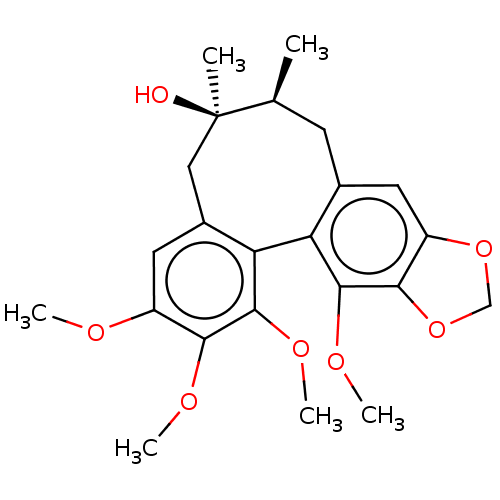
 GOMISIN A BDBM50485612
GOMISIN A BDBM50485612 BDBM50582612 (+/-)-Gomisin M1 CHEMBL463499
BDBM50582612 (+/-)-Gomisin M1 CHEMBL463499 US9365563, M2 BDBM236127 US9878991, Compound M2
US9365563, M2 BDBM236127 US9878991, Compound M2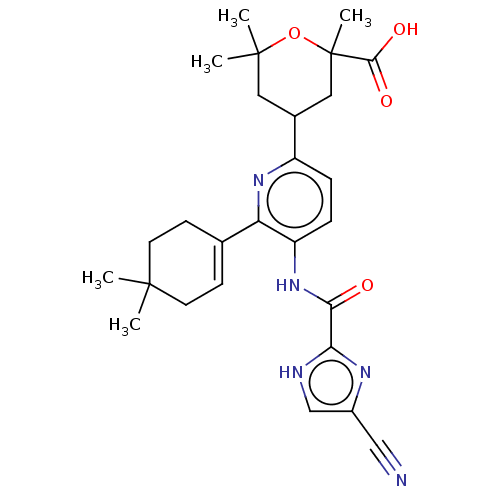 US10800764, Compound (I-M2) US10071991, Compound (I-M2) US11214566, Compound (I-M2) BDBM276741 US9611259, Compound (I-M2)
US10800764, Compound (I-M2) US10071991, Compound (I-M2) US11214566, Compound (I-M2) BDBM276741 US9611259, Compound (I-M2)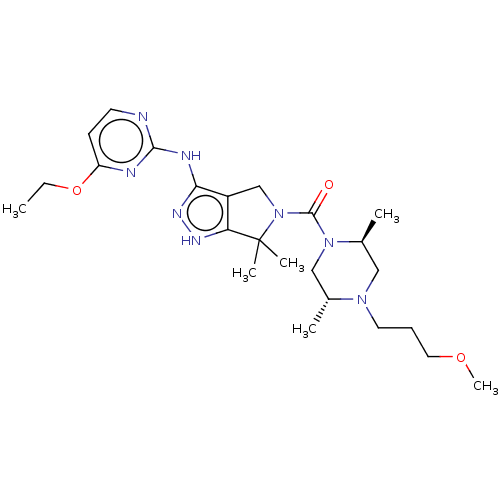 US11220518, Ex. No. M2 BDBM533505 US11780853, Example M2
US11220518, Ex. No. M2 BDBM533505 US11780853, Example M2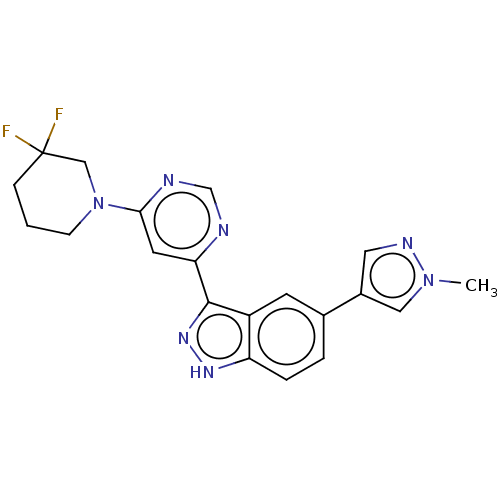 BDBM239392 US9416126, M2
BDBM239392 US9416126, M2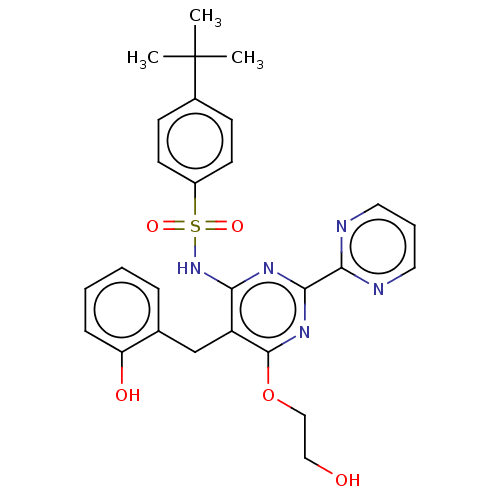 BDBM50485604 BOSENTAN M2
BDBM50485604 BOSENTAN M2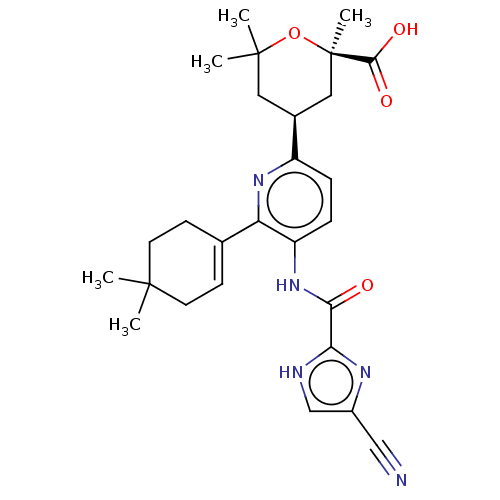 US10800764, Compound (I-M2-2R-4S) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S) BDBM276745 US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S)
US10800764, Compound (I-M2-2R-4S) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S) BDBM276745 US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S)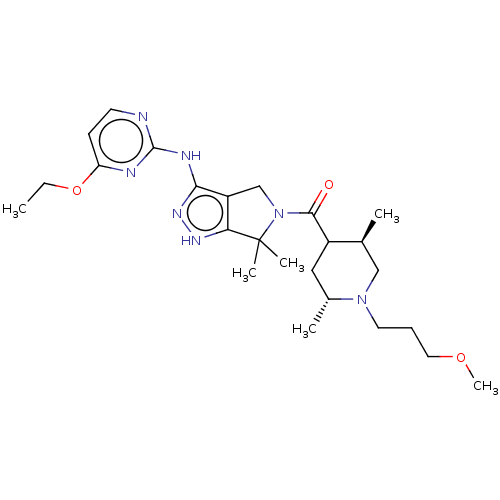 BDBM286382 US9518060, Example M2
BDBM286382 US9518060, Example M2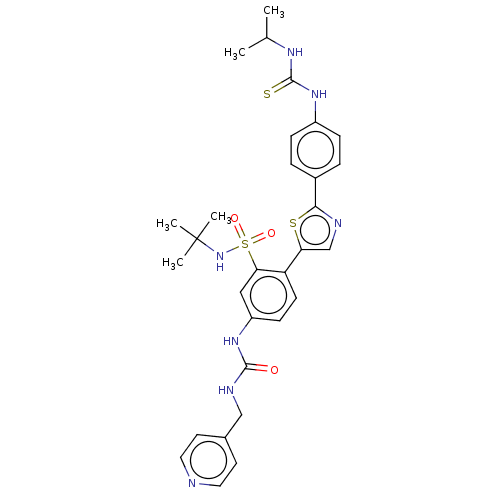 BDBM546481 US11291655, No M2
BDBM546481 US11291655, No M2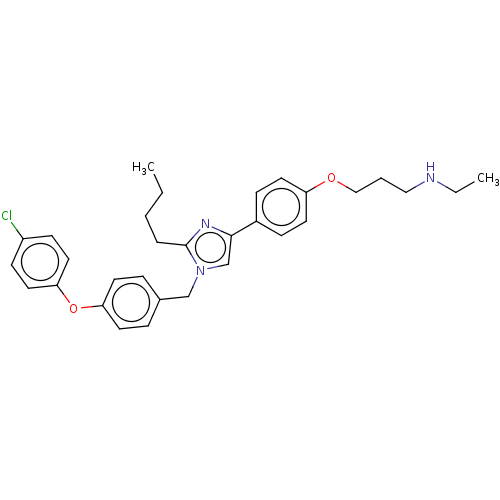 BDBM582520 US11524942, Compound M2
BDBM582520 US11524942, Compound M2 BDBM762733 US20250248955, Compound M2
BDBM762733 US20250248955, Compound M2 BDBM769657 US20250282736, Compound M2
BDBM769657 US20250282736, Compound M2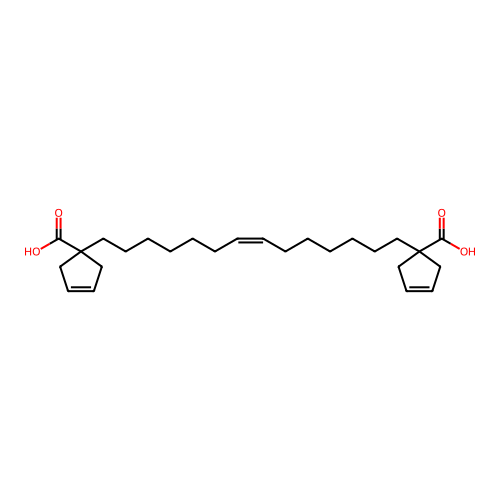 US20250011272, Example M2 BDBM711890
US20250011272, Example M2 BDBM711890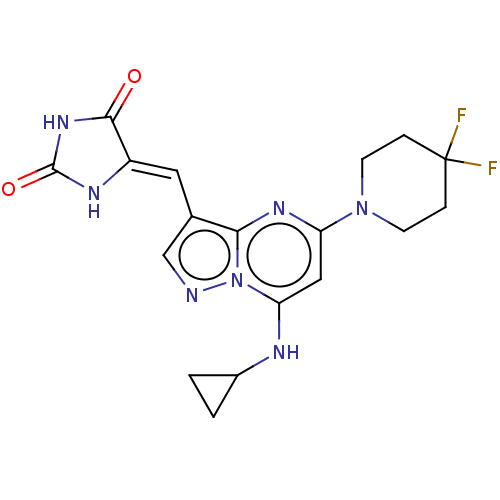 US9303033, M2, Example 25 BDBM218881
US9303033, M2, Example 25 BDBM218881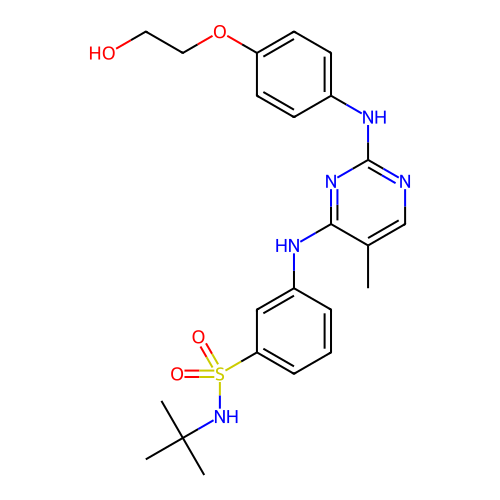 BDBM764864 US20250257069, Compound MMT3-72-M2
BDBM764864 US20250257069, Compound MMT3-72-M2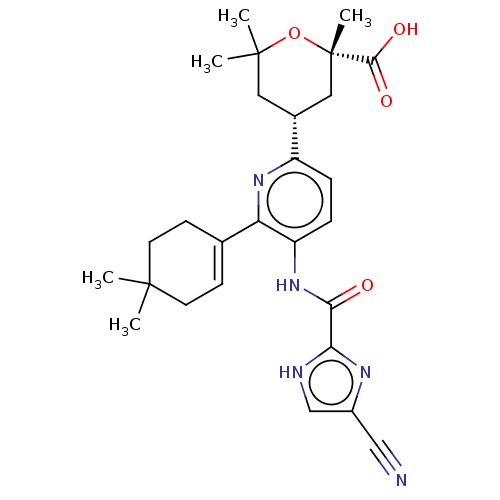 US10800764, Compound (I-M7-2R,4S) US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) BDBM276744
US10800764, Compound (I-M7-2R,4S) US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) BDBM276744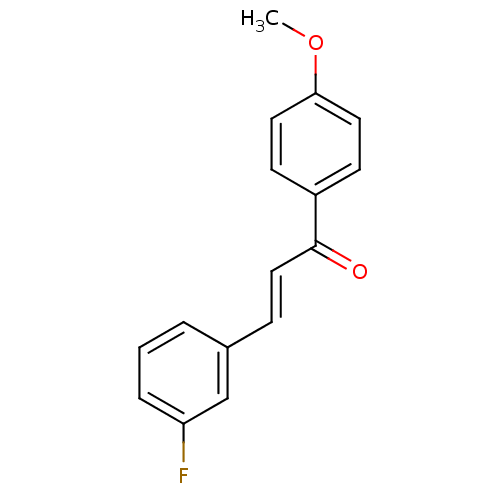 (2E)-3-(3-fluorophenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (M2) BDBM152634
(2E)-3-(3-fluorophenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (M2) BDBM152634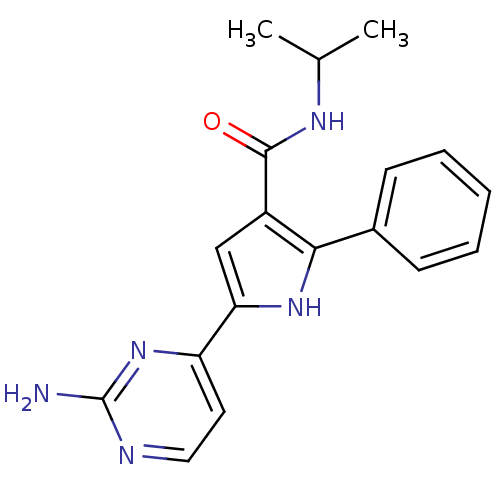 US9670191, M2 5-(2-Amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-2-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylicAcid Isopropylamide BDBM50329436 CHEMBL1270821
US9670191, M2 5-(2-Amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-2-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylicAcid Isopropylamide BDBM50329436 CHEMBL1270821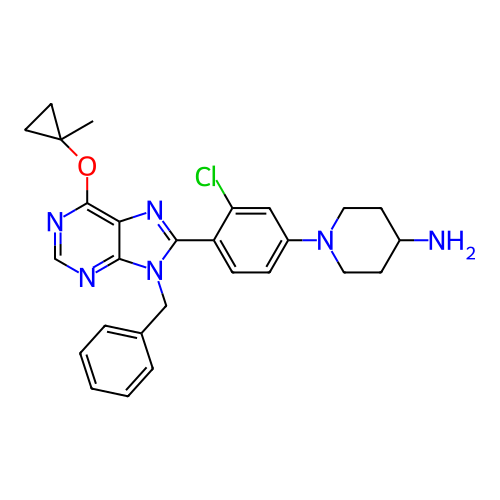 US20250195530, Example M2 1-(4-(9-benzyl- 6-(1-methyl- cyclopropoxy)- 9H-purin- 8-yl)-3- chlorophenyl) piperidin-4-amine BDBM751389
US20250195530, Example M2 1-(4-(9-benzyl- 6-(1-methyl- cyclopropoxy)- 9H-purin- 8-yl)-3- chlorophenyl) piperidin-4-amine BDBM751389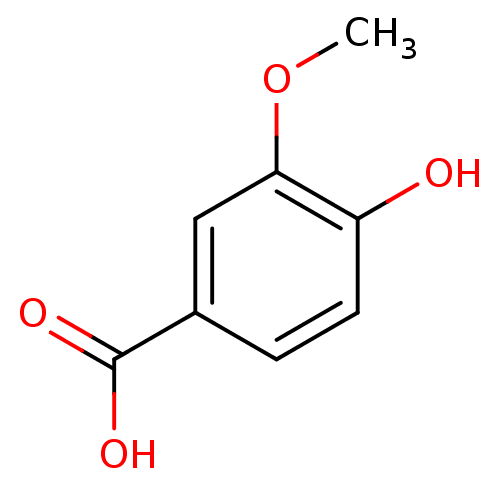 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid CHEMBL120568 Vanillic acid (M2) 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid BDBM50337364 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid 4-hydroxyl-3-methoxybenzoic acid Vanilic acid
3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid CHEMBL120568 Vanillic acid (M2) 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid BDBM50337364 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid 4-hydroxyl-3-methoxybenzoic acid Vanilic acid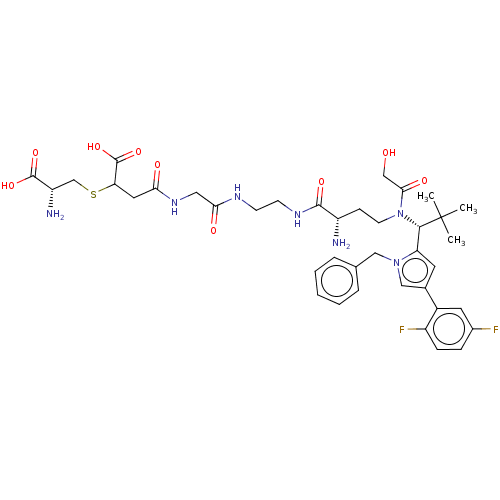 4-[(2-{[2-({(2S)-2-Amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)amino]-3-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-4-oxobutanoic acid/trifluoroacetic acid (1:1) US11071788, Example M2 BDBM509090
4-[(2-{[2-({(2S)-2-Amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)amino]-3-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-4-oxobutanoic acid/trifluoroacetic acid (1:1) US11071788, Example M2 BDBM509090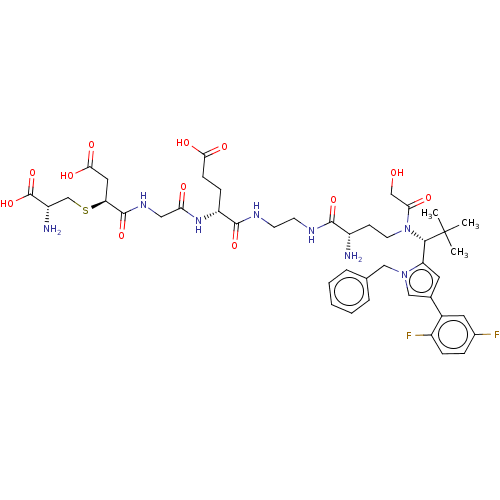 BDBM682022 N-(2-{[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-3-carboxypropanoyl)glycyl-N-[2-({(2S)-2-amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]-D-alpha-glutamine trifluoroacetic acid salt Regioisomer 2, Epimer Mixture US12059472, Example M2
BDBM682022 N-(2-{[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-3-carboxypropanoyl)glycyl-N-[2-({(2S)-2-amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]-D-alpha-glutamine trifluoroacetic acid salt Regioisomer 2, Epimer Mixture US12059472, Example M2
- Niu, YY; Yang, LM; Deng, KM; Yao, JH; Zhu, L; Chen, CY; Zhang, M; Zhou, JE; Shen, TX; Chen, HZ; Lu, Y Quantitative structure-selectivity relationship for M2 selectivity between M1 and M2 of piperidinyl piperidine derivatives as muscarinic antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 2260-6 (2007)
- Boyle, CD; Chackalamannil, S; Chen, LY; Dugar, S; Pushpavanam, P; Billard, W; Binch, H; Crosby, G; Cohen-Williams, M; Coffin, VL; Duffy, RA; Ruperto, V; Lachowicz, JE Benzylidene ketal derivatives as M2 muscarinic receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 2727-30 (2000)
- Lai, J; Bloom, JW; Yamamura, HI; Roeske, WR Amplification of the rat M2 muscarinic receptor gene by the polymerase chain reaction: functional expression of the M2 muscarinic receptor. Life Sci 47: 1001-13 (1990)
- Kiesewetter, DO; Lee, J; Lang, L; Park, SG; Paik, CH; Eckelman, WC Preparation of 18F-labeled muscarinic agonist with M2 selectivity. J Med Chem 38: 5-8 (1995)
- McKinney, M; Anderson, D; Forray, C; el-Fakahany, EE Characterization of the striatal M2 muscarinic receptor mediating inhibition of cyclic AMP using selective antagonists: a comparison with the brainstem M2 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250: 565-72 (1989)
- Drakopoulos, A; Tzitzoglaki, C; Ma, C; Freudenberger, K; Hoffmann, A; Hu, Y; Gauglitz, G; Schmidtke, M; Wang, J; Kolocouris, A Affinity of Rimantadine Enantiomers against Influenza A/M2 Protein Revisited. ACS Med Chem Lett 8: 145-150 (2017)
- Kozlowski, JA; Lowe, DB; Guzik, HS; Zhou, G; Ruperto, VB; Duffy, RA; McQuade, R; Crosby, G; Taylor, LA; Billard, W; Binch, H; Lachowicz, JE Diphenyl sulfoxides as selective antagonists of the muscarinic M2 receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 2255-7 (2001)
- Wang, J; Zhou, S; Cheng, Y; Cheng, L; Qin, Y; Zhang, Z; Bi, A; Xiang, H; He, X; Tian, X; Liu, W; Zhang, J; Peng, C; Zhu, Z; Huang, M; Li, Y; Zhuang, G; Tan, L Selective Covalent Targeting of Pyruvate Kinase M2 Using Arsenous Warheads. J Med Chem 66: 2608-2621 (2023)
- Arora, S; Joshi, G; Chaturvedi, A; Heuser, M; Patil, S; Kumar, R A Perspective on Medicinal Chemistry Approaches for Targeting Pyruvate Kinase M2. J Med Chem 65: 1171-1205 (2022)
- Tzitzoglaki, C; Wright, A; Freudenberger, K; Hoffmann, A; Tietjen, I; Stylianakis, I; Kolarov, F; Fedida, D; Schmidtke, M; Gauglitz, G; Cross, TA; Kolocouris, A Binding and Proton Blockage by Amantadine Variants of the Influenza M2 J Med Chem 60: 1716-1733 (2017)
- Dimitrijevs, P; Makrecka-Kuka, M; Bogucka, A; Hyvönen, M; Pantelejevs, T; Arsenyan, P Development of isoselenazolium chlorides as selective pyruvate kinase isoform M2 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 257:
- Palani, A; Dugar, S; Clader, JW; Greenlee, WJ; Ruperto, V; Duffy, RA; Lachowicz, JE Isopropyl amide derivatives of potent and selective muscarinic M2 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 14: 1791-4 (2004)
- Pei, XF; Gupta, TH; Badio, B; Padgett, WL; Daly, JW 6beta-Acetoxynortropane: a potent muscarinic agonist with apparent selectivity toward M2-receptors. J Med Chem 41: 2047-55 (1998)
- Böhme, TM; Keim, C; Dannhardt, G; Mutschler, E; Lambrecht, G Design and pharmacology of quinuclidine derivatives as M2-selective muscarinic receptor ligands. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 1241-3 (2001)
- Billard, W; Binch, H; Bratzler, K; Chen, LY; Crosby, G; Duffy, RA; Dugar, S; Lachowicz, J; McQuade, R; Pushpavanam, P; Ruperto, VB; Taylor, LA; Clader, JW Diphenylsulfone muscarinic antagonists: piperidine derivatives with high M2 selectivity and improved potency. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 2209-12 (2001)
- Li, J; Li, S; Guo, J; Li, Q; Long, J; Ma, C; Ding, Y; Yan, C; Li, L; Wu, Z; Zhu, H; Li, KK; Wen, L; Zhang, Q; Xue, Q; Zhao, C; Liu, N; Ivanov, I; Luo, M; Xi, R; Long, H; Wang, PG; Chen, Y Natural Product Micheliolide (MCL) Irreversibly Activates Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Suppresses Leukemia. J Med Chem 61: 4155-4164 (2018)
- Böhme, TM; Keim, C; Kreutzmann, K; Linder, M; Dingermann, T; Dannhardt, G; Mutschler, E; Lambrecht, G Structure-activity relationships of dimethindene derivatives as new M2-selective muscarinic receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 46: 856-67 (2003)
- Kumar, G; Sakharam, KA Tackling Influenza A virus by M2 ion channel blockers: Latest progress and limitations. Eur J Med Chem 267:
- Zlotos, DP; Buller, S; Tränkle, C; Mohr, K Bisquaternary caracurine V derivatives as allosteric modulators of ligand binding to M2 acetylcholine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 2529-32 (2001)
- Wang, Y; Chackalamannil, S; Chang, W; Greenlee, W; Ruperto, V; Duffy, RA; McQuade, R; Lachowicz, JE Design and synthesis of ether analogues as potent and selective M2 muscarinic receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11: 891-4 (2001)
- Elsinghorst, PW; Cieslik, JS; Mohr, K; Tränkle, C; Gütschow, M First gallamine-tacrine hybrid: design and characterization at cholinesterases and the M2 muscarinic receptor. J Med Chem 50: 5685-95 (2007)
- Wang, Y; Chackalamannil, S; Hu, Z; Clader, JW; Greenlee, W; Billard, W; Binch, H; Crosby, G; Ruperto, V; Duffy, RA; McQuade, R; Lachowicz, JE Design and synthesis of piperidinyl piperidine analogues as potent and selective M2 muscarinic receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10: 2247-50 (2001)
- PubChem, PC Discovery of novel allosteric modulators of the M1 muscarinic receptor: Agonist NMS competition at M2 PubChem Bioassay (2009)
- You, L; Zhu, H; Wang, C; Wang, F; Li, Y; Li, Y; Wang, Y; He, B Scutellarin inhibits Hela cell growth and glycolysis by inhibiting the activity of pyruvate kinase M2. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27: 5404-5408 (2017)
- Rathod, B; Chak, S; Patel, S; Shard, A Tumor pyruvate kinase M2 modulators: a comprehensive account of activators and inhibitors as anticancer agents. RSC Med Chem 12: 1121-1141 (2021)
- Braverman, AS; Tibb, AS; Ruggieri, MR M2 and M3 muscarinic receptor activation of urinary bladder contractile signal transduction. I. Normal rat bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316: 869-74 (2006)
- Del Bello, F; Bonifazi, A; Quaglia, W; Mazzolari, A; Barocelli, E; Bertoni, S; Matucci, R; Nesi, M; Piergentili, A; Vistoli, G Mode of interaction of 1,4-dioxane agonists at the M2 and M3 muscarinic receptor orthosteric sites. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24: 3255-9 (2014)
- Smith, TD; Annis, SJ; Ehlert, FJ; Leslie, FM N-[3H]methylscopolamine labeling of non-M1, non-M2 muscarinic receptor binding sites in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256: 1173-81 (1991)
- Drakopoulos, A; Tzitzoglaki, C; McGuire, K; Hoffmann, A; Konstantinidi, A; Kolokouris, D; Ma, C; Freudenberger, K; Hutterer, J; Gauglitz, G; Wang, J; Schmidtke, M; Busath, DD; Kolocouris, A Unraveling the Binding, Proton Blockage, and Inhibition of Influenza M2 WT and S31N by Rimantadine Variants. ACS Med Chem Lett 9: 198-203 (2018)
- Ning, X; Qi, H; Li, R; Li, Y; Jin, Y; McNutt, MA; Liu, J; Yin, Y Discovery of novel naphthoquinone derivatives as inhibitors of the tumor cell specific M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase. Eur J Med Chem 138: 343-352 (2017)
- Duque, MD; Ma, C; Torres, E; Wang, J; Naesens, L; Juárez-Jiménez, J; Camps, P; Luque, FJ; DeGrado, WF; Lamb, RA; Pinto, LH; Vázquez, S Exploring the size limit of templates for inhibitors of the M2 ion channel of influenza A virus. J Med Chem 54: 2646-57 (2011)
- Eleftheratos, S; Spearpoint, P; Ortore, G; Kolocouris, A; Martinelli, A; Martin, S; Hay, A Interaction of aminoadamantane derivatives with the influenza A virus M2 channel-docking using a pore blocking model. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 4182-7 (2010)
- Das, R; Pulugu, P; Singh, AA; Chatterjee, DR; Baviskar, S; Vyas, H; Behera, SK; Srivastava, A; Kumar, H; Shard, A Mechanistic Investigation of Thiazole-Based Pyruvate Kinase M2 Inhibitor Causing Tumor Regression in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Med Chem 67: 3339-3357
- Engel, WW; Eberlein, WG; Mihm, G; Hammer, R; Trummlitz, G Tricyclic compounds as selective muscarinic receptor antagonists. 3. Structure-selectivity relationships in a series of cardioselective (M2) antimuscarinics. J Med Chem 32: 1718-24 (1989)
- Zlotos, DP; Tränkle, C; Abdelrahman, A; Gündisch, D; Radacki, K; Braunschweig, H; Mohr, K 6H,13H-Pyrazino[1,2-a;4,5-a']diindole analogs: probing the pharmacophore for allosteric ligands of muscarinic M2 receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 1481-5 (2006)
- Wang, Y; Chackalamannil, S; Hu, Z; Greenlee, WJ; Clader, J; Boyle, CD; Kaminski, JJ; Billard, W; Binch, H; Crosby, G; Ruperto, V; Duffy, RA; Cohen-Williams, M; Coffin, VL; Cox, KA; Grotz, DE; Lachowicz, JE Improving the oral efficacy of CNS drug candidates: discovery of highly orally efficacious piperidinyl piperidine M2 muscarinic receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 45: 5415-8 (2002)
- McKinney, M; Anderson, DJ; Vella-Rountree, L; Connolly, T; Miller, JH Pharmacological profiles for rat cortical M1 and M2 muscarinic receptors using selective antagonists: comparison with N1E-115 muscarinic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257: 1121-9 (1991)
