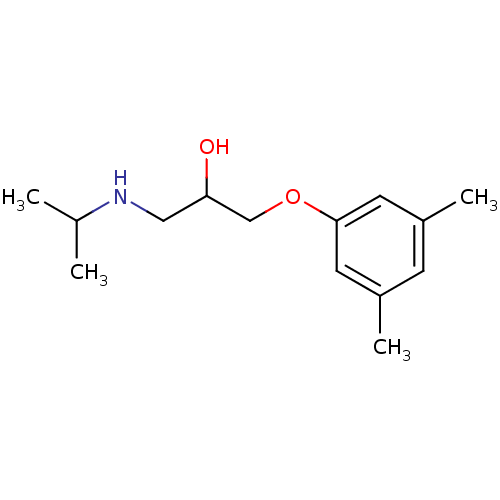
 CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719
CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719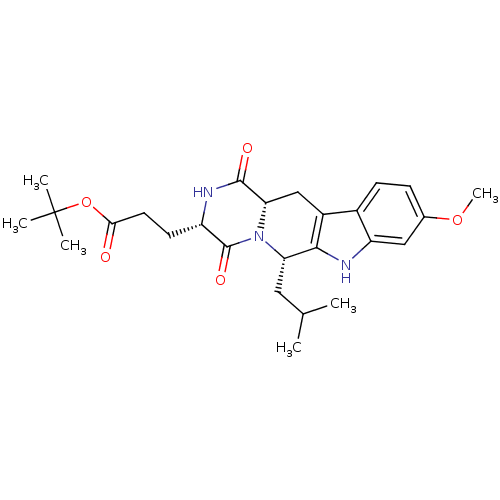 3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910
3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910
- Machacek, MR; Witter, DJ; Reutershan, MH; Altman, MD; Stupple, PA PRMT5 inhibitors US Patent US10947234 (2021)
- Vandyck, K; Raboisson, PJ; Deval, J; Beigelman, L; McGowan, D; Debing, Y Compounds targeting PRMT5 US Patent US11198699 (2021)
- Bobinski, TP; Smith, CR; Marx, MA; Ketcham, JM; Burns, AC; Lawson, JD; Kulyk, S; Kuehler, J; Ivetac, A MTA-cooperative PRMT5 inhibitors US Patent US11492351 (2022)
- Bergman, YE; Foitzik, RC; Morrow, BJ; Camerino, MA; Walker, SR; Lagiakos, HR; Feutrill, J; Stevenson, GI; Stupple, PA Tetrahydroisoquinoline derived PRMT5-inhibitors US Patent US10494376 (2019)
- Stupple, AE; Walker, SR; Stupple, PA Tetrahydroisoquinolines as PRMT5 inhibitors US Patent US10550096 (2020)
- Duncan, KW; Chesworth, R; Boriack-Sjodin, PA; Munchhof, MJ PRMT5 inhibitors and uses thereof US Patent US10118918 (2018)
- Duncan, KW; Chesworth, R; Boriack-Sjodin, PA; Munchhof, MJ; Jin, L PRMT5 inhibitors and uses therof US Patent US10391089 (2019)
- Smith, CR; Kulyk, S; Marx, MA; Lawson, JD; Ivetac, A; Wang, X; Burns, AC Aminopyridine-based MTA-Cooperative PRMT5 Inhibitors US Patent US20240368153 (2024)
- ZHANG, M; KONG, Y; JIANG, L; JIANG, B; DAI, G; HE, Y; HOU, B; SHAN, B; MEI, J PRMT5 INHIBITING COMPOUNDS AND USES THEREOF US Patent US20240262835 (2024)
- WANG, L; WU, H; MI, Y; LIU, Y; FU, X; WANG, M; SHI, H; GUO, J PRMT5 INHIBITOR AND THE USE THEREOF US Patent US20240376126 (2024)
- Yu, A; Lo, HY PRMT5 INHIBITORS AND METHODS OF TREATMENT US Patent US20250084060 (2025)
- Bergman, YE; Lessene, R; Ganame, D; Foitzik, RC; Morrow, BJ; Camerino, MA; Walker, SR; Lagiakos, HR; Feutrill, J; Stupple, PA Aminoindane-, aminotetrahydronaphthalene- and aminobenzocyclobutane-derived PRMT5-inhibitors US Patent US10005792 (2018)
- Smil, D; Eram, MS; Li, F; Kennedy, S; Szewczyk, MM; Brown, PJ; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D; Arrowsmith, CH; Vedadi, M; Schapira, M Discovery of a Dual PRMT5-PRMT7 Inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 6: 408-12 (2015)
- Chikkanna, D; Panigrahi, SK; Sammeta, SR; Gerd, W; Mikko, M Imidazolidin-2-one compounds as PRMT5 modulators US Patent US11365205 (2022)
- Lin, H; Luengo, JI Nucleoside protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 29: 1264-1269 (2019)
- Palte, RL; Schneider, SE; Altman, MD; Hayes, RP; Kawamura, S; Lacey, BM; Mansueto, MS; Reutershan, M; Siliphaivanh, P; Sondey, C; Xu, H; Xu, Z; Ye, Y; Machacek, MR Allosteric Modulation of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5). ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 1688-1693 (2020)
- Krzyzanowski, A; Esser, LM; Willaume, A; Prudent, R; Peter, C; 't Hart, P; Waldmann, H Development of Macrocyclic PRMT5-Adaptor Protein Interaction Inhibitors. J Med Chem 65: 15300-15311 (2022)
- Fu, S; Zheng, Q; Zhang, D; Lin, C; Ouyang, L; Zhang, J; Chen, L Medicinal chemistry strategies targeting PRMT5 for cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem 244: (2022)
- Lin, H; Luengo, J; Shetty, R; Hawkins, M Selective inhibitors of protein arginine methlytransferase 5 (PRMT5) US Patent US11078205 (2021)
- Luengo, J; Leal, RA; Lin, H; Shetty, R; Vaddi, K Selective inhibitors of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) US Patent US11220524 (2022)
- Lin, H; Luengo, J; Shetty, R; Hawkins, M Selective inhibitors of protein arginine methytransterase 5 (PRMT5) US Patent US11208416 (2021)
- Chikkanna, D; Panigrahi, SK; Sammeta, SR Substituted imidazolidin-2-one derivatives as PRMT5 inhibitors US Patent US11542275 (2023)
- Wang, Y; Zhao, L; Quan, X; Zheng, G; Sun, W; Yang, T; Zhan, K; Shi, Q SUBSTITUTED TRICYCLIC COMPOUND AS PRMT5 INHIBITOR AND USE THEREOF US Patent US20240116918 (2024)
- Duncan, KW; Chesworth, R; Boriack-Sjodin, PA; Munchhof, MJ; Jin, L Tetrahydro- and dihydro-isoquinoline PRMT5 inhibitors and uses thereof US Patent US10307413 (2019)
- Duncan, KW; Chesworth, R; Boriack-Sjodin, PA; Munchhof, MJ; Jin, L PRMT5 inhibitors containing a dihydro- or tetrahydroisoquinoline and uses thereof US Patent US9745291 (2017)
- Shen, Y; Gao, G; Yu, X; Kim, H; Wang, L; Xie, L; Schwarz, M; Chen, X; Guccione, E; Liu, J; Bedford, MT; Jin, J Discovery of First-in-Class Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) Degraders. J Med Chem 63: 9977-9989 (2020)
- Morley, A; Miller, R; La Thangue, N Compounds and methods useful in the treatment of a PRMT5-mediated disorder US Patent US11485731 (2022)
- Lin, H; Wang, M; Zhang, YW; Tong, S; Leal, RA; Shetty, R; Vaddi, K; Luengo, JI Discovery of Potent and Selective Covalent Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) Inhibitors. ACS Med Chem Lett 10: 1033-1038 (2019)
- Zheng, J; Li, B; Wu, Y; Wu, X; Wang, Y Targeting Arginine Methyltransferase PRMT5 for Cancer Therapy: Updated Progress and Novel Strategies. J Med Chem 66: 8407-8427 (2023)
- Mann, SA; Salsburg, A; Causey, CP; Knuckley, B The development and characterization of a chemical probe targeting PRMT1 over PRMT5. Bioorg Med Chem 27: 224-229 (2019)
- Pande, V; Sun, W; Beke, L; Berthelot, D; Brehmer, D; Brown, D; Corbera, J; Irving, S; Meerpoel, L; Nys, T; Parade, M; Robinson, C; Sommen, C; Viellevoye, M; Wu, T; Thuring, JW A Chemical Probe for the Methyl Transferase PRMT5 with a Novel Binding Mode. ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 2227-2231 (2020)
- McKinney, DC; McMillan, BJ; Ranaghan, MJ; Moroco, JA; Brousseau, M; Mullin-Bernstein, Z; O'Keefe, M; McCarren, P; Mesleh, MF; Mulvaney, KM; Robinson, F; Singh, R; Bajrami, B; Wagner, FF; Hilgraf, R; Drysdale, MJ; Campbell, AJ; Skepner, A; Timm, DE; Porter, D; Kaushik, VK; Sellers, WR; Ianari, A Discovery of a First-in-Class Inhibitor of the PRMT5-Substrate Adaptor Interaction. J Med Chem 64: 11148-11168 (2021)
- Liu, L; Li, J; Yang, M Inhibitors of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5), pharmaceutical products thereof, and methods thereof US Patent US11591326 (2023)
- Wang, Y; Hu, W; Yuan, Y Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) as an Anticancer Target and Its Inhibitor Discovery. J Med Chem 61: 9429-9441 (2018)
- Duncan, KW; Rioux, N; Boriack-Sjodin, PA; Munchhof, MJ; Reiter, LA; Majer, CR; Jin, L; Johnston, LD; Chan-Penebre, E; Kuplast, KG; Porter Scott, M; Pollock, RM; Waters, NJ; Smith, JJ; Moyer, MP; Copeland, RA; Chesworth, R Structure and Property Guided Design in the Identification of PRMT5 Tool Compound EPZ015666. ACS Med Chem Lett 7: 162-6 (2016)
- Structure-based discovery of a new series of nucleoside-derived ring-opening PRMT5 inhibitors.
- Luengo, J; Lin, H; Hawkins, M Substituted pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines as inhibitors of protein arginine methyl transferase 5 (PRMT5) US Patent US11524962 (2022)
- Bonday, ZQ; Cortez, GS; Grogan, MJ; Antonysamy, S; Weichert, K; Bocchinfuso, WP; Li, F; Kennedy, S; Li, B; Mader, MM; Arrowsmith, CH; Brown, PJ; Eram, MS; Szewczyk, MM; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D; Vedadi, M; Guccione, E; Campbell, RM LLY-283, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Arginine Methyltransferase 5, PRMT5, with Antitumor Activity. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 612-617 (2018)
- Rescue of fragile X syndrome phenotypes in Fmr1 KO mice by the small-molecule PAK inhibitor FRAX486.
- PRMT5: A novel regulator of Hepatitis B virus replication and an arginine methylase of HBV core.
- Discovery and In Vivo Efficacy of AZ-PRMT5i-1, a Novel PRMT5 Inhibitor with High MTA Cooperativity.
- Discovery of tetrahydroisoquinolineindole derivatives as first dual PRMT5 inhibitors/hnRNP E1 upregulators: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation.
- Zhu, K; Song, JL; Tao, HR; Cheng, ZQ; Jiang, CS; Zhang, H Discovery of new potent protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) inhibitors by assembly of key pharmacophores from known inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 3693-3699 (2018)
- Smith, CR; Aranda, R; Bobinski, TP; Briere, DM; Burns, AC; Christensen, JG; Clarine, J; Engstrom, LD; Gunn, RJ; Ivetac, A; Jean-Baptiste, R; Ketcham, JM; Kobayashi, M; Kuehler, J; Kulyk, S; Lawson, JD; Moya, K; Olson, P; Rahbaek, L; Thomas, NC; Wang, X; Waters, LM; Marx, MA Fragment-Based Discovery of MRTX1719, a Synthetic Lethal Inhibitor of the PRMT5•MTA Complex for the Treatment of J Med Chem 65: 1749-1766 (2022)
- Quiroz, RV; Reutershan, MH; Schneider, SE; Sloman, D; Lacey, BM; Swalm, BM; Yeung, CS; Gibeau, C; Spellman, DS; Rankic, DA; Chen, D; Witter, D; Linn, D; Munsell, E; Feng, G; Xu, H; Hughes, JME; Lim, J; Saurí, J; Geddes, K; Wan, M; Mansueto, MS; Follmer, NE; Fier, PS; Siliphaivanh, P; Daublain, P; Palte, RL; Hayes, RP; Lee, S; Kawamura, S; Silverman, S; Sanyal, S; Henderson, TJ; Ye, Y; Gao, Y; Nicholson, B; Machacek, MR The Discovery of Two Novel Classes of 5,5-Bicyclic Nucleoside-Derived PRMT5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer. J Med Chem 64: 3911-3939 (2021)
- Smith, CR; Aranda, R; Christensen, JG; Engstrom, LD; Gunn, RJ; Ivetac, A; Ketcham, JM; Kuehler, J; David Lawson, J; Marx, MA; Olson, P; Thomas, NC; Wang, X; Waters, LM; Kulyk, S Design and evaluation of achiral, non-atropisomeric 4-(aminomethyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one derivatives as novel PRMT5/MTA inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 71: (2022)
- Discovery of TNG908: A Selective, Brain Penetrant, MTA-Cooperative PRMT5 Inhibitor That Is Synthetically Lethal with MTAP-Deleted Cancers.
- Argikar, U; Blatter, M; Bednarczyk, D; Chen, Z; Cho, YS; Doré, M; Dumouchel, JL; Ho, S; Hoegenauer, K; Kawanami, T; Mathieu, S; Meredith, E; Möbitz, H; Murphy, SK; Parthasarathy, S; Soldermann, CP; Santos, J; Silver, S; Skolnik, S; Stojanovic, A Paradoxical Increase of Permeability and Lipophilicity with the Increasing Topological Polar Surface Area within a Series of PRMT5 Inhibitors. J Med Chem 65: 12386-12402 (2022)
- XU, S; LI, J; WANG, Z 4-(Aminomethyl)-6-(1-Methyl-1H-Pyrazol-4-YL)Isoquinolin-1(2H)-One Derivatives as MTA-Cooperative Inhibitors of PRMT5 US Patent US20250000854 (2025)
- Mao, R; Shao, J; Zhu, K; Zhang, Y; Ding, H; Zhang, C; Shi, Z; Jiang, H; Sun, D; Duan, W; Luo, C Potent, Selective, and Cell Active Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) Inhibitor Developed by Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Hit Optimization. J Med Chem 60: 6289-6304 (2017)
- Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-phenyl-tetrahydro-β-carboline-based first dual PRMT5/EGFR inhibitors as potential anticancer agents.
- Zhu, K; Jiang, C; Tao, H; Liu, J; Zhang, H; Luo, C Identification of a novel selective small-molecule inhibitor of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) by virtual screening, resynthesis and biological evaluations. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 1476-1483 (2018)
- Activation of the p53-MDM4 regulatory axis defines the anti-tumour response to PRMT5 inhibition through its role in regulating cellular splicing.
