 US9187397, 1 US11608309, Compound Curcumin US10669227, Compound Curcumin BDBM191763 US9187406, Curcumin curcumin
US9187397, 1 US11608309, Compound Curcumin US10669227, Compound Curcumin BDBM191763 US9187406, Curcumin curcumin ETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487886
ETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487886 US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191759
US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191759 BDBM50487871 DI-O-CHLOROPROPIONYLETHYL CURCUMIN
BDBM50487871 DI-O-CHLOROPROPIONYLETHYL CURCUMIN DI-O-CHLOROACETYLETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487872
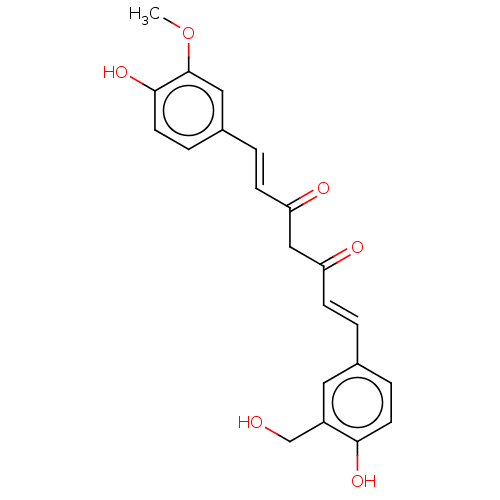
DI-O-CHLOROACETYLETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487872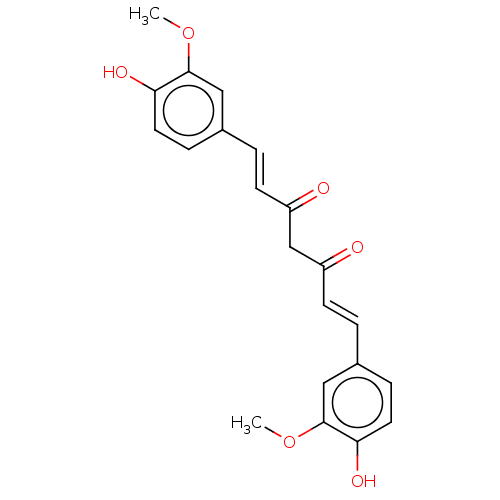 CHEMBL140 US20240131036, Example 8 CHEBI:3962 Curcumin US9409845, Table 1, Compound 21: curcumin BDBM50140172
CHEMBL140 US20240131036, Example 8 CHEBI:3962 Curcumin US9409845, Table 1, Compound 21: curcumin BDBM50140172 4-(4-hydroxybenzylidene) curcumin CHEMBL260079 BDBM50619501
4-(4-hydroxybenzylidene) curcumin CHEMBL260079 BDBM50619501 DI-O-(2-THIENOYL)CURCUMIN BDBM50487873
DI-O-(2-THIENOYL)CURCUMIN BDBM50487873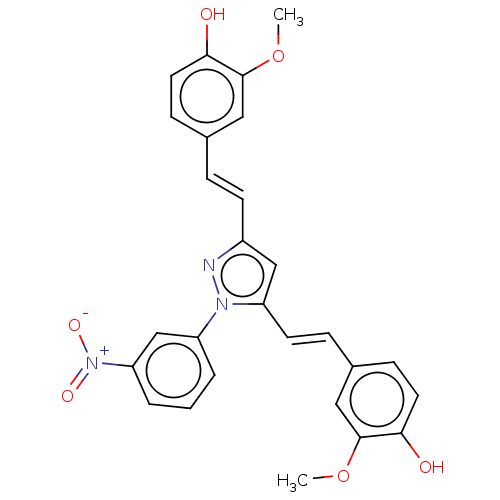 N-(3-Nitrophenylpyrazole)Curcumin BDBM50553256 CHEMBL258632
N-(3-Nitrophenylpyrazole)Curcumin BDBM50553256 CHEMBL258632 US9187397, 3a US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191758
US9187397, 3a US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191758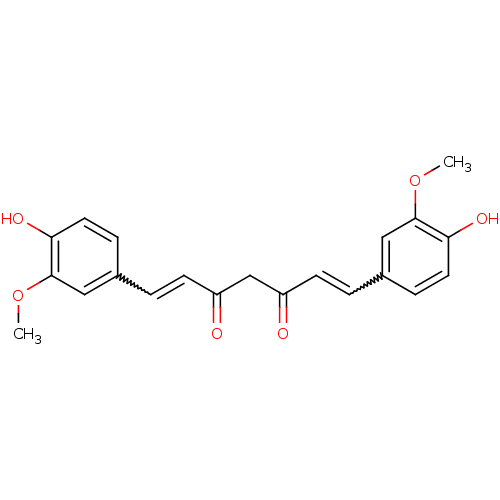 CHEMBL140 Turmeric yellow (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(3-methoxy-4-oxidanyl-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione CURCUMIN MLS000069631 Natural yellow 3 Diferuloylmethane cid_969516 BDBM29532 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione SMR000058237 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione Curcurmin
CHEMBL140 Turmeric yellow (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(3-methoxy-4-oxidanyl-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione CURCUMIN MLS000069631 Natural yellow 3 Diferuloylmethane cid_969516 BDBM29532 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione SMR000058237 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione Curcurmin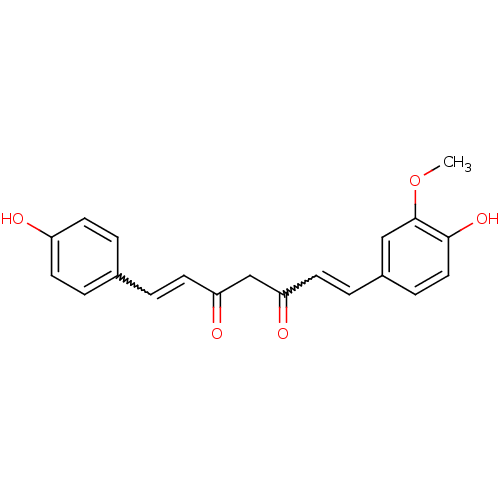 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 5-hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one curcumin II cid_5324476 BDBM50163744 CHEMBL179512 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione demethoxycurcumin
1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 5-hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one curcumin II cid_5324476 BDBM50163744 CHEMBL179512 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione demethoxycurcumin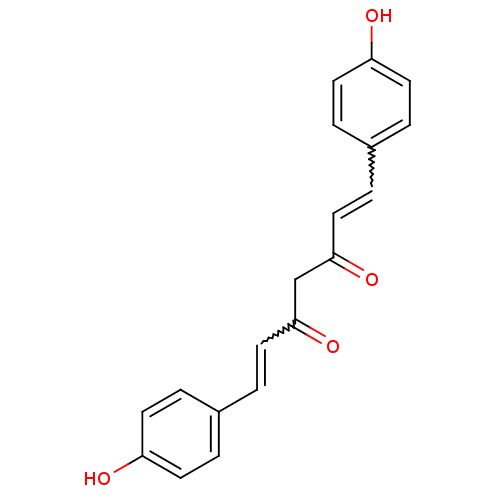 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one CHEMBL131770 (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one BDBM50059989 curcumin III bis-demethoxycurcumin 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3,6-heptatrien-5-one cid_5324473 CHEMBL105350 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione
5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one CHEMBL131770 (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one BDBM50059989 curcumin III bis-demethoxycurcumin 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3,6-heptatrien-5-one cid_5324473 CHEMBL105350 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione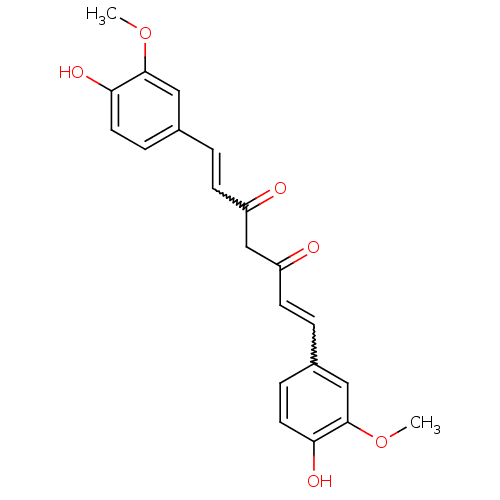 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione (E,E)-1,7-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione cid_5281767 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one diferuloylmethane curcurmin (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one ((E,E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione) 1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione BDBM50067040 1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadien-3,5-dione (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione CHEMBL116438 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione curcumin I (1Z,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione curcumine
(1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione (E,E)-1,7-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione cid_5281767 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one diferuloylmethane curcurmin (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one ((E,E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione) 1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione BDBM50067040 1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadien-3,5-dione (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione CHEMBL116438 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione curcumin I (1Z,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione curcumine
- Takahashi, T; Hijikuro, I; Sugimoto, H; Kihara, T; Shimmyo, Y; Niidome, T Curcumin derivative US Patent US8962674 (2015)
- Vander Jagt, DL; Deck, LM; Abcouwer, SF; Orlando, RA; Royer, RE; Weber, WM; Bobrovnikova-Marjon, EV; Hunsaker, LA Therapeutic curcumin derivatives US Patent US9187397 (2015)
- Nelson, KM; Dahlin, JL; Bisson, J; Graham, J; Pauli, GF; Walters, MA The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin. J Med Chem 60: 1620-1637 (2017)
- Liu, Z; Xie, Z; Jones, W; Pavlovicz, RE; Liu, S; Yu, J; Li, PK; Lin, J; Fuchs, JR; Marcucci, G; Li, C; Chan, KK Curcumin is a potent DNA hypomethylation agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 706-9 (2009)
- Johnson, F; Golub, L Curcumin analogues as zinc chelators and their uses US Patent US10669227 (2020)
- Hu, GX; Liang, G; Chu, Y; Li, X; Lian, QQ; Lin, H; He, Y; Huang, Y; Hardy, DO; Ge, RS Curcumin derivatives inhibit testicular 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 2549-51 (2010)
- Wang, JQ; Wang, X; Wang, Y; Tang, WJ; Shi, JB; Liu, XH Novel curcumin analogue hybrids: Synthesis and anticancer activity. Eur J Med Chem 156: 493-509 (2018)
- Shen, L; Ji, HF Insights into the inhibition of xanthine oxidase by curcumin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 5990-3 (2009)
- Kaur, S; Modi, NH; Panda, D; Roy, N Probing the binding site of curcumin in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis FtsZ--a structural insight to unveil antibacterial activity of curcumin. Eur J Med Chem 45: 4209-14 (2010)
- Lin, H; Hu, GX; Guo, J; Ge, Y; Liang, G; Lian, QQ; Chu, Y; Yuan, X; Huang, P; Ge, RS Mono-carbonyl curcumin analogues as 11ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23: 4362-6 (2013)