- Walsh, MJ; Brimacombe, KR; Veith, H; Bougie, JM; Daniel, T; Leister, W; Cantley, LC; Israelsen, WJ; Vander Heiden, MG; Shen, M; Auld, DS; Thomas, CJ; Boxer, MB 2-Oxo-N-aryl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-6-sulfonamides as activators of the tumor cell specific M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 6322-7 (2011)
- Li, F; Ma, C; DeGrado, WF; Wang, J Discovery of Highly Potent Inhibitors Targeting the Predominant Drug-Resistant S31N Mutant of the Influenza A Virus M2 Proton Channel. J Med Chem 59: 1207-16 (2016)
- Patle, R; Shinde, S; Patel, S; Maheshwari, R; Jariyal, H; Srivastava, A; Chauhan, N; Globisch, C; Jain, A; Tekade, RK; Shard, A Discovery of boronic acid-based potent activators of tumor pyruvate kinase M2 and development of gastroretentive nanoformulation for oral dosing. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 42: (2021)
- Wei, HB; Roeske, WR; Lai, J; Wanibuchi, F; Hidaka, K; Usuda, S; Yamamura, HI Pharmacological characterization of a novel muscarinic partial agonist, YM796, in transfected cells expressing the m1 or m2 muscarinic receptor gene. Life Sci 50: 355-63 (1992)
- Kovacs, I; Yamamura, HI; Waite, SL; Varga, EV; Roeske, WR Pharmacological comparison of the cloned human and rat M2 muscarinic receptor genes expressed in the murine fibroblast (B82) cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284: 500-7 (1998)
- Nassif-Makki, T; Tränkle, C; Zlotos, D; Bejeuhr, G; Cambareri, A; Pfletschinger, C; Kostenis, E; Mohr, K; Holzgrabe, U Bisquaternary ligands of the common allosteric site of M2 acetylcholine receptors: search for the minimum essential distances between the pharmacophoric elements. J Med Chem 42: 849-58 (1999)
- Rey-Carrizo, M; Barniol-Xicota, M; Ma, C; Frigolé-Vivas, M; Torres, E; Naesens, L; Llabrés, S; Juárez-Jiménez, J; Luque, FJ; DeGrado, WF; Lamb, RA; Pinto, LH; Vázquez, S Easily accessible polycyclic amines that inhibit the wild-type and amantadine-resistant mutants of the M2 channel of influenza A virus. J Med Chem 57: 5738-47 (2014)
- Takadoi, M; Terashima, S Synthesis and muscarinic M2 subtype antagonistic activity of unnatural ent-himbacine and an enantiomeric pair of (2'S,6'R)-diepihimbacine. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12: 2871-3 (2002)
- Rey-Carrizo, M; Gazzarrini, S; Llabrés, S; Frigolé-Vivas, M; Juárez-Jiménez, J; Font-Bardia, M; Naesens, L; Moroni, A; Luque, FJ; Vázquez, S New polycyclic dual inhibitors of the wild type and the V27A mutant M2 channel of the influenza A virus with unexpected binding mode. Eur J Med Chem 96: 318-29 (2015)
- Zlotos, DP; Tränkle, C; Holzgrabe, U; Gündisch, D; Jensen, AA Semisynthetic analogues of toxiferine I and their pharmacological properties ata7 nAChRs, muscle-type nAChRs, and the allosteric binding site of muscarinic M2 receptors. J Nat Prod 77: 2006-13 (2014)
- Wang, ZP; Liu, HZ; Zhu, L; Hu, YM; Cui, YY; Niu, YY; Lu, Y; Chen, HZ The effect of absolute configuration on activity, subtype selectivity (M3/M2) of 3a-acyloxy-6ß-acetoxyltropane derivatives as muscarinic M3 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 1234-9 (2013)
- Barniol-Xicota, M; Gazzarrini, S; Torres, E; Hu, Y; Wang, J; Naesens, L; Moroni, A; Vázquez, S Slow but Steady Wins the Race: Dissimilarities among New Dual Inhibitors of the Wild-Type and the V27A Mutant M2 Channels of Influenza A Virus. J Med Chem 60: 3727-3738 (2017)
- Rey-Carrizo, M; Torres, E; Ma, C; Barniol-Xicota, M; Wang, J; Wu, Y; Naesens, L; DeGrado, WF; Lamb, RA; Pinto, LH; Vázquez, S 3-Azatetracyclo[5.2.1.1(5,8).0(1,5)]undecane derivatives: from wild-type inhibitors of the M2 ion channel of influenza A virus to derivatives with potent activity against the V27A mutant. J Med Chem 56: 9265-74 (2013)
- Scapecchi, S; Matucci, R; Bellucci, C; Buccioni, M; Dei, S; Guandalini, L; Martelli, C; Manetti, D; Martini, E; Marucci, G; Nesi, M; Romanelli, MN; Teodori, E; Gualtieri, F Highly chiral muscarinic ligands: the discovery of (2S,2'R,3'S,5'R)-1-methyl-2-(2-methyl-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl)pyrrolidine 3-sulfoxide methyl iodide, a potent, functionally selective, M2 partial agonist. J Med Chem 49: 1925-31 (2006)
- Melchiorre, C; Bolognesi, ML; Chiarini, A; Minarini, A; Spampinato, S Synthesis and biological activity of some methoctramine-related tetraamines bearing a 11-acetyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-pyrido[2,3-b][1,4]-benzodiazepin-6-one moiety as antimuscarinics: a second generation of highly selective M2 muscarinic receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 36: 3734-7 (1993)
- ChEBML_1679921 Activity at human M2 receptor
- ChEBML_1679925 Activity at rat M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_804672 (CHEMBL1953194) Inhibition of M2 receptor
- ChEBML_138180 Affinity for Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_138182 Binding affinity towards muscarinic receptor M2
- ChEMBL_2521087 Inhibition of muscarinic M2 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_461638 (CHEMBL928756) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_495765 (CHEMBL1007884) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_538856 (CHEMBL1033099) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_601715 (CHEMBL1050450) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_700891 (CHEMBL1646450) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_745347 (CHEMBL1775467) Agonist activity at M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_761550 (CHEMBL1817430) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_801167 (CHEMBL1949038) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_818108 (CHEMBL2033750) Inhibition of M2 muscarinic receptor
- ChEMBL_876743 (CHEMBL2183214) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_882997 (CHEMBL2209831) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEBML_139642 Affinity towards human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_139750 Antagonistic activity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_139773 Binding affinity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_140091 Binding affinity towards human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEBML_140179 Binding affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_1278647 (CHEMBL3095635) Binding affinity to human M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_138182 (CHEMBL749203) Binding affinity towards muscarinic receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140093 (CHEMBL752970) Binding affinity towards muscarinic m2 receptor
- ChEMBL_140122 (CHEMBL748365) Binding affinity against Muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_140124 (CHEMBL748367) Binding affinity against muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_1579476 (CHEMBL3810545) Positive allosteric modulation of human M2
- ChEMBL_1904568 (CHEMBL4406926) Inhibition of M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1928903 (CHEMBL4432079) Inhibition of M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2300748 Agonist activity at rat M2 muscarinic receptor
- ChEMBL_2425875 Positive allosteric modulation of human M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_325911 (CHEMBL869381) Inhibition of human muscarinic receptor M2
- ChEMBL_442219 (CHEMBL892378) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_492756 (CHEMBL939444) Agonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_536129 (CHEMBL983583) Agonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_556755 (CHEMBL959818) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_581967 (CHEMBL1058947) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_714794 (CHEMBL1663600) Inhibition of human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_718166 (CHEMBL1679212) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_818587 (CHEMBL2032874) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_875653 (CHEMBL2184884) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_884092 (CHEMBL2215568) Binding affinity to M2 muscarinic receptor
- ChEBML_138181 Binding affinity to cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_139671 Binding affinity of compound to m2 muscarinic receptor
- ChEMBL_138186 (CHEMBL749207) Inhibitory activity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139623 (CHEMBL749005) Binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139751 (CHEMBL745192) Antagonistic activity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139752 (CHEMBL745193) Antagonistic activity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139756 (CHEMBL745197) Binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139757 (CHEMBL745198) Binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139886 (CHEMBL744473) In vitro affinity for muscarinic M2 receptor.
- ChEMBL_139887 (CHEMBL744474) Binding affinity towards human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_140091 (CHEMBL752968) Binding affinity towards human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_1885235 (CHEMBL4386817) Positive allosteric modulation of human M2 AchR
- ChEMBL_2163945 (CHEMBL5048806) Inhibition of M2 mAChR receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2207735 (CHEMBL5120443) Inhibition of muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2261725 (CHEMBL5216736) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_302412 (CHEMBL875203) Affinity for rat Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_320816 (CHEMBL872351) Affinity towards cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_321368 (CHEMBL881512) Inhibitory concentration against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_327856 (CHEMBL863986) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_496614 (CHEMBL1003789) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_546429 (CHEMBL1025828) Displacement of QNB from muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_552741 (CHEMBL965247) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_566272 (CHEMBL953575) Inhibition of human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_664963 (CHEMBL1259920) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_697210 (CHEMBL1640630) Binding affinity to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_818804 (CHEMBL2033490) Binding affinity to human recombinant M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_853235 (CHEMBL2154936) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_936427 (CHEMBL2317636) Binding affinity to human M2 muscarinic receptor
- ChEBML_140103 Compound was evaluated for the displacement of the muscarinic QNB in rat heart homogenate containing the pharmacologic M2 receptor (M2-QNB heart)
- ChEBML_139762 Binding affinity against cloned human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2.
- ChEBML_139772 Binding affinity against human cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2.
- ChEMBL_1352901 (CHEMBL3269418) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_138181 (CHEMBL749202) Binding affinity to cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_138183 (CHEMBL749204) Inhibition of binding affinity to muscarinic receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139759 (CHEMBL748895) Binding affinity for human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_1496345 (CHEMBL3579949) Inhibition of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_1522868 (CHEMBL3630586) Antagonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2249115 (CHEMBL5163325) Agonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2453688 Displacement of [3H]-epibatidine from M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_439691 (CHEMBL888802) Displacement of [3H]QNB from muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_658567 (CHEMBL1247900) Binding affinity to human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_767225 (CHEMBL1826471) Inhibition of M2 muscarinic receptor by NIMH PDSP
- ChEMBL_139616 (CHEMBL744781) Compound was tested for its potency at Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by inhibiting forskolin induced c-AMP formation in CHO-M2 cells
- ChEMBL_139617 (CHEMBL744782) Compound was tested for its potency towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by inhibiting forskolin induced c-AMP formation in CHO-M2 cells
- ChEMBL_139770 (CHEMBL747480) The binding affinity was measured as inhibition of binding of [3H]- oxotremorine-M m2 toMuscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in membranes of CHO cells
- ChEBML_139639 Dissociation constant for human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 was determined.
- ChEBML_139656 Stimulation of cAMP in CHO cells expressing human m2 receptor
- ChEBML_139763 Binding affinity towards the cloned human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140088 (CHEMBL752965) In vitro functional agonism against M2 muscarinic receptor (cAMP)
- ChEMBL_140105 (CHEMBL748286) Inhibition of muscarinic (M2) receptor isolated from rat atria
- ChEMBL_1979086 (CHEMBL4612221) Binding affinity to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2068303 (CHEMBL4723556) Binding affinity to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2474358 Binding affinity to human M2 receptor assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_2574753 Inhibition of M2 receptor (unknown origin) by radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_466554 (CHEMBL935646) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX384 from muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_485933 (CHEMBL1013936) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX384 from muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_604302 (CHEMBL1066758) Displacement of [3H]QNB from human muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_982013 (CHEMBL2428368) Binding affinity to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_139614 (CHEMBL880146) Compound was tested for its potency at M-2 receptor by inhibiting forskolin induced c-AMP formation in CHO-M2 cells human M2 receptor
- ChEBML_140175 Binding affinity at human cloned acetylcholine receptor M2 in CHO cells.