- Bhattacharya, SK; Cameron, KO; Dowling, MS; Ebner, DC; Edmonds, DJ; Fernando, DP; Filipski, KJ; Kung, DW; Lee, EC; Smith, AC; Tu, MM US Patent US9394285 (2016)
- Chang KO
- Clausen, JD; Kjellerup, L; Cohrt, KO; Hansen, JB; Dalby-Brown, W; Winther, AL Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 4564-4570 (2017)
- Shaw, S; Bian, Z; Zhao, B; Tarr, JC; Veerasamy, N; Jeon, KO; Belmar, J; Arnold, AL; Fogarty, SA; Perry, E; Sensintaffar, JL; Camper, DV; Rossanese, OW; Lee, T; Olejniczak, ET; Fesik, SW J Med Chem 61: 2410-2421 (2018)
- Miller, WH; Manley, PJ; Cousins, RD; Erhard, KF; Heerding, DA; Kwon, C; Ross, ST; Samanen, JM; Takata, DT; Uzinskas, IN; Yuan, CC; Haltiwanger, RC; Gress, CJ; Lark, MW; Hwang, SM; James, IE; Rieman, DJ; Willette, RN; Yue, TL; Azzarano, LM; Salyers, KL; Smith, BR; Ward, KW; Johanson, KO; Huffman, WF Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13: 1483-6 (2003)
- Zankel, TC; Isbell, SL; Ko, AA US Patent US10308607 (2019)
- Ko, B; Jang, Y; Kwak, SH; You, H; Kim, JH; Lee, JE; Park, HD; Kim, SK; Goddard, WA; Han, JH; Kim, YC J Med Chem 66: 14564-14582 (2023)
- Li, Z; Liao, C; Ko, BC; Shan, S; Tong, EH; Yin, Z; Pan, D; Wong, VK; Shi, L; Ning, ZQ; Hu, W; Zhou, J; Chung, SS; Lu, XP Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 3507-11 (2004)
- Ko, CC; Chen, YJ; Chen, CT; Liu, YC; Cheng, FC; Hsu, KC; Chow, LP J Biol Chem 289: 22078-89 (2014)
- Chen, CH; Lee, O; Yao, CN; Chuang, MY; Chang, YL; Chang, MH; Wen, YF; Yang, WH; Ko, CH; Chou, NT; Lin, MW; Lai, CP; Sun, CY; Wang, LM; Chen, YC; Hseu, TH; Chang, CN; Hsu, HC; Lin, HC; Chang, YL; Shih, YC; Chou, SH; Hsu, YL; Tseng, HW; Liu, CP; Tu, CM; Hu, TL; Tsai, YJ; Chen, TS; Lin, CL; Chiou, SJ; Liu, CC; Hwang, CS Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 6129-32 (2010)
- Ratni, H; Ebeling, M; Baird, J; Bendels, S; Bylund, J; Chen, KS; Denk, N; Feng, Z; Green, L; Guerard, M; Jablonski, P; Jacobsen, B; Khwaja, O; Kletzl, H; Ko, CP; Kustermann, S; Marquet, A; Metzger, F; Mueller, B; Naryshkin, NA; Paushkin, SV; Pinard, E; Poirier, A; Reutlinger, M; Weetall, M; Zeller, A; Zhao, X; Mueller, L J Med Chem 61: 6501-6517 (2018)
- Kim, M; Kim, G; Kang, M; Ko, D; Nam, Y; Moon, CS; Kang, HM; Shin, JS; Werz, O; Lee, KT; Lee, JY Bioorg Med Chem Lett 41: (2021)
- Lee, Y; Kim, H; Kim, H; Cho, HY; Jee, JG; Seo, KA; Son, JB; Ko, E; Choi, HG; Kim, ND; Kim, I J Med Chem 64: 6985-6995 (2021)
- Thomas, M; Brand, S; De Rycker, M; Zuccotto, F; Lukac, I; Dodd, PG; Ko, EJ; Manthri, S; McGonagle, K; Osuna-Cabello, M; Riley, J; Pont, C; Simeons, F; Stojanovski, L; Thomas, J; Thompson, S; Viayna, E; Fiandor, JM; Martin, J; Wyatt, PG; Miles, TJ; Read, KD; Marco, M; Gilbert, IH J Med Chem 64: 5905-5930 (2021)
- Cheng, MC; Li, CY; Ko, HC; Ko, FN; Lin, YL; Wu, TS J Nat Prod 69: 1305-9 (2006)
- Hillmann, P; Ko, GY; Spinrath, A; Raulf, A; von Kügelgen, I; Wolff, SC; Nicholas, RA; Kostenis, E; Höltje, HD; Müller, CE J Med Chem 52: 2762-75 (2009)
- An, S; Yu, J; Choi, H; Ko, H; Ahn, S; Shin, JC; Pyo, JJ; Jeong, LS; Noh, M Bioorg Med Chem 28: (2020)
- Cheng, MC; Li, CY; Ko, HC; Ko, FN; Lin, YL; Wu, TS J Nat Prod 69: 1305-9 (2006)
- Ko, HH; Weng, JR; Tsao, LT; Yen, MH; Wang, JP; Lin, CN Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 1011-4 (2004)
- Kwon, SH; Kim, S; Park, AY; Lee, S; Gadhe, CG; Seo, BA; Park, JS; Jo, S; Oh, Y; Kweon, SH; Ma, SX; Kim, WR; Kim, M; Kim, H; Kim, JE; Lee, S; Lee, J; Ko, HS J Med Chem 64: 15091-15110 (2021)
- Ko HY
- Ko J
- Bhattarai, BR; Ko, JH; Shrestha, S; Kafle, B; Cho, H; Kang, JH; Cho, H Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1075-7 (2010)
- Nishii, H; Chiba, T; Morikami, K; Fukami, TA; Sakamoto, H; Ko, K; Koyano, H Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1405-9 (2010)
- Lee, W; Ko, KR; Kim, HK; Lee, DS; Nam, IJ; Lim, S; Kim, S J Nat Prod 81: 1343-1356 (2018)
- Ko, KS; Steffey, ME; Brandvold, KR; Soellner, MB ACS Med Chem Lett 4: 779-783 (2013)
- Yang, HY; Tae, J; Seo, YW; Kim, YJ; Im, HY; Choi, GD; Cho, H; Park, WK; Kwon, OS; Cho, YS; Ko, M; Jang, H; Lee, J; Choi, K; Kim, CH; Lee, J; Pae, AN Eur J Med Chem 63: 558-69 (2013)
- Nam, M; Kim, T; Kwak, J; Seo, SH; Ko, MK; Lim, EJ; Min, SJ; Cho, YS; Keum, G; Baek, DJ; Lee, J; Pae, AN Eur J Med Chem 97: 245-58 (2015)
- Jackson, JJ; Shibuya, GM; Ravishankar, B; Adusumilli, L; Bradford, D; Brockstedt, DG; Bucher, C; Bui, M; Cho, C; Colas, C; Cutler, G; Dukes, A; Han, X; Hu, DX; Jacobson, S; Kassner, PD; Katibah, GE; Ko, MYM; Kolhatkar, U; Leger, PR; Ma, A; Marshall, L; Maung, J; Ng, AA; Okano, A; Pookot, D; Poon, D; Ramana, C; Reilly, MK; Robles, O; Schwarz, JB; Shakhmin, AA; Shunatona, HP; Sreenivasan, R; Tivitmahaisoon, P; Xu, M; Zaw, T; Wustrow, DJ; Zibinsky, M J Med Chem 65: 12895-12924 (2022)
- Ko, S; Lee, MK; Shin, D; Park, H Bioorg Med Chem 17: 7769-74 (2009)
- Lim, CJ; Woo, SE; Ko, SI; Lee, BH; Oh, KS; Yi, KY Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 4684-4686 (2016)
- Son, S; Ko, SK; Jang, M; Lee, JK; Kwon, MC; Kang, DH; Ryoo, IJ; Lee, JS; Hong, YS; Kim, BY; Jang, JH; Ahn, JS J Nat Prod 80: 1378-1386 (2017)
- Patel, M; Ko, SS; McHugh, RJ; Markwalder, JA; Srivastava, AS; Cordova, BC; Klabe, RM; Erickson-Viitanen, S; Trainor, GL; Seitz, SP Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 2805-10 (1999)
- Walpole, C; Ko, SY; Brown, M; Beattie, D; Campbell, E; Dickenson, F; Ewan, S; Hughes, GA; Lemaire, M; Lerpiniere, J; Patel, S; Urban, L J Med Chem 41: 3159-73 (1998)
- Lee, CC; Kuo, CJ; Ko, TP; Hsu, MF; Tsui, YC; Chang, SC; Yang, S; Chen, SJ; Chen, HC; Hsu, MC; Shih, SR; Liang, PH; Wang, AH J Biol Chem 284: 7646-55 (2009)
- Quang, TH; Ngan, NT; Ko, W; Kim, DC; Yoon, CS; Sohn, JH; Yim, JH; Kim, YC; Oh, H Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 5787-91 (2014)
- Ryu, CK; Kang, HY; Lee, SK; Nam, KA; Hong, CY; Ko, WG; Lee, BH Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 461-4 (2000)
- Kim, J; Lee, D; Park, C; So, W; Jo, M; Ok, T; Kwon, J; Kong, S; Jo, S; Kim, Y; Choi, J; Kim, HC; Ko, Y; Choi, I; Park, Y; Yoon, J; Ju, MK; Kim, J; Han, SJ; Kim, TH; Cechetto, J; Nam, J; Sommer, P; Liuzzi, M; Lee, J; No, Z ACS Med Chem Lett 3: 678-682 (2012)
- Jeon, WS; Moon, K; Park, SH; Chun, H; Ko, YH; Lee, JY; Lee, ES; Samal, S; Selvapalam, N; Rekharsky, MV; Sindelar, V; Sobransingh, D; Inoue, Y; Kaifer, AE; Kim, K J Am Chem Soc 127: 12984-9 (2005)
- Kim, YK; Kwon, O; Park, H; Park, J; Choi, HG; Son, JB; Ko, E; Kim, SY; Lee, S; Kang, SY; Ko, YK; Park, J US Patent US11447480 (2022)
- Ferraris, D; Ko, YS; Pahutski, T; Ficco, RP; Serdyuk, L; Alemu, C; Bradford, C; Chiou, T; Hoover, R; Huang, S; Lautar, S; Liang, S; Lin, Q; Lu, MX; Mooney, M; Morgan, L; Qian, Y; Tran, S; Williams, LR; Wu, QY; Zhang, J; Zou, Y; Kalish, V J Med Chem 46: 3138-51 (2003)
- Kim, NJ; Lee, KO; Koo, BW; Li, F; Yoo, JK; Park, HJ; Min, KH; Lim, JI; Kim, MK; Kim, JK; Suh, YG Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 3595-8 (2007)
- Mederski, WW; Dorsch, D; Osswald, M; Beier, N; Lues, I; Minck, KO; Schelling, P; Ladstetter, BJ Bioorg Med Chem Lett 5: 2665-2670 (1995)
- Ghobish, SA; Mohamed, KO; Farag, N; Farag, DB RSC Med Chem 15: 293-308 (2024)
- Mohammed, KO; Nissan, YM Chem Biol Drug Des 84: 473-88 (2014)
- Bugge, S; Moen, IU; Sylte, KO; Sundby, E; Hoff, BH Eur J Med Chem 94: 175-94 (2015)
- Narayanan, D; Tran, KT; Pallesen, JS; Solbak, SMØ; Qin, Y; Mukminova, E; Luchini, M; Vasilyeva, KO; González Chichón, D; Goutsiou, G; Poulsen, C; Haapanen, N; Popowicz, GM; Sattler, M; Olagnier, D; Gajhede, M; Bach, A J Med Chem 65: 14481-14526 (2022)
- Yerdelen, KO; Koca, M; Anil, B; Sevindik, H; Kasap, Z; Halici, Z; Turkaydin, K; Gunesacar, G Bioorg Med Chem Lett 25: 5576-82 (2015)
- Pontius, A; Krick, A; Mesry, R; Kehraus, S; Foegen, SE; Mu¨ller, M; Klimo, K; Gerha¨user, C; Ko¨nig, GM J Nat Prod 71: 1793-1799 (2008)
- Mattei, P; Boehringer, M; Di Giorgio, P; Fischer, H; Hennig, M; Huwyler, J; Koçer, B; Kuhn, B; Loeffler, BM; Macdonald, A; Narquizian, R; Rauber, E; Sebokova, E; Sprecher, U Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 1109-13 (2010)
- Bosnar, M; Kragol, G; Koštrun, S; Vujasinovic, I; Bošnjak, B; Bencetic Mihaljevic, V; Marušic Ištuk, Z; Kapic, S; Hrvacic, B; Brajša, K; Tavcar, B; Jelic, D; Glojnaric, I; Verbanac, D; Culic, O; Padovan, J; Alihodžic, S; Erakovic Haber, V; Spaventi, R J Med Chem 55: 6111-23 (2012)
- Schwardt, O; Rabbani, S; Hartmann, M; Abgottspon, D; Wittwer, M; Kleeb, S; Zalewski, A; Smieško, M; Cutting, B; Ernst, B Bioorg Med Chem 19: 6454-73 (2011)
- ZakoSek, M; Mihevc, SP; Majdic, G; Ko{hacek over (s)}ak, U; Gobec, S US Patent US20230331674 (2023)
- ChEMBL_2473762 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human HCT-116 cells with MTAP KO assessed as decrease in SMDA level incubated for 48 hrs by immunofluorescence analysis
- ChEMBL_2517705 Inhibition of human PRMT5
- ChEMBL_2289491 Inhibition of PRMT5 human PRMT5 using [3H]-SAM as substrate by radioactive methylation assay
- ChEMBL_2289495 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2333331 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2339692 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2434629 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2464366 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2477442 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2487925 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2490609 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2494903 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2538781 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 complex from methylating SmD3
- ChEMBL_1827493 (CHEMBL4327367) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1890800 (CHEMBL4392554) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1899169 (CHEMBL4401284) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1924043 (CHEMBL4426999) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1933903 (CHEMBL4479555) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2224736 (CHEMBL5138249) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2434643 Inhibition of human PRMT5 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2467199 Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2538780 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 complex from methylating histone 4 (H4)
- PRMT5 Biochemical Assay (No MTA) MTA is excluded.
