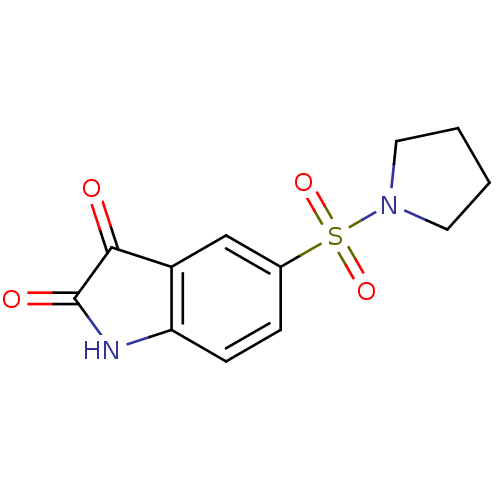
BDBM10309 5-(pyrrolidine-1-sulfonyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-2,3-dione::5-[1-(Pyrrolidinyl)sulfonyl]isatin::Isatin Sulfonamide 20
SMILES O=C1Nc2ccc(cc2C1=O)S(=O)(=O)N1CCCC1
InChI Key InChIKey=QKCWUYHXHMXOLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Activity Spreadsheet -- Enzyme Inhibition Constant Data from BindingDB
 Found 9 hits for monomerid = 10309
Found 9 hits for monomerid = 10309
Affinity DataKi: 1.40E+3nM ΔG°: -8.11kcal/mole IC50: 2.80E+3nMpH: 7.5 T: 2°CAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 3.00E+3nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 9.00E+3nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: 1.20E+4nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: >5.00E+4nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: >5.00E+4nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: >5.00E+4nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataKi: >5.00E+4nMAssay Description:The substrate peptides terminating in AMC/AFC are processed by caspases with or without inhibitors, and the accumulation of AMC/AFC was assessed with...More data for this Ligand-Target Pair
Affinity DataIC50: 2.80E+3nMAssay Description:Inhibition of caspase 3 in human SK-N-SH cells assessed as accumulation of fluorogenic 7-amino-4-methyl coumarin by flurometric assayMore data for this Ligand-Target Pair