- ChEMBL_138855 (CHEMBL748616) Binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart.
- ChEMBL_139656 (CHEMBL745634) Stimulation of cAMP in CHO cells expressing human m2 receptor
- ChEMBL_139763 (CHEMBL748899) Binding affinity towards the cloned human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140180 (CHEMBL744097) Binding affinity towards rat Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 was determined
- ChEMBL_1700418 (CHEMBL4051400) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_1823731 (CHEMBL4323495) Displacement of [3H] NMS from muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2023085 (CHEMBL4676898) Displacement of [3H]nicotine from muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin)
- ChEMBL_2309508 Binding affinity to M2 receptor (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_2329130 Binding affinity at human muscarinic M2 receptor assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_302560 (CHEMBL875217) In vitro inhibitory activity against cloned human M2 muscarinic receptor
- ChEMBL_451100 (CHEMBL900173) Inhibition of [3H]NMS dissociation from porcine muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_635227 (CHEMBL1117838) Inhibition of human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_635569 (CHEMBL1118804) Inhibition of human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_811392 (CHEMBL2013604) Orthosteric antagonist activity at M2 receptor by AS-MS analysis
- ChEMBL_811393 (CHEMBL2013605) Negative allosteric modulation at M2 receptor by AS-MS analysis
- ChEMBL_946139 (CHEMBL2343541) Antagonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 receptor isolated from brain
- ChEMBL_138347 (CHEMBL747777) Muscarinic receptor M2 in rat heart using [3H]QNB (quinuclidinyl benzylate) radioligand as a M2 non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist at a concentration of 0.12 nM
- ChEBML_139760 Binding affinity against human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in transfected CHO cells
- ChEBML_140095 Dissociation constant for the blocking of brainstem muscarinic M2 receptor was reported.
- ChEBML_140104 Displacement of [3H]methylscopolamine binding to muscarinic M2 receptor in rat heart.
- ChEBML_140108 Displacement of [3H]QNB from rat brain stem muscarinic receptor 2 (M2)
- ChEBML_140120 In vitro binding affinity towards muscarinic receptor in heart (M2) was determined
- ChEMBL_1632014 (CHEMBL3874720) Binding affinity to rat M2 receptor by radio-ligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_1704885 (CHEMBL4056118) Antagonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 receptor by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_1972434 (CHEMBL4605252) Displacement of [3H]-QNB from Wistar rat heart muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_2286664 Antagonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_432434 (CHEMBL917429) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_659574 (CHEMBL1248869) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor by radioligand displacement assay
- ChEMBL_684915 (CHEMBL1286330) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX384 from human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEMBL_788047 (CHEMBL1919026) Agonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_815535 (CHEMBL2025064) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_815538 (CHEMBL2025067) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_858565 (CHEMBL2166010) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_859013 (CHEMBL2168635) Inhibition of human muscarinic M2 receptor by cell based functional assay
- ChEBML_139765 Binding affinity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells.
- ChEBML_140042 Binding affinity towards muscarinic receptor of gastric fundus containing Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_140043 Displacement of [3H]QNB from Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 from rat heart homogenates
- ChEBML_140121 Tested in vitro for the binding affinity against muscarinic receptor subtype 2 (M2)
- ChEBML_1685391 Activity at human M2 receptor assessed as increase in acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization
- ChEBML_31582 Evaluated for the inhibition of adenylate cyclase at M2 receptor in rat heart
- ChEMBL_1367095 Displacement of [3H]-NMS from Sprague-Dawley rat muscarinic M2 receptor in heart
- ChEMBL_138172 (CHEMBL858421) Inhibition of [3H]NMS binding to rat heart Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139224 (CHEMBL745699) Dissociation constant at muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 guinea pig heart(atria force).
- ChEMBL_139641 (CHEMBL748254) Affinity for human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO-K1 cells
- ChEMBL_139979 (CHEMBL751165) M2 agonist activity estimated by depression of isolated guinea pig left atrium
- ChEMBL_140095 (CHEMBL752972) Dissociation constant for the blocking of brainstem muscarinic M2 receptor was reported.
- ChEMBL_140097 (CHEMBL752974) Dissociation constant for the blocking of heart muscarinic M2 receptor was reported.
- ChEMBL_140108 (CHEMBL752109) Displacement of [3H]QNB from rat brain stem muscarinic receptor 2 (M2)
- ChEMBL_1895724 (CHEMBL4397759) Binding affinity to muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_2107606 (CHEMBL4816281) Agonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_337456 (CHEMBL862220) Binding affinity to cloned human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_340035 (CHEMBL862030) Inhibition of [3H]NMS dissociation from muscarinic M2 receptor in hepes buffer
- ChEMBL_457003 (CHEMBL923346) Displacement of [3H]N-methylscopolamine from muscarinic M2 receptor in rat heart
- ChEMBL_470967 (CHEMBL923036) Binding affinity to human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_550724 (CHEMBL1006038) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in insect Sf9 cells
- ChEMBL_935576 (CHEMBL2320112) Positive allosteric modulation of rat muscarinic M2 receptor assessed as acetylcholine response
- ChEMBL_98894 (CHEMBL703402) Binding affinity at [3H]CD radiolabeled muscarinic M2 receptor in rat cortex.
- ChEMBL_98897 (CHEMBL709389) Binding affinity at [3H]QNB radiolabeled muscarinic M2 receptor in rat cortex.
- ChEMBL_98898 (CHEMBL709390) Binding affinity at [3H]QNB radiolabeled muscarinic M2 receptor in rat heart.
- ChEBML_138225 Binding affinity against the muscarinic M2 (brainstem) subtype was evaluated using [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate
- ChEBML_139764 Binding affinity against human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]N-methylscopolamine as radioligand
- ChEBML_140112 Displacement of [3H]QNB (quinuclidinyl benzylate) from muscarinic M2 receptor of rat heart homogenates.
- ChEBML_140123 Compound was evaluated for binding affinity against Muscarinic M2 receptor using radioligand binding assay
- ChEBML_140189 Displacement of [3H](-)-quinuclidinyl benzilate(QNB) from muscarinic (M2) receptor in rat heart homogenates
- ChEBML_98896 Binding affinity at [3H]QNB and GppNHp radiolabeled muscarinic M2 receptor in rat heart.
- ChEMBL_139225 (CHEMBL745700) Dissociation constant at muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of guinea pig heart(atria rate).
- ChEMBL_139889 (CHEMBL744476) Compound was tested for binding affinity against human cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140176 (CHEMBL745628) Binding affinity against m-AcChR subtype Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart.
- ChEMBL_140178 (CHEMBL745630) Binding affinity to m-AcChR subtype Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart
- ChEMBL_1632010 (CHEMBL3874716) Displacement of [3H]-N-Methylscopolamine from human M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cells
- ChEMBL_1656067 (CHEMBL4005537) Binding affinity to Influenza A virus M2 transmembrane domain by analytical ultracentrifugation method
- ChEMBL_2261388 (CHEMBL5216399) Binding affinity to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition constant
- ChEMBL_31582 (CHEMBL646376) Evaluated for the inhibition of adenylate cyclase at M2 receptor in rat heart
- ChEMBL_320907 (CHEMBL881234) Binding affinity for rat heart muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate
- ChEMBL_450046 (CHEMBL899143) Displacement of [3H]QNB from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_468559 (CHEMBL932106) Displacement of [3H]NMS from rat muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_556678 (CHEMBL958965) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_788148 (CHEMBL1919229) Agonist activity at rat recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor by HTS cell based assay
- ChEMBL_788152 (CHEMBL1919233) Agonist activity at human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor by HTS cell based assay
- ChEBML_131447 Binding affinity against mouse Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using heart tissue and [3H]N-methylscopolamine
- ChEBML_140039 Binding affinity against mouse Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using heart tissue and [3H]N-methylscopolamine
- ChEBML_140118 Inhibition of binding of [3H]N-methylscopolamine to muscarinic receptor (M2) in rat heart homogenates
- ChEBML_140188 Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity towards muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brainstem
- ChEBML_1688491 Inhibition of Respiratory syncytial virus A2 M2-1 by luciferase reporter-based RSV minigenome assay
- ChEMBL_1366833 (CHEMBL3297343) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX384 from human recombinant M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_139341 (CHEMBL749945) Compound is evaluated for in vitro receptor binding affinity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139624 (CHEMBL749006) Binding affinity of [3H]QNB to CHO cells expressing human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139767 (CHEMBL748903) Compound was tested for its binding affinity against cloned human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139782 (CHEMBL857186) Inhibitory activity was evaluated against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in A9 L cells
- ChEMBL_139885 (CHEMBL857563) Affinity for Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells by [3H]NMS displacement.
- ChEMBL_139918 (CHEMBL748586) Inhibition of [3H]- N-methyl-scopolamine ([3H]NMS) dissociation from porcine cardiac M2-receptors
- ChEMBL_140026 (CHEMBL745569) Ability to dissociate radioligand [3H]NMS from muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of porcine heart
- ChEMBL_140038 (CHEMBL744018) Binding affinity against mouse M2 muscarinic receptor using heart tissue and [3H]N-methylscopolamine
- ChEMBL_140041 (CHEMBL744021) Inhibition of [3H]N-methylscopolamine to rat muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 from heart tissue
- ChEMBL_140045 (CHEMBL745720) Inhibition of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart
- ChEMBL_1700417 (CHEMBL4051399) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK1 cells
- ChEMBL_1746222 (CHEMBL4180732) Positive allosteric modulation of human M2 receptor assessed as increase in acetylcholine-induced response
- ChEMBL_1804550 (CHEMBL4303774) Activity of compound against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) by displacement of 3H-QNB
- ChEMBL_2260073 (CHEMBL5215084) Inhibition of human HDAC1 incubated for 30 mins by SpectraMax M2 microplate reader analysis
- ChEMBL_2260074 (CHEMBL5215085) Inhibition of human HDAC2 incubated for 30 mins by SpectraMax M2 microplate reader analysis
- ChEMBL_2260075 (CHEMBL5215086) Inhibition of human HDAC6 incubated for 30 mins by SpectraMax M2 microplate reader analysis
- ChEMBL_340033 (CHEMBL861240) Inhibition of [3H]NMS dissociation from muscarinic M2 receptor in Na,K,Pi buffer
- ChEMBL_395700 (CHEMBL909208) Inhibition of [3H]NMS binding to human cloned M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_461881 (CHEMBL929017) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_936174 (CHEMBL2320131) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human M2 muscarinic receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells
- ChEMBL_937323 (CHEMBL2319086) Partial agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells calcium response
- ChEMBL_937333 (CHEMBL2319367) Partial agonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells calcium response
- ChEMBL_98750 (CHEMBL704479) Ability to displace [3H](-)-quinuclidinyl benzilate(QNB) from M2 receptor in rat heart homogenate
- ChEMBL_98896 (CHEMBL709388) Binding affinity at [3H]QNB and GppNHp radiolabeled muscarinic M2 receptor in rat heart.
- ChEBML_139666 Compound was evaluated for displacement of [3H]-QNB from human Muscarinic m2 receptor in CHO cells.
- ChEBML_139909 Allosteric inhibition of [3H]NMS (N-methyl-scopolamine) dissociation from porcine cardiac Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEBML_139982 In vitro negative chronotropic effect on electrically driven guinea pig atria(mediated by Muscarinic M2 receptor)
- ChEBML_140092 Binding affinity towards human muscarinic M2 receptor in CHO-KI cells using [3H]- QNB as radioligand
- ChEBML_98899 The binding affinity was measured on muscarine M2 receptor using [3H]- N-Me-SCOPOL as radioligand.
- ChEMBL_139640 (CHEMBL748253) Inhibition of [3H]NMS binding to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_139891 (CHEMBL744478) Inhibition of [3H]-NMS binding to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in transfected CHO cells.
- ChEMBL_140039 (CHEMBL744019) Binding affinity against mouse Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using heart tissue and [3H]N-methylscopolamine
- ChEMBL_140044 (CHEMBL744024) Inhibition of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brain membrane
- ChEMBL_140047 (CHEMBL745864) Inhibition of [3H]- Oxo-M binding at Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brain membranes.
- ChEMBL_140110 (CHEMBL752111) Binding affinity was measured against muscarinic (M2) receptor in rat using [3H]QN as radioligand
- ChEMBL_140174 (CHEMBL745478) Binding affinity against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by displacement of [3H]QNB in rat myocardium
- ChEMBL_140182 (CHEMBL744099) Inhibition of [3H]N-methylscopolamine binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart membranes
- ChEMBL_140187 (CHEMBL744904) Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brainstem
- ChEMBL_140188 (CHEMBL744905) Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity towards muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brainstem
- ChEMBL_1434807 (CHEMBL3384036) Inhibition of purified human N-terminal His-tagged PK-M2 by LDH-coupled continuous assay
- ChEMBL_1559772 (CHEMBL3779725) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX384 from human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_1929132 (CHEMBL4432308) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium response
- ChEMBL_429186 (CHEMBL913820) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl-scopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cells
- ChEMBL_450372 (CHEMBL900655) Antagonist activity at cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by measuring calcium mobilization
- ChEMBL_468550 (CHEMBL930974) Antagonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_525848 (CHEMBL972958) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in insect Sf9 cells
- ChEMBL_659455 (CHEMBL1248508) Displacement of [3H]-AFDX-384 from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells
- ChEMBL_828579 (CHEMBL2060094) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization
- ChEMBL_936423 (CHEMBL2317632) Binding affinity to human M2 muscarinic receptor expressed in cell membranes by radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_98749 (CHEMBL874151) Tested against muscarinic M2 receptor by displacement of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate from rat cerebellum membrane
- ChEMBL_1700423 (CHEMBL4051405) Ratio of binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as dissociation rate constant to binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as association rate constant
- ChEBML_140172 In vitro receptor binding against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat heart was determined using [3H]pirenzepine
- ChEMBL_139758 (CHEMBL748894) Binding affinity of compound was determined towards human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]QNB radioligand
- ChEMBL_139982 (CHEMBL751168) In vitro negative chronotropic effect on electrically driven guinea pig atria(mediated by Muscarinic M2 receptor)
- ChEMBL_140052 (CHEMBL745869) Inhibitory activity against [3H]N-methyl-scopolamine binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat cerebellum
- ChEMBL_140107 (CHEMBL748288) Binding affinity against M2 receptor in rat brainstem cells using radioligand [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate ([3H]QNB)
- ChEMBL_1442051 (CHEMBL3373419) Displacement of [3H]NMS from pig muscarinic M2 receptor after 120 mins by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_429169 (CHEMBL914425) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl-scopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO K1 cells
- ChEMBL_441417 (CHEMBL891646) Displacement of 1-[N-methyl- 3H]scopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in Sf9 cells
- ChEMBL_468830 (CHEMBL932203) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl Scopolamine from human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_491019 (CHEMBL982067) Displacement of [3H]N-methylscopolamine chloride from human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cells
- ChEMBL_605045 (CHEMBL1071305) Agonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 expressed in CHO cells assessed as stimulation of calcium mobilization
- ChEMBL_643620 (CHEMBL1212484) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX 384 from human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_815846 (CHEMBL2026109) Displacement of [3H]-N-methyl scopolamine from muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in CHO cell membrane
- ChEMBL_98895 (CHEMBL703403) Tested for binding affinity to [3H]QNB and GppNHp radiolabeled muscarinic M2 receptor in rat heart
- ChEMBL_98899 (CHEMBL709391) The binding affinity was measured on muscarine M2 receptor using [3H]- N-Me-SCOPOL as radioligand.
- ChEBML_139761 Binding affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells using [3H]-QNB as radioligand
- ChEBML_139766 Binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells using [3H]-QNB as radioligand.
- ChEBML_140037 Binding affinity to the rat cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using 0.3 nM [3H]N-methylscopolamine as radioligand
- ChEBML_140113 Compound tested in vitro for displacement of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate from rat cerebellum membrane expressing muscarinic M2 receptor
- ChEBML_140173 Compound was tested for binding activity against rat muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]QNB as the radioligand
- ChEBML_1711438 Displacement of [3H]AF-DX 384 from human recombinant M2 receptor after 60 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_138227 (CHEMBL744918) In vitro ability to contract isolated guinea pig ileum was used to estimate M2/M3 agonist effect
- ChEMBL_139350 (CHEMBL752398) Binding affinity for muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by measuring displacement of [3H]QNB from guinea pig heart
- ChEMBL_139619 (CHEMBL744784) Reversal of forskolin-stimulated accumulation of adenylate cyclase in transfected CHO cells, against Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139631 (CHEMBL748244) Displacement of [3H]NMS binding to human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using membranes from transfected CHO cells
- ChEMBL_139634 (CHEMBL748247) Inhibitory activity against [3H]quinuclidinyl Benzilate binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in the absence of GTP
- ChEMBL_139635 (CHEMBL748248) Inhibitory activity against [3H]quinuclidinyl Benzilate binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in the presence of GTP
- ChEMBL_139769 (CHEMBL747479) Inhibition of [3H]- oxotremorine-M binding to human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cell membranes
- ChEMBL_139771 (CHEMBL747481) Inhibition of [3H]- quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cell membrane
- ChEMBL_140025 (CHEMBL859326) Effective concentration required to inhibit dissociation of [3H]NMS from porcine heart ventricles muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2.
- ChEMBL_140116 (CHEMBL858424) Compound was tested for inhibiting [3H]N-Methyl-scopolamine Binding to Muscarinic receptor (M2) in Rat Heart
- ChEMBL_140117 (CHEMBL748360) Compound was tested for inhibiting [3H]N-Methyl-scopolamine Binding to Muscarinic receptor (M2) in Rat Heart
- ChEMBL_140197 (CHEMBL745149) Inhibition of binding of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat cerebral cortical membranes
- ChEMBL_1616174 (CHEMBL3858243) Inhibition of NPM-ALK phosphorylation in human SUP-M2 cells after 2 to 3 hrs by ELISA
- ChEMBL_1700446 (CHEMBL4051428) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells after 2 hrs
- ChEMBL_1895752 (CHEMBL4397787) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from rat heart muscarinic M2 receptor after 60 mins by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2013850 (CHEMBL4667428) Positive allosteric modulation of human M2 receptor/Gqi5 in presence of EC20 glutamate by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_2023165 (CHEMBL4676978) Inhibition of [3H]-methyl-quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to rat heart muscarinic M2 receptor by radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_2250313 (CHEMBL5164523) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_2290800 Displacement of [3H]NMS from human M2 receptor stably expressed in HEK293T cells by Cheng-Prusoff equation analysis
- ChEMBL_491217 (CHEMBL992813) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by liquid scintillation counter
- ChEMBL_539040 (CHEMBL1035714) Inhibition of human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor-Gqi5 chimeric protein expressed in CHO cells by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_581961 (CHEMBL1058941) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cells by microplate scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_596256 (CHEMBL1048032) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_605173 (CHEMBL1067395) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by microplate scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_789190 (CHEMBL1924274) Displacement of [3H]NMS from recombinant human M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells after 16 hrs
- ChEMBL_940446 (CHEMBL2329444) Displacement of [3H]NMS from muscarinic M2 receptor in Sprague-Dawley rat left atria after 60 mins
- ChEBML_138160 Inhibitory constant by the inhibition of [3H]N-methylscopolamine (NMS) binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart
- ChEMBL_138163 (CHEMBL748227) Inhibition of binding of [3H]N-Methyl-scopolamine to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart tissue membranes.
- ChEMBL_139625 (CHEMBL749007) Binding affinity of compound labeled by [3H]QNB in CHO cells selectively expressing human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139632 (CHEMBL748245) In vitro affinity is evaluated, using quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) as radioligand in human cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139633 (CHEMBL748246) In vitro affinity is evaluated, using quinuclidynyl benzylate (QNB) as radioligand in human cloned Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139910 (CHEMBL746846) Allosteric potency against the dissociation of radioligand [3H]N-methylscopolamine from the porcine cardiac Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140037 (CHEMBL744017) Binding affinity to the rat cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using 0.3 nM [3H]N-methylscopolamine as radioligand
- ChEMBL_140046 (CHEMBL745721) In vitro Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 binding was evaluated in rat brain membranes by using [3H]- Oxo-M
- ChEMBL_140094 (CHEMBL752971) Reduction of dissociation rate of [3H]N-methylscopolamine ([3H]NMS) from muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of pig heart
- ChEMBL_140109 (CHEMBL752110) Binding affinity was measured against muscarinic (M2) receptor at 10 uM in rat using [3H]QN as radioligand
- ChEMBL_140171 (CHEMBL745475) In vitro binding affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]-QNB as radioligand from rat heart tissue
- ChEMBL_140190 (CHEMBL744907) Compound was tested for its binding affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]NMS from rat heart
- ChEMBL_140193 (CHEMBL744910) Compound was tested for the binding affinity against rat heart Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by quinuclidinyl binding assay.