- ChEMBL_2289487 Inhibition of PRMT5 human PRMT5 using Biotinylated H4 derived peptide and [3H]-SAM as substrate by radioactive methylation assay
- ChEMBL_2289490 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2309051 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2430116 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2253721 (CHEMBL5167931) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) by biochemical assay
- ChEMBL_2433905 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) by HotSpot profiling analysis
- ChEMBL_2289497 Inhibition of human PRMT5 by fluorescence-based SAHH-coupled assay
- ChEMBL_1496150 (CHEMBL3578931) Inhibition of human full length PRMT5 expressed in Sf9 cells
- ChEMBL_2224742 (CHEMBL5138255) Binding affinity to PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_2430146 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) by radiometric-based scintillation proximity assay
- ChEBML_1663895 Binding affinity to PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) by surface plasmon resonance assay
- ChEMBL_2163239 (CHEMBL5048100) Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) using Histone H2A as substrate
- ChEMBL_2289488 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as enzymatic activity by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2434651 Inhibition of PRMT5 methylation (unknown origin) by in-cell Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2163197 (CHEMBL5048058) Inhibition of PRMT5 methyltransferase activity in MTAP knockout human HCT-116 cells assessed as inhibition of PRMT5- mediated SDMA modification level incubated for 96 hrs by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_1775669 (CHEMBL4232661) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using H4R3 as substrate by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1827524 (CHEMBL4327398) Binding affinity to PRMT5 (unknown origin)/MEP50 (unknown origin) by SPR assay
- ChEMBL_2163193 (CHEMBL5048054) Binding affinity to human PRMT5 assessed as dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2339693 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as suppression of sDMA level
- ChEMBL_2434648 Inhibition of recombinant human PRMT5 (2 to 637 residues) incubated for 60 mins
- ChEMBL_2118743 (CHEMBL4827809) Activity at human wild type PRMT5/HA-tagged WDR77 hetero octameric complex expressed in HEK293 (Expi293) cells assessed as PRMT5 adduct formation incubated for 6 hrs by LC-MS analysis
- ChEMBL_2197017 (CHEMBL5109533) Inhibition of PRMT5 methyltransferase activity in MTAP knockout human HCT-116 cells assessed as inhibition of PRMT5-mediated SDMA modification level incubated for 96 hrs by In-cell Western analysis
- ChEMBL_2163198 (CHEMBL5048059) Inhibition of PRMT5 methyltransferase activity in human HCT-116 cells expressing wild type MTAP assessed as inhibition of PRMT5- mediated SDMA modification level incubated for 96 hrs by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2030362 (CHEMBL4684520) Inhibition of recombinant human PRMT5 using histone H2A as substrate by hotspot assay
- ChEMBL_2332266 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using histone peptide/SAM as substrate by AlphaLisa assay
- ChEMBL_2197018 (CHEMBL5109534) Inhibition of PRMT5 methyltransferase activity in human HCT-116 cells expressing wild type MTAP assessed as inhibition of PRMT5-mediated SDMA modification level incubated for 96 hrs by In-cell Western analysis
- ChEMBL_2476844 Inhibition of tetracycline-inducible FLAG-tagged human PARL stably transfected in HEK293T harboring FITR/PARL KO
- ChEMBL_1496155 (CHEMBL3578936) Binding affinity to human full length PRMT5-MEP50 complex by Surface plasmon resonance method
- ChEMBL_2118741 (CHEMBL4827807) Covalent inhibition of human PRMT5 assessed as initial binding constant by LC-MS analysis
- ChEMBL_2163232 (CHEMBL5048093) Binding affinity to MTA-bound human PRMT5 assessed as dissociation constant by SPR assay
- ChEMBL_2289493 Inhibition of human PRMT5 using H4R3 S1ac and [3H]-SAM as substrate by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2515311 Binding affinity to human PRMT5 incubated for 45 mins by Kinobead based pull down assay
- ChEMBL_480051 (CHEMBL927990) Inhibition of mouse PKCtheta in KO cells assessed as blockade of anti CD28-stimulated IL2 production
- ChEMBL_2277375 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) incubated for 15 mins measured after 60 min by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2339676 Binding affinity to Full-length human PRMT5/human MEP50 assessed as dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_951490 (CHEMBL2350643) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using [3H]SAM after 1 hr by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_1775685 (CHEMBL4232677) Inhibition of N-terminal FLAG-tagged human PRMT5 using histone H4 substrate incubated fro 60 mins
- ChEMBL_2163205 (CHEMBL5048066) Binding affinity to human PRMT5 assessed as dissociation constant in presence of MTA by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2163208 (CHEMBL5048069) Binding affinity to human PRMT5 assessed as dissociation constant in presence of SAM by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2263121 (CHEMBL5218132) Binding affinity to PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) assessed as dissociation constant by FITC- Competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_2263122 (CHEMBL5218133) Binding affinity to PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition constant by FITC- Competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_2339656 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human U-87 MG cells incubated for 3 days by western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2339659 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human U-87 MG cells incubated for 4 mins by western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2339677 Binding affinity to Full-length human PRMT5/human MEP50 assessed as equilibrium dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2434640 Inhibition of human PRMT5 expressed in HEK293 cells coexpressing MEP50 incubated for 60 mins by chemiluminescent assay
- ChEMBL_2522651 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MCF7 cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2522653 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MINO cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2522654 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human BJAB cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2522655 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human REC1 cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2154863 (CHEMBL5039523) Agonist activity at STING KO human THP-1 dual cells incubated for 20 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_2163234 (CHEMBL5048095) Inhibition of streptavidin sensor chip immobilized biotinylated human PRMT5/MEP50 assessed as dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2465250 Binding affinity to biotinylated PRMT5/MEP50 complex (unknown origin) in presence of MTA by surface plasmon resonance analysis
- ChEMBL_2487890 Inhibition of human PRMT5/MEP50 using Histone H2 as substrate and SAM as cofactor by radiometric HotSpot assay
- ChEMBL_2522652 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MAVER-1 cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2522656 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human U-2940 cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2571722 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using [3H-SAM] as substrate incubated for 1 hr by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_2322358 Agonist activity at STING in human STHP1-Dual KO-STING cells incubated for 20 hrs by Quanti-luc reagent based assay
- ChEMBL_2354137 Agonist activity at STING in PMA-differentiated human THP1-Dual KO-STING cells incubated for 24 hrs by QUANTI-Blue assay
- ChEBML_1526059 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using biotinylated histone H4-derived peptide as substrate after 60 mins by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2465078 Inhibition of PRMT5 in MTAP-null human HAP1 cells incubated for 24 hrs by SDMA in-cell western assay
- ChEMBL_2522650 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MDA-MB-468 cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2522657 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human ZR-75-1 cells assessed as decrease in SDMA level incubated for 3 days
- ChEMBL_2149843 (CHEMBL5034305) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as effect on H3R8/H4R3 methylation incubated for 30 mins by Alphascreen assay
- ChEMBL_2461858 Inhibition of PRMT5 methyltransferase activity (unknown origin) using histone H4/SAM as substrate incubated for 80 mins by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2487931 Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) incubated for 1 hr in presence of 3H-SAM by topcount plate reader analysis
- ChEMBL_2522649 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on SDMA level incubated for 3 days by ELISA analysis
- ChEMBL_1676360 (CHEMBL4026503) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) incubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition measured after 60 mins by AlphaLisa method
- ChEMBL_1890806 (CHEMBL4392560) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Granta-519 assessed as reduction in sDMA production after 3 days by Western blotting analysis
- ChEMBL_1890811 (CHEMBL4392565) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human A549 cells assessed as reduction in sDMA production incubated for 48 hrs by immunohistochemistry analysis
- ChEMBL_2339662 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human A427 cells assessed as reduction in sDMA level incubated for 72 hrs by liquid scintillation analysis
- ChEMBL_2339689 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as decrease in sDMA modification incubated for 2 days by fluorescence based assay
- ChEMBL_2339699 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MCF7 cells assessed as suppression of arginine sDMA incubated for 3 days by target engagement assay
- ChEMBL_1735605 (CHEMBL4151141) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MCF7 cells assessed as reduction in SmBB'-Rme2s levels after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_1807715 (CHEMBL4307074) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Granta-519 assessed as reduction in sDMA production incubated for 3 days by Western blotting analysis
- ChEMBL_1896036 (CHEMBL4398071) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 60 mins by AlphaLisa assay
- ChEMBL_2339658 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Granta-519 cells assessed as suppression of sDMA level incubated for 3 days by western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_1735598 (CHEMBL4151134) Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 complex (unknown origin) expressed in Sf9 insect cells using SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKVLRDK-Biotin as substrate by surface plasmon resonance assay
- ChEMBL_1890812 (CHEMBL4392566) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)/MEP50 (unknown origin) using [3H]-SAM and histone H2A incubated for 60 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_2118729 (CHEMBL4827795) Displacement of fluorophore-labeled RIOK1 from human PRMT5/WDR77 hetero octameric complex expressed in Sf9 cells by competition fluorescence polarization (FP) assay
- ChEMBL_2122987 (CHEMBL4832220) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)-mediated H3R8 methylation using histone H3 and SAM as substrate incubated for 30 mins by AlphaScreen assay
- ChEMBL_2122988 (CHEMBL4832221) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)-mediated H4R3 methylation using histone H4 and SAM as substrate incubated for 30 mins by AlphaScreen assay
- ChEMBL_2263123 (CHEMBL5218134) Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) incubated for 1 to 2 hrs in presence of tracer 21 by competitive fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2263135 (CHEMBL5218146) Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) incubated for 1 to 2 hrs in presence of tracer 50 by competitive fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2339657 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human U-87 MG cells assessed as suppression of sDMA level incubated for 3 days by western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522711 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on SESN1 expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522712 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on BAX expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522713 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on CDKN1 expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522714 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on MDM2 expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522715 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on PHLDA3 expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522716 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on TRIM22 expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522717 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on EGR2 expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522718 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as effect on GADD45A expression incubated for 2 to 4 days by Western blot analysis
- ChEMBL_1735607 (CHEMBL4151143) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MCF7 cells assessed as skipping of Mdm4 exon 6 mRNA splicing after 72 hrs by qRT-PCR method
- ChEMBL_1827495 (CHEMBL4327369) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)/MEP50 (unknown origin) using histone H4 as substrate preincubated for 60 mins in presence of enzyme and SAM
- ChEMBL_2118744 (CHEMBL4827810) Disruption of human N-terminal SmBiT peptide-tagged PRMT5/ N-terminal LgBiT tagged RIOK1 complex expressed in permeabilized HEK293T cells by NanoBiT assay
- ChEMBL_2448897 Binding affinity to human recombinant flag His-tagged PRMT5 ( 1 to 637 residues) expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2511555 Inhibition of human PRMT5/MEP50 using Histone H2A and [3H]SAM as substrate incubated for 30 mins to 1 hr by HotSpot kinase assay
- ChEMBL_879136 (CHEMBL2209107) Inhibition of PRMT5 using histone H3 as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by addition of [3H]SAM and incubated for 60 mins
- PRMT5 Enzyme Inhibitory Activity Assay Experimental objective: To test the inhibitory effect of compounds on PRMT5 enzyme activity. Experimental materials: PRMT5 enzyme. Experimental operation: Test compounds were added at a certain concentration (0.17 nM to 99010 nM) to a white transparent bottomed 384-well plate using LABCYTE Echo 550, then PRMT5 was added, and a vehicle control (with DMSO and without compound) and a blank control (with DMSO and without PRMT5) were set up. The plate was incubated at 25° C. for 30 min, then added with substrate, and reacted at 25° C. for 90 min. After 90 min, the detection reagent was added to the 384-well plate using PerkinElmer LANCE Ultra TR-FRET standard method to combine with the enzyme-substrate reaction product. After 1 hour of reaction at 25° C., the signal was detected on a PerkinElmer EnVision 2105 Multimode Plate Reader.
- ChEMBL_1450371 (CHEMBL3378208) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as incorporation of tritium-labeled methyl group to lysine or arginine residues of peptide substrate by radioactive assay
- ChEMBL_2100039 (CHEMBL4808435) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of symmetric dimethylation of arginine incubated for 3 days by fluorescence based cellular target engagement assay
- ChEMBL_2118114 (CHEMBL4827180) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using SAM as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition measured after 4 hrs by AlphaLISA method
- ChEMBL_2434642 Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) using H4 peptide as substrate incubated for 25 mins in presence of [3H]-SAM by liquid scintillation counter method
- ChEMBL_2465087 Binding affinity to apo-PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as dissociation constant incubated for 1 hr in presence of Me0 peptide by double titration based analysis
- ChEMBL_2473751 Binding affinity to apo PRMT5 (1 to 637 residues)(unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells assessed as dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2473763 Inhibition of PRMT5 in human HCT-116 cells expressing wild-type MTAP assessed as decrease in SMDA level incubated for 48 hrs by immunofluorescence analysis
- ChEMBL_2160781 (CHEMBL5045531) Agonist activity at STING in human THP1 Dual KO-STING cells assessed as IRF reporter activation incubated for 20 hrs by quanti-blue SEAP reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_1890810 (CHEMBL4392564) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) assessed as reduction in SAH formation using histone H2A and SAM incubated for 60 mins by high throughput mass spectrometry
- ChEMBL_2433320 Inhibition of MAT2A in MTAP-knock out human HCT-116 cells assessed as reduction in PRMT5-mediated symmetrical demethylation of arginine (SDMA) measured after 96 hrs
- ChEMBL_2434634 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using histone H4 as substrate preincubated for 30 mins followed by SAM addition and measured after 120 mins by Topcount method
- PRMT5 Chemiluminescent Assay The PRMT5 activity is measured by using “PRMT5 Chemiluminescent Assay Kit” from BPS Bioscience, Catalog Number 52002L as per the instructions of the manufacturer. Briefly, the PRMT5 enzyme is incubated with S-adenosylmethionine in a 96-well plate precoated with histone H4 peptide substrate. Next, a highly specific antibody that recognizes methylated R3 residue of Histone H4 is added followed by a horseradkish peroxidase-labeled (HRP-labeled) secondary antibody. Detection is done by the addition of the HRP substrate to produce chemiluminescence that can be measured quantitatively.Compounds were serially diluted 3-fold and dosed from 10 uM down to 0 uM. Compounds were tested in duplicates to generate an eight-point dose response for the calculation of their IC50s.
- ChEMBL_2160782 (CHEMBL5045532) Agonist activity at STING in mouse RAW-Lucia ISG-KO-STING cells assessed as IRF reporter activation incubated for 20 hrs by quanti-blue SEAP reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_2160784 (CHEMBL5045534) Agonist activity at STING in human THP1-Dual KO-STING cells assessed as NF-kappaB reporter activation incubated for 20 hrs by quanti-blue SEAP reporter gene assay
- ChEMBL_2072973 (CHEMBL4728507) Inhibition of human PRMT5/MEP50 assessed as reduction in methyltransferase activity using histone 4 peptide as substrate in presence of [3H]SAM incubated for 30 mins
- ChEMBL_2217502 (CHEMBL5130634) Inhibition of PRMT5 methyltransferase activity in human MTAP -/- Calu-6 cells assessed as reduction in SmB SDMA levels measured after 2 days by HTRF based assay
- ChEMBL_2253703 (CHEMBL5167913) Displacement of [3H]-SAM from PRMT5 (unknown origin) using peptide substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition for 60 mins by radioactive biochemical assay
- ChEMBL_1890808 (CHEMBL4392562) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human A549 cells assessed as reduction in sDMA production after 48 hrs by Hoechst Stain/HCS CellMask Deep Red Stain based immunohistochemistry method
- ChEMBL_2253679 (CHEMBL5167889) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using histone H4 (1 to 21 residues) peptide/SAM as substrate incubated for 210 mins in presence of SAM by AlphaLISA assay
- ChEMBL_2339687 Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) using histone H4 peptide as substrate preincubated for 30 mins followed by substrate addition and measured for 60 mins by AlphaScreen analysis
- ChEMBL_1827496 (CHEMBL4327370) Inhibition of human recombinant PRMT5/MEP50 expressed in 293-F cells using histone 4 peptide as substrate after 90 mins in presence of [3H]SAM by autoradiographic analysis
- ChEMBL_2339683 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using H4(1-21)S1ac as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition and measured for 60 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_2434639 Inhibition of full-length PRMT5 (unknown origin) expressed in insect cells coexpressing 6His-tagged MEP50 using histone H4 peptide as substrate incubated for 4 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay
- ChEMBL_2473752 Binding affinity to apo PRMT5 (1 to 637 residues)(unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells assessed as dissociation constant in presence of MTA by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_2473753 Binding affinity to apo PRMT5 (1 to 637 residues)(unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells using SAM as substrate assessed as dissociation constant by SPR analysis
- ChEMBL_828319 (CHEMBL2050393) Inhibition of His6X-tagged PRMT5 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cells using [14C]-S-adenosyl-L-methionine and histone H4 peptide after 8 mins by scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_2026413 (CHEMBL4680571) Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) using biotin-labeled histone H4-20 peptide as substrate incubated for 8 mins in presence of [3H]-SAM cofactor by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_2076028 (CHEMBL4731562) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human A549 cells assessed as reduction in arginine dimethylation of SmD1/3 after 48 hrs by Hoechst Stain/ CellMask Deep Red Stain based immunohistochemistry method
- ChEMBL_2465075 Displacement of C-terminal 5'-TAMRA labeled histone H4 Me0 peptide (1 to 21) from PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) incubated for 30 mins in presence of MTA by fluorescence anisotropy
- ChEMBL_2465076 Displacement of C-terminal 5'-TAMRA labeled histone H4 Me2 peptide (1 to 21) from PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) incubated for 30 mins in presence of SAM by fluorescence anisotropy
- ChEMBL_2026543 (CHEMBL4680701) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human Z138 cells assessed as reduction in symmetrical dimethylation of arginine containing substrate using SmD3 as substrate incubated for 4 days by In-cell western assay
- ChEMBL_2118734 (CHEMBL4827800) Displacement of fluorophore-labeled RIOK1 from human PRMT5/WDR77 hetero octameric complex expressed in Sf9 cells measured up to 4 hrs at10 mins time interval competition fluorescence polarization (FP) assay
- MTase-Glo Methyl Transferase Assay Table 1: The PRMT5 inhibitory activity of test compounds was determined using the MTase-Glo™ assay (Promega), which monitors the product (S-adenosyl homocysteine or SAH) of methyltransferase reactions. The PRMT5 MTase-Glo assays were conducted in a 384-well white ProxiPlate (PerkinElmer, catalog no.: 6008280) in a total volume of 12 μL. The PRMT5 enzymatic reaction (in 4 μL) contained 50 nM PRMT5/MEP50 (Reaction Biology Corp, catalog no.: HMT-22-148), 25 μM S-adenosyl methionine (SAM, Promega), 5 μM Histone H4 peptide (1-21) (BPS Bioscience, catalog no.: 52018-2) and five-fold serially diluted compounds in a reaction buffer of 50 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 50 mM NaCl, 0.01% Tween 20, 0.01% BSA, and 1 mM DTT. The test compounds were pre-incubated with PRMT5/MEP50 and Histone H4 peptide for 20 minutes at room temperature before the addition of SAM to initiate the PRMT5 reaction. The reaction was allowed to proceed for 1 hour at 37° C. and was terminated by 2 μL of 3× MTase-Glo™ Reagent (Promega) and 150 μM EPZ015666 (Selleck, catalog no.: 1616391-65-1). After a 30-minute incubation at room temperature, 6 μL of MTase-Glo™ Detection Solution (Promega) was added and the plate was incubated at room temperature for an additional 30 minutes. The light signal corresponding to the amount of SAH produced by the PRMT5 reaction was subsequently measured using an Envision multimode reader (PerkinElmer).