- Deck, LM; Hunsaker, LA; Vander Jagt, TA; Whalen, LJ; Royer, RE; Vander Jagt, DL Activation of anti-oxidant Nrf2 signaling by enone analogues of curcumin. Eur J Med Chem 143: 854-865 (2018)
- Mayadevi, M; Sherin, DR; Keerthi, VS; Rajasekharan, KN; Omkumar, RV Curcumin is an inhibitor of calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II. Bioorg Med Chem 20: 6040-7 (2012)
- Kim, TH; Kim, JK; Ito, H; Jo, C Enhancement of pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity of curcumin by radiolytic transformation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 1512-4 (2011)
- Brown, A; Shi, Q; Moore, TW; Yoon, Y; Prussia, A; Maddox, C; Liotta, DC; Shim, H; Snyder, JP Monocarbonyl curcumin analogues: heterocyclic pleiotropic kinase inhibitors that mediate anticancer properties. J Med Chem 56: 3456-66 (2013)
- Zhang, Y; Liu, Z; Wu, J; Bai, B; Chen, H; Xiao, Z; Chen, L; Zhao, Y; Lum, H; Wang, Y; Zhang, H; Liang, G New MD2 inhibitors derived from curcumin with improved anti-inflammatory activity. Eur J Med Chem 148: 291-305 (2018)
- Wang, J; Zhang, X; Yan, J; Li, W; Jiang, Q; Wang, X; Zhao, D; Cheng, M Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of curcumin analogues as novel LSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: (2019)
- Pauff, JM; Hille, R Inhibition studies of bovine xanthine oxidase by luteolin, silibinin, quercetin, and curcumin. J Nat Prod 72: 725-31 (2009)
- Khor, PY; Mohd Aluwi, MFF; Rullah, K; Lam, KW Insights on the synthesis of asymmetric curcumin derivatives and their biological activities. Eur J Med Chem 183: (2019)
- Ryu, EK; Choe, YS; Lee, KH; Choi, Y; Kim, BT Curcumin and dehydrozingerone derivatives: synthesis, radiolabeling, and evaluation for beta-amyloid plaque imaging. J Med Chem 49: 6111-9 (2006)
- Zang, WB; Wei, HL; Zhang, WW; Ma, W; Li, J; Yao, Y Curcumin hybrid molecules for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: Structure and pharmacological activities. Eur J Med Chem 265:
- Okuda, M; Hijikuro, I; Fujita, Y; Teruya, T; Kawakami, H; Takahashi, T; Sugimoto, H Design and synthesis of curcumin derivatives as tau and amyloidß dual aggregation inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 5024-5028 (2016)
- Minassi, A; Sánchez-Duffhues, G; Collado, JA; Muñoz, E; Appendino, G Dissecting the pharmacophore of curcumin. Which structural element is critical for which action? J Nat Prod 76: 1105-12 (2013)
- Ettari, R; Previti, S; Di Chio, C; Maiorana, S; Allegra, A; Schirmeister, T; Zappalà, M Drug Synergism: Studies of Combination of RK-52 and Curcumin against Rhodesain of ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 806-810 (2020)
- Badavath, VN; Baysal, I; Ucar, G; Sinha, BN; Jayaprakash, V Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity of Novel Pyrazoline Analogues: Curcumin Based Design and Synthesis. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 56-61 (2016)
- Enyeart, JA; Liu, H; Enyeart, JJ Curcumin inhibits ACTH- and angiotensin II-stimulated cortisol secretion and Ca(v)3.2 current. J Nat Prod 72: 1533-7 (2009)
- Sharma, M; Manoharlal, R; Shukla, S; Puri, N; Prasad, T; Ambudkar, SV; Prasad, R Curcumin modulates efflux mediated by yeast ABC multidrug transporters and is synergistic with antifungals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53: 3256-65 (2009)