- ChEMBL_1517984 (CHEMBL3618841) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells after 30 mins by GTPgamma35S binding assay
- ChEMBL_1627310 (CHEMBL3869831) Binding affinity to human M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells measured after 90 mins by radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_1668375 (CHEMBL4018263) Antagonist activity at recombinant human M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_1700445 (CHEMBL4051427) Displacement of [3H]Dimethyl-W84 from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells after 2 hrs
- ChEMBL_1784189 (CHEMBL4255706) Binding affinity to Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 wild-type M2 proton channel by isothermal calorimetric titration
- ChEMBL_1784190 (CHEMBL4255707) Binding affinity to Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 M2 proton channel S31N mutant by isothermal calorimetric titration
- ChEMBL_1864043 (CHEMBL4365018) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX 384 from recombinant human M2 receptor after 60 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_1895742 (CHEMBL4397777) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2060796 (CHEMBL4716049) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin) expressed in A9 cells by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEBML_139893 Compound was evaluated for the competitive inhibition of [3H]methylscopolamine binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of mouse cerebral cortex
- ChEBML_140183 Binding affinity was determined from the inhibition of contraction of guinea pig ileum which has Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 subtype.
- ChEBML_222112 Compound was tested for the inhibition of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brain membrane
- ChEMBL_1292393 (CHEMBL3123986) Agonist activity at muscarinic M2 receptor in albino guinea pig left atrium assessed as stimulation of electrically-induced response
- ChEMBL_139888 (CHEMBL744475) Binding affinity towards cloned human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 stably expressed in CHO-K1 cells using [3H]N-methylscopolamine
- ChEMBL_1772769 (CHEMBL4229761) Inhibition of Influenza A virus M2 V27A mutant expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes by two-electrode voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_1895738 (CHEMBL4397773) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO-K1 cells by radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_2035465 (CHEMBL4689623) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX384 from human recombinant M2 receptor incubated for 1 hr by radiometric scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_750515 (CHEMBL1786276) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl Scopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_800614 (CHEMBL1947646) Inhibition of NPM-ALK autophosphorylation in human ALCL SUP-M2 cells after 2 to 3 hrs by sandwich ELISA
- ChEMBL_937319 (CHEMBL2319082) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as inhibition of Ach-induced calcium response
- ChEMBL_937329 (CHEMBL2319092) Antagonist activity at rat muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as inhibition of Ach-induced calcium response
- ChEBML_138346 Binding affinity against Muscarinic receptor M2 in rat brain using [3H]QNB (quinuclidinyl benzylate) radioligand at a concentration of 0.12 nM
- ChEBML_139352 Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in guinea pig heart using (-)-[3H]-QNB as radioligand
- ChEBML_139754 Antimuscarinic potency and subset specificity was characterised by its inhibition of the [3H]NMS Binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 subtype
- ChEMBL_138173 (CHEMBL748235) Binding affinity to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by measuring its ability to displace [3H]N-methylscopolamine binding in rat heart
- ChEMBL_139618 (CHEMBL744783) In Vitro activity at the cloned Human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 determined by receptor selection and amplification technology (R-SAT).
- ChEMBL_139753 (CHEMBL745194) Antimuscarinic potency and subset specificity was characterised by inhibition of the [3H]NMS Binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 subtype
- ChEMBL_139755 (CHEMBL745196) Binding affinity (Ki) against binding of [3H]NMS to membranes from CHO cells expressing cloned human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_139893 (CHEMBL744480) Compound was evaluated for the competitive inhibition of [3H]methylscopolamine binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of mouse cerebral cortex
- ChEMBL_140036 (CHEMBL744016) Binding affinity of compound for cardiac Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat using 0.3 nM [3H]N-methylscopolamine as radioligand
- ChEMBL_140053 (CHEMBL745870) Inhibitory activity against [3H]N-methyl-scopolamine in rat Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 cerebellum in the presence GPP(NH)P
- ChEMBL_140183 (CHEMBL744900) Binding affinity was determined from the inhibition of contraction of guinea pig ileum which has Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 subtype.
- ChEMBL_1438414 (CHEMBL3383643) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells by microplate scintillation counting based radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_1453980 (CHEMBL3366674) Inhibition of influenza A virus wild type M2 proton channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes by two-electrode voltage clamp analysis
- ChEMBL_1455702 (CHEMBL3366377) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 Y104A mutant expressed in Flp-In-CHO cells by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1455703 (CHEMBL3366378) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 Y177Q mutant expressed in Flp-In-CHO cells by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1455705 (CHEMBL3366380) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 W422A mutant expressed in Flp-In-CHO cells by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1459948 (CHEMBL3367783) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor transfected in CHO cells after 120 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_1465997 (CHEMBL3406979) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cell membranes after 4 hrs by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1539162 (CHEMBL3738806) Agonist activity at human wild-type M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells assessed as cAMP level by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1972534 (CHEMBL4605352) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor stably expressed in CHO-K9 cells by radioligand competitive binding assay
- ChEMBL_2150084 (CHEMBL5034546) Displacement of [3H]-N-methyl Scopolamine Chloride from human M2 receptor membranes incubated for 2 hrs by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEMBL_222112 (CHEMBL843708) Compound was tested for the inhibition of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate binding to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat brain membrane
- ChEMBL_429191 (CHEMBL913825) Activity at muscarinic M2 receptor in Albino Dunkin-Hartley guinea pig left atria assessed as inhibition of methacholine-induced bradycardia
- ChEMBL_748301 (CHEMBL1781311) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells after 1 hr by scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_776522 (CHEMBL1913619) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human recombinant M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells after 2 hrs by filter binding assay
- ChEMBL_776585 (CHEMBL1913682) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human recombinant M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells after 24 hrs by filter binding assay
- ChEMBL_826079 (CHEMBL2045510) Displacement of [3H]N-methylscopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells after 120 mins by scintillation counting
- ChEBML_1697999 Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cell membranes after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_138179 (CHEMBL882169) Inhibition of binding of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to muscarinic receptors in membranes of CHO cells transfected with Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_138346 (CHEMBL747776) Binding affinity against Muscarinic receptor M2 in rat brain using [3H]QNB (quinuclidinyl benzylate) radioligand at a concentration of 0.12 nM
- ChEMBL_139352 (CHEMBL752400) Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in guinea pig heart using (-)-[3H]-QNB as radioligand
- ChEMBL_139354 (CHEMBL752402) Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity against muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in guinea pig heart using (-)-[3H]-QNB as radioligand
- ChEMBL_139768 (CHEMBL748904) Inhibition of binding of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to muscarinic receptors in membranes of CHO cells transfected with Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140191 (CHEMBL744908) Compound was tested for the Binding affinity against rat heart Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by Radio ligand [3H]quinuclidinyl binding assay
- ChEMBL_140192 (CHEMBL744909) Compound was tested for the binding affinity against rat heart Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by Radio ligand [3H]quinuclidinyl binding assay.
- ChEMBL_1436827 (CHEMBL3387200) Agonist activity at muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin) expressed in CHOK1 cells after 3 mins by calcium flux/FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_1455316 (CHEMBL3362680) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as intracellular calcium level by fluorescence/summary (Abse5) assay
- ChEMBL_1455317 (CHEMBL3362681) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as intracellular calcium level by fluorescence/summary (Abse5) assay
- ChEMBL_1455701 (CHEMBL3366376) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from wild-type human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in Flp-In-CHO cells by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1455704 (CHEMBL3366379) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 Y177Q/T423H mutant expressed in Flp-In-CHO cells by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_1539139 (CHEMBL3738647) Antagonist activity at human wild-type M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells assessed as acetylcholine-induced cAMP by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1556436 (CHEMBL3772467) Inhibition of Influenza A virus wild type M2 proton channel infected in Xenopus laevis oocytes after 2 mins by TEVC assay
- ChEMBL_1700412 (CHEMBL4051394) Binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell suspension after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700413 (CHEMBL4051395) Binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenate after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700419 (CHEMBL4051401) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells after 60 mins by scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1895747 (CHEMBL4397782) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells after 3 hrs by beta counting method
- ChEMBL_2279649 Displacement of [3H]N-methylscopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in human HEK293T cell membranes by radioligand competition binding based analysis
- ChEMBL_687867 (CHEMBL1291431) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells after 16 hrs by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_956584 (CHEMBL2380034) Displacement of [3H] N-methylscopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cells after 30 mins by scintillation counting analysis
- ChEBML_139630 Compound was evaluated for inhibitory activity for Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to label antagonist site (RQNB) in CHO cells
- ChEBML_140050 Inhibition of binding of [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat heart atria at 10e-5 M of compound concentration
- ChEMBL_1700402 (CHEMBL4051384) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells after 3 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700411 (CHEMBL4051393) Binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in live adherent CHOK9 cells after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1709496 (CHEMBL4119545) Displacement of [3H]NMS from recombinant human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHOK1 cell membranes after 120 mins by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1749031 (CHEMBL4183541) Displacement of [3H]NMS from muscarinic receptor M2 in Sprague-Dawley rat brain homogenates after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1895759 (CHEMBL4397794) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells after 3 hrs by microbeta2 scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2106935 (CHEMBL4815610) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cell membranes assessed as inhibition constant by radioligand competition analysis
- ChEMBL_2129868 (CHEMBL4839297) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization
- ChEMBL_2237594 (CHEMBL5151490) Displacement of [3H]N-methylscopolamine from human muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor stably expressed in CHO cells by radioligand competition binding based analysis
- ChEMBL_2288190 Inhibition of recombinant PGAM1 (unknown origin) assessed as decrease in absorbance in presence of LDH, pyruvate kinase M2 and NADH by spectroscopic analysis
- ChEMBL_2288197 Allosteric inhibition of PGAM1 (unknown origin) assessed as decrease in absorbance in presence of LDH, pyruvate kinase M2 and NADH by spectroscopic analysis
- ChEMBL_562972 (CHEMBL1015371) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl scopolamine from human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells coexpressing Gqi5 by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_581791 (CHEMBL1061578) Antagonist activity against human cloned muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization by FLIPR
- ChEMBL_745615 (CHEMBL1775985) Inhibition of human recombinant ribonucleotide reductase M2/M1 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) after 30 mins by [3H]CDP reduction method
- ChEMBL_797807 (CHEMBL1944263) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization by fluorescence assay
- ChEMBL_886298 (CHEMBL2212341) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization by FLIPR assay
- ChEBML_138164 The compound was tested for the inhibition of binding of [3H]N-Methyl-scopolamine to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart tissue membranes
- ChEBML_138344 Evaluated for its binding affinity at human muscarinic receptor m2 by displacement of [3H]NMS binding using membranes from transfected chinese hamster ovarian cell
- ChEBML_140184 Compound was evaluated for its affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2, using [3H]- N-methyl-scopolamine, a radioligand displacement assay in rat heart membranes
- ChEMBL_139630 (CHEMBL749164) Compound was evaluated for inhibitory activity for Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 using [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to label antagonist site (RQNB) in CHO cells
- ChEMBL_140185 (CHEMBL744902) Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity for Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 by measuring displacement of [3H]- NMS ligand from rat cardiac cells.
- ChEMBL_1633576 (CHEMBL3876368) Displacement of [3H]AF-DX 384 from human recombinant M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells measured after 60 mins by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1700415 (CHEMBL4051397) Displacement of [3H]UNSW-MK259 from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells after 3 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1871943 (CHEMBL4373110) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human M2 AChR expressed in CHO cell membranes after 1 to 2 hrs by liquid scintillation spectrometry method
- ChEMBL_2250308 (CHEMBL5164518) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 assessed as intracellular calcium mobilization by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_510511 (CHEMBL996047) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl Scopolamine from human muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells coexpressed with Gqi5 by scintillation proximity assay
- ChEMBL_562390 (CHEMBL1018823) Antagonist activity at human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_829282 (CHEMBL2060129) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells assessed as calcium mobilization for 6 mins by Calcium4-based staining
- ChEMBL_138159 (CHEMBL748223) Inhibition of carbachol-induced release of alpha-amylase from pancreatic acinar cells from that of rat ileum contained the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 subtypes
- ChEMBL_138164 (CHEMBL748228) The compound was tested for the inhibition of binding of [3H]N-Methyl-scopolamine to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart tissue membranes
- ChEMBL_138165 (CHEMBL872664) The compound was tested for the inhibition of binding of [3H]N-Methyl-scopolamine to muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 of rat heart tissue membranes.
- ChEMBL_138344 (CHEMBL747774) Evaluated for its binding affinity at human muscarinic receptor m2 by displacement of [3H]NMS binding using membranes from transfected chinese hamster ovarian cell
- ChEMBL_140024 (CHEMBL859328) Binding of [3H]N-methylscopolamine at porcine heart Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 that inhibits the dissociation of [3H]NMS half maximally (pEC50diss) was reported
- ChEMBL_140111 (CHEMBL752112) Binding affinity was measured as selectivity for sigma 1 site over muscarinic (M2) receptor at 10 uM in rat using [3H]QN as radioligand
- ChEMBL_1700416 (CHEMBL4051398) Displacement of [3H]UR-AP060 from human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenate after 3 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1737680 (CHEMBL4153430) Displacement of [3H]-QNB/[3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO cells after 90 mins by microbeta scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1890398 (CHEMBL4392152) Displacement of [3H]-QNB/[3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO cells after 90 mins by microbeta scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1895360 (CHEMBL4397395) Displacement of [3H]-QNB/[3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO cells after 90 mins by microbeta scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1895732 (CHEMBL4397767) Displacement of [3H]-QNB from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO-K1 cells incubated for 120 mins by radioligand competition binding assay
- ChEMBL_1972408 (CHEMBL4605226) Displacement of [3H]N-methylscopolamine from human muscarinic M2 receptor transiently expressed in HEK293T cell membranes incubated for 1 hr by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1981909 (CHEMBL4615171) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human recombinant muscarinic receptor M2 expressed in CHO-K1 cell membranes incubated for 2 hrs by scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2023306 (CHEMBL4677119) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from muscarinic M2 receptor (unknown origin) expressed in CHO-K1 cell membranes assessed as inhibition constant by radioligand competition analysis
- ChEMBL_2026001 (CHEMBL4679814) Antagonist activity at human recombinant muscarinic receptor M2 expressed in CHO-K1 cells assessed as EC80 acetylcholine-induced calcium flux incubated for 30 mins
- ChEMBL_2293184 Positive allosteric modulator activity at rat M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 assessed as maximal response to ACh by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_2293185 Positive allosteric modulator activity at human M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 assessed as maximal response to ACh by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_519765 (CHEMBL939028) Activation of rat muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing chimeric Gqi5 protein assessed as potentiation of acetylcholine-induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization
- ChEMBL_982012 (CHEMBL2428367) Displacement of N-methyl [3H]-scopolamine from recombinant human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting
- ChEMBL_138184 (CHEMBL749205) Compound was evaluated for its ability to displace [3H]- N-methyl-scopolamine ([3H]NMS) binding to cloned CHO cell lines expressing Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
- ChEMBL_140196 (CHEMBL744913) In vitro binding affinity towards Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 was determined by measuring its ability to displace [3H]-AF-DX 384 from rat heart membranes
- ChEMBL_1436836 (CHEMBL3387209) Antagonist activity at muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (unknown origin) expressed in CHOK1 cells after 15 mins by calcium flux/FLIPR assay in presence of acetylcholine
- ChEMBL_1668530 (CHEMBL4018418) Agonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHO cells assessed as increase in cAMP accumulation after 2 hrs by cAMP-Glo assay
- ChEMBL_1676741 (CHEMBL4026884) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl-scopolamine from human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-FlpIn cells after 6 hrs by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1676756 (CHEMBL4026899) Agonist activity at recombinant human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells assessed as upregulation in ERK1/2 phosphorylation after 5 mins by alphascreen assay
- ChEMBL_1704896 (CHEMBL4056129) Antagonist activity at human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-transfected with Gqi5 in presence of EC80 acetylcholine by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_1904413 (CHEMBL4406635) Displacement of [3H]-QNB/[3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO cell membranes after 90 mins by microbeta scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2023308 (CHEMBL4677121) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Galpha15 assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization relative to acetylcholine
- ChEMBL_2060789 (CHEMBL4716042) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human recombinant muscarinic receptor M2 expressed in CHO-K9 cell membranes measured after 3 hrs by radioligand competition binding assay
- ChEMBL_2104992 (CHEMBL4813495) Positive allosteric modulation of human muscarinic acetylcholine M2/Gqi5 receptor expressed in CHO cells in presence of acetylcholine at EC20 concentration by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_625133 (CHEMBL1115154) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells coexpressing Gqi5 chimeric G-protein assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization
- ChEBML_138349 The compound was tested in vitro for binding activity against M2 muscarinic receptor in homogenates of the brainstem of rat using [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) as radioligand
- ChEMBL_139657 (CHEMBL745635) Compound was evaluated for its binding affinity at human muscarinic receptor m2 by displacement of [3H]NMS radioligand using membranes from transfected chinese hamster ovarian cell
- ChEMBL_1676736 (CHEMBL4026879) Displacement of [3H]N-methyl-scopolamine bromide from human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293T cell membranes after 1 hr by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1676750 (CHEMBL4026893) Agonist activity at recombinant human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of forskolin-mediated cAMP accumulation after 10 mins by FRET assay
- ChEMBL_1809278 (CHEMBL4308637) Displacement of [3H]-QNB/[3H]-NMS from human recombinant Muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in stable CHO cells after 90 mins by microbeta scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_2219879 (CHEMBL5133213) Inhibition of human muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 in the presence of acetylcholine at EC80 concentration by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_510506 (CHEMBL995214) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells coexpressed with Gqi5 assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_652864 (CHEMBL1226067) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 chimeric G-protein assessed as effect on calcium mobilization by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_659443 (CHEMBL1248353) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells coexpressing Galpha16 subunit assessed as increase of acetylcholine-induced calcium flux by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_1275613 (CHEMBL3090744) Inhibition of Influenza A virus Udorn/72 M2 ion channel V27A mutant expressed in Xenopus oocyte plasma membranes after 2 mins by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1275615 (CHEMBL3090746) Inhibition of Influenza A virus Udorn/72 M2 ion channel S31N mutant expressed in Xenopus oocyte plasma membranes after 2 mins by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_138349 (CHEMBL747778) The compound was tested in vitro for binding activity against M2 muscarinic receptor in homogenates of the brainstem of rat using [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) as radioligand
- ChEMBL_1972565 (CHEMBL4605383) Displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells measured after 60 mins by Hoechst H33342 dye based confocal plate reader assay
- ChEMBL_2503978 Displacement of [3H]NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cell membrane assessed as inhibition constant incubated for 90 mins by competitive radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_849488 (CHEMBL2149595) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells coexpressing Galpha16 subunit assessed as intracellular calcium mobilization after 10 to 15 mins by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_140048 (CHEMBL745865) Inhibition of binding of 0.1 nM [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat cerebral cortical membranes of transfected CHO cells in the absence of GTP
