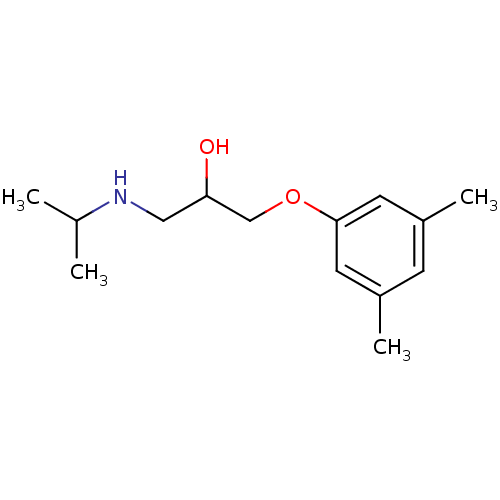
 CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719
CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719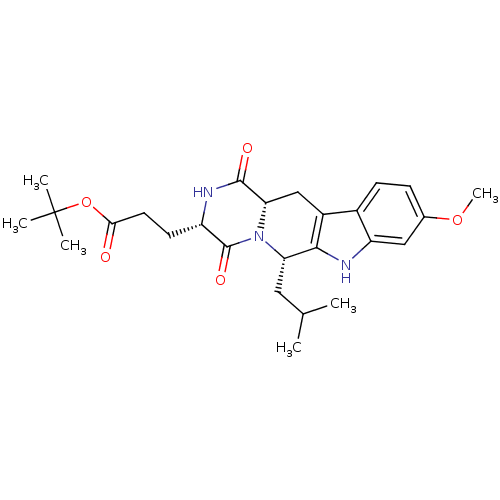 3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910
3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910
- TERSTIEGE, I; SCHIESSER, S IRAK4 Inhibitors US Patent US20240300923 (2024)
- TERSTIEGE, I; GARRISON, AT; MURPHY, JJ; KWAPIEN, K IRAK4 PROTACS US Patent US20240374588 (2024)
- Bryan, MC; Do, S; Katsumoto, T; Liang, J; Rajapaksa, NS; Kiefer, Jr., JR; Fu, L IRAK4 modulators US Patent US10899772 (2021)
- Chan, T; Guckian, K; Jenkins, T; Thomas, J; Vessels, J; Kumaravel, G; Meissner, R; Lyssikatos, J; Lucas, B; Leaf, I; Duffield, J IRAK4 inhibiting agents US Patent US10577367 (2020)
- Ammann, S; Bacon, EM; Brizgys, G; Chin, E; Chou, C; Cottell, JJ; Ndukwe, M; Shatskikh, M; Taylor, JG; Wright, NE; Yang, Z; Zipfel, SM Thiadiazole IRAK4 compounds US Patent US11046686 (2021)
- Ammann, S; Bacon, EM; Brizgys, G; Chin, E; Chou, C; Cottell, JJ; Ndukwe, M; Shatskikh, M; Taylor, JG; Wright, NE; Yang, Z; Zipfel, SM Thiadiazole IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US11702414 (2023)
- Bothe, U; Günther, J; Nubbemeyer, R; Siebeneicher, H; Ring, S; Bömer, U; Peters, M; Rausch, A; Denner, K; Himmel, H; Sutter, A; Terebesi, I; Lange, M; Wengner, AM; Guimond, N; Thaler, T; Platzek, J; Eberspächer, U; Schäfer, M; Steuber, H; Zollner, TM; Steinmeyer, A; Schmidt, N Discovery of IRAK4 Inhibitors J Med Chem 67: 1225-1242 (2024)
- Altman, MD; Andresen, BM; Brubaker, JD; Donofrio, A; Fischmann, T; Gibeau, CR; Lesburg, CA; Lim, J; Maclean, JK; Mansoor, UF; Northrup, AB; Sanders, JM; Smith, GF; Torres, L Inhibitors of IRAK4 activity US Patent US9943516 (2018)
- Lim, J; Altman, MD; Childers, ML; Gibeau, CR; Ho, GD; Tsui, H Carboxamide inhibitors of IRAK4 activity US Patent US10155765 (2018)
- Xu, J; Cai, Q; Cha, MY; Kim, M IRAK4 inhibitor and use thereof US Patent US10562902 (2020)
- Lim, J; Altman, MD; Brubaker, JD; Gibeau, CR Pyrazolopyrimidine inhibitors of IRAK4 activity US Patent US10329294 (2019)
- Lim, J; Altman, MD; Brubaker, JD; Gibeau, CR Pyrrolopyridazine inhibitors of IRAK4 activity US Patent US10040798 (2018)
- Lim, J; Altman, MD; Brubaker, JD; Gibeau, CR Pyrrolotriazine inhibitors of IRAK4 activity US Patent US10329295 (2019)
- Terstiege, I; Schiesser, S; Xue, Y; Chang, H; Berggren, AI Substituted indazoles as IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US11866405 (2024)
- Lim, J; Altman, MD; Gibeau, CR Thienopyrazine inhibitors of IRAK4 activity US Patent US10040802 (2018)
- Sabnis, RW Novel IRAK4 Inhibitors for Treating Asthma. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 1219-1220 (2022)
- Nunes, J; McGonagle, GA; Eden, J; Kiritharan, G; Touzet, M; Lewell, X; Emery, J; Eidam, H; Harling, JD; Anderson, NA Targeting IRAK4 for Degradation with PROTACs. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1081-1085 (2019)
- Chen, Y; Tso, K; Heckrodt, TJ; Li, H; Yen, R; Lin, N; Singh, R; Taylor, V; Masuda, ES; Park, G; Payan, DG Bicyclic pyrimidine compounds as potent IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 73: (2022)
- Bryan, MC; Do, S; Drobnick, J; Gobbi, A; Katsumoto, T; Kiefer, Jr., JR; Liang, J; Rajapaksa, NS; Chen, Y; Fu, L; Lai, KW; Liu, Z; Wai, J; Wang, F Pyrazolo[ 1,5a]pyrimidine derivatives as IRAK4 modulators US Patent US11034698 (2021)
- Arora, N; Chen, S; Hermann, JC; Kuglstatter, A; Labadie, SS; Lin, CJ; Lucas, MC; Moore, AG; Papp, E; Talamas, FX; Wanner, J; Zhai, Y Pyrazolo[1,5a]pyrimidine derivatives as IRAK4 modulators US Patent US9255110 (2016)
- Ahmad, S; Li, L; Negash, LA; Hynes, J Thienopyridines and benzothiophenes useful as IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US10829496 (2020)
- Sabnis, RW Thienopyridinyl and Thiazolopyridinyl Compounds as IRAK4 Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 12: 532-533 (2021)
- Nair, SK; Paidi, VR; Sarkunam, K; Sistla, RK; Hynes, J; Murugesan, N Tricyclic heteroaryl compounds useful as IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US12286428 (2025)
- Bryan, MC; Drobnick, J; Gobbi, A; Kolesnikov, A; Chen, Y; Rajapaksa, N; Ndubaku, C; Feng, J; Chang, W; Francis, R; Yu, C; Choo, EF; DeMent, K; Ran, Y; An, L; Emson, C; Huang, Z; Sujatha-Bhaskar, S; Brightbill, H; DiPasquale, A; Maher, J; Wai, J; McKenzie, BS; Lupardus, PJ; Zarrin, AA; Kiefer, JR Development of Potent and Selective Pyrazolopyrimidine IRAK4 Inhibitors. J Med Chem 62: 6223-6240 (2019)
- Zhang, Y; Wang, J; Tan, H; Li, J; Li, J; Chen, S Isothiazolo[5,4-D]pyrimidine compound as IRAK4 inhibitor US Patent US11459337 (2022)
- Ahmad, S; Li, L; Wu, H; Hynes, J Thienopyridinyl and thiazolopyridinyl compounds useful as IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US12304916 (2025)
- Lee, KL; Allais, CP; Dehnhardt, CM; Gavrin, LK; Han, S; Hepworth, D; Lee, A; Lovering, FE; Mathias, JP; Owen, DR; Papaioannou, N; Saiah, E; Strohbach, JW; Trzupek, JD; Wright, SW; Zapf, CW Bicyclic-fused heteroaryl or aryl compounds as IRAK4 modulators US Patent US10174000 (2019)
- Chen, Y; Ning, Y; Bai, G; Tong, L; Zhang, T; Zhou, J; Zhang, H; Xie, H; Ding, J; Duan, W Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of IRAK4-Targeting PROTACs. ACS Med Chem Lett 12: 82-87 (2021)
- Zhang, X; He, S; Ma, H Heteroaryl compounds as inhibitors of irak4, compositions and applications thereof US Patent US20250074919 (2025)
- Ye, Z; Feng, Y; Li, S IRAK4 DEGRADATION AGENT, AND PREPARATION METHOD THEREFOR AND USE THEREOF US Patent US20240368194 (2024)
- Cumming, IA; Degorce, SL; Aagaard, A; Braybrooke, EL; Davies, NL; Diène, CR; Eatherton, AJ; Felstead, HR; Groombridge, SD; Lenz, EM; Li, Y; Nai, Y; Pearson, S; Robb, GR; Scott, JS; Steward, OR; Wu, C; Xue, Y; Zhang, L; Zhang, Y Identification and optimisation of a pyrimidopyridone series of IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 63: (2022)
- Rajapaksa, NS; Gobbi, A; Drobnick, J; Do, S; Kolesnikov, A; Liang, J; Chen, Y; Sujatha-Bhaskar, S; Huang, Z; Brightbill, H; Francis, R; Yu, C; Choo, EF; DeMent, K; Ran, Y; An, L; Emson, C; Maher, J; Wai, J; McKenzie, BS; Lupardus, PJ; Zarrin, AA; Kiefer, JR; Bryan, MC Discovery of Potent Benzolactam IRAK4 Inhibitors with Robust in Vivo Activity. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 327-333 (2020)
- Jenkins, T; Vessels, J Macrocyclic compounds as IRAK4 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases US Patent US9617282 (2017)
- Degorce, SL; Anjum, R; Dillman, KS; Drew, L; Groombridge, SD; Halsall, CT; Lenz, EM; Lindsay, NA; Mayo, MF; Pink, JH; Robb, GR; Scott, JS; Stokes, S; Xue, Y Optimization of permeability in a series of pyrrolotriazine inhibitors of IRAK4. Bioorg Med Chem 26: 913-924 (2018)
- Negash, LA; Ahmad, S Benzo[5,6][1,4]dioxino[2,3-b]pyridine compounds useful as IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US12391702 (2025)
- Seganish, WM; Fischmann, TO; Sherborne, B; Matasi, J; Lavey, B; McElroy, WT; Tulshian, D; Tata, J; Sondey, C; Garlisi, CG; Devito, K; Fossetta, J; Lundell, D; Niu, X Discovery and Structure Enabled Synthesis of 2,6-Diaminopyrimidin-4-one IRAK4 Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 942-7 (2015)
- Smith, GF; Altman, MD; Andresen, B; Baker, J; Brubaker, JD; Chen, H; Chen, Y; Childers, M; Donofrio, A; Ferguson, H; Fischer, C; Fischmann, TO; Gibeau, C; Hicks, A; Jin, S; Kattar, S; Kleinschek, MA; Leccese, E; Lesburg, C; Li, C; Lim, J; Liu, D; Maclean, JKF; Mansoor, F; Moy, LY; Mulrooney, EF; Necheva, AS; Presland, J; Rakhilina, L; Yang, R; Torres, L; Zhang-Hoover, J; Northrup, A Identification of quinazoline based inhibitors of IRAK4 for the treatment of inflammation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 2721-2726 (2017)
- Kargbo, RB PROTAC Degradation of IRAK4 for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative and Cardiovascular Diseases. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1251-1252 (2019)
- Wu, H; Hynes, J Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrrolo[1,2-b]pyridazinyl compounds useful as IRAK4 inhibitors US Patent US12304914 (2025)
- WEI, N; JIN, H; ZHENG, Y; ZHOU, F; HUANG, M SULFOXIMIDE SUBSTITUTED INDAZOLE IRAK4 KINASE INHIBITOR, PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF AND USE THEREOF US Patent US20240132473 (2024)
- Zhai, W; Lu, Y; Zhu, Y; Zhou, M; Ye, C; Shi, ZZ; Qian, W; Hu, T; Chen, L Discovery and optimization of a potent and selective indazolamine series of IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 31: (2021)
- Chen, Y; Singh, R; Lin, N; Taylor, V; Masuda, ES; Payan, DG Discovery of 5-Aryl-2,4-diaminopyrimidine Compounds as Potent and Selective IRAK4 Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 714-719 (2022)
- Hanisak, J; Seganish, WM; McElroy, WT; Tang, H; Zhang, R; Tsui, HC; Fischmann, T; Tulshian, D; Tata, J; Sondey, C; Devito, K; Fossetta, J; Garlisi, CG; Lundell, D; Niu, X Efforts towards the optimization of a bi-aryl class of potent IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 4250-5 (2016)
- Sabnis, RW Novel IRAK4 Inhibitors for Treating Asthma, COPD, Cancer, Autoinflammatory Diseases, and Autoimmune Diseases. ACS Med Chem Lett 14: 1617-1618 (2023)
- Hao, Y; Ma, J; Wang, J; Yu, X; Li, Z; Wu, S; Tian, S; Ma, H; He, S; Zhang, X Synthesis and evaluation of dihydrofuro[2,3-b]pyridine derivatives as potent IRAK4 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 258:
- Peterson, EA; Pfaffenbach, M; Gao, F; Bolduc, P; Xin, Z; Evans, R 2H-INDAZOLE DERIVATIVES AS IRAK4 INHIBITORS AND THEIR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF DISEASE US Patent US20250268877 (2025)
- Bhide, RS; Keon, A; Weigelt, C; Sack, JS; Schmidt, RJ; Lin, S; Xiao, HY; Spergel, SH; Kempson, J; Pitts, WJ; Carman, J; Poss, MA Discovery and structure-based design of 4,6-diaminonicotinamides as potent and selective IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4908-4913 (2017)
- Gummadi, VR; Boruah, A; Ainan, BR; Vare, BR; Manda, S; Gondle, HP; Kumar, SN; Mukherjee, S; Gore, ST; Krishnamurthy, NR; Marappan, S; Nayak, SS; Nellore, K; Balasubramanian, WR; Bhumireddy, A; Giri, S; Gopinath, S; Samiulla, DS; Daginakatte, G; Basavaraju, A; Chelur, S; Eswarappa, R; Belliappa, C; Subramanya, HS; Booher, RN; Ramachandra, M; Samajdar, S Discovery of CA-4948, an Orally Bioavailable IRAK4 Inhibitor for Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 2374-2381 (2020)
- Degorce, SL; Anjum, R; Bloecher, A; Carbajo, RJ; Dillman, KS; Drew, L; Halsall, CT; Lenz, EM; Lindsay, NA; Mayo, MF; Pink, JH; Robb, GR; Rosen, A; Scott, JS; Xue, Y Discovery of a Series of 5-Azaquinazolines as Orally Efficacious IRAK4 Inhibitors Targeting MyD88 J Med Chem 62: 9918-9930 (2019)
- Sabnis, RW Novel Tricyclic Heteroaryl Compounds as IRAK4 Inhibitors for Treating Cancer, Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. ACS Med Chem Lett 13: 336-337 (2022)
- Wright, SW; Farley, KA; Han, S; Knafels, JD; Lee, KL In Retrospect: Root-Cause Analysis of Structure-Activity Relationships in IRAK4 Inhibitor Zimlovisertib (PF-06650833). ACS Med Chem Lett 15: 540-545 (2024)
- Dolan, BM; Duron, SG; Campbell, DA; Vollrath, B; Shankaranarayana Rao, BS; Ko, HY; Lin, GG; Govindarajan, A; Choi, SY; Tonegawa, S Rescue of fragile X syndrome phenotypes in Fmr1 KO mice by the small-molecule PAK inhibitor FRAX486. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 5671-6
- Peterson, EA; Pfaffenbach, M; Gao, F; Bolduc, P; Xin, Z; Evans, R IMIDAZO[1,2-A]PYRIDINE DERIVATIVES AS IRAK4 INHIBITORS AND THEIR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF DISEASE US Patent US20240116922 (2024)
- Degorce, SL; Aagaard, A; Anjum, R; Cumming, IA; Diène, CR; Fallan, C; Johnson, T; Leuchowius, KJ; Orton, AL; Pearson, S; Robb, GR; Rosen, A; Scarfe, GB; Scott, JS; Smith, JM; Steward, OR; Terstiege, I; Tucker, MJ; Turner, P; Wilkinson, SD; Wrigley, GL; Xue, Y Improving metabolic stability and removing aldehyde oxidase liability in a 5-azaquinazoline series of IRAK4 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 28: (2020)
- McElroy, WT; Tan, Z; Ho, G; Paliwal, S; Li, G; Seganish, WM; Tulshian, D; Tata, J; Fischmann, TO; Sondey, C; Bian, H; Bober, L; Jackson, J; Garlisi, CG; Devito, K; Fossetta, J; Lundell, D; Niu, X Potent and Selective Amidopyrazole Inhibitors of IRAK4 That Are Efficacious in a Rodent Model of Inflammation. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 677-82 (2015)
- Nair, S; Kumar, SR; Paidi, VR; Sistla, R; Kantheti, D; Polimera, SR; Thangavel, S; Mukherjee, AJ; Das, M; Bhide, RS; Pitts, WJ; Murugesan, N; Dudhgoankar, S; Nagar, J; Subramani, S; Mazumder, D; Carman, JA; Holloway, DA; Li, X; Fereshteh, MP; Ruepp, S; Palanisamy, K; Mariappan, TT; Maddi, S; Saxena, A; Elzinga, P; Chimalakonda, A; Ruan, Q; Ghosh, K; Bose, S; Sack, J; Yan, C; Kiefer, SE; Xie, D; Newitt, JA; Saravanakumar, SP; Rampulla, RA; Barrish, JC; Carter, PH; Hynes, J Optimization of Nicotinamides as Potent and Selective IRAK4 Inhibitors with Efficacy in a Murine Model of Psoriasis. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1402-1409 (2020)
- Bolduc, PN; Pfaffenbach, M; Evans, R; Xin, Z; Henry, KL; Gao, F; Fang, T; Silbereis, J; Vera Rebollar, J; Li, P; Chodaparambil, JV; Metrick, C; Peterson, EA A Tiny Pocket Packs a Punch: Leveraging Pyridones for the Discovery of CNS-Penetrant Aza-indazole IRAK4 Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 15: 714-721
- Lim, J; Altman, MD; Baker, J; Brubaker, JD; Chen, H; Chen, Y; Fischmann, T; Gibeau, C; Kleinschek, MA; Leccese, E; Lesburg, C; Maclean, JK; Moy, LY; Mulrooney, EF; Presland, J; Rakhilina, L; Smith, GF; Steinhuebel, D; Yang, R Discovery of 5-Amino-N-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-carboxamide Inhibitors of IRAK4. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 683-8 (2015)