- PRMT5 Inhibition Based on TR-FRET Assay Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is a type II arginine methyltransferase that catalyze mono- and symmetric demethylation on arginine residues of histone or non-histone proteins in presence of S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet or SAM) a cofactor responsible for donating the methyl group. PRMT5 is reported to be overexpressed in several human cancers. To identify compounds that inhibit the PRMT5 and decrease its activity, a TR-FRET based assay has been established. Time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) HTS assays are homogeneous proximity assays where the interaction of two dye-labeled binding partners is detected by the energy transfer between a donor and an acceptor dye and the subsequent light emission by the acceptor dye. PRMT5 catalyzes Histone H4 peptide [1-16] which is biotin tagged to the Lysine amino acid at carboxyl end, in presence of S-adenosyl-1-methionine (SAM) to methylate the peptide. The antibody specific to mono methylated H4 peptide (H4R3) with Ig conjugate binds to the methylated peptide, indirectly binding to the Europium lanthanide. SureLight Allophycocyanin-Streptavidin binds to the biotin tag of the peptide, therefore accepting the energy transferred from the Europium lanthanide. This energy transfer between Europium to SureLight Allophycocyanin is a direct measure of the activity/inhibition of the PRMT5 enzyme.
- ChEMBL_1334936 (CHEMBL3239252) Inhibition of HA-tagged recombinant PRMT5 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293T cells using [3H]SAM and histone H4 (1 to 20) as substrate after 8 mins by P81 filter binding assay
- ChEMBL_1735597 (CHEMBL4151133) Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 complex (unknown origin) expressed in Sf9 insect cells using SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKVLRDK-Biotin as substrate measured after 2 hrs in presence of [3H]-SAM by topcount scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_1775682 (CHEMBL4232674) Inhibition of human 6xHis-tagged PRMT5 expressed in bacterial expression system using histone H2A as substrate after 2 hrs in presence of by S-[methyl-3H]adenosylmethionine by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_2152069 (CHEMBL5036616) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human HCT116-MTAP null cells assessed as reduction in symmetric dimethylation of arginine using SAM as substrate incubated for 48 hrs by Hoechst 33342 staining based assay
- ChEMBL_2197015 (CHEMBL5109531) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using H2A and 3H-SAM as substrates preincubated for 20 mins followed by substrate addition incubated for 60 mins in presence of MTA by radiometric HotSpot assay
- ChEMBL_2225434 (CHEMBL5138947) Inhibition of human full length recombinant FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to 637 residues) using histone H2A as substrate incubated for 20 mins in presence of [3H]-SAM by radioisotope-based filter assay
- ChEMBL_1827494 (CHEMBL4327368) Inhibition of full-length human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 expressed in Sf9 insect cells using histone H2A as peptide after 120 mins in presence of SAM by high throughput mass spectrometer assay
- ChEMBL_2434641 Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin) using biotinylated H4 derived peptide as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate and [3H]-SAM addition and measured after 60 mins by microbeta liquid scintillation counting method
- PRMT5:MEP50 HotSpot Assay Table B2: The assay uses recombinant full-length histone H2A as the PRMT5 substrate. Enzymatic transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine to the histone H2A protein generated a radiolabeled histone H2A4 by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions also were conducted in the presence of MTA to determine whether the compounds exhibit MTA-cooperative activity. Briefly, compounds of the present invention were solubilized in 100% DMSO at a highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC50 determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound was 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRMT5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity. 1 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex (Reaction Biology Corporation) was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 5 μM full-length histone H2A for 20 min at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM tritiated S-adenosyl methionine (final concentration) and the reaction was allowed to proceed for 60 min. The reaction was stopped and transferred to filter paper for detection. The amount of tritiated H2A in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter.
- ChEMBL_1775678 (CHEMBL4232670) Inhibition of human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end) expressed in HEK293 cells using biotinylated H2A as substrate measured after 60 mins in presence of SAM by high throughput mass spectrometer assay
- ChEMBL_1989160 (CHEMBL4622707) Inhibition of PRMT5 in human MCF7 cells assessed as reduction in symmetrically dimethylated nuclear protein level incubated for 3 days by Alexafluor-488 conjugate anti-rabbit antibody/DAPI staining based IN cell analyzer method
- ChEMBL_2473750 Inhibition of PRMT5 (1 to 637 residues)/MEP504 (2 to 342 residues)(unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells using histone H4/SAM as substrate incubated for 5 hrs by MTase Glo assay
- TR-FRET Assay Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is a type II arginine methyltransferase that catalyze mono- and symmetric demethylation on arginine residues of histone or non-histone proteins in presence of S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet or SAM) a cofactor responsible for donating the methyl group. PRMT5 is reported to be overexpressed in several human cancers. To identify compounds that inhibit the PRMT5 and decrease its activity, a TR-FRET based assay has been established. Time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer (TR-FRET) HTS assays are homogeneous proximity assays where the interaction of two dye-labeled binding partners is detected by the energy transfer between a donor and an acceptor dye, and the subsequent light emission by the acceptor dye. PRMT5 catalyzes Histone H4 peptide [1-16] which is biotin tagged to the Lysine amino acid at carboxyl end, in presence of S-adenosyl-1-methionine (SAM) to methylate the peptide. The antibody specific to mono methylated H4 peptide (H4R3) with Ig conjugate binds to the methylated peptide, indirectly binding to the Europium lanthanide. SureLight Allophycocyanin-Streptavidin binds to the biotin tag of the peptide, therefore accepting the energy transferred from the Europium lanthanide. This energy transfer between Europium to SureLight Allophycocyanin is a direct measure of the activity/inhibition of the PRMT5 enzyme.
- ChEMBL_2522327 Uncompetitive inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using [3H]SAM as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant incubated for 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522328 Competitive inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using [3H]SAM as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant incubated for 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_1711282 (CHEMBL4121331) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues) /human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using substrate measured after 60 mins by Alphalisa assay
- ChEMBL_1890801 (CHEMBL4392555) Inhibition of PRMT5 (unknown origin)/MEP50 (unknown origin) using histone H2 as substrate preincubated for 15 to 20 mins followed by S-[methyl-3H]adenosyl-L-methionine addition measured after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_2339661 Binding affinity to N-terminal 6xHis-tagged full length human PRMT5/MEP50 expressed in sf21 cells using S-Adenosyl-L-methionine as substrate assessed as dissociation constant incubated for 25 to 60 mins by liquid scintillation analysis
- ChEMBL_1711284 (CHEMBL4121333) Inhibition of full length recombinant human FLAG-tagged PRMT5/full length recombinant human His6-tagged MEP50 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells using biotinylated histone peptide as substrate in presence of [3H]-SAM by Topcount method
- ChEMBL_2465090 Substrate competitive inhibition of human PRMT5/MEP50 complex preincubated for 30 mins with [3H]SAM followed by incubation with 10 uM histone H4 (1 to 21) peptide for 2.5 hrs by radioactive flash plate based scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_2465095 Substrate competitive inhibition of human PRMT5/MEP50 complex preincubated for 30 mins with [3H]SAM followed by incubation with 1 uM histone H4 (1 to 21) peptide for 2.5 hrs by radioactive flash plate based scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_2522331 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using H4 as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522332 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using H2A as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522333 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using Sm3d as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522334 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using FUBP1 as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522335 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using HNRNPH1 as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_1468799 (CHEMBL3411809) Displacement of [3H]-SAM from recombinant His6-tagged PRMT5 (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) incubated for 5 mins prior to H4(1 to 20)-BTN peptide addition measured after 8 mins by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_1807714 (CHEMBL4307073) Binding affinity to human recombinant PRMT5/MEP50 expressed in baculovirus infected High-five cells using histone 4 peptide as substrate assessed as inhibitory constant in presence of [3H]SAM measured upto 120 mins by jump dilution experiment based assay
- ChEMBL_1827492 (CHEMBL4327366) Inhibition of full-length N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (unknown origin) (1 to 637 residues) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells using histone H4 as peptide after 5 hrs in presence of [H3]AdoMet by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_1871587 (CHEMBL4372754) Inhibition of recombinant full-length N-terminal His6-tagged PRMT5 (unknown origin) using AcH4-21 peptide substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate/14C-methyl-SAM addition and measured after 15 mins by phosphorimaging analysis based radioisotopic assay
- ChEMBL_2076029 (CHEMBL4731563) Binding affinity to N-terminal FLAG-tagged human PRMT5 (1 to 637 residues)/N-terminal thrombin His-tagged MEP50 (2 to 342 residues) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 cells by streptavidin coated sensor chip based surface plasmon resonance analysis
- ChEMBL_2339702 Binding affinity to PRMT5/MEP50 (unknown origin) using histone H4 peptide assessed as inhibition constant preincubated for 24 hrs followed by substrate addition and measured for 2 hrs in the presence of SAM by MTase-Glo Methyl Transferase Assay
- ChEMBL_2473749 Inhibition of PRMT5 (1 to 637 residues)/MEP504 (2 to 342 residues)(unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells using histone H4/SAM as substrate incubated for 5 hrs in presence of MTA by MTase Glo assay
- ChEMBL_2522329 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using [3H]SAM as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- SPR Binding Assay Table A2: In vivo biotinylated PRMT5-MEP50 was diluted to 4.5 μM in 25 mM Bicine pH 7.6, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, and 0.05% Tween-20 and injected at 5 μl/min flow rate into flow cell 2 (FC2) of a Series S Sensor Chip SA (Cytiva) in a Biacore T200 or in a Biacore 8K plus (Cytiva). SPR screening was performed in MTA running buffer (25 mM Bicine pH 7.6, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, 20 μM MTA, 0.05% Tween-20 and 2% DMSO). The biotinylated PRMT5-MEP50 surface was equilibrated with MTA running buffer for 12 hours prior to the start. The test compound affinity was determined using multi-cycle injection of each fragment from 0.001 to 500 μM over the PRMT5•MTA at a flow rate of 30 μl/min and with association and dissociation times of 20 and 60 seconds respectively. PRMT5•MTA surface activity was confirmed at the initiation, and the end of the run by titration of EPZ015666 (KD=11 and 13 μM respectively). Subsequently, compound titration was repeated in SAM-running buffer (25 mM Bicine pH 7.6, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM TCEP, 20 μM SAM, 0.05% Tween-20, and 2% DMSO). The PRMT5•SAM surface was equilibrated for at least 5 hours prior to compound titration and the PRMT5•SAM surface activity was confirmed at the end of the fragment titration run by titration of EPZ015666 (KD<1 nM). After double referencing, the steady-state response was extracted for each fragment concentration and was fit to the Langmuir isotherm equation to determine the equilibrium dissociation constant (KD).
- Chemiluminescent Assay A PRMT5 chemiluminescent assay was used to measure the 1050 activity of PRMT5. Biotinylated histone peptides were synthesized and attached to 384-well plates. Compound serial dilutions were performed and added to the assay plate. Histone H4 monomethyl R3 antibody was obtained from Abcam. A master mix for each well was prepared and human PRMT5/MEP50 (expressed in HEK293 cells) diluted in assay buffer to a concentration of 5 ng/μL. The reaction was incubated and slowly rotated for 60 minutes at the point of PRMT5/MEP50 addition. The supernatant from the wells was removed and blocking buffer was added to each well and rotated for 10 minutes. The primary antibody was diluted and added to every well for 60 minutes, before it was removed and the wells washed. The horse radish peroxidase (HRP)-coupled secondary antibody was diluted and added to each well with an incubation time of 30 minutes. The HRP chemiluminescent substrate was added to every well. The plate was read on a Flourstar Omega BMG Labtech instrument (Ortenberg, Germany) and the analysis of IC50 was performed using the Flourstar Omega BMG Labtech software.
- Chemiluminescent Assay A PRMT5 chemiluminescent assay was used to measure the IC50 activity of PRMT5 of the compounds of Examples 1A to 7 above. Biotinylated histone peptides were synthesized and attached to 384-well plates. Compound serial dilutions were performed and added to the assay plate. Histone H4 monomethyl R3 antibody was obtained from Abcam. A master mix for each well was prepared and human PRMT5/MEP50 (expressed in HEK293 cells) diluted in assay buffer to a concentration of 5 ng/μL. The reaction was incubated and slowly rotated for 60 minutes at the point of PRMT5/MEP50 addition. The supernatant from the wells was removed and blocking buffer was added to each well and rotated for 10 minutes. The primary antibody was diluted and added to every well for 60 minutes, before it was removed and the wells washed. The horse raddish peroxidase (HRP)-coupled secondary antibody was diluted and added to each well with an incubation time of 30 minutes. The HRP chemiluminescent substrate was added to every well. The plate was read on a Flourstar Omega BMG Labtech instrument (Ortenberg, Germany) and the analysis of IC50 was performed using the Flourstar Omega BMG Labtech software.
- PRMT5 Biochemical Assay The assay was carried out in 384-well low volume black plates in a reaction mixture containing 10 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex, biotinylated histone H4 peptide, 3 μM S-adenosylmethionine and 0-10 μM compound in buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5), 0.005% BSA, 1 mM TCEP and 0.002% Tween-20. The PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme was incubated with compounds disclosed herein and biotinylated histone H4 peptide for 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was initiated by addition of S-adenosylmethionine. After reacting at room temperature for 120 minutes, the detection solution containing Eu-labeled antibody and dye-labeled acceptor in detection buffer was added to the reaction mixture. Plates were sealed and incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes, and the TR-FRET signals (excitation 337 nm, emission 665/620 nm) were recorded on a PHERAstar FSX plate reader (BMG Labtech). The inhibition percentage of PRMT5/MEP50 activity in presence of increasing concentrations of compounds was calculated based on the ratio of fluorescence at 665 nm to that at 620 nm. The concentration of MTA is 800nM.
- PRMT5 assay Compounds were solubilized in DMSO and serially diluted, using 3-fold dilutions, into 100% DMSO at a concentration 50-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Following dilution, 1 ul was added to an empty 96-well microtiter plate. PRMT5/MEP50 protein complex was combined with H4(1-21) peptide (SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKV) in PRMT5 assay buffer (50 mM Tris pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM TCEP) and 44 ul was added to the microtiter plate containing compound. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) was prepared by combining 3H labelled SAM with unlabelled SAM in PRMT5 assay buffer such that the final SAM concentration was 10 uM and the specific activity was 0.2 uCi/ul. The reaction was initiated by adding 5 ul of SAM stock to the microtiter plate. The final reaction conditions were 10 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex, 200 nM peptide and 1 uM SAM. Following a 25 minute incubation at room temperature, the reaction was stopped with the addition of 100 uL of 20% TCA. The 3H-peptide product was captured using a 96-well filter plate (MSIPN4B, Millipore) and washed 5 times with PBS buffer. Scintillation fluid (100 ul) was added to the dried filter plate and counted in a liquid scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4-parameter dose response equation using Pfizer proprietary software.
