-label Reader (Perkin Elmer) and IC50 values were calculated by fitting the data to a four-parameter equation using XLFit4 (IDBS). Monoamine Oxidase Assays Briefly, a fixed amount of MAO (0.25 μg for MAO-A and 0.5 μg for MAO-B) was incubated on ice for 15 minutes in the reaction buffer, in the absence and/or in the presence of various concentrations of inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 50 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. After leaving the enzyme(s) interacting with the inhibitor, 60 to 90 μM of kynuramine was added to each reaction for MAO-B and MAO-A assay respectively, and the reaction was left for 1 hour at 37° C. in the dark. The oxidative deamination of the substrate was stopped by adding 50 μL (v/v) of NaOH 2N. The conversion of kynuramine to 4-hydroxyquinoline, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 360 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure levels of fluorescence produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor. The maximum of oxidative deamination activity was obtained by measuring the amount of 4-hydroxyquinoline formed from kynuramine deamination in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of MAO enzymes. Multiplex dose response to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases specifically Cdc42 activated mutant University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Target Team Leader for the Center: Larry Sklar (lsklar@salud.unm.edu) Dose Response Assay Background and Significance: Ras and related small molecular weight GTPases function in the regulation of signaling and cell growth, and collectively serve to control cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [Tekai et al. 2001; Wennerberg et al. 2005]. The Ras-related GTPases are divided into four subfamilies with the Rab proteins regulating membrane transport, Rho proteins (including Rac and Cdc 42) regulating cytoskeletal rearrangements and responses to signaling, Arf/Sar proteins regulating membrane and microtubule dynamics as well Multiplex dose response to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases specifically Rab2 wildtype University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Target Team Leader for the Center: Larry Sklar (lsklar@salud.unm.edu) Dose Response Assay Background and Significance: Ras and related small molecular weight GTPases function in the regulation of signaling and cell growth, and collectively serve to control cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [Takai et al. 2001; Wennerberg et al. 2005]. The Ras-related GTPases are divided into four subfamilies with the Rab proteins regulating membrane transport, Rho proteins (including Rac and Cdc 42) regulating cytoskeletal rearrangements and responses to signaling, Arf/Sar proteins regulating membrane and microtubule dynamics as well Multiplex dose response to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases specifically Rac activated mutant University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Target Team Leader for the Center: Larry Sklar (lsklar@salud.unm.edu) Dose Response Assay Background and Significance: Ras and related small molecular weight GTPases function in the regulation of signaling and cell growth, and collectively serve to control cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [Takai et al. 2001; Wennerberg et al. 2005]. The Ras-related GTPases are divided into four subfamilies with the Rab proteins regulating membrane transport, Rho proteins (including Rac and Cdc 42) regulating cytoskeletal rearrangements and responses to signaling, Arf/Sar proteins regulating membrane and microtubule dynamics as well Multiplexed dose response to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases specifically Rac wildtype University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Target Team Leader for the Center: Larry Sklar (lsklar@salud.unm.edu) Dose Response Assay Background and Significance: Ras and related small molecular weight GTPases function in the regulation of signaling and cell growth, and collectively serve to control cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [Takai et al. 2001; Wennerberg et al. 2005]. The Ras-related GTPases are divided into four subfamilies with the Rab proteins regulating membrane transport, Rho proteins (including Rac and Cdc 42) regulating cytoskeletal rearrangements and responses to signaling, Arf/Sar proteins regulating membrane and microtubule dynamics as well Multiplexed dose response to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases specifically Ras wildtype University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Target Team Leader for the Center: Larry Sklar (lsklar@salud.unm.edu) Dose Response Assay Background and Significance: Ras and related small molecular weight GTPases function in the regulation of signaling and cell growth, and collectively serve to control cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [Tekai et al. 2001; Wennerberg et al. 2005]. The Ras-related GTPases are divided into four subfamilies with the Rab proteins regulating membrane transport, Rho proteins (including Rac and Cdc 42) regulating cytoskeletal rearrangements and responses to signaling, Arf/Sar proteins regulating membrane and microtubule dynamics as well Competitive Inhibition Assay Analysis of the inhibition activation of flNS3 by the inhibitors was performed with the standard assay, allowing the inhibitor to preincubate with NS3 and NS4 for 15 min. prior to addition of substrate. CA Inhibition Assay An Applied Photophysics stopped-flow instrument has been used for assaying the CA catalysed CO2 hydration activity. Phenol red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM) has been used as an indicator, working at the absorbance maximum of 557 nm, with 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5) as buffer, and 20 mM Na2SO4 (for maintaining constant the ionic strength), following the initial rates of the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 10-100 s. The CO2 concentrations ranged from 1.7 to 17 mM for thedetermination of the kinetic parameters and inhibition constants19. For each inhibitor at least six traces of the initial 5-10% of the reaction have been used for determining the initial velocity. The uncatalyzed rates were determined in the same manner and subtracted from the total observed rates. Stock solutions of inhibitor (0.1 mM) were prepared in distilled-deionized water and dilutionsup to 0.01 nM were done thereafter with distilled deionized water. Inhibitor and enzyme solutions were preincubated together for 15 min-72 h at room temperature(15 min) or 4 °C (all other incubation times) prior to assay, in order to allow for the formation of the E-I complex or for the eventual active site mediated hydrolysis of the inhibitor. ChEMBL_38359 (CHEMBL651291) In vitro inhibitory activity against Bak-Bh3 peptide binding to the Bcl-2 IMAP Assay Cdk9/cyclinT1 is purchased from Millipore, cat #14-685. The final total protein concentration in the assay 4 nM. The 5TAMRA-cdk7tide peptide substrate, 5TAMRA-YSPTSPSYSPTSPSYSTPSPS--COOH, is purchased from Molecular Devices, cat#R7352. The final concentration of peptide substrate is 100 nM. The ATP substrate (Adenosine-5'-triphosphate) is purchased from Roche Diagnostics, cat#1140965. The final concentration of ATP substrate is 6 uM. IMAP (Immobilized Metal Assay for Phosphochemicals) Progressive Binding reagent is purchased from Molecular Devices, cat#R8139. Fluorescence polarization (FP) is used for detection. The 5TAMRA-cdk7tide peptide is phosphorylated by Cdk9/cyclinT1 kinase using the ATP substrate. The Phospho-5TAMRA-cdk7tide peptide substrate is bound to the IMAP Progressive Binding Reagent. Kinetics Assay for IC50 Determination IC50 determinations for cSrc kinases were measured with the HTRF KinEASE-TK assay from Cisbio according to the manufacturer instructions. A biotinylated poly-Glu-Tyr substrate peptide was phosphorylated by cSrc. After completion of the reaction, an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody labeled with europium cryptate and streptavidin labeled with the fluorophore XL665 were added. The FRET between europium cryptate and XL665 was measured to quantify the phosphorylation of the substrate peptide. Kinase, substrate peptide, and inhibitor were preincubated for 2 h before the reaction was started by addition of ATP. A Tecan Safire2 plate reader was used to measure the fluorescence of the samples at 620 nm (Eu-labeled antibody) and 665 nm (XL665 labeled streptavidin) 60 us after excitation at 317 nm. The quotient of both intensities for reactions made with eight different inhibitor concentrations was fit to a Hill four-parameter equation to determine IC50 values. Each reaction was performed in duplicate, and at least three independent determinations of each IC50 were made. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Assay (FRET) The enzymatic reaction started by the addition fluorogenic peptide substrate, MAPKKide to the buffer containing LF and inhibitor compound. Cleavage of the substrate by LF released the fluorophore and full fluorescence was restored. Fluorescence intensity (Ex: 320 nm, Em: 420 nm) was monitored for 15 min at room temperature and the Ki values were calculated using the program BatchKi (BioKin Ltd., Pullman, WA). ChEBML_1703652 Inhibition of Rho-associated protein kinase 1 (unknown origin) ChEMBL_2274001 Inhibition of human USP7 using Ub-Rho as substrate ChEMBL_2213969 (CHEMBL5127101) Inhibition of UCHL1 (unknown origin) using Ub-Rho as substrate preincubated for 30 mins followed by substrate addition ChEMBL_1875746 (CHEMBL4377140) Inhibition of human PNP assessed as inhibitor constant for enzyme-inhibitor complex formation LSD1 Assay The compounds of the invention can be tested for their ability to inhibit LSD1. The ability of the compounds of the invention to inhibit LSD1 can be tested as follows. Human recombinant LSD1 protein was purchased from BPS Bioscience Inc. In order to monitor LSD1 enzymatic activity and/or its inhibition rate by our inhibitor(s) of interest, di-methylated H3-K4 peptide (Millipore) was chosen as a substrate. The demethylase activity was estimated, under aerobic conditions, by measuring the release of H2O2 produced during the catalytic process, using the Amplex Red peroxide/peroxidase-coupled assay kit (Invitrogen).Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of various concentrations of inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 75 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in triplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, 12.5 μM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 1 hour at 37° C. in the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 30 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 μM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure level of H2O2 produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor.The maximum demethylase activity of LSD1 was obtained in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of LSD1. The Ki (IC50) of each inhibitor was estimated at half of the maximum activity. Enzymatic Assay Methods: A peptide mobility shift assay was used to quantify the phosphorylation of the JAKtide (JAK-2 and JAK-3) or the IRS-1 peptide (JAK-1 and Tyk-2). Reactions were carried out in a 384-well plate (Matrical MP-101) in a 10 microliter total volume. Reaction mixtures contained 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM magnesium chloride, 0.01% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.0005% Tween-20, ATP (4 micromolar for JAK-2 and JAK-3, 40 micromolar for JAK-1 and 7 micromolar for Tyk-2)), 2% DMSO and 1 micromolar peptide substrate (JAKtide for JAK-2 and JAK-3 or IRS-1 peptide for JAK-1 and Tyk-2). Compounds were diluted serially in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide and tested in an 11 point dose response in duplicate or quadruplicate (200 nl of compound/DMSO was added per 10 microliter reaction). The reactions were initiated by the addition of enzyme to the final concentration of 2 nM JAK-2, 1 nM JAK-3, 7 nM Tyk2 or 20 nM JAK-1. The assay was run for 240 minutes for JAK-1, 150 minutes for JAK-2, 90 minutes for JAK-3. Inhibition of Cellular Release of Amyloid Peptide 1-40 Chinese hamster ovary cells are transfected with the human gene for amyloid precursor protein. The cells are plated at a density of 8000 cells/well into 96-well microtiter plates and cultivated for 24 hours in DMEM cell culture medium containing 10% FCS. The test compound is added to the cells at various concentrations, and the cells are cultivated for 24 hours in the presence of the test compound. The supernatants are collected, and the concentration of amyloid peptide 1-40 is determined using state of the art immunoassay techniques, for example sandwich ELISA, homogenous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) immunoassay, or electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay. The potency of the compound is calculated from the percentage of inhibition of amyloid peptide release as a function of the test compound concentration. ChEMBL_45240 (CHEMBL658943) The equilibrium dissociation constant of the inhibitor-enzyme complex of human Carbonic anhydrase II Spectrophotometric Assay Enzyme activities were measured in the presence of the test inhibitor in spectrophotometric assay. In Vitro Kinase Inhibition Assay IC50 is the inhibitor concentration, which inhibits 50% of kinase activity that catalyzes the transfer of the terminal phosphate from radiolabeled ATP to the peptide substrate. Use of radiolabeled ATP allows this transfer to be monitored by scintillation counting. Biological Assays-Inhibition of LSD1 Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of at least eight 3-fold serial dilutions of the respective inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 75 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in duplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, KM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 30 minutes at 37° C. in the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 5 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 μM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure level of H2O2 produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor.The maximum demethylase activity of LSD1 was obtained in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of LSD1. The IC50 value of each inhibitor was calculated with GraphPad Prism Software. LSD1 Assay Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of various concentrations of inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 75 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in triplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, 12.5 μM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 1 hour at 37° C. in the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 30 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 μM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Luminescent Kinase Assay Inhibition of TgCDPK1 and CpCDPK1 was determined using a luminescent kinase assay which measures ATP depletion in the presence of the Syntide 2 peptide substrate (KinaseGlo. Notably, both kinases were tested at the same ATP concentration which allows direct comparison of inhibitor potencies due to these enzymes possessing similar Kms for this cofactor. ChEBML_4308 Measuring the affinity of leukotriene synthesis inhibitor for 5-Lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) by using [125I]L-691831 as radioligand. ChEMBL_4309 (CHEMBL618417) Measuring the affinity of leukotriene synthesis inhibitor for 5-lipoxygenase activating protein by using [125I]L-691831 as radioligand. In Vitro Inhibitory Activity Assay For the inhibitory activity measurement of each compound, the compound of the present invention or staurosporine was first serially diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Next, the HER2 protein, the substrate peptide (final concentration: 0.5 uM), manganese chloride (final concentration: 10 mM), ATP (final concentration: 6 uM), and the solution of the compound of the present invention in DMSO (final concentration of DMSO: 5%) were added into a buffer solution for kinase reaction (15 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 2 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.01% Tween 20), and the mixture was incubated at 25° C. for 40 minutes for kinase reaction. The reaction was terminated by adding EDTA (final concentration: 30 mM) thereto. Finally, the unphosphorylated substrate peptide (S) and the