- Pfaffenbach, M; Bolduc, PN; Xin, Z; Gao, F; Evans, R; Fang, T; Chodaparambil, JV; Henry, KL; Li, P; Mathieu, S; Metrick, C; Vera Rebollar, JA; Gu, RF; Mccarl, CA; Silbereis, J; Peterson, EA Discovery of BIO-8169─A Highly Potent, Selective, and Brain-Penetrant IRAK4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Neuroinflammation. J Med Chem 67: 8383-8395
- Chen, Y; Ning, Y; Chen, Z; Xue, Y; Wu, Q; Duan, W; Ding, J; Zhou, J; Xie, H; Zhang, H Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 2,3-dihydrobenzofuran IRAK4 inhibitors for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Med Chem 256: (2023)
- Scott, JS; Degorce, SL; Anjum, R; Culshaw, J; Davies, RDM; Davies, NL; Dillman, KS; Dowling, JE; Drew, L; Ferguson, AD; Groombridge, SD; Halsall, CT; Hudson, JA; Lamont, S; Lindsay, NA; Marden, SK; Mayo, MF; Pease, JE; Perkins, DR; Pink, JH; Robb, GR; Rosen, A; Shen, M; McWhirter, C; Wu, D Discovery and Optimization of Pyrrolopyrimidine Inhibitors of Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4) for the Treatment of Mutant MYD88 J Med Chem 60: 10071-10091 (2017)
- Weiss, MM; Zheng, X; Ji, N; Browne, CM; Campbell, V; Chen, D; Enerson, B; Fei, X; Huang, X; Klaus, CR; Li, H; Mayo, M; McDonald, AA; Paul, A; Rong, H; Sharma, K; Shi, Y; Slavin, A; Walther, DM; Yuan, K; Zhang, Y; Zhu, X; Kelleher, J; Walker, D; Mainolfi, N Discovery of KT-413, a Targeted Protein Degrader of IRAK4 and IMiD Substrates Targeting MYD88 Mutant Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J Med Chem 67: 10548-10566
- Chen, Y; Bai, G; Ning, Y; Cai, S; Zhang, T; Song, P; Zhou, J; Duan, W; Ding, J; Xie, H; Zhang, H Design and synthesis of Imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine IRAK4 inhibitors for the treatment of mutant MYD88 L265P diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Med Chem 190: (2020)
- Zou, Y; Wang, X; Chen, P; Zheng, Z; Li, X; Chen, Z; Guo, M; Zhou, Y; Sun, C; Wang, R; Zhu, W; Zheng, P; Cho, WJ; Cho, YC; Liang, G; Tang, Q Fragment-Based Anti-inflammatory Agent Design and Target Identification: Discovery of AF-45 as an IRAK4 Inhibitor to Treat Ulcerative Colitis and Acute Lung Injury. J Med Chem 67: 10687-10709
- Chaudhary, D; Robinson, S; Romero, DL Recent advances in the discovery of small molecule inhibitors of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) as a therapeutic target for inflammation and oncology disorders. J Med Chem 58: 96-110 (2015)
- Lee, KL; Ambler, CM; Anderson, DR; Boscoe, BP; Bree, AG; Brodfuehrer, JI; Chang, JS; Choi, C; Chung, S; Curran, KJ; Day, JE; Dehnhardt, CM; Dower, K; Drozda, SE; Frisbie, RK; Gavrin, LK; Goldberg, JA; Han, S; Hegen, M; Hepworth, D; Hope, HR; Kamtekar, S; Kilty, IC; Lee, A; Lin, LL; Lovering, FE; Lowe, MD; Mathias, JP; Morgan, HM; Murphy, EA; Papaioannou, N; Patny, A; Pierce, BS; Rao, VR; Saiah, E; Samardjiev, IJ; Samas, BM; Shen, MWH; Shin, JH; Soutter, HH; Strohbach, JW; Symanowicz, PT; Thomason, JR; Trzupek, JD; Vargas, R; Vincent, F; Yan, J; Zapf, CW; Wright, SW Discovery of Clinical Candidate 1-{[(2S,3S,4S)-3-Ethyl-4-fluoro-5-oxopyrrolidin-2-yl]methoxy}-7-methoxyisoquinoline-6-carboxamide (PF-06650833), a Potent, Selective Inhibitor of Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase 4 (IRAK4), by Fragment-Based Drug Design. J Med Chem 60: 5521-5542 (2017)
- Evans, R; Bolduc, PN; Pfaffenbach, M; Gao, F; May-Dracka, T; Fang, T; Hopkins, BT; Chodaparambil, JV; Henry, KL; Li, P; Metrick, C; Nelson, A; Trapa, P; Thomas, A; Burkly, L; Peterson, EA The Discovery of 7-Isopropoxy-2-(1-methyl-2-oxabicyclo[2.1.1]hexan-4-yl)-N-(6-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide (BIO-7488), a Potent, Selective, and CNS-Penetrant IRAK4 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. J Med Chem 67: 4676-4690
- Chesworth, R; Zawistoski, MP; Lefker, BA; Cameron, KO; Day, RF; Mangano, FM; Rosati, RL; Colella, S; Petersen, DN; Brault, A; Lu, B; Pan, LC; Perry, P; Ng, O; Castleberry, TA; Owen, TA; Brown, TA; Thompson, DD; DaSilva-Jardine, P Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 2729-33 (2004)
- Dampalla, CS; Miller, MJ; Kim, Y; Zabiegala, A; Nguyen, HN; Madden, TK; Thurman, HA; Machen, AJ; Cooper, A; Liu, L; Battaile, KP; Lovell, S; Chang, KO; Groutas, WC Eur J Med Chem 254: (2023)
- Clausen, JD; Kjellerup, L; Cohrt, KO; Hansen, JB; Dalby-Brown, W; Winther, AL Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4564-4570 (2017)
- Shaw, S; Bian, Z; Zhao, B; Tarr, JC; Veerasamy, N; Jeon, KO; Belmar, J; Arnold, AL; Fogarty, SA; Perry, E; Sensintaffar, JL; Camper, DV; Rossanese, OW; Lee, T; Olejniczak, ET; Fesik, SW J Med Chem 61: 2410-2421 (2018)
- Miller, WH; Alberts, DP; Bhatnagar, PK; Bondinell, WE; Callahan, JF; Calvo, RR; Cousins, RD; Erhard, KF; Heerding, DA; Keenan, RM; Kwon, C; Manley, PJ; Newlander, KA; Ross, ST; Samanen, JM; Uzinskas, IN; Venslavsky, JW; Yuan, CC; Haltiwanger, RC; Gowen, M; Hwang, SM; James, IE; Lark, MW; Rieman, DJ; Stroup, GB; Azzarano, LM; Salyers, KL; Smith, BR; Ward, KW; Johanson, KO; Huffman, WF J Med Chem 43: 22-6 (2000)
- Zankel, TC; Isbell, SL; Ko, AA US Patent US10308607 (2019)
- Ko, B; Jang, Y; Kim, MH; Lam, TT; Seo, HK; Jeong, P; Choi, M; Kang, KW; Lee, SD; Park, JH; Kim, M; Han, SY; Kim, YC Eur J Med Chem 262:
- Li, Z; Liao, C; Ko, BC; Shan, S; Tong, EH; Yin, Z; Pan, D; Wong, VK; Shi, L; Ning, ZQ; Hu, W; Zhou, J; Chung, SS; Lu, XP Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 3507-11 (2004)
- Ko, CC; Chen, YJ; Chen, CT; Liu, YC; Cheng, FC; Hsu, KC; Chow, LP J Biol Chem 289: 22078-89 (2014)
- Shih, KC; Shiau, CW; Chen, TS; Ko, CH; Lin, CL; Lin, CY; Hwang, CS; Tang, CY; Chen, WR; Huang, JW Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 4490-7 (2011)
- Ratni, H; Ebeling, M; Baird, J; Bendels, S; Bylund, J; Chen, KS; Denk, N; Feng, Z; Green, L; Guerard, M; Jablonski, P; Jacobsen, B; Khwaja, O; Kletzl, H; Ko, CP; Kustermann, S; Marquet, A; Metzger, F; Mueller, B; Naryshkin, NA; Paushkin, SV; Pinard, E; Poirier, A; Reutlinger, M; Weetall, M; Zeller, A; Zhao, X; Mueller, L J Med Chem 61: 6501-6517 (2018)
- Kim, M; Kim, G; Kang, M; Ko, D; Nam, Y; Moon, CS; Kang, HM; Shin, JS; Werz, O; Lee, KT; Lee, JY Bioorg Med Chem Lett 41: (2021)
- Park, HK; Jeong, H; Ko, E; Lee, G; Lee, JE; Lee, SK; Lee, AJ; Im, JY; Hu, S; Kim, SH; Lee, JH; Lee, C; Kang, S; Kang, BH J Med Chem 60: 7569-7578 (2017)
- Bardelle, C; Cross, D; Davenport, S; Kettle, JG; Ko, EJ; Leach, AG; Mortlock, A; Read, J; Roberts, NJ; Robins, P; Williams, EJ Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18: 2776-80 (2008)
- Cheng, MC; Li, CY; Ko, HC; Ko, FN; Lin, YL; Wu, TS J Nat Prod 69: 1305-9 (2006)
- Hillmann, P; Ko, GY; Spinrath, A; Raulf, A; von Kügelgen, I; Wolff, SC; Nicholas, RA; Kostenis, E; Höltje, HD; Müller, CE J Med Chem 52: 2762-75 (2009)
- An, S; Yu, J; Choi, H; Ko, H; Ahn, S; Shin, JC; Pyo, JJ; Jeong, LS; Noh, M Bioorg Med Chem 28: (2020)
- Cheng, MC; Li, CY; Ko, HC; Ko, FN; Lin, YL; Wu, TS J Nat Prod 69: 1305-9 (2006)
- Ng, LT; Ko, HH; Lu, TM Bioorg Med Chem 17: 4360-6 (2009)
- Kwon, SH; Kim, S; Park, AY; Lee, S; Gadhe, CG; Seo, BA; Park, JS; Jo, S; Oh, Y; Kweon, SH; Ma, SX; Kim, WR; Kim, M; Kim, H; Kim, JE; Lee, S; Lee, J; Ko, HS J Med Chem 64: 15091-15110 (2021)
- Dolan, BM; Duron, SG; Campbell, DA; Vollrath, B; Shankaranarayana Rao, BS; Ko, HY; Lin, GG; Govindarajan, A; Choi, SY; Tonegawa, S Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 5671-6
- Malwal, SR; Mazurek, B; Ko, J; Xie, P; Barnes, C; Varvitsiotis, C; Zimmerman, MD; Olatunji, S; Lee, J; Xie, M; Sarathy, J; Caffrey, M; Strynadka, NCJ; Dartois, V; Dick, T; Lee, BNR; Russell, DG; Oldfield, E J Med Chem 66: 7553-7569 (2023)
- Bhattarai, BR; Ko, JH; Shrestha, S; Kafle, B; Cho, H; Kang, JH; Cho, H Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1075-7 (2010)
- Ko, K; Kim, HJ; Ho, PS; Lee, SO; Lee, JE; Min, CR; Kim, YC; Yoon, JH; Park, EJ; Kwon, YJ; Yun, JH; Yoon, DO; Kim, JS; Park, WS; Oh, SS; Song, YM; Cho, WK; Morikawa, K; Lee, KJ; Park, CH J Med Chem 61: 2949-2961 (2018)
- Lee, W; Ko, KR; Kim, HK; Lee, DS; Nam, IJ; Lim, S; Kim, S J Nat Prod 81: 1343-1356 (2018)
- Ko, KS; Steffey, ME; Brandvold, KR; Soellner, MB ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 779-783 (2013)
- Yang, HY; Tae, J; Seo, YW; Kim, YJ; Im, HY; Choi, GD; Cho, H; Park, WK; Kwon, OS; Cho, YS; Ko, M; Jang, H; Lee, J; Choi, K; Kim, CH; Lee, J; Pae, AN Eur J Med Chem 63: 558-69 (2013)
- Nam, M; Kim, T; Kwak, J; Seo, SH; Ko, MK; Lim, EJ; Min, SJ; Cho, YS; Keum, G; Baek, DJ; Lee, J; Pae, AN Eur J Med Chem 97: 245-58 (2015)
- Jackson, JJ; Shibuya, GM; Ravishankar, B; Adusumilli, L; Bradford, D; Brockstedt, DG; Bucher, C; Bui, M; Cho, C; Colas, C; Cutler, G; Dukes, A; Han, X; Hu, DX; Jacobson, S; Kassner, PD; Katibah, GE; Ko, MYM; Kolhatkar, U; Leger, PR; Ma, A; Marshall, L; Maung, J; Ng, AA; Okano, A; Pookot, D; Poon, D; Ramana, C; Reilly, MK; Robles, O; Schwarz, JB; Shakhmin, AA; Shunatona, HP; Sreenivasan, R; Tivitmahaisoon, P; Xu, M; Zaw, T; Wustrow, DJ; Zibinsky, M J Med Chem 65: 12895-12924 (2022)
- Srivastava, AS; Ko, S; Watterson, SH; Pattoli, MA; Skala, S; Cheng, L; Obermeier, MT; Vickery, R; Discenza, LN; D'Arienzo, CJ; Gillooly, KM; Taylor, TL; Pulicicchio, C; McIntyre, KW; Yip, S; Li, P; Sun, D; Wu, DR; Dai, J; Wang, C; Zhang, Y; Wang, B; Pawluczyk, J; Kempson, J; Zhao, R; Hou, X; Rampulla, R; Mathur, A; Galella, MA; Salter-Cid, L; Barrish, JC; Carter, PH; Fura, A; Burke, JR; Tino, JA ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 2195-2203 (2020)
- Lim, CJ; Woo, SE; Ko, SI; Lee, BH; Oh, KS; Yi, KY Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 4684-4686 (2016)
- Son, S; Ko, SK; Jang, M; Lee, JK; Kwon, MC; Kang, DH; Ryoo, IJ; Lee, JS; Hong, YS; Kim, BY; Jang, JH; Ahn, JS J Nat Prod 80: 1378-1386 (2017)
- Batt, DG; Bertrand, MB; Delucca, GV; Galella, MA; Ko, SS; Langevine, CM; Liu, Q; Shi, Q; Srivastava, AS; Tino, JA; Watterson, SH US Patent US10106559 (2018)
- Walpole, C; Ko, SY; Brown, M; Beattie, D; Campbell, E; Dickenson, F; Ewan, S; Hughes, GA; Lemaire, M; Lerpiniere, J; Patel, S; Urban, L J Med Chem 41: 3159-73 (1998)
- Guo, RT; Cao, R; Liang, PH; Ko, TP; Chang, TH; Hudock, MP; Jeng, WY; Chen, CK; Zhang, Y; Song, Y; Kuo, CJ; Yin, F; Oldfield, E; Wang, AH Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 10022-7 (2007)
- Quang, TH; Ngan, NT; Ko, W; Kim, DC; Yoon, CS; Sohn, JH; Yim, JH; Kim, YC; Oh, H Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 5787-91 (2014)
- Ryu, CK; Kang, HY; Lee, SK; Nam, KA; Hong, CY; Ko, WG; Lee, BH Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 461-4 (2000)
- Ji, SH; Kim, HB; Song, Y; Chung, HW; Lee, DH; Jung, C; Ko, Y; Han, SJ Bioorg Med Chem Lett 102:
- Jeon, WS; Moon, K; Park, SH; Chun, H; Ko, YH; Lee, JY; Lee, ES; Samal, S; Selvapalam, N; Rekharsky, MV; Sindelar, V; Sobransingh, D; Inoue, Y; Kaifer, AE; Kim, K J Am Chem Soc 127: 12984-9 (2005)
- Choi, HG; Ko, E; Cho, J; Son, JB; Ko, YK; Park, J; Kim, SY; Kang, SY; Lee, S; Ryu, HY; Kim, ND; Kim, SB; Lee, S; Kim, D; Lee, SJ; Cho, S; Lee, K; Yu, K; Choi, M; Koo, JW; Hoe, H US Patent US11117892 (2021)
- Ferraris, D; Duvall, B; Ko, YS; Thomas, AG; Rojas, C; Majer, P; Hashimoto, K; Tsukamoto, T J Med Chem 51: 3357-9 (2008)
- Suh, YG; Kim, NJ; Koo, BW; Lee, KO; Moon, SH; Shin, DH; Jung, JW; Paek, SM; Chang, DJ; Li, F; Kang, HJ; Le, TV; Chae, YN; Shin, CY; Kim, MK; Lim, JI; Ryu, JS; Park, HJ J Med Chem 51: 6318-33 (2008)
- Raddatz, P; Jonczyk, A; Minck, KO; Rippmann, F; Schittenhelm, C; Schmitges, CJ J Med Chem 35: 3525-36 (1992)
- Ghobish, SA; Mohamed, KO; Farag, N; Farag, DB RSC Med Chem 15: 293-308 (2024)
- Mohammed, KO; Nissan, YM Chem Biol Drug Des 84: 473-88 (2014)
- Bugge, S; Moen, IU; Sylte, KO; Sundby, E; Hoff, BH Eur J Med Chem 94: 175-94 (2015)
- Narayanan, D; Tran, KT; Pallesen, JS; Solbak, SMØ; Qin, Y; Mukminova, E; Luchini, M; Vasilyeva, KO; González Chichón, D; Goutsiou, G; Poulsen, C; Haapanen, N; Popowicz, GM; Sattler, M; Olagnier, D; Gajhede, M; Bach, A J Med Chem 65: 14481-14526 (2022)
- Yerdelen, KO; Koca, M; Anil, B; Sevindik, H; Kasap, Z; Halici, Z; Turkaydin, K; Gunesacar, G Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 5576-82 (2015)
- Pontius, A; Krick, A; Mesry, R; Kehraus, S; Foegen, SE; Mu¨ller, M; Klimo, K; Gerha¨user, C; Ko¨nig, GM J Nat Prod 71: 1793-1799 (2008)
- Mattei, P; Boehringer, M; Di Giorgio, P; Fischer, H; Hennig, M; Huwyler, J; Koçer, B; Kuhn, B; Loeffler, BM; Macdonald, A; Narquizian, R; Rauber, E; Sebokova, E; Sprecher, U Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1109-13 (2010)
- Bosnar, M; Kragol, G; Koštrun, S; Vujasinovic, I; Bošnjak, B; Bencetic Mihaljevic, V; Marušic Ištuk, Z; Kapic, S; Hrvacic, B; Brajša, K; Tavcar, B; Jelic, D; Glojnaric, I; Verbanac, D; Culic, O; Padovan, J; Alihodžic, S; Erakovic Haber, V; Spaventi, R J Med Chem 55: 6111-23 (2012)
- Schwardt, O; Rabbani, S; Hartmann, M; Abgottspon, D; Wittwer, M; Kleeb, S; Zalewski, A; Smieško, M; Cutting, B; Ernst, B Bioorg Med Chem 19: 6454-73 (2011)
- ZakoSek, M; Mihevc, SP; Majdic, G; Ko{hacek over (s)}ak, U; Gobec, S US Patent US20230331674 (2023)
- ChEMBL_2447196 Inhibition of human IRAK4
- ChEMBL_356039 (CHEMBL870864) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_458449 (CHEMBL941767) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_467815 (CHEMBL936449) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_479339 (CHEMBL921622) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_498305 (CHEMBL973443) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_500021 (CHEMBL970459) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_556506 (CHEMBL956501) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_606976 (CHEMBL1073303) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_616302 (CHEMBL1102105) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_655542 (CHEMBL1244586) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_701564 (CHEMBL1656203) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_742131 (CHEMBL1769191) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_755597 (CHEMBL1805337) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_793904 (CHEMBL1932877) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_813565 (CHEMBL2019674) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_815115 (CHEMBL2024840) Inhibition of IRAK4