- ChEMBL_1663865 (CHEMBL4013546) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues)/human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using histone H4 as substrate in presence of [3H]-SAM after 60 mins by chemiluminescent assay
- ChEMBL_1807709 (CHEMBL4307068) Inhibition of human recombinant PRMT5/MEP50 expressed in baculovirus infected High-five cells using histone 4 peptide as substrate in presence of [3H]SAM preincubated for 20 mins followed by [3H]SAM addition and measured after 30 mins by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1890799 (CHEMBL4392553) Inhibition of full length N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (unknown origin)/MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 insect cells using H4(1-21) peptide SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKV as substrate measured after 25 minutes in the presence of [3H]SAM by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_2522330 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using [3H]SAM as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522336 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using H4 as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522337 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using H2A as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522338 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using Sm3d as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522339 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using FUBP1 as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2522340 Inhibition of Flag-tagged human PRMT5/his-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using HNRNPH1 as substrate assessed as apparent inhibition constant preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 30 mins by Cheng-Prusoff plot analysis
- ChEMBL_2339698 Inhibition of full-length recombinant PRMT5/full-length recombinant MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 cells using biotinylated H4R3(Mel) peptide as substrate preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition and measured for 150 minutes in the presence of SAM by methylation assay
- ChEMBL_2354803 Inhibition of N-terminal/C-terminal human recombinant full-length FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to 637 residues)/C-terminal human His-tagged MEP50 (2 to 342 residues) using histone H2A as substrate and 3H-SAM as cosubstrate incubated for 60 mins by scintillation counter analysis
- ChEMBL_1827497 (CHEMBL4327371) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues) /human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells pretreated for 15 mins followed by substrate and [3H]-SAM addition measured after 60 mins by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_2465097 Inhibition of PRMT5/MEP50 complex (unknown origin) preincubated with enzyme for 2 hrs in spin columns followed by incubation with histone H4 (1 to 21) peptide and SAM for 5 hrs followed by incubation in flashplate for 1 hr by spin column/FlashPlate based scintillation counting analysis
- PRMT5:MEP50 FlashPlate Assay Table B1: The assay uses purified human, PRMT5 enzyme to convert S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine plus histone H4 L-arginine to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine plus histone H4 [methyl-3H]-L-arginine. The assay was carried out using Streptavidin-coated FlashPlates (Perkin Elmer), which contained a scintillant embedded in the plastic of the plate. The histone H4 peptide substrate was conjugated with biotin, which binds to the streptavidin-coated well of the plate, placing the H4 peptide in close proximity to the side well and the scintillant. The transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine to the bound histone H4 peptide generated a radiolabeled histone H4, which was quantitated by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions also were conducted in the presence and absence of MTA to determine whether the compounds exhibit MTA-cooperative activity. Briefly, compounds of the present invention were solubilized in 100% DMSO at a highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC, determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound was 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRMT5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity, 3 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex (Reaction Biology Corporation) was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 40 nM histone H4 peptide (amino acids 1-15)-Biotin conjugate for 20 min at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM tritiated S-adenosyl methionine (final concentration) and the reaction is allowed to proceed for 20 min. The reaction was stopped and the amount of bound, tritiated H4 peptide in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter.
- PRMT5:MEP50 FlashPlate Assay The assay uses purified human, PRMT5 enzyme to convert S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine plus histone H4 L-arginine to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine plus histone H4 [methyl 3H]-L-arginine. The assay was carried out using Streptavidin-coated FlashPlates (Perkin Elmer), which contained a scintillant embedded in the plastic of the plate. The histone H4 peptide substrate was conjugated with biotin, which binds to the streptavidin-coated well of the plate, placing the H4 peptide in close proximity to the side well and the scintillant. The transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine to the bound histone H4 peptide generated a radiolabeled histone H4, which was quantitated by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions also were conducted in the presence of 20u MTA. Briefly, compounds of the present invention were solubilized in 100% DMSO at a highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC50 determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound was 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRMT5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity, 3 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex (Reaction Biology Corporation) was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 40 nM histone H4 peptide (amino acids 1-15)-Biotin conjugate for 20 min at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM tritiated S-adenosyl methionine (final concentration) and the reaction is allowed to proceed for 20 min. The reaction was stopped and the amount of bound, tritiated H4 peptide in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter. The IC50 value for each compound was calculated from each 10-point dose-response curve for samples plus and minus MTA using GraphPad Prism software.
- PRMT5:MEP50 FlashPlate Assay with MTA The assay uses purified human, PRMT5 enzyme to convert S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine plus histone H4 L-arginine to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine plus histone H4 [methyl-3H]-L-arginine. The assay was carried out using Streptavidin-coated FlashPlates (Perkin Elmer), which contained a scintillant embedded in the plastic of the plate. The histone H4 peptide substrate was conjugated with biotin, which binds to the streptavidin-coated well of the plate, placing the H4 peptide in close proximity to the side well and the scintillant. The transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine to the bound histone H4 peptide generated a radiolabeled histone H4, which was quantitated by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions also were conducted in 2uM MTA to determine whether the compounds exhibit MTA-cooperative activity. Briefly, compounds of the present invention were solubilized in 100% DMSO at a highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC50 determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound was 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRMT5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity, 3 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex (Reaction Biology Corporation) was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 40 nM histone H4 peptide (amino acids 1-15)-Biotin conjugate for 20 min at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM tritiated S-adenosyl methionine (final concentration) and the reaction is allowed to proceed for 20 min. The reaction was stopped and the amount of bound, tritiated H4 peptide in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter. The IC50 value for each compound was calculated from each 10-point dose-response curve for samples plus MTA using GraphPad Prism software.
- PRMT5:MEP50 FlashPlate Assay without MTA The assay uses purified human, PRMT5 enzyme to convert S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine plus histone H4 L-arginine to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine plus histone H4 [methyl 3H]-L-arginine. The assay was carried out using Streptavidin-coated FlashPlates (Perkin Elmer), which contained a scintillant embedded in the plastic of the plate. The histone H4 peptide substrate was conjugated with biotin, which binds to the streptavidin-coated well of the plate, placing the H4 peptide in close proximity to the side well and the scintillant. The transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine to the bound histone H4 peptide generated a radiolabeled histone H4, which was quantitated by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions also were conducted in the absence of MTA. Briefly, compounds of the present invention were solubilized in 100% DMSO at a highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC50 determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound was 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRMT5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity, 3 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex (Reaction Biology Corporation) was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 40 nM histone H4 peptide (amino acids 1-15)-Biotin conjugate for 20 min at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM tritiated S-adenosyl methionine (final concentration) and the reaction is allowed to proceed for 20 min. The reaction was stopped and the amount of bound, tritiated H4 peptide in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter. The IC50 value for each compound was calculated from each 10-point dose-response curve for samples plus and minus MTA using GraphPad Prism software.
- PRMT5:MEP50 FlashPlate Assay without MTA The assay uses purified human, PRMT5 enzyme to convert S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine plus histone H4 L-arginine to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine plus histone H4 [methyl-3H]-L-arginine. The assay was carried out using Streptavidin-coated FlashPlates (Perkin Elmer), which contained a scintillant embedded in the plastic of the plate. The histone H4 peptide substrate was conjugated with biotin, which binds to the streptavidin-coated well of the plate, placing the H4 peptide in close proximity to the side well and the scintillant. The transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine to the bound histone H4 peptide generated a radiolabeled histone H4, which was quantitated by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions also were conducted to determine whether the compounds exhibit MTA-cooperative activity. Briefly, compounds of the present invention were solubilized in 100% DMSO at a highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC50 determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound was 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRMT5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity, 3 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex (Reaction Biology Corporation) was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 40 nM histone H4 peptide (amino acids 1-15)-Biotin conjugate for 20 min at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM tritiated S-adenosyl methionine (final concentration) and the reaction is allowed to proceed for 20 min. The reaction was stopped and the amount of bound, tritiated H4 peptide in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter. The IC50 value for each compound was calculated from each 10-point dose-response curve for samples minus MTA using GraphPad Prism software.
- ChEMBL_1711276 (CHEMBL4121325) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues) /human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using substrate pretreated for 15 mins followed by substrate and [3H]-SAM addition measured after 60 mins by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_1989159 (CHEMBL4622706) Inhibition of recombinant Avi-tagged PRMT5 (2 to 637)/ His-tagged MEP50 (2 to 342) (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 cells using biotinylated H4R3 (Me1) peptide as substrate in presence of SAM preincubated for 60 mins followed by substrate addition after 150 mins by biochemical methylation assay
- PRMT5/MEP50 HotSpot Methyltransferase Assay Table 2: The assay used recombinant full-length histone H2A as the substrate of PRMT5. Enzymatic transfer of the tritiated methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-[methyl-3H]methionine (3H-SAM) to the histone H2A protein generated a radiolabeled histone H2A by measuring in a scintillation counter to determine the activity of PRMT5 enzyme in the presence and absence of compound. The assay reactions were conducted in the presence of 100 nM MTA. Briefly, compounds were solubilized in 100% DMSO at the highest concentration of 10 mM. For IC50 determinations, the initial starting concentration for the serial dilutions of each compound is 50 μM. Control samples lacking compound, PRTM5/MEP50 complex or various reaction components also were prepared and processed in parallel with compound test samples. SAH was used as a positive control for assay validation. To measure PRMT5 inhibitory activity, 1 nM PRTM5/MEP50 complex was preincubated with test compound in assay buffer containing 5 μM full-length histone H2A for 15 minutes at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was initiated by adding 1 μM 3H-SAM (final concentration) and the mixture was incubated at 30° C. for 1 hour. The reaction was stopped and transferred to filter paper for detection. The amount of tritiated H2A in each sample was determined using a scintillation counter.
- ChEBML_1663864 Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues) /human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using histone H4 as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate/S-adenosyl methionine addition measured after 60 mins by alpha LISA assay
- ChEMBL_1663864 (CHEMBL4013545) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues) /human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using histone H4 as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate/S-adenosyl methionine addition measured after 60 mins by alpha LISA assay
- ChEMBL_1775672 (CHEMBL4232664) Inhibition of human PRMT5 expressed in insect cells co-expressing His-tagged MEP50 using Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly- Lys-Gly-Gly-Lys-Gly-Leu-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-NH2 peptide as substrate after 4 hrs in presence of SAM by Transcreene EPIGEN methyltransferase assays
- ChEMBL_2163192 (CHEMBL5048053) Inhibition of MTA-bound human PRMT5 co-complexed with MEP50 using biotin labelled histone H4 peptide (1 to 15) as substrate assessed as inhibition of tritiated methyl group transfer from SAM to histone H4 preincubated for 20 mins followed by SAM addition and measured after 20 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_1775674 (CHEMBL4232666) Inhibition of human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end)/human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end) expressed in HEK293 cells using biotinylated H4 derived peptide as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition measured after 60 mins in presence of [3H]SAM by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1890798 (CHEMBL4392552) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (1 to 637 residue) /full length human N-terminal His tagged MEP50 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells assessed as reduction in methyl transfer from [3H]-SAM to biotinylated histone H4 peptide H-SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKVLRDK-Biotin measured after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1910923 (CHEMBL4413369) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues)/human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using H4 peptide as substrate preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate and [3H]SAM addition and measured after 1 hr by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2163191 (CHEMBL5048052) Inhibition of human PRMT5 co-complexed with MEP50 in absence of MTA using biotin labelled histone H4 peptide (1 to15) as substrate assessed as inhibition of tritiated methyl group transfer from SAM to histone H4 preincubated for 20 mins followed by SAM addition and measured after 20 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized in DMSO and serially diluted, using 3-fold dilutions, into 100% DMSO at a concentration 50-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Following dilution, 1 ul was added to an empty 96-well microtiter plate. PRMT5/MEP50 protein complex was combined with H4(1-21) peptide (SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKV) in PRMT5 assay buffer (50 mM Tris pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM TCEP) and 44 ul was added to the microtiter plate containing compound. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) was prepared by combining 3H labelled SAM with unlabelled SAM in PRMT5 assay buffer such that the final SAM concentration was 10 uM and the specific activity was 0.2 uCi/ul. The reaction was initiated by adding 5 ul of SAM stock to the microtiter plate. The final reaction conditions were 10 nM PRMT5/MEP50 complex, 200 nM peptide and 1 uM SAM. Following a 25 minute incubation at room temperature, the reaction was stopped with the addition of 100 uL of 20% TCA. The 3H-peptide product was captured using a 96-well filter plate (MSIPN4B, Millipore) and washed 5 times with PBS buffer. Scintillation fluid (100 ul) was added to the dried filter plate and counted in a liquid scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4-parameter dose response equation using Pfizer proprietary software.
- ChEMBL_1711283 (CHEMBL4121332) Inhibition of recombinant human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5 (2 to end residues) /human N-terminal His-tagged MEP50 (2 to end residues) expressed in HEK293F cells using biotinylated H4 derived peptide as substrate pretreated for 15 mins followed by substrate and [3H]-SAM addition measured after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting method
- PRMT5 Biochemical Assay The assays were all performed in a buffer consisting of 20 mM Bicine (pH=7.6), 1 mM TCEP, 0.005% BSG, and 0.002% Tween20, prepared on the day of use. Compounds in 100% DMSO (1 ul) were spotted into a polypropylene 384-well V-bottom plates (Greiner) using a Platemate Plus outfitted with a 384-channel head (Thermo Scientific). DMSO (1 ul) was added to Columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows A-H for the maximum signal control and 1 ul of SAH, a known product and inhibitor of PRMT5/MEP50, was added to columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows I-P for the minimum signal control. A cocktail (40 ul) containing the PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme and the peptide was added by Multidrop Combi (Thermo-Fisher). The compounds were allowed to incubate with PRMT5/MEP50 for 30 min at 25 degrees Celsius, then a cocktail (10 ul) containing 3H-SAM was added to initiate the reaction (final volume=51 ul). The final concentrations of the components were as follows: PRMT5/MEP50 was 4 nM, 3H-SAM was 75 nM, peptide was 40 nM, SAH in the minimum signal control wells was 100 uM, and the DMSO concentration was 1%. The assays were stopped by the addition of non-radioactive SAM (10 ul) to a final concentration of 600 uM, which dilutes the 3H-SAM to a level where its incorporation into the peptide substrate is no longer detectable. 50 ul of the reaction in the 384-well polypropylene plate was then transferred to a 384-well Flashplate and the biotinylated peptides were allowed to bind to the streptavidin surface for at least 1 hour before being washed three times with 0.1% Tween20 in a Biotek ELx405 plate washer. The plates were then read in a PerkinElmer TopCount plate reader to measure the quantity of 3H-labeled peptide bound to the Flashplate surface, measured as disintegrations per minute (dpm) or alternatively, referred to as counts per minute (cpm).
- PRMT5 Biochemical Assay The assays were all performed in a buffer consisting of 20 mM Bicine (pH=7.6), 1 mM TCEP, 0.005% BSG, and 0.002% Tween20, prepared on the day of use. Compounds in 100% DMSO (1 ul) were spotted into a polypropylene 384-well V-bottom plates (Greiner) using a Platemate Plus outfitted with a 384-channel head (Thermo Scientific). DMSO (1 ul) was added to Columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows A-H for the maximum signal control and 1 ul of SAH, a known product and inhibitor of PRMT5/MEP50, was added to columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows I-P for the minimum signal control. A cocktail (40 ul) containing the PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme and the peptide was added by Multidrop Combi (Thermo-Fisher). The compounds were allowed to incubate with PRMT5/MEP50 for 30 min at 25 degrees Celsius, then a cocktail (10 ul) containing 3H-SAM was added to initiate the reaction (final volume=51 ul). The final concentrations of the components were as follows: PRMT5/MEP50 was 4 nM, 3H-SAM was 75 nM, peptide was 40 nM, SAH in the minimum signal control wells was 100 uM, and the DMSO concentration was 1%. The assays were stopped by the addition of non-radioactive SAM (10 ul) to a final concentration of 600 uM, which dilutes the 3H-SAM to a level where its incorporation into the peptide substrate is no longer detectable. 50 ul of the reaction in the 384-well polypropylene plate was then transferred to a 384-well Flashplate and the biotinylated peptides were allowed to bind to the streptavidin surface for at least 1 hour before being washed three times with 0.1% Tween20 in a Biotek ELx405 plate washer. The plates were then read in a PerkinElmer TopCount plate reader to measure the quantity of 3H-labeled peptide bound to the Flashplate surface, measured as disintegrations per minute (dpm) or alternatively, referred to as counts per minute (cpm).
