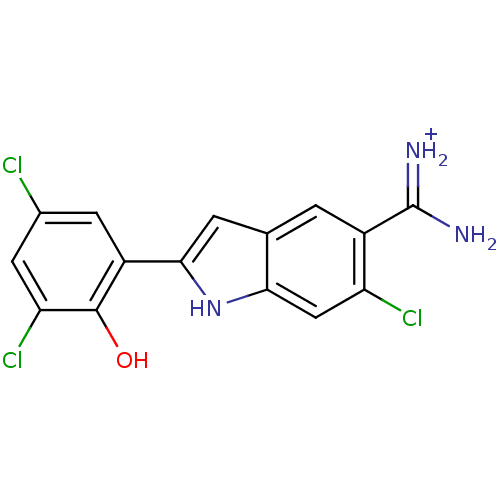
Affinity DataKi: 300nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 310nM ΔG°: -8.78kcal/molepH: 7.4 T: 2°CAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 1.90E+3nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 4.70E+3nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 4.70E+3nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 9.50E+3nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 9.50E+3nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 1.70E+4nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 1.70E+4nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 3.20E+4nMAssay Description:Each enzyme was assayed with a set of different concentrations of each inhibitor. After addition of the appropriate substrate, the rate of hydrolysis...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair