Target (27)
Compound (202)
Article Title (63)
Assay (541)
Kuduk, SD; Zheng, FF; Sepp-Lorenzino, L; Rosen, N; Danishefsky, SJ Synthesis and evaluation of geldanamycin-estradiol hybrids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 1233 -8 (1999) Saitoh, T; Kuramochi, K; Imai, T; Takata, K; Takehara, M; Kobayashi, S; Sakaguchi, K; Sugawara, F Podophyllotoxin directly binds a hinge domain in E2 of HPV and inhibits an E2/E7 interaction in vitro. Bioorg Med Chem 16: 5815 -25 (2008) Devraj, R; Barrett, JF; Fernandez, JA; Katzenellenbogen, JA; Cushman, M Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of ellipticine-estradiol conjugates. J Med Chem 39: 3367 -74 (1996) Yarger, JG; Nye, SH 6-substituted demethyl-estradiol derivatives as selective ER-β agonists US Patent US9422324 (2016) Kim, HY; Sohn, J; Wijewickrama, GT; Edirisinghe, P; Gherezghiher, T; Hemachandra, M; Lu, PY; Chandrasena, RE; Molloy, ME; Tonetti, DA; Thatcher, GR Click synthesis of estradiol-cyclodextrin conjugates as cell compartment selective estrogens. Bioorg Med Chem 18: 809 -21 (2010) Phan, CM; Liu, Y; Kim, BM; Mostafa, Y; Taylor, SD Inhibition of steroid sulfatase with 4-substituted estrone and estradiol derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 5999 -6005 (2011) Abdel-Magid, AF Prostaglandin e2 synthase-1 inhibitors as potential treatment for osteoarthritis: patent highlight. ACS Med Chem Lett 3: 703 -704 (2012) Poirier, D; Boivin, RP; Tremblay, MR; Bérubé, M; Qiu, W; Lin, SX Estradiol-adenosine hybrid compounds designed to inhibit type 1 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Med Chem 48: 8134 -47 (2005) Wetzel, EA; Hanson, AM; Troutfetter, CL; Burkett, DJ; Sem, DS; Donaldson, WA Synthesis and evaluation of 17α-triazolyl and 9α-cyano derivatives of estradiol. Bioorg Med Chem 28: (2020) Friesen, RW; Mancini, JA Microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 (mPGES-1): a novel anti-inflammatory therapeutic target. J Med Chem 51: 4059 -67 (2008) Wiegard, A; Hanekamp, W; Griessbach, K; Fabian, J; Lehr, M Pyrrole alkanoic acid derivatives as nuisance inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1. Eur J Med Chem 48: 153 -63 (2012) Sam, KM; Boivin, RP; Auger, S; Poirier, D 16-propyl derivatives of estradiol as inhibitors of 17-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4: 2129 -2132 (1994) Boivin, RP; Luu-The, V; Lachance, R; Labrie, F; Poirier, D Structure-activity relationships of 17alpha-derivatives of estradiol as inhibitors of steroid sulfatase. J Med Chem 43: 4465 -78 (2000) Lawate, SS; Covey, DF Trifluoromethylacetylenic alcohols as affinity labels: inactivation of estradiol dehydrogenase by a trifluoromethylacetylenic secostradiol. J Med Chem 33: 2319 -21 (1990) Koeberle, A; Laufer, SA; Werz, O Design and Development of Microsomal Prostaglandin E2 Synthase-1 Inhibitors: Challenges and Future Directions. J Med Chem 59: 5970 -86 (2016) Riendeau, D; Aspiotis, R; Ethier, D; Gareau, Y; Grimm, EL; Guay, J; Guiral, S; Juteau, H; Mancini, JA; Méthot, N; Rubin, J; Friesen, RW Inhibitors of the inducible microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase (mPGES-1) derived from MK-886. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15: 3352 -5 (2005) Wang, Z; Yang, D; Mohanakrishnan, AK; Fanwick, PE; Nampoothiri, P; Hamel, E; Cushman, M Synthesis of B-ring homologated estradiol analogues that modulate tubulin polymerization and microtubule stability. J Med Chem 43: 2419 -29 (2000) Ahmed, N; Dubuc, C; Rousseau, J; Bénard, F; van Lier, JE Synthesis, characterization, and estrogen receptor binding affinity of flavone-, indole-, and furan-estradiol conjugates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17: 3212 -6 (2007) Lim, C; Lee, M; Park, EJ; Cho, R; Park, HJ; Lee, SJ; Cho, H; Lee, SK; Kim, S Sulfonamide derivatives of styrylheterocycles as a potent inhibitor of COX-2-mediated prostaglandin E2 production. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 6938 -41 (2010) Kanai, N; Lu, R; Bao, Y; Wolkoff, AW; Vore, M; Schuster, VL Estradiol 17 beta-D-glucuronide is a high-affinity substrate for oatp organic anion transporter. Am J Physiol 270: 326 -31 (1996) Zhou, L; Jeong, IH; Xue, S; Xue, M; Wang, L; Li, S; Liu, R; Jeong, GH; Wang, X; Cai, J; Yin, J; Huang, B Inhibition of the Ubiquitin Transfer Cascade by a Peptidomimetic Foldamer Mimicking the E2 N-Terminal Helix. J Med Chem 66: 491 -502 (2023) Tran, TD; Park, H; Kim, HP; Ecker, GF; Thai, KM Inhibitory activity of prostaglandin E2 production by the synthetic 2'-hydroxychalcone analogues: Synthesis and SAR study. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 1650 -3 (2009) Hajduk, PJ; Dinges, J; Miknis, GF; Merlock, M; Middleton, T; Kempf, DJ; Egan, DA; Walter, KA; Robins, TS; Shuker, SB; Holzman, TF; Fesik, SW NMR-based discovery of lead inhibitors that block DNA binding of the human papillomavirus E2 protein. J Med Chem 40: 3144 -50 (1997) Koeberle, A; Zettl, H; Greiner, C; Wurglics, M; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M; Werz, O Pirinixic acid derivatives as novel dual inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 and 5-lipoxygenase. J Med Chem 51: 8068 -76 (2008) Nakao, Y; Oku, N; Matsunaga, S; Fusetani, N Cyclotheonamides E2 and E3, new potent serine protease inhibitors from the marine sponge of the genus Theonella. J Nat Prod 61: 667 -70 (1998) Cameron, KO; Lefker, BA; Ke, HZ; Li, M; Zawistoski, MP; Tjoa, CM; Wright, AS; DeNinno, SL; Paralkar, VM; Owen, TA; Yu, L; Thompson, DD Discovery of CP-533536: an EP2 receptor selective prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) agonist that induces local bone formation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 2075 -8 (2009) Greiner, C; Zettl, H; Koeberle, A; Pergola, C; Northoff, H; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M; Werz, O Identification of 2-mercaptohexanoic acids as dual inhibitors of 5-lipoxygenase and microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1. Bioorg Med Chem 19: 3394 -401 (2011) Waltenberger, B; Wiechmann, K; Bauer, J; Markt, P; Noha, SM; Wolber, G; Rollinger, JM; Werz, O; Schuster, D; Stuppner, H Pharmacophore modeling and virtual screening for novel acidic inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 (mPGES-1). J Med Chem 54: 3163 -74 (2011) Qiu, W; Campbell, RL; Gangloff, A; Dupuis, P; Boivin, RP; Tremblay, MR; Poirier, D; Lin, SX A concerted, rational design of type 1 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors: estradiol-adenosine hybrids with high affinity. FASEB J 16: 1829 -31 (2002) Boutin, S; Roy, J; Maltais, R; Alata, W; Calon, F; Poirier, D Identification of steroidal derivatives inhibiting the transformations of allopregnanolone and estradiol by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 10. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28: 3554 -3559 (2018) Dickmann, LJ; Isoherranen, N Quantitative prediction of CYP2B6 induction by estradiol during pregnancy: potential explanation for increased methadone clearance during pregnancy. Drug Metab Dispos 41: 270 -4 (2013) James, DA; Swamy, N; Paz, N; Hanson, RN; Ray, R Synthesis and estrogen receptor binding affinity of a porphyrin-estradiol conjugate for targeted photodynamic therapy of cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9: 2379 -84 (1999) Fox, BM; Beck, HP; Roveto, PM; Kayser, F; Cheng, Q; Dou, H; Williamson, T; Treanor, J; Liu, H; Jin, L; Xu, G; Ma, J; Wang, S; Olson, SH A selective prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype 2 (EP2) antagonist increases the macrophage-mediated clearance of amyloid-beta plaques. J Med Chem 58: 5256 -73 (2015) Choi, D; Piao, YL; Wu, Y; Cho, H Control of the intracellular levels of prostaglandin E2 through inhibition of the 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase for wound healing. Bioorg Med Chem 21: 4477 -84 (2013) Shiro, T; Takahashi, H; Kakiguchi, K; Inoue, Y; Masuda, K; Nagata, H; Tobe, M Synthesis and SAR study of imidazoquinolines as a novel structural class of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22: 285 -8 (2011) Leese, MP; Leblond, B; Smith, A; Newman, SP; Di Fiore, A; De Simone, G; Supuran, CT; Purohit, A; Reed, MJ; Potter, BV 2-substituted estradiol bis-sulfamates, multitargeted antitumor agents: synthesis, in vitro SAR, protein crystallography, and in vivo activity. J Med Chem 49: 7683 -96 (2006) Zhou, J; Tracy, TS; Remmel, RP Correlation between bilirubin glucuronidation and estradiol-3-gluronidation in the presence of model UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 substrates/inhibitors. Drug Metab Dispos 39: 322 -9 (2011) Maltais, R; Ayan, D; Poirier, D Crucial Role of 3-Bromoethyl in Removing the Estrogenic Activity of 17ß-HSD1 Inhibitor 16ß-(m-Carbamoylbenzyl)estradiol. ACS Med Chem Lett 2: 678 -681 (2011) Hanson, RN; Hua, E; Hendricks, JA; Labaree, D; Hochberg, RB Synthesis and evaluation of 11ß-(4-substituted phenyl) estradiol analogs: transition from estrogen receptor agonists to antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem 20: 3768 -80 (2012) Huang, H; Feng, X; Xiao, Z; Liu, L; Li, H; Ma, L; Lu, Y; Ju, J; She, Z; Lin, Y Azaphilones and p-terphenyls from the mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium chermesinum (ZH4-E2) isolated from the South China Sea. J Nat Prod 74: 997 -1002 (2011) He, S; Li, C; Liu, Y; Lai, L Discovery of highly potent microsomal prostaglandin e2 synthase 1 inhibitors using the active conformation structural model and virtual screen. J Med Chem 56: 3296 -309 (2013) Loe, DW; Almquist, KC; Cole, SP; Deeley, RG ATP-dependent 17 beta-estradiol 17-(beta-D-glucuronide) transport by multidrug resistance protein (MRP). Inhibition by cholestatic steroids. J Biol Chem 271: 9683 -9 (1996) Sugiyama, D; Kusuhara, H; Shitara, Y; Abe, T; Meier, PJ; Sekine, T; Endou, H; Suzuki, H; Sugiyama, Y Characterization of the efflux transport of 17beta-estradiol-D-17beta-glucuronide from the brain across the blood-brain barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298: 316 -22 (2001) Svouraki, A; Garscha, U; Kouloura, E; Pace, S; Pergola, C; Krauth, V; Rossi, A; Sautebin, L; Halabalaki, M; Werz, O; Gaboriaud-Kolar, N; Skaltsounis, AL Evaluation of Dual 5-Lipoxygenase/Microsomal Prostaglandin E2 Synthase-1 Inhibitory Effect of Natural and Synthetic Acronychia-Type Isoprenylated Acetophenones. J Nat Prod 80: 699 -706 (2017) Maltais, R; Ayan, D; Trottier, A; Barbeau, X; Lagüe, P; Bouchard, JE; Poirier, D Discovery of a non-estrogenic irreversible inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 from 3-substituted-16β-(m-carbamoylbenzyl)-estradiol derivatives. J Med Chem 57: 204 -22 (2014) Maltais, R; Trottier, A; Delhomme, A; Barbeau, X; Lagüe, P; Poirier, D Identification of fused 16ß,17ß-oxazinone-estradiol derivatives as a new family of non-estrogenic 17ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 93: 470 -80 (2015) Lauro, G; Strocchia, M; Terracciano, S; Bruno, I; Fischer, K; Pergola, C; Werz, O; Riccio, R; Bifulco, G Exploration of the dihydropyrimidine scaffold for the development of new potential anti-inflammatory agents blocking prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 enzyme (mPGES-1). Eur J Med Chem 80: 407 -15 (2014) Mohd Aluwi, MF; Rullah, K; Yamin, BM; Leong, SW; Abdul Bahari, MN; Lim, SJ; Mohd Faudzi, SM; Jalil, J; Abas, F; Mohd Fauzi, N; Ismail, NH; Jantan, I; Lam, KW Synthesis of unsymmetrical monocarbonyl curcumin analogues with potent inhibition on prostaglandin E2 production in LPS-induced murine and human macrophages cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26: 2531 -8 (2016) Hanke, T; Dehm, F; Liening, S; Popella, SD; Maczewsky, J; Pillong, M; Kunze, J; Weinigel, C; Barz, D; Kaiser, A; Wurglics, M; Lämmerhofer, M; Schneider, G; Sautebin, L; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M; Werz, O Aminothiazole-featured pirinixic acid derivatives as dual 5-lipoxygenase and microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 inhibitors with improved potency and efficiency in vivo. J Med Chem 56: 9031 -44 (2013) Liedtke, AJ; Keck, PR; Lehmann, F; Koeberle, A; Werz, O; Laufer, SA Arylpyrrolizines as inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or as dual inhibitors of mPGES-1 and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX). J Med Chem 52: 4968 -72 (2009) Zhao, L; Jin, C; Mao, Z; Gopinathan, MB; Rehder, K; Brinton, RD Design, synthesis, and estrogenic activity of a novel estrogen receptor modulator--a hybrid structure of 17beta-estradiol and vitamin E in hippocampal neurons. J Med Chem 50: 4471 -81 (2007) Sugiyama, D; Kusuhara, H; Shitara, Y; Abe, T; Sugiyama, Y Effect of 17 beta-estradiol-D-17 beta-glucuronide on the rat organic anion transporting polypeptide 2-mediated transport differs depending on substrates. Drug Metab Dispos 30: 220 -3 (2002) Lobaccaro, C; Pons, JF; Duchesne, MJ; Auzou, G; Pons, M; Nique, F; Teutsch, G; Borgna, JL Steroidal affinity labels of the estrogen receptor. 3. Estradiol 11 beta-n-alkyl derivatives bearing a terminal electrophilic group: antiestrogenic and cytotoxic properties. J Med Chem 40: 2217 -27 (1997) Laplante, Y; Cadot, C; Fournier, MA; Poirier, D Estradiol and estrone C-16 derivatives as inhibitors of type 1 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: blocking of ER+ breast cancer cell proliferation induced by estrone. Bioorg Med Chem 16: 1849 -60 (2008) Ouellet, E; Ayan, D; Poirier, D Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of a modified estradiol-core bearing a fused¿-lactone as non-estrogenic inhibitor of 17ß-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21: 5510 -3 (2011) Bäurle, S; Nagel, J; Peters, O; Bräuer, N; Ter Laak, A; Preusse, C; Rottmann, A; Heldmann, D; Bothe, U; Blume, T; Zorn, L; Walter, D; Zollner, TM; Steinmeyer, A; Langer, G Identification of a Benzimidazolecarboxylic Acid Derivative (BAY 1316957) as a Potent and Selective Human Prostaglandin E2 Receptor Subtype 4 (hEP4-R) Antagonist for the Treatment of Endometriosis. J Med Chem 62: 2541 -2563 (2019) Hieke, M; Greiner, C; Dittrich, M; Reisen, F; Schneider, G; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M; Werz, O Discovery and biological evaluation of a novel class of dual microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1/5-lipoxygenase inhibitors based on 2-[(4,6-diphenethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)thio]hexanoic acid. J Med Chem 54: 4490 -507 (2011) De Simone, R; Chini, MG; Bruno, I; Riccio, R; Mueller, D; Werz, O; Bifulco, G Structure-based discovery of inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1, 5-lipoxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein: promising hits for the development of new anti-inflammatory agents. J Med Chem 54: 1565 -75 (2011) Cushman, M; He, HM; Katzenellenbogen, JA; Lin, CM; Hamel, E Synthesis, antitubulin and antimitotic activity, and cytotoxicity of analogs of 2-methoxyestradiol, an endogenous mammalian metabolite of estradiol that inhibits tubulin polymerization by binding to the colchicine binding site. J Med Chem 38: 2041 -9 (1995) Blouin, M; Han, Y; Burch, J; Farand, J; Mellon, C; Gaudreault, M; Wrona, M; Lévesque, JF; Denis, D; Mathieu, MC; Stocco, R; Vigneault, E; Therien, A; Clark, P; Rowland, S; Xu, D; O'Neill, G; Ducharme, Y; Friesen, R The discovery of 4-{1-[({2,5-dimethyl-4-[4-(trifluoromethyl)benzyl]-3-thienyl}carbonyl)amino]cyclopropyl}benzoic acid (MK-2894), a potent and selective prostaglandin E2 subtype 4 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 53: 2227 -38 (2010) Sharif, NA; Xu, SX; Williams, GW; Crider, JY; Griffin, BW; Davis, TL Pharmacology of [3H]prostaglandin E1/[3H]prostaglandin E2 and [3H]prostaglandin F2alpha binding to EP3 and FP prostaglandin receptor binding sites in bovine corpus luteum: characterization and correlation with functional data. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286: 1094 -102 (1998) Ciobanu, LC; Boivin, RP; Luu-The, V; Labrie, F; Poirier, D Potent inhibition of steroid sulfatase activity by 3-O-sulfamate 17alpha-benzyl(or 4'-tert-butylbenzyl)estra-1,3,5(10)-trienes: combination of two substituents at positions C3 and c17alpha of estradiol. J Med Chem 42: 2280 -6 (1999) Lister, MD; Glaser, KB; Ulevitch, RJ; Dennis, EA Inhibition studies on the membrane-associated phospholipase A2 in vitro and prostaglandin E2 production in vivo of the macrophage-like P388D1 cell. Effects of manoalide, 7,7-dimethyl-5,8-eicosadienoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide. J Biol Chem 264: 8520 -8 (1989)
ChEMBL_66867 (CHEMBL675206) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol (E2) from sheep uterine estrogen receptor ChEMBL_100268 (CHEMBL712011) Agonist activity in transcriptional activation assay in MCF-7-2a cells compared to estradiol E2 ChEMBL_88150 (CHEMBL693235) Stimulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in human endometrial Ishikawa cells with 1 nM E2 estradiol ChEMBL_88151 (CHEMBL693236) Stimulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in human endometrial Ishikawa cells with 1 nM E2 estradiol ChEMBL_103299 (CHEMBL712253) Anti-estrogenicity for 50% inhibition of the MVLN cell luciferase activity due to 0.1 nM E2 (estradiol) ChEMBL_1358461 (CHEMBL3281629) Displacement of radiolabeled estradiol from estradiol receptor in rat uterine cytosol ChEMBL_838505 (CHEMBL2078133) TP_TRANSPORTER: inhibition of estradiol-17beta-glucuronide uptake(estradiol-17beta-glucuronide:0.02uM) in OATP1B1-expressing HEK293 cells ChEMBL_515889 (CHEMBL993943) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full-length human estrogen receptor beta by radiometric assay relative to estradiol ChEMBL_1910802 (CHEMBL4413248) Inhibition of E2-activated human PDHK2 ChEMBL_582704 (CHEMBL1051801) Antagonist activity against prostaglandin E2 receptor ChEMBL_879294 (CHEMBL2208692) Inhibition of human estradiol 17beta-dehydrogenase ChEBML_67517 Displacement of [3H]estradiol from Estrogen receptor alpha ChEBML_67826 Displacement of [3H]estradiol from Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_331401 (CHEMBL867043) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from ERalpha ChEMBL_331402 (CHEMBL867044) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from ERbeta ChEMBL_381820 (CHEMBL869166) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human ERalpha ChEMBL_381821 (CHEMBL869167) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human ERbeta ChEMBL_526667 (CHEMBL968170) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor ChEMBL_66548 (CHEMBL677815) Inhibition of estradiol binding to estrogen receptor ChEMBL_815206 (CHEMBL2025223) Displacement of [3H]-17beta-estradiol from ERalpha ChEMBL_815207 (CHEMBL2025224) Displacement of [3H]-17beta-estradiol from ERbeta Estrogen Receptor Binding Assay. Arzoxifene and its analogues were assayed in the standard ER competitive radioligand binding assay, using full length human recombinant ER-alpha and ER-beta with [3H]-estradiol. IC50 values were calculated from binding of the sample expressed as a percentage relative to E2 (50 nM, 100%). Relative binding affinity (RBA; relative to E2) was calculated from IC50 (E2)/IC50 (sample). The samples were assayed in triplicate at least five concentrations. ChEBML_67369 Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_207426 (CHEMBL813050) Inhibition of estradiol-stimulated T-47D cell proliferation. ChEMBL_438780 (CHEMBL889118) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha ChEMBL_438781 (CHEMBL889119) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human recombinant ERbeta ChEMBL_504921 (CHEMBL946607) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha ChEMBL_509492 (CHEMBL1008128) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human recombinant ERbeta ChEMBL_65914 (CHEMBL677160) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from estrogen receptor (ER) ChEMBL_67517 (CHEMBL872900) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from Estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67826 (CHEMBL677222) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_1700822 (CHEMBL4051804) Inhibition of human placental cytosolic 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2/E2 substrate and NAD+ after 20 mins by HPLC based radio-detection method ChEMBL_305014 (CHEMBL829449) Inhibitory concentration against human prostaglandin E2 synthase (mPGES-1) ChEMBL_429971 (CHEMBL917701) Displacement of [3H]E2 from ERalpha ligand binding domain ChEMBL_429972 (CHEMBL917702) Displacement of [3H]E2 from ERbeta ligand binding domain ChEMBL_217747 (CHEMBL823810) Inhibition of estradiol-stimulated ZR-75-1-cell proliferation ChEMBL_217753 (CHEMBL824422) Inhibition of estradiol-stimulated ZR-75-1-cell proliferation ChEMBL_2273897 Displacement of [3H]-17beta-estradiol to estrogen receptor (unknown origin) ChEMBL_313633 (CHEMBL835777) pIC50 for 1 nM estradiol-induced Ishikawa cell proliferation ChEMBL_398763 (CHEMBL908035) Inhibition of estradiol to estrone conversion in MG63 cells ChEMBL_448344 (CHEMBL898603) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from recombinant human ERalpha ChEMBL_448345 (CHEMBL898604) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from recombinant human ERbeta ChEMBL_630247 (CHEMBL1106456) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human placental 17beta-HSD2 ChEMBL_450189 (CHEMBL900460) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human ERalpha ligand binding domain ChEMBL_450190 (CHEMBL900461) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human ERbeta ligand binding domain ChEMBL_803011 (CHEMBL1954168) Displacement of [3H]E2 from rat ERbeta1 after 90 mins ChEBML_67812 Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_172928 (CHEMBL779965) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in immature rat ChEMBL_1744049 (CHEMBL4178559) Displacement of estradiol from human ERalpha expressed in yeast cells ChEMBL_1744050 (CHEMBL4178560) Displacement of estradiol from human ERbetaa expressed in yeast cells ChEMBL_207428 (CHEMBL872717) Apparent binding affinity against estradiol-stimulated T-47D cell proliferation ChEMBL_65909 (CHEMBL679353) Binding affinity for estrogen receptor, by competition with [3H]estradiol ChEMBL_66378 (CHEMBL673767) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in squirrel monkey ChEMBL_66403 (CHEMBL677097) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in immature rabbit ChEMBL_66409 (CHEMBL677103) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in immature rabbit ChEMBL_66410 (CHEMBL677104) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in immature rat ChEMBL_66411 (CHEMBL677105) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in mature rat ChEMBL_66539 (CHEMBL677806) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from estrogen receptor in immature rat ChEMBL_66540 (CHEMBL677807) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from estrogen receptor in mature rat ChEMBL_66852 (CHEMBL680737) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in mature rat ChEMBL_67019 (CHEMBL677493) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor-ligand binding domain ChEMBL_68148 (CHEMBL680724) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor in squirrel monkey ChEMBL_808084 (CHEMBL1961192) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from rat uterine cytosolic estrogen receptor ChEMBL_99795 (CHEMBL874174) Inhibition of estradiol-stimulated MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cell proliferation ChEBML_67502 Inhibition of binding of 17 beta-estradiol to human Estrogen receptor alpha ChEBML_67682 Binding affinity towards estrogen receptor beta by [3H]17-beta-estradiol displacement. ChEBML_67827 Inhibition of binding of 17 beta-estradiol to human Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_1282735 (CHEMBL3102032) Displacement of FITC-estradiol from human ERalpha by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_217754 (CHEMBL881549) Apparent binding affinity against estradiol-stimulated ZR-75-1-cell proliferation ChEMBL_468678 (CHEMBL951130) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from purified full length human ERalpha receptor ChEMBL_468679 (CHEMBL951131) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from purified full length human ERbeta receptor ChEMBL_552852 (CHEMBL958057) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD2 using 17-beta-estradiol substrate ChEMBL_65915 (CHEMBL677161) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from