- PRMT5-MEP50 Enzyme Methylation Assay 1 PRMT5/MEP50 biochemical assay is a direct measurement of the methylation activity of the enzyme complex on a short peptide substrate derived from the N-terminus of H4 histone. Methylation experiment is performed with recombinant protein. The assessment of inhibitory effect (IC50) of small molecules is measured by the effectiveness of the compounds to inhibit this reaction.In this assay, the potency (IC50) of each compound was determined from a twenty-point (1:2 serial dilution; top compound concentration of 100000 nM) titration curve using the following outlined procedure. To each well of a white ProxiPlus 384 well-plate, 100 nL of compound (1% DMSO in final assay volume of 10 μL) was dispensed, followed by the addition of 8 μL of 1× assay buffer (50 mM Bicine pH 8.0, 1 mM DTT, 0.004% Tween20, 0.01% BSA) containing 0.5 nM of Full-length (FL)-PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex (recombinant proteins from baculovirus-transfected Sf21 cells: FL-PRMT5; MW=73837 kDa). Plates were sealed and placed in a 37° C. humidified chamber for 30 minutes pre-incubation with compounds. Subsequently, each reaction was initiated by the addition of 2 μL 1× assay buffer containing 75 nM biotinylated H4R3(Me1) peptide, and 15 μM S-(5′-Adenosyl)-L-Methionine Chloride (SAM). The final reaction in each well of 10 μL consists of 0.5 nM PRMT5-MEP50, 75 nM biotinylated-peptide, and 15 μM. Methylation reactions were allowed to proceed for 150 minutes in a sealed plate at 37° C. Reactions were immediately quenched by the addition of 1 μL of 10% formic acid. Plates were then frozen and shipped to SAMDI Tech Inc. to determine the percent conversion from K4R3(Me1) to K4R3(Me2). IC50 values were determined by 7 parameters biphasic fit model plotting the percent product conversion vs. (Log10) compound concentrations.
- PRMT5/MEP50 Enzyme Assay The assays were all performed in a buffer consisting of 20 mM Bicine (pH=7.6), 1 mM TCEP, 0.005% BSG, and 0.002% Tween20, prepared on the day of use. Compounds in 100% DMSO (1 ul) were spotted into a polypropylene 384-well V-bottom plates (Greiner) using a Platemate Plus outfitted with a 384-channel head (Thermo Scientific). DMSO (1 ul) was added to Columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows A-H for the maximum signal control and 1 ul of SAH, a known product and inhibitor of PRMT5/MEP50, was added to columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows I-P for the minimum signal control. A cocktail (40 ul) containing the PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme and the peptide was added by Multidrop Combi (Thermo-Fisher). The compounds were allowed to incubate with PRMT5/MEP50 for 30 min at 25 degrees Celsius, then a cocktail (10 ul) containing 3H-SAM was added to initiate the reaction (final volume=51 ul). The final concentrations of the components were as follows: PRMT5/MEP50 was 4 nM, 3H-SAM was 75 nM, peptide was 40 nM, SAH in the minimum signal control wells was 100 uM, and the DMSO concentration was 1%. The assays were stopped by the addition of non-radioactive SAM (10 ul) to a final concentration of 600 uM, which dilutes the 3H-SAM to a level where its incorporation into the peptide substrate is no longer detectable. 50 ul of the reaction in the 384-well polypropylene plate was then transferred to a 384-well Flashplate and the biotinylated peptides were allowed to bind to the streptavidin surface for at least 1 hour before being washed three times with 0.1% Tween20 in a Biotek ELx405 plate washer. The plates were then read in a PerkinElmer TopCount plate reader to measure the quantity of 3H-labeled peptide bound to the Flashplate surface, measured as disintegrations per minute (dpm) or alternatively, referred to as counts per minute (cpm).
- PRMT5/MEP50 Enzyme Assays on Peptide Substrates The assays were all performed in a buffer consisting of 20 mM Bicine (pH=7.6), 1 mM TCEP, 0.005% BSG, and 0.002% Tween20, prepared on the day of use. Compounds in 100% DMSO (1 ul) were spotted into a polypropylene 384-well V-bottom plates (Greiner) using a Platemate Plus outfitted with a 384-channel head (Thermo Scientific). DMSO (1 ul) was added to Columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows A-H for the maximum signal control and 1 ul of SAH, a known product and inhibitor of PRMT5/MEP50, was added to columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows I-P for the minimum signal control. A cocktail (40 ul) containing the PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme and the peptide was added by Multidrop Combi (Thermo-Fisher). The compounds were allowed to incubate with PRMT5/MEP50 for 30 min at 25 degrees Celsius, then a cocktail (10 ul) containing 3H-SAM was added to initiate the reaction (final volume=51 ul). The final concentrations of the components were as follows: PRMT5/MEP50 was 4 nM, 3H-SAM was 75 nM, peptide was 40 nM, SAH in the minimum signal control wells was 100 uM, and the DMSO concentration was 1%. The assays were stopped by the addition of non-radioactive SAM (10 ul) to a final concentration of 600 uM, which dilutes the 3H-SAM to a level where its incorporation into the peptide substrate is no longer detectable. 50 ul of the reaction in the 384-well polypropylene plate was then transferred to a 384-well Flashplate and the biotinylated peptides were allowed to bind to the streptavidin surface for at least 1 hour before being washed three times with 0.1% Tween20 in a Biotek ELx405 μlate washer. The plates were then read in a PerkinElmer TopCount plate reader to measure the quantity of 3H-labeled peptide bound to the Flashplate surface, measured as disintegrations per minute (dpm) or alternatively, referred to as counts per minute (cpm).
- ChEMBL_2076027 (CHEMBL4731561) Inhibition of full-length human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5/full length N-terminal His6-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells assessed as reduction of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine formation using human recombinant histone H2A (1 to 130 residues) and S-adenosyl-L-methionine as substrate after 60 mins by rapidfire mass spectrometry analysis
- HTRF Binding Assay Table A1: A recombinant human dual expressed Avi PRMT5/His-MEP50) protein (corresponding to amino acids for PRMT5 2-637, and 2-342 for MEP50 expressed in baculovirus) was incubated with target fragments in final buffer (25 mM ADA pH 7.2, 30 μM MTA, 1 mM TCEP, 50 mM NaCl, 0.002% Tween, 5 nM proprietary Tracer binding compound prepared in-house), overnight at 2-8° C. After overnight incubation the binding is monitored after the addition of 0.5 nM Anti-His-Tb (Cisbio) after 1 hr incubation at RT (˜20-24 hrs total binding time). The HTRF signal was measured using a Clariostar reader (BMG) excitation filter (Ex Tr), dichroic filter (LP TP) and emission filters (F 665-10 and F 620-10) manufacturer's instructions.
- ChEMBL_1890807 (CHEMBL4392561) Inhibition of full-length human N-terminal FLAG-tagged PRMT5/full length N-terminal His6-tagged MEP50 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 insect cells assessed as reduction of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine formation using human recombinant histone H2A (1 to 130 residues) as substrate after 1 hr in the presence of S-adenosyl-L-methionine by high throughput mass spectrometry
- ChEMBL_2026542 (CHEMBL4680700) Inhibition of human full length FLAG-tagged PRMT5/human His6-tagged MEP50 expressed in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells assessed as reduction in tritium incorporation into peptide substrate using human Histone H4 (1 to 15 residues) and [3H]SAM as substrate preincubated with enzyme and H4 for 30 mins followed by [3H]SAM addition and measured after 120 mins by radioactive flashplate assay
- PRMT5 Inhibitory Activity Assay In Vitro 1. Enzyme Reaction Process(1) 1× Assay buffer (modified Tris buffer) was configured.(2) Dilute compound: the compound was dissolved in 100% DMSO and the compound solution was added to a 384-well plate using Echo 550.(3) Configure enzyme solution: PRMT5 was added to 1× assay buffer to prepare enzyme solution 1; PRMT5 and MTA was added to 1× assay buffer to prepare enzyme solution 2.(4) Configure substrate solution: peptide segments and [3H]—SAM was added to 1× assay buffer.(5) 15 μL of enzyme solution was added to the 384-well plate, and 15 μL of 1× assay buffer was added to the negative control well, and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes.(6) 15 μL of substrate solution was added to each well, and incubated at room temperature for 90 minutes.(7) Configure termination reaction solution: pre-cooled SAM was added to 1× assay buffer.(8) 10 μL of termination reaction solution was added to each well to terminate the reaction.(9) 25 μL/well of the mixed solution was transferred to Flashplate and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature.(10) the Flashplate three was washed times with dH2O+0.1% Tween-20 solution.(11) the radiometric values was readed with Microbeta.
- Enzyme Assay The assays were all performed in a buffer consisting of 20 mM Bicine (pH=7.6), 1 mM TCEP, 0.005% BSG, and 0.002% Tween20, prepared on the day of use. Compounds in 100% DMSO (1 ul) were spotted into a polypropylene 384-well V-bottom plates (Greiner) using a Platemate Plus outfitted with a 384-channel head (Thermo Scientific). DMSO (1 ul) was added to Columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows A-H for the maximum signal control and 1 ul of SAH, a known product and inhibitor of PRMT5/MEP50, was added to columns 11, 12, 23, 24, rows I-P for the minimum signal control. A cocktail (40 ul) containing the PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme and the peptide was added by Multidrop Combi (Thermo-Fisher). The compounds were allowed to incubate with PRMT5/MEP50 for 30 min at 25 degrees Celsius, then a cocktail (10 ul) containing 3H-SAM was added to initiate the reaction (final volume=51 ul). The final concentrations of the components were as follows: PRMT5/MEP50 was 4 nM, 3H-SAM was 75 nM, peptide was 40 nM, SAH in the minimum signal control wells was 100 uM, and the DMSO concentration was 1%. The assays were stopped by the addition of non-radioactive SAM (10 ul) to a final concentration of 600 uM, which dilutes the 3H-SAM to a level where its incorporation into the peptide substrate is no longer detectable. 50 ul of the reaction in the 384-well polypropylene plate was then transferred to a 384-well Flashplate and the biotinylated peptides were allowed to bind to the streptavidin surface for at least 1 hour before being washed three times with 0.1% Tween20 in a Biotek ELx405 plate washer.
- Enzyme Methylation Assay In this assay, the potency (IC50) of each compound was determined from a twenty-point (1:2 serial dilution; top compound concentration of 100000 nM) titration curve using the following outlined procedure. To each well of a white ProxiPlus 384 well-plate, 100 nL of compound (1% DMSO in final assay volume of 10 μL) was dispensed, followed by the addition of 8 μL of 1× assay buffer (50 mM Bicine pH 8.0, 1 mM DTT, 0.004% Tween20, 0.01% BSA) containing 0.5 nM of Full-length (FL)-PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex (recombinant proteins from baculovirus-transfected Sf21 cells: FL-PRMT5; MW=73837 kDa and FL-MEP50; MW=38614). Plates were sealed and placed in a 37° C. humidified chamber for 30 minutes pre-incubation with compounds. Subsequently, each reaction was initiated by the addition of 2 μL 1× assay buffer containing 75 nM biotinylated H4R3(Me1) peptide, and 15 μM S-(5′-Adenosyl)-L-Methionine Chloride (SAM). The final reaction in each well of 10 μL consists of 0.5 nM PRMT5-MEP50, 75 nM biotinylated-peptide, and 15 μM SAM. Methylation reactions were allowed to proceed for 150 minutes in a sealed plate at 37° C. Reactions were immediately quenched by the addition of 1 μL of 10% formic acid. Plates were then frozen and shipped to SAMDI Tech Inc. to determine the percent conversion from K4R3(Me1) to K4R3(Me2).
- PRMT5-MEP50 Enzyme Methylation Assay 2 PRMT5/MEP50 biochemical assay is a direct measurement of the methylation activity of the enzyme complex on a short peptide substrate derived from the N-terminus of H4 histone. Methylation experiment is performed with recombinant protein. The assessment of inhibitory effect (IC50) of small molecules is measured by the effectiveness of the compounds to inhibit this reaction.In this assay, the potency (IC50) of each compound was determined from a twenty-point (1:2 serial dilution; top compound concentration of 100000 nM) titration curve using the following outlined procedure. To each well of a white ProxiPlus 384 well-plate, 100 nL of compound (1% DMSO in final assay volume of 10 μL) was dispensed, followed by the addition of 8 μL of 1× assay buffer (50 mM Bicine pH 8.0, 1 mM DTT, 0.004% Tween20, 0.01% BSA) containing 0.5 nM of Full-length (FL)-PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex (recombinant proteins from baculovirus-transfected Sf21 cells: FL-MEP50; MW=38614). Plates were sealed and placed in a 37° C. humidified chamber for 30 minutes pre-incubation with compounds. Subsequently, each reaction was initiated by the addition of 2 μL 1× assay buffer containing 75 nM biotinylated H4R3(Me1) peptide, and 15 μM S-(5′-Adenosyl)-L-Methionine Chloride (SAM). The final reaction in each well of 10 μL consists of 0.5 nM PRMT5-MEP50, 75 nM biotinylated-peptide, and 15 μM. Methylation reactions were allowed to proceed for 150 minutes in a sealed plate at 37° C. Reactions were immediately quenched by the addition of 1 μL of 10% formic acid. Plates were then frozen and shipped to SAMDI Tech Inc. to determine the percent conversion from K4R3(Me1) to K4R3(Me2). IC50 values were determined by 7 parameters biphasic fit model plotting the percent product conversion vs. (Log10) compound concentrations.
- PRMT5-MEP50 Enzyme Activity The histone H4 peptide was diluted with carbonate-bicarbonate buffer and prepared to 100 μg/mL, and then dispensed onto the plate per 100 μL and reacted at 37° C. for 1 hour. PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex and S-adenosylmethionine were diluted with histone methyltransferase reaction buffer to prepare 5 μg/mL and 2 μM, respectively, and then 20 μL of PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex and 25 μL of S-adenosylmethionine were dispensed onto the plate prepared above. 5 μL of the compound diluted with 10% dimethyl sulfoxide solution was added thereto and reacted at room temperature for 2 hours (final volume=50 μL). The concentration of the compound was diluted 1:5 from 10 μM until the lowest concentration of 0.128 nM, and 8 points were used for the test. After preparing the primary antibody by diluting 1:2000 with blocking buffer, 100 μL was added to the plate and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour. After preparing horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody by diluting 1:10,000 with blocking buffer, 100 μL was added to the plate and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour. 100 μL of TMB substrate was added and reacted for 3 minutes at room temperature, and 100 μL of 1 N sulfuric acid was then added to terminate the reaction. Then, the absorbance at 450 nm was measured to calculate the IC50 value of the compound.
- Biochemical Assay Molecular Biology: Full-length human PRMT5 (NM_006109.3) transcript variant 1 clone was amplified from a fetal brain cDNA library, incorporating flanking 5′ sequence encoding a FLAG tag (MDYKDDDDK) (SEQ ID NO.:4) fused directly to Ala 2 of PRMT5. Full-length human MEP50 (NM_024102) clone was amplified from a human testis cDNA library incorporating a 5′ sequence encoding a 6-histidine tag (MHHHHHH) (SEQ ID NO.:5) fused directly to Arg 2 of MEP50. The amplified genes were sublconed into pENTR/D/TEV (Life Technologies) and subsequently transferred by Gateway attL×attR recombination to pDEST8 baculvirus expression vector (Life Technologies).Protein Expression. Recombinant baculovirus and Baculovirus-Infected Insect Cells (BIIC) were generated according to Bac-to-Bac kit instructions (Life Technologies) and Wasilko, 2006, respectively. Protein over-expression was accomplished by infecting exponentially growing Spodoptera frugiperda (SF9) cell culture at 1.2×106 cell/ml with a 5000 fold dilution of BIIC stock. Infections were carried out at 27° C. for 72 hours, harvested by centrifugation, and stored at −80° C. for purification.