- Rodrigues, FC; Anil Kumar, NV; Thakur, G Developments in the anticancer activity of structurally modified curcumin: An up-to-date review. Eur J Med Chem 177: 76-104 (2019)
- Appiah-Opong, R; de Esch, I; Commandeur, JN; Andarini, M; Vermeulen, NP Structure-activity relationships for the inhibition of recombinant human cytochromes P450 by curcumin analogues. Eur J Med Chem 43: 1621-31 (2008)
- Hosseini-Zare, MS; Sarhadi, M; Zarei, M; Thilagavathi, R; Selvam, C Synergistic effects of curcumin and its analogs with other bioactive compounds: A comprehensive review. Eur J Med Chem 210: (2021)
- Batie, S; Lee, JH; Jama, RA; Browder, DO; Montano, LA; Huynh, CC; Marcus, LM; Tsosie, DG; Mohammed, Z; Trang, V; Marshall, PA; Jurutka, PW; Wagner, CE Synthesis and biological evaluation of halogenated curcumin analogs as potential nuclear receptor selective agonists. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 693-702 (2013)
- Liu, W; Zhang, W; Xing, LZ; Zhao, YD; Xu, J; Li, RJ; Zhang, YX 4-Arylidene curcumin derivatives in vitro inhibit α-Synuclein aggregation and disaggregate the preformed fibril. Bioorg Med Chem 96: (2023)
- Ao, GZ; Zhou, MZ; Li, YY; Li, SN; Wang, HN; Wan, QW; Li, HQ; Hu, QH Discovery of novel curcumin derivatives targeting xanthine oxidase and urate transporter 1 as anti-hyperuricemic agents. Bioorg Med Chem 25: 166-174 (2017)
- Zhang, W; Bai, H; Han, L; Zhang, H; Xu, B; Cui, J; Wang, X; Ge, Z; Li, R Synthesis and biological evaluation of curcumin derivatives modified with α-amino boronic acid as proteasome inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 2459-2464 (2018)
- Mazumder, A; Neamati, N; Sunder, S; Schulz, J; Pertz, H; Eich, E; Pommier, Y Curcumin analogs with altered potencies against HIV-1 integrase as probes for biochemical mechanisms of drug action. J Med Chem 40: 3057-63 (1997)
- Ai, Y; Zhu, B; Ren, C; Kang, F; Li, J; Huang, Z; Lai, Y; Peng, S; Ding, K; Tian, J; Zhang, Y Discovery of New Monocarbonyl Ligustrazine-Curcumin Hybrids for Intervention of Drug-Sensitive and Drug-Resistant Lung Cancer. J Med Chem 59: 1747-60 (2016)
- Lee, KH; Ab Aziz, FH; Syahida, A; Abas, F; Shaari, K; Israf, DA; Lajis, NH Synthesis and biological evaluation of curcumin-like diarylpentanoid analogues for anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-tyrosinase activities. Eur J Med Chem 44: 3195-200 (2009)
- Di Martino, RM; De Simone, A; Andrisano, V; Bisignano, P; Bisi, A; Gobbi, S; Rampa, A; Fato, R; Bergamini, C; Perez, DI; Martinez, A; Bottegoni, G; Cavalli, A; Belluti, F Versatility of the Curcumin Scaffold: Discovery of Potent and Balanced Dual BACE-1 and GSK-3ß Inhibitors. J Med Chem 59: 531-44 (2016)
- Majhi, A; Rahman, GM; Panchal, S; Das, J Binding of curcumin and its long chain derivatives to the activator binding domain of novel protein kinase C. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 1591-8 (2010)
- Das, J; Pany, S; Panchal, S; Majhi, A; Rahman, GM Binding of isoxazole and pyrazole derivatives of curcumin with the activator binding domain of novel protein kinase C. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 6196-202 (2011)