Estrogen receptor in MCF-7 cells ChEMBL_66547 (CHEMBL677814) Displacement of [3H]- Estradiol from Estrogen receptor of rat uterine cytosol ChEMBL_66550 (CHEMBL677817) Displacement of [3H]- Estradiol from Estrogen receptor of rat uterine cytosol ChEMBL_66552 (CHEMBL677819) Equilibrium dissociation constant for rat uterine estrogen receptor binding [3H]estradiol ChEMBL_66864 (CHEMBL675203) Irreversible inhibition of [3H]estradiol binding to lamb uterine estrogen receptor ChEMBL_67488 (CHEMBL679325) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human Estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67508 (CHEMBL682292) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_68140 (CHEMBL680716) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from MCF-7 cell lysate ChEMBL_460516 (CHEMBL926596) Inhibition of human COX1-mediated conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin-E2 ChEMBL_532974 (CHEMBL989644) Binding affinity to HPV1a recombinant E2 protein by surface plasmon resonance method ChEMBL_532978 (CHEMBL989648) Binding affinity to HPV11 recombinant E2 protein by surface plasmon resonance method ChEMBL_532980 (CHEMBL989650) Binding affinity to HPV16 recombinant E2 protein by surface plasmon resonance method ChEMBL_72863 (CHEMBL683959) Binding affinity of second enantiomer (E2) against human glucagon receptor was determined ChEBML_1581929 Displacement of [3H]-17beta-estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha expressed in rabbit reticulocytes ChEBML_1581930 Displacement of [3H]-17beta-estradiol from human recombinant ERbeta expressed in rabbit reticulocytes ChEBML_1664056 Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full-length human ERalpha receptor by scintillation counting ChEBML_67363 Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from full length human estrogen receptor alpha ChEBML_67680 Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from full length human estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_1484215 (CHEMBL3537876) Inhibition of SULT1A1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as 17beta-estradiol sulfation ChEMBL_2496599 Displacement of [3H]17 beta estradiol from human ERalpha by radioligand binding assay ChEMBL_2496600 Displacement of [3H]17 beta estradiol from human ERbeta by radioligand binding assay ChEMBL_305778 (CHEMBL827967) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_305813 (CHEMBL829466) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_320908 (CHEMBL881235) Antagonistic activity against estrogen receptor beta in presence of 0.1 nM estradiol ChEMBL_320911 (CHEMBL881238) Antagonistic activity against estrogen receptor alpha in presence of 0.1 nM estradiol ChEMBL_536779 (CHEMBL984573) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human estrogen receptor alpha/estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_610117 (CHEMBL1074482) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_618687 (CHEMBL1102465) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from human ERalpha expressed in SF9 cells ChEMBL_635744 (CHEMBL1120283) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human recombinant full length ERalpha ChEMBL_635745 (CHEMBL1120284) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human recombinant full length ERbeta ChEMBL_67037 (CHEMBL677875) Binding affinity for human estrogen receptor alpha by displacement of [3H]estradiol ChEMBL_67038 (CHEMBL677876) Relative binding affinity for human estrogen receptor alpha compared to [3H]estradiol ChEMBL_67202 (CHEMBL678290) Relative binding affinity for human estrogen receptor beta compared to [3H]-estradiol ChEMBL_67365 (CHEMBL676819) Binding affinity towards estrogen receptor alpha by [3H]17-beta-estradiol displacement. ChEMBL_67502 (CHEMBL679893) Inhibition of binding of 17 beta-estradiol to human Estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67520 (CHEMBL682303) Inhibition of binding of 17 beta-estradiol to human Estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67682 (CHEMBL682169) Binding affinity towards estrogen receptor beta by [3H]17-beta-estradiol displacement. ChEMBL_67821 (CHEMBL677051) Inhibition of binding of 17 beta-estradiol to human Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_67827 (CHEMBL677223) Inhibition of binding of 17 beta-estradiol to human Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_826711 (CHEMBL2051158) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from ERalpha after 4 hrs by scintillation counting ChEMBL_826712 (CHEMBL2051159) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from ERbeta after 4 hrs by scintillation counting ChEMBL_1577036 (CHEMBL3807012) Antagonist activity at ERalpha (unknown origin) transfected in 17beta-estradiol induced-HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-mediated protein transcriptional activity after 8 hrs by Luciferase reporter gene assay Binding Assay The ER binding affinity of the compounds was determined using an in vitro competitive radioligand binding assay was [2,4,6,7-3H(N)]-Estradiol ([3H]E2), a natural high affinity ER ligand, and bacterially expressed GST fusion ER-alpha or ER-beta ligand binding domain (LBD) protein. ChEMBL_310691 (CHEMBL837410) Agonist activity as alkaline phosphatase induction in Ishikawa endometrial cells compared to E2 ChEMBL_312806 (CHEMBL837766) Inhibition of 10e-9 M E2 stimulated MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation ChEMBL_619036 (CHEMBL1102078) Binding affinity to ubiquitin E2 variant domain of human Tsg101 by fluorescent anisotropy ChEMBL_637922 (CHEMBL1166108) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human ERalpha after 16 hrs by scintillation counting ChEMBL_637923 (CHEMBL1166109) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human ERbeta after 16 hrs by scintillation counting ChEMBL_700705 (CHEMBL1645744) Inhibition of [3H]E2 binding to human placental 17beta-HSD2 after 20 mins ChEMBL_100276 (CHEMBL712018) Inhibition of estradiol induced estrogen receptor transcriptional activation in MCF-7-2a cells ChEMBL_101112 (CHEMBL710208) Inhibition of 17-beta-estradiol (10e-11 M) mediated MCF-7 cell proliferation ChEMBL_1664056 (CHEMBL4013737) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full-length human ERalpha receptor by scintillation counting ChEMBL_2280986 Displacement of [3H]-17beta-estradiol from bovine uterine estrogen receptor by competitive binding assay ChEMBL_306592 (CHEMBL832939) Inhibition of human estrogen receptor 2 using tritiated estradiol incubated for 3 hr ChEMBL_306604 (CHEMBL833494) Inhibition of human estrogen receptor 2 using tritiated estradiol incubated for 20 hr ChEMBL_312915 (CHEMBL826597) Antagonist effect against 10 pM 17-beta-estradiol induced MCF-7 cell proliferation ChEMBL_326622 (CHEMBL863381) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from recombinant human ERalpha expressed in 293T cells ChEMBL_326623 (CHEMBL868723) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from recombinant human ERbeta expressed in 293T cells ChEMBL_545688 (CHEMBL1034370) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_545689 (CHEMBL1034371) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled estradiol from human recombinant ERbeta by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_66404 (CHEMBL677098) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from Estrogen receptor of rabbit uterine tissue ChEMBL_66405 (CHEMBL677099) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from Estrogen receptor of rabbit uterine tissue ChEMBL_66542 (CHEMBL677809) In vitro displacement of [3H]estradiol from estrogen receptor of rat uterine cystol ChEMBL_67363 (CHEMBL873603) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from full length human estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67680 (CHEMBL682167) Displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol from full length human estrogen receptor beta ChEBML_159933 The compound was evaluated for prostaglandin E2 inhibition using recombinant Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 ChEMBL_1497878 (CHEMBL3582785) Displacement of [3H]-E2 from estrogen receptor-alpha (unknown origin) by scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_1497879 (CHEMBL3582786) Displacement of [3H]-E2 from estrogen receptor-beta (unknown origin) by scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_225530 (CHEMBL848481) In vitro inhibitory effect on production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in rat synovial cells. ChEMBL_496057 (CHEMBL998487) Inhibition of COX1 assessed as inhibition of arachidonic acid conversion to prostaglandin-E2 release ChEMBL_532975 (CHEMBL989645) Binding affinity to HPV1a recombinant E2 protein activator domain by surface plasmon resonance assay ChEMBL_532976 (CHEMBL989646) Binding affinity to HPV1a recombinant E2 protein hinge domain by surface plasmon resonance assay ChEMBL_544743 (CHEMBL1010180) Inhibition of human platelet COX1 assessed as effect on prostaglandin E2 production by ELISA ChEMBL_653105 (CHEMBL1226308) Displacement of E2-Alexa633 from GFP-tagged GPR30 expressed in COS7 cells by FACS ChEMBL_653106 (CHEMBL1226309) Displacement of E2-Alexa633 from GFP-tagged ERalpha expressed in COS7 cells by FACS ChEMBL_653107 (CHEMBL1226310) Displacement of E2-Alexa633 from GFP-tagged ERbeta expressed in COS7 cells by FACS ChEMBL_67504 (CHEMBL682288) Inhibition of [3H]E2 binding to estrogen receptor alpha in MCF-7 cell lysate ChEBML_67512 Ability to displace [3H]17-beta-estradiol from Estrogen receptor alpha by scintillation proximity assay. ChEBML_67823 Ability to displace [3H]17-beta-estradiol from Estrogen receptor beta by scintillation proximity assay. ChEMBL_1487741 (CHEMBL3533735) Inhibition of OATP1B1 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells using estradiol-17beta-glucuronide substrate ChEMBL_1770486 (CHEMBL4222598) Inhibition of UGT1A1 in human liver microsomes assessed as decrease in estradiol-3 glucuronidation ChEMBL_535112 (CHEMBL983675) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full length biotinylated human ERalpha by scintillation proximity assay ChEMBL_535113 (CHEMBL983676) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full length biotinylated human ERbeta by scintillation proximity assay ChEMBL_552857 (CHEMBL958062) Inhibition of 17-beta-HSD1-mediated 17-beta-estradiol formation in human T47D cells ChEMBL_66071 (CHEMBL683101) Inhibition of estradiol binding to estrogen receptor in Human Breast cancer cytosol (3.3% ethanol) ChEMBL_67173 (CHEMBL681157) In vitro inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_815209 (CHEMBL2025226) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from human full length recombinant ERalpha by scintillation proximity assay ChEMBL_815210 (CHEMBL2025227) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from human full length recombinant ERbeta by scintillation proximity assay ChEMBL_1476878 (CHEMBL3429912) Antagonist activity at ER alpha in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced PR expression treated for 24 hrs after incubation with estradiol for 30 mins by laser scanning imaging cytometer analysis ChEMBL_1284702 (CHEMBL3107402) Inhibition of COX-2 in human whole blood assessed as prostaglandin E2 production by RIA ChEMBL_158938 (CHEMBL767826) The compound was evaluated for prostaglandin E2 inhibition using recombinant Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 ChEMBL_159933 (CHEMBL769658) The compound was evaluated for prostaglandin E2 inhibition using recombinant Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 ChEMBL_2168580 (CHEMBL5053639) Displacement of fluorescent-labeled E2 from LBD of ERalpha (unknown origin) by TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_2168581 (CHEMBL5053640) Displacement of fluorescent-labeled E2 from LBD of ERbeta (unknown origin) by TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_532977 (CHEMBL989647) Binding affinity to HPV1a recombinant E2 protein DNA binding domain by surface plasmon resonance assay ChEMBL_787297 (CHEMBL1919075) Inhibition of human placental microsomal 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]E2 as substrate by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_838278 (CHEMBL2076226) TP_TRANSPORTER: increase in dihydrofluorescein intracellular accumulation (dihydrofluorescein: 1 uM) in SK-E2 cells (expressing BSEP) ChEMBL_838294 (CHEMBL2076242) TP_TRANSPORTER: increase in bodipy intracellular accumulation (Bodipy: 0.2 uM) in SK-E2 cells (expressing BSEP) ChEMBL_1436369 (CHEMBL3389572) Inhibition of OATP1B1 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells using [3H]estradiol-17beta-glucuronide substrate ChEMBL_1436370 (CHEMBL3389573) Inhibition of OATP1B3 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells using [3H]estradiol-17beta-glucuronide substrate ChEMBL_1519264 (CHEMBL3624761) Antagonist activity at progesterone receptor in human MCF cells assessed as estradiol-induced receptor response ChEMBL_306408 (CHEMBL828749) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to rat ER beta expressed in Escherichia coli ChEMBL_306421 (CHEMBL828092) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to rat ER alpha expressed in Escherichia coli ChEMBL_306448 (CHEMBL829092) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to mouse ER beta expressed in Escherichia coli ChEMBL_306464 (CHEMBL829541) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to mouse ER alpha expressed in Escherichia coli ChEMBL_492828 (CHEMBL940317) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from ERalpha in rat uteri cytosol by competitive radiometric binding assay ChEMBL_544137 (CHEMBL1014266) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 assessed as conversion of [14C]estradiol to [14C]estrone using NADP+ ChEMBL_67167 (CHEMBL681151) In vitro displacement of 0.5 nM [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human Estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67329 (CHEMBL678663) In vitro displacement of 0.5 nM [3H]17-beta-estradiol from human Estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_67341 (CHEMBL677746) In vitro inhibitory concentration against [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor 2 ChEMBL_751834 (CHEMBL1785589) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human full-length ERbeta receptor by competitive radiometric binding assay ChEMBL_863171 (CHEMBL2175782) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha expressed in Sf21 cells after 2 hrs ChEMBL_863172 (CHEMBL2175783) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from human recombinant ERbeta expressed in Sf21 cells after 2 hrs ChEMBL_877515 (CHEMBL2184039) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 assessed as conversion of estrone to estradiol by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1832421 (CHEMBL4332429) Binding affinity to CD81 (unknown origin) assessed as disruption of interaction between CD81 the HCV envelope protein E2 by measuring Kd for CD81/E2 interaction at 5 uM by surface plasmon resonance assay (Rvb = 1.3 nM) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 Tritiated E1 was incubated with 17beta-HSD1, cofactor, and inhibitor. The amount of labeled E2 formed was quantified by HPLC. Detection and quantification of the steroids were performed using a radioflow detector (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad). The conversion rate was calculated: %conversion = (%E2/ (%E2 +%E1) x 100). Each value was calculated from at least three independent experiments. ChEMBL_1750754 (CHEMBL4185514) Inhibition of NEDD8 (unknown origin) assessed as decrease in formation of E2-UBL thioester reaction product ChEMBL_1750756 (CHEMBL4185516) Inhibition of SAE (unknown origin) assessed as decrease in formation of E2-UBL thioester reaction product ChEMBL_1750757 (CHEMBL4185517) Inhibition of ATG7 (unknown origin) assessed as decrease in formation of E2-UBL thioester reaction product ChEMBL_1750758 (CHEMBL4185518) Inhibition of UBA6 (unknown origin) assessed as decrease in formation of E2-UBL thioester reaction product ChEMBL_2031808 (CHEMBL4685966) Displacement of fluorescent-labelled E2 from recombinant human GST-tagged ERalpha by LanthaScreen TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_2031809 (CHEMBL4685967) Displacement of fluorescent-labelled E2 from recombinant human GST-tagged ERbeta by LanthaScreen TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_633223 (CHEMBL1119430) Antagonist activity at ERbeta expressed in yeast assessed as inhibition of E2-induced alpha-galactosidase activity ChEMBL_633226 (CHEMBL1119433) Antagonist activity at ERalpha expressed in yeast assessed as inhibition of E2-induced alpha-galactosidase activity ChEMBL_715249 (CHEMBL1664450) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human placental 17beta-HSD2 after 10 mins by fluid scintillation counting ChEMBL_1590441 (CHEMBL3830811) Inhibition of human 17-beta-HSD14 using estradiol as substrate after 15 mins by fluorimetric assay ChEMBL_2193599 (CHEMBL5105959) Displacement of fluorescent labeled 17beta-estradiol from human ERbeta ligand binding domain by TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_306229 (CHEMBL831137) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor beta expressed in Escherichia coli ChEMBL_306245 (CHEMBL831155) Inhibition of [3H]17-beta-estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor alpha expressed in Escherichia coli ChEMBL_320910 (CHEMBL881237) Binding affinity towards human estrogen receptor beta in a competitive binding assay using fluorescently labelled estradiol ChEMBL_320912 (CHEMBL881339) Binding affinity towards human estrogen receptor alpha in a competitive binding assay using fluorescently labelled estradiol ChEMBL_492829 (CHEMBL940318) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from ERbeta receptor in rat uteri cytosol by competitive radiometric binding assay ChEMBL_508157 (CHEMBL1008215) Inhibition of neutrophil elastase activation in beta-estradiol differentiated mouse EcoM-G cells after 24 hrs ChEMBL_508158 (CHEMBL1008216) Inhibition of cathepsin G activation in beta-estradiol differentiated mouse EcoM-G cells after 24 hrs ChEMBL_508159 (CHEMBL1008217) Inhibition of proteinase-3 activation in beta-estradiol differentiated mouse EcoM-G cells after 24 hrs ChEMBL_514253 (CHEMBL975500) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD1 assessed as conversion of [3H]estrone to [3H]17beta-estradiol ChEMBL_514254 (CHEMBL975501) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD2 assessed as conversion of [3H]17beta-estradiol to [3H]estrone ChEMBL_536773 (CHEMBL984567) Inhibition of estradiol-induced coactivator peptide SRC binding to recombinant estrogen receptor by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_552334 (CHEMBL1006006) Inhibition of human MRP2-mediated estradiol-17-beta-glucuronide transport in Sf9 cells inverted membrane vesicles ChEMBL_649075 (CHEMBL1218773) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human ERalpha ligand binding domain expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) ChEMBL_65908 (CHEMBL679352) Antiestrogenic activity in MCF-7-2a cells as concentration required to reduce estradiol effect by 50% ChEMBL_67203 (CHEMBL838887) In vitro binding affinity towards human Estrogen receptor 2 using [3H]17-beta-estradiol as radioligand ChEMBL_67518 (CHEMBL682301) In vitro binding affinity towards human Estrogen receptor alpha using [3H]17-beta-estradiol as radioligand ChEMBL_684637 (CHEMBL1285470) Inhibition of human placenta 17beta-HSD2 using [2,4,6,7-3H]-17beta-estradiol as substrate after 10 mins ChEMBL_752205 (CHEMBL1786581) Inhibition of fluorescence-labeled 17beta-estradiol binding to ERalpha receptor after 2 hrs by fluorometric analysis Estrone Detection Assay for Evaluation of HSD17beta13 Activity The liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) estrone detection assay monitors the conversion of estradiol to estrone by HSD17B13. This assay was undertaken in a 96wp format (Eppendorf deep well Plate 96/500) in an 80 µl reaction volume containing: 4 µM of Estradiol (E2; Cayman; #10006315), 6 mM NAD+ (Sigma; #N0623) and 30 nM HSD17B13 enzyme (in-house; E. coli expressed His-tagged, purified, soluble protein) in a reaction containing 1 M potassium phosphate buffer pH 7.4, with 0.5% vehicle (DMSO). Reactions were incubated for 2 hours at 26.5° C., and estradiol (E2) conversion to estrone (E1) was quantitated by LC-MS/MS based analyte detection for both E2 and E1 using LCMS grade reagents.Reactions were terminated by the addition of two volumes of acetonitrile (MeCN; LCMS grade; CAS# 75/05/8) containing deuterated (D4)-E1 used as internal standard (Clear Synth; #CS-T-54273; 500 ng/mL final concentration). Samples were applied to pre-prepared Bond Elut-C18 extraction cartridges (3 mL; Agilent; #12102028), washed and eluted in MeCN. Eluates were dried under nitrogen and re-suspended in 60% methanol (LCMS grade methanol; CAS# 67/56/1) before submission for analysis. Aqueous linearity for E2 and E1 were included for quantification. ChEMBL_1439099 (CHEMBL3384914) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human placental microsomal 17beta-HSD2 after 20 mins by cell-free assay ChEMBL_1486828 (CHEMBL3535467) Noncompetitive inhibition of MRP4-mediated E2-17betaG transport in human MRP4 expressing HEK293 cells by Dixon plot ChEMBL_1489317 (CHEMBL3533496) Noncompetitive inhibition of MRP1-mediated E2-17betaG transport in human MRP1 expressing HEK293 cells by Dixon plot ChEMBL_2074723 (CHEMBL4730257) Displacement of [3H]-17beta-E2 from human ERbeta LBD by solid phase competitive radio ligand binding assay ChEMBL_2212559 (CHEMBL5125508) Displacement of 3H-E2 from ERalpha in human MCF7 incubated for 2 hrs by competition binding assay ChEMBL_313095 (CHEMBL836811) Inhibition of 10e-9 M E2 stimulated transcriptional activation in ER+MCF-7/2a breast cancer cells ChEMBL_313096 (CHEMBL836812) Inhibition of 10e-9 M E2 stimulated transcriptional activation in ER+MCF-7/2a breast cancer cells ChEMBL_940755 (CHEMBL2330135) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human recombinant ERbeta receptor after overnight incubation by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_940756 (CHEMBL2330136) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human recombinant ERalpha receptor after overnight incubation by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEBML_67500 In vitro concentration required to inhibit [3H]estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor alpha expressed in 293T cells ChEBML_67820 In vitro concentration required to inhibit [3H]estradiol binding to human estrogen receptor beta expressed in 293T cells ChEMBL_1649843 (CHEMBL3998977) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full length recombinant human ESR1 expressed in insect cells by radiometric assay ChEMBL_1717009 (CHEMBL4132009) Antagonist activity at ER in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced cell proliferation ChEMBL_454488 (CHEMBL886514) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full length human recombinant ERalpha after 3 hrs by scintillation proximity assay ChEMBL_454489 (CHEMBL886515) Displacement of [3H]estradiol from full length human recombinant ERbeta after 3 hrs by scintillation proximity assay ChEMBL_544744 (CHEMBL1010181) Inhibition of human recombinant COX2 expressed in Sf21 cells assessed as effect on prostaglandin E2 production by ELISA ChEMBL_775981 (CHEMBL1912979) Displacement of [3H]E2 from estrogen receptor in JW rabbit uterus after 2 hrs by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_823597 (CHEMBL2044598) Inhibition of human placenta microsomal 17betaHSD2 using [3H]E2 as substrate after 20 mins by radioflow detection assay ChEMBL_103159 (CHEMBL711304) Compound concentration required to induce transcriptional activation in MVLN cells comparable to 50% of 0.1 nM estradiol response ChEMBL_103160 (CHEMBL707870) Compound concentration required to induce transcriptional activation in MVLN cells equal to 50% of 0.1 nM estradiol response ChEMBL_1584556 (CHEMBL3820547) Inhibition of human placental microsomal aromatase using testosterone as substrate assessed as formation of estradiol after 10 mins ChEMBL_2149318 (CHEMBL5033716) Displacement of fluorescent estradiol from full-length ERalpha (unknown origin) measured after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_2316391 