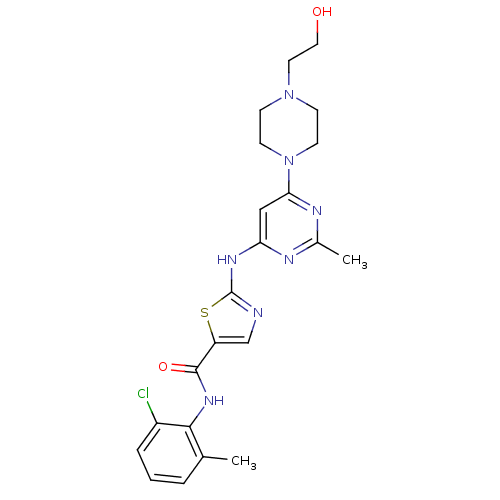
 Found 5 Enz. Inhib. hit(s) with Target = 'Serine/threonine-protein kinase SIK2' and Ligand = 'BDBM13216'
Found 5 Enz. Inhib. hit(s) with Target = 'Serine/threonine-protein kinase SIK2' and Ligand = 'BDBM13216' Affinity DataIC50: 3.5nMAssay Description:The IC50 for the inhibition of ABL1 by dasatinib, by C7 and by B3 is approximately 1.5 nM, 5.1 nM and 1.6 nM, and of SRC is 1.5 nM, 1.5 nM and 1.5 nM...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: <20nMAssay Description:The IC50 for the inhibition of ABL1 by dasatinib, by C7 and by B3 is approximately 1.5 nM, 5.1 nM and 1.6 nM, and of SRC is 1.5 nM, 1.5 nM and 1.5 nM...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKd: 6.40nMAssay Description:Binding constant for SIK2 kinase domainMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKd: 6.40nMAssay Description:Kinase inhibitors are a new class of therapeutics with a propensity to inhibit multiple targets. The biological consequences of multi-kinase activity...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKd: 6.40nMAssay Description:Binding constant for full-length SNF1LK2More data for this Ligand-Target Pair