- Sanabria-Ríos, DJ; Rivera-Torres, Y; Rosario, J; Gutierrez, R; Torres-García, Y; Montano, N; Ortíz-Soto, G; Ríos-Olivares, E; Rodríguez, JW; Carballeira, NM Chemical conjugation of 2-hexadecynoic acid to C5-curcumin enhances its antibacterial activity against multi-drug resistant bacteria. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 5067-71 (2015)
- Selvam, C; Jachak, SM; Thilagavathi, R; Chakraborti, AK Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking of curcumin analogues as antioxidant, cyclooxygenase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 1793-7 (2005)
- Konno, H; Endo, H; Ise, S; Miyazaki, K; Aoki, H; Sanjoh, A; Kobayashi, K; Hattori, Y; Akaji, K Synthesis and evaluation of curcumin derivatives toward an inhibitor of beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 685-90 (2014)
- Li, Y; Peng, P; Tang, L; Hu, Y; Hu, Y; Sheng, R Design, synthesis and evaluation of rivastigmine and curcumin hybrids as site-activated multitarget-directed ligands for Alzheimer's disease therapy. Bioorg Med Chem 22: 4717-25 (2014)
- Xu, YY; Cao, Y; Ma, H; Li, HQ; Ao, GZ Design, synthesis and molecular docking ofa,ß-unsaturated cyclohexanone analogous of curcumin as potent EGFR inhibitors with antiproliferative activity. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 388-94 (2012)
- Yan, J; Hu, J; Liu, A; He, L; Li, X; Wei, H Design, synthesis, and evaluation of multitarget-directed ligands against Alzheimer's disease based on the fusion of donepezil and curcumin. Bioorg Med Chem 25: 2946-2955 (2017)
- Qiu, X; Du, Y; Lou, B; Zuo, Y; Shao, W; Huo, Y; Huang, J; Yu, Y; Zhou, B; Du, J; Fu, H; Bu, X Synthesis and identification of new 4-arylidene curcumin analogues as potential anticancer agents targeting nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway. J Med Chem 53: 8260-73 (2010)
- Ahmad, W; Kumolosasi, E; Jantan, I; Bukhari, SN; Jasamai, M Effects of novel diarylpentanoid analogues of curcumin on secretory phospholipase A2 , cyclooxygenases, lipo-oxygenase, and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1. Chem Biol Drug Des 83: 670-81 (2014)
- Liu, Z; Fang, L; Zhang, H; Gou, S; Chen, L Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of multifunctional tacrine-curcumin hybrids as new cholinesterase inhibitors with metal ions-chelating and neuroprotective property. Bioorg Med Chem 25: 2387-2398 (2017)
- Mohd Aluwi, MF; Rullah, K; Yamin, BM; Leong, SW; Abdul Bahari, MN; Lim, SJ; Mohd Faudzi, SM; Jalil, J; Abas, F; Mohd Fauzi, N; Ismail, NH; Jantan, I; Lam, KW Synthesis of unsymmetrical monocarbonyl curcumin analogues with potent inhibition on prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-induced murine and human macrophages cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 2531-8 (2016)
- Zuo, Y; Huang, J; Zhou, B; Wang, S; Shao, W; Zhu, C; Lin, L; Wen, G; Wang, H; Du, J; Bu, X Synthesis, cytotoxicity of new 4-arylidene curcumin analogues and their multi-functions in inhibition of both NF-¿B and Akt signalling. Eur J Med Chem 55: 346-57 (2012)
- Yuan, M; Luo, M; Song, Y; Xu, Q; Wang, X; Cao, Y; Bu, X; Ren, Y; Hu, X Identification of curcumin derivatives as human glyoxalase I inhibitors: A combination of biological evaluation, molecular docking, 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 1189-96 (2011)