- ChEMBL_1471014 (CHEMBL3420061) Inhibition of wild type Influenza A virus (A/udorn/1972(H3N2)) M2 channel expressed in Xenopus oocyte plasma membranes after 2 mins by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1471017 (CHEMBL3420249) Inhibition of Influenza A virus (A/udorn/1972(H3N2)) M2 V27A mutant channel expressed in Xenopus oocyte plasma membranes after 2 mins by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1700434 (CHEMBL4051416) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 2 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700435 (CHEMBL4051417) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 4 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700436 (CHEMBL4051418) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 8 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700437 (CHEMBL4051419) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 15 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700438 (CHEMBL4051420) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 30 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700443 (CHEMBL4051425) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 0.2 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700444 (CHEMBL4051426) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cells assessed as W84 pIC50 at 0.1 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1784206 (CHEMBL4255723) Binding affinity to Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 wild-type M2 proton channel expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes at pH 5.5 by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1784214 (CHEMBL4255731) Binding affinity to Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 M2 proton channel S31N mutant expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes at pH 5.5 by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1792814 (CHEMBL4264733) Inhibition of wild type Influenza A virus (A/chicken/Hubei/327/2004(H5N1)) M2 channel expressed in yeast after 46 to 48 hrs by yeast growth restoration assay
- ChEMBL_1895773 (CHEMBL4397808) Competitive displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells using 0.2 nM [3H]-NMS after 3 hrs by microbeta2 scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1895774 (CHEMBL4397809) Competitive displacement of [3H]-NMS from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells using 2 nM [3H]-NMS after 3 hrs by microbeta2 scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1972545 (CHEMBL4605363) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells incubated in dark measured after 60 mins by Hoechst H33342 dye based confocal plate reader assay
- ChEMBL_2025989 (CHEMBL4679802) Displacement of [3H]NMS from human recombinant muscarinic receptor M2 expressed in CHO-K1 cell membranes assessed as inhibition constant incubated for 1 hr by Radioligand binding assay
- ChEMBL_2219911 (CHEMBL5133245) Inhibition of rat muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 preincubated with compound followed by acetylcholine addition at EC80 concentration by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_2219915 (CHEMBL5133249) Inhibition of human muscarinic acetylcholine M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 preincubated with compound followed by acetylcholine addition at EC80 concentration by calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_1700439 (CHEMBL4051421) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenates assessed as W84 pIC50 at 0.4 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700440 (CHEMBL4051422) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenates assessed as W84 pIC50 at 1 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700441 (CHEMBL4051423) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenates assessed as W84 pIC50 at 2 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1700442 (CHEMBL4051424) Competitive binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenates assessed as W84 pIC50 at 4 nM after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1972542 (CHEMBL4605360) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells incubated in dark at 22 degree C for 2 hrs by FACSCalibur flow cytometric saturation binding study
- ChEMBL_496880 (CHEMBL998549) Antagonist activity at human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells coexpressing chimeric G protein Gqi5 assessed as inhibition of acetylcholine-induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_664707 (CHEMBL1260774) Positive allosteric modulation of muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 assessed as effect on acetylcholine-induced intracellular calcium mobilization after 1 hr by FLIPR assay
- ChEMBL_140049 (CHEMBL745866) Inhibition of binding of 0.1 nM [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate to Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in rat cerebral cortical membranes of transfected CHO cells in the presence of 10 uM GTP
- ChEMBL_1676752 (CHEMBL4026895) Agonist activity at recombinant human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing beta-arrestin assessed as increase in beta-arrestin recruitment after 24 hrs by Bright-Glo luminescence assay
- ChEMBL_1895767 (CHEMBL4397802) Agonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing HA-Galphaq/i5 assessed as induction of Galphaq/i5-mediated IP1 accumulation after 1 hr by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1972547 (CHEMBL4605365) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells at 22 +/- 1 degree C preincubated for 180 mins followed by atropine addition by flow cytometric saturation binding study
- ChEMBL_1972548 (CHEMBL4605366) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells at 22 +/- 1 degree C preincubated for 120 mins followed by atropine addition by flow cytometric saturation binding study
- ChEMBL_1972549 (CHEMBL4605367) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells at 22 +/- 1 degree C preincubated for 110 mins followed by atropine addition by flow cytometric saturation binding study
- ChEMBL_1700424 (CHEMBL4051406) Binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in CHOK9 cell homogenate assessed as ratio of dissociation rate constant to association rate constant after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_2300456 Binding affinity to C-terminal amidated influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 (H3N2) M2 transmembrane domain (22 to 46 residues) in DPC micelles at pH 8 assessed as dissociation constant by ITC analysis
- ChEMBL_1700425 (CHEMBL4051407) Binding affinity to human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in live adherent CHOK9 cells assessed as ratio of dissociation rate constant to association rate constant after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting assay
- ChEMBL_1364624 (CHEMBL3291757) Inhibition of wild type Influenza A virus (A/udorn/72(H3N2)) M2 channel expressed in Xenopus oocyte plasma membrane incubated for 2 mins measured over 48 to 72 hrs by two-electrode voltage clamp method
- ChEMBL_1676748 (CHEMBL4026891) Agonist activity at Gi/o protein-coupled recombinant human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-FlpIn cells preincubated for 60 mins followed by [35S]GTPgammaS addition measured after 30 mins by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1701013 (CHEMBL4051995) Inhibition of Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 wild-type M2 proton channel expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes at pH 5.5 after 2 mins at -20 mV holding potential by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_2106941 (CHEMBL4815616) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in human HEK293T cells coexpressing NlucN-mini-Gsi assessed as inhibition of iperoxo-induced mini-Gsi recruitment by measuring equilibrium binding constant by nano-luciferase technique
- M2 Receptor Affinity Test The M2 receptor membrane protein was prepared at 100 μg/mL by Biology Department of WuXi AppTec, and compound was serially diluted in a 2.5-fold gradient in DMSO to obtain 10 concentrations. Radioisotope 3H-NMS was prepared at 0.2 nM in an assay buffer (10 mM HEPES, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 7.40). In formal testing, the experimental system comprising 1 μL of the test compound, 100 μL of M2 receptor membrane protein and 100 μL of radioisotope was shaken in a shaker at 300 RPM for 2 h at room temperature. A GF/C plate (Perkin Elmer, Cat No. 6055690) was prefoamed with 0.3% PEI, and the membrane proteins in the reaction solution were collected by filtration onto the GF/C plate
- ChEMBL_1784201 (CHEMBL4255718) Inhibition of Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 wild-type M2 proton channel expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes assessed as blockade of inward currents at pH 5.5 after 2 mins by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1784202 (CHEMBL4255719) Inhibition of Influenza A virus A/Udorn/72 wild-type M2 proton channel expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes assessed as blockade of inward currents at pH 5.5 after 5 mins by two-electrode voltage clamp assay
- ChEMBL_1676738 (CHEMBL4026881) Agonist activity at human recombinant muscarinic M2 receptor co-expressed with Galphaqi5-HA in African green monkey COS7 cells assessed as IP accumulation after 2 hrs in presence of myo-[3H]inositol by liquid scintillation counting method
- ChEMBL_1836507 (CHEMBL4336640) Inhibition of Influenza A virus (A/WSN/1933(H1N1)) CEN using m7G[5']-ppp-[5'] [m2'-O]GAA UAU(-Cy3) GCA UCA CUA GUA AGC UUU GCU CUA(-BHQ2)-3' as substrate measured after 60 mins by fluorescence assay
- ChEMBL_1807452 (CHEMBL4306811) Agonist activity at human Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in HEK cells co-expressing Glosensor construct assessed as decrease in isoproterenol-induced cAMP accumulation incubated for 7 mins in presence of isoproterenol by Glosensor cAMP reagent/plate reader based luminescence assay
- ChEMBL_1895768 (CHEMBL4397803) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing HA-Galphaq/i5 assessed as inhibition of carbachol-induced IP1 accumulation pre-incubated for 30 mins followed by carbachol addition and measured after 1 hr by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_935578 (CHEMBL2320114) Positive allosteric modulation of human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K1 cells assessed as leftward shift in acetylcholine response treated for 144 secs prior to acetylcholine addition measured for 5 mins by Fluo-4-AM based calcium mobilization assay
- ChEMBL_1780205 (CHEMBL4237197) Positive allosteric modulation of human M2 receptor expressed in CHO cells co-expressing Gqi5 assessed as increase in acetylcholine-induced calcium mobilization pretreated for 2.5 mins followed by acetylcholine addition and measured after 1 min by Fluo-4-AM dye based assay
- ChEMBL_2060793 (CHEMBL4716046) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells assessed as unspecific binding at Kd incubated in dark at 22 degree C for 2 hrs in presence of atropine by FACSCantoII flow cytometric saturation binding study relative to control
- ChEMBL_2060799 (CHEMBL4716052) Binding affinity to human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells assessed as unspecific binding at Kd incubated in dark at 22 degree C for 2 hrs in presence of atropine by FACSCalibur flow cytometric saturation binding study relative to control
- ChEMBL_1700406 (CHEMBL4051388) Competitive antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in HEK293 cells coexpressing HA tagged Galpha-protein qi5 assessed as inhibition of 0.1 uM carbachol-induced IP1 accumulation preincubated for 30 mins followed by carbachol addition measured after 1 hr by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1700407 (CHEMBL4051389) Competitive antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in HEK293 cells coexpressing HA tagged Galpha-protein qi5 assessed as inhibition of 1 uM carbachol-induced IP1 accumulation preincubated for 30 mins followed by carbachol addition measured after 1 hr by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1700408 (CHEMBL4051390) Competitive antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in HEK293 cells coexpressing HA tagged Galpha-protein qi5 assessed as inhibition of 10 uM carbachol-induced IP1 accumulation preincubated for 30 mins followed by carbachol addition measured after 1 hr by HTRF assay
- ChEMBL_1972531 (CHEMBL4605349) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing HA-Galphaq/i5 assessed as inhibition of carbachol-induced IP1 accumulation at 37 degree C pre-incubated for 30 mins followed by carbachol addition and measured after 60 mins by HTRF assay
- M2 Receptor Affinity Test The M2 receptor membrane protein was prepared at 100 μg/mL by Biology Department of WuXi AppTec, and compounds were serially diluted in a 2.5-fold gradient in DMSO to obtain 10 concentrations. Radioisotope 3H-NMS was prepared at 0.2 nM in an assay buffer (10 mM HEPES, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 7.40). In formal testing, the experimental system comprising 1 μL of the test compound, 100 μL of M2 receptor membrane protein and 100 μL of radioisotope was shaken in a shaker at 300 RPM for 2 h at room temperature. A GF/C plate (Perkin Elmer, Cat No. 6055690) was prefoamed with 0.3% PEI, and the membrane proteins in the reaction solution were collected by filtration onto the GF/C plate. The signal values were read by a Perkin Elmer Microbeta2 instrument and the inhibition rate for each concentration point was shown as a percentage.
- In Vitro Kinase Assays Biological activities of the MMT3-72 and its active metabolite MMT3-72-M2 were evaluated against JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK2 using kinase assays (FIG. 3 , Table 1). The compound MMT3-72 showed modest inhibitory activities against JAK1 and JAK2 (199.3 nM and 448.3 nM, respectively) and poor inhibitory activities against JAK3 and TYK2 (6821 nM and 2976 nM, respectively). However, the active metabolite MMT3-72-M2 showed strong inhibitory activities against JAK1 (2.0 nM), JAK2 (16.3 nM), and TYK2 (55.2 nM), but only weak inhibitory activities against JAK3 (701.3 nM). In comparison, fedratinib strongly inhibited JAK1 (10.1 nM) and JAK2 (15.6 nM), but poorly inhibited JAK3 and TYK2. The inhibitory profiles of JAK1, 2, and TYK2 of MMT3-72-M2 may have advantages to treat UC since JAK2/TYK2/IL-12/IL-23 signaling is strongly implicated in UC, while JAK1 isoform has long been identified as potential target in treating IBD as seen in Upadacitinib. In addition, MMT3-72-M2 showed poor inhibitory activities against JAK3 that may also be preferred in treating UC to reduce the unwanted adverse effects. Tofacitinib inhibited JAK3 with an IC50 of 1.6 nM and showed serious adverse effects. JAK3 inhibition has been shown to potentially lead to lymphopenia and thus hypothetically to an increased risk of infection.
- ChEMBL_1972538 (CHEMBL4605356) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cells co-expressing HA-Galphaq/i5 assessed as inhibition of carbachol-induced IP1 accumulation at 22 degree C pre-incubated for 180 mins followed by carbachol addition and further incubated at 37 degree C for 90 mins by HTRF assay
- Muscarinic Receptor Binding Assay The study of binding to human muscarinic M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 receptors was performed using commercial membranes (Perkin Elmer) prepared from CHO-K1 cells. Radioligand binding experiments were conducted in 96 polypropylene well plates in a total volume of 200 ul. All reagents were dissolved in assay binding buffer (PBS with calcium and magnesium, SIGMA), except compounds that were dissolved in DMSO 100%. Non-specific binding (NSB) was measured in the presence of 1 uM atropine. [3H]-NMS was used as the radioligand at a concentration of 1 nM for M2, M3 and M5 and 0.3 nM for M1 and M4. [3H]-NMS and antagonists were incubated with membranes that express human muscarinic receptors M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 at concentrations of 8.1, 10, 4.9, 4.5 and 4.9 ug/well, respectively. After an incubation period of two hours with gentle shaking, 150 ul of the reaction mix were transferred to 96 GF/C filter plates (Millipore), previously treated with wash buffer.
- ChEMBL_2106942 (CHEMBL4815617) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in human HEK293T cells coexpressing NlucN-mini-Gsi assessed as inhibition of iperoxo-induced mini-Gsi recruitment by measuring right ward shift of iperoxo-concentration-response curves at 58 nM preincubated for 120 mins followed by iperoxo-addition and measured by nano-luciferase technique
- ChEMBL_2106943 (CHEMBL4815618) Antagonist activity at human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 expressed in human HEK293T cells coexpressing NlucN-mini-Gsi assessed as inhibition of iperoxo-induced mini-Gsi recruitment by measuring right ward shift of iperoxo-concentration-response curves at 16 uM preincubated for 120 mins followed by iperoxo-addition and measured by nano-luciferase technique
- Inhibition Assay Antibacterial activity as measured by the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) and minimal bactericidal concentrations of compounds are well known (see., e.g., National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards 2000 Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests: approved standard, 7th ed. M2-A7, vol. 20, no. 1, Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, Pa.).
- Human RNR Inhibition Effect The inhibitory activity against the ribonucleotide reduction reaction (hereinafter referred to as RNR reaction) of the test compound was determined by measuring the formation of deoxycytidine diphosphate (hereinafter referred to as dCDP) from cytidine diphosphate (hereinafter referred to as CDP) by the following method.Human M1 subunit and human M2 subunit (mutant lacking amino terminal 59 amino acids), which are fused a histidine tag at the amino terminus, are overexpressed in Escherichia coli and are solubilized after collection, and histidine tagged human M1 and M2 proteins were purified on a nickel chelate column.For measuring the inhibitory activity of the test compound against the RNR reaction, the method described in the document [CANCER RESEARCH 64, 1-6, 2004] was referred to.
- Mtb EHB Inhibition Assay Enzyme activity was measured by monitoring the appearance of fluorescent product, 6-methoxy-naphthaldehyde (ex@330 nm and em@ 465 nm) on a SpectraMax M2 microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). Assays were performed in triplicate. IC50 values were determined by regression of at least five datum points, with a minimum of two datum points in the linear region of the curve on either side of the IC50 values.
- Muscarinic Receptor Binding Assay The study of binding to human muscarinic M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 receptors was performed using commercial membranes (Perkin Elmer) prepared from CHO-K1 cells. Radioligand binding experiments were conducted in 96 polypropylene well plates in a total volume of 200 μl. All reagents were dissolved in assay binding buffer (PBS with calcium and magnesium, SIGMA), except compounds that were dissolved in DMSO 100%. Non-specific binding (NSB) was measured in the presence of 1 μM atropine. [3H]-NMS was used as the radioligand at a concentration of 1 nM for M2, M3 and M5 and 0.3 nM for M1 and M4. [3H]-NMS and antagonists were incubated with membranes that express human muscarinic receptors M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 at concentrations of 8.1, 10, 4.9, 4.5 and 4.9 μg/well, respectively. After an incubation period of two hours with gentle shaking, 150 μl of the reaction mix were transferred to 96 GF/C filter plates (Millipore), previously treated with wash buffer (Tris 50 mM; NaCl 100 mM; pH: 7.4), containing 0.05% PEI (Sigma) during one hour. Bound and free [3H]-NMS were separated by rapid vacuum filtration in a manifold from Millipore and washed four times with ice cold wash buffer. After drying 30 min, 30 μl of OPTIPHASE Supermix were added to each well and radioactivity quantified using a Microbeta microplate scintillation counter.
- Receptors Binding Assay The study of binding to human muscarinic M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 receptors was performed using commercial membranes (Perkin Elmer) prepared from CHO-K1 cells. Radioligand binding experiments were conducted in 96 polypropylene well plates in a total volume of 200 μl. All reagents were dissolved in assay binding buffer (PBS with calcium and magnesium, SIGMA), except compounds that were dissolved in DMSO 100%. Non-specific binding (NSB) was measured in the presence of 1 μM atropine. [3H]-NMS was used as the radioligand at a concentration of 1 nM for M2, M3 and M5 and 0.3 nM for M1 and M4. [3H]-NMS and antagonists were incubated with membranes that express human muscarinic receptors M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 at concentrations of 8.1, 10, 4.9, 4.5 and 4.9 μg/well, respectively.After an incubation period of two hours with gentle shaking, 150 μl of the reaction mix were transferred to 96 GF/C filter plates (Millipore), previously treated with wash buffer (Tris 50 mM; NaCl 100 mM; pH: 7.4), containing 0.05% PEI (Sigma) during one hour. Bound and free [3H]-NMS were separated by rapid vacuum filtration in a manifold from Millipore and washed four times with ice cold wash buffer. After drying 30 min, 30 μl of OPTIPHASE Supermix were added to each well and radioactivity quantified using a Microbeta microplate scintillation counter.
- ChEMBL_1972560 (CHEMBL4605378) Displacement of 4-(2-((1E,3E)-5-((E)-3,3-Dimethyl-1-(6-oxo-6-((2-(4-(4-(1-(2-oxo-2-(11-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepin-5-yl)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)amino)hexyl)-5-sulfoindolin-2-ylidene)penta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)butane-1-sulfonate Bis(hydrotrifluoroacetate) fluorescent tracer from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells by FACSCalibur flow cytometry
- ChEMBL_1972561 (CHEMBL4605379) Displacement of 4-(2-((1E,3E)-5-((E)-3,3-Dimethyl-1-(6-oxo-6-((2-(4-(4-(1-(2-oxo-2-(11-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepin-5-yl)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)amino)hexyl)indolin-2-ylidene)penta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)butane-1-sulfonate Tris(hydrotrifluoroacetate fluorescent tracer from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells measured after 60 mins by Hoechst H33342 dye based confocal plate reader assay
- ChEMBL_1972562 (CHEMBL4605380) Displacement of 4-(2-((1E,3E)-5-((E)-3,3-Dimethyl-1-(6-oxo-6-((2-(4-(4-(1-(2-oxo-2-(11-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepin-5-yl)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)amino)hexyl)-5-sulfoindolin-2-ylidene)penta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)butane-1-sulfonate Bis(hydrotrifluoroacetate) fluorescent tracer from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells measured after 60 mins by Hoechst H33342 dye based confocal plate reader assay
- ChEMBL_1972563 (CHEMBL4605381) Displacement of 4-(2-((1E,3E)-5-((E)-3,3-Dimethyl-1-(6-oxo-6-((2-(3-(1-(4-(1-(2-oxo-2-(11-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepin-5-yl)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido)ethyl)-amino)hexyl)-5-sulfoindolin-2-ylidene)penta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)butane-1-sulfonateHydrotrifluoroacetate fluorescent tracer from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells measured after 60 mins by Hoechst H33342 dye based confocal plate reader assay
- ChEMBL_1972564 (CHEMBL4605382) Displacement of 4-(2-((1E,3E)-5-((E)-1-(6-((3,5-Bis((2-(3-(1-(4-(1-(2-oxo-2-(11-oxo-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepin-5-yl)ethyl)piperidin-4-yl)butyl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanamido)ethyl)carbamoyl)benzyl)amino)-6-oxohexyl)-3,3-dimethyl-5-sulfoindolin-2-ylidene)penta-1,3-dien-1-yl)-3,3-dimethyl-3H-indol-1-ium-1-yl)butane-1-sulfonate Tris(hydrotrifluoroacetate) fluorescent tracer from human muscarinic M2 receptor expressed in CHO-K9 cells measured after 60 mins by Hoechst H33342 dye based confocal plate reader assay
- K562 Cell Adhesion Assay (alpha4beta7 Mediated Adhesion/MAdCAM-1) M2 anti-FLAG antibody coated 96-well plates were coated with recombinant FLAG-hMAdCAM-1 contained in Dulbecco PBS. The compounds to be tested were added. Stably transfected K562 cells expressing human alpha4beta7 integrin that had been labeled with carboxymethyl fluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFDA-SE) were added to each well and allowed to adhere for 1 h at room temperature. Plates were washed, and then cells were lysed. The plate was read on a 96-well fluorescent plate reader at 485 nm excitation and 530 nm emission.
- Binding Assay Binding affinity (Ki) of compounds was measured by inhibition of radioligand binding to membranes from CHO cells expressing human M1, M2, M3, M4 and M5 receptors. Membranes were prepared by nitrogen cavitation and differential centrifugation as previously described (Hoare et al., Mol. Pharmacol. 2003 March; 63(3): 751-65). The radioligand employed was tritiated N-methylscopolamine, used at a concentration of 1.5 nM. A dose-response of twelve concentrations of compound was used, ranging from 10 M to 32 M. The assay buffer was 50 mM HEPES, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, pH-adjusted to pH 7.4.
- Cell-based Compound Screen Compound stocks were prepared at a 10 mM concentration in dimethyl sulfoxide.T. brucei bloodstream forms (100 µl at 2.0 × 10^4 parasites/ml) were plated in 96-well plates and mixed with 100 µl of compounds diluted in HMI-9 medium with 10% FBS (Me2SO at <0.2%). Parasites not treated with compounds were also platedas controls. After 48 h of incubation at 37 °C and 5% CO2, 20µl of alamarBlue (Invitrogen) was added, and the assays were developed for 4 h. Fluorescence measurements were obtained using a SpectraMax M2 microplate reader (Molecular Devices) with excitation at 544 nm and emission at 590 nm (590-nm cutoff).