- ChEMBL_2291577 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2292030 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2332946 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2431712 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2445435 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2483209 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2496365 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2500309 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2516290 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2545937 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2568942 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_328639 (CHEMBL863888) Inhibitory activity against IRAK4
- ChEMBL_773541 (CHEMBL1839907) Inhibition of recombinant IRAK4
- ChEMBL_813705 (CHEMBL2019907) Inhibition of human IRAK4
- ChEMBL_959519 (CHEMBL2384686) Inhibition of human IRAK4
- ChEMBL_959954 (CHEMBL2383896) Inhibition of human IRAK4
- ChEMBL_1352453 (CHEMBL3270974) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1441601 (CHEMBL3376481) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1444238 (CHEMBL3380177) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1459006 (CHEMBL3369599) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1465696 (CHEMBL3405457) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1505336 (CHEMBL3595104) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1526986 (CHEMBL3637446) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1542829 (CHEMBL3742719) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1544030 (CHEMBL3750402) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1545840 (CHEMBL3748848) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1548602 (CHEMBL3757421) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1730341 (CHEMBL4145877) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1770392 (CHEMBL4222504) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1776348 (CHEMBL4233340) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1778380 (CHEMBL4235372) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1831750 (CHEMBL4331758) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2024270 (CHEMBL4678083) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2025898 (CHEMBL4679711) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2035333 (CHEMBL4689491) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2193539 (CHEMBL5105899) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2236408 (CHEMBL5150304) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2236950 (CHEMBL5150846) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_773460 (CHEMBL1840412) Inhibition of IRAK4 by spectrophotometry
- ChEMBL_961816 (CHEMBL2389956) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_993109 (CHEMBL2446684) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1509409 (CHEMBL3603417) Inhibition of human IRAK4 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1526987 (CHEMBL3637447) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC
- ChEMBL_774578 (CHEMBL1908795) Binding constant for IRAK4 kinase domain
- ChEMBL_831786 (CHEMBL2065149) Inhibition of IRAK4 by FRET assay
- ChEMBL_1991901 (CHEMBL4625636) Inhibition of IRAK4 in mouse whole blood
- ChEMBL_2307215 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by Kinase assay
- ChEMBL_2500312 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by Kinase assay
- ChEMBL_801395 (CHEMBL1948125) Inhibition of IRAK4 using ATP as substrate
- ChEMBL_1444378 (CHEMBL3372369) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by radiochemical assay
- ChEMBL_1546696 (CHEMBL3748221) Inhibition of human IRAK4 using MBP as substrate
- ChEMBL_2292258 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by Ambit kinase assay
- ChEMBL_2500310 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by Ambit kinase assay
- ChEMBL_2538007 Inhibition of human IRAK4 by discoverX kinome scan assay
- ChEMBL_1444245 (CHEMBL3380184) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by TR-FRET assay
- ChEMBL_1823760 (CHEMBL4323524) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by cell based assay
- ChEMBL_2286277 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) phosphorylation by cell based assay
- ChEMBL_2445668 Binding affinity to IRAK4 (unknown origin) assessed as dissociation constant
- ChEMBL_2500308 Inhibition of wild type human IRAK4 (164 to 460 residues)
- ChEMBL_2500313 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by discoverX kinome scan assay
- ChEMBL_831571 (CHEMBL2064934) Inhibition of Irak4 in presence of 10 uM ATP
- ChEMBL_876569 (CHEMBL2188526) Inhibition of human recombinant IRAK4 by radiometric kinase assay
- ChEMBL_2359569 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by Z-LYTE enzymatic kinase assay
- ChEMBL_2496345 Binding affinity to IRAK4 (unknown origin) by kinomescan competition binding assay
- ChEMBL_1444247 (CHEMBL3380186) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) by fluorescence polarization based kinase assay
- ChEMBL_1445027 (CHEMBL3372435) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) in presence of 1 mM ATP
- ChEMBL_2286276 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) in presence of ATP by enzymatic assay
- ChEMBL_2528324 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) in BGG-buffer in presence of ATP
- ChEMBL_1828581 (CHEMBL4328455) Inhibition of human IRAK4 using MBP as substrate by [gamma-33P]-ATP assay
- ChEMBL_2065443 (CHEMBL4720696) Inhibition of human IRAK4 using MBP as substrate by [gamma-33P]-ATP assay
- ChEMBL_2328294 Inhibition of full-length IRAK4 (unknown origin) in presence of ATP by DELFIA assay
- ChEMBL_2476844 Inhibition of tetracycline-inducible FLAG-tagged human PARL stably transfected in HEK293T harboring FITR/PARL KO
- ChEMBL_1633281 (CHEMBL3876073) Inhibition of human recombinant full length His-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system
- ChEMBL_1823759 (CHEMBL4323523) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) in presence of 5 mM ATP by enzymatic assay
- ChEMBL_2024271 (CHEMBL4678084) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human THP-1 cells by cell based anti-inflammatory assay
- ChEMBL_2209829 (CHEMBL5122778) Inhibition of IRAK4 in IL1-stimulated human KARPAS-299 cells assessed as fluorescence intensity
- ChEMBL_2514825 Binding affinity to human IRAK4 incubated for 45 mins by Kinobead based pull down assay
- ChEMBL_480051 (CHEMBL927990) Inhibition of mouse PKCtheta in KO cells assessed as blockade of anti CD28-stimulated IL2 production
- ChEMBL_1676865 (CHEMBL4027008) Binding affinity to wild type human IRAK4 (M1 to S460) expressed in mammalian expression system
- ChEMBL_2153906 (CHEMBL5038453) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) in presence of MBP as substrate by ADP-Glo assay
- ChEMBL_2328295 Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC cells assessed as reduction in R848-stimulated TNF-alpha production
- ChEMBL_2431369 Inhibition of human IRAK4 using biotinylated peptide substrate incubated for 3 hrs by microplate reader assay
- ChEMBL_2504922 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) incubated for 1 hr in presence of ATP by Mesoscale assay
- ChEMBL_1676840 (CHEMBL4026983) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human KARPAS299 cells assessed as reduction in IL-1 stimulated IRAK4 phosphorylation at Thr345/Ser346 residues preincubated for 1 hr followed by IL-1 stimulation for 10 mins by flow cytometry analysis
- ChEMBL_1794356 (CHEMBL4266473) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human KARPAS299 cells assessed as reduction in IL-1 stimulated IRAK4 phosphorylation at Thr345/Ser346 residues preincubated for 1 hr followed by IL-1 stimulation for 10 mins by flow cytometry analysis
- ChEMBL_1520136 (CHEMBL3625600) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using 5FAM-RKRQGSVRRRVHCCOOH as substrate after 30 mins by IMAP assay
- ChEMBL_2154863 (CHEMBL5039523) Agonist activity at STING KO human THP-1 dual cells incubated for 20 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay
- ChEBML_1696732 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using fluorescent labelled IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide as substrate after 60 mins by caliper assay
- ChEMBL_1444243 (CHEMBL3380182) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using fluoresceinated peptide and ATP after 60 mins by by Caliper assay
- ChEMBL_2302061 Inhibition of human GST-tagged IRAK4 incubated for 30 mins in presence of ATP by fluorescent polarization assay
- ChEMBL_886749 (CHEMBL2210063) Inhibition of recombinant IRAK4 after 1 hr by scintillation counter analysis in presence of gamma-[33P]ATP
- ChEMBL_2322358 Agonist activity at STING in human STHP1-Dual KO-STING cells incubated for 20 hrs by Quanti-luc reagent based assay
- ChEMBL_2354137 Agonist activity at STING in PMA-differentiated human THP1-Dual KO-STING cells incubated for 24 hrs by QUANTI-Blue assay
- ChEMBL_1504266 (CHEMBL3592269) Inhibition of human IRAK4 assessed as phosphorylation of fluorescent peptide substrate after 30 mins by fluorescent polarization reader
- ChEMBL_1666151 (CHEMBL4015947) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC assessed as reduction in R848-stimulated TNF alpha production after 3 hrs
- ChEMBL_1676864 (CHEMBL4027007) Inhibition of recombinant full length N-terminal His6-tagged human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells
- ChEMBL_1696732 (CHEMBL4047622) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using fluorescent labelled IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide as substrate after 60 mins by caliper assay
- ChEMBL_1934080 (CHEMBL4479732) Inhibition of full-length recombinant human His-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system by Z'-LYTE assay
- ChEMBL_2019460 (CHEMBL4673038) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human MV4-11 cells assessed as modulation of phospho-IRAK1 level by immunoblotting analysis
- ChEMBL_2076054 (CHEMBL4731588) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using methylcoumarin-labeled peptide as substrate in presence of ATP by FRET assay
- ChEMBL_2369184 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using peptide substrate incubated for 1 hrs in presence of ATP by fluorescence microplate reader
- IRAK4 Kinase Assay The IRAK4-inhibitory activity of the inventive substances was measured in the IRAK4 TR-FRET assay (TR-FRET=Time Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) described hereinafter.Recombinant fusion protein from N-terminal GST (glutathione S-transferase) and human IRAK4, expressed in baculovirus-infected insect cells (Hi5, BTI-TN-5B1-4, cell line purchased from Invitrogen, catalogue No. B855-02) and purified via affinity chromatography, was used as enzyme. The substrate used for the kinase reaction was the biotinylated peptide biotin-Ahx-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQASFAEPG (C-terminus in amide form) which can be purchased, for example, from Biosyntan GmbH (Berlin-Buch).
- ChEMBL_1443095 (CHEMBL3380801) Inhibition of human IRAK4 incubated for 20 mins prior to MgCl2 addition measured after 90 mins by mobility shift assay
- ChEMBL_1672108 (CHEMBL4022137) Inhibition of IRAK4 in Lewis rat whole blood assessed as reduction in R848-stimulated TNF alpha production after 4 hrs
- ChEMBL_1859153 (CHEMBL4360009) Inhibition of recombinant IRAK4 (unknown origin) using KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR as substrate in presence of [gamma33P]-ATP by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2076058 (CHEMBL4731592) Inhibition of wild-type human partial length IRAK4 (M1 to S460 residues) expressed in mammalian expression system by Kinomescan method
- ChEMBL_2209828 (CHEMBL5122777) Inhibition of human recombinant IRAK4 assessed as unphosphorylated KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR peptide substrate measured after 2 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis
- ChEMBL_2299726 Inhibition of human IRAK4 using biotinylated FGLARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVARTQTVRGT peptide as substrate incubated for 1 hr in presence of ATP by ELISA assay
- SPR Binding Assay IRAK4 protein. N-terminal His-TEV-AVI tagged catalytical domain of human IRAK4 (a.a. 163-460) was co-expressed with Bir A in insect cells, and purified to >95% homogeneity by a combination of Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, ion-exchange and size-exclusion chromatography. Phosphorylation and mono-biotinylation of purified IRAK4 were confirmed by mass spectrometric analysis.IRAK4 SPR. IRAK4 SPR was set up on Biacore T200 or S200 by using Biotin CAPture kit (Cytiva). In brief, purified IRAK4 in capture buffer (25 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, pH7.4) was captured onto a CAP sensor surface via the interaction of biotin to streptavidin Typical capture level is between 1,000 RU to 2,000 RU, Compound binding kinetics to IRAK4 was examined with running buffer (25 mM Hepes, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, 2% DMSO, pH7.4). Serially diluted compounds were injected at 50 μl/min in single-cycle for 60-s association of each injection followed by 360-s dissociation at the end.