Antagonist activity against ERalpha in estradiol stimulated HEK293T cells measuring luciferase activity after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter assay ChEMBL_2316395 Antagonist activity against ERbeta in estradiol stimulated HEK293T cells measuring luciferase activity after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter assay ChEMBL_2455250 Inhibition of human HSD17B13 using estradiol and NAD as substrate incubated for 2 hrs by Envision plate reader analysis ChEMBL_313068 (CHEMBL835873) Antagonist activity as inhibition of 1 nM 17-beta-estradiol stimulated alkaline phosphatase induction in Ishikawa endometrial cells ChEMBL_544140 (CHEMBL1013421) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 expressed in HEK 293 cells assessed as conversion of [14C]estrone to [14C]estradiol Competitive Radioligand-Binding Assay Estrogen receptor (ERβ) binding affinity of the NRBAs was also determined using an in vitro competitive radioligand-binding assay with [3H]-estradiol ([3H]-E2, PerkinElmer), a high affinity ligand for both ERα and ERβ. The equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) of [3H]-E2 was determined by incubating increasing concentrations of [3H]-E2 (0.01 to 10 nM) with bacterially expressed ERα or ERβ ligand binding domain (LBD) at 4° C. for 18 hours (h). Non-specific binding was determined by adding 1000 nM E2 to the incubation mixture. It was determined that the minimum concentration of [3H]-E2 required to saturate ERα and ERβ binding sites in the incubation mixture was 1 nM, respectively. The binding affinity of the NRBAs was determined under identical conditions by incubating increasing concentrations (3×10−2 to 1,000 nM) of ligand with isolated ER LBD and 1 nM [3H]-E2. Following incubation, bound and free [3H]-E2 were separated by using vacuum filtration with the Harvester (PerkinElmer). Briefly, the incubation mixture was filtered through a high affinity protein binding filter, and washed several times to remove any unbound radioactivity. The filter plate was air dried and sealed on the bottom. Scintillation cocktail was added to each well and the top of the plate was sealed. Radioactivity was counted in a TopCount NXT Microplate Scintillation Counter. ChEMBL_143041 (CHEMBL750290) Affinity for rat Tachykinin receptor 1 determined in displacement screening by using radioligand 3,4-[3H]-(L-Pro e2) SP. ChEMBL_1561162 (CHEMBL3777355) Displacement of [3H]-E2 from human ER-alpha incubated for 16 to 20 hrs by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_1561163 (CHEMBL3777356) Displacement of [3H]-E2 from human ER-beta incubated for 16 to 20 hrs by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_1781487 (CHEMBL4253004) Displacement of [3H]E2 from human recombinant ERalpha assessed as receptor binding after 45 mins by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_322407 (CHEMBL871883) Tested for prostaglandin E2 production as a function of COX-2 inhibition using endotoxin-treated murine RAW 264.7 macrophages ChEMBL_1345989 (CHEMBL3258023) Displacement of [2,4,6,7-3H]-estradiol from estrogen receptor in immature rat uterine cytosol by dextran-coated charcoal-adsorption assay ChEMBL_1490069 (CHEMBL3536010) Inhibition of OATP1B3-mediated [3H]estradiol 17beta-glucuronide uptake in human OATP1B3 expressing HEK293/PDZK1 cells by scintillation counting ChEMBL_1717005 (CHEMBL4132005) Displacement of [3H]17beta-estradiol from ER in human MCF7 cells after 18 hrs by microbeta scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1869284 (CHEMBL4370350) Antagonist activity at ERalpha in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-driven PR response by microplate cytometry ChEMBL_2327364 Displacement of [3H]estradiol from human ER-alpha expressed in Sf21 cells incubated for 120 mins by scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_448350 (CHEMBL898609) Antagonist activity at ERalpha expressed in yeast AH109 assessed as inhibition of 17-beta-estradiol induced alpha-galactosidase activity ChEMBL_492826 (CHEMBL940315) Displacement of fluorescein labeled estradiol from human recombinant ERalpha expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_492827 (CHEMBL940316) Displacement of fluorescein labeled estradiol from human recombinant ERbeta expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_555024 (CHEMBL957999) Inhibition of human recombinant 17beta-HSD1 expressed in HEK293 cell lysate assessed as conversion of radiolabeled estrone to estradiol ChEMBL_555026 (CHEMBL958789) Inhibition of human recombinant 17beta-HSD2 expressed in HEK293 cell lysate assessed as conversion of radiolabeled estrone to estradiol ChEMBL_555345 (CHEMBL954745) Inhibition of human recombinant 11beta-HSD1 expressed in HEK293 cell lysate assessed as conversion of radiolabeled estrone to estradiol ChEMBL_647642 (CHEMBL1219993) Displacement of [2,4,6,7-3H]estradiol from human ERalpha expressed in HeLa cells after 18 hrs by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_67194 (CHEMBL678129) In vitro inhibition of 1 nM 17-beta-estradiol induced transcriptional activation in T47D cells expressing estrogen receptor beta ChEMBL_841251 (CHEMBL2089654) Displacement of fluorescent labelled PGC-1alpha from estradiol-ERalpha complex after 2 to 4 hrs by TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_841252 (CHEMBL2089655) Displacement of fluorescent labelled PGC-1alpha from estradiol-ERbeta complex after 2 to 4 hrs by TR-FRET assay ChEBML_1684948 Antagonist activity at rat EP1 receptor expressed in African green monkey COS1 cells assessed as inhibition of prostaglandin-E2-induced increase in intracellular calcium level preincubated for 60 secs followed by prostaglandin-E2 addition measured for 60 secs by Fluo 4-AM dye based fluorescence assay Estrogen Receptor Binding Assay. The binding affinities were determined by a competitive radiometric binding assay using [3H]estradiol as tracer. The Kd for 3H-estradiol was determined by saturation binding to ER receptors. The IC50 values for compounds were converted to Ki using Cheng-Prusoff equation. Evaluation of HSD17f313 Activity Assay Table 3: The liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) estrone detection assay monitors the conversion of estradiol to estrone by HSD17B13. This assay was undertaken in a 96 wp format (Eppendorf deep well Plate 96/500) in an 80 μl reaction volume containing: 4 μM of Estradiol (E2; Cayman; Ser. No. 10/006,315), 6 mM NAD+(Sigma; #N0623) and 30 nM HSD17B13 enzyme (in-house; E. coli expressed His-tagged, purified, soluble protein) in a reaction containing 1M potassium phosphate buffer pH 7.4, with 0.5% vehicle (DMSO). Reactions were incubated for 2 hours at 26.5° C., and estradiol (E2) conversion to estrone (E1) was quantitated by LC-MS/MS based analyte detection for both E2 and E1 using LCMS grade reagents.Reactions were terminated by the addition of two volumes of acetonitrile (MeCN; LCMS grade; CAS #75/05/8) containing deuterated (D4)-E1 used as internal standard (Clear Synth; #CS-T-54273; 500 ng/mL final concentration). Samples were applied to pre-prepared Bond Elut-C18 extraction cartridges (3 mL; Agilent; Ser. No. 12/102,028), washed and eluted in MeCN. Eluates were dried under nitrogen and re-suspended in 60% methanol (LCMS grade methanol; CAS #67/56/1) before submission for analysis. Aqueous linearity for E2 and E1 were included for quantification. ChEMBL_1501406 (CHEMBL3588435) Antagonist activity at human EP2 receptor overexpressed in human ECV304 cells assessed as inhibition of prostaglandin E2-induced cAMP production ChEMBL_1501407 (CHEMBL3588436) Antagonist activity at rat EP2 receptor overexpressed in human ECV304 cells assessed as inhibition of prostaglandin E2-induced cAMP production ChEMBL_1501408 (CHEMBL3588437) Antagonist activity at mouse EP2 receptor overexpressed in human ECV304 cells assessed as inhibition of prostaglandin E2-induced cAMP production ChEMBL_1619745 (CHEMBL3861914) Inhibition of purified human placental microsomal 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 substrate and NAD+ by HPLC based radioactive displacement assay ChEMBL_1861100 (CHEMBL4361956) Inhibition of mouse liver homogenate 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1861111 (CHEMBL4361967) Inhibition of rat liver homogenate 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1863754 (CHEMBL4364729) Inhibition of mouse liver homogenate 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1898529 (CHEMBL4400644) Inhibition of mouse liver homogenate 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_81576 (CHEMBL689336) Dissociation constant after binding to human papillomavirus E2 DNA-binding domain (DBD) by observing the changes in [15N]-HSQC spectra. ChEMBL_1491711 (CHEMBL3536903) Inhibition of human MRP2-mediated estradiol-17beta-D-glucuronide formation using inside-out membrane vesicles by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_1934443 (CHEMBL4480095) Inhibition of full length human ERalpha expressed in human HEC1 cells in presence of estradiol by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2493321 Inhibition of human CYP1B1 overexpressed in CHO cells assessed as protein catalyzed estradiol hydroxylation in living cells by measuring residual activity ChEMBL_306447 (CHEMBL829091) Inhibitory concentration against human ER beta expressed in Escherichia coli was determined using [3H]17-beta-estradiol as radio ligand ChEMBL_306463 (CHEMBL829540) Inhibitory concentration against human ER alpha expressed in Escherichia coli was determined using [3H]17-beta-estradiol as radio ligand ChEMBL_544139 (CHEMBL1013420) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 expressed in HEK 293 cells assessed as conversion of [14C]estrone to [14C]estradiol using NADH ChEMBL_544141 (CHEMBL1013422) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 expressed in HEK 293 cells assessed as conversion of [14C]estrone to [14C]estradiol using NADPH ChEMBL_66406 (CHEMBL677100) Inhibitory activity against Estrogen receptor by displacement of [3H]17-beta-estradiol in ER-rich cytosol from rabbit uterine tissue ChEMBL_67501 (CHEMBL679892) In vitro inhibition of transcriptional activation induced by 1 nM 17-beta estradiol in T47D cells expressing estrogen receptor alpha ChEMBL_67516 (CHEMBL682300) Binding affinity for Estrogen receptor alpha of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) by displacement of [3H]17-alpha-estradiol ChEMBL_99805 (CHEMBL710408) In vitro antagonist effect on estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activation in MCF-7 cells against 10 pM 17-beta-estradiol Binding Assay Recombinant ER-α or ER-β ligand binding domain (LBD) was combined with [3H]E2 (PerkinElmer, Waltham, Mass.) in buffer A (10 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 1.5 mM disodium EDTA, 0.25 M sucrose, 10 mM sodium molybdate, 1 mM PMSF) to determine the equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) of [3H]E2. Protein was incubated with increasing concentrations of [3H]E2 with and without a high concentration of unlabeled E2 at 4° C. for 18h in order to determine total and non-specific binding. Non-specific binding was then subtracted from total binding to determine specific binding. Ligand binding curves were analyzed by nonlinear regression with one site saturation to determine the Kd of E2 (ER-α: 0.65 nM; ER-β: 1.83 nM). In addition, the concentration of [3H]E2 required to saturate ER-α and ER-β LBD was determined to be 1-3 nM.Increasing concentrations of two β-SERMs (14m and 12u) (range: 10−11 to 10−6 M) were incubated with [3H]E2 (1-2 nM) and ER LBD using the conditions described above. Following incubation, plates were harvested with GF/B filters on the Unifilter-96 Harvester (PerkinElmer) and washed three times with ice-cold buffer B (50 mM Tris, pH 7.2). The filter plates were dried at room temperature, then Microscint-O cocktail was added to each well and the filter plates were sealed with TopSeal-A. Radioactivity was counted in a TopCount NXT Microplate Scintillation Counter using the settings for [3H] in Microscint cocktail (PerkinElmer).The specific binding of [3H]E2 at each concentration of compound was determined by subtracting the nonspecific binding of [3H]E2 (determined by incubating with 10−6 M unlabeled E2) and expressing it as a percentage of the specific binding in the absence of compound. The concentration of compound that reduced the specific binding of [3H]E2 by 50% (IC50) was determined by computer-fitting the data with SigmaPlot and non-linear regression with the four parameter logistic curve. The equilibrium binding constant (Ki) of each compound was then calculated by: Ki=Kd×IC50/(Kd+L), where Kd is the equilibrium dissociation constant of [3H]E2, and L is the concentration of [3H]E2. ChEMBL_1541061 (CHEMBL3744292) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD2 in human placental microsomal fraction using E2/NAD+ as substrate/cofactor after 20 mins by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1826276 (CHEMBL4326150) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from human EP2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cell membranes after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_1861097 (CHEMBL4361953) Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1863749 (CHEMBL4364724) Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1898526 (CHEMBL4400641) Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_938945 (CHEMBL2328434) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD2 in human MDA-MB-231 cells using [3H]E2 as substrate after 6 hrs by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1287642 (CHEMBL3110898) Mixed-type inhibition of ER-alpha (unknown origin) expressed in ER-negative human SKBR3 cells coexpressing ERE using estradiol as substrate ChEMBL_1363487 (CHEMBL3291709) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD2 microsomal fraction using tritiated estradiol as substrate assessed as formation of estrone by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1363489 (CHEMBL3291711) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD1 cytosolic fraction using tritiated estrone as substrate assessed as formation of estradiol by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1363494 (CHEMBL3291985) Inhibition of mouse liver 17beta-HSD2 microsomal fraction using tritiated estradiol as substrate assessed as formation of estrone by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1484074 (CHEMBL3537109) Inhibition of human OATP1B1 expressed in CHO cells using [3H]estradiol 17beta-D-glucuronide as substrate by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_1484212 (CHEMBL3537873) Inhibition of human SULT1A1 expressed in Escherichia coli assessed as 17beta-estradiol sulfation at 100 nM by Michaelis-Menten equation analysis ChEMBL_1486476 (CHEMBL3531466) Inhibition of human recombinant UGT1A1 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in estradiol 3-glucuronidation by LC-MS/MS method ChEMBL_1580951 (CHEMBL3812619) Positive allosteric modulation of human FSHR expressed in rat granulocytes assessed as FSH-induced estradiol production after 72 hrs by radioimmunossay ChEMBL_1767338 (CHEMBL4219450) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled estradiol (fluoromone) from human recombinant full-length estrogen receptor alpha after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_1767339 (CHEMBL4219451) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled estradiol (fluoromone) from human recombinant full-length estrogen receptor beta after 2 hrs by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_2228974 (CHEMBL5142487) Inhibition of UGT1A1 in human liver microsomes using beta-estradiol as substrate incubated for 40 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_527767 (CHEMBL978703) Agonist activity at human ERalpha expressed in african green monkey CV1 cells by luciferase reporter gene assay relative to 17beta estradiol ChEMBL_1539819 (CHEMBL3736957) Antagonist activity at ERalpha in human T47D-KBLuc cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transcriptional activity by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1649547 (CHEMBL3998681) Inhibition of recombinant human PDK1 in presence of E1 protein and PDC core E2/E3BP incubated for 10 mins by titration assay ChEMBL_1649549 (CHEMBL3998683) Inhibition of recombinant human PDK3 in presence of E1 protein and PDC core E2/E3BP incubated for 10 mins by titration assay ChEMBL_1649550 (CHEMBL3998684) Inhibition of recombinant human PDK4 in presence of E1 protein and PDC core E2/E3BP incubated for 10 mins by titration assay ChEMBL_1861108 (CHEMBL4361964) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD2 in human MDA-MB-231 cells using [3H]-E2 as substrate after 6 hrs by radio-HPLC analysis ChEMBL_794210 (CHEMBL1932035) Inhibition of human microsomal 17beta-HSD2 in cell-free system using [2,4,6,7-3H]E2 as substrate after 20 mins by radioflow detector ChEMBL_938947 (CHEMBL2328436) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 in human placental cytosolic fraction using [3H]E1 as substrate assessed as formation of E2 by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_938948 (CHEMBL2328437) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD2 in human placental microsomal fraction using [3H]E2 as substrate assessed as formation of E1 by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1822722 (CHEMBL4322486) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from human recombinant estrogen receptor expressed in insect cells incubated for 17 hrs by radioactive receptor binding assay ChEMBL_2249199 (CHEMBL5163409) Antagonist activity at ERalpha expressed in HEK293/Gal4 cells incubated for 24 hrs in presence of estradiol by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1471515 (CHEMBL3420078) Inhibition of 17 beta-HSD1 in human T47D cells assessed as inhibition of transformation of [14C]E1 to [14C]E2 after overnight incubation ChEMBL_1524156 (CHEMBL3631241) Inhibition of human placental microsomal 17beta HSD2 using unlabeled- and labelled [2,4,6,7-3H]-E2 as substrate incubated for 20 mins by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1524162 (CHEMBL3631247) Inhibition of mouse liver microsomal 17beta HSD2 using unlabeled- and labelled [2,4,6,7-3H]-E2 as substrate incubated for 20 mins by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1524167 (CHEMBL3631252) Inhibition of rat liver microsomal 17beta HSD2 using unlabeled- and labelled [2,4,6,7-3H]-E2 as substrate incubated for 20 mins by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1898536 (CHEMBL4400651) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD2 in human using MDA-MB-231 cells using [3H]-E2 as substrate after 6 hrs by cell-based assay ChEMBL_2324328 Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]E2 as substrate measured after 20 mins in presence of NAD+ by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_736715 (CHEMBL1695096) Inhibition of Prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 in IL1-beta stimulated microsomal fraction of human A549 cell assessed as PGE2 level by RP-HPLC ChEMBL_768581 (CHEMBL1832600) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 in human T47D cells expressing estrogen receptor assessed as conversion of [14C]-E1 to [14C]-E2 after 24 hrs ChEMBL_1287641 (CHEMBL3110897) Competitive inhibition of ER-alpha (unknown origin) ligand binding pocket expressed in ER-negative human SKBR3 cells coexpressing ERE using estradiol as substrate ChEMBL_1367283 (CHEMBL3300204) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD2 microsomal fraction using [2, 4, 6, 7-3H]-estradiol as substrate after 20 mins by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_1767356 (CHEMBL4219468) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled estradiol (fluoromone) from human recombinant full-length untagged estrogen receptor alpha expressed in Spodoptera frugiperda by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_1767357 (CHEMBL4219469) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled estradiol (fluoromone) from human recombinant full-length untagged estrogen receptor beta expressed in insect cells by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_2468473 Inhibition of human CYP1B1 over-expressed in CHO cells preincubated for 3 hrs followed media replacement containing estradiol without compound measured after 3 hrs ChEMBL_619853 (CHEMBL1106730) Inhibition of human 17beta-HSD7 expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of reduction of [14C]estrone into [14C]estradiol after 7 hrs Competitive Radiometric Binding Assay Binding affinities were also determined by a competitive radiometric binding assay using 2 nM [3H]estradiol as tracer (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA) and full-length purified human ERα (Pan Vera/Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), as reported previously. The RBA values were calculated using the following equation: IC50 estradiol/IC50 compound×100. ChEBML_1696129 Displacement of [3H]E2 from GST-fused ERbeta-LBD (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 incubated for 1 hr by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1282732 (CHEMBL3102029) Antagonist activity at ERbeta (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of E2-induced receptor activation after 22 hrs by cell-based luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1646099 (CHEMBL3995155) Inhibition of human placental microsomal 17beta-HSD2 using [2,4,6,7-3H]-E2 as substrate after 20 mins in presence of NAD+ by RP-HPLC method ChEMBL_1668111 (CHEMBL4017999) Antagonist activity at CMX-GAL4N fused human ERalpha expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in E2 induced response by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1769949 (CHEMBL4222061) Antagonist activity at ERalpha (unknown origin) expressed in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced response by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2168592 (CHEMBL5053651) Antagonist activity at ERalpha (unknown origin) expressed in human U2OS cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transactivation by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2168593 (CHEMBL5053652) Antagonist activity at ERbeta (unknown origin) expressed in human U2OS cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transactivation by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2173335 (CHEMBL5058469) Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ measured after 20 mins by HPLC method ChEMBL_2217339 (CHEMBL5130471) Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HS2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate in presence of NAD+ measured after 10 mins by HPLC method ChEBML_1685129 Antagonist activity at ERalpha (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced response after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEBML_68138 Tested by protection experiments to demonstrate the inactivation of estradiol dehydrogenase and the kinetic parameter Ki app was reported at a concentration of 20 uM ChEMBL_1361782 (CHEMBL3292467) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced cell proliferation after 5 days by WST-8 assay ChEMBL_1494637 (CHEMBL3529887) Inhibition of OATP1B1 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction of [3H]estradiol-17beta-glucuronide uptake after 3 mins by beta-counting ChEMBL_1494638 (CHEMBL3529888) Inhibition of OATP1B3 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction of [3H]estradiol-17beta-glucuronide uptake after 3 mins by beta-counting ChEMBL_1664063 (CHEMBL4013744) Downregulation of ERalpha in human MCF-7 cells assessed as reduction of estradiol-induced GREB1 mRNA levels after 24 hrs by RT-PCR method ChEMBL_1664064 (CHEMBL4013745) Downregulation of ERalpha in human MCF-7 cells assessed as reduction of estradiol-induced PgR mRNA levels after 24 hrs by RT-PCR method ChEMBL_1664065 (CHEMBL4013746) Downregulation of ERalpha in human MCF-7 cells assessed as reduction of estradiol-induced pS2 mRNA levels after 24 hrs by RT-PCR method ChEMBL_1744042 (CHEMBL4178552) Inhibition of human 17beta-HSD2 expressed in HEK293 cell lysates incubated for 10 mins using [2,4,6,7-3H]-estradiol and NAD+ by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1934447 (CHEMBL4480099) Displacement of fluorescein-labeled PGC1alpha peptide from human GST-tagged ERalpha LBD