- AlphaLISA Enzyme Inhibitory Assay General Procedure for PRMT5/MEP50 AlphaLISA Enzyme Inhibitory Assays: Assays were performed in the buffer consisting of 50 mM Tris, pH 8.5, 5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM NaCl with 0.01% Tween20 and 1 mM DTT added right before the assay. 2.5 μL of compound solution in the assay buffer with 4% DMSO and 5 μL of PRMT5/MRP50 complex/SAM mixture solution in the assay buffer which was pre-incubated for 30 minutes were added into a white low volume 384 well microtiter plate. This mixture solution was incubated for 15 minutes with gentle shaking at room temperature. Methyl transfer reaction was initiated by adding 2.5 μL of Biotin-H4 (1-21) peptide substrate solution in the assay buffer. Final concentrations of PRMT5/MEP50, SAM, Biotin-H4 peptide substrate, and DMSO were 25 nM, 10 μM, 30 nM, and 1%, respectively. The reaction was allowed to perform for 120 minutes in dark with gentle shaking at room temperature after which 5 μL of Anti-H4R3-Me AlphaLISA acceptor beads in detection buffer from the manufacturer was added into the reaction mixture followed by incubation for 60 minutes. 10 μL of Streptavidin labeled AlphaLISA donor beads in detection buffer was added into the mixture followed by 30 minute incubation. Final acceptor and donor beads concentrations were 10 μg/mL. Plates were read on an Envision multimode plate reader from PerkinElmer (Waltham Mass., USA) with an excitation wavelength of 680 nm and emission wavelength of 615 nm. IC50 values of inhibitors were obtained by fitting the fluorescence intensity vs inhibitor concentrations in a sigmoidal dose-response curve (variable slopes, four parameters) using Prism 7.
- Enzyme Inhibition Assay Assay 1: Compounds were tested for inhibition of methyltransferase activity in a radioisotope filter binding assay, similar to previously described in A selective inhibitor of PRMT5 with in vivo and in vitro potency in MCL models. Chan-Penebre et al., Nat Chem Biol. (2015) 11(6):432-7. In the standard PRMT5/MEP50 enzyme inhibition assay, compounds were tested in a 10-dose IC50 mode with 3- or 5-fold serial dilution, in singlet, starting at 1, 10, or 100 μM. Control compound, SAH (S-(5′-Adenosyl)-L-homocysteine), was tested in 10-dose IC50 mode with 3-fold serial dilution starting at 100 μM. Reactions were carried out at 1 μM 3H-SAM (PerkinElmer) and 5 μM histone H2A as substrates for methyl transfer. Following a 60 min incubation at 30° C., the reaction was stopped with 20% TCA. Each reaction was spotted on a filter plate (Multiscreen FB Filter plate, Millipore) and washed 5 times in PBS, after which scintillation fluid was added and signal was detected in a scintillation counter. Percent enzyme activity was calculated based on no inhibitor DMSO control as 100% activity. EC50 values were determined in GraphPad Prism 8 using the [inhibitor] vs. response Variable slope (four parameters) function.
- Biochemical Assay General Materials.S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), bicine, KCl, Tween20, dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), bovine skin gelatin (BSG), and Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride solution (TCEP) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich at the highest level of purity possible. 3H-SAM was purchase from American Radiolabeled Chemicals with a specific activity of 80 Ci/mmol. 384-well streptavidin Flashplates were purchased from PerkinElmer.Substrates.Peptide representative of human histone H4 residues 1-15 was synthesized with a C-terminal linker-affinity tag motif and a C-terminal amide cap by 21st Century Biochemicals. The peptide was high high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) purified to greater than 95% purity and confirmed by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS). The sequence was Ac-SGRGKGGKGLGKGGA[K-Biot]-amide (SEQ ID NO.:3).Molecular Biology:Full-length human PRMT5 (NM_006109.3) transcript variant 1 clone was amplified from a fetal brain cDNA library, incorporating flanking 5′ sequence encoding a FLAG tag (MDYKDDDDK) (SEQ ID NO.:4) fused directly to Ala 2 of PRMT5. Full-length human MEP50 (NM_024102) clone was amplified from a human testis cDNA library incorporating a 5′ sequence encoding a 6-histidine tag (MHHHHHH) (SEQ ID NO.:5) fused directly to Arg 2 of MEP50. The amplified genes were sublconed into pENTR/D/TEV (Life Technologies) and subsequently transferred by Gateway attL×attR recombination to pDEST8 baculvirus expression vector (Life Technologies).
- Determination of the value of binding affinity constant (KO between the compound and BRD4 BD2 protein The purity of BRD4 BD2 protein used in the experiment was greater than 95%, and the protein concentration was 46.33 uM. The 96-well plate was purchased from Corning (black, #3694). The multifunctional microplate reader was a product of TECAN, model: SPARK 10M. Buffer: 100 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.5), 2% ethylene glycol (Sigma) and 0.01% Trition X-100 (Sigma). The experimental water was Millipore-Q pure water.The Ki value of the compound and BRD4 BD2 protein was measured according to the FP test procedures for detecting the Ki value of the compound and BRD4 BD1 protein except that the BRD4 BD1 protein was replaced with the BRD4 BD2 protein.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 0.002% Tween20, 1 mM TCEP, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 30 μl in assay buffer, with 300 nM histone H4 based AcH4-23 (Anaspec: AS-65002) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 2.5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 20 minutes at 37° C. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer: NET155001MC) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 30 minutes incubation at 37° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 25 μL of 8M Guanidine HCl. Prepare streptavidin YSI SPA beads (Perkinelmer: RPNQ0012) at 0.3 mg/mL in assay buffer. To each reaction, add 150 μL of SPA beads suspension, and incubated while shaking at room temperature for 30 minutes. The plate was centrifuged at 100×g for 30 second before reading in a scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4 parameters with Hill Slope using GraphPad Prism software. See Table 2, below (PRMT5 IC50).
- Enzyme Activity Assay Experimental procedure: The histone H4 peptide was diluted with carbonate-bicarbonate buffer and prepared to 100 μg/mL, and then dispensed onto the plate per 100 μL and reacted at 37° C. for 1 hour. PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex and S-adenosylmethionine were diluted with histone methyltransferase reaction buffer to prepare 5 μg/mL and 2 μM, respectively, and then 20 μL of PRMT5-MEP50 enzyme complex and 25 μL of S-adenosylmethionine were dispensed onto the plate prepared above. 5 μL of the compound diluted with 10% dimethyl sulfoxide solution was added thereto and reacted at room temperature for 2 hours (final volume=50 μL). The concentration of the compound was diluted 1:5 from 10 μM until the lowest concentration of 0.128 nM, and 8 points were used for the test. After preparing the primary antibody by diluting 1:2000 with blocking buffer, 100 μL was added to the plate and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour. After preparing horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody by diluting 1:10,000 with blocking buffer, 100 μL was added to the plate and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour. 100 μL of TMB substrate was added and reacted for 3 minutes at room temperature, and 100 μL of 1 N sulfuric acid was then added to terminate the reaction.
- Evaluation of the inhibitory activity against PRMT5 enzyme activity A 1× enzyme reaction buffer (10 mM Tris 8.0 (Sigma, Cat. No. T2694-1L), 0.01% Tween-20 (Sigma, Cat. No. P2287-100ML), and 1 mM DTT (Sigma, Cat. No. D0632-10G)) was prepared. PRMT5 (Active Motif, Cat. No. 31921) and [3H]—SAM (PerkinElmer, Cat. No. NET155VO01MC) were added to the 1× enzyme reactionbuffer, to prepare a 25/15× mixed solution (PRMT5 final concentration: 5 nM, [3H]—SAM final concentration: 0.3 μM). 15 L of this solution was transferred into a 384-well microplate (Corning 384-well Polypropylene Storage Microplates, Cat. No. 3657) with various concentrations of the compounds (DMSO final concentration 1%), and incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes. A polypeptide substrate, GL-27 (Ac-SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKVGG-K) (Biotin) (GL Biochem, Cat. No. 342095), was added into the 1× enzyme reaction buffer to prepare a 25/10× substrate solution. Then 10 μL of the polypeptide substrate solution (final concentration of the polypeptide substrate: 100 nM) was added, the reaction was performed at room temperature for 120 minutes, and then 5 μL 6× ice cold SAM (Sigma, Cat. No. A7007-100MG) solution was added to stop the reaction (SAM final concentration: 0.125 mM). 25 μL of the reaction system was transferred into a FlashPlate (Streptavidin FlashPlate HTS PLUS, High Capacity, 384-well, Perkin Elmer, Cat. No. SMP410A001PK), and incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. After washed three times with distilled water containing 0.1% Tween-20, the microplate was read on a MicroBeta reader for CPM data (Counts Per Minute). After the CPM original data of the compounds at various concentrations were obtained, the data were normalized according to Inh %=(Max−Sample)/(Max−Min)*100%, and the enzyme activity inhibition rate Inh % at each concentration point was obtained (wherein Max was the CPM value of a positive well with the enzyme, Min was the CPM value of a negative well without the enzyme, and Sample was the CPM value of the sample well treated with the compounds). Then the inhibition rate Inh % (Y) corresponding to each concentration (X) was input in EXCEL, and the IC 50 value (the half inhibitory concentration) of each compound was calculated with the XLfit plug-in according to the built-in four-parameter fitting equation Y=Bottom+(Top−Bottom)/(1+(IC50/X)*HillSlope).
- PRMT5 Cell Target Engagement (TE) Assay The PRMT5 TE assay is a biomarker assay for identifying compounds that inhibit symmetric dimethylation of arginine (SDMA) of PRMT5 substrates. This assay detects symmetrically dimethylated nuclear proteins using high content imaging technology. Detection of the expression of symmetrically dimethylated nucleo proteins is through a mixture of primary rabbit monoclonal antibodies to SDMA (CST 13222), which in turn recognized by an Alexafluor 488 dye-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody. The IN Cell Analyzer 2200 measures nuclear Alexafluor 488 fluorescent dye intensity that is directly related to the level of expression of symmetrically dimethylated nuclear proteins at the single cell level. Nuclear AF488 dye intensities are compared to the mean value for DMSO treated cells (MIN) to report percent of inhibition for each compound-treated well.In this assay, the cell potency (EC50) of each compound was determined from a ten point (1:3 serial dilution; top compound concentration of 10000 nM) titration curve using the following outlined procedure. Each well of a BD falcon collagen coated black/clear bottom 384-well plate was seeded with 4000 MCF-7 cells and allowed to attach for 5 hours. Media from cell plate was removed at 0.5 mm above the bottom of the plate and replaced with 30 μL of fresh media containing 1.2× compounds in 0.1% DMSO. Cells were treated for 3 days in 37° C. CO2 incubator. On day 3, cells were fixed with Cytofix, permeablized with 0.4% Triton-X-100/Cytofix, and washed with D-PBS without Ca/Mg. Cells were blocked with Licor Odessey blocking reagent for one hour at room temperature, followed by incubation with anti-SDMA (1:1000) antibody at 4° C. overnight. 1° antibody was removed, followed by three washings with DPBS without Ca/Mg and 0.05% Tween20. Hoechst (5 μg/ml), Cell Mask deep stain (1:2000) and Alexa488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (2 μg/mL) was added for 1 hour at room temperature. A final washing step (three washes) was performed before sealing plate for imaging on In Cell Analyzer 2200. Images from analyzer were uploaded to Columbus (at WP) for image analysis. IC50 values were determined by 4 parameters robust fit of percent fluorescence units vs. (Log10) compound concentrations.
- Test on the inhibitory activity of the compounds of the invention against PRMT5 enzyme by radioisotopic method Test method: A 1× enzyme reaction buffer (10 mM Tris 8.0 (Sigma, Cat. No. T2694-1L), 0.01% Tween-20 (Sigma, Cat. No. P2287-100 ML), 1 mM DTT (Sigma, Cat. No. D0632-10G)) was prepared. PRMT5 (Active Motif, Cat. No. 31921) and [3H]SAM (PerkinElmer, Cat. No. NET155V001MC) were added to the 1×enzyme reaction buffer, to prepare a 25/15× mixed solution (PRMT5 final concentration: 5 nM, [3H]SAM final concentration: 0.3 μM). 15 μL of this solution was transferred into a 384-well microplate (Corning 384-well Polypropylene Storage Microplates, Cat. No. 3657) with various concentrations of the compounds (DMSO final concentration 1%), and incubated at room temperature for 60 minutes. A polypeptide substrate, GL-27 (Ac-SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKVGG-K (Biotin) (GL Biochem, Cat. No. 342095)), was added into the 1×enzyme reaction buffer to prepare a 25/10× substrate solution. Then 10 μL of the polypeptide substrate solution (final concentration of the polypeptide substrate: 100 nM) was added, a reaction was stirred at room temperature for 120 minutes, and then 5 μL 6× ice cold SAM (Sigma, Cat. No. A7007-100 MG) solution was added to stop the reaction (SAM final concentration: 0.125 mM). 25 L of the reaction mixture was transferred into a FlashPlate (Streptavidin FlashPlate HTS PLUS, High Capacity, 384-well, Perkin Elmer, Cat. No. SMP410A001PK), and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. After washed three times with distilled water containing 0.1% Tween-20, the microplate was read on a MicroBeta reader for CPM data (Counts Per Minute). After the CPM raw data of the compounds at various concentrations were obtained, the data were normalized according to Inh %=(Max-Sample)/(Max-Min)*100%, and the enzyme activity inhibition rate Inh % at each concentration point was obtained (wherein Max is the CPM value of a positive well with the enzyme, Min is the CPM value of a negative well without the enzyme, and Sample is the CPM value of the sample well treated with the compounds). Then the inhibition rate Inh % (Y) corresponding to each concentration (X) was input in EXCEL, and the IC50 value (the half maximal inhibitory concentration) of each compound was calculated with the XLfit plug-in according to the built-in four-parameter fitting equation Y=Bottom+(Top-Bottom)/(1+(IC50/X)*HillSlope).
- The radiometric assay for PRMT5 After dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide respectively, the test compounds were added into an Echo Qualified 384-well plate and diluted to the desired concentrations. The diluted test compounds were transferred from the Echo Qualified 384-well plate to a 384-well reaction plate using an Echo 550 instrument, and dimethyl sulfoxide was transferred into both the control and blank wells. PRMT5 was added to 1×reaction buffer (including 10 mM Tris-HCl; pH 8.0; 0.01% Tween-20; 1 mM DTT) to form a 1.67× enzyme solution (at an enzyme concentration of 5 nM). A polypeptide substrate and [3H]-SAM were added to 1× reaction buffer to form a 2.5× substrate solution (the terminal concentrations of the substrates were 100 nM and 250 nM, respectively). At a volume of 15 μL/well, the 1.67× enzyme solution was added into wells of the 384-well reaction plate. In case of the blank wells, the enzyme solution was replaced with 15 L of the 1× reaction buffer. The reaction plate was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 1 min, and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. To each well of the 384-well reaction plate, 10 L of the 2.5× substrate solution was added, centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 1 min, and reacted at 25° C. for 60 min. To each well of the 384-well reaction plate, 5 L of reaction stop solution (which was 125 μM cold SAM solution) was added to terminate the reaction. From each well of the test plate, 25 μL was measured and transferred to Flashplate and left at room temperature for 1 h. Thereafter, the Flashplate was washed with 0.1% Tween-20 solution three times. Readings were taken with MicroBeta 2. The data was converted into the inhibition rate data.
- PRMT5 Biochemical Assay A histone H4 derived peptide is used as substrate (amino acid sequence: Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Lys-Gly-Leu-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-NH2). Full-length PRMT5 enzyme (NCBI Reference sequence NP_006100.2) was co-expressed with His6-MEP50 in insect cells and purified via Nickel immobilized metal affinity and gel filtration chromatography ( the enzyme ).The 6 μL reactions are run in Greiner brand black 384-well low volume assay plates. All reactions contained assay buffer (phosphate buffered saline, 0.01% (v/v) Tween-20, 0.01% (w/v) albumin from chicken egg white, 1 mM Dithiothreitol, 1 μM peptide substrate, 1 μM S-Adenosyl methionine, and 15 ng/reaction enzyme, with the enzyme being omitted from negative control reactions. Compounds were added in a volume of 100 nL from dilution series prepared in DMSO, positive and negative control reactions receiving the same volume DMSO without compound. The plates were sealed with adhesive seals and incubated for 4 hours at 37 degree Celsius. Reaction progress was measured using the Transcreener EPIGEN methyltransferase assay (BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wis.) as recommended by the manufacturer. To each reaction 2 μL detection mix were added, containing coupling enzymes, fluorescence polarisation tracer, and AMP antibody. Plates were incubated for 90 minutes before being read on a PerkinElmer EnVision plate reader in fluorescence polarisation mode. IC50 values were obtained from the raw readings by calculating percent inhibition (%1) for each reaction relative to controls on the same plate (% I=(I−CN)/(CP−CN) where CN/CP are the averages of the negative/positive reactions, respectively), then fitting the % I data vs. compound concentration [I] to % l=(A+((B−A)/(1+((C/[I]){circumflex over ( )}D)))) where A is the lower asymptote, B is the upper asymptote, C is the IC50 value, and D is the slope.