- ChEMBL_2473762 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human HCT-116 cells with MTAP KO assessed as decrease in SMDA level incubated for 48 hrs by immunofluorescence analysis
- ChEMBL_2069399 (CHEMBL4724652) Inhibition of human full length N-terminal His6-tagged recombinant IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus-infected Sf21 cells by Z'-LYTE assay
- ChEMBL_2083795 (CHEMBL4739586) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide as substrate in presence of ATP measured after 60 mins by fluorescence assay
- ChEMBL_1991895 (CHEMBL4625630) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide and ATP as substrate incubated for 60 mins by fluorescence based caliper assay
- ChEMBL_2157678 (CHEMBL5042338) Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using FL- IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide as substrate in presence of ATP incubated for 60 mins by fluorescence assay
- ChEMBL_2496322 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using FAM-labeled peptide as substrate incubated for 10 mins in presence of ATP by mobility shift assay
- ChEMBL_1444239 (CHEMBL3380178) Inhibition of N-terminal GST-fused full-length human IRAK4 (1 to 460 amino acids) assessed as reduction in phosphorylated substrates by Caliper assay
- ChEMBL_1520142 (CHEMBL3625606) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC assessed as reduction of IL1beta-induced TNFalpha production treated 30 mins before IL1beta stimulation measured after 5 hrs
- ChEMBL_1794380 (CHEMBL4266497) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal His6-tagged full length IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells in presence of 5000 uM ATP
- ChEMBL_2527337 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) in presence of ATP Km treated at 2 hrs followed by IGF1 ligand addition for 15 mins by ELISA analysis
- ChEMBL_2160781 (CHEMBL5045531) Agonist activity at STING in human THP1 Dual KO-STING cells assessed as IRF reporter activation incubated for 20 hrs by quanti-blue SEAP reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_1666191 (CHEMBL4015987) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC assessed as reduction in R848-stimulated TNF alpha production by measuring plasma protein binding corrected IC50 after 3 hrs
- ChEMBL_1877974 (CHEMBL2189040) Inhibition of recombinant full length human IRAK4 A81V using myelin basic protein as substrate after 40 mins by [gamma-33ATP] by radiometric scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_2160782 (CHEMBL5045532) Agonist activity at STING in mouse RAW-Lucia ISG-KO-STING cells assessed as IRF reporter activation incubated for 20 hrs by quanti-blue SEAP reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_2160784 (CHEMBL5045534) Agonist activity at STING in human THP1-Dual KO-STING cells assessed as NF-kappaB reporter activation incubated for 20 hrs by quanti-blue SEAP reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_1696735 (CHEMBL4047625) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC assessed as reduction in LTA-stimulated IL6 production pretreated for 30 mins followed by LTA stimulation after 5 hrs by ELISA
- ChEMBL_1859084 (CHEMBL4359940) Inhibition of human recombinant full length His6-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using H-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR as substrate incubated for 90 mins by fluorescence polarisation assay
- ChEMBL_2086518 (CHEMBL4767781) Inhibition of recombinant human His-tagged full length IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using Ser/Thr07 peptide as substrate incubated for 1 hr by Z'lyte assay
- ChEMBL_1520143 (CHEMBL3625715) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC assessed as reduction of TLR 7/8 agonist R848-induced TNFalpha production treated 30 mins before R848 stimulation measured after 5 hrs
- ChEMBL_1844703 (CHEMBL4345130) Inhibition of recombinant full-length N-terminal His6-tagged human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using H-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR peptide as substrate after 90 mins by fluorescence polarisation assay
- ChEMBL_2073913 (CHEMBL4729447) Inhibition of recombinant human full-length His-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using 5-FAM-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK-COOH as substrate measured after 240 mins by mobility shift assay
- ChEMBL_2441673 Inhibition of IRAK4 (unknown origin) using biotinylated peptide (IRAK1 activation loop sequence 360-389) as substrate incubated for 2 hrs in presence of 1 mM ATP by mesoscale detection method
- ChEMBL_2526407 Inhibition of IRAK4 in human HeLa cells lysate pre incubated for 15 mins followed by ATP acyl phosphate probe addition and measured after 10 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis
- ChEMBL_2526530 Inhibition of IRAK4 in human HeLa cells lysate pre incubated for 15 mins followed by ADP acyl phosphate probe addition and measured after 10 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis
- ChEMBL_2543900 Inhibition of human wild type IRAK4 using RB-CTF as substrate preincubated for 2 hrs followed by ATP addition and measured every 2 mins for 2.5 hrs by spectrophotometric analysis
- ChEMBL_1822992 (CHEMBL4322756) Binding affinity to recombinant full-length human N-terminal his-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using IRAK1 peptide as substrate incubated for 1 hr by TR-FRET assay
- ChEMBL_1991896 (CHEMBL4625631) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human PBMC assessed as inhibition of LTA-induced IL-6 production preincubated for 30 mins followed by LTA-stimulation and measured after 5 hrs by ELISA
- ChEMBL_2583246 Inhibition of human IRAK4 using myelin basic protein as substrate preincubated for 20 mins followed by [gamma-33P]-ATP addition and measured after 120 mins by radiometric Hot-SpotSM Kinase assay
- ChEMBL_1666148 (CHEMBL4015944) Inhibition of N-terminal His6-tagged human full length IRAK4 preincubated for 20 mins followed by biotinylated-AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR substrate addition in presence of ATP measured after 60 mins by DELFIA method
- ChEMBL_1672106 (CHEMBL4022135) Inhibition of recombinant human full length GST tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RP7030 peptide as substrate after 30 mins in presence of ATP by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1991897 (CHEMBL4625632) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of LTA-induced IL-6 production preincubated for 30 mins followed by LTA-stimulation and measured after 5 hrs by ELISA
- ChEBML_1970689 Inhibition of recombinant full length human His-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using serine/threonine-7 peptide as substrate incubated for 60 mins in presence of ATP by Z'-LYTE assay
- ChEMBL_1676839 (CHEMBL4026982) Inhibition of recombinant full length His-tagged human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using 5-FAM-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK-COOH as substrate after 240 mins in presence of ATP by mobility shift assay
- ChEMBL_1794351 (CHEMBL4266468) Inhibition of recombinant full length His-tagged human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using 5-FAM-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK-COOH as substrate after 240 mins in presence of ATP by mobility shift assay
- ChEMBL_1844704 (CHEMBL4345131) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of R848-induced IL-6 production preincubated for 90 mins followed by R848 stimulation and measured after 3.5 hrs by MSD assay
- ChEMBL_1844742 (CHEMBL4345169) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of R848-induced IFN alpha production preincubated for 90 mins followed by R848 stimulation and measured after 3.5 hrs by MSD assay
- ChEMBL_2019404 (CHEMBL4672982) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human THP-1 cells assessed as inhibition of LTA-induced TNF-alpha production preincubated for 60 mins followed by LTA stimulation and measured after 5 hrs by ELISA
- ChEMBL_1520137 (CHEMBL3625601) Inhibition of IRAK4-mediated NFkappaB activation in human THP1-XBlue cells assessed as LPS-induced secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase activity treated 1 hr before LPS challenge measured after 5 hrs by spectrophotometer analysis
- ChEMBL_1666192 (CHEMBL4015988) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as reduction R848-induced IL-6 secretion by measuring plasma protein binding corrected IC50 preincubated for 30 mins prior to R848 addition after 4 hrs
- ChEMBL_1924896 (CHEMBL4427852) Inhibition of human recombinant N-terminal GST-tagged full-length IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells using 5FAM-RKRQGSVRRRVH-COOH as substrate in presence of ATP by IMAP fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2019457 (CHEMBL4673035) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of TLR2-mediated LTA-induced IL-6 release preincubated for 1 hr followed by LTA stimulation and measured after 16 hrs by ELISA
- ChEMBL_2504928 Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of R848-induced IL-1beta production preincubated with compound for 1 hr followed by R848 stimulation and measured after 4 hrs by MSD assay
- IRAK4 Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 is a human purified recombinant enzyme (His-TEV-IRAK1 (194-712) IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International based in Bagnols/C ze FR).Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition is performed in streptavidin coated 384 well FlashPlate (PerkinElmer #SMP410A). His-TEV-IRAK4 (20 ng/well), ATP (2 μM, [33P]ATP 0.25 μCi/well), STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM) and compounds in DMSO (range of concentrations from 20 μM to 1 nM) or controls (2% DMSO) are incubated for 3 hours at 30° C. in assay buffer: Hepes pH 7.0 50 mM, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol DTT 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Tween-20 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM.Kinase reaction is stopped by addition of EDTA. Supernatant is discarded, plates are washed three times with 150 mM NaCl and radioactivity is then measured in a Microbeta Trilux reader.
- IRAK4 Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 is a human purified recombinant enzyme (His-TEV-IRAK1 (194-712). IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International based in Bagnols/C ze FR). Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition was performed in streptavidin coated 384 well FlashPlate (PerkinElmer #SMP410A). His-TEV-IRAK4 (20 ng/well), ATP (2 μM, [33P]ATP 0.25 μCi/well), STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM) and compounds in DMSO (range of concentrations from 20 μM to 1 nM) or controls (2% DMSO) were incubated for 3 hours at 30° C. in assay buffer: Hepes pH7.0 50 mM, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol DTT 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Tween-20 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM. Kinase reaction was stopped by addition of EDTA. Supernatant was discarded, plates were washed three times with 150 mM NaCl and radioactivity was then measured in a Microbeta Trilux reader.
- ChEMBL_1466547 (CHEMBL3407004) Inhibition of N-terminal GST tagged human recombinant full-length IRAK4 expressed in Sf9 insect cells assessed as reduction in substrate phosphorylation using RP7030 peptide substrate and ATP incubated for 30 mins fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1576571 (CHEMBL3804242) Inhibition of N-terminal GST-tagged human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus preincubated for 5 mins using myelin basic protein as substrate measured after 60 mins in presence of [gamma-33P]ATP by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2019459 (CHEMBL4673037) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of TLR5-mediated FLA-ST-induced IL-6 release preincubated for 1 hr followed by FLA-ST stimulation and measured after 16 hrs by ELISA
- Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 is a human purified recombinant enzyme (His-TEV-IRAK1 (194-712). IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International based in Bagnols/C ze FR).Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition was performed in streptavidin coated 384well FlashPlate (PerkinElmer #SMP410A). His-TEV-IRAK4 (20 ng/well), ATP (2 μM, [33P]ATP 0.25 Ci/well), STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM) and compounds in DMSO (range of concentrations from 20 M to 1 nM) or controls (2% DMSO) were incubated for 3 hours at 30° C. in assay buffer: Hepes pH7.0 50 mM, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol DTT 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Tween-20 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM.
- ChEMBL_1509418 (CHEMBL3603426) Inhibition of IRAK4-dependent TLR4 signaling in human THP1-XBlue cells containing NF-kappaB-inducible SEAP reporter gene assessed as inhibition of LPS-EK-induced TLR4 activation incubated at 37 degC for 1 hr by spectrophotometry
- ChEMBL_1808272 (CHEMBL4307631) Inhibition of N-terminal GST-tagged human IRAK4 (2 to end residues) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using Ser/Thr 7 peptide as substrate in presence of ATP after 1 hr by Z'-LYTE assay
- ChEMBL_2019458 (CHEMBL4673036) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human whole blood assessed as inhibition of IL-1R-mediated IL-1beta-induced IL-6 release preincubated for 1 hr followed by IL-1beta stimulation and measured after 16 hrs by ELISA
- ChEMBL_2073933 (CHEMBL4729467) Displacement of polymer supported probe 25 binding to IRAK4 in human THP-1 cell lysates preincubated for 45 mins under shaking condition followed by probe addition and measured after 30 mins by mass spectrometry based chemoproteomic analysis
- ChEMBL_2229344 (CHEMBL5142857) Inhibition of recombinant human full-length His-tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells using KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 2 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis
- ChEMBL_2376891 Inhibition of N-terminal GST-tagged recombinant human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected Hi-5 cells using biotinylated-Ahx-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQASFAEPG peptide as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate/ATP addition measured after 45 mins by TR-FRET assay
- ChEMBL_2381493 Inhibition of recombinant human full length his-tagged IRAK4 expressed in insect cells using KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR as peptide substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 2 hrs in presence of ATP by LC-MS/MS analysis
- Enzymatic Assay Kinase activities were assayed using the Transcreener-Fluorecescence polarization platform (BelBrook Labs, Madison, Wis., USA) that measures amounts of the reaction product, ADP. The IRAK4 reaction conditions were optimized using an IRAK1-derived peptide (sequence H-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR) to provide a linear reaction rate over the course of a 90 min incubation, which resulted in 10-12% conversion of the starting ATP to ADP. Final IRAK4 assay conditions were 1.25 nM IRAK4; 125 uM ATP; 10 uM MgC2; 125 uM peptide in reaction buffer (25 mM HEPES (pH7.4); 2 mM Dithiothreitol; 0.015% Brij-35; and 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide. The IRAK1 activity was optimized similarly, yielding final assay conditions of 3 mM IRAK1; 62.5 uM ATP; 5 uM MgCl2, and 62.5 uM IRAK1 peptide in reaction buffer for 60 min.
- IRAK4 Kinase Inhibitory Activity Assay The inhibitory activity (IC50) of the compound on IRAK4 kinase under Km ATP was detected by mobility shift assay (MSA). Ten drug concentration gradients were set (initial concentration 1 μM, 3-fold dilution, 2 duplicate wells per concentration). IRAK4 kinase was added to the kinase buffer solution, which was transfered to a test plate, and then FAM-labeled peptide and ATP (37 μM) were added. After incubation at 28° C. for a period of time, 10 μL of termination buffer was added to terminate the reaction. The conversion rate data was read with Caliper, and then the conversion rate was converted into inhibition rate data. According to the inhibition rate data of each concentration, the IC50 of half inhibitory concentration was calculated by Logit method (Table 3).
- ChEMBL_1500328 (CHEMBL3588639) Inhibition of recombinant N-terminal GST-tagged full length human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus-infected insect Sf9 cells using 5FAM-RKRQGSVRRRVH-COOH as substrate assessed as substrate phosphorylation after 30 mins by immobilized metal ion affinity-based fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_1500343 (CHEMBL3588654) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human THP1-XBlue cells assessed as suppression of TLR4 agonist LPS-induced activation of NF-kappaB preincubated for 1 hr followed by LPS challenge measured after 5 hrs by secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase reporter gene assay
- Transcreener-Fluorecescence Polarization Assay Kinase activities were assayed using the Transcreener-Fluorecescence polarization platform (BelBrook Labs, Madison, Wis., USA) that measures amounts of the reaction product, ADP. The IRAK4 reaction conditions were optimized using an IRAK1-derived peptide (sequence H-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR) to provide a linear reaction rate over the course of a 90 min incubation, which resulted in 10-12% conversion of the starting ATP to ADP. Final IRAK4 assay conditions were 1.25 nM IRAK4; 125 μM ATP; 10 μM MgCl2; 125 μM peptide in reaction buffer (25 mM HEPES (pH7.4); 2 mM Dithiothreitol; 0.015% Brij-35; and 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide. The IRAK1 activity was optimized similarly, yielding final assay conditions of 1.5 nM IRAK1; 62.5 μM ATP; 5 μM MgCl2, and 62.5 μM IRAK1 peptide in reaction buffer for 60 min.
- ChEMBL_1859087 (CHEMBL4359943) Inhibition of IRAK4 in human THP1-Xblue-MD2-CD14 cells assessed as reduction in LPS-induced NFkappaB transcription by measuring alkaline phosphatase level preincubated for 1 hr followed by LPS stimulation and measured after 20 hrs by quanti-blue reagent based reporter assay
- ChEMBL_1924897 (CHEMBL4427853) Inhibition of recombinant N-terminal GST-tagged full-length IRAK4 in human THP1-XBlue cells assessed as decrease in NF-kappaB level preincubated for 1 hr followed by stimulation with LPS for 4 to 5 hrs measured after 30 mins by spectrophotometric analysis
- IRAK4 Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International based in Bagnols/C ze FR).Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition is performed in streptavidin coated 384 well FlashPlate (PerkinElmer #SMP410A). His-TEV-IRAK4 (20 ng/well), ATP (2 μM, [33P]ATP 0.25 μCi/well), STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM) and compounds in DMSO (range of concentrations from 20 μM to 1 nM) or controls (2% DMSO) are incubated for 3 hours at 30° C. in assay buffer: Hepes pH7.0 50 mM, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol DTT 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Tween-20 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM. Kinase reaction is stopped by addition of EDTA. Supernatant is discarded, plates are washed three times with 150 mM NaCl and radioactivity is then measured in a Microbeta Trilux reader.
- IRAK4 Kinase Assay The kinase activity of IRAK4 is determined by its ability to catalyze the phosphorylation of a fluorescent polypeptide substrate. The extent of phosphorylation is measured using the IMAP technology (Molecular Devices) where the phosphorylated fluorescent substrate binds to the large M (III)-based nanoparticles which reduces the rotational speed of the substrate and thus increases its fluorescent polarization (FP).20 μL reaction mixture contains 10 mM TriHCl, pH 7.2, 0.5 nM GST tagged IRAK4 (SignalChem), 100 nM fluorescent peptide substrate (RP7030, Molecular Devices), 100 μM ATP, 1 mM DDT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.01% Tween 20. The reaction is initiated by the addition of ATP. After incubation for 30 minutes at 25° C., 60 μL of Progressive IMAP Reagent (Molecular Devices) is added to stop the reaction. Change in RP7030's FP is determined by a FP reader (Analyst HT, LJL BioSystems).
- IRAK4 Kinase Assay The kinase activity of IRAK4 is determined by its ability to catalyze the phosphorylation of a fluorescent polypeptide substrate. The extent of phosphorylation is measured using the IMAP technology (Molecular Devices) where the phosphorylated fluorescent substrate binds to the large M(III)-based nanoparticles which reduces the rotational speed of the substrate and thus increases its fluorescent polarization (FP).20 μL reaction mixture contains 10 mM TriHCl, pH 7.2, 0.5 nM GST tagged IRAK4 (SignalChem), 100 nM fluorescent peptide substrate (RP7030, Molecular Devices), 100 μM ATP, 1 mM DDT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.01% Tween 20. The reaction is initiated by the addition of ATP. After incubation for 30 minutes at 25° C., 60 μL of Progressive IMAP Reagent (Molecular Devices) is added to stop the reaction. Change in RP7030's FP is determined by a FP reader (Analyst HT, LJL BioSystems).
- ChEMBL_2019402 (CHEMBL4672980) Inhibition of recombinant full length N-terminal His6-tagged human IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus infected sf9 cells using biotinylated histone H3 as substrate preincubated for 30 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins in presence of ATP by TR-FRET assay
- Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 is a human purified recombinant enzyme (His-TEV-IRAK4 (1-460)). In this assay, IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International). Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition is performed in 384-well format based on a luminescence assay (ADP-Glo Kinase Assay from Promega). Purified human recombinant IRAK4 (0.3 ug/ml) and serial diluted compounds in DMSO (range of concentration from 10 uM to 0.5 nM) or controls (1% DMSO) are incubated for 15 minutes at RT in assay buffer containing 50 mM Hepes pH 7.0, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol (DTT) 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Triton X-100 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM. The kinase reaction is then initiated by the addition of ATP (2 uM) and the peptidic substrate STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM). After 2 hours of incubation at RT, the reaction is stopped and the unconsumed ATP depleted by the addition of ADP-Glo Reagent according to supplier instructions. After 40 minutes of incubation at RT, the Kinase Detection Reagent is then added to the assay plate according to supplier instructions. After 20 minutes of incubation at RT, the luminescence signal is measured with a plate-reading luminometer (PerkinElmer Envision or equivalent reader).
- IRAK4 Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- IRAK4 Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LabChip 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- IRAK4 Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2. 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITITYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- IRAK4 Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LabChip 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- IRAK4 Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP® 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, MA) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- IRAK4 Inhibition Assay he assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP® 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, MA) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- Transcreener-Fluorecescence Polarization Assay The IRAK4 reaction conditions were optimized using an IRAK1-derived peptide (sequence H-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR) to provide a linear reaction rate over the course of a 90 min incubation, which resulted in 10-12% conversion of the starting ATP to ADP. Final IRAK4 assay conditions were 1.25 nM IRAK4; 125 uM ATP; 10 uM MgCl2; 125 uM peptide in reaction buffer (25 mM HEPES (pH7.4); 2 mM Dithiothreitol; 0.015% Brij-35; and 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide. The IRAK1 activity was optimized similarly, yielding final assay conditions of 1.5 nM IRAK1; 62.5 uM ATP; 5 uM MgCl2, and 62.5 uM IRAK1 peptide in reaction buffer for 60 min.Assays of compounds for kinase inhibition were performed using inhibitors serially-diluted in dimethyl sulfoxide, which was accomplished with a LabCyte Echo 555 liquid dispenser. 384 well assay plates spotted with compound received 4 ul of a 2× substrate (ATP+peptide) mix in reaction buffer, followed by 4 ul of 2× enzyme diluted in reaction buffer. Reactions were halted at 60 (IRAK1) or 90 (IRAK4) min by addition of 6 ul of detection buffer, containing EDTA (40 nM final concentration), 0.95 ug of the ADP-binding antibody ADP2, ADP tracer (3 nM final concentration), and 25 uM HEPES. Following a 1 hr incubation, fluorescence polarization of the ADP2-antibody TRACER complex was read on a Tecan M1000 plate reader using a 635/20 excitation filter in combination with a 670/20 emission filter. Delta milli-P values were analyzed using Genedata software to fit dose-response curves and compute compound Ki values, using ATP Km values of 642 um and 83.2 uM for IRAK4 and IRAK1, respectively.