after 2 hrs in presence of estradiol-beta by TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_622102 (CHEMBL1114101) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor in human Ishikawa cells assessed as 17-beta-estradiol-induced alkaline phosphatase activity after 3 days by chemiluminescence assay Radioligand Displacement Assay Binding affinity was measured by a scintillation proximity binding assay using [3H]4-OHT (for ERRgamma) or [3H]estradiol (for ERalpha) as radioligand. Estrogen Receptor Binding Assay and Ishikawa Assay The binding affinities were determined by a competitive radiometric binding assay using [3H]estradiol as tracer. The Kd for 3H-estradiol was determined by saturation binding to ER receptors. The IC50 values for compounds were converted to Ki using Cheng-Prusoff equation. Estrogenic stimulation and antagonism were measured in Ishikawa human endometrial tumor cells by alkaline phosphatase quantitation. The data were fitted to a linear interpolation to derive IC50 values for the antagonist mode and a percentage efficacy was calculated that blocks the 17beta-estradiol (1nM) stimulus. Estrogen Receptor Binding Assay. Relative binding affinities were determined by a competitive radiometric binding assay using [3H]estradiol as tracer, and purified full-length human ER. Hydroxyapatite was used to adsorb the receptor-ligand complexes, and free ligand was washed away. The binding affinities are expressed as relative binding affinity (RBA) values with the RBA of estradiol set to 100%. The values given are the average +/- range or SD of two to three independent determinations. Estradiol binds to ERalpha with a Kd of 0.2 nM and to ERbeta with a Kd of 0.5 nM. ChEMBL_1287299 (CHEMBL3111007) Inhibition of 17-beta HSD1 in human T47D cells assessed as transformation of [14C]E1 to [14C]E2 after 24 hrs by thin layer chromatography ChEMBL_1687824 (CHEMBL4038394) Inhibition of BRD4 (unknown origin) expressed in human H1299 cells co-expressing HPV16-LCR/E2 after 24 hrs by Bright Glo-luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1696128 (CHEMBL4047018) Displacement of [3H]E2 from GST-fused ERalpha-LBD (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 incubated for 1 hr by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1696129 (CHEMBL4047019) Displacement of [3H]E2 from GST-fused ERbeta-LBD (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 incubated for 1 hr by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1789617 (CHEMBL4261351) Inhibition of mouse microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate after 20 mins in presence of NAD+ by radio-flow detector based analysis ChEMBL_1826278 (CHEMBL4326152) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from recombinant human full length EP1 receptor expressed in Chem-1 cell membranes after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_1826279 (CHEMBL4326153) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from recombinant human full length EP3 receptor expressed in Chem-1 cell membranes after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_1826280 (CHEMBL4326154) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from recombinant human full length EP4 receptor expressed in Chem-1 cell membranes after 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_2017938 (CHEMBL4671516) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from full-length recombinant human EP4 receptor expressed in HEK293 cell membranes measured after 120 mins by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_2017939 (CHEMBL4671517) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from full-length recombinant human EP3 receptor expressed in HEK293 cell membranes measured after 120 mins by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_2017940 (CHEMBL4671518) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from full-length recombinant human EP2 receptor expressed in HEK293 cell membranes measured after 120 mins by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_2017941 (CHEMBL4671519) Displacement of [3H]prostaglandin E2 from full-length recombinant human EP1 receptor expressed in HEK293 cell membranes measured after 60 mins by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1337645 (CHEMBL3242833) Antagonist activity at human Gal4-fused ER-alpha expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced effect by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1337649 (CHEMBL3242837) Antagonist activity at human Gal4-fused ER-beta expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced effect by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1869281 (CHEMBL4370347) Antagonist activity at ERalpha in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-driven cell growth measured after 7 days by SYTOX green-based assay ChEMBL_1870077 (CHEMBL4371244) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor beta (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced response after 22 hrs by cell-based luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1870096 (CHEMBL4371263) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor alpha (unknown origin) assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced response after 22 hrs by cell-based luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2222785 (CHEMBL5136119) Displacement of [3H]-estradiol from recombinant full-length human estrogen beta receptor expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells incubated overnight by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_2447867 Binding affinity to Estrogen receptor in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition constant incubated for 24 hrs in presence of [3H]-estradiol by scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_474434 (CHEMBL935185) Antagonist activity at human ER ligand binding domain expressed in african green monkey COS7 cells in presence of 17-beta-estradiol by Gal4 hybrid assay ChEMBL_527053 (CHEMBL980129) Antiestrogenic activity at estrogen receptor alpha expressed in yeast cells assessed as inhibition of 17-beta-estradiol-induced beta-galactosidase activity by two hybrid assay ChEMBL_622103 (CHEMBL1114102) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor in human MCF7 cells assessed as 17-beta-estradiol-induced cell proliferation after 24 hrs by [14C]thymidine incorporation assay ChEMBL_775706 (CHEMBL1912091) Transactivation activity of glucocorticoid receptor in HFF assessed as induction of aromatase activity by measuring beta-estradiol activity after 18 to 24 hrs by ELISA ChEMBL_822871 (CHEMBL2037903) Antagonist activity at Estrogen receptor expressed in human Ishikawa cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced increase in alkaline phosphatase after 3 days by spectrophotometry ChEMBL_988475 (CHEMBL2438124) Inhibition of human placenta 17beta-HSD2 microsomal fraction using unlabeled, [2,4,6,7-3H]-estradiol as substrate after 20 mins by HPLC analysis in presence of NAD+ ChEMBL_1539818 (CHEMBL3736956) Antagonist activity at luciferase-fused ERalpha in human HEK293 cells expressing eYFP assessed as reduction of E2-induced estrogenic activity after 2 hrs by BRET assay ChEMBL_1717011 (CHEMBL4132011) Antagonist activity at ER in human Ishikawa cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced alkaline phosphatase induction after 72 hrs by PNPP substrate based spectophotometric method ChEMBL_1789612 (CHEMBL4261346) Inhibition of human placental microsomal fraction 17beta-HSD2 using [3H]-E2 as substrate after 20 mins in presence of NAD+ by radio-flow detector based analysis ChEMBL_1846277 (CHEMBL4346818) Inhibition of recombinant CDK2/Cyclin E2 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus expression system using biotinylated-histone H1 as substrate measured after 60 mins by HTRF assay ChEBML_1685205 Inhibition of recombinant human 17beta-HSD2 expressed in HEK293 cells using estradiol as substrate after 10 mins in presence of radiolabeled tracer substrate by scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1343606 (CHEMBL3254234) Apparent inhibition of human placental microsomal aromatase assessed as [C14]estrone/[C14]estradiol formation using 0.075 to 0.515 uM [C14]androstenedione substrate by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_1484075 (CHEMBL3537110) Inhibition of human OATP1B3 expressed in BacMam baculovirus virus infected HEK MSR2 cells using [3H]estradiol 17beta-D-glucuronide as substrate by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_1562015 (CHEMBL3779189) Inhibition of CDK8 (unknown origin) expressed in 7dF3 clone of human HEK293 cells preincubated for 2 hrs followed by addition of beta-estradiol by luciferase assay ChEMBL_1649840 (CHEMBL3998974) Antagonist activity at ERalpha in tamoxifen-sensitive human MCF7:WS8 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced response after 18 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1684871 (CHEMBL4035350) Inhibition of human CYP1B1 expressed in Escherichia coli DH5alpha coexpressing human NADPH-P450 reductase using 4-estradiol as substrate in presence of NADP+ by HPLC analysis ChEMBL_2249242 (CHEMBL5163452) Antagonist activity at ERalpha Y537S mutant degradation in human SK-BR-3 cells incubated for 24 hrs in presence of beta-estradiol by luciferase gene assay ChEMBL_2249243 (CHEMBL5163453) Antagonist activity at ERalpha D538G mutant degradation in human SK-BR-3 cells incubated for 24 hrs in presence of beta-estradiol by luciferase gene assay ChEMBL_651562 (CHEMBL1227814) Antagonist activity at human wild type ERbeta expressed in HEK293T cells co-expressing ERE assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced transactivation by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_651565 (CHEMBL1227817) Antagonist activity at human wild type ERalpha expressed in HEK293T cells co-expressing ERE assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced transactivation by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_861318 (CHEMBL2173706) Inhibition of human placenta 17beta-HSD2 microsomal fraction using unlabelled and [2,4,6,7-3H]estradiol as substrate after 20 mins by HPLC analysis in presence of NAD+ ChEMBL_879539 (CHEMBL2208948) Inhibition of 17beta-HSD1 in human T47D cells assessed as decrease in transformation of [14C]estrone to [14C]-estradiol after 24 hrs by thin layer chromatography Inhibition of 17beta-HSD2 Tritiated E2 was incubated with 17beta-HSD2, cofactor, and inhibitor. The amount of labeled E1 formed was quantified by HPLC. Detection and quantification of the steroids were performed using a radioflow detector (Berthold Technologies, Bad Wildbad). The conversion rate was calculated: %conversion = (%E1/ (%E2 +%E1) x 100). Each value was calculated from at least three independent experiments. ChEBML_1684873 Inhibition of recombinant CYP1A1 (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli DH5alphaF'Iq coexpressing human NADPH-P450 reductase using E2-d4 as substrate after 10 mins in presence of NADP+ ChEMBL_1337650 (CHEMBL3242838) Inhibition of steroid sulfatase in human MCF7 cells assessed as conversion of [3H]E1S to [3H]E1 and [3H]E2 after 5 hrs by liquid scintillation counting ChEMBL_1649548 (CHEMBL3998682) Inhibition of N-terminal His6-SUMO tagged recombinant human PDK2 in presence of E1 protein and PDC core E2/E3BP incubated for 10 mins by titration assay ChEMBL_1791556 (CHEMBL4263475) Antagonist activity at full length ERalpha (unknown origin) assessed as reduction in E2 induced response after 24 hrs by cell based ERE-driven luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1791557 (CHEMBL4263476) Antagonist activity at full length ERbeta (unknown origin) assessed as reduction in E2 induced response after 24 hrs by cell based ERE-driven luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1361049 (CHEMBL3295681) Antagonist activity at ER in human MCF7:WS8 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced cell growth by measuring DNA level after 7 days by fluorescence analysis ChEMBL_2246242 (CHEMBL5160452) Inhibition of STS in human MCF7 cells assessed as reduction in [3H]estradiol and [3H]estrone formation using [3H]estrone sulfate as substrate incubated for 20 hrs ChEMBL_536775 (CHEMBL984569) Inhibition of estradiol-induced coactivator peptide SRC1 binding to estrogen receptor alpha expressed in human HEC1 cells after 24 hrs by luciferase based mammalian two-hybrid assay ChEMBL_718372 (CHEMBL1679904) Antagonist activity at human ERalpha LBD in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced cell proliferation after up to 6 days by celltiter-glo assay ChEMBL_1336447 (CHEMBL3242591) Inhibition of LPS-induced COX-2 in peritoneal macrophage of C57BL/J6 mouse assessed as prostaglandin E2 formation preincubated for 1 hr followed by LPS challenge by radioimmunoassay ChEMBL_1670395 (CHEMBL4020283) Inhibition of BRD4 in human H1299 cells assessed as decrease in HPV LCR-E2-EP400-mediated transcriptional repression after 24 hrs by Bright-Glo luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1684873 (CHEMBL4035352) Inhibition of recombinant CYP1A1 (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli DH5alphaF'Iq coexpressing human NADPH-P450 reductase using E2-d4 as substrate after 10 mins in presence of NADP+ ChEMBL_1684874 (CHEMBL4035353) Inhibition of recombinant CYP1B1 (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli DH5alphaF'Iq coexpressing human NADPH-P450 reductase using E2-d4 as substrate after 10 mins in presence of NADP+ ChEMBL_1891475 (CHEMBL4393302) Antagonist activity at FLAG-tagged ERalpha (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in E2-induced ER-alpha-mediated transcriptional activity by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2031821 (CHEMBL4685979) Antagonist activity at ERalpha (unknown origin) expressed in human U2OS cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transactivation measured after 21 hrs by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2031822 (CHEMBL4685980) Antagonist activity at ERbeta (unknown origin) expressed in human U2OS cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transactivation measured after 21 hrs by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1684870 (CHEMBL4035349) Inhibition of human CYP1B1 expressed in Escherichia coli DH5alpha coexpressing human NADPH-P450 reductase using 4-estradiol as substrate in presence of NADP+ by Michaelis-Menten plot analysis ChEMBL_1890699 (CHEMBL4392453) Inhibition of recombinant rat UGT1A1 using beta-estradiol as substrate preincubated for 5 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_2046646 (CHEMBL4701345) Inhibition of estrogen sulfotransferase in human liver cytosol incubated for 30 mins in presence of [3H]-estradiol and adenosine -3'-phosphate 5'-phosphosulfate by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_2074716 (CHEMBL4730250) Antagonist activity at full length human ERalpha receptor assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced activation incubated for 22 to 24 hrs by cell based luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2074717 (CHEMBL4730251) Antagonist activity at full length human ERbeta receptor assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced activation incubated for 22 to 24 hrs by cell based luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2198168 (CHEMBL5110684) Inhibition of estrone sulfatase in human MCF7 cells assessed as inhibition of [3H]estrone and [3H]estradiol formation using [3H]estrone sulfate as substrate incubated for 20 hrs ChEMBL_1891729 (CHEMBL4393556) Inhibition of ovine COX1 assessed as reduction in prostaglandin E2 production incubated for 10 mins before arachidonic acid addition and measured after 25 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_1984040 (CHEMBL4617446) Antagonist activity at human Gal4-fused ERalpha expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transcriptional activation after 24 hrs by luciferase/beta-galactosidase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1984042 (CHEMBL4617448) Antagonist activity at human Gal4-fused ERbeta expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transcriptional activation after 24 hrs by luciferase/beta-galactosidase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1339080 (CHEMBL3243177) Antagonist activity at ERbeta (unknown origin) expressed in human HepG2 cells assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced transcriptional activation after 24 hrs by ERE-luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1934446 (CHEMBL4480098) Displacement of europium-labeled SRC1 peptide from full length human recombinant ERalpha expressed in baculovirus expression system after 1.5 hrs in presence of estradiol-beta by TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_536774 (CHEMBL984568) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor alpha expressed in human HEC1 cells assessed as inhibition of 1 nM estradiol-induced transcriptional activity after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_536780 (CHEMBL984574) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor alpha expressed in human HEC1 cells assessed as inhibition of 100 nM estradiol-induced transcriptional activity after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_969612 (CHEMBL2406604) Antagonist activity at Gal4 DBD-fused human ERalpha LBD expressed in HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced transcriptional activation after 20 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1646098 (CHEMBL3995154) Inhibition of human placental cytosolic 17beta-HSD1 assessed as reduction in activation of [2,4,6,7-3H]-E1 substrate to E2 after 10 mins in presence of NADH by RP-HPLC method ChEMBL_1891730 (CHEMBL4393557) Inhibition of COX2 (unknown origin) assessed as reduction in prostaglandin E2 production incubated for 10 mins before arachidonic acid addition and measured after 25 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_2381114 Inhibition of recombinant 17beta-HSD10 (unknown origin) using E2 as substrate and NAD+ as cofactor preincubated for 5 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 20 mins by fluorometric assay ChEMBL_2469668 Antagonist activity at C-terminal RLucII-fused human ER-alpha expressed in HEK293T cells co-expressing CoA-YFP-fused LXXLL coactivator motif from NCOA2 in presence of E2 by BRET assay ChEMBL_101082 (CHEMBL708494) Antagonism of estrogen action in a mammary tumor cell line was assayed via inhibition of MCF-7 cell proliferation stimulated by 10 e-11 M 17-beta-estradiol (in vitro) ChEMBL_1674627 (CHEMBL4024656) Induction of selective estrogen receptor alpha degradation in human MCF7 cells harboring TK-ERE-Luc assessed as reduction in estradiol-induced GREB1 mRNA expression after 24 hrs by TaqMan assay ChEMBL_1890700 (CHEMBL4392454) Inhibition of UGT1A1 in human liver microsomes using beta-estradiol as substrate preincubated for 5 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_1890701 (CHEMBL4392455) Inhibition of UGT1A1 in rat liver microsomes using beta-estradiol as substrate preincubated for 5 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by LC-MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_1993610 (CHEMBL4627505) Displacement of [3H]17-beta estradiol from GST-fused human recombinant ERalpha ligand binding domain expressed in Escherichia coli BL21alpha cells incubated for 1 hr by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1993611 (CHEMBL4627506) Displacement of [3H]17-beta estradiol from GST-fused human recombinant ERbeta ligand binding domain expressed in Escherichia coli BL21alpha cells incubated for 1 hr by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1619749 (CHEMBL3861918) Inhibition of N-terminal 6His-tagged human human HSD17B14 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS using E2 substrate and NAD+ incubated for 2 hrs using purified enzyme by fluorimetric assay ChEMBL_1739715 (CHEMBL4155465) Binding affinity to recombinant 17beta-HSD14 (unknown origin) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 pLysS strain using E2 as substrate in presence of NAD measured continuously for 15 mins by fluorimetric method ChEMBL_1759878 (CHEMBL4194886) Binding affinity to BRD4 in human H1299 cells stably expressing E2 and HPV16-LCR luciferase reporter incubated for 24 hrs by Bright-Glo luciferase reporter gene assay based BRD4 engagement assay ChEMBL_1670787 (CHEMBL4020675) Binding affinity to recombinant human GFP-fused ERalpha LBD (301 to 553 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) after 40 mins in presence of 17beta-estradiol by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_1670788 (CHEMBL4020676) Binding affinity to recombinant human GFP-fused ERbeta LBD (259 to 498 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) after 40 mins in presence of 17beta-estradiol by fluorescence polarization assay ChEMBL_1674615 (CHEMBL4024644) Induction of selective estrogen receptor alpha degradation in human MCF7 cells harboring TK-ERE-Luc assessed as reduction in estradiol-induced transcriptional activity after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1993615 (CHEMBL4627510) Antagonist activity at ERbeta (unknown origin) expressed in human HeLa cells assessed as inhibition of E2-induced transcriptional activity measured after 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay based Schild plot analysis ChEMBL_2060600 (CHEMBL4715601) Inhibition of recombinant N-terminal His-tagged human PTP1B (E2 to N321) expressed in Escherichia coli expression system assessed by dephosphorylation of substrate pNPP measured for 4 mins by plate reader analysis ChEMBL_2381116 Mixed type inhibition of recombinant 17beta-HSD10 (unknown origin) using E2 as substrate and NAD+ as cofactor preincubated for 5 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 20 mins by fluorometric assay ChEMBL_1776993 (CHEMBL4233985) Antagonist activity at full length recombinant human ERalpha expressed in baculovirus expression system assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced Euphorium-labelled LTERHKILHRLLQEGSPSD peptide recruitment after 1.5 hrs by time-resolved fluorescence assay ChEMBL_1776994 (CHEMBL4233986) Antagonist activity at full length recombinant human ERbeta expressed in baculovirus expression system assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced Euphorium-labelled QAQQKSLLQQLLTE peptide recruitment after 1.5 hrs by time-resolved fluorescence assay Enzyme Inhibition on the Conversion of E2 to E1 by 17beta-HSD1 For steady-state kinetic study of hybrid inhibitors, a Fluorolog 3 instrument was used to monitor the fluorescent signal of NADPH formed during estradiol oxidation, through which the substrate conversion is monitored. The excitation wavelength was 340 nm, and the emission wavelength was 460 nm. A standard curve monitoring the increase of fluorescence (cps) caused by an increase of NADPH revealed that the formation of 1 uM NADPH corresponds to a 316,000 cps increase. The Km for E2 in the absence of EM-1745, and four apparent Km values in the presence of 0.5, 2, 4, and 7 nM EM-1745 were obtained. Ki was further determined by a plot of Km vs. the inhibitor concentration. Estrogen Receptor Binding and Transcription Activation Assay Relative binding affinities were determined by a competitive radiometric binding assay using [3H]estradiol as tracer, and purified full-length human ER. Hydroxyapatite was used to adsorb the receptor-ligand complexes, and free ligand was washed away. The binding affinities are expressed as relative binding affinity (RBA) values with the RBA of estradiol set to 100%. The values given are the average +/- range or SD of two to three independent determinations. Estradiol binds to ERalpha with a Kd of 0.2 nM and to ERbeta with a Kd of 0.5 nM. EC50/IC50 values were obtained from transcription activation by ER gene transfection in human endometrial cancer cells. Competitive Binding Assay Competitive binding of estrogen to GPR30 and ER alpha were conducted using COS-7 cells transfected with GPR30-GFP or ER alpha-GFP and fluorescent estrogen, E2-Alexa633 labeled as a reporter. ChEMBL_1750176 (CHEMBL4184936) Antagonist activity at CMV-fused ERalpha-LBD-GAL4-DBD (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced receptor transactivation after 16 hrs by bright-Glo luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1750177 (CHEMBL4184937) Antagonist activity at CMV-fused ERbeta-LBD-GAL4-DBD (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced receptor transactivation after 16 hrs by bright-Glo luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1778275 (CHEMBL4235267) Antagonist activity at recombinant human ERalpha expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced YFP-fused SRC1 coactivator recruitment measured after 1 hr in presence of Coelenterazine H by BRET assay ChEMBL_1859158 (CHEMBL4360014) Antagonist activity at human full-length ERalpha expressed in non-human mammalian expression system assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced response measured after 22 to 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1859159 (CHEMBL4360015) Antagonist activity at human full-length ERbeta expressed in non-human mammalian expression system assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced response measured after 22 to 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_616793 (CHEMBL1103117) Antagonist activity at human recombinant ERalpha LBD expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of 0.3 nM estradiol-induced transcriptional activation after 16 to 18 hrs by GAL4-dependent luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_616795 (CHEMBL1103119) Antagonist activity at human recombinant ERbeta LBD expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as inhibition of 0.3 nM estradiol-induced transcriptional activation after 16 to 18 hrs by GAL4-dependent luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1284733 (CHEMBL3107542) Inhibition of COX-1 in mouse J774 cells using arachidonic acid as substrate assessed as inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition measured after 30 mins by RIA ChEMBL_1668112 (CHEMBL4018000) Antagonist activity at estrogen receptor in mouse GT1-7 cells harboring beta-galactosidase reporter gene assessed as reduction in 17beta-estradiol induced response measured after 20 to 24 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1678645 (CHEMBL4028922) Inhibition of human MRP2 overexpressed in Sf9 cell membrane vesicles assessed as uptake of [3H]-estradiol-17beta-D-glucuronide in presence of ATP and GSH measured after 20 mins by membrane vesicle transport assay ChEMBL_1678647 (CHEMBL4028924) Inhibition of human MRP4 overexpressed in Sf9 cell membrane vesicles assessed as uptake of [3H]-estradiol-17beta-D-glucuronide in presence of ATP and GSH measured after 20 mins by membrane vesicle transport assay ChEMBL_2369988 Inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B13 using estradiol and NAD as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis ChEMBL_2369989 Inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B11 using estradiol and NAD as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis ChEMBL_2369992 Inhibition of recombinant mouse full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B13 using estradiol and NAD as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis ChEMBL_2447868 Antagonist activity at wildtype Estrogen receptor (unknown origin) transfected in SK-BR-3 cells co-transfected with estrogen receptor element incubated for 24 hrs in presence of beta-estradiol by Dual-Glo reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1484073 (CHEMBL3537108) Inhibition of human MRP2 expressed in baculovirus-infected Sf9 cell membrane vesicle using [3H]estradiol 17beta-D-glucuronide as substrate preincubated with vesicles for 5 mins prior to substrate addition by liquid scintillation counting analysis ChEMBL_1497344 (CHEMBL3579293) Antagonist activity at human estrogen receptor alpha expressed in CHOK1 cells assessed as inhibition of beta-estradiol-induced protein interaction with steroid receptor co-activator peptide after overnight incubation by beta-galactosidase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_1678646 (CHEMBL4028923) Inhibition of human MRP3 overexpressed in Sf9 insect cell membrane vesicles assessed as uptake of [3H]-estradiol-17beta-D-glucuronide in presence of ATP and GSH measured after 10 mins by membrane vesicle transport assay ChEMBL_2370015 Uncompetitive inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B13 using estradiol and NAD as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis ChEMBL_2370016 Uncompetitive inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B11 using estradiol and NAD as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis ChEMBL_2370018 Uncompetitive inhibition of recombinant mouse full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B13 using estradiol and NAD as substrate preincubated for 10 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 40 mins by MALDI-TOF-MS analysis ChEMBL_786678 (CHEMBL1921531) Inhibition of human placental 17beta-HSD2 assessed as formation of [2,4,6,7-3H]-estrone using [2,4,6,7-3H]-estradiol as substrate after 20 mins by radio flow detector-based HPLC analysis in presence of NAD+ as cofactor ChEMBL_1284732 (CHEMBL3107541) Inhibition of LPS-induced COX-2 in mouse J774 cells using arachidonic acid as substrate assessed as inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production preincubated for 15 mins followed by substrate addition measured after 30 mins by RIA ChEMBL_2369991 Inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B13 expressed in HEK293 cells using estradiol as substrate preincubated for 30 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 3 hrs by rapidfire MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_1792852 (CHEMBL4264771) Inhibition of recombinant mouse full-length 17beta-HSD10 (2 to 261 residues) assessed as reduction in transformation of [14C]-E2 to E1 after 48 hrs in presence of 1 mM NAD+ cofactor by liquid scintillation counting method ChEMBL_1721239 (CHEMBL4136239) Antagonist activity at recombinant human His6-tagged ERalpha LBD (298 to 554 residues) expressed in Escherichia coli assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced fluorescein-labeled PGC1alpha coactivator peptide binding after overnight incubation by Lantascreen TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_2113959 (CHEMBL4822809) Antagonist activity at ERalpha (unknown origin) expressed in human HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced transcriptional activities by measuring ERE driven reporter gene expression measured after 24 hrs by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2113960 (CHEMBL4822810) Antagonist activity at ERbeta (unknown origin) expressed in human HEK293T cells assessed as inhibition of 17beta-estradiol-induced transcriptional activities by measuring ERE driven reporter gene expression measured after 24 hrs by dual luciferase reporter gene assay ChEMBL_2370017 Uncompetitive inhibition of recombinant human full-length C-terminal His-tagged HSD17B13 expressed in HEK293 cells using estradiol as substrate preincubated for 30 mins followed by substrate addition and measured after 3 hrs by rapidfire MS/MS analysis ChEMBL_2251629 (CHEMBL5165839) Inhibition of recombinant N-terminal GST/His6-fusion tagged human CDK2/Cyclin E2 expressed in Sf9 insect cells incubated for 20 mins followed by [33P]gamma-ATP addition and measured after 2 hrs by radiometric HotSpot Kinase assay ChEMBL_1721240 (CHEMBL4136240) Antagonist activity at recombinant human His6-tagged ERalpha LBD (298 to 554 residues) D538G mutant expressed in Escherichia coli assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced fluorescein-labeled PGC1alpha coactivator peptide binding after overnight incubation by Lantascreen TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_1721241 (CHEMBL4136241) Antagonist activity at recombinant human His6-tagged ERalpha LBD (298 to 554 residues) Y537S mutant expressed in Escherichia coli assessed as inhibition of estradiol-induced fluorescein-labeled PGC1alpha coactivator peptide binding after overnight incubation by Lantascreen TR-FRET assay ChEMBL_1667760 (CHEMBL4017648) Antagonist activity at rat EP1 receptor expressed in African green monkey COS1 cells assessed as decrease in prostaglandin E2-induced increase in intracellular calcium level incubated for 90 mins measured for 60 secs by Fluo 4-AM dye based fluorescence assay Estrogen Receptor Binding Assay and Cell-Based Transcriptional Assay The binding affinities were determined by a competitive radiometric binding assay using [3H]estradiol as tracer. The Kd for 3H-estradiol was determined by saturation binding to ER receptors. The IC50 values for compounds were converted to Ki using Cheng-Prusoff equation. The functional activity and selectivity was measured using a transcription assay in the cotransfected human prostate cancer PC3/ER (alpha or beta)-ERE cell line, and EC50 values were determined by computer fit to a concentration-response curve. Sulfatase Assay The extent of in vitro inhibition of sulfatase activities was assessed using intact monolayers of JEG-3 cells. Sulfatase activity was measured using [6,7-3H] EIS over 3 hrs, determined by measuring the total amount of 3H-labeled estrone and estradiol formed. Sulfatase Inhibition Assay The extent of in vitro inhibition of sulfatase activities was assessed using intact monolayers of JEG-3 cells. Sulfatase activity was measured using [6,7-3H] E1S over 3 hrs, determined by measuring the total amount of 3H-labeled estrone and estradiol formed. Competition-Based Ligand Binding Assay. Ligand binding was determined using a scintillation proximity assay with streptavidin-coated polyvinyltoluene scintillation beads (Amersham) and biotinylated receptor. Receptor-bound [3H]-E2 was determined by scintillation counting (Perkin-Elmer). The IC50 values were calculated using a four-parameter logistic equation. Binding Assay The method employed was adapted from the scientific literature and described in detail by Osbourn et al. (1993, Biochemistry, 32, 6229-6236). Recombinant human ERalpha and ERR proteins were purified from transfected Sf9-cells. The in vitro assays involved the use of either ERalpha or ERbeta proteins and [3H]E2, at a fixed concentration of 0.5 nM, as the labeled ligand. Recombinant human ERalpha or ERbeta proteins were dissolved in binding buffer (10 mM Tris-HCL, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 1 mM DTT, 1 mg/ml BSA) and duplicate aliquots were then incubated with [3H]E2 at a final concentration of 0.5 nM, together with a vehicle control (0.4% DMSO), or the same amount of vehicle containing increasing concentrations of unlabeled steroid ligands as competitors. After incubation for 2 h at 25 C., the unbound ligands were removed and the amounts of [3H]E2 bound to either ERalpha or ERbeta proteins were measured. Inhibition Assay The method employed was adapted from the scientific literature and described in detail by Osboum et al. (1993, Biochemistry, 32, 6229-6236). Recombinant human ERalpha and ERbeta proteins were purified from transfected Sf9-cells. The in vitro assays involved the use of either ERalpha or ERbeta proteins and [3H]E2, at a fixed concentration of 0.5 nM, as the labeled ligand. Recombinant human ERalpha or ERbeta proteins were dissolved in binding buffer (10 mM Tris-HCL, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 1 mM DTT, 1 mg/ml BSA) and duplicate aliquots were then incubated with [3H]E2 at a final concentration of 0.5 nM, together with a vehicle control (0.4% DMSO), or the same amount of vehicle containing increasing concentrations of unlabeled steroid ligands as competitors. After incubation for 2 h at 25 C., the unbound ligands were removed and the amounts of [3H]E2 bound to either ERalpha or ERbeta proteins were measured. Binding Assay The competition assay was performed in a 96-well plate (polystyrene*) which binds <2.0% of the total input [3H]-17beta-estradiol and each data point was gathered in triplicate. 100 uG/100 uL of the receptor preparation was aliquoted per well. A saturating dose of 2.5 nM [3H]17beta-estradiol+competitor (or buffer) in a 50 uL volume was added in the preliminary competition when 100x and 500x competitor were evaluated, only 0.8 nM [3H]17beta-estradiol was used. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 2.5 h. At the end of this incubation period 150 uL of ice-cold dextran coated charcoal (5% activated charcoal coated with 0.05% 69K dextran) was added to each well and the plate was immediately centrifuged at 99 g for 5 minutes at 4 C. 200 uL of the supernatant solution was then removed for scintillation counting. Samples were counted to 2% or 10 minutes, whichever occurs first. Evaluation of HSD17B2 Activity Assay Table 2: The fluorescence based detection assay monitors the conversion of the co-factor NAD+ to NADH, which occurs coincident with the conversion of estradiol to estrone by HSD17B2. These assays were performed in 384 well plates (Greiner V-shape PP-microplate). The 20 μl reaction volume contained: 0.7 μM estradiol (E2); 6 mM NAD+ (Sigma); 250 nM HSD17B2 enzyme (Origene; Cat #TP303293); 0.25 M potassium phosphate buffer pH 7.4, 0.75% vehicle (DMSO). Reactions were incubated for 2 hours at 37° C., and the reaction was stopped by freezing the reaction plates at −80° C. Zero time samples were frozen immediately.The conversion of NAD+ to NADH was quantitated using NAD-Glo kits (Promega; Cat #G9062) according to the manufacturers' instructions. A volume of 15 μL of enzyme reaction mixture was added to 15 μL of reconstituted Glo reagent, and the plates were incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Luminescence was quantitated on a Tecan Spark Reader®. A standard curve of NADH (0.1-50 μL) in potassium phosphate buffer pH 7.4/1% DMSO was run on each plate.Activity of the enzyme in the absence of E2 was used to evaluate specificity of conversion. Enzyme activity in the presence of test samples was expressed as a percentage of the uninhibited enzyme in the presence of 1% DMSO vehicle only, and was plotted versus inhibitor concentration. Non-linear regression was performed using a four-parameter logistic model and GraphPad Prism software. ER-alpha Radioligand Binding Assay and ERE-Luciferase Reporter Assay. Radioligand binding assay was performed by using 96-well microtiterplates containing ER, 17beta-estradiol, and the test compound to be tested and SPAbeads. After incubation at room temperature for 2-4 h, the reaction was terminated by centrifugation. The radioactivity was counted in a Packard Topcount scintillation counter. Nonspecific binding was defined as the remaining radioactivity in the presence of 10 uM nonradioactive 17beta-estradiol. Assays were performed in triplicate. HELNalpha, a human cervix adenocarcinoma cell line derived from HeLa cells stably transfected with the reporter gene and the expression plasmid ERalpha, were used to quantify the antiestrogenic and estrogenic effects of compounds on ERE ER-alpha Radioligand Binding Assay and ERE-Luciferase Reporter Assay. Radioligand binding assay was performed by using 96-well microtiterplates containing ER, 17beta-estradiol, and the test compound to be tested and SPAbeads. After incubation at room temperature for 2-4 h, the reaction was terminated by centrifugation. The radioactivity was counted in a Packard Topcount scintillation counter. Nonspecific binding was defined as the remaining radioactivity in the presence of 10 uM nonradioactive 17beta-estradiol. Assays were performed in triplicate. HELNalpha, a human cervix adenocarcinoma cell line derived from HeLa cells stably transfected with the reporter gene and the expression plasmid ERalpha, were used to quantify the antiestrogenic and estrogenic effects of compounds on ERE. ER-beta Radioligand Binding Assay and ERE-Luciferase Reporter Assay. Radioligand binding assay was performed by using 96-well microtiterplates containing ER, 17beta-estradiol, and the test compound to be tested and SPAbeads. After incubation at room temperature for 2-4 h, the reaction was terminated by centrifugation. The radioactivity was counted in a Packard Topcount scintillation counter. Nonspecific binding was defined as the remaining radioactivity in the presence of 10 uM nonradioactive 17beta-estradiol. Assays were performed in triplicate. HELNbeta, a human cervix adenocarcinoma cell line derived from HeLa cells stably transfected with the reporter gene and the expression plasmid ERbeta, were used to quantify the antiestrogenic and estrogenic effects of compounds on ERE. Pseudotyped HCV particle (HCVpp) reporter assay Plasmids expressing HCV E1 and E2 envelope proteins of GT1a H77 strain (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94:8738-43) or GT1b Con1 strain (Science 1999 285:110-3) were constructed by cloning the nucleic acids encoding the last 60 amino acids of HCV core protein and all of the HCV E1 and E2 proteins into pcDNA3.1(+) vector. Plasmid pVSV-G expressing the glycoprotein G of the vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV G) is from Clontech (cat #631530). The HIV packaging construct expressing the firefly luciferase reporter gene was modified based on the envelope defective pNL.4.3.Luc-R .E vector (Virology 1995 206:935-44) by further deleting part of the HIV envelope protein. Human ERalpha Reporter Assa All reagents used in this assay was supplied in the Human ERα Reporter Assay by Indigo Biosciences # IB00401. In an effort to screen selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs), the Human ERα Reporter Assay, supplied by Indigo Biosciences, was utilized to quantify antagonist functional activity against the human estrogen receptor. Reporter cells were thawed at 37° C. and added to pre-warmed to 37° C. cell recovery medium (CRM). Stock concentration of 17β-estradiol was serially diluted in CRM. Diluted 17β-estradiol was added to CRM containing reporter cells resulting in a working concentration of 1.6 nM (2×). Cells plus 17β-estradiol were dispensed in a kit-supplied white walled 96-well plate. Concentrated stocks of test compounds were diluted to 2× working concentrations in cell screening medium (CSM). 2× concentrated compounds were added to the plated cells in a dose-dependent manner resulting in a final concentration range of 1E-11 to 1E-5 M and a final 17β-estradiol concentration of 8E-10 M. Assay plates were incubated for 24 hours in a humidified 37° C. incubator. Culture medium was removed from the assay plates by inversion. Detection substrate and buffer was warmed to room temperature, mixed thoroughly, and immediately added to the assay plates. Assay plates were incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature protected from light. Luminescence was measured in a Synergy HTX luminescence plate reader. Data is processed utilizing GraphPad Prism 7 by graphing the relative light units measured at each compound concentration. Human ERalpha Reporter Assay All reagents used in this assay was supplied in the Human ERα Reporter Assay by Indigo Biosciences #IB00401. In an effort to screen selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs), the Human ERα Reporter Assay, supplied by Indigo Biosciences, was utilized to quantify antagonist functional activity against the human estrogen receptor. Reporter cells were thawed at 37° C. and added to pre-warmed to 37° C. cell recovery medium (CRM). Stock concentration of 17β-estradiol was serially diluted in CRM. Diluted 17β-estradiol was added to CRM containing reporter cells resulting in a working concentration of 1.6 nM (2×). Cells plus 17β-estradiol were dispensed in a kit-supplied white walled 96-well plate. Concentrated stocks of test compounds were diluted to 2× working concentrations in cell screening medium (CSM). 2× concentrated compounds were added to the plated cells in a dose-dependent manner resulting in a final concentration range of 1E-11 to 1E-5 M and a final 17β-estradiol concentration of 8E-10 M. Assay plates were incubated for 24 hours in a humidified 37° C. incubator. Culture medium was removed from the assay plates by inversion. Detection substrate and buffer was warmed to room temperature, mixed thoroughly, and immediately added to the assay plates. Assay plates were incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature protected from light. Luminescence was measured in a Synergy HTX luminescence plate reader. Data is processed utilizing GraphPad Prism 7 by graphing the relative light units measured at each compound concentration. In Vitro Assay The method employed was adapted from the scientific literature and described in detail by Osbourn et al. (1993, Biochemistry, 32, 6229-6236). Recombinant human ERα and ERβ proteins were purified from transfected Sf9-cells. The in vitro assays involved the use of either ERα or ERβ proteins and [3H]E2, at a fixed concentration of 0.5 nM, as the labeled ligand. Recombinant human ERα or ERβ proteins were dissolved in binding buffer (10 mM Tris-HCL, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 1 mM DTT, 1 mg/ml BSA) and duplicate aliquots were then incubated with [3H]E2 at a final concentration of 0.5 nM, together with a vehicle control (0.4% DMSO), or the same amount of vehicle containing increasing concentrations of unlabeled steroid ligands as competitors. After incubation for 2 h at 25° C., the unbound ligands were removed and the amounts of [3H]E2 bound to either ERα or ERβ proteins were measured. The average amounts of [3H]E2 bound to either ERα or ERβ proteins at each concentration of competitor were used to make inhibition curves. IC50 values were subsequently determined by a non-linear, least squares regression analysis. Inhibition constants (Ki) were calculated using the equation of Cheng and Prusoff (Cheng et al., 1973, Biochem. Pharmacol., 22, 3099-3108), using the measured IC50 of the tested compounds, the concentration of radioligand employed in the assay, and the historical values for the Kd of the radioligand, which were established as 0.2 nM and 0.13 nM for ERα and ERβ, respectively. Biochemical Antagonist Activity on Wild Type (WT) and Mutants Antagonistic potency of compounds was evaluated using LanthaScreen TR-FRET ERα Coactivator Assay (ThermoFisher) with modifications. It is a competition assay, where binding of a test compound to a complex comprised of (i) His6-ERα298-554 protein representing ERα ligand-binding domain, (ii) Tb-labeled His6 antibody, (iii) a fluorescein-labeled PGC1a coactivator peptide (EAEEPSLLKKLLLAPANTQ), and (iv) estradiol, results in a decrease of the TR-FRET signal due to dissociation of the coactivator peptide. His6-ERα298-554 proteins were expressed as WT or D538G or Y537S mutants in E. coli and purified by affinity chromatography. The assay works in a homogeneous mix-and-read format. In a typical experiment, a 4 μL mixture of 0.5 nM His6-ERα298-554, 0.5 nM Tb-labeled His6 antibody, 250 nM PGC1a peptide, and 3 nM estradiol (or 10 nM estradiol) in 100 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.4, 0.01% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 5 mM DTT, was added to 40 nL test compound in DMSO and incubated overnight at room temperature. The TR-FRET 520:495 nm emission ratio was calculated and used to determine the IC50 value from a dose response curve fit to the 4-parameter logistic equation. Biochemical Assay Through the Molecular Library Probe Production Center Network (MLPCN), at least 300,000 compounds were screened using a TR-FRET method, an ALPHASCREEN method or both, and tested for their ability to inhibit SUMOylation of a target protein via SUMO E1 or SUMO E2. The assays were based on SUMOylation of the target protein RanGAP1, which is a protein that is efficiently SUMOylated with only the SUMO E1 and E2 enzymes, and does not use E3 ligases. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay was the primary assay followed by a chemoluminescence-based secondary assay using ALPHA screen to eliminate false positive hits. Then, the hits were screened by a poly-ubiquitination assay using ubiquitin, ubiquitin E1, Ubc5 and Apc11 to eliminate inhibitors not specific to SUMOylation. The screening identified a potent family of SUMOylation inhibitors based on a tricyclic scaffold. In Vitro 17bHSD4 Enzyme Assay 10 concentration of compounds (0.2 μl) in DMSO was added to GREINER FLUOTRAC 200 384 well plate (781076) using ECHO dispensing (BECKMAN COULTER). 