phosphorylated peptide (P) were separated and detected by microcapillary electrophoresis using LabChip EZ Reader II (PerkinElmer Inc.). SARS-CoV 3CL Protease Inhibition Assay The effects of compound on enzyme activity were measured by using a fluorogenic peptide cleavage assay. Enhanced fluorescence caused by cleavage of the substrate peptide was monitored at 538 nm with excitation at 355 nm. The initial velocities of the inhibited reactions of 50 nM SARS 3CL protease and 6 uM fluorogenic substrate were plotted against the different inhibitor concentrations to obtain the IC50. Inhibitor Screening Assay The inhibitor screening assays were performed in 96-well format with 1152 small molecules found in the Prestwick chemical library (Prestwick Chemical, France). Malachite Green Assay A colorimetric assay for the release of inorganic phosphate upon hydrolysis of ATP was used to determine the potency of Hsp 90 inhibitor against enzyme. ChEMBL_160728 (CHEMBL873426) Tested for the inhibition of HIV-2 protease Src IC50 Determination IC50 values were determined with the Z lyte assay system (Invitrogen). The reactions were performed in 384-well small volume plates from Greiner (#784076). The kinase reaction for cSrc consisted of kinase buffer, kinase, peptide and ATP. For each IC50 determination, 16 different concentrations of inhibitor (range from 250,000 to 10 nM) were used in triplicate and at least three independent experiments were performed. Before starting the kinase reaction, enzyme and inhibitor were incubated for 40 min. Following the kinase reaction, Development Solution (included with the kit) was added to cleave the remaining unphosphorylated peptide. Following a 1 h incubation time with Development Solution, Stop Solution (included with the kit) was added to the reaction mixture. Fluorescence was then measured with a Spectramax M5 plate reader from Molecular Devices or a Safire2 from Tecan. Upon excitation of coumarin at 400 nm, fluorescence emission was measured at 445 nm (coumarin) and 520 nm (fluorescein). The ratio of coumarin to fluorescein emission was used to calculate the percentage of phosphorylation of the peptide by the kinase. TACE Inhibition Assay The compounds were tested for TACE inhibition using fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay. TACE catalyzed cleavage of the substrate peptide liberates the fluoropore from the proximity of the adjacent quenching moiety, and an increase in fluorescence signal results. HER2-Phosphorylating Activity For setting the conditions for the method for measuring the in vitro inhibitory activity of a compound against HER2-phosphorylating activity, ProfilerPro Peptide 22 from PerkinElmer Inc. was used as a substrate on the basis of the report (PLoS One, 6 (7), e21487, 2011) on HER2 kinase reaction using, as a substrate, a peptide having the same sequence (5-FAM-EEPLYWSFPAKKK-CONH2) as that of ProfilerPro Peptide 22. The purified recombinant human HER2 protein used in the test was purchased from Carna Biosciences, Inc. Also, staurosporine (Eur. J. Biochem., 234, p. 317-322, 1995; and Nat. Biotechnol., 26 (1), p. 127-132, 2008), which is a multikinase inhibitor having Her2 inhibitory activity, was purchased from Enzo Life Sciences, Inc. (item No.: ALX-380-014) and used as a positive control in this test.For the inhibitory activity measurement of each compound, the compound of the present invention or staurosporine was first serially diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Next, the HER2 protein, the substrate peptide (final concentration: 0.5 uM), manganese chloride (final concentration: 10 mM), ATP (final concentration: 6 uM), and the solution of the compound of the present invention in DMSO (final concentration of DMSO: 5%) were added into a buffer solution for kinase reaction (15 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 2 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.01% Tween 20), and the mixture was incubated at 25° C. for 40 minutes for kinase reaction. The reaction was terminated by adding EDTA (final concentration: 30 mM) thereto. Finally, the unphosphorylated substrate peptide (S) and the phosphorylated peptide (P) were separated and detected by microcapillary electrophoresis using LabChip EZ Reader II (PerkinElmer Inc.). The amount of phosphorylation reaction was determined from the respective peak heights of S and P. The compound concentration which can suppress the phosphorylation reaction by 50% was defined as an IC50 value (nM). ULK1 inhibition assay ULK1 inhibition assay is a screening assay to identify compounds that inhibit kinase activity of ULK1 using the ULKtide peptide. In some embodiments, the method contacting a candidate compound, ULK1 and a recombinant ULKtide peptide (or variant thereof); detecting phosphorylation of the recombinant peptide in the presence and absence of the candidate compound; and identifying a compound that inhibits kinase activity of ULK1 if phosphorylation of the recombinant peptide is decreased in the presence of the candidate compound compared to in the absence of the candidate compound. CA Inhibition Assay An Applied Photophysics stopped-flow instrument has been used for assaying the CA catalyzed CO2 hydration activity [Khalifah et al., J. Biol. Chem., 246:2561-73]. Phenol red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM) has been used as an indicator, working at the absorbance maximum of 557 nm, with 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.4 for hCA I and II) or with 20 mM Tris (pH 8.4, for ScCA) as buffers, and 20 mM NaClO4 (for maintaining constant the ionic strength), following the initial rates of the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 10-100 s. The CO2 concentrations ranged from 1.7 to 17 mM for the determination of the kinetic parameters and inhibition constants. For each inhibitor at least six traces of the initial 5%-10% of the reaction have been used for determining the initial velocity. The uncatalyzed rates were determined in the same manner and subtracted from the total observed rates. Stock solutions of inhibitor (10 mM) were prepared in distilled-deionized water and dilutions up to 0.001 nM were done thereafter with the assay buffers. Inhibitor and enzyme solutions were preincubated together for 15 min at room temperature prior to assay, in order to allow for the formation of the E-I complex. The concentration of the enzymes in the assays was of 8.0 nM for hCA I, of 5.9nM for hCA II and of 12.5 nM for ScCA, respectively. Biological Assay The compounds of the invention can be tested for their ability to inhibit LSD1. The ability of the compounds of the invention to inhibit LSD1 can be tested as follows. Human recombinant LSD1 protein was purchased from BPS Bioscience Inc (catalog reference number 50100: human recombinant LSD1, GenBank accession no. NM_015013, amino acids 158-end with N-terminal GST tag, MW: 103 kDa). In order to monitor LSD1 enzymatic activity and/or its inhibition rate by our inhibitor(s) of interest, di-methylated H3-K4 peptide (Anaspec) was chosen as a substrate. The demethylase activity was estimated, under aerobic conditions, by measuring the release of H2O2 produced during the catalytic process, using the Amplex Red hydrogen peroxide/peroxidase assay kit (Invitrogen).Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of at least eight 3-fold serial dilutions of the respective inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 75 uM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in duplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, KM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 30 minutes at 37° C. in the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 5 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 uM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure level of H2O2 produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor. The maximum demethylase activity of LSD1 was obtained in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of LSD1. The IC50 value of each inhibitor was calculated with GraphPad Prism Software. Enzymatic Assay A peptide mobility shift assay was used to quantify the phosphorylation of the JAKtide (JAK2 and JAK3) or the IRS-1 peptide (JAK1 and Tyk2). Reactions were carried out in a 384-well plate (Matrical MP-101) in a 10 L total volume. Reaction mixtures contained 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM magnesium chloride, 0.01% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.0005% Tween-20, ATP (4 M for JAK2 and JAK3, 40 M for JAK1 and 7 M for Tyk2)), 2% DMSO and 1 M peptide substrate (JAKtide for JAK2 and JAK3 and IRS-1 peptide for JAK1 and Tyk2). Compounds were diluted serially in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide and tested in an 11 point dose response in duplicate or quadruplicate (200 nl of compound/DMSO was added per 10 L reaction). The reactions were initiated by the addition of enzyme to the final concentration of 2 nM JAK2, 1 nM JAK3, 12 nM Tyk2 or 20 nM JAK1. The assay was run for 240 minutes for JAK1, 150 minutes for JAK2, 90 minutes for JAK3 and 70 minutes for Tyk2. ChEMBL_1875747 (CHEMBL4377141) Inhibition of human PNP assessed as inhibitor constant for enzyme-inhibitor-substrate complex formation Kinase Inhibition Assay For kinase inhibition assays, the final concentrations of the enzymes were 15, 14.5, 14.5, and 8.8 nM for CLK1, CLK2, CLK3, and Dyrk1A (Invitrogen, catalog no. PV3785), respectively. The compound concentrations ranged from 15503 to 121 nM and from 1550 to 12 nM. The RS domainderived peptide (GRSRSRSRSR) (Anaspec, catalog no. 61722) for CLK1 and CLK3, Dyrktide (RRRFRPASPLRGPPK) (Anaspec, catalog no. 62698) for Dyrk1A, and S6K peptide for CLK2 were used as substrates at a concentration of 5 μM. ChEBML_73023 Tested for the inhibition against the human dihydrofolate reductase Protease Inhibition Assay All enzyme assays were performed under initial velocity and steady-state conditions. The conditions for the enzyme catalyzed hydrolysis of the cleavage site peptide VSQN-(beta-naphthylalanine)-PIV were established with respect to time and enzyme concentration to yield linear initial velocity data. IC50 is inhibitor concentration, which inhibits 50% peptide cleavage activity of HIV protease. The detection of product was monitored with fluorescence (excitation 270 nm, emission 330 nm). In vitro binding of inhibitor to hCA-II Inhibitor binding to CA II was determined using a fluorescence competition assay. Displacement of dansylamide and binding of the inhibitor was determined by measuring and comparing the average fluorescence intensities of the treated versus control reactions. Binding constants were estimated from a Dixon plot of the data (reciprocal of the average fluorescence intensity versus inhibitor concentration) Shift AlphaScreen Assay The AlphaScreen Assay is modified to include the testing of inhibitors against ADAMTS-5 in the presence of 50% Lewis rat plasma in order to determine the effects of plasma protein binding on inhibitor potency. The ratio between the IC50 of the inhibitor against ADAMTS-5 in 50% Lewis rat plasma versus the IC50 of the inhibitor in buffer is calculated and is described as the plasma shift of the inhibitor. The assay is completed in the same manner using 10 nM ADAMTS-5 instead of 2.1 nM. A similar assay is used with dog ADAMTS-4 in the presence of 25% dog plasma. JAK Enzymatic Assay Methods: A peptide mobility shift assay was used to quantify the phosphorylation of the JAKtide (JAK-2 and JAK-3) or the IRS-1 peptide (JAK-1 and Tyk-2). Reactions were carried out in a 384-well plate (Matrical MP-101) in a 10 microliter total volume. Reaction mixtures contained 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM magnesium chloride, 0.01% bovine serum albumin (BSA), 0.0005% Tween-20, ATP (4 micromolar for JAK-2 and JAK-3, 40 micromolar for JAK-1 and 7 micromolar for Tyk-2)), 2% DMSO and 1 micromolar peptide substrate (JAKtide for JAK-2 and JAK-3 or IRS-1 peptide for JAK-1 and Tyk-2). Compounds were diluted serially in 100% dimethyl sulfoxide and tested in an 11 point dose response in duplicate or quadruplicate (200 nl of compound/DMSO was added per 10 microliter reaction). The reactions were initiated by the addition of enzyme to the final concentration of 2 nM JAK-2, 1 nM JAK-3, 7 nM Tyk2 or 20 nM JAK-1. The assay was run for 240 minutes for JAK-1, 150 minutes for JAK-2, 90 minutes for JAK-3 and 60 minutes for Tyk-2. KDR Kinase Inhibition Assay Conditions for assaying the in vitro inhibitory activity of the compound against KDR kinase activity were set with reference to the statement in the LabChip.TM. series reagent supplies price list of Caliper Life Sciences, Inc. that FL-Peptide 22 is adaptable as a substrate peptide to KDR kinase activity assay. The purified recombinant human KDR protein used in the test is a house purified product. For the inhibitory activity assay on the compound, the compound of the present invention was first serially diluted with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Next, the purified human KDR protein FL-Peptide 22 (final concentration: 1.5 uM), magnesium chloride (final concentration: 10 mM), ATP (final concentration: 200 uM), and each DMSO solution of the compound of the present invention (final concentration of DMSO: 5%) were added into a buffer solution for reaction (100 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 1 mM DTT, 0.003% Brij 35, 0.04% Tween-20, 0.05% CHAPSO) supplemented with a phosphatase inhibitor cocktail. Fluorescence Polarization Assay Assays effective in monitoring the inhibition of the MLL binding to menin were developed during experiments performed during the development of embodiments of the present invention. A fluorescein-labeled 12-amino acid peptide derived from MLL containing the high affinity menin binding motif was produced (Yokoyama et al., Cell., 2005. 123(2): p. 207-18., herein incorporated by reference in its entirety). Upon binding of the peptide (1.7 kDa) to the much larger menin (-67 kDa), the rotational correlation time of the fluorophore (peptide labeled with fluorescein at N-terminus) changes significantly, resulting in a substantial increase in the measured fluorescence polarization and fluorescence anisotropy (excitation at 500 nm, emission at 525 nm). The fluorescence polarization (FP) assay was utilized to determine the Kd for the binding of menin and the MLL peptide using a serial dilution of menin and 50 nM fluorescein-labeled MLL peptide. Inhibition Assay The assay was monitored spectrophotometrically through the consumption of beta-NADPH. The inhibitor assays contained inhibitor at concentrations of 0.1-15 mM cyclic analogues and 5-35 mM phosphonic acid derivates. Mobility Shift Assay (MSA) Type B The active BTK assay consisted of phosphorylated form of full length BTK. The assay was performed in a buffer solution utilized in the inactive BTK assay. The enzyme inhibitor complexes was incubated for 30 minutes at the room temperature and the kinase activation reaction was initiated by the addition of 1 μM Srctide peptide substrate and 16M ATP. After incubation at room temperature for 60 minutes, the reaction was stopped and the mobility shift was measured as described above for the inactive BTK assay. The data of inactive and active BTK assays was fit to a 4 parameter logistic model to calculate the IC50 value. Inhibitor Assay The assay mixture (100 L) containing 50 mM MOPS (pH 6.5), 2 mM pNPP and PTP1B were monitored at 405 nm for 2 min at 30 C. CA Inhibition Assay An Applied Photophysics stopped-flow instrument has been used for assaying the CA catalysed CO2 hydration activity [Khalifah et al., J. Biol. Chem., 246:2561-2573]. Phenol red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM) has been used as indicator, working at the absorbance maximum of 557 nm, with 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5) as buffer, and 20 mM Na2SO4 (for maintaining constant the ionic strength), following the initial rates of the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 10-100 s. The CO2 concentrations ranged from 1.7 to 17 mM for the determination of the kinetic parameters and inhibition constants. For each inhibitor, at least six traces of the initial 5-10% of the reaction have been used for determining the initial velocity. The uncatalyzed rates were determined in the same manner and subtracted from the total observed rates. Stock solutions of inhibitor (0.1 mM) were prepared in distilled-deionized water and dilutions up to0.01 nM were done thereafter with distilled-deionized water. Inhibitor and enzyme solutions were preincubated together for 15 min at room