- ChEMBL_2145199 (CHEMBL5029479) Inhibition of full length human N-terminal GST-fusion tagged IRAK4 expressed in baculovirus expression system using FAM-labelled peptide as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and further incubated for 1 hr in presence of ATP at Km concentration by caliper mobility shift assay
- Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 is a human purified recombinant enzyme (His-TEV-IRAK4 (1-460)).In this assay, IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International). Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition is performed in 384-well format based on a luminescence assay (ADP-Glo Kinase Assay from Promega). Purified human recombinant IRAK4 (0.3 μg/ml) and serial diluted compounds in DMSO (range of concentration from 10 μM to 0.5 nM) or controls (1% DMSO) are incubated for 15 minutes at RT in assay buffer containing 50 mM Hepes pH 7.0, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol (DTT) 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Triton X-100 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM. The kinase reaction is then initiated by the addition of ATP (2 μM) and the peptidic substrate STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM). After 2 hours of incubation at RT, the reaction is stopped and the unconsumed ATP depleted by the addition of ADP-Glo Reagent according to supplier instructions. After 40 minutes of incubation at RT, the Kinase Detection Reagent is then added to the assay plate according to supplier instructions. After 20 minutes of incubation at RT, the luminescence signal is measured with a plate-reading luminometer (PerkinElmer Envision or equivalent reader).
- Enzymatic Assay IRAK4 is a human purified recombinant enzyme (His-TEV-IRAK4 (1-460)).In this assay, IRAK4 hydrolyses ATP, autophosphorylates and phosphorylates a Serine/Threonine generic peptidic substrate (STK: 61ST1BLC from CisBio International). Measurement of IRAK-4 inhibition is performed in 384-well format based on a luminescence assay (ADP-Glo Kinase Assay from Promega). Purified human recombinant IRAK4 (0.3 μg/ml) and serial diluted compounds in DMSO (range of concentration from 10 μM to 0.5 nM) or controls (1% DMSO) are incubated for 15 minutes at RT in assay buffer containing 50 mM Hepes pH 7.0, Fatty acid-free BSA 0.1%, Dithiothreitol (DTT) 2 mM, MgCl2 10 mM, EGTA 0.5 mM, Triton X-100 0.01%, MnCl2 5 mM. The kinase reaction is then initiated by the addition of ATP (2 μM) and the peptidic substrate STK1-biotin peptide (300 nM). After 2 hours of incubation at RT, the reaction is stopped and the unconsumed ATP depleted by the addition of ADP-Glo Reagent according to supplier instructions. After 40 minutes of incubation at RT, the Kinase Detection Reagent is then added to the assay plate according to supplier instructions. After 20 minutes of incubation at RT, the luminescence signal is measured with a plate-reading luminometer (PerkinElmer Envision or equivalent reader).
- Potency of IRAK4 Inhibitor Compounds in IRAK4 Enzyme Assay The inhibitory activity of compounds against IRAK4 were determined in an enzymatic assay using mass spectrometry readout. Ten point half-log compound concentration response curves, with a top concentration of 1 μM or 10 μM, were generated from 10 mM stocks of compound solubilized in DMSO using an Echo 655 (Labcyte Inc) and added to 384 well assay plates (Greiner #781280). To the assay plates, 10 μL of human recombinant IRAK4 protein (Life Technologies #PV4002) diluted to a final concentration of 0.2 nM in assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl, 5 mM glutathione, 0.01% BSA, 3 mM ATP) was added. The enzyme was incubated with the compounds at room temperature for 15 minutes before a peptide substrate (KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR, Innovagen custom synthesis, 10 mM in DMSO) was added to each well to a final concentration of 10 μM using an Echo 655 (Labcyte Inc). After two hours at room temperature, the reaction was stopped with 65 μL of 0.4% formic acid (Merck #33015). The unphosphorylated and phosphorylated peptide were measured by LC-MS/MS on a Waters TQ-S mass spectrometer. Peaks were integrated using the TargetLynx software and the ratios between phosphorylated and unphosphorylated peptides were calculated.
- Potency of IRAK4 Inhibitor Compounds in IRAK4 Enzyme Assay The inhibitory activity of compounds against IRAK4 were determined in an enzymatic assay using mass spectrometry readout. Ten point half-log compound concentration response curves, with a top concentration of 1 μM or 10 μM, were generated from 10 mM stocks of compound solubilized in DMSO using an Echo 655 (Labcyte Inc) and added to 384 well assay plates (Greiner #781280). To the assay plates, 10 μL of human recombinant IRAK4 protein (Life Technologies #PV4002) diluted to a final concentration of 0.2 nM in assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl, 5 mM glutathione, 0.01% BSA, 3 mM ATP) was added. The enzyme was incubated with the compounds at room temperature for 15 minutes before a peptide substrate (KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR, Innovagen custom synthesis, 10 mM in DMSO) was added to each well to a final concentration of 10 μM using an Echo 655 (Labcyte Inc). After two hours at room temperature, the reaction was stopped with 90 μL of 0.4% formic acid (Merck #33015). The unphosphorylated and phosphorylated peptide were measured by LC-MS/MS on a Waters TQ-S mass spectrometer. Peaks were integrated using the TargetLynx software and the ratios between phosphorylated and unphosphorylated peptides were calculated.
- Biological Assay Kinase activities were assayed using the Transcreener-Fluorecescence polarization platform (BelBrook Labs, Madison, Wis., USA) that measures amounts of the reaction product, ADP. The IRAK4 reaction conditions were optimized using an IRAK1-derived peptide (sequence H-KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR) to provide a linear reaction rate over the course of a 90 min incubation, which resulted in 10-12% conversion of the starting ATP to ADP. Final IRAK4 assay conditions were 1.25 nM IRAK4; 125 uM ATP; 10 uM MgCl2; 125 uM peptide in reaction buffer (25 mM HEPES (pH7.4); 2 mM Dithiothreitol; 0.015% Brij-35; and 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide. The IRAK1 activity was optimized similarly, yielding final assay conditions of 3 mM IRAK1; 62.5 uM ATP; 5 uM MgCl2, and 62.5 uM IRAK1 peptide in reaction buffer for 60 min.Assays of compounds for kinase inhibition were performed using inhibitors serially-diluted in dimethyl sulfoxide, which was accomplished with a LabCyte Echo 555 liquid dispenser. 384 well assay plates spotted with compound received 4 ul of a 2× substrate (ATP+peptide) mix in reaction buffer, followed by 4 ul of 2× enzyme diluted in reaction buffer. Reactions were halted at 60 (IRAK1) or 90 (IRAK4) min by addition of 6 ul of detection buffer, containing EDTA (40 nM final concentration), 0.95 ug of the ADP-binding antibody ADP2, ADP tracer (3 nM final concentration), and 25 uM HEPES. Following a 1 hr incubation, fluorescence polarization of the ADP2-antibody TRACER complex was read on a Tecan M1000 plate reader using a 635/20 excitation filter in combination with a 670/20 emission filter.
- IRAK4 Enzymatic DELFIA Assay, Protocol B This is an in vitro assay to measure IRAK4 enzymatic activity utilizing the DELFIA (Dissociation-Enhanced Lanthanide Fluorescent Immunoassay, Perkin-Elmer) platform, with inactive, unphosphorylated (0-phos), human IRAK4 FL (Full Length) construct to characterize IRAK4 inhibitor and control compounds at 600 μM ATP (KM). The final amount of enzyme in the assay is 0.1 nM inactive, 0-phos, IRAK4 FL, final concentration of substrate is 50 nM, and final concentration of DMSO is 2.5%.The test compound is solubilized in DMSO to a stock concentration of 30 mM. The dose response plates were prepared with a 4 mM primary compound concentration, serialized in DMSO and spotted (1 μL) into 384-well polypropylene plates as before.To begin the assay, 19 uL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 uM ATP, 0.21 nM inactive, 0-phos, full-length recombinant human IRAK4 (GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into the polypropylene plates containing 1 μL of test compound as before. 20 uL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 100 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) was added to start the reaction, which was run for 90 minutes at RT and stopped by the addition of 20 μL 0.3M EDTA.50 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin-coated detection plate (DELFIA streptavidin coated plates, 384-well, white plates, Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) and incubated for 30 minutes at RT. The plates were washed 4× with 75 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody at 0.125 μg/mL (Cell Signaling Technology), plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.25 μg/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were then washed as before. 50 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) was added to the plate and incubated for 15 minutes at RT prior to being read on an Envision Model 2104 multi-label reader using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission wavelength for detection.
- Biological Assays against IRAK4 To measure the IC50 values of compounds herein against IRAK4, a Z′-LYTE assay (ThermoFisher) was used. Briefly, 2.5 μL. of different concentrations of the compounds in 1% DMSO were added to 2.4 μL kinase buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 0.01% BRIJ-35, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA) in each well of a 384-well plate (Corning Cat. #3676). 5 μL of 2×IRAK4/Ser/Thr 07 mixture (prepared in 50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 0.01% BRIJ-35, 10 mM MnCl2, 2 mM OTT, and 0.02% NaN3) and 2.5 μL of 4×ATP solution (4×ATP, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 0.01% BRIJ-35, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA) were added to each well. The plate was shaken for 30 seconds, and then incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes. 5 μL of a 1:100000 dilution of Development Reagent A was added to each well. The plate was shaken for 30 seconds and incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature. The plate was subsequently read on a fluorescence plate reader, and the emissions ratio was calculated to determine the ratio of Ser/Thr 07 phosphorylated by the reaction. Emissions Ratio=Coumarin Emission (443 nm)/Flourescein Emission (520 nm).
- IRAK4 Enzyme Assay The inhibitory activity of compounds against IRAK4 were determined in an enzymatic assay using mass spectrometry readout. Ten point half-log compound concentration response curves, with a top concentration of 1 μM or 10 μM, were generated from 10 mM stocks of compound solubilized in DMSO using an Echo 655 (Labcyte Inc) and added to 384 well assay plates (Greiner #781280). To the assay plates, 10 μL of human recombinant IRAK4 protein (Life Technologies #PV4002) diluted to a final concentration of 0.2 nM in assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl, 5 mM glutathione, 0.01% BSA, 3 mM ATP) was added. The enzyme was incubated with the compounds at room temperature for 15 minutes before a peptide substrate (KKARFSRFAGSSPSQSSMVAR, Innovagen custom synthesis, 10 mM in DMSO) was added to each well to a final concentration of 10 μM using an Echo 655 (Labcyte Inc). After two hours at room temperature, the reaction was stopped with 90 μL of 0.4% formic acid (Merck #33015). The unphosphorylated and phosphorylated peptide were measured by LC-MS/MS on a Waters TQ-S mass spectrometer. Peaks were integrated using the TargetLynx software and the ratios between phosphorylated and unphosphorylated peptides were calculated.
- IRAK4 Enzymatic DELFIA Assay, Protocol A This is an in vitro assay to measure IRAK4 enzymatic activity utilizing the DELFIA (Dissociation-Enhanced Lanthanide Fluorescent Immunoassay, Perkin-Elmer) platform, with the human IRAK4 FL (Full Length) construct to characterize IRAK4 inhibitor and control compounds at 0.6 mM ATP (KM). The final amount of enzyme in the assay is 0.1 nM IRAK4 FL, final concentration of substrate is 50 nM, and final concentration of DMSO is 2.5%. The test compound was solubilized in DMSO to a stock concentration of 30 mM. The dose response plates were prepared with a 4 mM primary compound concentration, and then diluted in DMSO in a four-fold series for a total of 11 data points. Compounds were prepared as a 40-fold multiple of the final in-assay concentration. To begin the assay, 19 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 0.21 nM Full-length phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 (GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into Ultra-Clear Polypropylene, 384-well, U-Bottom Plates (Corning Life Sciences). 1 μL of test compound from the dose-response plate was added to the reaction mixture and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature. Then 20 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 100 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) was added to start the reaction. The reaction was incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and stopped by the addition of 20 μL 0.3M EDTA. 50 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin coated detection plate (DELFIA streptavidin coated plates, 384-well, white plates, Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The plates were washed 4x with 75 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody at 0.125 μg/mL (Cell Signaling Technology), plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.25 ug/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were washed 4x with 50 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Then 50 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) were added to the plate and then read on an EnVision Model 2103 using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission wavelength for detection.
- IRAK4 Enzymatic DELFIA Assay, Protocol A This is an in vitro assay to measure IRAK4 enzymatic activity utilizing the DELFIA (Dissociation-Enhanced Lanthanide Fluorescent Immunoassay, Perkin-Elmer) platform, with the human IRAK4 FL (Full Length) construct to characterize IRAK4 inhibitor and control compounds at 0.6 mM ATP (KM). The final amount of enzyme in the assay is 0.1 nM IRAK4 FL, final concentration of substrate is 50 nM, and final concentration of DMSO is 2.5%.The test compound was solubilized in DMSO to a stock concentration of 30 mM. The dose response plates were prepared with a 4 mM primary compound concentration, and then diluted in DMSO in a four-fold series for a total of 11 data points. Compounds were prepared as a 40-fold multiple of the final in-assay concentration.To begin the assay, 19 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 0.21 nM Full-length phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 (GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into Ultra-Clear Polypropylene, 384-well, U-Bottom Plates (Corning Life Sciences). 1 μL of test compound from the dose-response plate was added to the reaction mixture and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature. Then 20 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 100 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) was added to start the reaction. The reaction was incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and stopped by the addition of 20 μL 0.3M EDTA.50 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin coated detection plate (DELFIA streptavidin coated plates, 384-well, white plates, Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The plates were washed 4× with 75 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody at 0.125 μg/mL (Cell Signaling Technology), plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.25 ug/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were washed 4× with 50 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Then 50 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) were added to the plate and then read on an EnVision Model 2103 using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission wavelength for detection.
- IRAK4 Enzymatic DELFIA Assay, Protocol B This is an in vitro assay to measure IRAK4 enzymatic activity utilizing the DELFIA (Dissociation-Enhanced Lanthanide Fluorescent Immunoassay, Perkin-Elmer) platform, with the human IRAK4 kinase domain (aa 154-460) construct to characterize IRAK4 inhibitor and control compounds at 0.6 mM ATP (KM). The final amount of enzyme in the assay is 114 μM IRAK4 kinase domain, final concentration of substrate is 200 nM, and final concentration of DMSO is 5%.The test compound was solubilized in DMSO to a stock concentration of 30 mM. The dose response plates were prepared with a 2 mM primary compound concentration, and then diluted in DMSO in a four-fold series for a total of 10 data points. Compounds were prepared as a 20-fold multiple of the final in-assay concentration. To begin the assay, 45 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 228 μM phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 kinase domain (aa 154-460; GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into Ultra-Clear Polypropylene, 96-well, U-Bottom Plates (Corning Life Sciences). 5 μL of test compound from the dose-response plate was added to the reaction mixture and incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. Then 50 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 400 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) were added to start the reaction. The reaction was incubated for 90 minutes at room temperature and stopped by the addition of 25 μL 0.5M EDTA. 100 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin coated detection plate (EvenCoat Streptavidin Coated Plates, 96-Well, R&D Systems) and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The plates were washed 4 times with 100 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) diluted 1:5000, plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.242 μg/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were washed 4x with 100 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Then 100 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution were added to the plate and then read on an EnVision Model 2103 using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission detection.
- IRAK4 Enzymatic DELFIA Assay, Protocol B This is an in vitro assay to measure IRAK4 enzymatic activity utilizing the DELFIA (Dissociation-Enhanced Lanthanide Fluorescent Immunoassay, Perkin-Elmer) platform, with the human IRAK4 kinase domain (aa 154-460) construct to characterize IRAK4 inhibitor and control compounds at 0.6 mM ATP (KM). The final amount of enzyme in the assay is 114 pM IRAK4 kinase domain, final concentration of substrate is 200 nM, and final concentration of DMSO is 5%.The test compound was solubilized in DMSO to a stock concentration of 30 mM. The dose response plates were prepared with a 2 mM primary compound concentration, and then diluted in DMSO in a four-fold series for a total of 10 data points. Compounds were prepared as a 20-fold multiple of the final in-assay concentrationTo begin the assay, 45 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 228 pM phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 kinase domain (aa 154-460; GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into Ultra-Clear Polypropylene, 96-well, U-Bottom Plates (Corning Life Sciences). 5 μL of test compound from the dose-response plate was added to the reaction mixture and incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. Then 50 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 400 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) were added to start the reaction. The reaction was incubated for 90 minutes at room temperature and stopped by the addition of 25 μL 0.5M EDTA.100 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin coated detection plate (EvenCoat Streptavidin Coated Plates, 96-Well, R&D Systems) and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The plates were washed 4 times with 100 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) diluted 1:5000, plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.242 μg/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were washed 4× with 100 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Then 100 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution were added to the plate and then read on an EnVision Model 2103 using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission detection.
- IRAK4 ADP-Glo Assay The ADP-Glo reagents were thawed at ambient temperature. The Kinase Detection Reagent was prepared by mixing kinase detection buffer with the lyophilized kinase detection substrate, and set aside.A stock volume of 5 Reaction Kinase Buffer was made with a final concentration of 100 mM MgCl2, 200 mM Tris-HCl, and 0.5 mg/ml of BSA, in distilled H2O with a final pH7.4. A 2 working stock volume of Reaction Kinase Buffer was made containing a final concentration of 100 μM DTT.The components of IRAK4 Enzyme were thawed on ice. Diluted IRAK4 in 1 Kinase Reaction Buffer (diluted from 2 buffer) was prepared at 5.0 ng/μl. A 250 μM working stock ATP Assay Solution was prepared in 1 Kinase Reaction Buffer (diluted from 2 buffer).The compound was diluted in DMSO from 250 μM in 4-fold series dilutions for 8 points. Then diluted 1:5 in 2 Reaction Buffer in a 96 well plate. 1.0 μl was transferred to a 384 well plate in duplicate. 2 μl of diluted Active IRAK4 was added (do not add to column 1) and 2 reaction buffer was added to column 1. 1 μl of 1 mg/ml stock solution of MBP substrate was added NOTE: MBP can be combined with ATP mix with equal volume and then added at 2 μl/well. Final reaction volume was 5 μl.The plate was centrifuged and the reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes or at 30 C. for 30 minutes.The reaction was terminated and the remaining ATP was depleted by adding 5 μl of ADP-Glo Reagent. The 384-well plate was centrifuged and then the reaction mixture was incubated for another 40 minutes at ambient temperature.