80 nl of 10 mM Estradiol (SIGMA, E8875) was added using Echo dispensing. The enzyme reaction was initiated by addition, using MULTIDROP COMBI dispensing (THERMO FISHER), of 40 μl of a mix containing recombinant 17bHSD4 (M1-N311) and NAD. Final assay conditions were 40 nM of 17bHSD4, 0.125 mM of NAD, 15 μM Estradiol and various concentrations of compound in buffer (5 mM EDTA (TEKNOVA E0306), 0.01% DDM (AFFYMETRIX D310) in 50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.4). After each addition plates were centrifuged for 1 min at 150×g (EPPENDORF, 5810R, A-4-81). NADH formation was measured by fluorescence intensity (FI) (Ex360/Em460) at time zero (to) and at 1.5 h (t1) in a PHERASTAR FSX (BMG LABTECH). FI for each sample was calculated as FI at t1 minus FI at t0. Radioligand Binding of Compounds to AR, GR and ER ReceptorsGR (human) (agonist radioligand) IM-9 cells (cytosol)[3H]dexamethasone 1.5 nM 1.5 nM triamcinolone (10 μM) 6 h 4° C. Scintillation counting (Clark, A. F et al. (1996) Invest. Ophtalmol. Vis. Sci., 37: 805-813).ER (nonselective) (human) (agonist radioligand) MCF-7 cells (cytosol)[3H]estradiol 0.4 nM 0.2 nM 17(3-estradiol (6 μM) 20 h 4° C. Scintillation counting(Parker, G. J et al. (2000) J. Biomol. Screen., 5: 77-88).AR (human) (agonist radioligand) LNCaP cells (cytosol)[3H]methyltrienolone 1 nM 0.8 nM mibolerone (1 μM) 24 h 4° C. Scintillation counting.Zava, D. T et al. (1979) Endocrinology, 104: 1007-1012.The results are expressed as a percent of control specific binding measured specific binding*100 control specific binding and as a percent inhibition of control specific binding 100-(measured specific binding*100) control specific binding obtained in the presence of compound. HSD17B13 Inhibition Assay HSD17B13 uses the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a cofactor during metabolism of beta-estradiol (substrate), converting NAD+ to the reduced form (NADH) and beta-estradiol to its product (estrone). Estrone production is quantified by LCMS, and used as a measure of HSD17B13 enzyme activity.HEK-cells stably expressing wild type human HSD17B13 were plated at 10,000 cells/well in 50 μL growth media (DMEM containing 10% heat inactivated FBS, 400 μg/ml geneticin, 1× L-Glutamine, and 1× Non-essential amino acids, Invitrogen 11965-092, 16140-071, 10131-027, 25030-081, 11140-050), into poly-D-lysine-coated 384-well plates (Corning Biocoat, 354663), and incubated overnight (with lid) at 37° C. (95% O2: 5% CO2). Following overnight incubation, intermediate compound plates (Greiner, 781280) containing 160 nL of 375×FAC test compound which had been serial diluted 1 in 3.162 in 100% DMSO for an 11 point concentration response curve, with duplicate points at each concentration, were diluted 1 in 187.5 with 30 μL warmed assay media (DMEM, 1× L-Glutamine, and 1× Non-essential amino acids) to give 2×FAC compound (80 μM top concentration) in 0.53% DMSO. Growth media was then removed from the cell plates and replaced with 10 μL of 2×FAC test compound, and incubated for 1 hour (with lid) at 37° C. (95% O2: 5% CO2), before the addition of 25 μM FAC beta-estradiol in assay media/0.2% DMSO. The reaction was incubated for 2 hours (with lid) at 37° C. (95% O2: 5% CO2), after which 10 μL of reaction was transferred from assay plate to a new 384-well deep-well plate (Matrix 4325) and diluted 1 in 10 with 90 μL of stop reagent (50% methanol in water containing internal standard 17b-estradiol-2,3,4-13C3). Amount of product (estrone) was then quantified by LCMS. Data expressed as product area ratio (PAR) were then normalized to control wells using Activity Base (IDBS). In Vitro 17bHSD13 Enzyme Assay Final assay conditions were 80 nM of 17bHSD13, 0.5 mM of NAD, 20 μM Estradiol and various concentrations of compound in buffer (5 mM EDTA (TEKNOVA E0306), 0.01% DDM (AFFYMETRIX D310) in 50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.4). After 2.5 h the reaction were stopped by addition of 20 μl of 0.6% Formic acid (MERCK 5.33002) and samples were analyzed using LC-MS/MS.SCIEX LC-MS/MS system: Sample was injected with CTC analytical injector, SHIMATZU LC pumps LC20 and analyzed on the SCIEX API 5000 LCMSMS system with the following settings. Samples were chromatographed on a WATERS, SYMMETRY, C8, 3.5 μm, 2.1×50 mm) column at constant flow rate of 0.5 mL/min. The mobile phases consist of A (water with 0.2% formic acid) and B (acetonitrile with 0.2% formic acid). The LC gradient profile is as follows: 50% B during 0 to 0.5 min, a linear increase to 100% B during 0.5 to 1 min, hold at 100% B during 1 to 1.6 min then back to 50% B from 1.6 to 2 min. The run time was 2 min with retention times of approximately 0.8 and 1.07 min for Estradiol and Estrone, respectively. Detection was performed on a API 5000 LC/MS/MS system with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer, a TURBO V ion source, in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode at positive polarity with APCI probe. The MRM pairs were m/z 273.1 to m/z 107.0 and m/z 271.3 to 107.0. for Estradiol and Estrone, respectively. Estrone Detection Assay for Evaluation of HSD17I313 Activity Reactions were terminated by the addition of two volumes of acetonitrile (MeCN; LCMS grade; CAS #75/05/8) containing deuterated (D4)-E1 used as internal standard (Clear Synth; #CS-T-54273; 500 ng/mL final concentration). Samples were applied to pre-prepared Bond Elut-C18 extraction cartridges (3 mL; Agilent; Ser. No. 12/102,028), washed and eluted in MeCN. Eluates were dried under nitrogen and re-suspended in 60% methanol (LCMS grade methanol; CAS #67/56/1) before submission for analysis. Aqueous linearity for E2 and E1 were included for quantification.[0357]Analysis of samples was undertaken on a XBridge BEH C18 column (Waters; #186003033) using 0.1% Diethyl Amine in MeCN (mobile phase A; DEA CAS #109-89-7) and 0.1% Diethyl Amine in milli-Q water (mobile phase B) in a 3 min gradient allowing 25% B. Analytes were detected in negative mode using MRM analysis, with E2 having a RT of 1.85 min and E1 having a RT of 2 min. In Vitro Enzyme Activity and Drug Binding Ub-charging of E2 enzyme was performed for 90 min at 30° C. in a reaction containing 0.1 μM GST-E1, 3.3 μM E2/UbcH7, 10 μM FLAG-Ub and 0.188 μM PINK1 (all R&D systems). In a separate reaction 0.75 μM Parkin (Ubiquigent) was preincubated with 20 μM compound 4 (or equal volume of DMSO). Both reactions were diluted in Ub buffer (final concentration: 20 mM HEPES pH 7.2, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM EGTA, 500 μM TCEP and 10% ATP regeneration system (20 mM HEPES pH 7.6, 10 mM ATP, 300 mM phosphocreatine, 10 mM MgCl2, 10% glycerol, 1.5 mg/mL creatine phosphokinase (all Sigma Aldrich))). 1 U Apyrase (Sigma) was added per 9 μL reaction and both reactions were combined and incubated for an additional 30 min. 100 μL of 1×LDS buffer was added per 10 μL reaction and samples were split for −/+DTT (20 mM final). hPGDH Inhibitor Screening Biochemical Assay The in vitro biochemical assay can be performed in white, 384 plates in total 20 μl reaction volume consisting of 10 nM of 15-PGDH/HPGD (R&D System #5660-DH), 15 μM Prostaglandin E2 (Sigma, Cat #P5640-10MG) and 0.25 mM β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide sodium salt (Sigma, Cat #N0632-5G) made in reaction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.01% Tween 20) at 10-point dose response curve for test/tool compounds. Briefly, 5 μl (4×) of compounds solution and 5 μl (final concentration, 10 nM) of enzyme solution is added to white 384 well plates and incubated for 10 mins at 37° C. 5 μl (4×) of Prostaglandin E2 and 5 μl (4×) of β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide sodium salt is added to the wells and incubated for 10 mins at rt. Fluorescence is recorded at ex/em=340 nm/485 nm. The percentage (%) inhibition of enzyme activity was determined relative to positive control (1% DMSO) and IC50 was calculated using GraphPad prism software (four parameter-variable slope equation). Enzymatic Assay (Inhibition of Type 1 17beta-HSD) The enzymatic reaction was performed in the reaction buffer containing substrate, [14C]-estrone, and the test inhibitors. After the reaction, radiolabeled steroids were extracted from the reaction mixture, and solvent was evaporated to dryness. Steroids were dissolved and separated on TLC plates. Radioactivity signals were detected and quantified using a PhosphoImager (Sunny Vale, CA). The percentage of transformation of [14C]-E1 into [14C]-E2 was calculated. The IC50 values were calculated using an unweighted iterative least-squares method for four-parameter logistic curve fitting (DE50 program, CHUL Research Center, Quebec). Biochemical Assay A hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase inhibition screening biochemical assay can be performed to assess the synthesized inhibitors provided herein. Provided herein is an exemplary biochemical assay for hPGDH inhibitor screening.The in vitro biochemical assay can be performed in white, 384 plates in total 20 μl reaction volume consisting of 10 nM of 15-PGDH/HPGD (R&D System #5660-DH), 15 μM Prostaglandin E2 (Sigma, Cat #P5640-10MG) and 0.25 mM (3-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide sodium salt (Sigma, Cat #N0632-5G) made in reaction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.01% Tween 20) at 10-point dose response curve for test/tool compounds. Briefly, 5 μl (4×) of compounds solution and 5 μl (final concentration, 10 nM) of enzyme solution is added to white 384 well plates and incubated for 10 mins at 37° C. 5 μl (4×) of Prostaglandin E2 and 5 μl (4×) of β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide sodium salt is added to the wells and incubated for 10 mins at room temperature. Fluorescence is recorded at ex/em=340 nm/485 nm. The percentage (%) inhibition of enzyme activity was determined relative to positive control (1% DMSO) and IC50 was calculated using GraphPad prism software (four parameter-variable slope equation). Estrogen Receptor Coactivator Assay It is a competition assay, where binding of a test compound to a complex comprised of (i) His6-ERα298-554 protein representing ERα ligand-binding domain, (ii) Tb-labeled His6 antibody, (iii) a fluorescein-labeled PGC1α coactivator peptide (EAEEPSLLKKLLLAPANTQ), and (iv) estradiol, results in a decrease of the TR-FRET signal due to dissociation of the coactivator peptide. His6-ERα298-554 proteins were expressed as WT or D538G or Y537S mutants in E. coli and purified by affinity chromatography. The assay works in a homogeneous mix-and-read format. In a typical experiment, a 4 μL mixture of 0.5 nM His6-ERα298-554, 0.5 nM Tb-labeled His6 antibody, 250 nM PGC1a peptide, and 3 nM estradiol in 100 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.4, 0.01% Tween-20, 0.02% NaN3, 5 mM DTT, was added to 40 nL test compound in DMSO and incubated overnight at room temperature. The TR-FRET 520:495 nm emission ratio was calculated and used to determine the IC50 value from a dose response curve fit to the 4-parameter logistic equation. The antagonist activity with respect to estrogen receptors in this test is given by the concentration which inhibits 50% of the estrogen receptor activity (or IC50) in nM. Competition Binding Assay Run the competition binding assay in a buffer containing 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1.5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1 mg/mL ovalbumin, and 5 mM DTT, using 0.025 μCi per well 3H-estradiol (118 Ci/mmol, 1 mCi/mL), 7.2 ng/well ERα (wild type), or 7.2 ng/well ERα (Y537S mutant) or 7.7 ng/well ERβ receptor. Add the test compound at 10 different concentrations ranging from 10,000 nM to 0.5 nM, and determine nonspecific binding in the presence of 1 μM of 1713 estradiol. Incubate the binding reaction (140 μL) for 4 hours at room temperature, and then add cold dextran-charcoal buffer (70 μL) (containing per 50 mL of assay buffer, 0.75 g of charcoal and 0.25 g of dextran) to each reaction. Mix the plates for 8 minutes on an orbital shaker at 4° C. and then centrifuge at 3000 rpm at 4° C. for 10 minutes. Transfer an aliquot (120 μL) of the mixture to another 96-well, white flat bottom plate (Costar) and add Perkin Elmer Optiphase Supermix scintillation fluid (175 μL) to each well. Seal the plates and shake vigorously on an orbital shaker. After an incubation of 2.5 hours, read the plates in a Wallac Microbeta counter. Cell Response Assay The rat EP1 receptor-expressing cells were washed with the assay buffer. 100 μL of a fluorescent calcium indicator (Calcium kit II, Fluo 4 (Dojindo Laboratories).The intracellular calcium concentration was measured as a fluorescent signal using FDSS (registered trademark) 7000 (manufactured by Hamamatsu Photonics K. K.). 50 μL of each test compound (final concentrations: 1 nM to 10 μM) was added to each well after 20 seconds from initiating the reading of the fluorescent signal, and the fluorescence signal was measured for 60 seconds. Then, 50 μL of a prostaglandin E2 buffer solution was added to each well (final concentration 10 nM) and the fluorescence signal was measured for 60 seconds. Competition-Based Ligand Binding Assay and Transactivation Assay. Ligand binding was determined using a scintillation proximity assay with streptavidin-coated SPA beads (Amersham) and biotinylated receptor. Receptor-bound [3H]estrone was determined by scintillation counting (Perkin-Elmer). The binding IC50 value (the concentration of compound required for 50% inhibition of [3H]estrone binding to ER was calculated using XL-fit one-site dose response. To determine the agonist activity of the compounds on receptors, the full length receptors were stably expressed under ERE promoter with luciferase as reporter in Hela cells. The transactivation EC50 (the concentration of compound required to achieve 50% of transactivation caused by 10 nM estradiol) was calculated using XL-fit one-site dose response. HSD10B1 Enzymatic Blocking Assay To screen compounds of the disclosure for their ability to block HSD17B10 function, an enzymatic blocking assay was performed. For the assay, HSD17B10 activity was measured by detecting NADH formation from oxidation of Estradiol using a NADH Glo luminescence assay (Promega, #Cat. No. G9062). Compounds of the disclosure were evaluated in a dose titration assay where the compounds were titrated at 10-point dose curve using an Echo-555 liquid handling dispenser. HSD17B10 (Seq. ID NO: 5, expressed in mammalian cells) was added at a final concentration of 31.25 ng/well in a buffer containing 0.2M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, into a low volume white 384-well assay plate. Compounds were incubated with the enzyme for 30 minutes at room temperature. The assay reaction was then initiated by addition of 25 μM Estradiol substrate (Sigma, catalog #E2758-250MG, CAS: 50-28-2) and 500 μM NAD co-factor, and the reaction mixture was incubated for 3 hours at room temperature. DMSO at a concentration of 0.5% was used as a negative control and a no substrate control was used a positive control in the assay. Detection reagent was then added as per manufacturer's instructions, and the plate was subsequently incubated in the dark for 1 hour at room temperature, NADH generated was detected in the luminescence mode on the Envision Perkin Elmer plate reader. The IC50 values were determined using Dotmatics analysis software. HSD17B1 Enzymatic Blocking Assay To screen compounds of the disclosure for their ability to block HSD17B1 function, an enzymatic blocking assay was performed. For the assay, HSD17B1 activity was measured by detecting NADH formation from oxidation of Estradiol using a NADH Glo luminescence assay (Promega, #Cat. No. G9062). Compounds of the disclosure were evaluated in a dose titration assay where the compounds were titrated at 10-point dose curve using an Echo-555 liquid handling dispenser. HSD17B1 (SEQ ID NO: 2, expressed in mammalian cells) was added at a final concentration of 25 ng/well in a buffer containing 0.2M Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, into a low volume white 384-well assay plate. Compounds were incubated with the enzyme for 30 minutes at room temperature. The assay reaction was then initiated by addition of 25 μM Estradiol substrate (Sigma, catalog #E2758-250MG, CAS: 50-28-2) and 500 μM NAD co-factor, and the reaction mixture was incubated for 3 hours at room temperature. DMSO at a concentration of 0.5% was used as a negative control and a ‘no substrate’ control was used a positive control in the assay. Detection reagent was then added as per manufacturer's instructions, and the plate was subsequently incubated in the dark for 1 hour at room temperature, NADH generated was detected in the luminescence mode on the Envision Perkin Elmer plate reader. The IC50 values were determined using Dotmatics analysis software. HSD17B2 Enzymatic Blocking Assay To screen compounds of the disclosure for their ability to block HSD17B2 function, an enzymatic blocking assay was performed. For the assay, HSD17B2 activity was measured by detecting NADH formation from oxidation of Estradiol using a NADH Glo luminescence assay (Promega, #Cat. No. G9062). Compounds of the disclosure were evaluated in a dose titration assay where the compounds were titrated at 10-point dose curve using an Echo-555 liquid handling dispenser. HSD17B2 (SEQ ID NO: 3, expressed in mammalian cells) was added at a final concentration of 2 ng/μL in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, Pluronic F-127 0.05%, Tween20 0.01%, BSA 0.01% into a low volume white 384-well assay plate. Compounds were incubated with the enzyme for 15 min at 20° C. The assay reaction was then initiated by addition of 1.8 μM Estradiol substrate (Sigma, catalog #E2758-250MG, CAS: 50-28-2) and 650 μM NAD co-factor, and the reaction mixture was incubated for 45 min at 20° C. DMSO at a concentration of 0.5% was used as a negative control and a ‘no substrate’ control was used a positive control in the assay. Detection reagent was then added as per manufacturer's instructions, and the plate was subsequently incubated in the dark for 1 hour at room temperature, NADH generated was detected in the luminescence mode on the Envision Perkin Elmer plate reader. HSD17B4 Enzymatic Blocking Assay To screen compounds of the disclosure for their ability to block HSD17B4 function, an enzymatic blocking assay was performed. For the assay, HSD17B4 activity was measured by detecting NADH formation from oxidation of Estradiol using a NADH Glo luminescence assay (Promega, #Cat. No. G9062). Compounds of the disclosure were evaluated in a dose titration assay where the compounds were titrated at 10-point dose curve using an Echo-555 liquid handling dispenser. HSD17B4 (SEQ ID NO: 4, expressed in mammalian cells) was added at a final concentration of 2.5 ng/μL in a buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, Pluronic F-127 0.05%, Tween20 0.01%, BSA 0.01%, into a low volume white 384-well assay plate. Compounds were incubated with the enzyme for 15 min at 20° C. The assay reaction was then initiated by addition of 23.46 μM Estradiol substrate (Sigma, catalog #E2758-250MG, CAS: 50-28-2) and 1500 μM NAD co-factor, and the reaction mixture was incubated for 45 min at 20° C. DMSO at a concentration of 0.5% was used as a negative control and a ‘no substrate’ control was used a positive control in the assay. Detection reagent was then added as per manufacturer's instructions, and the plate was subsequently incubated in the dark for 1 hour at room temperature, NADH generated was detected in the luminescence mode on the Envision Perkin Elmer plate reader. Cell Response Assay The rat EP1 receptor-expressing cells were washed with the assay buffer. 100 μL of a fluorescent calcium indicator (Fluo-4 NW Calcium Assay Kit (Molecular Probes). The intracellular calcium concentration was measured as a fluorescent signal using FlexStation (registered trademark) (manufactured by Molecular Devices). 50 μL of each test compound that had been diluted with the assay buffer (final concentrations: 1 nM to 10 μM) was added to each well after 20 seconds from initiating the reading of the fluorescent signal, and the fluorescence signal was measured for 60 seconds. Then, 50 μL of a prostaglandin E2 buffer solution was added to each well (final concentration 10 nM) and the fluorescence signal was measured for 60 seconds. HSD17b13 NAD(P)H-Glo Biochemical Assay HSD17b13 enzyme was diluted in 1× assay buffer to the desired enzyme concentration based on the specific activity of the enzyme lot. 20 uL of diluted enzyme was added to each well along with 2.5 uL of 10× inhibitor solution. Assay plate was incubated at RT for 20 minutes, and then 2.5 uL of a 10× substrate/cofactor mix was added to each well for a final concentration of 50 uM estradiol and 1 mMNAD+. Assay plate was incubated at 37° C. for 3 hours. NAD(P)H-Glo Detection System reagents were prepared according to manufacturer's specifications, and 25 uL was added to each well. After incubating for 1 hour at RT, luminescence was measured. UGT1A1 Inhibition Assay KCI838 was incubated at seven increasing concentrations with human UGT1A1-expressed Supersomes (0.25 mg/mL), alamethicin (25 μg/mL) and UDPGA (5 mM) in the presence of the probe substrate estradiol (10 μM) for 30 min at 37 C. The UGT1A1 inhibitor, atazanavir, was screened alongside the test compounds as a positive control. The reactions were terminated by quenching with one volume of methanol containing an analytical internal standard. The samples will be centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min at 4 C. The metabolites were monitored by LC-MS/MS and a decrease in the formation of the metabolite compared to the vehicle control was used to calculate an IC50 value (test compound concentration which produces 50% inhibition). Luciferase Assay Estrogen receptor-negative CV-1 kidney cells are maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium with 4.5 g/L glucose supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 100 units/ml penicillin-streptomycin at 37° C. in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. The cells are then plated in 6-well dishes at a density of 2×10^5 cells per well in phenol-red free Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 10% charcoal-dextran-stripped fetal bovine serum. CV-1 cells are transfected using LipofectAMINE reagent according to the manufacturer's protocol. Transfections containing 1.5 μg of reporter plasmid (containing ERE-tk-luciferase containing a single ERE cloned upstream of the thymidine kinase promoter and luciferase gene) and 0.5 μg of either ERα or ERβ expression vector (containing CMV-ERα or CMV-ERβ full length coding sequence respectively). The next day, cells receive no treatment (controls) or are treated with estradiol alone (1 nM) or estradiol plus a compound of the invention (at varying concentrations). After 16-24 hours, cells are harvested and assayed for luciferase activity. At the outset, cell monolayers are washed twice with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline and incubated for 15 minutes in 250 μl of 1× cell culture lysis reagent (Promega, Madison, Wis.). Cell extracts are transferred to a fresh tube and assayed using the luciferase assay system (Promega). For each assay, 10 μl of extract is diluted with 90 μl of 1× cell culture lysis reagent. Luminescence is read using an AutoLumat LB953 luminometer. PDK Inhibition Assay To determine the IC50 for PDK inhibitors, a mixture containing 0.05-0.2 μM PDK, 6μM E1, with or without 0.5 μM of the PDC core E2/E3BP, and various amounts of inhibitor was incubated at 25 °C for 10 min in a buffer of 20 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 10 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT, 0.02% (v/v) Tween 20, and 0.1 mg/ml bovine serumalbumin before the addition of 50 μM ATP to initiate the reaction. All inhibition titrations were performed at 10 dose points ranging from 31.6 to 1 mM in a 3.162-fold dilution series, with each inhibitor concentration tested in duplicate. The remaining steps were described previously [Wynn et al., J. Biol. Chem., 283:25305-25315]. Inhibitory Activity Assay Microsomes were prepared from COS-1 cells transiently transfected with a plasmid containing human mPGES-1 cDNA, and used as mPGES-1 enzyme. The mPGES-1 enzyme was diluted with a sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) containing reduced glutathione (2.5 mM) and EDTA (1 mM), DMSO or a DMSO solution of a test compound (final concentration of DMSO was 1%) was added to the enzyme, and the mixture was preincubated at 4° C. for 15 minutes. Then, PGH2 as the substrate was added at a final concentration of 1 μM to start the enzymatic reaction, and after incubation at 4° C. for 4 minutes, a solution of ferric chloride (25 mM) and citric acid (50 mM) was added to terminate the enzymatic reaction. Generated PGE2 was measured by using Prostaglandin E2 Express EIA Kit (Cayman Chemical). Binding Assay ERRα/ERRβ/ERα : In an ERR beta binding assay, GST-bound ERR alpha LBD was used so that a final concentration was 10 nM and a fluorescein-conjugated coactivator PGC1a was 250 nM, and all experiments other than that was the same as the ERR gamma binding assay.In an ER alpha binding assay, a GST-bound ER alpha ligand-binding domain (LBD) was added to a 384 well plate to which the arylethene derivative of the present invention was added to a final concentration of 7.3 nM. Then, a fluorescein-conjugated coactivator PGC1a and a Tb-a-GST antibody were added to 250 nM and 5 nM, respectively, and beta-estradiol as an agonist was added to a final concentration of 4 nM. All subsequent experiments was the same as the ERR gamma binding assay. Fluorescence Polarization Assay Peptides and the ERα LBD were diluted in 1× PBS buffer [140 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM K2HPO4, and 2 mM KH2PO4 (pH 7.4)]. Peptide concentrations were determined by the absorbance at 492 nm, using a fluorescein extinction coefficient of 83000. Fluorescence polarization assays were conducted in 96-well round-bottom black opaque plates (Costar) using 2-fold serial dilutions of the ERα LBD, to final protein concentrations from 10 to 0.0098 μM, in PBS containing 0.1 mM DTT, 20 μM 17β-estradiol, 0.04 mg/mL BSA, and 100 nM fluorescein-labeled peptide. Solutions were incubated in the dark for 30 min at room temperature before being read on a PerkinElmer Fusion plate reader using a 485 nm fluorescein excitation filter and a 535 nm emission filter with a polarizer. ERalpha (Wild Type), ERalpha (Y537S Mutant) and ERbeta Competition Binding Assay The purpose of the following ER competition binding assays is to determine the affinity of a test compound against ERα (wild type), ERα (Y537S mutant), and ERβ.Run the competition binding assay in a buffer containing 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1.5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1 mg/mL ovalbumin, and 5 mM DTT, using 0.025 μCi per well 3H-estradiol (118 Ci/mmol, 1 mCi/mL), 7.2 ng/well ERα (wild type), or 7.2 ng/well ERα (Y537S mutant) or 7.7 ng/well ERβ receptor. Add the test compound at 10 different concentrations ranging from 10,000 nM to 0.5 nM, and determine nonspecific binding in the presence of 1 μM of 17-β estradiol. Incubate the binding reaction (140 μL) for 4 hours at room temperature, and then add cold dextran-charcoal buffer (70 μL) (containing per 50 mL of assay buffer, 0.75 g of charcoal and 0.25 g of dextran) to each reaction. Mix the plates for 8 minutes on an orbital shaker at 4° C. and then centrifuge at 3000 rpm at 4° C. for 10 minutes. Transfer an aliquot (120 μL) of the mixture to another 96-well, white flat bottom plate (Costar) and add Perkin Elmer Optiphase Supermix scintillation fluid (175 μL) to each well. Seal the plates and shake vigorously on an orbital shaker. After an incubation of 2.5 hours, read the plates in a Wallac Microbeta counter. Calculate the IC50 using a 4-parameter logistic curve fit and calculate % inhibition at 10 μM. Convert the IC50 values for the compound to Ki using Cheng-Prusoff equation. 