temperature prior to assay, in order to allow for the formation of the E-I complex. CA Inhibition Assay An Applied Photophysics stopped-flow instrument has been used for assaying the CA catalysed CO2 hydration activity [Khalifah et al., J. Biol. Chem., 246:2561-2573]. Phenol red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM) has been used as indicator, working at the absorbance maximum of 557 nm, with 10-20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5, for α-CAs) or TRIS (pH 8.3 for β-CAs) as buffers, and 20 mM Na2SO4 (for α-CAs) or 20 mM NaCl− for β-CAs (for maintaining constant the ionic strength), following the initial rates of the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 10-100 s. The CO2 concentrations ranged from 1.7 to 17 mM for the determination of the kinetic parameters and inhibition constants. For each inhibitor, at least six traces of the initial 5-10% of the reaction have been used for determining the initial velocity. The uncatalyzed rates were determined in the same manner and subtracted from the total observed rates. Stock solutions of inhibitor (10 mM) were prepared in distilled-deionized water and dilutions up to 0.01 nM were done thereafter with distilled-deionized water. Inhibitor and enzyme solutions were preincubated together for 15 min at room temperature prior to assay, in order to allow for the formation of the E-I complex. The inhibition constants were obtained by nonlinear least-square methods using PRISM 3, whereas the kinetic parameters for the uninhibited enzymes from Lineweaver-Burk plots, as reported earlier. CA Inhibition Assay An Applied Photophysics stopped-flow instrument has been used for assaying the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration activity [Khalifah et al., J. Biol. Chem., 246:2561-2573]. Phenol red (at a concentration of 0.2 mM)has been used as indicator, working at the absorbance maximum of 557 nm with 10-20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5, for α-CAs) or TRIS (pH 8.3 for β-CAs) as buffers, and20 mM Na2SO4 (for α-CAs) or 20 mM NaCl for β-CAs (for maintaining constant the ionic strength), following the initial rates of the CA-catalyzed CO2 hydration reaction for a period of 10-100 s. The CO2 concentrations ranged from 1.7 to 17 mM for the determination of the kinetic parameters and inhibition constants. For each inhibitor, at least six traces of the initial 5-10% of the reaction have been used for determining the initial velocity. The uncatalyzed rates were determined in the same manner and subtracted from the total observed rates. Stock solutions of inhibitor (10 mM) were prepared in distilled deionized water and dilutions up to 0.01 nM were done thereafter with distilled-deionized water. Inhibitor andenzyme solutions were preincubated together for 15 min at room temperature prior to assay in order to allow for the formation of the E-I complex. The inhibition constants were obtained by non-linear least-squares methods using PRISM 3, whereas the kinetic parameters for the uninhibited enzymes from Lineweaver-Burk plots,as reported earlier. ChEMBL_46814 (CHEMBL657058) The compound was tested for Ki value against rat whole brain P2 membrane preparation in absence of enzyme inhibitor PMSF ChEMBL_46816 (CHEMBL657060) The compound was tested for Ki value against rat whole brain P2 membrane preparation in presence of enzyme inhibitor PMSF. Kinase Assay Activated Akt isoforms and pleckstrin homology domain deletion constructs were assayed utilizing a GSK-derived biotinylated peptide substrate. The extend of peptide was determined by Homogeneous Time Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) using a lanthanide chelate (Lance)-coupled monoclonal antibody specific for the phosphopeptide in combination with a streptavidin-linked allophycocyanin (SA-APC) fluorophore which will bind to the biotin moiety on the peptide. SARS-CoV 3CL Protease Inhibition Assay The effects of compound on enzyme activity were measured by using a fluorogenic peptide cleavage assay. Enhanced fluorescence caused by cleavage of the substrate peptide was monitored at 538 nm with excitation at 355 nm. The Ki measurements were performed at two fixed inhibitor concentrations and various substrate concentrations. Antimalarial Testing In Vitro (IC50) and Measurement of Inhibition Constant (Ki) The concentration of inhibitor that inhibited 50% of the parasite growth (IC50) was determined from the sigmoidal curve obtained by plotting the percentages of [3H]-hypoxanthine incorporation against drug concentrations. The activity of pfDHFR-TS was determined spectrophotometrically using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. The Ki values of the inhibitors for the wild-type and mutant enzymes were determined by fitting to the equation IC50 = Ki(1 + ([S]/Km)), where IC50 is the concentration of inhibitor that inhibits 50% of the enzyme activity under the standard assay condition and Km is the Michaelis constant for the substrate H2folate. Kinase Inhibition Assay Enzymatic reactions were initiated by adding kinase to the reaction mixture containing ATP, [gamma-33P] ATP, peptide substrate and test inhibitor compound. The reactions were terminated after 10 min at 23 °C. The reaction mix was then transferred to filter plates for scintillation counting. Each inhibitor compound was added to the reaction to produce an 11-point dose-response curve (0.0001 to 10 uM). The IC50 values were estimated from data fit to the equation: y =Vmax X (1 - (x/(K + x)). ChEMBL_143851 (CHEMBL747208) The compound was tested for the binding affinity against Neuropeptide Y receptor type 2 In Vitro Enzyme Assay The proteolytic cleavage of N-acyl aminocoumarins by cathepsins was conducted in Dynatech Microfluor fluorescence 96-well microtiter plates, and readings were taken on a Molecular Devices Spectra Max Gemini XS instrument. The excitation wavelength was 355 nm and the emission wavelength was 450 nm for peptidyl-AMC substrates. Generation of AMC was monitored over 5 min. The dissociation constants (Ki) were determined from the IC50 values taken from plots of Vi/Vo versus inhibitor concentration, where Vo is the velocity in the absence of the inhibitor and Vi is the velocity with the inhibitor. The IC50 values were converted to Ki by the equation Ki = IC50 - Et/2, where Et is the enzyme concentration. ChEBML_60356 The compound was evaluated for the dissociation constant for inhibiting the binding of [3H]-SCH- 23390 at Dopamine receptor D1 ChEBML_164495 Inhibitory activity against peptide binding to the RRE RNA was determined ChEBML_34991 Displacement of [125I]- ANP from the Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Clearance Receptor. ChEBML_34995 Displacement of [125I]- ANP from the Atrial natriuretic peptide receptor A. ChEMBL_154313 (CHEMBL762798) Inhibition of the isolated native E. coli peptide deformylase (PDF) Profiling Assay to determine GST-GSH interactions in multiplex bead-based assays University of New Mexico Assay Overview: Assay Support: NIH I RO3 MH081231-01 HTS to identify specific small molecule inhibitors of Ras and Ras-related GTPases PI: Angela Wandinger-Ness, Ph.D. Co-PI: Larry Sklar, Ph.D. Assay Development: Zurab Surviladze, Ph.D. Assay Implementation: Zurab Surviladze, Danuta Wlodek, Terry Foutz, Mark Carter, Anna Waller Profiling Assay Background and Significance: The objective of the HTS associated with this counterscreen was to identify small molecule regulators of Ras and Ras-related GTPases (see Summary Report and PubChem AIDs 1333, 1334, 1335, 1336, 1337, 1339, 1340, 1341). The primary HTS assay was a no-wash fluorescent GTP-binding assay adapted to multiplexed, high-throughput measurements whereby multiple GTPases were simultaneously screened against the MLSCN library. The specificity is based on the observation that individual GTPases including wt and activated forms exhibit measurably distinct affinities for Bodipy-FI-GTP vs GTP. The assay DHODH Inhibition Assay The assays were carried out by using a colorimetric DCIP method, which uses the colorimetric reagent 2, 6-dichlorophenolindophenol as the final electron acceptor. DCIP reduction is stoichiometrically equivalent to oxidation of dihydroorotate. Changes in absorbance were quantified on a plate reader and data were analyzed to measure the reduction of DCIP as a decrease in absorbance at 600 nm. For the determination of the IC50 values (concentration of inhibitor required for 50% inhibition) different inhibitor concentrations were applied. BTK Inhibitory Activity With regard to the setting of the conditions for a method for measuring the inhibitory activity of a compound against BTK kinase activity in vitro, it is described in the consumable reagent supplies price list for LabChip (registered trademark) series of PerkinElmer, Inc. that FL-PEPTIDE 2 corresponds to a substrate peptide for the measurement of BTK kinase activity. Therefore, FL-PEPTIDE 2 was used as a substrate. The purified recombinant human BTK protein used in the test was purchased from Carna Biosciences, Inc.With regard to the measurement of the inhibitory activity of the compounds, firstly, the compounds of the present invention were diluted stepwise with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Subsequently, BTK protein, a substrate peptide (final concentration was 1 μM), magnesium chloride (final concentration was 10 mM), ATP (final concentration was 45 μM), and a DMSO solution of the compounds of the present invention (final concentration of DMSO was 5%) were added to a buffer solution for kinase reaction (20 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 2 mM dithiotheitol, 0.01% Triton X-100), and after the solution was incubated for 40 minutes at 25° C., a kinase reaction was carried out. The reaction was terminated by adding EDTA thereto in order to obtain a final concentration of 30 mM. Finally, a substrate peptide that was not phosphorylated (S) and a phosphorylated peptide (P) were separated and detected by microchannel capillary electrophoresis using a LabChip EZ Reader II (PerkinElmer, Inc.). The amounts of phosphorylation reaction were determined from the respective peak heights of S and P, and the compound concentration at which the phosphorylation reaction could be suppressed in 50% was defined as the IC50 value (nM). Immunofluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) Assay The FRET assay was performed essentially as described in Gruninger-Leitch et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry (2002) 277(7) 4687-93 (Substrate and inhibitor profile of BACE (beta-secretase) and comparison with other mammalian aspartic proteases). In summary, a peptide is designed that is cleaved by the protease. The peptide is labelled with dabcyl at the N terminus and Lucifer Yellow at the C-terminus, such that for an intact peptide the Lucifer Yellow fluorescence is quenched by the dabcyl. When the peptide is cut by BACE2, the quenching is removed and a fluorescent signal is generated. The assay was performed as described in Grueninger et al. 2002 at pH 4.5 using a substrate concentration of 5 μM. A FRET peptide based on the TMEM27 sequence was devised. dabcyl-QTLEFLKIPS-LucY (SEQ ID NO: 1). BACE2 had a high activity against this sequence, which is unrelated to the known APP-based substrates. Conversely, BACE1 had insignificant activity against this peptide. Inhibition Assay The assay is based on the principle that binding of the agonist to the RORγ causes a conformational change around helix 12 in the ligand binding domain, resulting in higher affinity for the co-activator peptide. The Fluorescein-D22 co-activator peptide used in the assay is recruited in the absence of a ligand. Binding of the co-activator peptide, causes an increase in the TR-FRET signal while binding of an inhibitor decreases the recruitment of the co-activator peptide, causing a decrease in the TR-FRET signal compared to a control with no test compound. The assay was performed using a two-step procedure, pre-incubation step with the test compound followed by the detection step on addition of the anti-GST tagged terbium (Tb) and fluorescein tagged fluorophores as the acceptor.Test compounds or reference compounds such as T0901317 (Calbiochem) were dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) to prepare 10.0 mM stock solutions and diluted to the desired concentration. The final concentration of DMSO in the reaction was 4% (v/v). The assay mixture was prepared by mixing 10 nM of the GST-tagged ROR gamma ligand binding domain (LBD) in the assay buffer containing 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM DTT and 0.01% BSA with or without the desired concentration of the test compound. The reaction was incubated at 22° C. for 1 hour. The pre-incubation step was terminated by addition of the detection mixture containing 300 nM Fluorescein-D22 co-activator peptide and 10 nM lantha screen Tb-anti GST antibody into the reaction mixture. After shaking for 5 minutes the reaction was further incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and read at 4° C. on an Infinite F500 reader as per the kit instructions (Invitrogen). Inhibition Assay Chinese hamster ovary cells are transfected with the human gene for amyloid precursor protein. The cells are plated at a density of 8000 cells/well into 96-well microtiter plates and cultivated for 24 hours in DMEM cell culture medium containing 10% FCS. The test compound is added to the cells at various concentrations, and the cells are cultivated for 24 hours in the presence of the test compound. The supernatants are collected, and the concentration of amyloid peptide 1-40 is determined using state of the art immunoassay techniques, for example sandwich ELISA, homogenous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) immunoassay, or electro-chemiluminescence immunoassay. The potency of the compound is calculated from the percentage of inhibition of amyloid peptide release as a function of the test compound concentration. Binding Assay The binding properties of the test compounds on adenosine receptors were determined in binding studies with radioligands. For this purpose, membrane preparations of the human adenosine receptor subtypes were produced from cell lines having recombinant receptor expression (CHO cells for the A1 receptor, HEK293 cells for the A2a, A2b and A3 receptors). The following radioligands were used in the experiments: [3H]-DPCPX for the A1 receptor, [3H]-CGS 21680 for the A2a receptor, [3H]-CPX for the A2b receptor and [125I]-AB-MECA for the A3 receptor. The test substances were each tested in 8 different concentrations and 2 repeat tests per concentration. The displacement of the particular radioligand by the test compound was expressed as percentage inhibition of the specific binding of the controls. Biological Assay The compounds of the invention can be tested for their ability to inhibit LSD1. The ability of the compounds of the invention to inhibit LSD1 can be tested as follows. Human recombinant LSD1 protein was purchased from BPS Bioscience Inc (catalog reference number 50100: human recombinant LSD1, GenBank accession no. NM_015013, amino acids 158-end with N-terminal GST tag, MW: 103 kDa). In order to monitor LSD1 enzymatic activity and/or its inhibition rate by our inhibitor(s) of interest, di-methylated H3-K4 peptide (Anaspec) was chosen as a substrate. The demethylase activity was estimated, under aerobic conditions, by measuring the release of H2O2 produced during the catalytic process, using the Amplex Red hydrogen peroxide/peroxidase assay kit (Invitrogen).Briefly, a fixed amount of LSD1 was incubated on ice for 15 minutes, in the absence and/or in the presence of at least eight 3-fold serial dilutions of the respective test compound (e.g., from 0 to 75 uM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition. Within the experiment, each concentration of inhibitor was tested in duplicate. After leaving the enzyme interacting with the inhibitor, KM of di-methylated H3-K4 peptide was added to each reaction and the experiment was left for 30 minutes at 37° C. In the dark. The enzymatic reactions were set up in a 50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 buffer. At the end of the incubation, Amplex Red reagent and horseradish peroxidase (HPR) solution were added to the reaction according to the recommendations provided by the supplier (Invitrogen), and left to incubate for 5 extra minutes at room temperature in the dark. A 1 uM H2O2 solution was used as a control of the kit efficiency. The conversion of the Amplex Red reagent to resorufin due to the presence of H2O2 in the assay, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 