- Biochemical Assay The enzyme and peptide solution were incubated with compound for 15 minutes at room temp before the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. The standard 5ul reaction mixture contained 500uM ATP, 2uM peptide (STK1 Peptide), 0.75 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50nM HEPES, pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3, 0.01% BSA, 0.1mM Orthovanadate, 5nM MgCl2, 0.025% NP-40, 1mM DTT). After 120 min of incubation at room temperature, 5ul of Stop and Detect Solution *1:100 Cryptate labeled anti-phosphorylated peptide antibody solution and 125nM Tracer in a 50 nM HEPES pH 7.0 detection buffer containing sufficient EDTA) was added. The plate was then further incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and read on Envision 2013 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340nm/615nm/665nM, respectively.
- Kinase Assay The kinase activity of IRAK4 is determined by its ability to catalyze the phosphorylation of a fluorescent polypeptide substrate. The extent of phosphorylation is measured using the IMAP technology (Molecular Devices) where the phosphorylated fluorescent substrate binds to the large M(III)-based nanoparticles which reduces the rotational speed of the substrate and thus increases its fluorescent polarization (FP).20 μL reaction mixture contains 10 mM TriHCl, pH 7.2, 0.5 nM GST tagged IRAK4 (SignalChem), 100 nM fluorescent peptide substrate (RP7030, Molecular Devices), 100 μM ATP, 1 mM DDT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.01% Tween 20. The reaction is initiated by the addition of ATP. After incubation for 30 minutes at 25° C., 60 μL of Progressive IMAP Reagent (Molecular Devices) is added to stop the reaction. Change in RP7030's FP is determined by a FP reader (Analyst HT, LJL BioSystems).
- IRAK4 Enzymatic DELFIA Assay, Protocol A This is an in vitro assay to measure IRAK4 enzymatic activity utilizing the DELFIA (Dissociation-Enhanced Lanthanide Fluorescent Immunoassay, Perkin-Elmer) platform, with the human IRAK4 FL (Full Length) construct to characterize IRAK4 inhibitor and control compounds at 600 μM ATP (KM). The final amount of enzyme in the assay is 0.1 nM IRAK4 FL, final concentration of substrate is 50 nM, and final concentration of DMSO is 2.5%.The test compound was solubilized in DMSO to a stock concentration of 30 mM. The dose response plates were prepared with a 4 mM primary compound concentration (40-fold multiple of the final in-assay concentration), and diluted in DMSO in a four-fold series for a total of 11 data points. 1 μL of the compound dilution plate is spotted into ultra-clear polypropylene, 384-well, U-bottom plates (Corning Life Sciences).To begin the assay, 19 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 0.21 nM Full-length phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 (GenBank ID AF445802) are aliquoted into the polypropylene, 384-well, U-bottom plates containing 1 μL of test compound, mixed briefly and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature (RT). Then, 20 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 100 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) is added to start the reaction. The reaction is incubated for 60 minutes at RT and stopped by the addition of 20 μL 0.3M EDTA.50 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin-coated detection plate (DELFIA streptavidin coated plates, 384-well, white plates, Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) and incubated for 30 minutes at RT. The plates were washed 4× with 75 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody at 0.125 μg/mL (Cell Signaling Technology), plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.25 μg/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were then washed as before. 50 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) was added to the plate and incubated for 15 minutes at RT prior to being read on an Envision Model 2104 multi-label reader using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission wavelength for detection.
- Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 μL prepared from 15 μL additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- Inhibition Assay The assays were performed in U-bottom 384-well plates. The final assay volume was 30 L prepared from 15 L additions of enzyme and substrates (fluoresceinated peptide and ATP) and test compounds in assay buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.015% Brij 35 and 4 mM DTT). The reaction was initiated by the combination of IRAK4 with substrates and test compounds. The reaction mixture was incubated at room temperature for 60 min. and terminated by adding 45 μL of 35 mM EDTA to each sample. The reaction mixture was analyzed on the Caliper LABCHIP 3000 (Caliper, Hopkinton, Mass.) by electrophoretic separation of the fluorescent substrate and phosphorylated product. Inhibition data were calculated by comparison to no enzyme control reactions for 100% inhibition and vehicle-only reactions for 0% inhibition. The final concentrations of reagents in the assays are ATP, 500 μM; FL-IPTSPITTTYFFFKKK peptide 1.5 μM; IRAK4, 0.6 nM; and DMSO, 1.6%.
- IRAK4 Biochemical Assay IRAK4 enzyme (Carna Biosciences, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Japan) activity was measured by detecting phosphorylated peptide substrate formation using an antibody against the phosphorylated peptide substrate. This is a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) immunoassay, based on the STK1 KinEASE Assay (Cisbio, Bedford, Mass.). The assay was designed as a simple two-step, endpoint assay (a 5 μl enzyme reaction followed by 5 μl stop and detect Solution) performed in ProxiPlate-384 Plus plates (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, Mass.). Staurosporine, a non-selective kinase inhibitor was used as a positive control. Compounds diluted in DMSO were spotted into 384 well plates using a Labcyte Echo 550 Liquid Handling System prior to addition of IRAK4 enzyme and peptide substrate. Reaction solutions were delivered using a Multi-Flo (Bio-Tek Instruments). The enzyme and peptide solution was incubated with compound for 15 minutes at room temp before the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. The standard 5 μl reaction mixture contained 500 μM ATP, 2 M peptide (STK1 Peptide), 0.75 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3, 0.01% BSA, 0.1 mM Orthovanadate, 5 mM MgC2, 0.025% NP-40, 1 mM DTT). After 120 min of incubation at room temperature, 5 μl of Stop and Detect Solution (1:100 Cryptate labeled anti-phosphorylated peptide antibody solution and 125 nM Tracer in a 50 mM HEPES pH 7.0 detection buffer containing sufficient EDTA) was added. The plate was then further incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and read on Envision 2103 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340 nm/615 nm665 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensities at 615 nm and 665 nm emission wavelengths were expressed as aratio (665 nm/615 nm). Percentage of inhibition was calculated as below:% Inhibition=100×(Ratiosample−Ratio0% Inhibition)/(Ratio100% Inhibition−Ratio0% Inhibition)The 0% inhibition value comes from control wells lacking inhibitor. The 100% inhibition value comes from control wells containing a saturating amount of known inhibitor staurosporine.
- Potency of IRAK4 Inhibitor Compounds in cKit Enzyme Assay Potency of IRAK4 Inhibitor Compounds in cKit Enzyme Assay. Evaluation of the effects of the IRAK4 inhibitor compounds on the activity of the human cKit kinase quantified by measuring the phosphorylation of the substrate Ulight-TK peptide using a human recombinant enzyme and the LANCE detection method at Eurofins CEREP, catalog item 3070, SOP no 1C768: The test compound, reference compound or water (control) are mixed with the enzyme (0.38 ng) in a buffer containing 40 mM Hepes/Tris (pH 7.4), 0.8 mM EGTA/Tris, 8 mM MgCl2, 1.6 mM DTT and 0.008% Tween 20. Thereafter, the reaction is initiated by adding 100 nM of the substrate Ulight-TK peptide and 50 μM ATP, and the mixture is incubated for 30 min at room temperature. For control basal measurements, the enzyme is omitted from the reaction mixture. Following incubation, the reaction is stopped by adding 13 mM EDTA. After 5 min, the anti-phopho-PT66 antibody labeled with europium chelate is added. After 60 more min, the fluorescence transfer is measured at lex=337 nm, lem=620 nm and lem=665 nm using a microplate reader (Envision, Perkin Elmer). The enzyme activity is determined by dividing the signal measured at 665 nm by that measured at 620 nm (ratio). The results are expressed as a percent inhibition of the control enzyme activity. The standard inhibitory reference compound is staurosporine, which is tested in each experiment at several concentrations to obtain an inhibition curve from which its IC50 value is calculated.
- IMAP Technology The kinase activity of IRAK4 is determined by its ability to catalyze the phosphorylation of a fluorescent polypeptide substrate. The extent of phosphorylation is measured using IMAP technology (Molecular Devices) where the phosphorylated fluorescent substrate binds to the large M(III)-based nanoparticles which reduces the rotational speed of the substrate and thus increases its fluorescent polarization (FP).Specific compounds of the instant invention were tested in the assay described above and were found to have IC50 values of ≦20 μM against substrate.Procedure: A 20 μl reaction mixture contains 10 mM TriHCl, pH 7.2, 0.5 nM GST tagged IRAK4 (SignalChem), 100 nM fluorescent peptide substrate (RP7030, Molecular Devices), 100 μM ATP, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.01% Tween 20. The reaction is initiated by the addition of ATP. After incubation for 30 minutes at 25° C., 60 μl of Progressive IMAP Reagent (Molecular Devices) is added to stop the reaction. Change in RP7030's FP is determined by a FP reader (Analyst HT, LJL BioSystems).
- IRAK4 Biochemical Assay IRAK4 enzyme (Carna Biosciences, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Japan) activity was measured by detecting phosphorylated peptide substrate formation using an antibody against the phosphorylated peptide substrate. This is a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) immunoassay, based on the STK1 KinEASE Assay (Cisbio, Bedford, Mass.). The assay was designed as a simple two-step, endpoint assay (a 5 μl enzyme reaction followed by 5 μl stop and detect Solution) performed in ProxiPlate-384 Plus plates (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, Mass.). Staurosporine, a non-selective kinase inhibitor was used as a positive control. Compounds diluted in DMSO were spotted into 384 well plates using a Labcyte Echo 550 Liquid Handling System prior to addition of IRAK4 enzyme and peptide substrate. Reaction solutions were delivered using a Multi-Flo (Bio-Tek Instruments). The enzyme and peptide solution was incubated with compound for 15 minutes at room temp before the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. The standard 5 μl reaction mixture contained 500 μM ATP, 2 μM peptide (STK1 Peptide), 0.75 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3, 0.01% BSA, 0.1 mM Orthovanadate, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.025% NP-40, 1 mM DTT). After 120 min of incubation at room temperature, 5 μl of Stop and Detect Solution (1:100 Cryptate labeled anti-phosphorylated peptide antibody solution and 125 nM Tracer in a 50 mM HEPES pH 7.0 detection buffer containing sufficient EDTA) was added. The plate was then further incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and read on Envision 2103 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340 nm/615 nm/665 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensities at 615 nm and 665 nm emission wavelengths were expressed as a ratio (665 nm/615 nm). Percentage of inhibition was calculated as below:% Inhibition=100×(RatioSample−Ratio0% Inhibition)/(Ratio100% Inhibition−Ratio0% Inhibition)The 0% inhibition value comes from control wells lacking inhibitor. The 100% inhibition value comes from control wells containing a saturating amount of known inhibitor staurosporine.
- IMAP technology (Molecular Devices) A 20 ul reaction mixture contains 10 mM TriHCl, pH 7.2, 0.5 nM GST tagged IRAK4 (SignalChem), 100 nM fluorescent peptide substrate (RP7030, Molecular Devices), 100 uM ATP, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.01% Tween 20. The reaction is initiated by the addition of ATP. After incubation for 30 minutes at 25° C., 60 ul of Progressive IMAP Reagent (Molecular Devices) is added to stop the reaction. Change in RP7030's FP is determined by a FP reader (Analyst HT, LJL BioSystems).
- Biological Assay IRAK4 enzyme (Carna Biosciences, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Japan) activity was measured by detecting phosphorylated peptide substrate formation using an antibody against the phosphorylated peptide substrate. This is a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) immunoassay, based on the STK1 KinEASE Assay (Cisbio, Bedford, Mass.). The assay was designed as a simple two-step, endpoint assay (a 5 μl enzyme reaction followed by 5 μl stop and detect Solution) performed in ProxiPlate-384 Plus plates (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, Mass.). Staurosporine, a non-selective kinase inhibitor was used as a positive control. Compounds diluted in DMSO were spotted into 384 well plates using a Labcyte Echo 550 Liquid Handling System prior to addition of IRAK4 enzyme and peptide substrate. Reaction solutions were delivered using a Multi-Flo (Bio-Tek Instruments). The enzyme and peptide solution was incubated with compound for 15 minutes at room temp before the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. The standard 5 μl reaction mixture contained 500 μM ATP, 2 μM peptide (STK1 Peptide), 0.75 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3, 0.01% BSA, 0.1 mM Orthovanadate, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.025% NP-40, 1 mM DTT). After 120 min of incubation at room temperature, 5 μl of Stop and Detect Solution (1:100 Cryptate labeled anti-phosphorylated peptide antibody solution and 125 nM Tracer in a 50 mM HEPES pH 7.0 detection buffer containing sufficient EDTA) was added. The plate was then further incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and read on Envision 2103 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340 nm/615 nm/665 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensities at 615 nm and 665 nm emission wavelengths were expressed as a ratio (665 nm/615 nm).
- Methods for Evaluating TAK1 Modulators Accordingly, the present disclosure is directed to the use of these compounds in the preparation and execution of screening assays for compounds which modulate the function of the TAK1 (and/or an IRAK, such as IRAK4). For example, the compounds of this disclosure can be useful for isolating receptor mutants, which are established screening tools for potent compounds. Furthermore, the compounds of this disclosure can be useful in establishing or determining of protein binding sites, geometry of potential binding pockets, as well as the binding site of other compounds to TAK1, e.g., by competitive inhibition. The compounds of the instant disclosure can also be useful for the evaluation of putative specific modulators of TAK1.
- Determination of the value of binding affinity constant (KO between the compound and BRD4 BD2 protein The purity of BRD4 BD2 protein used in the experiment was greater than 95%, and the protein concentration was 46.33 uM. The 96-well plate was purchased from Corning (black, #3694). The multifunctional microplate reader was a product of TECAN, model: SPARK 10M. Buffer: 100 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.5), 2% ethylene glycol (Sigma) and 0.01% Trition X-100 (Sigma). The experimental water was Millipore-Q pure water.The Ki value of the compound and BRD4 BD2 protein was measured according to the FP test procedures for detecting the Ki value of the compound and BRD4 BD1 protein except that the BRD4 BD1 protein was replaced with the BRD4 BD2 protein.
- Biochemical Assay Biochemical Assay: The biochemical assay is in a AlphaScreen format. The kinase reaction is based on the IRAK-4 phosphorylation of a biotin labeled peptide. The phosphopeptide is incubated with anti-phosphothreonine antibody as well as streptavidin- and protein A-coated beads. Binding of the protein-A coated beads to the antibody and the streptavidin beads to the peptide, leads to an energy transfer from one bead to the other, ultimately producing a luminescent/fluorescent signal.Generally, the kinase reaction is carried out at 1 nM IRAK4, 1.6 μM peptide, 1 mM ATP in reaction buffer 50 mM Hepes, 60 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM MnCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.01% BSA, 0.01% Tween-20) for 3.5 h at RT.
- Biochemical Assay The biochemical assay is in a AlphaScreen format. The kinase reaction is based on the IRAK-4 phosphorylation of a biotin labeled peptide. The phosphopeptide is incubated with anti-phosphothreonine antibody as well as streptavidin- and protein A-coated beads. Binding of the protein-A coated beads to the antibody and the streptavidin beads to the peptide, leads to an energy transfer from one bead to the other, ultimately producing a luminescent/fluorescent signal.Generally, the kinase reaction is carried out at 1 nM IRAK4, 1.6 μM peptide, 1 mM ATP in reaction buffer 50 mM Hepes, 60 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM MnCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.01% BSA, 0.01% Tween-20) for 3.5 h at RT.
- Biochemical Assay The biochemical assay is in a AlphaScreen format. The kinase reaction is based on the IRAK-4 phosphorylation of a biotin labeled peptide. The phosphopeptide is incubated with anti-phosphothreonine antibody as well as streptavidin- and protein A-coated beads. Binding of the protein-A coated beads to the antibody and the streptavidin beads to the peptide, leads to an energy transfer from one bead to the other, ultimately producing a luminescent/fluorescent signal.Generally, the kinase reaction is carried out at 1 nM IRAK4, 1.6 μM peptide, 10 μM ATP in reaction buffer 50 mM Hepes, 60 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM MnCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.01% BSA, 0.01% Tween-20) for 3.5 h at RT.
- IRAK4 Kinase Activity Assay The compounds were prepared with DMSO to 100 times the final reaction concentration and diluted to 10 concentrations in sequence at a 3-fold dilution ratio starting from 1 μM. Then 0.25 μL was transferred to a 384-well plate using Echo550. A 1× kinase buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH=7.5, 0.0015% Brij-35, 10 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT) was used to prepare a kinase solution of 2.5 times the final concentration. Then 10 μL of the kinase solution of 2.5 times the final concentration was added to each compound well, shaken and mixed uniformly, and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. A 1× kinase buffer was used to prepare a mixed solution of ATP and substrate Kinase Substrate 8 with a concentration of 25/15 times the final concentration. 15 μL of the mixed solution of ATP and the substrate with a concentration of 25/15 times the final concentration were added to each well (the final concentration of IRAK4 kinase was 1 nM, the final concentration of the substrate was 3 μM, and the final concentration of ATP was 15.6 μM), shaken and mixed uniformly, and reacted at room temperature for 60 min. Finally, 30 μL of stopping solution (100 mM HEPES, pH=7.5, 0.0015% Brij-35, 0.2% Coating Reagent #3, 50 mM EDTA) was added to terminate the reaction. CaliperEZ Reader II was used to read data about conversion rates that was then converted into data about inhibition rates.