- Iranshahi, M; Chini, MG; Masullo, M; Sahebkar, A; Javidnia, A; Chitsazian Yazdi, M; Pergola, C; Koeberle, A; Werz, O; Pizza, C; Terracciano, S; Piacente, S; Bifulco, G Can Small Chemical Modifications of Natural Pan-inhibitors Modulate the Biological Selectivity? The Case of Curcumin Prenylated Derivatives Acting as HDAC or mPGES-1 Inhibitors. J Nat Prod 78: 2867-79 (2015)
- Tanaka, R; Tsujii, H; Yamada, T; Kajimoto, T; Amano, F; Hasegawa, J; Hamashima, Y; Node, M; Katoh, K; Takebe, Y Novel 3alpha-methoxyserrat-14-en-21beta-ol (PJ-1) and 3beta-methoxyserrat-14-en-21beta-ol (PJ-2)-curcumin, kojic acid, quercetin, and baicalein conjugates as HIV agents. Bioorg Med Chem 17: 5238-46 (2009)
- Inhibition Assay Table 10: The efficacy of MMP-2 inhibition was as follows: compound 6>compound 7>compound 8. Although compound 6 showed similar efficacy as curcumin when comparing MMP-2 inhibitory potency, the amide-containing compounds are much more soluble than the famously insoluble curcumin. The amide-containing curcumin derivatives are much more potent inhibitors of MMP-13 (Collagenase-3) than curcumin and even more potent than compound 1 (Table 9 and 10).:
- ChEMBL_1982621 (CHEMBL4615883) Inhibition of Trypanosoma brucei rhodesain in presence of curcumin using Cbz-Phe-Arg-AMC as substrate incubated for 30 mins by fluorometric assay
- Cellular Firefly Luciferase Assay (AP-1) Curcumin is a known inhibitor of the AP-1 activation cascade. Therefore, modification of the structure of curcumin could lead to analogs with enhanced activity. The library consisting of three series of curcumin analogs were used to examine the role of the enone functionality in aryl systems where the spacer is 7-carbons (as in curcumin), 5-carbons or 3-carbons in length. In addition, the importance of aryl ring substituents was assessed. The AP-1 activities of curcumin and analogs were determined by a cellular firefly luciferase assay. This assay utilized a commercially available cell line (Panomics 293-luc cellular assay) developed for screening inhibitors of AP-1. This cell line is stably transfected with a luciferase reporter controlled by an AP-1 dependent promoter. The cell is stimulated with phorbol ester which activates AP-1. AP-1 then binds to one of three promoter regions on the cells DNA leading to the production of a luciferase enzyme. Luciferin is added to the cell lysates and the luciferase enzyme catalyzes a cleavage of luciferin leading to the emission of light.
- Inhibition of MMPs It has been observed that 50 and 100 μM concentrations of curcumin decreased TNFα production by endotoxin-stimulated human monocytes (HMs) in culture by 80-90% (lower concentrations of curcumin, 10 and 20 μM, had no effect). However, this inhibitory effect was associated with some precipitation of the curcumin in cell culture and with significant cytotoxicity. It was hypothesized that increasing the solubility of curcumin will: (i) enhance its efficacy as an inhibitor of cytokine expression, (ii) reduce its cytotoxicity, and (iii) preserve (perhaps even enhance; see below) its potency, as an MMP inhibitor (MMPI) compound, which was found to be similar to that of the Zn++ chelating compound, 1,10-O-phenanthroline (FIG. 1). However, it should be noted that excessive inhibition of MMP activity may not be desirable therapeutically because a minimal, or basal, level of MMPs may be necessary for optimal defense of the host.