- In-vitro Yeast α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity was evaluated at 37 °C, by using 0.1M phosphatebuffer (pH6.8) [28]. The enzyme(EC3.2.1.20, Saccharomyces cerevisiae purchased from sigma; catalog # G5003) (0.2 U/mL) was incubated with test compounds and phosphate buffer at 37 °C for 15 min. After 15min of incubation, 0.7 mM of substrate i.e. p-nitrophenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside (Sigma; catalog # N1377) was added and the change in absorbance was recorded at 400 nm for 30min by using spectrophotometer (SpectraMax M2, Molecular Devices, CA, USA). Test compound was replaced with DMSO in control experiments (7.5% final concentration).Acarbose was used as the standard inhibitor.
- ATR Biochemical Potency Assay ATR enzyme was made by ChemPartner (batch: CP-ATR-20161102-M2). 2× enzyme solutions were prepared in 1× kinase base buffer. 10 μl of 2× enzyme solution (final concentration: 2.5 nM) was added to each well of the 384-well assay plate containing 60 nl compound in each well. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 10 minutes. 2× peptide solutions were prepared with FAM-labeled peptide and ATP in the 1× kinase base buffer. 10 μl of 2× peptide solution was added to each well of the 384-well assay plate, which was incubated at 28° C. for 240 min. 40 μl of stop buffer was added to stop reaction. Data were collected by Caliper.
- Microscale Thermophoresis Assay The binding affinity of COMPOUND I and compounds of the invention to human sRAGE (the soluble extracellular domain of the human receptor for advanced glycation endproducts) was measured using microscale thermophoresis.Microscale Thermophoresis System (Monolith NT.115 Pico, NanoTemper, Inc) was used to determine the binding affinity of COMPOUND I and metabolites M1, M2, M3, M5, M6 and M7 to recombinant human sRAGE. sRAGE was labeled with NT-647-NHS fluorescence dye. Around 5 nM sRAGE was subsequently added to compounds at concentrations from 600 nM to 20 pM and incubated for 5 minutes at 25° C. in buffer containing 25 mM Hepes (pH 7.5), 5 mM CaCl2), 5 mM MgCl2, 50 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween20 and 1% DMSO before proceeding to microscale thermophoresis.
- In Vitro M4 &M2 Functional Assay The functional activity of compounds at the M4 and M2 receptors was determined by measuring changes in the level of intracellular calcium ions caused by signalling cascades mediated by the receptor. Intracellular Calcium levels were measured using a calcium sensitive fluorescent dye, calcium 5 (Molecular Devices) The changes in fluorescence were monitored by a fluorescent imager, FLiPR Tetra (Molecular devices). Increases in intracellular calcium were readily detected upon activation of both receptors by the muscarinic receptor agonist Acetylcholine.CHOK1 cells stably expressing human M4 or M2 receptor and co-expressing the accessory g-protein Gα16 were routinely grown as monolayers in Hams-F12 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone), 500 ug/mL Geneticin and 250 ug/mL zeocin (both invitrogen) in 5% CO2 at 37° C. Once confluent is cells cryopreserved by freezing at −186° C. in freezing solution (90% FBS 10% DMSO) (Sigma-Aldrich Co.). Twenty-four hours prior to testing cells resuscitated and freezing media removed via centrifugation, cells then seeded in a black walled clear bottom 384 well plates (Corning) at a density of 15,000 cells/well in Hams F12 media supplemented with 10% FBS. On the day of assay, growth media was removed and replaced with 63 μl of Calcium 5 dye solution (Molecular Devices) in assay buffer (HBSS, 20 mM HEPES, 0.1% BSA, 1 mM Probenecid pH7.4 (Sigma-Aldrich Co.)) per well (each vial of Calcium 5 resuspended in 27 mL of assay buffer). Cells were then incubated for 45 minutes at 37° C., 5% CO2. Compound was serially diluted in DMSO (log/half log) before being diluted 1:20 with assay buffer. 7 μl of compound diluted in assay buffer was then added to cells on FLiPR tetra and fluorescence intensity measured for 5 minutes. EC50 values for compounds were determined from ten point half log scale dose-response studies and represent the concentration of compound required to prevent 50% inhibition of its own maximal response. Curves were generated using the average of duplicate wells for each data point and analyzed using non-linear regression of four parameter dose response. Percentage Relative efficacy (RE) to an EC100 concentration of acetylcholine was reported for all compounds. The results are set out in Table 3 below in which the term No Response means that there was no significant response of calcium flux in the assay indicative of agonism.
- α-Chymotrypsin Inhibition Assay The α-chymotrypsin inhibition activity was evaluated in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer pH 7.6 with 10 mM CaCl2. α-Chymotrypsin (bovine pancreas) at the final concentration of 12 units/mL (prepared in buffer mentioned above) with the various concentrations of test compounds, prepared in DMSO, was incubated at 30 °C for25 min. The reaction was started by the addition of the substrate, N-succinyl-L-phenylalanine-p-nitroanilide (SPpNA; 0.4 mM final concentration prepared in the buffer as above). The change in absorbance by released p-nitroaniline was continuously monitored at 410 nm [Cloudhary et al., Phytochem. Lett., 4:404-406]. All the experiments were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 μL using a micro-plate reader (SpectraMax M2, Molecular Devices, CA, USA).
- Inhibition Assay Reaction mixtures consisting of 25 μL (1 unit/well) of Jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) urease, 55 μL of buffer at pH 6.8, 100 mM of urea, and 5 μL of various concentrations of test compounds were incubated at 30° C. for 15 min in 96-well plates. Subsequently 45 μL phenol reagents (1% w/v phenol and 0.005% w/v sodium nitroprussside), and 70 μL of alkali reagent (0.5% w/v NaOH and 0.1% w/v NaOCl) were added to each well. Urease activity through indophenols method was confirmed by the production of ammonia, as described by Weatherburn [12]. After 50 min, the increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured in a microplate reader SpectraMax M2 (Molecular Devices, CA, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 μL.
- HTRF Assay The UAE enzymatic reaction totals 50 μL and contains 50 mmol HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% BSA, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 uM ATP, 8 nM GST-Ubc-2, 35 nM flag-ubiquitin, 1 nM recombinant human UAE or mouse UAE. Compounds for this hUAE 1050 assay are tested at 10 point 3-fold dilution. The top concentration for this assay is 1 μM. Each compound is ordered in duplicate on the same plate. The enzymatic reaction mixture is incubated for 90 minutes at room temperature (24 degrees C.) in a 384 well plate prior to termination with a stop solution (0.1 M HEPES/0.05% Tween20, 20 mmol EDTA, 410 mM KF, 0.5 nM Eu Cryptate anti-FLAG M2-K antibody (Cis-bio International), 8 ug/mL Anti-GST XL-APC (Prozyme)). After incubation for 120 minutes, quantification of the FRET is performed on the Pherostar (BMG).
- Scintillation Proximity Assay In the present assay, the activity of the test substances on human full-length PDE2A3 enzyme was determined using the [3H]-cGMP scintillation proximity assay (SPA) modified from the Amersham TRKQ7100 instructions (GE Healthcare, Arlington Heights, Ill., USA). PDE2A3 protein was obtained from FLAG purification of sf21 insect cells using standard affinity purification procedures for this tag (anti-FLAG M2, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo., USA). Briefly, the SPA assays were performed using PDE SPA yttrium silicate beads (Perkin Elmer RPNQ0024; PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, Mass., USA) which bind preferentially to the linear nucleotide, GMP, compared to the cyclic nucleotide, cGMP. The, 3H-GMP product was detected using a Wallac MicroBeta scintillation counter. The reaction time was chosen with respect to the amount of time in which 10-20% of substrate was hydrolyzed by the enzyme. The assay was validated using PDE2-selective literature compounds.
- Discovery of novel allosteric modulators of the M1 muscarinic receptor: Agonist NMS competition at M2 Assay Provider: P. Jeffrey Conn Assay Provider Affiliation: Vanderbilt University Grant Title: Discovery of novel allosteric modulators of the M1 muscarinic receptor Grant Number: 1 R03 MH077606-01 The M1 muscarinic receptor is thought to be an important therapeutic target in schizophrenia. A cell-based fluorometric calcium assay was developed for high throughput screening. This assay was used to identify compounds with high selectivity for the M1 receptor subtype that act at an allosteric site on the receptor, thus providing increased specificity for this single receptor subtype. It is anticipated that these compounds will provide important tools for the study of muscarinic receptor function in the CNS. Agents that enhance cholinergic transmission or activate muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) have been developed to ameliorate the loss of cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's Disease (AD). While cholinergic agents have been partially successful in improving c
- In Vitro Determination of sEH Inhibition Activity Assay The fluorescent assay was used with purified recombinant human or mouse sEH proteins. The enzymes were incubated at 30° C. with the inhibitors ([I]final=0.4-100,000 nM) for 5 min in 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer (200 μL, pH 7.4) containing 0.1 mg/mL of BSA and 1% of DMSO. The substrate (CMNPC) was then added ([S]final=5 μM). Activity was assessed by measuring the appearance of the fluorescent 6-methoxynaphthaldehyde product (λex=330 nm, λem=465 nm) every 30 seconds for 10 min at 30° C. on a SpectraMax M2 (Molecular Devices). Results were obtained by regression analysis from a linear region of the curve. All measurements were performed in triplicate and the mean is reported. t-TUCB, a classic sEH inhibitor, was run in parallel and the obtained IC50s were corroborated with reported literature values, to validate the experimental results.
- Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme (UAE) HTRF Assay The UAE enzymatic reaction totals 50 μL and contains 50 mmol HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% BSA, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 uM ATP, 8 nM GST-Ubc-2, 35 nM flag-ubiquitin, 1 nM recombinant human UAE or mouse UAE. Compounds for this hUAE IC50 assay are tested at 10 point 3-fold dilution. The top concentration for this assay is 1 μM. Each compound is ordered in duplicate on the same plate. The enzymatic reaction mixture is incubated for 90 minutes at room temperature (24 degrees C.) in a 384 well plate prior to termination with a stop solution (0.1 M HEPES/0.05% Tween20, 20 mmol EDTA, 410 mM KF, 0.5 nM Eu Cryptate anti-FLAG M2-K antibody (Cis-bio International), 8 ug/mL Anti-GST XL-APC (Prozyme)). After incubation for 120 minutes, quantification of the FRET is performed on the Pherostar (BMG).
- Urease Inhibition Assay Reaction mixture consisting of 25 µL of Jack bean (Canavalia ensiformis) urease (1 unit/well), 55 µL of 100 mM urea dissolved in phosphate buffer (4 mM concentration of 6.80 pH, and 5 µL of various concentrations of test compound (from 0.5 to 0.00625 mM) were incubated at 30 °C for 15 min in 96-well plates.In kinetic experiments, various concentrations of both substrate and test compounds were used. Subsequently 45 µL phenol reagents (1% w/v phenol and 0.005% w/v sodium nitroprusside), and 70 µL of alkali reagent (0.5% w/v NaOH and 0.1% w/v NaOCl) were added to each well. Urease activity was measured through Weatherburn indophenols method by the production of ammonia [21]. After 50 min duration, the increasing absorbance at 630 nm was measured in a microplate reader (SpectraMax M2, Molecular Devices, CA, USA). All reactions were performed in triplicate in a final volume of 200 lL. Thiourea was used as the standard inhibitor of urease [15].
- Creating an a7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Recognition Domain from the Acetylcholine-binding Protein Assay Description 2 Assays used to generate Ki or EC50 values. 1) SPA Assay - Quick screen binding assays were performed using 100 ul of 0.2 mg/ml anti-mouse SPA antibody-binding beads (Amersham Biosciences) mixed with 33.6 u of monoclonal anti-FLAG M2 antibody from mouse (Sigma) in 0.1 M NaPO4 buffer, pH 7.0 (SPA mixture). Media (5 ul) collected 2 days after transfection were added to the mixture and finally 10 ul of ()-[3H]epibatidine (PerkinElmer Life Sci- ences) was added at a final concentration of 10 nM. Solutions were each counted for 1 min on either a Beckman LS 6500 liquid scintillation counter or Wallac 1450 Microbeta Trilux. Negative and positive controls consisted of media (5 ul) from the respective transfections. Nonexpressing mutants were transfected and verified de novo in triplicate. Western immu- noblots were also performed upon media (15 ul) from transfec- tions to verify the lack of expression. Competition curves and direct binding were measured fol- lowing the pro
- Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator (PAM): Analog Dose Response with rM4 Assay Provider: Colleen Niswender Assay Provider Affiliation: Vanderbilt University Grant Title: Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator(PAM) Grant Number: MH077607-1 To date, five muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) subtypes have been identified (M1-M5) and play important roles in mediating the actions of ACh in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Of these, M1 and M4 are the most heavily expressed in the CNS and represent attractive therapeutic targets for cognition, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. In contrast, the adverse effects of cholinergic agents are thought to be primarily due to activation of peripheral M2 and M3 mAChRs. Due to the high sequence homology and conservation of the orthosteric ACh binding site among the mAChR subtypes, development of chemical agents that are selective for a single subtype has been largely unsuccessful, and in the absence of highly selective activators of M4, it has been impo
- Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator (PAM): NMS Competition at rM4 Assay Provider: Colleen Niswender Assay Provider Affiliation: Vanderbilt University Grant Title: Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator(PAM) Grant Number: MH077607-1 To date, five muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) subtypes have been identified (M1-M5) and play important roles in mediating the actions of ACh in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Of these, M1 and M4 are the most heavily expressed in the CNS and represent attractive therapeutic targets for cognition, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. In contrast, the adverse effects of cholinergic agents are thought to be primarily due to activation of peripheral M2 and M3 mAChRs. Due to the high sequence homology and conservation of the orthosteric ACh binding site among the mAChR subtypes, development of chemical agents that are selective for a single subtype has been largely unsuccessful, and in the absence of highly selective activators of M4, it has been impo
- Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator(PAM) : Activity with human M4 Assay Provider: Colleen Niswender Assay Provider Affiliation: Vanderbilt University Grant Title: Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator(PAM) Grant Number: MH077607-1 To date, five muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) subtypes have been identified (M1-M5) and play important roles in mediating the actions of ACh in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Of these, M1 and M4 are the most heavily expressed in the CNS and represent attractive therapeutic targets for cognition, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. In contrast, the adverse effects of cholinergic agents are thought to be primarily due to activation of peripheral M2 and M3 mAChRs. Due to the high sequence homology and conservation of the orthosteric ACh binding site among the mAChR subtypes, development of chemical agents that are selective for a single subtype has been largely unsuccessful, and in the absence of highly selective activators of M4, it has been imp
- Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator(PAM): Analog Potency Assay Provider: Colleen Niswender Assay Provider Affiliation: Vanderbilt University Grant Title: Discovery of a Highly Selective in vitro and in vivo M4 Positive Allosteric Modulator(PAM) Grant Number: MH077607-1 To date, five muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) subtypes have been identified (M1-M5) and play important roles in mediating the actions of ACh in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Of these, M1 and M4 are the most heavily expressed in the CNS and represent attractive therapeutic targets for cognition, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. In contrast, the adverse effects of cholinergic agents are thought to be primarily due to activation of peripheral M2 and M3 mAChRs. Due to the high sequence homology and conservation of the orthosteric ACh binding site among the mAChR subtypes, development of chemical agents that are selective for a single subtype has been largely unsuccessful, and in the absence of highly selective activators of M4, it has been imp
- Enzyme Assay The SAE enzymatic reaction totals 50 μl and contains 50 mM HEPES Hemisodium (pH 7.5), 0.05% BSA, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 μM ATP, 250 μM GSH, 0.01 μM Ubc9-GST, 0.125 μM Sumo-Flag and 0.11 nM recombinant human SAE enzyme. The enzymatic reaction mixture, with and without inhibitor, Is incubated at 24° C. for 105 min in a 384-well plate before termination with 25 μM of Stop/Detection buffer (0.1M HEPES Hemisodium pH 7.5, 0.05% Tween20, 20 mM EDTA, 410 mM KF, 0.53 nM Europium-Cryptate labeled monoclonal anti-Flag M2 Antibody (CisBio International) and 8.125 μg/ml PHYCOLINK goat anti-GST allophycocyanin (XL-APC) antibody (Prozyme)). After incubation for 2 hours at 24° C., quantification of FRET is performed on the Pherostar (BMG Labtech). Percentage inhibition values at a single concentration or enzyme inhibition (IC50) values are determined from those curves. One skilled in the art will appreciate that the values generated either as percentage inhibition at a single concentration or IC50 values are subject to experimental variation.
- Glucokinase Activity Assay Recombinant human liver glucokinase was expressed as a FLAG fusion protein in E. coli, and purified on ANTIFLAG M2 AFFINITY GEL (Sigma). The assay was carried out at 30° C. in a 96-well plate. In the plate was distributed 69 μl each of assay buffer (25 mM Hepes Buffer: pH=7.2, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ATP, 0.5 mM TNAD, 1 mM dithiothreitol), to which was added 1 μl of a DMSO solution of the compound or DMSO as control. Then, 20 μl of pre-ice-cooled enzyme mixture (FLAG-GK, 20 U/ml G6PDH) was distributed thereto, to which was added 10 μl of 25 mM glucose as substrate to initiate the reaction (final glucose concentration=2.5 mM). After starting the reaction, the absorbance at 405 nm was measured every 30 seconds for 10 minutes to evaluate the compound based on the initial increase for 5 minutes. FLAG-GK was added so that the increase of absorbance after 5 minutes fell between 0.05 to 0.1 in the presence of 1% DMSO.
- Muscarinic M2 Receptor Binding Assay Cell membrane homogenates (60 μg protein) were incubated for 60 minutes at 22° C. with 2 nM [3H]AF-DX 384 in the absence or presence of the test compound in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 120 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM EDTA. Nonspecific binding was determined in the presence of 1 μM atropine. Following incubation, the samples were filtered rapidly under vacuum through glass fiber filters (GF/B, Packard) presoaked with 0.3% PEI and rinsed several times with ice-cold 50 mM Tris-HCl using a 96-sample cell harvester (Unifilter, Packard). The filters were dried then counted for radioactivity in a scintillation counter (Topcount, Packard) using a scintillation cocktail (Microscint 0, Packard). The results were expressed as a percent inhibition of the control radioligand specific binding, from which the Ki was calculated. Data were analyzed using software developed at Cerep (Hill software) and validated by comparison with data generated by the commercial software SigmaPlot®4.0 for Windows® (© 1997 by SPSS Inc.).
- Synthesizing Selective Agonists for the ?7 Nicotinic Receptor with in situ Click-Chemistry on Acetylcholine Binding Protein Templates. Assay Description 2 Assays used to generate Ki or EC50 values. 1) SPA Assay - Quick screen binding assays were performed using 100 l of 0.2 mg/ml anti-mouse SPA antibody-binding beads (Amersham Biosciences) mixed with 33.6 g of monoclonal anti-FLAG M2 antibody from mouse (Sigma) in 0.1 M NaPO4 buffer, pH 7.0 (SPA mixture). Media (5l) collected 2 days after transfection were added to the mixture and finally 10 l of (+)-[3H]epibatidine (PerkinElmer Life Sciences) was added at a final concentration of 10 nM. Solutions were each counted for 1 min on either a Beckman LS 6500 liquid scintillation counter or Wallac 1450 Microbeta Trilux. Negative and positive controls consisted of media (5 l) from the respective transfections. Nonexpressing mutants were transfected and verified de novo in triplicate. Western immunoblots were also performed upon media (15 l) from transfections to verify the lack of expression. Competition curves and direct binding were measured following the protocol p
- Activation Assay Using an sGCα 1 gene (NCBI accession No. BC028384.2) and an sGCβ1 gene (NCBI accession No. BC047620.1), an N-terminal FLAG tag-fused sGCα1 and an sGCβ1 expression baculovirus were prepared. These viruses were transfected into insect cells Sf9 (Cat. No. 11496-015, Gibco) to express a protein. From the cell lysates of the insect cells, heterodimers of the N-terminal FLAG tag-fused sGCα1 and sGCβ1 were purified with an M2 Affinity Gel (Sigma-Aldrich, Inc.) to obtain a human sGC.An Example compound was dissolved in DMSO and diluted 20-fold with ultrapure water. 2 uL of the diluted Example compound solution (maximum concentration of 100 uM), 2 uL of a substrate solution [0.5 uM triethanolamine buffer solution, 0.03 uM dithiothreitol, 0.01 uM GTP, 0.04 uM MgCl2, and 0.03 uM sodium nitroprusside (SNP)], and 6 uL of a human enzyme suspension were added to 384-well plates (manufactured by Greiner Bio-One), and incubated at room temperature for one hour. The measurement of the amount of cGMP was carried out, using an HTRF reagent (Cisbio).