- Biochemical Assay The 2-hour 1 mM ATP Biochemical Assay employed a MesoScale Detection (MSD) format. The kinase reaction was based on the IRAK4 phosphorylation of a biotin labeled peptide (IRAK1 activation loop sequence 360-389).The kinase reaction in 30 μl was carried out in wells of a 384 well polypropylene assay plate, with 0.1 nM IRAK4, 1.6 μM of biotinylated peptide substrate and 1 mM ATP in 50 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 60 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM MnCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.01% BSA, 0.01% BSA, and 1% DMSO (from compound DMSO stocks), for 2 hour at room temperature. The activity was quenched with 11 μl of 70 mM EDTA, pH 8.To detect the phosphorylated biotinylated peptide substrate, 30 μl of the quenched reaction mixture was added to equivalent wells of a 384 well streptavidin coated MesoScale plate (Meso Scale Discovery #L21SA-1). After a 1 hour incubation of the plate for 1 hour at room temperature with gentle mixing, the plate wells were washed 3 times with 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.02% Tween-20.A 25 μl volume of 1:500 anti-P-Threonine Rabbit polyclonal Antibody plus 1:500 Goat-anti-Rabbit Sulfo Tag Antibody (Meso Scale Discovery R32AB-1) in 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.02% Tween-20 plus 2% BSA was then added to each well. After a 1-hour incubation of the plate for 1 hour at room temperature with gentle mixing, the plate wells were washed, 3 times with 50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.02% Tween-20. A 40 μl volume of 2×MSD Read Buffer (Meso Scale Discovery R92TC-1) was added to each well, and the plate was read immediately in an MSD Plate Reader (Meso Scale Discovery).
- Determination of IRAK4 Kinase Activity The following methods were used to determine the inhibition degree of the preferred compound of the present invention on IRAK4 kinase activity in vitro. In this evaluation, the HTRF KinEASE-STK S1 Serine/Threonine kinase kit produced by Cisbio was used to determine the phosphorylation degree of biotinylated polypeptide substrate by homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence technique (HTRF).Detailed methods can be referred to the kit instructions, and the experimental process was briefly described as follows. Firstly, the compounds of the present invention were dissolved in DMSO, and the final concentration was 10 mM. Then, the buffer solution provided in the kit was used for equal gradient dilution, so that the final concentration range of the tested compound in the reaction system was 16000 nM-0.008 nM, and the final concentration of DMSO is less than 2%.The adenosine triphosphate (ATP) concentration in the test was the corresponding ATP Km value (300 μM) determined in advance. Compounds, kinase, biotinylated polypeptide substrate and ATP were incubated at 37 C. for 1 h for kinase reaction, then anti-phosphorylated Serine/Threonine antibody coupled with compound of europium element and modified XL665 streptavidin were added into the reaction system to terminate the reaction, and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. After incubation, the fluorescence intensity of each well at emission wavelengths of 615 nm and 665 nm was determined on the microplate reader FLUOstar Omega under the excitation wavelength of 337 nm in HTRF mode, and the Ratio value was calculated by using the formula Ratio=(665 nm/615 nm) 104. Compared with the fluorescence intensity ratio of the control group, the inhibition rates of the compound at each concentration were calculated, and then the IC 50 value of the compound was calculated by fitting the nonlinear curve of logarithmic concentration-inhibition rate with GraphPad Prism5.
- In Vitro Enzymatic Activity Evaluation The inhibitory activity of the test compounds against human IRAK4 was evaluated by measuring IC50 values in a 33P-labeled kinase activity assay (Reaction Biology Corp).Buffer conditions: 20 mM Hepes (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 0.02% Brij35, 0.02 mg/mL BSA, 0.1 mM Na3VO4, 2 mM DTT, 1% DMSO.Procedures: The test compound was dissolved in DMSO at room temperature to prepare a 10 mM solution for later use. The substrate was dissolved in fresh buffer, to which the kinase was added and mixed well. The DMSO solution containing the test compound was added to the above mixed reaction system by an acoustic technique (Echo 550). The concentrations of the compounds in reaction system were 10 μM, 3.33 μM, 1.11 μM, 0.370 μM, 0.123 μM, 41.2 nM, 13.7 nM, 4.57 nM, 1.52 nM, and 0.508 nM. After 15 minutes of incubation, the reaction was started by adding 33P-ATP (activity: 0.01 μCi/μL; the corresponding concentration is listed in Table 1). Supplier's catalog number, lot number and concentration information in the reaction system for IRAK4 and its substrate are listed in Table 1. After 120 minutes of reaction at room temperature, the resulting solution was loaded on P81 ion exchange chromatography paper sheet (Whatman #3698-915). After repeated washing with 0.75% phosphoric acid solution, the radioactivity of the phosphorylated substrate residue on the paper sheet was measured. The kinase activity data are shown as a comparison of the kinase activity of the test compound and the kinase activity of the blank (DMSO only) and a curve was fitted using Prism4 software (GraphPad) to give IC50 values.
- IRAK4 TR-FRET assay For the assay, 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM were prepared from a 2 mM solution of the test substance in DMSO. 50 nl of the respective solution were pipetted into a black low-volume 384-well microtitre plate (Greiner Bio-One, Frickenhausen, Germany), 2 μl of a solution of IRAK4 in assay buffer [50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM dithiothreitol, 30 μM activated sodium orthovanadate, 0.1% (w/v) of bovine gamma-globulin (BGG), 0.04% (v/v) nonidet-P40 (Sigma)] were added and the mixture was incubated for 15 min to allow prebinding of the substances to the enzyme prior to the kinase reaction. The kinase reaction was then started by addition of 3 μl of a solution of adenosine triphosphate (ATP, 1.67 mM=final concentration in 5 μl of assay volume: 1 mM) and peptide substrate (0.83 μM=final concentration in 5 μl assay volume: 0.5 μM) in assay buffer, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for the reaction time of 45 min. The concentration of the IRAK4 was adjusted to the respective activity of the enzyme and set such that the assay was carried out in the linear range. Typical concentrations were in the order of about 0.2 nM. The reaction was stopped by addition of 5 μl of a solution of TR-FRET detection reagents [0.1 μM streptavidin-XL665 (Cisbio Bioassays; France, catalogue No. 610SAXLG)] and 1.5 nM anti-phosphoserine antibody [Merck Millipore, STK Antibody , catalogue No. 35-002] and 0.6 nM LANCE EU-W1024-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody (Perkin-Elmer, product No. AD0077; alternatively, it is possible to use a terbium cryptate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody from Cisbio Bioassays) in aqueous EDTA solution (100 mM EDTA, 0.4% [w/v] bovine serum albumin [BSA] in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5).The resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for 1 h to allow formation of a complex of the biotinylated phosphorylated substrate and the detection reagents. The amount of the phosphorylated substrate was then evaluated by measuring the resonance energy transfer from europium chelate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody to streptavidin-XL665. To this end, the fluorescence emissions at 620 nm and 665 nm were measured after excitation at 350 nm in a TR-FRET measuring instrument, for example a Rubystar (BMG Labtechnologies, Offenburg, Germany) or a Viewlux (Perkin-Elmer). The ratio of the emissions at 665 nm and 622 nm was taken as a measure of the amount of phosphorylated substrate. The data were normalized (enzyme reaction without test substance=0% inhibition; all other assay components but no enzyme=100% inhibition).
- Biochemical Assay The enzyme and peptide solution was incubated with compound for 15 minutes at room temp before the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. The standard 5l reaction mixture contained 500 μM ATP, 2 μM peptide (STK1 Peptide), 0.75 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3, 0.01% BSA, 0.1 mM Orthovanadate, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.025% NP-40, 1 mM DTT). After 120 min of incubation at room temperature, 5 μl of Stop and Detect Solution (1:100 Cryptate labeled anti-phosphorylated peptide antibody solution and 125 nM Tracer in a 50 mM HEPES pH 7.0 detection buffer containing sufficient EDTA) was added. The plate was then further incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and read on Envision 2103 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340 nm/615 nm/665 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensities at 615 nm and 665 nm emission wavelengths were expressed as a ratio (665 nm/615 nm).
- Kinase Activity Assay Procedure: A 20 μl reaction mixture contains 10 mM TriHCl, pH 7.2, 0.5 nM GST tagged IRAK4 (SignalChem), 100 nM fluorescent peptide substrate (RP7030, Molecular Devices), 100 μM ATP, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.01% Tween 20. The reaction is initiated by the addition of ATP. After incubation for 30 minutes at 25° C., 60 μl of Progressive IMAP Reagent (Molecular Devices) is added to stop the reaction. Change in RP7030's FP is determined by a FP reader (Analyst HT, LJL BioSystems).Analytical LCMS Conditions: Condition A: Phenomenex Luna C18 (4.6×250 mm), 95:5 to 5:95 water:MeCN (0.05% TFA), over 10 min, hold 6 min. Condition B: Agilent SBC (3.0×50 mm), solvent A: H20-0.1% TFA; solvent B: ACN-0.1% TFA; GRADIENT TABLE: 0 min:10% B, 0.3 min: 10% B, 1.5 min: 95% B, 2.70 min: 95% B, 2.76 min: 10% B, stop time 3.60 min.
- Radiometric Protein Kinase Assay A radiometric protein kinase assay was used for measuring the kinase activity of the Dog (Canis lupus familiaris) IRAK4, JAK1, JAK2, SYK kinases. All kinase assays were performed in 96-well FlashPlates in a 50 μl reaction volume. The reaction cocktail was pipetted in four steps in the following order:20 μl of assay buffer (standard buffer)5 ml of test compound (in 10% DMSO)20 μl enzyme/substrate mixμl of ATP solution (in H2O) The reaction cocktails were incubated at 30° C. for 60 minutes. The reaction was stopped with 50 μl of 2% (v/v) H3PO4, plates were aspirated and washed two times with 200 μl 0.9% (w/v) NaCl. Incorporation of 33Pi was determined with a microplate scintillation counter.IC50 calculation: the residual activity (in %) for each well of a particular plate was calculated by using the following formula: Res. Activity (%)=100×[(cpm of compound−low control)/(high control−low control)]
- Biochemical Assay A Z′-Lyte assay based on a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) readout was developed for measuring IRAK4-dependent phosphorylation of a FRET-peptide substrate as described by Thermo Fisher Scientific (Grand Island, N.Y.). At a starting concentration of 1.5 mM, the identified compounds were serially diluted with 100% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in 3-fold increments, into Greiner bio-one 96-well plates (cat. #: 650201, Greiner bio-one, Monroe, N.C.). Compounds were then transferred to intermediate Greiner bio-one 96-well plates and diluted 10-fold with Kinase assay buffer (25 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM MnCl2, 1 mM EGTA, and 0.01% Brij-35, 2 mM DTT). Three μL of the serially diluted compounds were then transferred in duplicate to low-volume 384-well black proxiplates (cat. #: 6008269; Perkin Elmer, Akron, Ohio), to give duplicate twelve-point concentration curves. Six μl of a 2.5× solution of IRAK4 enzyme (cat #: 40064, BPS Bioscience, San Diego, Calif.) in kinase buffer was added to each well, followed by a 10 minutes pre-incubation step. Reactions were initiated by adding 6 μl of a 2.5× substrate mix of ATP and Z′-Lyte Ser/Thr 7 peptide (cat. #: PV3180, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Grand Island, N.Y.) and proceeded at room temperature for 1 hour. The final concentration of key reagents in the 15 uL kinase reactions were 2 μM substrate, 2 nM enzyme, and 1 mM ATP, with dose responses starting at 30 μM compound. At the end of the kinase reactions, 5 μl of developing solution (as instructed in for cat. #: PV3180, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Grand Island, N.Y.) was added to each well and incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. All wells were read on an Envision 2105 Multilabel fluorescence plate reader (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, Mass.) at 400 nm excitation and 460 nm/530 nm emission. Plus and minus 100% inhibition controls were used to calculate percent inhibition and IC50 curves were generated using Graphpad Prism (La Jolla, Calif.).
- Human whole blood IRAK4 degradation flow assay Whole blood was collected in heparinized tubes and plated on the same day as draw (day 0). Whole blood was aliquoted into deep well plates. Compound plates were prepared and a 10 point, 5-fold dilution was performed with a final DMSO concentration of 0.1%. Compound was added to whole blood deep well plate, sealed and incubated at 37° C., 5% CO2 for 20 hours (for 4 hour treatment, compounds were prepared and added the following day). Following the treatment incubation period (day 1), BD lyse fix (BD #558049) was added to the whole blood plate, placed on plate shaker for 30 seconds and incubated for 10 mins at room temperature. Whole blood was then spun down and washed two times with PBS/0.5% BSA, aspirated to pellet and placed into −80° C. freezer until further processing for flow. On the flow run day, whole blood plates were thawed and samples were transferred to PCR plates. The pre-perm staining cocktail (CD3 Ax488/CD8 BUV805/CD14 BUV395/CD16/56 BV711/CD19 BV785) was added to samples and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Samples were washed two times and permeabilized with Methanol for 10 minutes at 4° C. Samples were washed two times and the post-perm staining cocktail (CD4 PE/IRAK4 Ax647 BD #560315) was added and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Samples were washed two times with PBS/BSA and run on a BD LSRFortessa. Mononuclear cells are gated by SSCH/FSCH and single cells. Monocytes are then gated through CD14 positive gate and lymphocytes are gated through CD14 negative gate. To determine absolute DC50 and max degradation values, MFI values were normalized to DMSO max and 20 hour 10 μM min control. Twenty hour dose curves were calculated using a 4 parameter logistic regression curve fit, no constraints (Top doses were removed if hook effects were observed and the bottom was constrained to 0).
- Inhibitory Effects of Compounds on Kinase Activity Assay 1) IRAK4 kinase was dissolved in kinase buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT and 0.01% Brij-35) to a final concentration of 6 nM.[0542]2) The substrate peptide FAM-P8 and ATP were dissolved in the above kinase buffer. The final concentrations of the IRAK4 substrate peptide FAM-P8 and ATP were 3 μM and 10 μM respectively.[0543]3) Dilution of the compounds: the compound was first diluted to 50 μM, and then diluted down with a 4-fold gradient of DMSO. The solution without the compound and kinase is used as a blank control, corresponding to the “minimum value” shown below; and the solution without the compound but with kinase, adenosine 5′-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate, DMSO and buffer is used as a positive control, corresponding to the “maximum value” shown below. 4) Kinase reaction and termination: 10 μL of kinase buffer was added to a 384-well plate containing 5 μL of the compound to be tested, and incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes. Another 10 μL of buffer containing the substrate peptide and adenosine 5′-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate was added to the 384-well plate. After incubation at 28° C. for one hour, 25 μL stop solution (100 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 50 mM EDTA, 0.2% Coating Reagent #3 and 0.015% Brij-35) was added to each well to terminate the reaction.[0544]5) Data reading: the CaliperEZ Reader II instrument was used to read the conversion rate data. Conditions: downstream voltage −500V, upstream voltage −2250V, base pressure −0.5 PSI, and screening pressure −1.2 PSI.[0545]6) Data calculation: the conversion rate data was copied from CaliperEZ Reader II and converted into inhibition rate data. The calculation formula is as follows:Inhibitionpercentage(%)=(maximumvalue-conversionrate)/(maximumvalue-minimumvalue)*100%IC50 values were fitted using XLFit excel add-in version 5.4.0.8,Y=Bottom+(Top−Bottom)/(1+(IC50 /X){circumflex over ( )}HillSlope) Fitting formula
- Kinase Assay For the assay, 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM were prepared from a 2 mM DMSO solution of the test substance. 50 nl of the respective solution were pipetted into a black low-volume 384-well microtitre plate (Greiner Bio-One, Frickenhausen, Germany), 2 μl of a solution of IRAK4 in assay buffer [50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM dithiothreitol, 30 μM activated sodium orthovanadate, 0.1% (w/v) of bovine gamma-globulin (BGG) 0.04% (v/v) nonidet-P40 (Sigma)] were added and the mixture was incubated for 15 min to allow prehinding of the substances to the enzyme prior to the kinase reaction. The kinase reaction was then started by addition of 3 μl of a solution of adenosine triphosphate (ATP, 1.67 mM=final concentration in 5 μl of assay volume: 1 mM) and peptide substrate (0.83 μM=final concentration in 5 μl assay volume: 0.5 μM) in assay buffer, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for the reaction time of 45 min. The concentration of the IRAK4 was adjusted to the respective activity of the enzyme and set such that the assay was carried out in the linear range. Typical concentrations were in the order of about 0.2 nM. The reaction was stopped by addition of 5 μl of a solution of TR-FRET detection reagents [0.1 μM streptavidin-XL665 (Cisbio Bioassays; France, catalogue No. 610SAXLG)] and 1.5 nM anti-phosphoserine antibody [Merck Millipore, STK Antibody , catalogue No. 35-002] and 0.6 nM LANCE ELI-W1024-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody (Perkin-Elmer, product No. AD0077; alternatively, it is possible to use a terbium cryptate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody from Cisbio Bioassays) in aqueous EDTA solution (100 mM EDTA, 0.4% [w/v] bovine serum albumin [BSA] in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5).
- Kinase Assay For the assay, 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM were prepared from a 2 mM solution of the test substance in DMSO. For the assay, 50 nl of the respective solution were pipetted into a black low-volume 384-well microtitre plate (Greiner Bio-One, Frickenhausen, Germany), 2 μl of a solution of Irak4 in assay buffer [50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM dithiothreitol, 30 μM activated sodium orthovanadate, 0.1% (w/v) of bovine gamma-globulin (BGG) 0.04% (v/v) nonidet-P40 (Sigma)] were added and the mixture was incubated for 15 min to allow prebinding of the substances to the enzyme prior to the kinase reaction. The kinase reaction was then started by addition of 3 μl of a solution of adenosine triphosphate (ATP, 1.67 mM=final concentration in 5 μl of assay volume: 1 μM) and peptide substrate (0.83 μM=final concentration in 5 μl assay volume: 0.5 μM) in assay buffer, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for the reaction time of 45 min. The concentration of the Irak4 was adjusted to the respective activity of the enzyme and set such that the assay was carried out in the linear range. Typical concentrations were in the order of about 0.2 nM. The reaction was stopped by addition of 5 μl of a solution of TR-FRET detection reagents [0.1 μM streptavidin-XL665 (Cisbio Bioassays; France, catalogue No. 610SAXLG) and 1.5 nM anti-phosphoserin antibody [Merck Millipore, STK Antibody, catalogue No. 35-002] and 0.6 nM LANCE EU-W1024-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody (Perkin-Elmer, product No. AD0077, alternatively it is possible to use a terbium cryptate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody from Cisbio Bioassays) in aqueous EDTA solution (100 mM EDTA, 0.4% [w/v] bovine serum albumin [BSA] in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5).