17beta-HSD13 Biochemical Assay More specifically, recombinant 17β-HSD13 protein was assayed in a buffer containing 200 mM Tris pH 7.5, 0.01% Triton X-100, and 0.02% BSA into a 384-well assay plate. Compounds were incubated with 17β-HSD13 (final 50 nM) and NAD+ (final 10 mM) at room temperature for 1 h prior to substrate addition. The assay reaction was then initiated by addition of β-estradiol (final 20 μM), and the reaction mixture was incubated for 2 hours at room temperature. Product formation was detected with chemiluminescence by adding equal volume of NAD+/NADH Glo reagent (Promega, #G9062) and read on a PHERAstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH). IC50 values were determined with GraphPad Prism®, where log-transformed concentration values and the inhibition data were fitted to a four-parameter logistic equation. Y=Bottom+(Top−Bottom)/(1+10{circumflex over ( )}((Log IC50−X)*HillSlope)). Binding Assay Measurement of EP2 receptor binding action was performed in accordance with the method of Abramovitz et al. (Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1483, 285 (2000)). A test compound dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (final concentration: 1.0 (V/V) %) and [3H]prostaglandin E2 (NET-428, manufactured by PerkinElmer) (final concentration: 10 nM) were added to a buffer solution (10 mM MES-KOH (pH 6.0), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA) in which 10 μg of a membrane fraction of HEK293 cells expressing human EP2 receptor (ES-562-M, manufactured by Euroscreen) was suspended, and then incubated at 30° C. for 60 minutes. The membrane fraction was recovered on glass fiber filter paper (GF/B, manufactured by Whatman) using a cell harvester (M30R, manufactured by Brandel), and after washing with a buffer solution (10 mM MES-KOH (pH 6.0), 10 mM MgCl2), radioactivity was measured with a liquid scintillation analyzer (2000CA, manufactured by Packard). Binding Assay In an ERR alpha binding assay, GST-bound ERR alpha LBD was used, and all experiments other than that was the same as the ERR gamma binding assay.In an ERR beta binding assay, GST-bound ERR alpha LBD was used so that a final concentration was 10 nM and a fluorescein-conjugated coactivator PGC1a was 250 nM, and all experiments other than that was the same as the ERR gamma binding assay.In an ER alpha binding assay, a GST-bound ER alpha ligand-binding domain (LBD) was added to a 384 well plate to which the arylethene derivative of the present invention was added to a final concentration of 7.3 nM. Then, a fluorescein-conjugated coactivator PGC1a and a Tb-a-GST antibody were added to 250 nM and 5 nM, respectively, and beta-estradiol as an agonist was added to a final concentration of 4 nM. All subsequent experiments was the same as the ERR gamma binding assay. Competitive Binding Assay Competitive binding assays were performed by incubating rhER alpha (α) and beta 1 (β1) receptors with 10 nM [3H]estradiol (the radio ligand) in the presence or absence of increasing concentrations, 0.25 to 250,000 nM, of the phenolic test compounds of Tables 1 to 3 (nM is nano molar). Each data point is the average of at least two assays. Stock solutions of the compounds of Tables 1 to 3 were prepared at 10×E-2 M in 100% ethanol, water or DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide). Compounds were diluted 10 fold in binding buffer and then 1:4 in the final assay mix. The final concentration of ethanol or DMSO in the assay well was 5%. The highest concentration of the hydrolysis test compound was 2.5×E-4 M (250,000 nM). The residual monomers of Tables 1 to 3 were tested at seven concentrations over log increments. The lowest concentration was 2.5×E-10 M (0.25 nM). Pharmaceutical Assay To determine the HECT E3 ligase selectivity of the compounds, a panel of biochemical HECT E3 ligase autoubiquitinylation assays was employed (Smurf-1, Smurf-2, WWP1, WWP2, ITCH, Nedd4, Nedd4L and E6AP). The conjugation of ubiquitin to a protein substrate is a multistep process. In an initial ATP-requiring step, a thioester bond is formed between the carboxyl terminus of ubiquitin and an internal cystein residue of the ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1). Activated ubiquitin is then transferred to a specific cystein residue of an ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2). E2s donate ubiquitin to a HECT E3 ligase (E3) from which it is transferred to the substrate protein. HECT E3 ligases can auto-ubiquitinylate. This event is detected in the TR-FRET (Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) assay used in this panel. The reaction mix contains E1, E2, tagged-E3, biotin-conjugated ubiquitin, the compound and ATP in a suitable buffer and is incubated for 45 minutes to allow auto-ubiquitinylation of the E3 ligase. To measure the extent of ubiquitinylated E3 ligase by TR-FRET, the donor fluorophore Europium cryptate (Eu3+ cryptate), conjugated to streptavidin which subsequently binds to biotinylated ubiquitin, and the modified allophycocyanin XL665 (HTRF primary acceptor fluorophore) coupled to a tag-specific antibody (HA, His or GST), which recognizes the respective E3 ligase fusion proteins, are added after the reaction is complete. When these two fluorophores are brought together by a biomolecular interaction (in this case ubiquitinylation of the E3 ligase), a portion of the energy captured by the Cryptate during excitation is released through fluorescence emission at 620 nm, while the remaining energy is transferred to XL665. This energy is then released by XL665 as specific fluorescence at 665 nm. Light at 665 nm is emitted only through FRET with Europium. Because Europium Cryptate is present in the assay, light at 620 nm is detected even when the biomolecular interaction does not bring XL665 within close proximity. In Vitro PDHK1 Activity Assay The inhibitory potency of compounds of PDHK1 activity was determined in an enzymatic assay. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDHc) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. PDHc has three subunits E1, E2 and E3. E1 has 3 serine phosphorylation sites S293, S232, S300. If E1 was phosphorylated, PDH will be inactivated. PDHK can phosphorylate PDH protein (also named PDHE1) in PDH complex (PDC) to inactivate it. In the PDHK1 enzymatic assays, the final reaction mixture contains 1 nM of PDHK1 (in house purification from Escherichia coli), 25 nM of PDHE1 (in house purification from Escherichia coli) and 20 μM of ATP, and the experiment was reacted at 30° C. for 45 minutes. After adding detection reagent AlphaScreen Histidine (Nickel Chelate, from Perkin Elmer), and anti-phosphorylation s-293 antibody (from Abcam), Anti-Rabbit IgG Alpha (from Perkin Elmer)), the plate was incubated at 30° C. for 60 min before measuring the light change using a luminometer (Envision). ERalpha (Wild Type), ERalpha (Y537ERalpha (Wild Type), ERalph (Y537S Mutant) and ERbeta Competition Binding Assay The purpose of the following ER competition binding assays is to determine the affinity of a test compound against ERα (wild type), ERα (Y537S mutant), and ERβ.Run the competition binding assay in a buffer containing 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 1.5 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1 mg/mL ovalbumin, and 5 mM DTT, using 0.025 μCi per well 3H-estradiol (118 μCi/mmol, 1 mCi/mL), 7.2 ng/well ERα (wild type), or 7.2 ng/well ERα (Y537S mutant) or 7.7 ng/well ERβ receptor. Add the test compound at 10 different concentrations ranging from 10,000 nM to 0.5 nM, and determine nonspecific binding in the presence of 1 μM of 17-β estradiol. Incubate the binding reaction (140 μL) for 4 hours at room temperature, and then add cold dextran-charcoal buffer (70 μL) (containing per 50 mL of assay buffer, 0.75 g of charcoal and 0.25 g of dextran) to each reaction. Mix the plates for 8 minutes on an orbital shaker at 4° C. and then centrifuge at 3000 rpm at 4° C. for 10 minutes. Transfer an aliquot (120 μL) of the mixture to another 96-well, white flat bottom plate (Costar) and add Perkin Elmer Optiphase Supermix scintillation fluid (175 μL) to each well. Seal the plates and shake vigorously on an orbital shaker. After an incubation of 2.5 hours, read the plates in a Wallac Microbeta counter. Calculate the IC50 using a 4-parameter logistic curve fit and calculate % inhibition at 10 μM. Convert the IC50 values for the compound to Ki using Cheng-Prusoff equation. The results of this assay demonstrate Examples 1, 1A, and 1B (and others) bind to recombinant ERα wild type and ERα mutant (Y537S) as shown in Table 7 below and Example 1B was also determined to bind to ERβ with a Ki (nM) ERβ competition of 0.11±0.07, n=3. Biochemical Assay For the biochemical assay panel, 50 nl of the test compounds, reference compounds and buffer/DMSO control are transferred to the respective wells of a 384-well white GREINER "SMALL VOLUME" PS plate. The assay panel is run at room temperature on a Biomek FX liquid handling workstation. To the assay plates containing 50 nl compound or control solutions in 90% DMSO, 4.5 ul of E3 ligase solution were added per well, followed by 4.5 ul of the pre-incubated E1/E2/Ub mix or the pre-diluted ubiquitin (LOW control). Plates are shaken vigorously after each addition. In this assay the compound concentrations range from 3 nM to 10 uM in an 8-point dose-response curve. After 45 min of incubation the ubiquitinylation reactions were stopped by adding 4.5 ul 2 mM NEM, immediately followed by 4.5 ul of a detection solution including the XL665-labeled antibody and the streptavidin-coupled europium to give a total volume of 18 ul. After an incubation time of 45 min in the dark, the plates are transferred into the Pherastar fluorescence reader to measure the TR-FRET signal. Binding Activity of Compound of the Present Invention to Estrogen Receptor ER The binding activity of the compound to ER was determined using the LanthaScreen TR-FRET ER Alpha Coactivator Assay kit (brand: Thermo, Cat. No: A15885). The ER receptor agonist Estradiol (brand: Sigma, Cat. No: E8875-25) was diluted 10-fold with DMSO in a 96-well V-bottom plate. The highest concentration was 100 μM, 8 concentrations in total. The test compound was diluted 10-fold with DMSO. The highest concentration was 3000 μM, 8 concentrations in total. The compound was then further diluted 50-fold with the detection buffer Nuclear Receptor Buffer E (containing 5 mM DTT) provided in the kit, 10 μL of the diluted compound was transferred to a 96-well half-area microplate (brand: Corning, Cat. No: 3694), 5 μL of ER-LBD protein (4× concentration) was added to the test compound, then a mixture of 5 μL of fluorescein-coactivator peptide and Tb-labeled anti-GST antibody (4× concentration) was added, and the experiment was performed in duplicate. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 2 h, the fluorescence values (Excitation 337, Emission 520/495 nm) were detected using the PHERAstar instrument, and the 520:495 ratio was calculated. With the log value of the final concentration of the compound as the X axis and the 520/495 ratio as the Y axis, data was input into the software Graphpad Prism 9, and the EC50 value was calculated by four-parameter fitting. ERα TR-FRET Test 1x Tris-HCl (Sigma, PHG0002) protein buffer was prepared and mixed for later use. The compound to be detected was prepared into a stock solution with a concentration of 2 mM and then subjected to serial 3-fold gradient dilution, resulting in a total of 10 concentrations. The diluted compounds were respectively added to a reaction plate by means of Echo 550, with 100 nL per well, and at the same time 5 nL of estradiol (Sigma, 491187; final concentration 1.5 nM) was added to each well.Preparation of 1x protein mixed solution: firstly, 2x GST-ERalpha-LBD (Invitrogen, A15677)/MAb anti-GST-Eu (Cisbio, 61GSTKLA) mixed solution was prepared according to the following table.Final Working Concentration ofconcentration concentration stock solutionSubstance (nM) (nM) (nM)GST-ERalpha-LBD 2 4 20100MAb anti-GST-Eu 2.5 ng/well 50 nl/well 50 ug/ml2x biotin-SRC2/streptavidin-XL665 (Cisbio, 610SAXLA) mixed solution was prepared.Final Working Concentration ofconcentration concentration stock solutionSubstance (nM) (nM) (nM)Biotin-SRC2 75 150 1000000Streptavidin-XL665 50 ng/well 50 nl/well 1 mg/mlThe above 2x GST-NR-LBD/ MAb anti-GST-Eu solution and 2x biotin-SRC2/streptavidin-XL665 solution were uniformly mixed at a volume ratio of 1:1; and the 1x protein mixed solution was added to each well of a 384-well plate, with 20 uL being added per well, the 384-well plate was put into a centrifuge and centrifuged at room temperature at 1000 rpm for 10 seconds, and it was taken out, then left to stand at room temperature for 3 h, and then read by EnVision multifunctional microplate reader.The values at 665 and 615 (nm) were read out, and with the value at 615 as the correction value, the final value was expressed as the value at 665/the value at 615. Detection of the Antagonism of the Human Prostaglandin D Receptor Signal 5. 1 Detection PrincipleBinding of prostaglandin D2 to the human PGD receptor induces activation of membrane-bound adenylate cyclases and leads to the formation of cAMP. In the presence of the phosphodiesterase inhibitor IBMX, the cAMP which has accumulated as a result of this stimulation and is released by cell lysis is employed in a competitive detection method. In this test, the cAMP present in the lysate competes with a fluorescently labelled cAMP (cAMP-d2) for binding to an anti-cAMP antibody labelled with an Eu cryptate.The absence of cellular cAMP leads to a maximum signal owing to this cAMP-d2 molecule binding to the antibody. Excitation of the cAMP-d2 molecule at 337 nm leads to a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to the Eu cryptate molecules of the anti-cAMP antibody (labelled therewith), followed by a long-lasting emission signal at 665 nm (and also at 620 nM). The two signals are measured in a suitable measuring device in a time-resolved manner, i.e. once the background fluorescence has subsided. Any increase of the low FRET signal owing to prostglandin E2 administration (measured as change in the well ratio=emission665nm/emission620nm*10 000) indicates the action of antagonists.5.2. Detection Method5.2.1. Test for Antagonism (Figures Per Well of a 384-Well Plate):4 μl of a cAMP-d2/cell suspension (625 000 cells/ml) were added to a test plate with the substance solutions (0.05 μl; 100% DMSO, concentration range 0.8 nM-16.5 μM) already charged. After 20 minutes of pre-incubation at room temperature (RT), 2 μl of a 3×PGD2 solution (6 nM, in PBS-IBMX) were added and the mixture was incubated in the presence of the agonist for a further 30 min at RT (volume: 6 μl). The reaction was then stopped by addition of 2 μl of lysis buffer and the mixture was incubated at RT for a further 20 min prior to the actual measurement (volume: 8 μl). HBV Replication Inhibition Assay HBV replication inhibition by the compounds of this invention could be determined in cells infected or transfected with HBV, or cells with stably integrated HBV, such as HepG2.2.15 cells (Sells et al. 1987). In this example, HepG2.2.15 cells were maintained in cell culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), Geneticin, L-glutamine, penicillin and streptomycin. HepG2.2.15 cells could be seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 40,000 cells/well and be treated with serially diluted compounds at a final DMSO concentration of 0.5% either alone or in combination by adding drugs in a checker box format. Cells were incubated with compounds for three days, after which medium was removed and fresh medium containing compounds was added to cells and incubated for another three days. At day 6, supernatant was removed and treated with DNase at 37° C. for 60 minutes, followed by enzyme inactivation at 75° C. for 15 minutes. Encapsidated HBV DNA was released from the virions and covalently linked HBV polymerase by incubating in lysis buffer (Affymetrix QS0010) containing 2.5 μg proteinase K at 50° C. for 40 minutes. HBV DNA was denatured by addition of 0.2 M NaOH and detected using a branched DNA (BDNA) QuantiGene assay kit according to manufacturer recommendation (Affymetrix). HBV DNA levels could also be quantified using qPCR, based on amplification of encapsidated HBV DNA extraction with QuickExtraction Solution (Epicentre Biotechnologies) and amplification of HBV DNA using HBV specific PCR probes that can hybridize to HBV DNA and a fluorescently labeled probe for quantitation. In addition, cell viability of HepG2.2.15 cells incubated with test compounds alone or in combination was determined by using CellTitre-Glo reagent according to the manufacturer protocol (Promega). The mean background signal from wells containing only culture medium was subtracted from all other samples, and percent inhibition at each compound concentration was calculated by normalizing to signals from HepG2.2.15 cells treated with 0.5% DMSO using equation E1.% inhibition=(DMSOave−Xi)/DMSOave×100% E1:where DMSOave is the mean signal calculated from the wells that were treated with DMSO control (0% inhibition control) and Xi is the signal measured from the individual wells. EC50 values, effective concentrations that achieved 50% inhibitory effect, were determined by non-linear fitting using Graphpad Prism software (San Diego, Calif.) and equation E2Y=Y min+(Y max−Y min)/(1+10(Log EC50−X)×HillSlope) E2:where Y represents percent inhibition values and X represents the logarithm of compound concentrations. ER Transcription Assay (MCF7 Cells) The ER transcription assay is a reporter assay that is based on the ability of ER to induce transcription from a luciferase reporter gene containing estrogen response elements (EREs) in the promoter/enhancer region. When the reporter gene is transfected in MCF7 cells (containing endogenous ER), transcription is reflected by the level of luciferase expression.MCF7 cells are maintained in DMEM/F12 (Gibco, catalog number 11330) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number 100-106). A day before transfection, cells are split into a T75 flask at a cell density of 300,000 cells/mL (10 mL total) and allowed to attach overnight in a humidified CO2 incubator at 37° C.Next day, prior to transfection, media is switched to DMEM/F12 (Gibco, catalog number 21041) supplemented with 10% charcoal-stripped serum (Gemini Bio-Products, catalog number 100-119). MCF7 cells are then bulk transfected, using Lipofectin (Invitrogen, catalog number 18292) with the following plasmids: 7x-TK-ERE-Luc3 (ER reporter gene) and pCMV-Renilla (normalization control). Briefly, for each T75 flask, 32.5 μL of Lipofectin is added to 617.5 μL of OptiMEM (Gibco #11058) and incubated for 30 min at 37 C. Approximately 20 ug DNA is mixed in OptiMEM (Invitrogen) to a total volume of 650 μL. Following incubation, the OptiMEM-DNA mixture is added to the OptiMEM-Lipofectin mix and incubated for 15 minutes at 37° C. The DNA-Lipofectin mixture is then added directly to the T75 flask and the flask is returned to the incubator.After overnight incubation, compound is added to individual wells of a 96-well plate in a 10 μL volume of media at 10× concentration along with 1713 estradiol whose final concentration is 0.1 nM. Normally, DMSO (used as a vehicle) is included to achieve a final concentration of 0.1% when added to the cells. Transfected cells are trypsinized, resuspended in DMEM/F12/10% charcoal-stripped serum and added to the 96-well plate at 25,000 cells/well in 90 μL of media. The plate is then returned to the incubator for 24 hours.After incubation with compounds for 24 hours, Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities are measured to determine ER transcriptional activity. Media is removed from 96-well plates by decanting and blotting on paper towels. Cells are lysed with 40 ul/well of 1× passive lysis buffer (25 mM Tris Phosphate, 2 mM CDTA, 10% Glycerol, 0.5% Triton X-100 and 2 mM DTT before use) and allowed incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes.Firefly luciferase activity is measured by adding 30 ul Firefly luciferase assay buffer (20 mM Tricine, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1.07 mM (MgCO3)4 Mg(OH)2*5H2O, 2.67 mM MgSO4, 33.3 mM DTT, 270 μM Coenzyme A, 470 μM luciferin, 530 μM ATP, reconstituted) per well, followed by measuring light units using a luminometer (BMG labtech FLUOstar OPTIMA). One second total read time after a one second delay.Renilla luciferase activity is measured by adding 50 ul Renilla luciferase assay buffer (1.1M NaCl, 2.2 mM Na2EDTA, 0.22 M KxPO4 (pH 5.1), 0.44 mg/mL BSA, 1.3 mM NaN3, 1.43 uM coelenterazine, final pH adjusted to 5.0), per well, followed by measuring light units using a luminometer. One second total read time after one second delay. If Firefly luciferase signal is high, Renilla assay must be done an hour after the Firefly assay due to incomplete squelching of Firefly signal.