- Enzyme Assay The total volume of the ATG7 enzymatic assay is 50 μL and contains 50 mM HEPES Hemisodium (pH 7.5), 0.05% BSA, 0.01% Tween-20, 25 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 10 μM ATP, 250 μM GSH, 5 nM ATG3-GST, 5 nM Flag-Gabarap, 100 μM TCEP and 0.15 nM recombinant human His-ATG7 enzyme. The enzymatic reaction mixture, with and without inhibitor, was incubated at 24° C. for 105 min in a 384-well plate before termination with 25 μM of Stop/Detection buffer (0.1M HEPES Hemisodium pH 7.5, 0.05% Tween20, 20 mM EDTA, 410 mM KF, 0.53 nM Europium-Cryptate labeled monoclonal anti-Flag M2 Antibody (CisBio International) and 8.125 μg/ml PHYCOLINK goat anti-GST allophycocyanin (XL-APC) antibody (Prozyme)). After incubation for 2 hours at 24° C., quantification of FRET is performed on the Pherostar (BMG Labtech). Percentage inhibition values at a single concentration or enzyme inhibition (IC50) values are determined from those curves. One skilled in the art will appreciate that the values generated either as percentage inhibition at a single concentration or IC50 values are subject to experimental variation.
- S-Adenosylhomocysteine Hydrolase (SAHase) Inhibition As a consequence of "D"-Isoneplanocin and "L"-Isoneplanocin, being isomers of Neplanocin A, which on one hand is a potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHase), a mechanism agreed upon as one source of its antiviral activity and on the other hand thought to contribute to cytotoxicity, the inhibitory efficiency on SAHase activity was assayed (source: rabbit erythrocytes). The inhibition of SAHase activity can be quantitated by the release of free homocysteine. SAHase from rabbit erythrocytes (Sigma) is dialyzed at 4° C. for 2 h in a buffer containing 20% glycerol and 50 mM potassium phosphate pH 7.4. The presence of adenosine deaminase insures that the reaction will proceed in the forward (hydrolysis) direction only. The enzyme preparation is incubated with or without the target compounds at different concentrations in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer pH 7.4 for 5 minutes at 37° C. before SAH is added. The formation of homocysteine is detected using the Measure-iT thiol quantitation reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions (Life technologies, Carlsbad, Calif.). Plates are read on Spectra Max M2 (Molecular Devices).
- BRAF V600E Enzyme Assay A competitive displacement assay was configured for B-Raf that monitors the amount of a fluorescently-tagged “tracer” bound to B-Raf via TR-FRET from an anti-tag Eu-labeled antibody also bound to B-Raf. For full-length FLAG-tagged B-Raf(V600E), the assay mixtures consisted of 25 mM K+HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Triton X-100, 1 mM DTT, 2% DMSO (from compound), 50 nM Tracer 1710 (ThermoFisher, PR9176A), 0.5 nM Eu anti-FLAG (M2)-cryptate Ab (Cisbio, 61FG2KLB) and 5 nM full-length, N-terminally FLAG-tagged B-Raf(V600E) (Origene Technologies, TP700031. Compounds were typically diluted in DMSO across an 11-point dosing range created using a 3-fold serial dilution protocol at a top dose of 10 μM. The assay was run in 384-well, polystyrene, low-volume, non-treated, white microtiter plates (Costar 4512) in a final volume of 12 μL. Low control wells included 1 μM of a potent B-Raf inhibitor as a control. The assays were incubated at ambient temperature (typically 22° C.) for 60 min and then read on a PerkinElmer EnVision microplate reader using standard TRF settings (λEx=320 nm, λEm=615 & 665 nm).
- Counterscreens for Selectivity Thrombin. In a 96-well white opaque plate, 80 μl of assay buffer was added to each well. Test compounds were added, and serially diluted as above, to generate a concentration range of approximately 1-100 μM. Human alpha-thrombin (Enzyme Research Labs) was diluted in assay buffer to a final concentration of 12.5 nM. 80 μl of this enzyme solution was added to the assay wells. The enzyme/compound mixtures were incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Fluorogenic substrate (Boc-Val-Pro-Arg-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin; Sigma) was added to assay wells at a final concentration of 20 μM. The assay plate was spun for 1 minute at 1500 g and then read at 37° C. in a SpectraMax M2 plate reader (λex=380 nm and λem=460 nm). Activity was quantified as the rate of change in fluorescence, which corresponds to the rate of substrate cleavage. IC50 values were determined as the concentration of inhibitor that produced 50% of the rate of change of control wells without any inhibitor. For compounds with activity <1 μM, the assay was repeated with a lower concentration range, typically from 10-1000 nM.
- BRAF V600E and V600K Enzyme Assay A competitive displacement assay was configured for B-Raf that monitors the amount of a fluorescently-tagged tracer bound to B-Raf via TR-FRET from an anti-tag Eu-labeled antibody also bound to B-Raf. For full-length FLAG-tagged B-Raf(V600E), the assay mixtures consisted of 25 mM K+HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Triton X-100, 1 mM DTT, 2% DMSO (from compound), 50 nM Tracer 1710 (ThermoFisher, PR9176A), 0.5 nM Eu anti-FLAG (M2)-cryptate Ab (Cisbio, 61FG2KLB) and 5 nM full-length, N-terminally FLAG-tagged B-Raf(V600E) (Origene Technologies, TP700031. When B-Raf(V600K) was assayed, the following substitutions were made: 15 nM Tracer 178 (ThermoFisher, PV5593), 2 nM Eu-anti-GST Ab (ThermoFisher, PV5595) and 5 nM N-terminally GST-tagged B-Raf(V600K) (331-end, SignalChem, B08-12DG). Compounds were typically diluted in DMSO across an 11-point dosing range created using a 3-fold serial dilution protocol at a top dose of 10 μM. The assay was run in 384-well, polystyrene, low-volume, non-treated, white microtiter plates (Costar 4512) in a final volume of 12 μL. Low control wells included 1 μM of a potent B-Raf inhibitor as a control.
- Enzyme Inhibition The HDAC activity inhibition assay was performed as follows to determine the ability of a test compound to inhibit HDAC enzymatic activity. Serial dilutions of HDAC inhibitors were prepared in HDAC assay buffer (25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 8) in 96-well assay plates (Fisher scientific, #07-200-309) and were pre-incubated for 2 hours at room temperature in the presence of 125 μg/ml BSA and purified HDAC1 (BPS Bioscience, San Diego, Calif., #50051), HDAC2 (BPS Bioscience, #50053), or HDAC3/NcoR2 (BPS Bioscience, #50003) at concentrations of 1.25, 1.32, and 0.167 μg/mL, respectively. Following pre-incubation, Fluor-de-Ly substrate (Enzo Life Sciences, Plymouth Meeting, Pa., BML-KI104-0050) was added to a final concentration of 10 μM and plates were further incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was stopped by addition of Trichostatin A (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, Mo., #T8552, final concentration: 100 nM) and trypsin (MP Biomedicals, Solon, Ohio, #02101179) was added to reach a final concentration of 100 μg/mL. After a 15 minute incubation at room temperature, fluorescence was recorded using a Spectramax M2 fluorometer (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, Calif.) with excitation at 365 nm and emission at 460 nm.
- Enzyme Inhibition The HDAC activity inhibition assay was performed as follows to determine the ability of a test compound to inhibit HDAC enzymatic activity. Serial dilutions of HDAC inhibitors were prepared in HDAC assay buffer (25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 8) in 96-well assay plates (Fisher scientific, #07-200-309) and were pre-incubated for 2 hours at room temperature in the presence of 1254 μg/ml BSA and purified HDAC1 (BPS Bioscience, San Diego, Calif., #50051), HDAC2 (BPS Bioscience, #50053), or HDAC3/NcoR2 (BPS Bioscience, #50003) at concentrations of 1.25, 1.32, and 0.167 vg/mL, respectively. Following pre-incubation, Fluor-de-Lys™ substrate (Enzo Life Sciences, Plymouth Meeting, Pa., BML-KI104-0050) was added to a final concentration of 10 μM and plates were further incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was stopped by addition of Trichostatin A (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, Mo., #T8552, final concentration: 100 nM) and trypsin (MP Biomedicals, Solon, Ohio, #02101179) was added to reach a final concentration of 100 μg/mL. After a 15 minute incubation at room temperature, fluorescence was recorded using a Spectramax M2 fluorometer (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, Calif.) with excitation at 365 nm and emission at 460 nm.
- HTRF Assay he UAE enzymatic reaction totals 50 μL and contains 50 mmol HEPES (pH 7.5), 0.05% BSA, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.1 uM ATP, 8 nM GST-Ubc-2, 35 nM flag-ubiquitin, 1 nM recombinant human UAE or mouse UAE. Compounds for this hUAE IC50 assay are tested at 10 point 3-fold dilution. The top concentration for this assay is 1 μM. Each compound is ordered in duplicate on the same plate. The enzymatic reaction mixture is incubated for 90 minutes at room temperature (24 degrees C.) in a 384 well plate prior to termination with a stop solution (0.1 M HEPES/0.05% Tween20, 20 mmol EDTA, 410 mM KF, 0.5 nM Eu Cryptate anti-FLAG M2-K antibody (Cis-bio International), 8 ug/mL Anti-GST XL-APC (Prozyme)). After incubation for 120 minutes, quantification of the FRET is performed on the Pherostar (BMG).From the Pherastar rawdata files, % inhibition vs. plate based controls is calculated. Dose response data is further processed in Genedata Condoseo, which performs as 4 parameter logistic fit and determines the IC50 (intercept at 50% inhibition) for each compound. The results are shown in the following table. For compounds whose values are marked with an asterisk (*), mouse UAE was used. For all other compounds, human UAE was used.
- Factor XIIa (FXIIa) Inhibitory Activity In a 96-well clear bottom plate, 80 μl of assay buffer was added to each well. Assay buffer consists of 0.5× Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (Invitrogen), buffered with 25 mM HEPES pH 7.4 (Invitrogen) and 0.5× Tris-buffered saline with Tween-20 0.05% (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Test compounds were first dissolved in DMSO (Sigma) and then 4 μl were added to test wells containing assay buffer. Serial dilutions using an automated multi-channel pipette were used to generate a concentration range of approximately 1-100 μM. Human FXIIa (Enzyme Research Labs) was diluted in assay buffer to a final concentration of 12.5 nM. 80 μl of this enzyme solution was added to the assay wells. The enzyme/compound mixtures were incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. Chromogenic substrate (Pefachrome XIIa; Enzyme Research Labs) was added to assay wells at a final concentration of 400 μM. The assay plate was spun for 1 minute at 1500 g and then read at 37° C. in a SpectraMax M2 plate reader (λ=405 nm). Activity was quantified as the rate of change in absorbance, which corresponds to the rate of substrate cleavage. IC50 values were determined as the concentration of inhibitor that produced 50% of the rate of change of control wells without any inhibitor. For compounds with activity <1 μM, the assay was repeated with a lower concentration range, typically from 10-1000 nM.
- HDAC Enzyme Inhibition The HDAC activity inhibition assay was performed as follows to determine the ability of a test compound to inhibit HDAC enzymatic activity. Serial dilutions of HDAC inhibitors were prepared in HDAC assay buffer (25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, pH 8) in 96-well assay plates (Fisher scientific, #07-200-309) and were pre-incubated for 2 hours at room temperature in the presence of 125 μg/ml BSA and purified HDAC1 (BPS Bioscience, San Diego, Calif., #50051), HDAC2 (BPS Bioscience, #50053), or HDAC3/NcoR2 (BPS Bioscience, #50003) at concentrations of 1.25, 1.32, and 0.167 μg/mL, respectively. Following pre-incubation, Fluor-de-Lys substrate (Enzo Life Sciences, Plymouth Meeting, Pa., BML-KI104-0050) was added to a final concentration of 10 μM and plates were further incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. The enzymatic reaction was stopped by addition of Trichostatin A (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, Mo., #T8552, final concentration: 100 nM) and trypsin (MP Biomedicals, Solon, Ohio, #02101179) was added to reach a final concentration of 100 μg/mL. After a 15 minute incubation at room temperature, fluorescence was recorded using a Spectramax M2 fluorometer (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, Calif.) with excitation at 365 nm and emission at 460 nm. IC50 values were calculated by using a sigmoidal dose-response (variable slope) equation in GraphPad Prism 5 for Windows (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, Calif.).
- Scintillation Proximity Assay (SPA) Human PDE4A3 coding sequence (amino acids 2 to 825 from the sequence with accession number NP_001104779) was cloned into the baculovirus expression vector pFastBac (Invitrogen) engineered to include an N-terminal His6 affinity tag and a C-terminal FLAG affinity tag to aid in purification. The recombinant Bacmid was isolated and used to transfect insect cells to generate a viral stock. To generate cell paste for purification, insect cells were infected with the virus stock and cells were harvested 72 hours after infection. Insect cell paste was lysed and after centrifugation, the supernatant was batch bound to Ni-NTA agarose (GE Healthcare) and eluted with 250 mM imidazole. This eluate was diluted with FLAG buffer (50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 1 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors) and batch bound to ant-FLAG M2 agarose (Sigma) overnight at 4° C. The agarose was packed into a column, washed with buffer and eluted with buffer containing elute using 250 μg/mL Flag-peptide. Fractions were analyzed using SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining and pooled based on purity. Pooled fractions were chromatographed on a S200 120 mL column (GE Healthcare) in 50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 2 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors. PDE4A3 fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining, pooled based on purity, dialyzed against 50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 20% glycerol, 2 mM TCEP, frozen and stored at −80° C.
- Scintillation Proximity Assay (SPA) Human PDE4C1 coding sequence (amino acids 2 to 712 from the sequence with accession number NP_000914.2) was cloned into the baculovirus expression vector pFastBac (Invitrogen) engineered to include an N-terminal His6 affinity tag and a C-terminal FLAG affinity tag to aid in purification. The recombinant Bacmid was isolated and used to transfect insect cells to generate a viral stock. To generate cell paste for purification, insect cells were infected with the virus stock and cells were harvested 72 hours after infection. Insect cell paste was lysed and after centrifugation, the supernatant was batch bound to Ni-NTA agarose (GE Healthcare) and eluted with 250 mM imidazole. This eluate was diluted with FLAG buffer (50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 1 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors) and batch bound to anti-FLAG M2 agarose (Sigma) overnight at 4° C. The agarose was packed into a column, washed with buffer and eluted with buffer containing elute using 250 μg/mL Flag-peptide. Fractions were analyzed using SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining and pooled based on purity. Pooled fractions were chromatographed on a S200 120 mL column (GE Healthcare) in 50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 2 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors. PDE4C1 fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining, pooled based on purity, dialyzed against 50 mM Tris HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 20% glycerol, 2 mM TCEP, frozen and stored at −80° C.
- Biological Assays For measuring Npt2a activity in a cell based assay, a stable CHO cell line with inducible Npt2a expression was generated. Therefore, CHO T-Rex cells (life technologies cat. R718-07) were stably transfected with doxycycline-inducible human NPT2a (pcDNA5TO-hNpt2a). The obtained CHO T-REx hNpt2a cells were routinely cultured in Dulbecco's MEM/F12 (4.5 g/l Glucose, Gibco cat. 21331-020; 500 mL) supplemented with 10 ml Glutamax 100×, Sodium pyruvate (7 mL of 100 mM solution), HEPES (10 mL of 1 M solution), Sodium bicarbonate (10 mL of 7.5% solution), 10% Fetal Bovine Serum Tetracycline free (Clontech cat. 631106, 500 ml), Penicillin-Streptomycin (5 mL of 100× Solution), Blasticidin 10 μg/mL and 400 μg/mL Hygromycin.Activity of Npt2a was detected by following depolarization of cellular membrane potential by influx of sodium phosphate using fluorescent membrane potential dye kit BLUE (Molecular devices cat. R8034). For Npt2a activity measurements, CHO T-Rex hNpt2a cells were seeded into 1536 well microtiter plates (GREINER Bio-One cat. 782092) with 750 cells/well in 7 μL/w of complete medium (2% Tetracycline-free FBS, 2% Poly-D-Lysine) without selective agents+Doxycycline 0.5 μg/mL to induce Npt2a gene expression, and grown for 24 h at 37° C., 5% carbon dioxide.On the day of experiment a 1×MPdye Loading Solution was freshly prepared by re-suspending 15 mg of Blue MPdye powder in 10 mL of NHE buffer sodium-free (140 mM N-Methyl-D-glucamine, 5.4 mM KCl, 1 mM CaCl2, 11 mM D(±)-Glucose water free, 1.2 mM MgCl2, 10 mM HEPES; pH 7.4 (adjusted with hydrochloric acid); sterile filtered). 5 μl medium was removed from plates by robotic manipulation, then 5 μL/well of sodium-free NHE buffer was added. After incubation for 2 min, this washing step was repeated once. Then, 5 μL/w of buffer was removed from plates and cells were incubated for 5 min at room temperature with 5 μL/w of MPdye Loading Solution (1× in Sodium-free NHE Buffer). Test compounds were added to the cells at final test concentrations between 50 μM and 1 nM (0.6 μL/well, final DMSO 0.6%, prepared in MPDye Loading Solution) and incubated for 5 min at room temperature.Plates were analyzed with an in house CCD camera device using a λexc 510-545 nm/λem 565-625 nm filter. Fluorescence was detected for 15 sec (background measurement M1). Activity of Npt2a was triggered by addition of 2 μL/well of 30 mM Na+ and 1 mM phosphate (prepared in a mixture of NHE Buffer Na+ free and NHE Buffer 140 mM Na+). Fluorescence was followed for 2-3 min (depolarization measurement M2). Data was normalized to cell number and dye loading efficiency by calculating M2/M1. This quotient was plotted against test compound concentration. Graph Pad Prism or equivalent in house software was used to create sigmoidal dose-response curves (variable slope) and determine IC50 values.
- Glucokinase-Activating Assay To test the exemplified compounds, the following assay was employed. Recombinant human liver glucokinase was expressed as a FLAG fusion protein in E. coli, and purified on ANTIFLAG M2 AFFINITY GEL (Sigma). The assay was carried out at 30° C. in a 96-well plate. In the plate was distributed 69 ul each of assay buffer (25 mM Hepes Buffer: pH=7.2, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ATP, 0.5 mM TNAD, 1 mM dithiothreitol), to which was added 1 ul of a DMSO solution of the compound or DMSO as control. Then, 20 ul of pre-ice-cooled enzyme mixture (FLAG-GK, 20 U/ml G6PDH) was distributed thereto, to which was added 10 ul of 25 mM glucose as substrate to initiate the reaction (final glucose concentration=2.5 mM). After starting the reaction, the absorbance at 405 nm was measured every 30 seconds for 10 minutes to evaluate the compound based on the initial increase for 5 minutes. FLAG-GK was added so that the increase of absorbance after 5 minutes fell between 0.05 to 0.1 in the presence of 1% DMSO. The OD values of the respective compounds were measured in the respective concentrations, wherein the OD value of DMSO as control is regarded as 100%. From the OD values at the respective concentrations, Emax (%, 2.5 mM Glu) and EC50 (nM, 2.5 mM Glu) were calculated and used as indicators of the GK activation capability of the compounds. According to the above assay, the GK activation capability of the exemplified compounds of the present invention was determined. The following table shows the results. Where different enantiomers of the same compound were tested, two numbers are provided. Where 3 numbers are provided, for example, Ex. #30, data for the racemic form is also shown.
- Human RNR Inhibition Effect First, test compounds were serially diluted with DMSO. Next, human M1 protein and human M2 protein were added to an aqueous albumin solution derived from 0.02% fetal bovine serum, DMSO solution of the compound of the present disclosure or the control DMSO solution (final concentration of DMSO was 1%) was added, and the mixture was allowed to stand for 20 minutes. Thereafter, the reaction buffer [50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.2) at the final concentration, 4 mM magnesium acetate at the final concentration, 100 mM potassium chloride at the final concentration, 6 mM dithiothreitol at the final concentration, 2 mM adenosine triphosphate at the final concentration, 0.24 mM nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate at final concentration] and 10 μM CDP at the final concentration were added and incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes to perform RNR reaction. Immediately after the reaction, the reaction was stopped by heating at 100° C. for 15 minutes, followed by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes. After the centrifugation, a portion (5 μL) of the resulting supernatant was analyzed with a high performance liquid chromatography (Shimadzu Corporation, Prominence) using Shim-pack XR-ODS (manufactured by Shimadzu GLC Co., 3.0×100 mm). Elution was carried out at a measurement wavelength of 265 nm at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min by a 9-minute concentration gradient from the 12:13 mixture of mobile phase A (10 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 6.7), 10 mM tetrabutylammonium, 0.25% methanol) and mobile phase B (50 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 6.7), 5.6 mM tetrabutylammonium, 30% methanol) to the same 2:3 mixture to measure the substrate CDP (RT 5.9 min) and the reaction product dCDP (RT 6.2 min).