540 nm, emission at 590 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure level of H2O2 produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor. The maximum demethylase activity of LSD1 was obtained in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of LSD1. The IC50 value of each inhibitor was calculated with GraphPad Prism Software. ChEBML_154319 Compound was evaluated for inhibitory activity against Peptide deformylase ChEMBL_89213 (CHEMBL699705) Inhibition constant (Ki) for human intestinal peptide carrier Monoamine Oxidase Assays Briefly, a fixed amount of MAO (0.25 μg for MAO-A and 0.5 μg for MAO-B) was incubated on ice for 15 minutes in the reaction buffer, in the absence and/or in the presence of various concentrations of inhibitor (e.g., from 0 to 50 μM, depending on the inhibitor strength). Tranylcypromine (Biomol International) was used as a control for inhibition.After leaving the enzyme(s) interacting with the inhibitor, 60 to 90 μM of kynuramine was added to each reaction for MAO-B and MAO-A assay respectively, and the reaction was left for 1 hour at 37° C. in the dark. The oxidative deamination of the substrate was stopped by adding 50 μL (v/v) of NaOH 2N. The conversion of kynuramine to 4-hydroxyquinoline, was monitored by fluorescence (excitation at 320 nm, emission at 360 nm) using a microplate reader (Infinite 200, Tecan). Arbitrary units were used to measure levels of fluorescence produced in the absence and/or in the presence of inhibitor.The maximum of oxidative deamination activity was obtained by measuring the amount of 4-hydroxyquinoline formed from kynuramine deamination in the absence of inhibitor and corrected for background fluorescence in the absence of MAO enzymes. ChEBML_141731 The compound was evaluated for the inhibition of NADH dehydrogenase ChEBML_155080 The compound was evaluated for the inhibitory activity against plasmin ChEBML_208132 The compound was evaluated for the inhibitory activity against thrombin ChEBML_212352 The compound was evaluated for the inhibitory activity against trypsin ChEBML_41716 The compound was evaluated for the inhibition human of Butyrylcholinesterase ChEMBL_211356 (CHEMBL815872) The compound was evaluated for the anti-tubulin activity. ChEMBL_73023 (CHEMBL682625) Tested for the inhibition against the human dihydrofolate reductase Enzyme Inhibition Assay The inhibitory activities of compounds of the invention against the GSK 3 enzyme isoform (Invitrogen), are evaluated by determining the level of activation/phosphorylation of the target peptide. The GSK3-α protein (500 ng/mL, 2.5 uL) is mixed with the test compound (2.5 uL at either 4 ug/mL, 0.4 ug/mL, 0.04 ug/mL, or 0.004 ug/mL) for 2 hr at RT. The FRET peptide (8 uM, 2.5 uL), which is a phosphorylation target for GSK3α, and ATP (40 uM, 2.5 uL) are then added to the enzyme/compound mixture and the resulting mixture incubated for 1 hr. Development reagent (protease, 5 uL) is added for 1 hr prior to detection in a fluorescence microplate reader (Varioskan Flash, ThermoFisher Scientific). Enzyme Inhibition The inhibitory activities of compounds of the invention against the GSK 3-alpha enzyme isoform (Invitrogen), are evaluated by determining the level of activation/phosphorylation of the target peptide. The GSK3-alpha protein (500 ng/mL, 2.5 uL) is mixed with the test compound (2.5 uL at either 4 ug/mL, 0.4 ug/mL, 0.04 ug/mL, or 0.004 ug/mL) for 2 hr at RT. The FRET peptide (8 uM, 2.5 uL), which is a phosphorylation target for GSK3alpha, and ATP (40 uM, 2.5 uL) are then added to the enzyme/compound mixture and the resulting mixture incubated for 1 hr. Development reagent (protease, 5 uL) is added for 1 hr prior to detection in a fluorescence microplate reader (Varioskan Flash, ThermoFisher Scientific). Functional Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerase (PPlase) Spectrophotometric Assay Cyclophilins are enzymes that catalyse the cis-trans isomerisation of peptide bonds to the amino acid proline. This event is important in many biological processes, including protein folding and signal transduction. Cyclosporins and the compounds of the present invention inhibit this catalytic activity. The method to measure this activity and its inhibition is similar to that described by Jankowski (Analytical Biochemistry, 252, 2, 299-307 (1997)). The assay measures the cis to trans isomerisation of a peptide substrate catalysed by a PPlase enzyme using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer. This assay is a manual single cuvette-based assay. A first order rate equation is fitted to the absorbance data to obtain a rate constant. The catalytic rate is calculated from the enzymatic rate minus the background rate. The Ki (the concentration required to produce half maximum inhibition) for an inhibitor is obtained from the rate constant plotted against the inhibitor concentration. KinEASE Assay IC50 determinations for activated Akt1 were measured with the KinEASE assay (Cisbio) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The kinases Akt1 (batch no. D8MN034U-L) was purchased from Millipore. 5 μL kinase solution (0.12 nM for Akt1) and 2.5 μL inhibitor solution (8% DMSO in HTRF buffer) were pre-incubated for 1 h before the reaction was started by addition of 2.5 μL of a solution containing ATP and substrate peptide. The final ATP and substrate concentrations were set at their respective Km values (50 μM and 250 nM, respectively, for Akt1). The biotinylated STK3 substrate peptide is then phosphorylated by Akt1 for 45 min. After completion of the reaction, 10 μL of a solution with an anti-phosphoserine/-threonine antibody labeled with Europium Cryptate and Streptavidin labeled with the fluorophore XL665 (0.5 μM for Akt1) were added simultaneously. The FRET between Europium Cryptate and XL665 was measured to quantify the extent of substrate pep
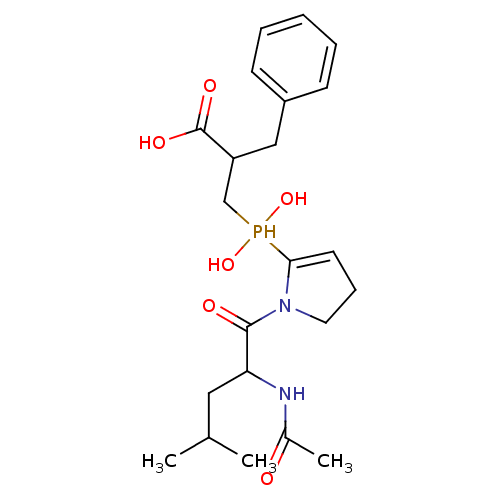 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 28 FII 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-4-methylpentanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. BDBM21464
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 28 FII 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-4-methylpentanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. BDBM21464 2-benzyl-3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 34 FII The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. BDBM21470
2-benzyl-3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 34 FII The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. BDBM21470 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 26 BDBM21462 2-benzyl-3-[hydroxy(pyrrolidin-2-yl)phosphoryl]propanoic acid
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 26 BDBM21462 2-benzyl-3-[hydroxy(pyrrolidin-2-yl)phosphoryl]propanoic acid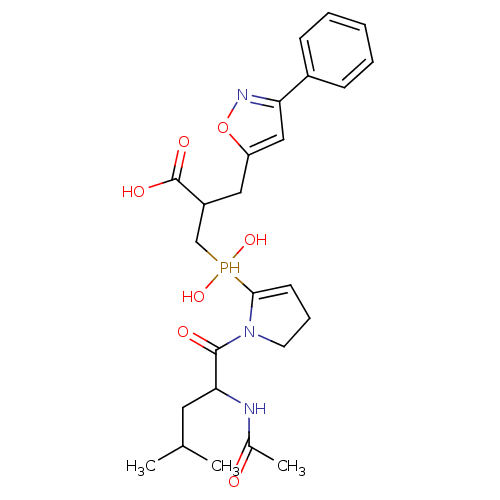 3-{[1-(2-acetamido-4-methylpentanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}-2-[(3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]propanoic acid The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. BDBM21473 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 40 FII
3-{[1-(2-acetamido-4-methylpentanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}-2-[(3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]propanoic acid The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. BDBM21473 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 40 FII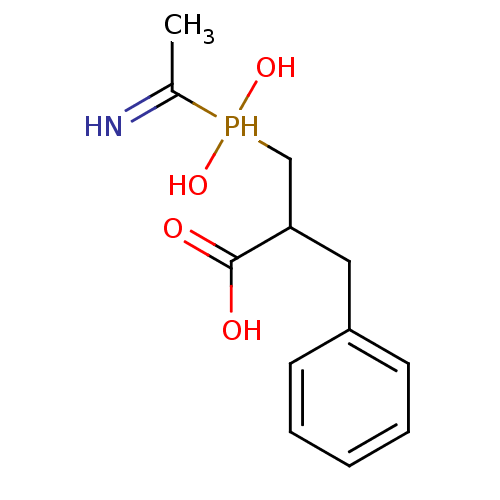 BDBM21459 3-[(1-aminoethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]-2-benzylpropanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 18 CHEMBL51566
BDBM21459 3-[(1-aminoethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]-2-benzylpropanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 18 CHEMBL51566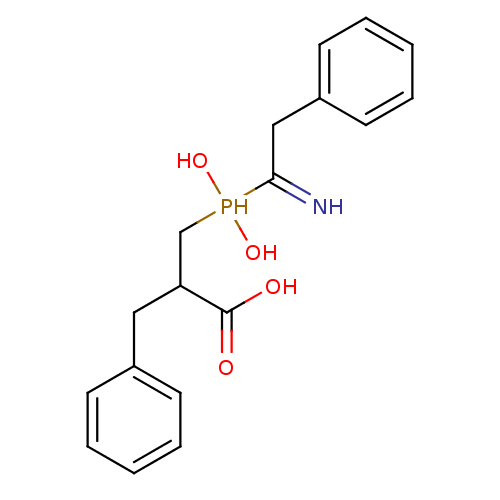 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 19 CHEMBL34068 3-[(1-amino-2-phenylethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]-2-benzylpropanoic acid BDBM21460