- Inhibition Assay Table 1 shows the IC50 of curcumin, compound 1, and compound 2, compared to a standard Zn++ binding & MMPI (matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor), 1,10-O-phenanthroline (o-phen), against purified human PMN MMP-8 (from EMD biologics, Inc., Gibbstown, N.J.) using a synthetic octapeptide containing the collagenase-susceptible glycine-isoleucine peptide bond and measuring the tripeptide breakdown products by HPLC (Waters Alliance 2695 System with a reverse phase C-18 column). Compound 1 was an excellent MMPI with an IC50 equivalent to that of 1,10-O-phenanthroline, while compound 2, which lacked substituents on the aryl moieties, did not show a dose response.
- Cellular Firefly Luciferase Assay (NFkB) The NF-kB activities of curcumin and analogs were determined by a cellular firefly luciferase assay. This assay utilized a commercially available cell line (Panomics 293T-luc cellular assay) developed for screening inhibitors of NF-kB. This cell line is stably transfected with a luciferase reporter controlled by an NF-kB dependent promoter. The cell is stimulated with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) which activates NF-kB. NF-kB then binds to one of six promoter regions on the cell's DNA leading to the production of a luciferase enzyme. Luciferin is added to the cell lysates and the luciferase enzyme catalyzes a cleavage of luciferin leading to the emission of light.
 US9187397, 1 US11608309, Compound Curcumin US10669227, Compound Curcumin BDBM191763 US9187406, Curcumin curcumin
US9187397, 1 US11608309, Compound Curcumin US10669227, Compound Curcumin BDBM191763 US9187406, Curcumin curcumin ETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487886
ETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487886 US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191759
US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191759 BDBM50487871 DI-O-CHLOROPROPIONYLETHYL CURCUMIN
BDBM50487871 DI-O-CHLOROPROPIONYLETHYL CURCUMIN DI-O-CHLOROACETYLETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487872
DI-O-CHLOROACETYLETHYL CURCUMIN BDBM50487872 CHEMBL140 US20240131036, Example 8 CHEBI:3962 Curcumin US9409845, Table 1, Compound 21: curcumin BDBM50140172
CHEMBL140 US20240131036, Example 8 CHEBI:3962 Curcumin US9409845, Table 1, Compound 21: curcumin BDBM50140172 4-(4-hydroxybenzylidene) curcumin CHEMBL260079 BDBM50619501
4-(4-hydroxybenzylidene) curcumin CHEMBL260079 BDBM50619501 DI-O-(2-THIENOYL)CURCUMIN BDBM50487873
DI-O-(2-THIENOYL)CURCUMIN BDBM50487873 N-(3-Nitrophenylpyrazole)Curcumin BDBM50553256 CHEMBL258632
N-(3-Nitrophenylpyrazole)Curcumin BDBM50553256 CHEMBL258632 US9187397, 3a US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191758
US9187397, 3a US9187397, 1 (curcumin) BDBM191758 CHEMBL140 Turmeric yellow (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(3-methoxy-4-oxidanyl-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione CURCUMIN MLS000069631 Natural yellow 3 Diferuloylmethane cid_969516 BDBM29532 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione SMR000058237 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione Curcurmin
CHEMBL140 Turmeric yellow (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(3-methoxy-4-oxidanyl-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione CURCUMIN MLS000069631 Natural yellow 3 Diferuloylmethane cid_969516 BDBM29532 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione SMR000058237 (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione Curcurmin 1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 5-hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one curcumin II cid_5324476 BDBM50163744 CHEMBL179512 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione demethoxycurcumin
1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 5-hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one curcumin II cid_5324476 BDBM50163744 CHEMBL179512 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,6E)-1-(4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-7-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione demethoxycurcumin 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one CHEMBL131770 (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one BDBM50059989 curcumin III bis-demethoxycurcumin 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3,6-heptatrien-5-one cid_5324473 CHEMBL105350 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione
5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one CHEMBL131770 (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one BDBM50059989 curcumin III bis-demethoxycurcumin 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3,6-heptatrien-5-one cid_5324473 CHEMBL105350 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione (E,E)-1,7-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione cid_5281767 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one diferuloylmethane curcurmin (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one ((E,E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione) 1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione BDBM50067040 1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadien-3,5-dione (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione CHEMBL116438 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione curcumin I (1Z,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione curcumine
(1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione (E,E)-1,7-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione cid_5281767 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one diferuloylmethane curcurmin (1E,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one ((E,E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione) 1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione BDBM50067040 1,7-bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadien-3,5-dione (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione CHEMBL116438 (1E,4Z,6E)-5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one 1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione curcumin I (1Z,6E)-1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione curcumine