- PRMT5 Biochemical Assay A histone H4 derived peptide is used as substrate (amino acid sequence: Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Lys-Gly-Leu-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-NH2). Full-length PRMT5 enzyme (NCBI Reference sequence NP_006100.2) was co-expressed with His6-MEP50 in insect cells and purified via Nickel immobilized metal affinity and gel filtration chromatography (“the enzyme”).The 6 μL reactions are run in Greiner brand black 384-well low volume assay plates. All reactions contained assay buffer (phosphate buffered saline, 0.01% (v/v) Tween-20, 0.01% (w/v) albumin from chicken egg white, 1 mM Dithiothreitol, 1 μM peptide substrate, 1 μM S-Adenosyl methionine, and 15 ng/reaction enzyme, with the enzyme being omitted from negative control reactions. Compounds were added in a volume of 100 nL from dilution series prepared in DMSO, positive and negative control reactions receiving the same volume DMSO without compound. The plates were sealed with adhesive seals and incubated for 4 hours at 37 degree Celsius. Reaction progress was measured using the Transcreener™ EPIGEN methyltransferase assay (BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wis.) as recommended by the manufacturer. To each reaction 2 μL detection mix were added, containing coupling enzymes, fluorescence polarisation tracer, and AMP antibody. Plates were incubated for 90 minutes before being read on a PerkinElmer EnVision™ plate reader in fluorescence polarisation mode. IC50 values were obtained from the raw readings by calculating percent inhibition (% I) for each reaction relative to controls on the same plate (% I=(I−CN)/(CP−CN) where CN/CP are the averages of the negative/positive reactions, respectively), then fitting the % I data vs. compound concentration [I] to % I=(A+((B−A)/(1+((C/[I]){circumflex over ( )}D)))) where A is the lower asymptote, B is the upper asymptote, C is the IC50 value, and D is the slope.
- PRMT5 Biomarker Assay The cell line TE11 was seeded at a density of 6,000 cells per well in 96 well optical quality tissue culture plates in DME medium and 10% foetal bovine serum, and allowed to adhere for 5 hours under standard culture conditions (37 degree Celsius, 5% CO2). Compound dilutions prepared in DMSO were added to the medium, with negative control wells reserved for treatment with DMSO only and maximum inhibition controls receiving a potent PRMT5 inhibitor compound at 1 μM concentration. After incubation for 72 hours, the cells were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature, washed with phosphate buffer saline and blocked with Odyssey blocking buffer (LI-COR, Lincoln, Nebr.). Rabbit anti-Di-Methyl Histone H4 Arginine 3 specific antibody (Epigentek) in Odyssey blocking buffer was added and incubated for 14 hours at 4 degree Celsius. After washing, anti-rabbit secondary antibody labelled with Alexa647 dye (LifeTechnologies) and Hoechst 33342 (1 μg/mL, SigmaAldrich) were added for 1 hour incubation. Plates were washed and read on a PerkinElmer Envision 2103 in fluorescence intensity scanning mode (24 scans across the well area). The plates were imaged on a PerkinElmer Phenix high content imaging platform. Using a Columbus image analysis pipeline, individual nuclei were located by Hoechst 33342 stain and the methylation level was calculated from the Alexa647-related intensity in the same area. IC50 values were obtained from the mean Alexa647-related intensity per cell by calculating percent inhibition (% I) for each well relative to controls on the same plate (% I=(I−CN)/(CP−CN) where CN/CP are the averages of the negative/maximum inhibition controls, respectively), then fitting the % I data vs. compound concentration [I] to [I] to % I=(A+((B−A)/(1+((C/[I]){circumflex over ( )}D)))) where A is the lower asymptote, B is the upper asymptote, C is the IC50 value, and D is the slope.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Brij35, 1 mM DTT, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 50 μl in assay buffer, with histone H2A (5 μM final) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 15 to 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 60 minutes incubation at 30° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of 20% TCA. Each reaction was spotted onto filter plate (Multi Screen FB Filter Plate, Millipore), and washed 5 times with PBS buffer, Scintillation fluid was added to the filter plate and read in a scintillation counter.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Brij35, 1 mM DTT, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 50 μl in assay buffer, with histone H2A (5 μM final) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 15 to 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 60 minutes incubation at 30° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of 20% TCA. Each reaction was spotted onto filter plate (MultiScreen FB Filter Plate, Millipore), and washed 5 times with PBS buffer, Scintillation fluid was added to the filter plate and read in a scintillation counter.
- HotSpot Assay HotSpot Assay. Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Brij35, 1 mM DTT, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 50 μl in assay buffer, with histone H2A (5 μM final) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 15 to 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 60 minutes incubation at 30° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of 20% TCA. Each reaction was spotted onto filter plate (MultiScreen FB Filter Plate, Millipore), and washed 5 times with PBS buffer, Scintillation fluid was added to the filter plate and read in a scintillation counter.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 0.0020 Tween20, 1 mM TCEP, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 30 μl in assay buffer, with 300 nM histone H4 based AcH4-23 (Anaspec: AS-65002) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 2.5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 20 minutes at 37° C. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer: NET155001MC) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 30 minutes incubation at 37° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 25 μL of 8M Guanidine HCl. Prepare streptavidin YSI SPA beads (Perkinelmer: RPNQ0012) at 0.3 mg/mL in assay buffer. To each reaction, add 150 μL of SPA beads suspension, and incubated while shaking at room temperature for 30 minutes. The plate was centrifuged at 100×g for 30 second before reading in a scintillation counter.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized, and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Brij35, 1 mM DTT, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 50 in assay buffer, with histone H2A (5 μM final) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 15 to 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 60 minutes incubation at 30° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of 20% TCA. Each reaction was spotted onto filter plate (MultiScreen FB Filter Plate, Millipore), and washed 5 times with PBS buffer, Scintillation fluid was added to the filter plate and read in a scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4 parameters with Hill Slope using GraphPad Prism software.
- Biochemical Assay Protocol Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.5, 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Brij35, 1 mM DTT, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 50 in assay buffer, with histone H2A (5 μM final) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 15 to 20 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer) to final concentration of 1 M. Following a 60 minutes incubation at 30° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 100 μL of 20% TCA. Each reaction was spotted onto filter plate (MultiScreen FB Filter Plate, Millipore), and washed 5 times with PBS buffer, Scintillation fluid was added to the filter plate and read in a scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4 parameters with Hill Slope using GraphPad Prism software.
- Revised Biochemical Assay Full-length PRMT5 enzyme (NCBI Reference sequence NP_006100.2) was co-expressed with Hiss-MEP50 in insect cells and purified via Nickel immobilized metal affinity and gel filtration chromatography (“the enzyme”).The 6 μL reactions are run in Greiner brand black 384-well low volume assay plates. All reactions contained assay buffer (phosphate buffered saline, 0.01% (v/v) Tween-20, 0.01% (w/v) albumin from chicken egg white, 1 mM Dithiothreitol, 1 μM peptide substrate, 1 μM S-Adenosyl methionine, and 15 ng/reaction enzyme, with the enzyme being omitted from negative control reactions. Compounds were added in a volume of 100 nL from dilution series prepared in DMSO, positive and negative control reactions receiving the same volume DMSO without compound. The plates were sealed with adhesive seals and incubated for 4 hours at 37 degree Celsius. Reaction progress was measured using the Transcreener™ EPIGEN methyltransferase assay (BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wis.) as recommended by the manufacturer. To each reaction 2 μL detection mix were added, containing coupling enzymes, fluorescence polarisation tracer, and AMP antibody. Plates were incubated for 90 minutes before being read on a PerkinElmer EnVision plate reader in fluorescence polarisation mode.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds were solubilized and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 0.002% Tween20, 1 mM TCEP, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 30 μl in assay buffer, with 300 nM histone H4 based AcH4-23 (Anaspec: AS-65002) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 2.5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 20 minutes at 37° C. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer: NET155001MC) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 30 minutes incubation at 37° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 25 μL of 8M Guanidine HCl. Prepare streptavidin YSI SPA beads (Perkinelmer: RPNQ0012) at 0.3 mg/mL in assay buffer. To each reaction, add 150 μL of SPA beads suspension, and incubated while shaking at room temperature for 30 minutes. The plate was centrifuged at 100×g for 30 second before reading in a scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4 parameters with Hill Slope using GraphPad Prism software.
- Flash plate assay Compounds were solubilized, and 3-fold diluted in 100% DMSO. These diluted compounds were further diluted in the assay buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 50 mM NaCl, 0.002% Tween20, 1 mM TCEP, 1% DMSO) for 10-dose IC50 mode at a concentration 10-fold greater than the desired assay concentration. Standard reactions were performed in a total volume of 30 μl in assay buffer, with 300 nM histone H4 based AcH4-23 (Anaspec: AS-65002) as substrate. To this was added the PRMT5/MEP50 complex diluted to provide a final assay concentration of 2.5 nM and the compounds were allowed to preincubate for 20 minutes at 37° C. The reaction was initiated by adding S-[3H-methyl]-adenosyl-L-methionine (PerkinElmer: NET155001MC) to final concentration of 1 μM. Following a 30 minutes incubation at 37° C., the reaction was stopped by adding 25 μL of 8M Guanidine HCl. Prepare streptavidin YSI SPA beads (Perkinelmer: RPNQ0012) at 0.3 mg/mL in assay buffer. To each reaction, add 150 μL of SPA beads suspension, and incubated while shaking at room temperature for 30 minutes. The plate was centrifuged at 100×g for 30 second before reading in a scintillation counter. IC50 values were determined by fitting the data to the standard 4 parameters with Hill Slope using GraphPad Prism software.
- Biochemical Assay Compounds of the invention may be tested for in vitro activity in the following assay: A histone H4 derived peptide is used as substrate (amino acid sequence: Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Lys-Gly-Leu-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-N H2). Full-length PRMT5 enzyme (NCBI Reference sequence NP_006100.2) was co-expressed with His6-MEP50 in insect cells and purified via Nickel immobilized metal affinity and gel filtration chromatography (the enzyme).The 6 μL assay reactions are run in Greiner brand black 384-well low volume plates. All reactions contained assay buffer (phosphate buffered saline, 0.01% (v/v) Tween-20, 0.01% (w/v) albumin from chicken egg white, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 200 nM peptide substrate, 1 μM S-Adenosyl methionine, and 15 ng/reaction enzyme, with the enzyme being omitted from negative control reactions. Compounds were added in a volume of 100 nL from dilution series prepared in DMSO, positive and negative control reactions receiving the same volume DMSO without compound. The plates were sealed with adhesive seals and incubated for 4 hours at 37° C. Reaction progress was measured using the Transcreener EPIGEN methyltransferase assay (BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wis.) as recommended by the manufacturer. To each reaction 2 μL detection mix were added, containing coupling enzymes, fluorescence polarisation tracer, and AMP antibody. Plates were incubated for 90 min before being read on a PerkinElmer EnVision plate reader in fluorescence polarisation mode.
- Revised Biochemical Assay Compounds of the invention may be tested for in vitro activity in the following assay: A histone H4 derived peptide is used as substrate (amino acid sequence: Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Lys-Gly-Leu-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-N H2). Full-length PRMT5 enzyme (NCBI Reference sequence NP_006100.2) was co-expressed with His6-MEP50 in insect cells and purified via Nickel immobilized metal affinity and gel filtration chromatography (the enzyme).The 6 μL reactions are run in Greiner brand black 384-well low volume assay plates. All reactions contained assay buffer (phosphate buffered saline, 0.01% (v/v) Tween-20, 0.01% (w/v) albumin from chicken egg white, 1 mM Dithiothreitol, 1 μM peptide substrate, 1 μM S-Adenosyl methionine, and 15 ng/reaction enzyme, with the enzyme being omitted from negative control reactions. Compounds were added in a volume of 100 nL from dilution series prepared in DMSO, positive and negative control reactions receiving the same volume DMSO without compound. The plates were sealed with adhesive seals and incubated for 4 hours at 37 degree Celsius. Reaction progress was measured using the Transcreener EPIGEN methyltransferase assay (BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wis.) as recommended by the manufacturer. To each reaction 2 μL detection mix were added, containing coupling enzymes, fluorescence polarisation tracer, and AMP antibody. Plates were incubated for 90 minutes before being read on a PerkinElmer EnVision plate reader in fluorescence polarisation mode.
- Determination of the value of binding affinity constant (KO between the compound and BRD4 BD1 protein The purity of BRD4 BD1 protein used in the experiment was greater than 95%, and the protein concentration was 43.4 uM. The 96-well plate was purchased from Corning (black, #3694). The multifunctional microplate reader was a product of TECAN, model: SPARK 10M. Buffer: 100 mM potassium phosphate (pH 6.5), 2% ethylene glycol (Sigma) and 0.01% Trition X-100 (Sigma). The experimental water was Millipore-Q pure water.The specific experimental steps were as follows.First, the compound to be tested was dissolved in ethylene glycol to prepare into a 10 mM standard stock solution. Subsequently, the standard stock solution of the compound to be tested was diluted into a working sample solution with the buffer in an EP tube and ready for use. The concentration of the prepared working sample solution was 5 times of the highest sample concentration required on the test plate (5×test compound solution).40 λL of a 5× test compound solution of a sample A was added to wells B1-B3 of a 96-well plate, and 40 μL of a 5× test compound solution of a sample B was added to wells B7-B9 of the 96-well plate, respectively. 20 uL of the buffer was added to the remaining wells, except for wells B1-B3 and B7-B9. Then, 20 uL of a solution was taken from wells B1-B3 to C1-C3, and this 2-fold dilution was repeated from C1-C3 until H4-H6; in the same way, 20 uL of a solution was taken from B7-B9 to C7-C9, this 2-fold dilution was repeated from C7-C9 until H10-H12. Finally, 80 uL of a mixed solution containing 2.5 nM Tracer and 37.5 nM BRD4 BD1 protein was added to each well.
- iochemical Assay Compounds of the invention may be tested for in vitro activity in the following assay: A histone H4 derived peptide is used as substrate (amino acid sequence: Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Lys-Gly-Leu-Gly-Lys-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-NH2). Full-length PRMT5 enzyme (NCBI Reference sequence NP-006100.2) was co-expressed with Hiss-MEP50 in insect cells and purified via Nickel immobilized metal affinity and gel filtration chromatograph.The 6 μL assay reactions are run in Greiner brand black 384-well low volume plates. All reactions contained assay buffer (phosphate buffered saline, 0.01% (v/v) Tween-20, 0.01% (w/v) albumin from chicken egg white, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 200 nM peptide substrate, 1 μM S-Adenosyl methionine, and 15 ng/reaction enzyme, with the enzyme being omitted from negative control reactions. Compounds were added in a volume of 100 nL from dilution series prepared in DMSO, positive and negative control reactions receiving the same volume DMSO without compound. The plates were sealed with adhesive seals and incubated for 4 hours at 37° C. Reaction progress was measured using the Transcreener™ EPIGEN methyltransferase assay (BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wis.) as recommended by the manufacturer. To each reaction 2 μL detection mix were added, containing coupling enzymes, fluorescence polarisation tracer, and AMP antibody. Plates were incubated for 90 min before being read on a PerkinElmer EnVision™ plate reader in fluorescence polarisation mode. IC50 values were obtained from the raw readings by calculating percent inhibition (% I) for each reaction relative to controls on the same plate (% I=(I−CN)/(CP−CN) where CN/CP are the averages of the negative/positive reactions, respectively), then fitting the % I data vs. compound concentration [I] to % I=(A+((B−A)/(1+((C/[I])^D)))) where A is the lower asymptote, B is the upper asymptote, C is the IC50 value, and D is the slope.
 CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719
CHEMBL1159714 Ko 707 BDBM50421719 3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910
3-((3S,6S)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester BDBM50305083 3-((3S,6S,12aS)-6-Isobutyl-9-methoxy-1,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydro-pyrazino[1',2':1,6]pyrido[3,4-b]indol-3-yl)-propionic acid tert-butyl ester Ko143 Ko-143 US9695174, Ko143 CHEMBL488910