- Human RNR Inhibition Effect For measuring the inhibitory activity of the test compound against the RNR reaction, the method described in Cancer Research 64, 1-6 (2004) was referred to.First, test compounds were serially diluted with DMSO. Next, human M1 protein and human M2 protein were added to an aqueous albumin solution derived from 0.02% fetal bovine serum, DMSO solution of the compound of the present disclosure or the control DMSO solution (final concentration of DMSO was 1%) was added, and the mixture was allowed to stand for 20 minutes. Thereafter, the reaction buffer [50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.2) at the final concentration, 4 mM magnesium acetate at the final concentration, 100 mM potassium chloride at the final concentration, 6 mM dithiothreitol at the final concentration, 2 mM adenosine triphosphate at the final concentration, 0.24 mM nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate at final concentration] and 10 μM CDP at the final concentration were added and incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes to perform RNR reaction. Immediately after the reaction, the reaction was stopped by heating at 100° C. for 15 minutes, followed by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes. After the centrifugation, a portion (5 μL) of the resulting supernatant was analyzed with a high performance liquid chromatography (Shimadzu Corporation, Prominence) using Shim-pack XR-ODS (manufactured by Shimadzu GLC Co., 3.0×100 mm). Elution was carried out at a measurement wavelength of 265 nm at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min by a 9-minute concentration gradient from the 12:13 mixture of mobile phase A (10 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 6.7), 10 mM tetrabutylammonium, 0.25% methanol) and mobile phase B (50 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 6.7), 5.6 mM tetrabutylammonium, 30% methanol) to the same 2: 3 mixture to measure the substrate CDP (RT 5.9 min) and the reaction product dCDP (RT 6.2 min).
- Inhibition Effect First, test compounds were serially diluted with DMSO. Next, human M1 protein and human M2 protein were added to an aqueous albumin solution derived from 0.02% fetal bovine serum, a DMSO solution of the compound of the present invention or the control DMSO solution (final concentration of DMSO was 1%) was added, and the mixture was allowed to stand for 20 minutes. Thereafter, the reaction buffer [50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.2) at the final concentration, 4 mM magnesium acetate at the final concentration, 100 mM potassium chloride at the final concentration, 6 mM dithiothreitol at the final concentration, 2 mM adenosine triphosphate at the final concentration, 0.24 mM nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate at final concentration] and 10 μM CDP at the final concentration were added and incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes to perform RNR reaction. Immediately after the reaction, the reaction was stopped by heating at 100° C. for 15 minutes, followed by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes. After the centrifugation, a portion (5 μL) of the resulting supernatant was analyzed with a high performance liquid chromatography (Shimadzu Corporation, Prominence) using Shim-pack XR-ODS (manufactured by Shimadzu GLC Co., 3.0×100 mm). Elution was carried out at a measurement wavelength of 265 nm at a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min by a 9-minute concentration gradient from the 12:13 mixture of mobile phase A (10 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 6.7), 10 mM tetrabutylammonium, 0.25% methanol) and mobile phase B (50 mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate (pH 6.7), 5.6 mM tetrabutylammonium, 30% methanol) to the same 2:3 mixture to measure the substrate CDP (RT 5.9 min) and the reaction product dCDP (RT 6.2 min).
- Biological Assays Human PDE4A3 coding sequence (amino acids 2 to 825 from the sequence with accession number NP_001104779) was cloned into the baculovirus expression vector pFastBac (Invitrogen) engineered to include an N-terminal His6 affinity tag and a c-terminal FLAG affinity tag to aid in purification. The recombinant Bacmid was isolated and used to transfect insect cells to generate a viral stock. To generate cell paste for purification, insect cells were infected with the virus stock and cells were harvested 72 hours after infection. Insect cell paste was lysed and after centrifugation, the supernatant was batch bound to Ni-NTA agarose (GE Healthcare) and eluted with 250 mM imidazole. This eluate was diluted with FLAG buffer (50 mM Tris HCL pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5% Glycerol, 1 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors) and batch bound to ant-FLAG M2 agarose (Sigma) overnight at 4° C. The agarose was packed into a column, washed with buffer and eluted with buffer containing elute using 250 ug/ml Flag-peptide. Fractions were analyzed using SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining and pooled based on purity. Pooled fractions were chromatographed on a S200 120 ml column (GE Healthcare) in 50 mM Tris HCL pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 10% Glycerol, 2 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors. PDE4A3 fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining, pooled based on purity, dialyzed against 50 mM Tris HCL pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 20% Glycerol, 2 mM TCEP, frozen and stored at −80° C.Human PDE4B1 coding sequence (amino acids 122 to 736 from the sequence with accession number Q07343) with the mutations resulting in the amino acid substitutions S134E, S654A, S659A, and S661A was cloned into the baculovirus expression vector pFastBac (Invitrogen) engineered to include a N-terminal His6 affinity tag to aid in purification followed by a thrombin cleavage site. The recombinant Bacmid was isolated and used to transfect insect cells to generate a viral stock. To generate cell paste for purification, insect cells were infected with the virus stock and cells were harvested 72 hours after infection as described in Seeger, T. F. et al., Brain Research 985 (2003) 113-126. Insect cell paste was lysed and after centrifugation, the supernatant was chromatographed on Ni-NTA agarose (Qiagen) as described in Seeger, T. F. et al., Brain Research 985 (2003) 113-126. Ni-NTA agarose eluting fractions containing PDE4 were pooled, diluted with Q buffer A (20 mM Tris HCl pH 8, 5% glycerol, 1 mM TCEP) to reduce NaCl to −100 mM and loaded on a Source 15Q (GE Healthcare) column. After washing with Q buffer A/10% buffer B to baseline, PDE4D was eluted with a gradient from 10% to 60% of Buffer B (20 mM Tris HCl pH 8, 1 M NaCl, 5% glycerol, 1 mM TCEP). PDE4D fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining, pooled based on purity, frozen and stored at −80° C.Human PDE4C1 coding sequence (amino acids 2 to 712 from the sequence with accession number NP_000914.2) was cloned into the baculovirus expression vector pFastBac (Invitrogen) engineered to include an N-terminal His6 affinity tag and a c-terminal FLAG affinity tag to aid in purification. The recombinant Bacmid was isolated and used to transfect insect cells to generate a viral stock. To generate cell paste for purification, insect cells were infected with the virus stock and cells were harvested 72 hours after infection. Insect cell paste was lysed and after centrifugation, the supernatant was batch bound to Ni-NTA agarose (GE Healthcare) and eluted with 250 mM imidazole. This eluate was diluted with FLAG buffer (50 mM Tris HCL pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5% Glycerol, 1 mM TCEP with protease inhibitors) and batch bound to ant-FLAG M2 agarose (Sigma) overnight at 4° C. The agarose was packed into a column, washed with buffer and eluted with buffer containing elute using 250 ug/ml Flag-peptide. Fractions were analyzed using SDS-PAGE Coomassie blue staining and pooled based on purity.
- In Vitro Assays for IDH1m (R132H or R132C) Inhibitors In the primary reaction, the reduction of α-KG acid to 2-HG is accompanied by a concomitant oxidation of NADPH to NADP. The amount of NADPH remaining at the end of the reaction time is measured in a secondary diaphorase/resazurin reaction in which the NADPH is consumed in a 1:1 molar ratio with the conversion of resazurin to the highly fluorescent resorufin. Uninhibited reactions exhibit a low fluorescence at the end of the assay, while reactions in which the consumption of NADPH by R132H IDH1 has been inhibited by a small molecule show a high fluorescence.The primary reaction is performed in a volume of 50 μL 1× Buffer (150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.05% (w/v) bovine serum albumin), contained 0.25 ug/mL (2.7 nM) IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132H heterodimer, 0.3 mM alpha-ketoglutarate, 4 μM NADPH, and either 300 μM NADP (saturated) or 30 μM NADP (without saturation), and 1 uL of 50× compound in DMSO. The mixture of compound, enzyme, and cofactor is pre-incubated at room temperature for 1 hr prior to the addition of alpha-ketoglutarate. To perform the secondary reaction, 10 uL of 1× buffer containing 36 μg/ml diaphorase and 30 mM resazurin is added to the primary reaction and incubated for a further 5 minutes at 25° C. Florescence is read on a Spectramax platereader at Ex 544 Em 590. Compounds or compound dilutions are prepared in 100% DMSO concentration and diluted 1:50 into the final reaction. IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132C is assayed under similar conditions except that 1X Buffer is 50 mM K2HPO4, pH 6.5; 10 mM MgCl2; 10% glycerol; 0.03% (w/v) bovine serum albumin and final concentrations are 0.4 ug/mL (4.3 nM) IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132C heterodimer, 0.02 mM alpha-ketoglutarate, 4 uM NADPH, and either 300 μM NADP (saturated) or 30 μM NADP (without saturation). IC50s are determined.IDH1 or IDH2 wildtype (wt) and mutant heterodimers are expressed and purified by methods known in the art. For example, IDH1 wt/R132m heterodimer is expressed and purified as follows. Co-expression of IDH1 wt-his and IDH1R132C-flag is carried out in sf9 insect cells. Cells (25 g) are resuspended in 250 ml of 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4, at 4° C. with stirring. Cells are disrupted with 4 passes through an M-Y110 Micro fluidizer (Microfluidics) set to 500 psi, and then centrifuged at 22,000 ref for 20 min at 4° C. The supernatant is harvested and loaded at 15 cm/h on a Histrap FF 5*1 ml column (GE) which is equilibrated with 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4. Host cell contaminants are removed by washing the column with equilibration buffer followed by equilibration buffer containing 20 mM imidazole and 60 mM imidazole to baseline. IDH1 wt-his homodimer and IDH1 wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag are eluted by equilibration buffer containing 250 mM imidazole. Fractions eluted by 250 mM imidazole are pooled together and loaded at 15 cm/h onto a column pre-packed with 10 ml ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel (Sigma), the column is equilibrated with 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4. After washing with equilibration buffer, IDH1 wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag heterodimer is eluted by equilibration buffer containing flag peptide (0.2 mg/ml). Aliquots of IDH1 wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag are flash frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −80° C. Same conditions are used for the purification of IDH1 wt-his/IDH1R132H-flag.
- In Vitro Assays for IDH1m (R132H or R132C) Inhibitors In the primary reaction, the reduction of α-KG acid to 2-HG is accompanied by a concomitant oxidation of NADPH to NADP. The amount of NADPH remaining at the end of the reaction time is measured in a secondary diaphorase/resazurin reaction in which the NADPH is consumed in a 1:1 molar ratio with the conversion of resazurin to the highly fluorescent resorufin. Uninhibited reactions exhibit a low fluorescence at the end of the assay, while reactions in which the consumption of NADPH by R132H IDH1 has been inhibited by a small molecule show a high fluorescence.The primary reaction is performed in a volume of 50 μL 1× Buffer (150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.05% (w/v) bovine serum albumin), contained 0.25 ug/mL (2.7 nM) IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132H heterodimer, 0.3 mM alpha-ketoglutarate, 4 μM NADPH, and either 300 μM NADP (saturated) or 30 μM NADP (without saturation), and 1 uL of 50× compound in DMSO. The mixture of compound, enzyme, and cofactor is pre-incubated at room temperature for 1 hr prior to the addition of alpha-ketoglutarate. To perform the secondary reaction, 10 uL of 1× buffer containing 36 μg/ml diaphorase and 30 mM resazurin is added to the primary reaction and incubated for a further 5 minutes at 25° C. Florescence is read on a Spectramax platereader at Ex 544 Em 590. Compounds or compound dilutions are prepared in 100% DMSO concentration and diluted 1:50 into the final reaction. IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132C is assayed under similar conditions except that 1× Buffer is 50 mM K2HP04, pH 6.5; 10 mM MgCl2; 10% glycerol; 0.03% (w/v) bovine serum albumin and final concentrations are 0.4 ug/mL (4.3 nM) IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132C heterodimer, 0.02 mM alpha-ketoglutarate, 4 uM NADPH, and either 300 μM NADP (saturated) or 30 μM NADP (without saturation). IC50s are determined.IDH1 or IDH2 wildtype (wt) and mutant heterodimers are expressed and purified by methods known in the art. For example, IDH1wt/R132m heterodimer is expressed and purified as follows. Co-expression of IDH1wt-his and IDH1R132C-flag is carried out in sf9 insect cells. Cells (25 g) are resuspended in 250 ml of 50 mM Tirs, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4, at 4° C. with stirring. Cells are disrupted with 4 passes through an M-Y110 Micro fluidizer (Microfluidics) set to 500 psi, and then centrifuged at 22,000 rcf for 20 min at 4° C. The supernatant is harvested and loaded at 15 cm/h on a Histrap FF 5*1 ml column (GE) which is equilibrated with 50 mM Tirs, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4. Host cell contaminants are removed by washing the column with equilibration buffer followed by equilibration buffer containing 20 mM imidazole and 60 mM imidazole to baseline. IDH1wt-his homodimer and IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag are eluted by equilibration buffer containing 250 mM imidazole. Fractions eluted by 250 mM imidazole are pooled together and loaded at 15 cm/h onto a column pre-packed with 10 ml ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel (Sigma), the column is equilibrated with 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4. After washing with equilibration buffer, IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag heterodimer is eluted by equilibration buffer containing flag peptide (0.2 mg/ml). Aliquots of IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag are flash frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −80° C. Same conditions are used for the purification of IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132H-flag.
- In Vitro Assays for IDH1m (R132H or R132C) Inhibitors In the primary reaction, the reduction of α-KG acid to 2-HG is accompanied by a concomitant oxidation of NADPH to NADP. The amount of NADPH remaining at the end of the reaction time is measured in a secondary diaphorase/resazurin reaction in which the NADPH is consumed in a 1:1 molar ratio with the conversion of resazurin to the highly fluorescent resorufin. Uninhibited reactions exhibit a low fluorescence at the end of the assay, while reactions in which the consumption of NADPH by R132H IDH1 has been inhibited by a small molecule show a high fluorescence.The primary reaction is performed in a volume of 50 μL 1× Buffer (150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.05% (w/v) bovine serum albumin), contained 0.25 ug/mL (2.7 nM) IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132H heterodimer, 0.3 mM alpha-ketoglutarate, 4 μM NADPH, and either 300 μM NADP (saturated) or 30 μM NADP (without saturation), and 1 uL of 50× compound in DMSO. The mixture of compound, enzyme, and cofactor is pre-incubated at room temperature for 1 hr prior to the addition of alpha-ketoglutarate. To perform the secondary reaction, 10 uL of 1× buffer containing 36 μg/ml diaphorase and 30 mM resazurin is added to the primary reaction and incubated for a further 5 minutes at 25° C. Florescence is read on a Spectramax platereader at Ex 544 Em 590. Compounds or compound dilutions are prepared in 100% DMSO concentration and diluted 1:50 into the final reaction. IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132C is assayed under similar conditions except that 1× Buffer is 50 mM K2HPO4, pH 6.5; 10 mM MgCl2; 10% glycerol; 0.03% (w/v) bovine serum albumin and final concentrations are 0.4 ug/mL (4.3 nM) IDH1 wt/IDH1 R132C heterodimer, 0.02 mM alpha-ketoglutarate, 4 uM NADPH, and either 300 μM NADP (saturated) or 30 μM NADP (without saturation). IC50s are determined.IDH1 or IDH2 wildtype (wt) and mutant heterodimers are expressed and purified by methods known in the art. For example, IDH1wt/R132m heterodimer is expressed and purified as follows. Co-expression of IDH1wt-his and IDH1R132C-flag is carried out in sf9 insect cells. Cells (25 g) are resuspended in 250 ml of 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4, at 4° C. with stirring. Cells are disrupted with 4 passes through an M-Y110 Micro fluidizer (Microfluidics) set to 500 psi, and then centrifuged at 22,000 rcf for 20 min at 4° C. The supernatant is harvested and loaded at 15 cm/h on a Histrap FF 5*1 ml column (GE) which is equilibrated with 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4. Host cell contaminants are removed by washing the column with equilibration buffer followed by equilibration buffer containing 20 mM imidazole and 60 mM imidazole to baseline. IDH1wt-his homodimer and IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag are eluted by equilibration buffer containing 250 mM imidazole. Fractions eluted by 250 mM imidazole are pooled together and loaded at 15 cm/h onto a column pre-packed with 10 ml ANTI-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel (Sigma), the column is equilibrated with 50 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, pH7.4. After washing with equilibration buffer, IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag heterodimer is eluted by equilibration buffer containing flag peptide (0.2 mg/ml). Aliquots of IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132C-flag are flash frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −80° C. Same conditions are used for the purification of IDH1wt-his/IDH1R132H-flag.
 GOMISIN A BDBM50485612
GOMISIN A BDBM50485612 BDBM50582612 (+/-)-Gomisin M1 CHEMBL463499
BDBM50582612 (+/-)-Gomisin M1 CHEMBL463499 US9365563, M2 BDBM236127 US9878991, Compound M2
US9365563, M2 BDBM236127 US9878991, Compound M2 US10800764, Compound (I-M2) US10071991, Compound (I-M2) US11214566, Compound (I-M2) BDBM276741 US9611259, Compound (I-M2)
US10800764, Compound (I-M2) US10071991, Compound (I-M2) US11214566, Compound (I-M2) BDBM276741 US9611259, Compound (I-M2) US11220518, Ex. No. M2 BDBM533505 US11780853, Example M2
US11220518, Ex. No. M2 BDBM533505 US11780853, Example M2 BDBM239392 US9416126, M2
BDBM239392 US9416126, M2 BDBM50485604 BOSENTAN M2
BDBM50485604 BOSENTAN M2 US10800764, Compound (I-M2-2R-4S) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S) BDBM276745 US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S)
US10800764, Compound (I-M2-2R-4S) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S) BDBM276745 US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2R,4S) BDBM286382 US9518060, Example M2
BDBM286382 US9518060, Example M2 BDBM546481 US11291655, No M2
BDBM546481 US11291655, No M2 BDBM582520 US11524942, Compound M2
BDBM582520 US11524942, Compound M2 BDBM762733 US20250248955, Compound M2
BDBM762733 US20250248955, Compound M2 BDBM769657 US20250282736, Compound M2
BDBM769657 US20250282736, Compound M2 US20250011272, Example M2 BDBM711890
US20250011272, Example M2 BDBM711890 US9303033, M2, Example 25 BDBM218881
US9303033, M2, Example 25 BDBM218881 BDBM764864 US20250257069, Compound MMT3-72-M2
BDBM764864 US20250257069, Compound MMT3-72-M2 US10800764, Compound (I-M7-2R,4S) US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) BDBM276744
US10800764, Compound (I-M7-2R,4S) US10071991, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) US11214566, Compound (I-M2-2S,4R) BDBM276744 (2E)-3-(3-fluorophenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (M2) BDBM152634
(2E)-3-(3-fluorophenyl)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (M2) BDBM152634 US9670191, M2 5-(2-Amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-2-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylicAcid Isopropylamide BDBM50329436 CHEMBL1270821
US9670191, M2 5-(2-Amino-pyrimidin-4-yl)-2-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylicAcid Isopropylamide BDBM50329436 CHEMBL1270821 US20250195530, Example M2 1-(4-(9-benzyl- 6-(1-methyl- cyclopropoxy)- 9H-purin- 8-yl)-3- chlorophenyl) piperidin-4-amine BDBM751389
US20250195530, Example M2 1-(4-(9-benzyl- 6-(1-methyl- cyclopropoxy)- 9H-purin- 8-yl)-3- chlorophenyl) piperidin-4-amine BDBM751389 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid CHEMBL120568 Vanillic acid (M2) 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid BDBM50337364 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid 4-hydroxyl-3-methoxybenzoic acid Vanilic acid
3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzoic acid CHEMBL120568 Vanillic acid (M2) 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxy-benzoic acid BDBM50337364 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid 4-hydroxyl-3-methoxybenzoic acid Vanilic acid 4-[(2-{[2-({(2S)-2-Amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)amino]-3-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-4-oxobutanoic acid/trifluoroacetic acid (1:1) US11071788, Example M2 BDBM509090
4-[(2-{[2-({(2S)-2-Amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]amino}-2-oxoethyl)amino]-3-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-4-oxobutanoic acid/trifluoroacetic acid (1:1) US11071788, Example M2 BDBM509090 BDBM682022 N-(2-{[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-3-carboxypropanoyl)glycyl-N-[2-({(2S)-2-amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]-D-alpha-glutamine trifluoroacetic acid salt Regioisomer 2, Epimer Mixture US12059472, Example M2
BDBM682022 N-(2-{[(2R)-2-Amino-2-carboxyethyl]sulphanyl}-3-carboxypropanoyl)glycyl-N-[2-({(2S)-2-amino-4-[{(1R)-1-[1-benzyl-4-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1H-pyrrol-2-yl]-2,2-dimethylpropyl}(glycoloyl)amino]butanoyl}amino)ethyl]-D-alpha-glutamine trifluoroacetic acid salt Regioisomer 2, Epimer Mixture US12059472, Example M2