- IRAK4 Kinase Assay For the assay, 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM were prepared from a 2 mM DMSO solution of the test substance. 50 nl of the respective solution were pipetted into a black low-volume 384-well microtitre plate (Greiner Bio-One, Frickenhausen, Germany), 2 μl of a solution of IRAK4 in assay buffer [50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM dithiothreitol, 30 μM activated sodium orthovanadate, 0.1% (w/v) of bovine gamma-globulin (BGG) 0.04% (v/v) nonidet-P40 (Sigma)] were added and the mixture was incubated for 15 min to allow prebinding of the substances to the enzyme prior to the kinase reaction. The kinase reaction was then started by addition of 3 μl of a solution of adenosine triphosphate (ATP, 1.67 mM=final concentration in 5 μl of assay volume: 1 mM) and peptide substrate (0.83 μM=final concentration in 5 μl assay volume: 0.5 μM) in assay buffer, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for the reaction time of 45 min. The concentration of the IRAK4 was adjusted to the respective activity of the enzyme and set such that the assay was carried out in the linear range. Typical concentrations were in the order of about 0.2 nM. The reaction was stopped by addition of 5 μl of a solution of TR-FRET detection reagents [0.1 μM streptavidin-XL665 (Cisbio Bioassays; France, catalogue No. 610SAXLG)] and 1.5 nM anti-phosphoserine antibody [Merck Millipore, STK Antibody , catalogue No. 35-002] and 0.6 nM LANCE EU-W1024-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody (Perkin-Elmer, product No. AD0077; alternatively, it is possible to use a terbium cryptate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody from Cisbio Bioassays) in aqueous EDTA solution (100 mM EDTA, 0.4% [w/v] bovine serum albumin [BSA] in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5).The resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for 1 h to allow formation of a complex of the biotinylated phosphorylated substrate and the detection reagents. The amount of the phosphorylated substrate was then evaluated by measuring the resonance energy transfer from europium chelate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody to streptavidin-XL665. To this end, the fluorescence emissions at 620 nm and 665 nm were measured after excitation at 350 nm in a TR-FRET measuring instrument, for example a Rubystar (BMG Labtechnologies, Offenburg, Germany) or a Viewlux (Perkin-Elmer). The ratio of the emissions at 665 nm and 622 nm was taken as a measure of the amount of phosphorylated substrate. The data were normalized (enzyme reaction without test substance=0% inhibition; all other assay components but no enzyme=100% inhibition). Typically, the test substances were tested on the same microtitre plates at 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM (20 μM, 5.7 μM, 1.6 μM, 0.47 μM, 0.13 μM, 38 nM, 11 nM, 3.1 nM, 0.89 nM, 0.25 nM and 0.073 nM). The dilution series were prepared prior to the assay (2 mM to 7.3 nM in 100% DMSO) by serial dilutions. The IC50 values were calculated by a 4-parameter fit.
- IRAK4 Kinase Assay For the assay, 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM were prepared from a 2 mM solution of the test substance in DMSO. 50 nl of the respective solution were pipetted into a black low-volume 384-well microtitre plate (Greiner Bio-One, Frickenhausen, Germany), 2 μl of a solution of IRAK4 in assay buffer [50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM dithiothreitol, 30 μM activated sodium orthovanadate, 0.1% (w/v) of bovine gamma-globulin (BGG) 0.04% (v/v) nonidet-P40 (Sigma)] were added and the mixture was incubated for 15 min to allow prebinding of the substances to the enzyme prior to the kinase reaction. The kinase reaction was then started by addition of 3 μl of a solution of adenosine triphosphate (ATP, 1.67 mM=final concentration in 5 μl of assay volume: 1 mM) and peptide substrate (0.83 μM=final concentration in 5 μl assay volume: 0.5 μM) in assay buffer, and the resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for the reaction time of 45 min. The concentration of the IRAK4 was adjusted to the respective activity of the enzyme and set such that the assay was carried out in the linear range. Typical concentrations were in the order of about 0.2 nM. The reaction was stopped by addition of 5 μl of a solution of TR-FRET detection reagents [0.1 μM streptavidin-XL665 (Cisbio Bioassays; France, catalogue No. 610SAXLG)] and 1.5 nM anti-phosphoserine antibody [Merck Millipore, STK Antibody , catalogue No. 35-002] and 0.6 nM LANCE EU-W1024-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody (Perkin-Elmer, product No. AD0077; alternatively, it is possible to use a terbium cryptate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody from Cisbio Bioassays) in aqueous EDTA solution (100 mM EDTA, 0.4% [w/v] bovine serum albumin [BSA] in 25 mM HEPES pH 7.5).The resulting mixture was incubated at 22° C. for 1 h to allow formation of a complex of the biotinylated phosphorylated substrate and the detection reagents. The amount of the phosphorylated substrate was then evaluated by measuring the resonance energy transfer from europium chelate-labelled anti-mouse-IgG antibody to streptavidin-XL665. To this end, the fluorescence emissions at 620 nm and 665 nm were measured after excitation at 350 nm in a TR-FRET measuring instrument, for example a Rubystar (BMG Labtechnologies, Offenburg, Germany) or a Viewlux (Perkin-Elmer). The ratio of the emissions at 665 nm and 622 nm was taken as a measure of the amount of phosphorylated substrate. The data were normalized (enzyme reaction without test substance=0% inhibition; all other assay components but no enzyme=100% inhibition). Typically, the test substances were tested on the same microtitre plates at 11 different concentrations in the range from 20 μM to 0.073 nM (20 μM, 5.7 μM, 1.6 μM, 0.47 μM, 0.13 μM, 38 nM, 11 nM, 3.1 nM, 0.89 nM, 0.25 nM and 0.073 nM). The dilution series were prepared prior to the assay (2 mM to 7.3 nM in 100% DMSO) by serial dilutions. The IC50 values were calculated using a 4-parameter fit.
- IRAK4 Monocyte TNFalpha Cell Based Assay Cryopreserved human monocytes (Stem Cell Technologies) were thawed, diluted in RPMI with GlutaMAX (Gibco 200 mM L-alanyl-L-glutamine) (10 mM HEPES, 1× Pen-Strep, 55 μM -mercaptoethanol, 1 mM Sodium pyruvate) media containing 10% FBS to 0.125×106 cells/ml and recovered at 37° C. for 2 hours. The cell suspension was then plated at a density of 5,000 cells/well onto black 384 well Greiner clear bottom plates. Plates were pre-spotted with test compounds and serially diluted in DMSO where 200 nL/well were delivered using the Echo 550 acoustic liquid dispenser (Labcyte ) for a final DMSO concentration of 0.5%. Plated cells were treated with compound for 1 hour at 37° C. Cells were then stimulated with 50 pg/ml of LPS (Sigma) excluding outside columns of plate used for unstimulated cell control wells. Cells were incubated for an additional 4 hours at 37° C. Cells were then spun out of the media and 5 μl of sample were taken and analyzed for total TNFα content using the TR-FRET Human TNFα detection system (CisBio). This system utilizes two labeled antibodies (cryptate and XL665) that bind to two different epitopes of the TNFα molecule and produce FRET signal proportional to the concentration of TNFα in the sample. Detection antibodies are mixed 50:50 and 5 μL were dispensed into each well. Plates were covered with clear seals and incubated at room temp overnight. The following morning plates were read using an Envision 2103 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340 nm/615 nm/665 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensities at 615 nm and 665 nm emission wavelengths were expressed as a ratio (665 nm/615 nm). Percent of control was calculated as follows:% Control=100×(RatioSample−Ratio0% stimulation)/(Ratio100% Stimulation−Ratio0% Stimulation)where unstimulated cells (0% stimulation) were the negative control and stimulated cells (100% stimulation) were used as the positive control.IRAK4 Biochemical Assay Procedure:IRAK4 enzyme (Carna Biosciences, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Japan) activity was measured by detecting phosphorylated peptide substrate formation using an antibody against the phosphorylated peptide substrate. This is a time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) immunoassay, based on the STK1 KinEASE Assay (Cisbio, Bedford, Mass.). The assay was designed as a simple two-step, endpoint assay (a 5 μl enzyme reaction followed by 5 μl stop and detect Solution) performed in ProxiPlate-384 Plus plates (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, Mass.). Staurosporine, a non-selective kinase inhibitor was used as a positive control. Compounds diluted in DMSO were spotted into 384 well plates using a Labcyte Echo 550 Liquid Handling System prior to addition of IRAK4 enzyme and peptide substrate. Reaction solutions were delivered using a Multi-Flo (Bio-Tek Instruments). The enzyme and peptide solution was incubated with compound for 15 minutes at room temp before the reaction was initiated by the addition of ATP. The standard 5 μl reaction mixture contained 500 □M ATP, 2 □M peptide (STK1 Peptide), 0.75 nM of IRAK4 in reaction buffer (50 mM HEPES, pH 7.0, 0.02% NaN3, 0.01% BSA, 0.1 mM Orthovanadate, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.025% NP-40, 1 mM DTT). After 120 min of incubation at room temperature, 5 □l of Stop and Detect Solution (1:100 Cryptate labeled anti-phosphorylated peptide antibody solution and 125 nM Tracer in a 50 mM HEPES pH 7.0 detection buffer containing sufficient EDTA) was added. The plate was then further incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and read on Envision 2103 Multilabeled reader (PerkinElmer) with excitation/emission/FRET emission at 340 nm/615 nm/665 nm, respectively. Fluorescence intensities at 615 nm and 665 nm emission wavelengths were expressed as a ratio (665 nm/615 nm).
- Screening Assay Against IRAK4 with ATP Table 2: Prepare Ix kinase base buffer and stop buffer for testing kinases: (1) base buffer: 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.0015% Brij-35; (2) stop buffer: 100 mM HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.015% Brij-35, 0.2% Coating Reagent #3, 50 mM EDTA. Then prepare compounds for testing: Dilute the compound to 50× of the final desired highest inhibitor concentration in reaction by 100% DMSO. Transfer 100 μL of this compound dilution to a well in a 96-well plate (source plate).Serially dilute the compounds by 3-fold for a total of 10 points. Transfer 10 μL of the compound from the source plate to a new 96-well plate (intermediate plate) and add 90 μL of Ix kinase buffer. Shake the mixture on the intermediate plate for 10 min. Transfer 5 μL of each well from the 96-well intermediate plate to a 384-well plate in duplicates. Add 10 μL of 2.5× enzyme solution to each well of the 384-well assay plate and incubate at room temperature for 10 min. Add 10 μL, of 2.5×FAM-labeled peptide and ATP solution and incubate at 28° C. for a period of time.
- 1RAK4 Kinase Activity Assay The KinEASE-STK SI serine/threonine kinase kit (Cisbio) was used to test the inhibitory effect of the compounds on the IRAK4 kinase activity, and the method is specifically as follows: A compound was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide, and the solution was diluted in the buffer of the kit with an equal gradient, such that the final concentration range of the test compound in the reaction systems was 10,000 nM-0.038 nM. Then 2.5 nM 1RAK4 kinase (Carna), 1 μM biotinylated polypeptide substrate (Cisbio) and 7 μM adenosine triphosphate (Sigma-Aldrich) were sequentially added, and the mixtures were incubated at 37° C. for 120 min. Subsequently, an anti-phosphoserine/threonine antibody (Cisbio) conjugated with a europium element compound and conjugated modified XL665 streptavidin (Cisbio) were added to the reaction systems to stop the reactions. After 1 h of incubation at room temperature, the fluorescence intensity of each well was measured at the excitation wavelength of 337 nm and the emission wavelengths of 620 nm and 665 nm with a microplate reader EnVision (PerkinElmer) in the HTRF mode, and Ratio values were calculated using the formula Ratio=(665 nm/620 nm)×10s. The inhibition rate of the compound at each concentration was calculated by comparing the fluorescence intensity ratio with that of the control group.
- Kinase Activity Inhibition Assay IRAK4 kinase (purchased from Life Technologies, Cat. No.: PR5612U) was diluted to 2 folds of the final concentration (the final concentration is 0.76 ng/μL) with reaction buffer (40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5; 20 mM MgCl2; 0.1 mg/mL BSA; 1 mM DTT), and added to a 384-well plate at 5 μL/well. The test drugs were 10-fold serial diluted from 10 μM to set six concentration points and added to the test wells of the 384-well plate at 2.5 μL/well. After incubation for 10 min at 25° C., 10 μM of ATP and 0.1 μg/L of an enzyme reaction substrate, myelin basic protein MBP (purchased from SignalChem, Cat. No.: M42-51N) were added at 2.5 L/well, and reacted at 25° C. for 60 minutes. After the reaction was completed, the kinase activity assay was performed using the ADP-Glo kinase assay kit (purchased from Promega, Cat. No.: V9102) according to the manufacture's instruction, i.e., 10 μL of ADP-Glo reaction reagent was first added and reacted at 25° C. for 40 minutes, 10 μL of the solution to be tested was taken and mixed with 10 μL of ADP-Glo detection reagent, and reacted at 25° C. for 30 minutes.
- Kinase Activity Inhibition Assay IRAK4 kinase (purchased from Life Technologies, Cat. No.: PR5612U) was diluted to 2 folds of the final concentration (the final concentration is 0.76 ng/4) with reaction buffer (40 mM Tris-HC1, pH 7.5; 20 mM MgCl2; 0.1 mg/mL BSA; 1 mM DTT), and added to a 384-well plate at 5 μL/well. The test drugs were 10-fold serial diluted from 10 μM to set six concentration points and added to the test wells of the 384-well plate at 2.5 μL/well. After incubation for 10 min at 25° C., 10 μM of ATP and 0.1 μg/μL of an enzyme reaction substrate, myelin basic protein MBP (purchased from Signal Chem, Cat. No.: M42-51N) were added at 2.5 μL/well, and reacted at 25° C. for 60 minutes. After the reaction was completed, the kinase activity assay was performed using the ADP-Glo kinase assay kit (purchased from Promega, Cat. No.: V9102) according to the manufacture's instruction, i.e., 10 μL of ADP-Glo reaction reagent was first added and reacted at 25° C. for 40 minutes, 10 μL of the reaction mixture was taken and mixed with 10 μL of ADP-Glo detection reagent, and reacted at 25° C. for 30 minutes.
- Determination of the value of binding affinity constant (KO between the compound and BRD4 BD1 protein The purity of BRD4 BD1 protein used in the experiment was greater than 95%, and the protein concentration was 43.4 uM. The 96-well plate was purchased from Corning (black, #3694). The multifunctional microplate reader was a product of TECAN, model: SPARK 10M. Buffer: 100 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.5), 2% ethylene glycol (Sigma) and 0.01% Trition X-100 (Sigma). The experimental water was Millipore-Q pure water.The specific experimental steps were as follows.First, the compound to be tested was dissolved in ethylene glycol to prepare into a 10 mM standard stock solution. Subsequently, the standard stock solution of the compound to be tested was diluted into a working sample solution with the buffer in an EP tube and ready for use. The concentration of the prepared working sample solution was 5 times of the highest sample concentration required on the test plate (5×test compound solution).40 λL of a 5× test compound solution of a sample A was added to wells B1-B3 of a 96-well plate, and 40 μL of a 5× test compound solution of a sample B was added to wells B7-B9 of the 96-well plate, respectively. 20 uL of the buffer was added to the remaining wells, except for wells B1-B3 and B7-B9. Then, 20 uL of a solution was taken from wells B1-B3 to C1-C3, and this 2-fold dilution was repeated from C1-C3 until H4-H6; in the same way, 20 uL of a solution was taken from B7-B9 to C7-C9, this 2-fold dilution was repeated from C7-C9 until H10-H12. Finally, 80 uL of a mixed solution containing 2.5 nM Tracer and 37.5 nM BRD4 BD1 protein was added to each well.
- Enzymatic DELFIA Assay Protocol A: To begin the assay, 19 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 0.21 nM Full-length phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 (GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into Ultra-Clear Polypropylene, 384-well, U-Bottom Plates (Corning Life Sciences). 1 μL of test compound from the dose-response plate was added to the reaction mixture and incubated for 20 minutes at room temperature. Then 20 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 100 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) was added to start the reaction. The reaction was incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature and stopped by the addition of 20 μL 0.3M EDTA.50 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin coated detection plate (DELFIA streptavidin coated plates, 384-well, white plates, Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The plates were washed 4× with 75 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody at 0.125 μg/mL (Cell Signaling Technology), plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.25 ug/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were washed 4× with 50 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Then 50 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) were added to the plate and then read on an EnVision Model 2103 using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission wavelength for detection.
- Enzymatic DELFIA Assay Protocol B: To begin the assay, 45 μL of reaction mixture containing 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, 228 μM phosphorylated recombinant human IRAK4 kinase domain (aa 154-460; GenBank ID AF445802) were aliquoted into Ultra-Clear Polypropylene, 96-well, U-Bottom Plates (Corning Life Sciences). 5 μL of test compound from the dose-response plate was added to the reaction mixture and incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. Then 50 μL of 20 mM HEPES pH=7.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.0025% Brij-35, 600 μM ATP, and 400 nM ERM-biotinylated peptide (AGAGRDKYKTLRQIR) were added to start the reaction. The reaction was incubated for 90 minutes at room temperature and stopped by the addition of 25 μL 0.5M EDTA.100 μL of the reaction mixture was transferred to a streptavidin coated detection plate (EvenCoat Streptavidin Coated Plates, 96-Well, R&D Systems) and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The plates were washed 4 times with 100 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Plates were then incubated with 50 μL per well of antibody cocktail of Anti-pERM antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) diluted 1:5000, plus Anti-Rabbit IgG EuN1 at 0.242 μg/ml (Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences) in a solution of 10 mM MOPS pH=7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 1% BSA, 0.1% Gelatin for 45 minutes. The plates were washed 4× with 100 μL per well of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20. Then 100 μL per well of DELFIA Enhancement Solution were added to the plate and then read on an EnVision Model 2103 using a 340 nm excitation wavelength and a 665 nm emission detection.
 CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719
CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719 3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910
3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910