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 19 CHEMBL34068 3-[(1-amino-2-phenylethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]-2-benzylpropanoic acid BDBM21460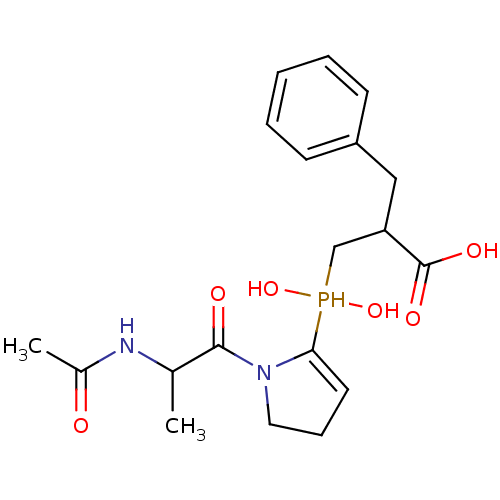 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 27 BDBM21463 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamidopropanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 27 BDBM21463 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamidopropanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid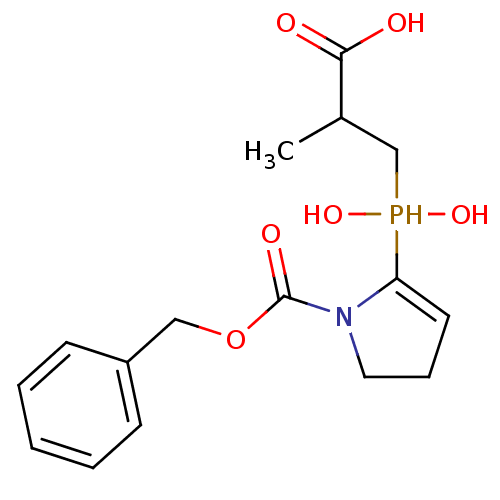 BDBM21455 3-({1-[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)-2-methylpropanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 14
BDBM21455 3-({1-[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)-2-methylpropanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 14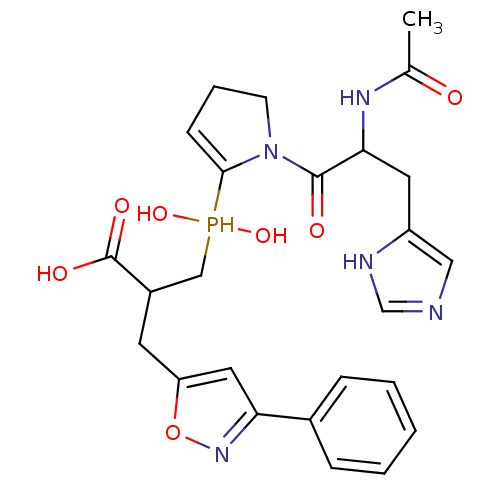 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 41 FII The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. 3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)-2-[(3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]propanoic acid BDBM21474
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 41 FII The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. 3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)-2-[(3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]propanoic acid BDBM21474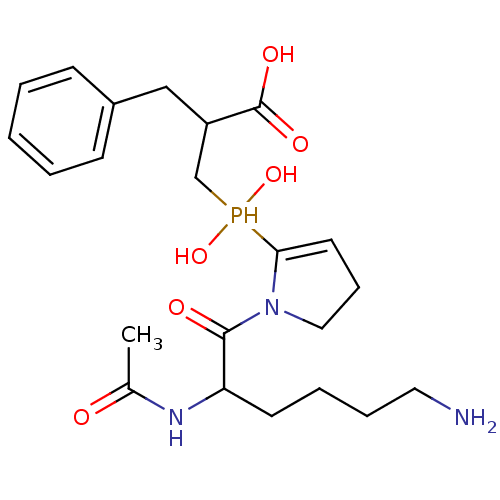 3-{[1-(6-amino-2-acetamidohexanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}-2-benzylpropanoic acid BDBM21465 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 29
3-{[1-(6-amino-2-acetamidohexanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}-2-benzylpropanoic acid BDBM21465 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 29 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 35 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-4-methylpentanamido)-2-phenylethyl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid BDBM21471
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 35 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-4-methylpentanamido)-2-phenylethyl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid BDBM21471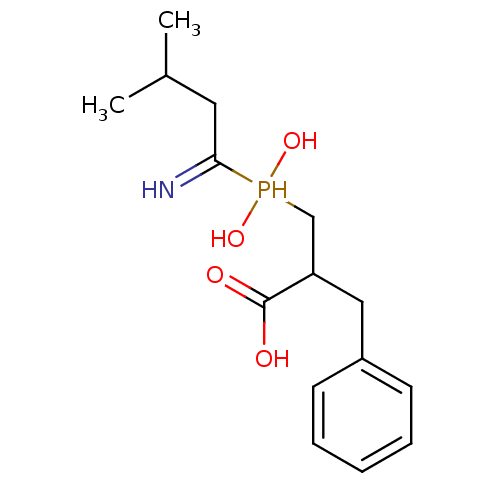 CHEMBL36716 3-[(1-amino-3-methylbutyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]-2-benzylpropanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 20 BDBM21461
CHEMBL36716 3-[(1-amino-3-methylbutyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]-2-benzylpropanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 20 BDBM21461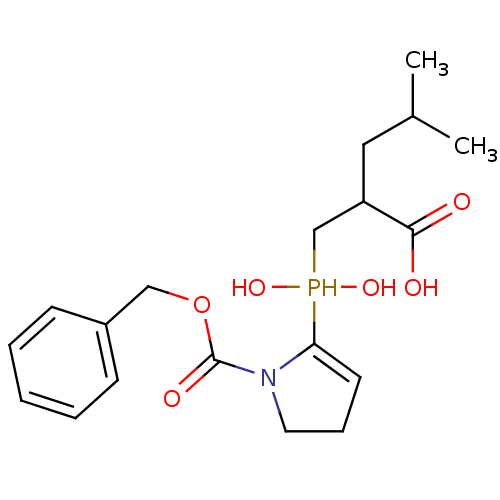 2-[({1-[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)methyl]-4-methylpentanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 13 BDBM21454
2-[({1-[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)methyl]-4-methylpentanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 13 BDBM21454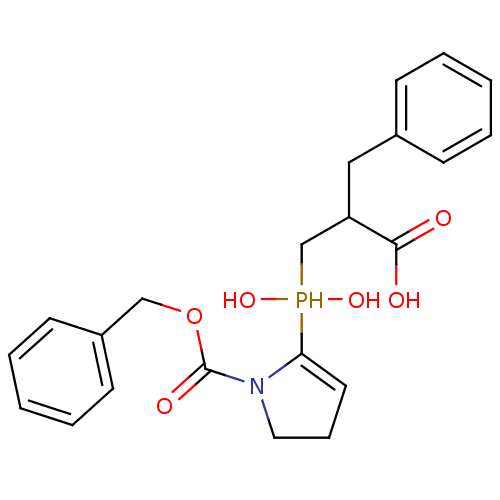 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 12 BDBM21452 2-benzyl-3-({1-[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 12 BDBM21452 2-benzyl-3-({1-[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 16 BDBM21457 2-benzyl-3-[(1-{[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}-2-phenylethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]propanoic acid
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 16 BDBM21457 2-benzyl-3-[(1-{[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}-2-phenylethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]propanoic acid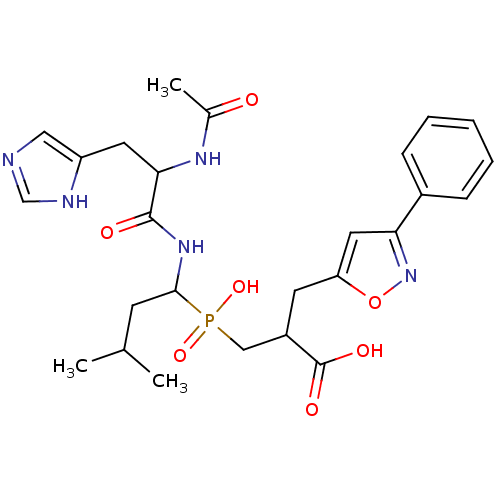 The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 44 FII BDBM21475 3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido]-3-methylbutyl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)-2-[(3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]propanoic acid
The second fraction of the HPLC chromatogram. Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 44 FII BDBM21475 3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido]-3-methylbutyl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)-2-[(3-phenyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]propanoic acid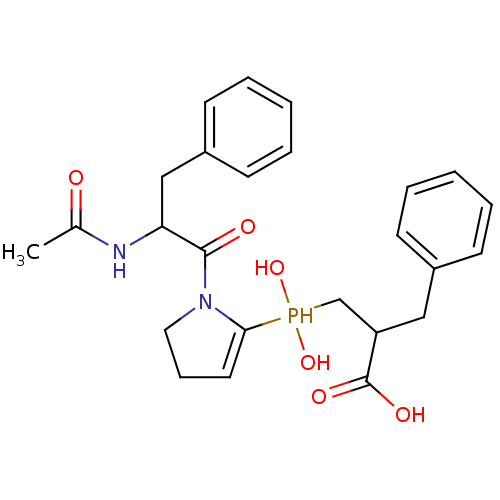 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 32 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-3-phenylpropanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid BDBM21468
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 32 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-3-phenylpropanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid BDBM21468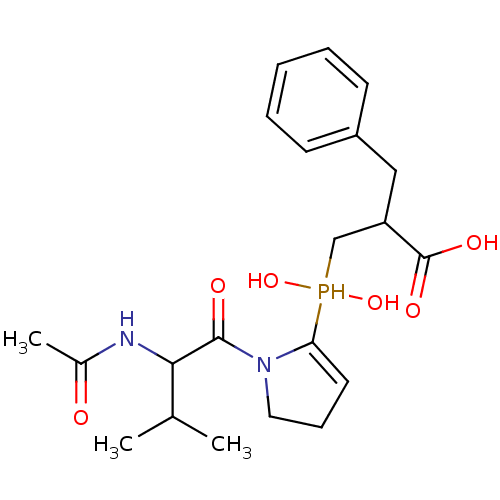 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 33 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-3-methylbutanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid BDBM21469
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 33 2-benzyl-3-{[1-(2-acetamido-3-methylbutanoyl)pyrrolidin-2-yl](hydroxy)phosphoryl}propanoic acid BDBM21469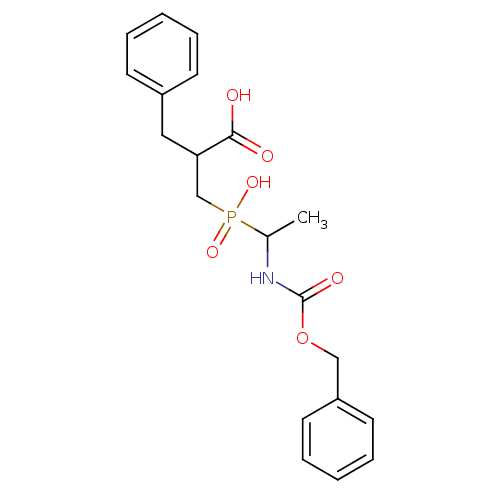 2-benzyl-3-[(1-{[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}ethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]propanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 15 BDBM21456
2-benzyl-3-[(1-{[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}ethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]propanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 15 BDBM21456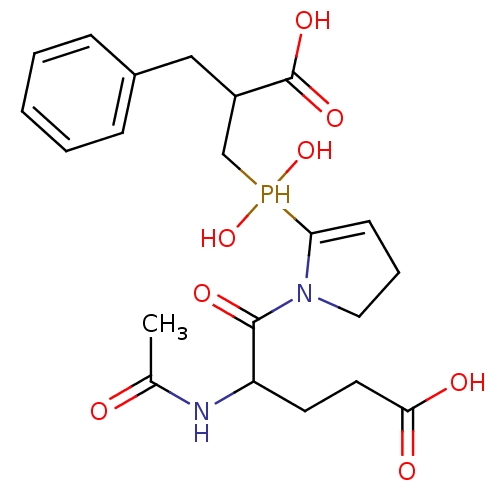 BDBM21466 5-{2-[(2-benzyl-2-carboxyethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]pyrrolidin-1-yl}-4-acetamido-5-oxopentanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 30
BDBM21466 5-{2-[(2-benzyl-2-carboxyethyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]pyrrolidin-1-yl}-4-acetamido-5-oxopentanoic acid Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 30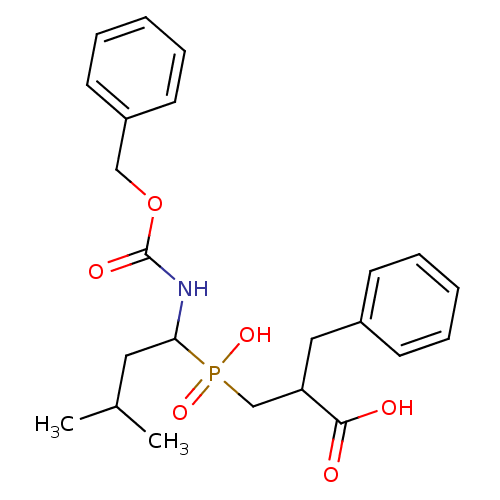 2-benzyl-3-[(1-{[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}-3-methylbutyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]propanoic acid BDBM21458 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 17
2-benzyl-3-[(1-{[(benzyloxy)carbonyl]amino}-3-methylbutyl)(hydroxy)phosphoryl]propanoic acid BDBM21458 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 17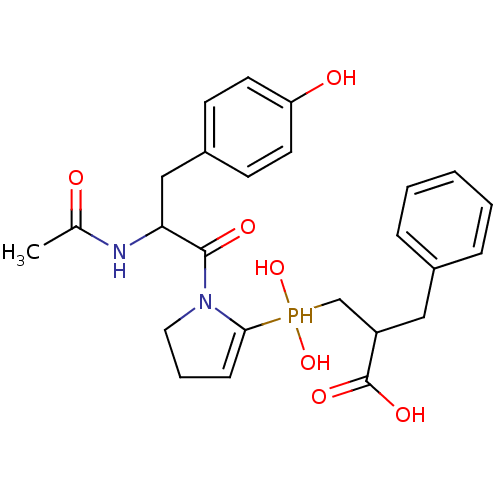 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 31 BDBM21467 2-benzyl-3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 31 BDBM21467 2-benzyl-3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid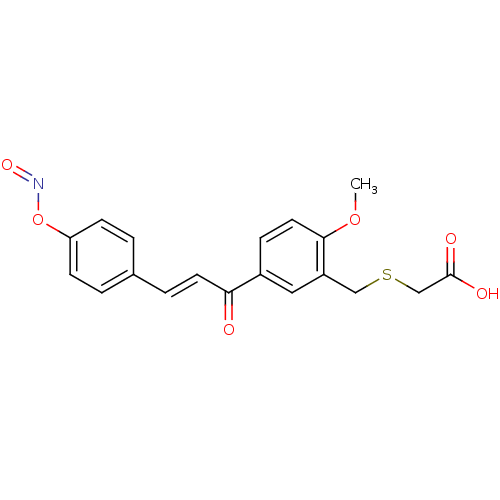 ATX inhibitor 2 BDBM103560
ATX inhibitor 2 BDBM103560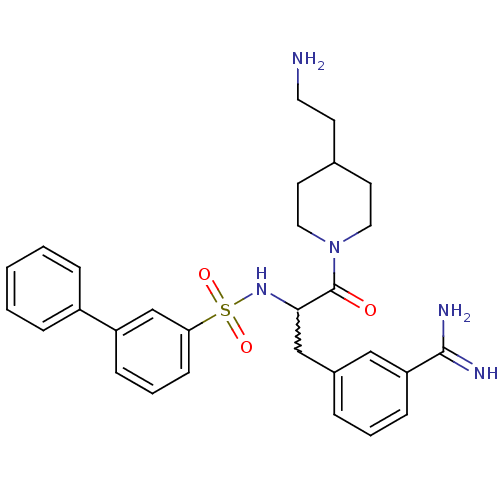 BDBM104895 US8569313, Inhibitor 2
BDBM104895 US8569313, Inhibitor 2 BDBM214779 OPRT inhibitor, 2
BDBM214779 OPRT inhibitor, 2 BDBM237291 CA inhibitor, 2
BDBM237291 CA inhibitor, 2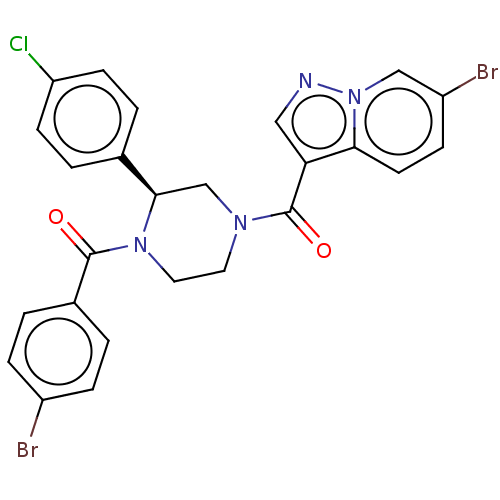 BDBM65493 eIF4A3 inhibitor, 2
BDBM65493 eIF4A3 inhibitor, 2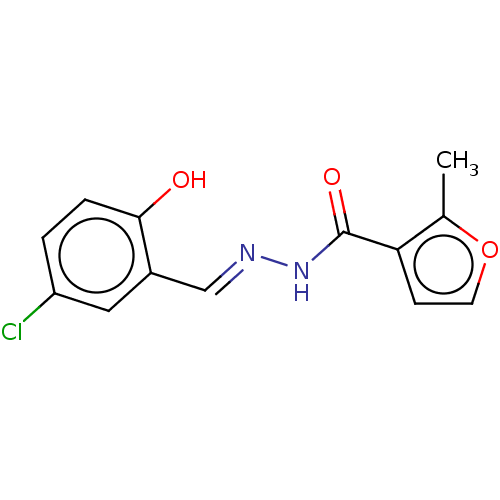 BDBM65496 SmNACE inhibitor, 2
BDBM65496 SmNACE inhibitor, 2 BDBM92346 GSK3 Inhibitor, 2
BDBM92346 GSK3 Inhibitor, 2 BDBM92357 HGXPRT Inhibitor, 2
BDBM92357 HGXPRT Inhibitor, 2 BDBM92442 MMP Inhibitor, 2
BDBM92442 MMP Inhibitor, 2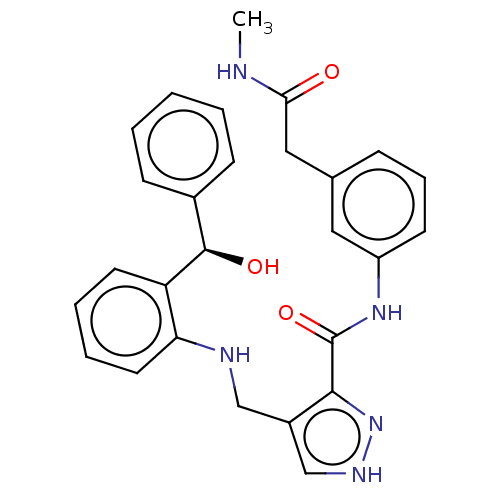 BTK inhibitor, 2 BDBM225237
BTK inhibitor, 2 BDBM225237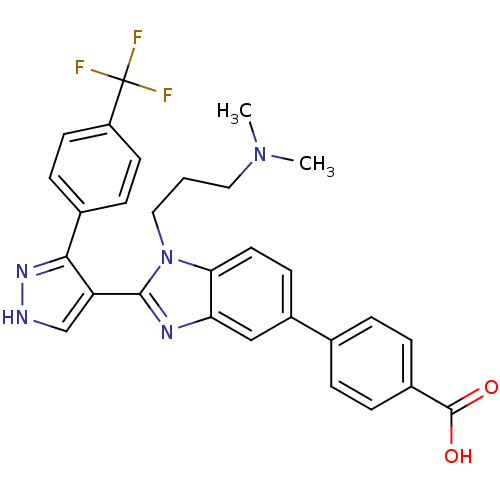 Benzimidazole Inhibitor, 2 BDBM93209
Benzimidazole Inhibitor, 2 BDBM93209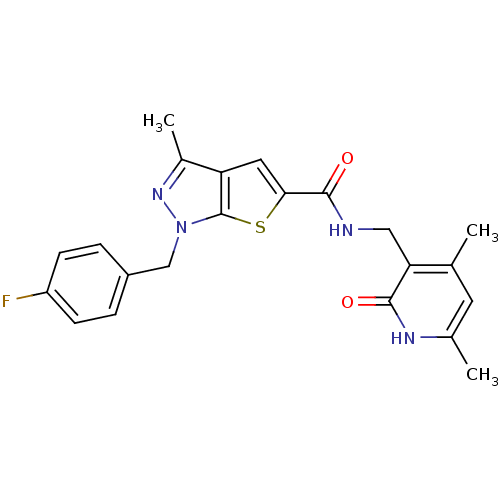 CB2 Inhibitor, 2 BDBM93026
CB2 Inhibitor, 2 BDBM93026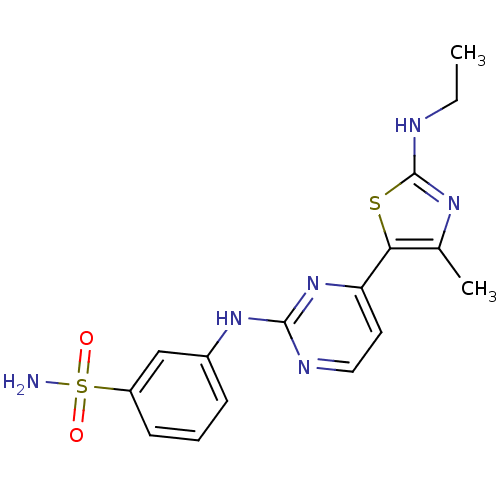 CDK Inhibitor, 2 BDBM81429
CDK Inhibitor, 2 BDBM81429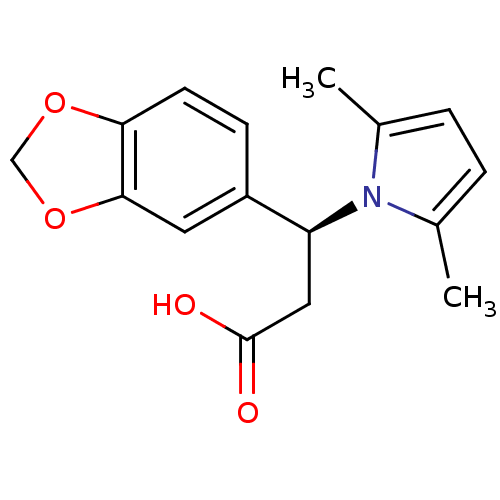 MgrA inhibitor, 2 BDBM81553
MgrA inhibitor, 2 BDBM81553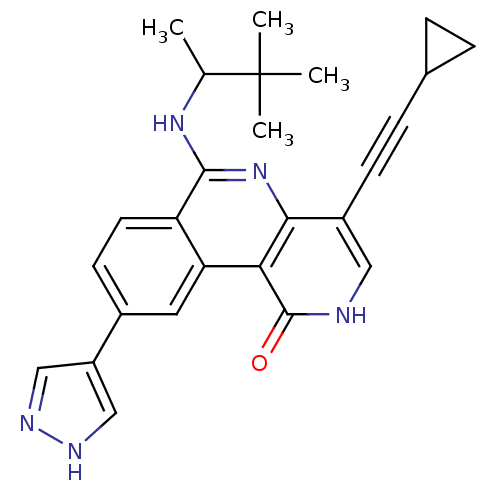 PDK1 inhibitor, 2 BDBM92402
PDK1 inhibitor, 2 BDBM92402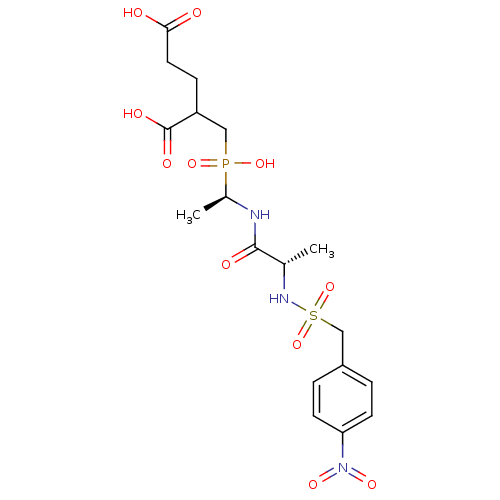 Phosphinate inhibitor 2 BDBM81616
Phosphinate inhibitor 2 BDBM81616 TIM inhibitor, 2 BDBM246597
TIM inhibitor, 2 BDBM246597 hCA inhibitor, 2 BDBM236545
hCA inhibitor, 2 BDBM236545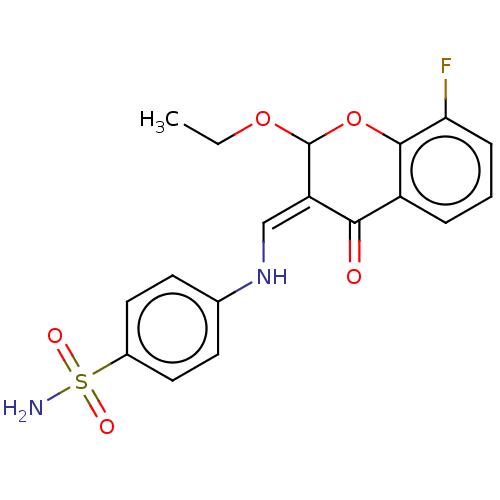 hCA inhibitor, 2 BDBM60962
hCA inhibitor, 2 BDBM60962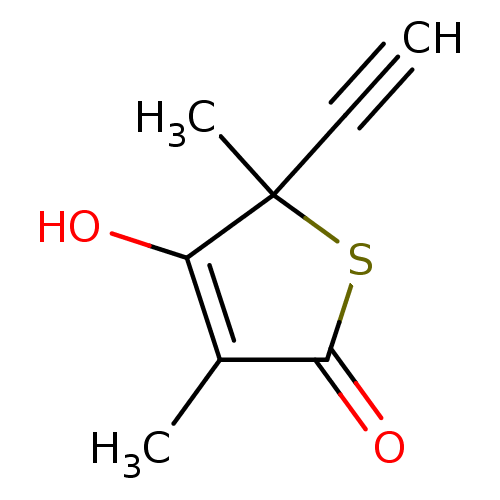 mtFabH inhibitor, 2 BDBM233055
mtFabH inhibitor, 2 BDBM233055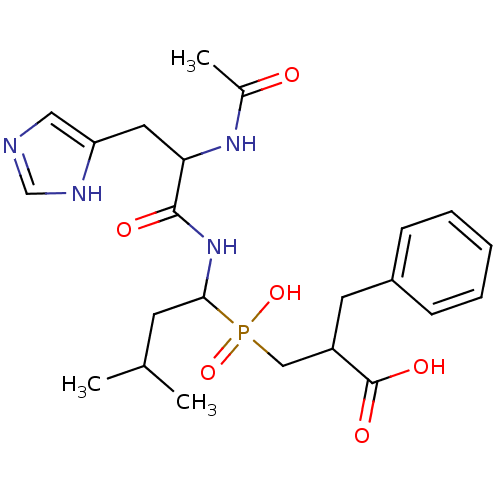 Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 36 2-benzyl-3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido]-3-methylbutyl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid BDBM21472
Phosphinic Peptide Inhibitor, 36 2-benzyl-3-({1-[2-acetamido-3-(1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido]-3-methylbutyl}(hydroxy)phosphoryl)propanoic acid BDBM21472