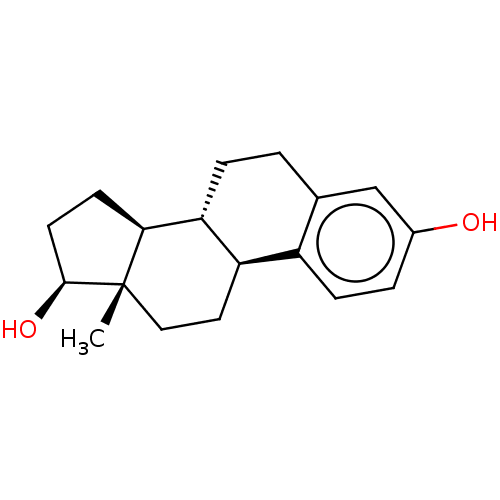 17beta-estradiol (E2) 17α-ethinylestradiol Ovocyclin US9561238, E2 [2,4,6,7-3H]-17beta-estradiol CHEMBL135 (1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-triene-5,14-diol US9034854, E2 CS336 [3H]]estradiol [2,4,6,7-3H]-E2 ESTRADIOL US9422324, E2 BDBM17292 [3H]-estradiol US9040509, E2 17 beta-Estradiol Estradiol-17 alpha
17beta-estradiol (E2) 17α-ethinylestradiol Ovocyclin US9561238, E2 [2,4,6,7-3H]-17beta-estradiol CHEMBL135 (1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-triene-5,14-diol US9034854, E2 CS336 [3H]]estradiol [2,4,6,7-3H]-E2 ESTRADIOL US9422324, E2 BDBM17292 [3H]-estradiol US9040509, E2 17 beta-Estradiol Estradiol-17 alpha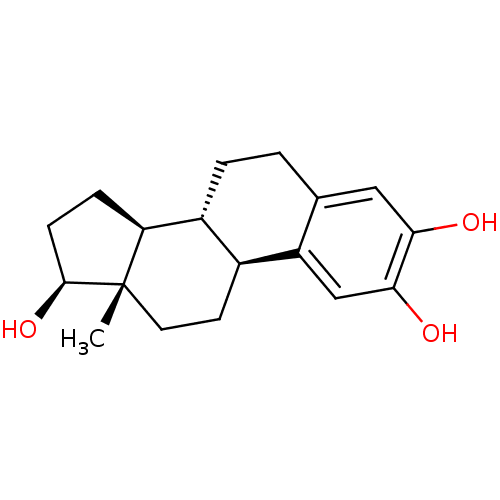 2-OH-estradiol 2-hydroxy-17beta-estradiol cid_247304 (17beta)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17-triol US10864248, Compound 2 2-OH-E2 BDBM50262140 CHEMBL467987 estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17beta-triol
2-OH-estradiol 2-hydroxy-17beta-estradiol cid_247304 (17beta)-estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17-triol US10864248, Compound 2 2-OH-E2 BDBM50262140 CHEMBL467987 estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17beta-triol US9878991, Compound E2 BDBM236119 US9365563, E2
US9878991, Compound E2 BDBM236119 US9365563, E2 BDBM286270 US11780853, Example E2 US9518060, Example E2 US11220518, Ex. No. E2
BDBM286270 US11780853, Example E2 US9518060, Example E2 US11220518, Ex. No. E2 US10584127, Compound E2-1.2 US10294230, Compound E2-1.2 BDBM388295 US11136328, Compound E2-1.2 US11752155, Compound E2-1.2B'
US10584127, Compound E2-1.2 US10294230, Compound E2-1.2 BDBM388295 US11136328, Compound E2-1.2 US11752155, Compound E2-1.2B' BDBM23952 ESTRADIOL
BDBM23952 ESTRADIOL BDBM25868 ESTRADIOL
BDBM25868 ESTRADIOL ESTRADIOL BDBM22422
ESTRADIOL BDBM22422 BDBM168073 US9073931, E2
BDBM168073 US9073931, E2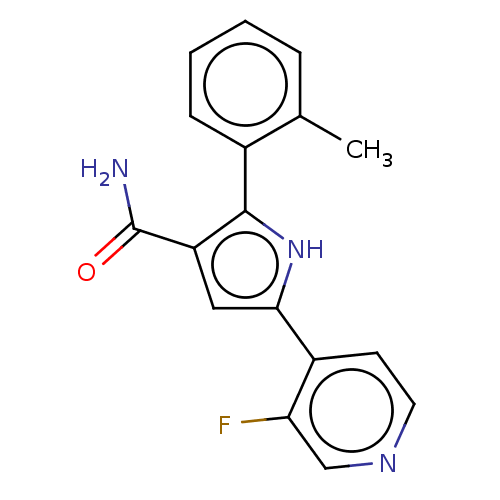 BDBM187245 US9670191, E2
BDBM187245 US9670191, E2 BDBM229618 US9340506, E2
BDBM229618 US9340506, E2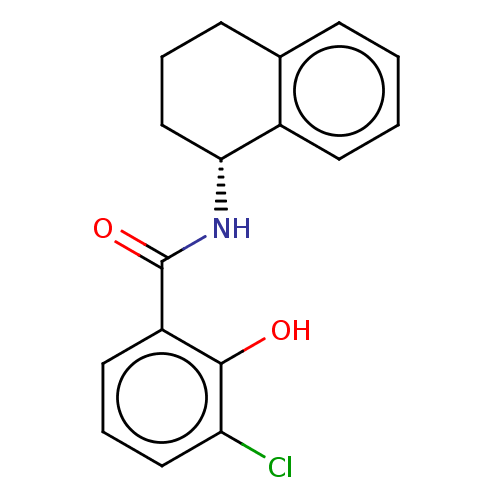 BDBM253797 US9459250, E2
BDBM253797 US9459250, E2 BDBM36490 E2-NH3+
BDBM36490 E2-NH3+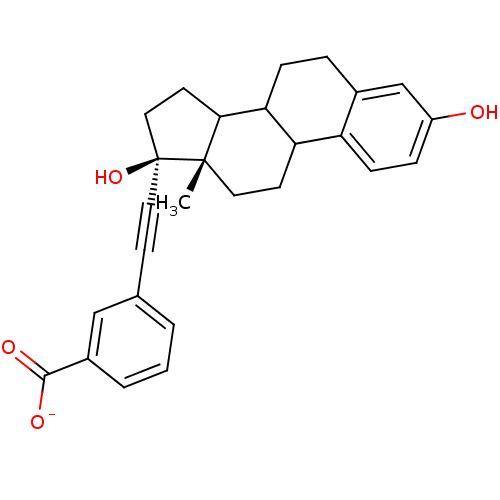 BDBM36491 E2-COO-
BDBM36491 E2-COO-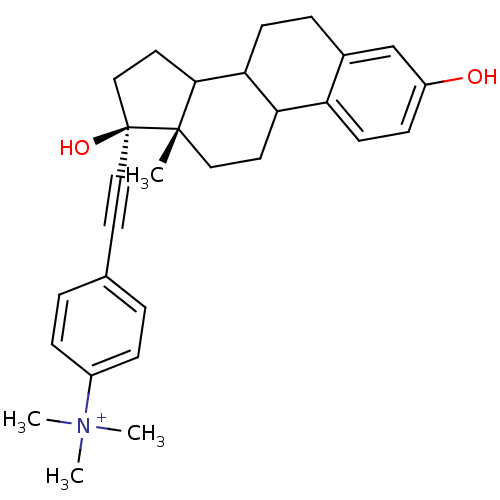 BDBM36492 E2-NMe3+
BDBM36492 E2-NMe3+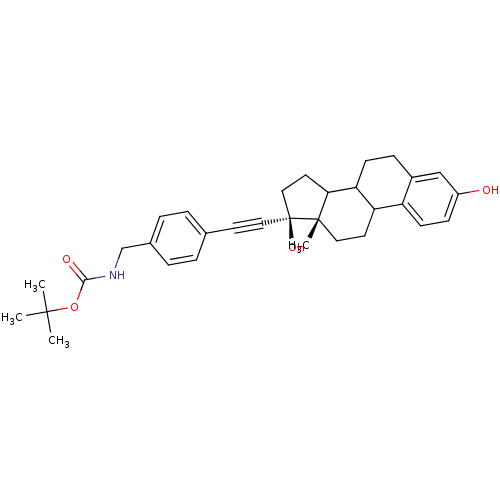 BDBM36493 E2-NB
BDBM36493 E2-NB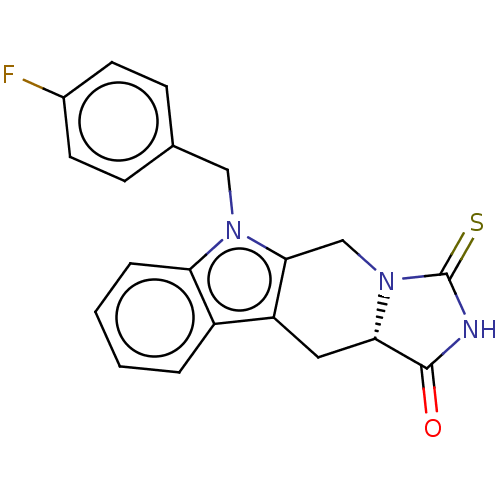 BDBM380539 US9926318, E2
BDBM380539 US9926318, E2 US8999981, E2 BDBM153932
US8999981, E2 BDBM153932 US9416126, E2 BDBM239259
US9416126, E2 BDBM239259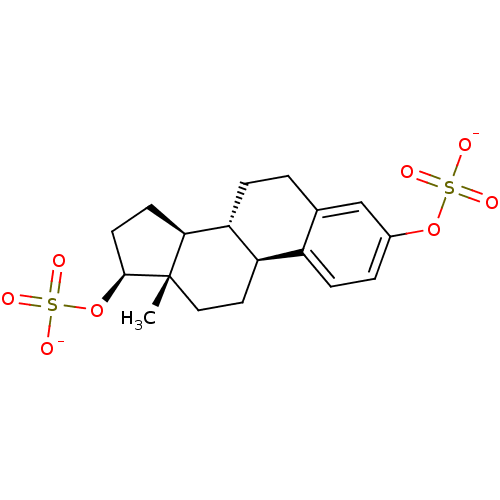 BDBM50270011 estradiol disulfate
BDBM50270011 estradiol disulfate BDBM519243 US11116757, No. E2
BDBM519243 US11116757, No. E2 BDBM567414 US11420968, Example E2
BDBM567414 US11420968, Example E2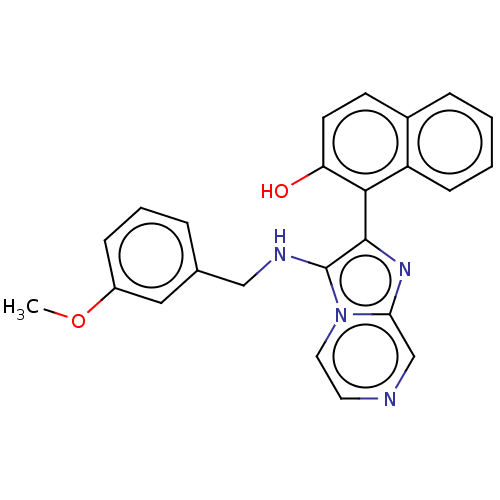 BDBM585372 US11530209, Compound E2
BDBM585372 US11530209, Compound E2 BDBM703001 US20240366813, Compound E2
BDBM703001 US20240366813, Compound E2 BDBM720105 US20250051321, Compound E2
BDBM720105 US20250051321, Compound E2 BDBM748526 US20250188030, Compound E2
BDBM748526 US20250188030, Compound E2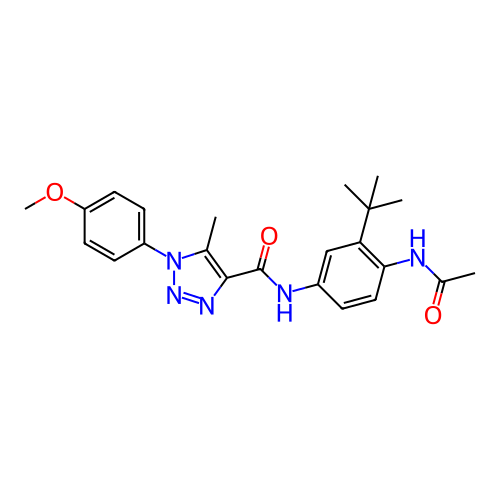 BDBM769613 US20250282736, Compound E2
BDBM769613 US20250282736, Compound E2 CHEMBL505589 BDBM50259922 Cyclotheonamide E2
CHEMBL505589 BDBM50259922 Cyclotheonamide E2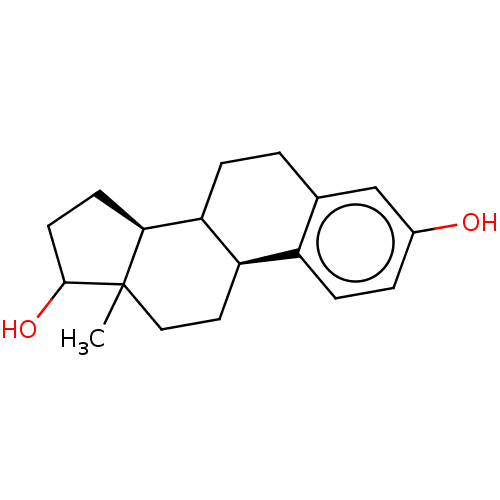 US10570077, Compound E2 BDBM435383
US10570077, Compound E2 BDBM435383 US11291655, No E2 BDBM546414
US11291655, No E2 BDBM546414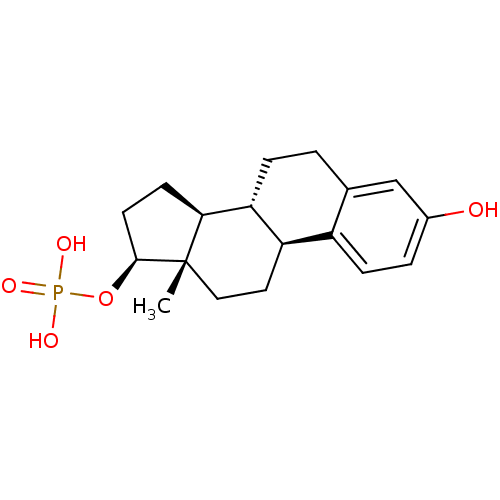 Estradiol phosphate BDBM50333647 CHEMBL1642763
Estradiol phosphate BDBM50333647 CHEMBL1642763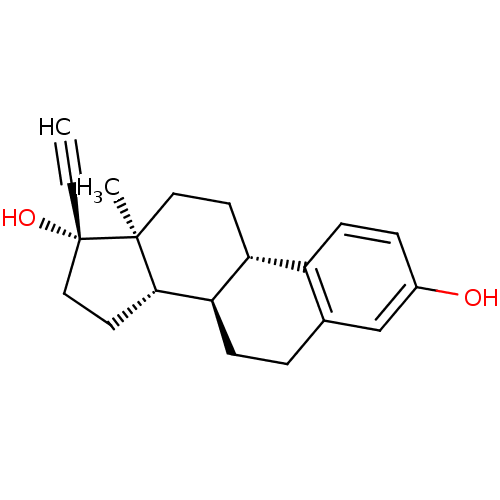 17-ethinyl-3,17-estradiol Ethinylestradiol CHEMBL691 17alpha-ethynylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol ETHINYL ESTRADIOL Ethynyl estradiol 17alpha-Ethinyl estradiol 17alpha-ethynylestradiol 17-ethinyl-3,17-oestradiol ethinyloestradiol 17-ethinylestradiol BDBM50187243
17-ethinyl-3,17-estradiol Ethinylestradiol CHEMBL691 17alpha-ethynylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17beta-diol ETHINYL ESTRADIOL Ethynyl estradiol 17alpha-Ethinyl estradiol 17alpha-ethynylestradiol 17-ethinyl-3,17-oestradiol ethinyloestradiol 17-ethinylestradiol BDBM50187243 BDBM361983 US10221182, Compound E2-1.5
BDBM361983 US10221182, Compound E2-1.5 BDBM361993 US10221182, Compound E2-1.4
BDBM361993 US10221182, Compound E2-1.4 BDBM362002 US10221182, Compound E2-1.7
BDBM362002 US10221182, Compound E2-1.7 BDBM362004 US10221182, Compound E2-1.16
BDBM362004 US10221182, Compound E2-1.16 BDBM433562 US10562878, Compound 170 E2
BDBM433562 US10562878, Compound 170 E2 BDBM433567 US10562878, Compound 172 E2
BDBM433567 US10562878, Compound 172 E2 BDBM433614 US10562878, Compound 134 E2
BDBM433614 US10562878, Compound 134 E2 BDBM433619 US10562878, Compound 165 E2
BDBM433619 US10562878, Compound 165 E2 BDBM433621 US10562878, Compound 166 E2
BDBM433621 US10562878, Compound 166 E2 BDBM433623 US10562878, Compound 173 E2
BDBM433623 US10562878, Compound 173 E2 BDBM433628 US10562878, Compound 152 E2
BDBM433628 US10562878, Compound 152 E2 BDBM433630 US10562878, Compound 153 E2
BDBM433630 US10562878, Compound 153 E2 BDBM433649 US10562878, Compound 184 E2
BDBM433649 US10562878, Compound 184 E2 BDBM433651 US10562878, Compound 187 E2
BDBM433651 US10562878, Compound 187 E2 BDBM433730 US10562878, Compound 205 E2
BDBM433730 US10562878, Compound 205 E2 BDBM433737 US10562878, Compound 147 E2
BDBM433737 US10562878, Compound 147 E2 BDBM433739 US10562878, Compound 148 E2
BDBM433739 US10562878, Compound 148 E2 BDBM433749 US10562878, Compound 164 E2
BDBM433749 US10562878, Compound 164 E2 BDBM433772 US10562878, Compound 140 E2
BDBM433772 US10562878, Compound 140 E2 BDBM433774 US10562878, Compound 139 E2
BDBM433774 US10562878, Compound 139 E2 BDBM433777 US10562878, Compound 20 E2
BDBM433777 US10562878, Compound 20 E2 BDBM433786 US10562878, Compound 155 E2
BDBM433786 US10562878, Compound 155 E2 BDBM433788 US10562878, Compound 136 E2
BDBM433788 US10562878, Compound 136 E2 BDBM433792 US10562878, Compound 21 E2
BDBM433792 US10562878, Compound 21 E2 BDBM433806 US10562878, Compound 22 E2
BDBM433806 US10562878, Compound 22 E2 BDBM433815 US10562878, Compound 154 E2
BDBM433815 US10562878, Compound 154 E2 BDBM433841 US10562878, Compound 234 E2
BDBM433841 US10562878, Compound 234 E2 BDBM433881 US10562878, Compound 142 E2
BDBM433881 US10562878, Compound 142 E2 BDBM433893 US10562878, Compound 145 E2
BDBM433893 US10562878, Compound 145 E2 BDBM433895 US10562878, Compound 146 E2
BDBM433895 US10562878, Compound 146 E2 BDBM433907 US10562878, Compound 161 E2
BDBM433907 US10562878, Compound 161 E2 BDBM433913 US10562878, Compound 143 E2
BDBM433913 US10562878, Compound 143 E2 BDBM433915 US10562878, Compound 144 E2
BDBM433915 US10562878, Compound 144 E2 BDBM433917 US10562878, Compound 159 E2
BDBM433917 US10562878, Compound 159 E2 BDBM433919 US10562878, Compound 160 E2
BDBM433919 US10562878, Compound 160 E2 BDBM595470 US11591313, Compound 038-E2
BDBM595470 US11591313, Compound 038-E2 BDBM595473 US11591313, Compound 039-E2
BDBM595473 US11591313, Compound 039-E2 BDBM617052 US11752155, Compound E2-22.2B'
BDBM617052 US11752155, Compound E2-22.2B' BDBM617053 US11752155, Compound E2-22.4B'
BDBM617053 US11752155, Compound E2-22.4B' BDBM617054 US11752155, Compound E2-22.6B'
BDBM617054 US11752155, Compound E2-22.6B'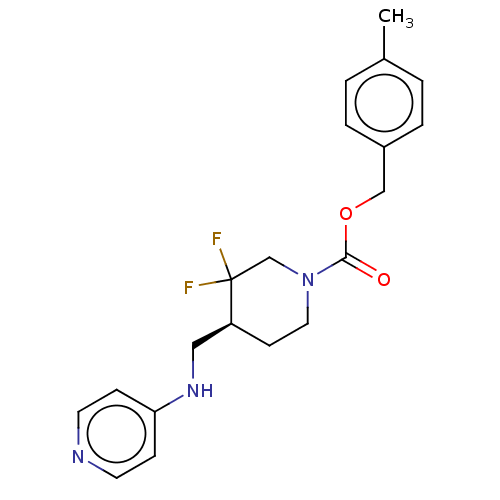 BDBM617055 US11752155, Compound E2-38.2B'
BDBM617055 US11752155, Compound E2-38.2B' BDBM701606 US12128028, Example 2 (E2)
BDBM701606 US12128028, Example 2 (E2) US10221182, Compound E2-1.3 BDBM361990
US10221182, Compound E2-1.3 BDBM361990 US10221182, Compound E2-1.6 BDBM362000
US10221182, Compound E2-1.6 BDBM362000 US10562878, Compound 133 E2 BDBM433612
US10562878, Compound 133 E2 BDBM433612 US10562878, Compound 138 E2 BDBM433790
US10562878, Compound 138 E2 BDBM433790 US10562878, Compound 141 E2 BDBM433879
US10562878, Compound 141 E2 BDBM433879 US10562878, Compound 156 E2 BDBM433802
US10562878, Compound 156 E2 BDBM433802 US10562878, Compound 157 E2 BDBM433889
US10562878, Compound 157 E2 BDBM433889 US10562878, Compound 158 E2 BDBM433891
US10562878, Compound 158 E2 BDBM433891 US10562878, Compound 163 E2 BDBM433745
US10562878, Compound 163 E2 BDBM433745 US10562878, Compound 185 E2 BDBM433658
US10562878, Compound 185 E2 BDBM433658 US10562878, Compound 188 E2 BDBM433667
US10562878, Compound 188 E2 BDBM433667 US10562878, Compound 195 E2 BDBM433750
US10562878, Compound 195 E2 BDBM433750 US10562878, Compound 206 E2 BDBM433735
US10562878, Compound 206 E2 BDBM433735 US10562878, Compound 231 E2 BDBM433821
US10562878, Compound 231 E2 BDBM433821 US10562878, Compound 60 E2 BDBM433828
US10562878, Compound 60 E2 BDBM433828 US10562878, Compound 61 E2 BDBM433832
US10562878, Compound 61 E2 BDBM433832 US10562878, Compound 62 E2 BDBM433837
US10562878, Compound 62 E2 BDBM433837 US10562878, Compound 64 E2 BDBM433844
US10562878, Compound 64 E2 BDBM433844 US11591313, Compound 040-E2 BDBM595475
US11591313, Compound 040-E2 BDBM595475 US20240246927, Patent ID E2 BDBM686266
US20240246927, Patent ID E2 BDBM686266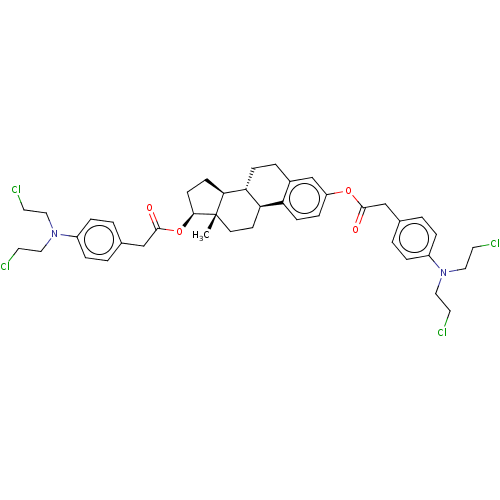 BDBM50016934 CHEBI:82520 ESTRADIOL MUSTARD
BDBM50016934 CHEBI:82520 ESTRADIOL MUSTARD BDBM50423528 6-Dehydro-Estradiol CHEMBL223967
BDBM50423528 6-Dehydro-Estradiol CHEMBL223967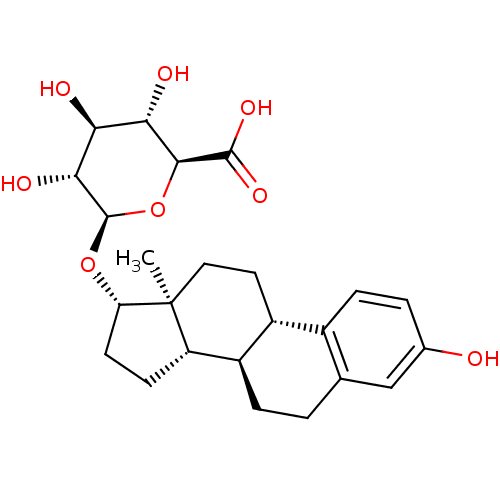 17beta-Estradiol-17-(beta-D-glucuronide) CHEMBL1697724 estradiol 17b glucuronide BDBM50344959 E17β-glucuronide
17beta-Estradiol-17-(beta-D-glucuronide) CHEMBL1697724 estradiol 17b glucuronide BDBM50344959 E17β-glucuronide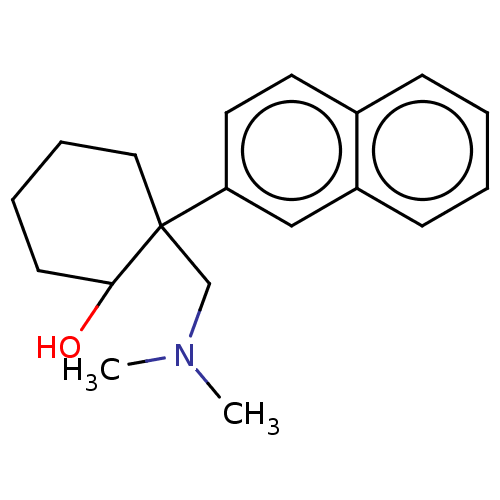 US10562878, Compound 163 E2 US10562878, Compound 163 E1 US10562878, Compound 148 E1 US10562878, Compound 147 E2 US10562878, Compound 147 E1 US10562878, Compound 148 E2 US10562878, Compound 164 E1 US10562878, Compound 164 E2 BDBM433736
US10562878, Compound 163 E2 US10562878, Compound 163 E1 US10562878, Compound 148 E1 US10562878, Compound 147 E2 US10562878, Compound 147 E1 US10562878, Compound 148 E2 US10562878, Compound 164 E1 US10562878, Compound 164 E2 BDBM433736 US10562878, Compound 144 E1 US10562878, Compound 159 E1 US10562878, Compound 159 E2 US10562878, Compound 143 E2 BDBM433912 US10562878, Compound 143 E1 US10562878, Compound 144 E2
US10562878, Compound 144 E1 US10562878, Compound 159 E1 US10562878, Compound 159 E2 US10562878, Compound 143 E2 BDBM433912 US10562878, Compound 143 E1 US10562878, Compound 144 E2 US10562878, Compound 153 E1 BDBM433613 US10562878, Compound 134 E2 US10562878, Compound 152 E2 US10562878, Compound 134 E1 US10562878, Compound 152 E1 US10562878, Compound 153 E2
US10562878, Compound 153 E1 BDBM433613 US10562878, Compound 134 E2 US10562878, Compound 152 E2 US10562878, Compound 134 E1 US10562878, Compound 152 E1 US10562878, Compound 153 E2 BDBM433633 US10562878, Compound cis 121 E2
BDBM433633 US10562878, Compound cis 121 E2 BDBM433708 US10562878, Compound trans 124 E2
BDBM433708 US10562878, Compound trans 124 E2 BDBM433717 US10562878, Compound trans 125 E2
BDBM433717 US10562878, Compound trans 125 E2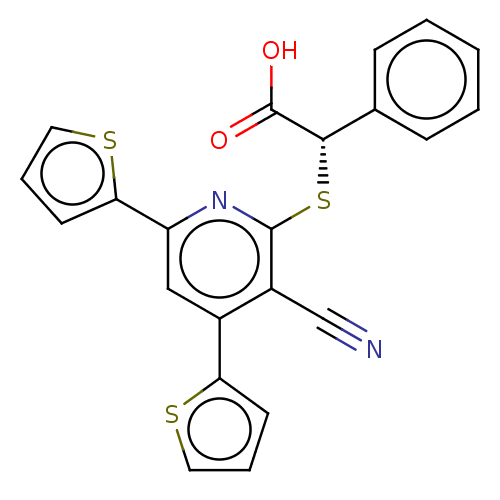 BDBM559876 US11375716, Formula Ia-iii-e2
BDBM559876 US11375716, Formula Ia-iii-e2 BDBM559878 US11375716, Formula Ia-xiv-e2
BDBM559878 US11375716, Formula Ia-xiv-e2 US10562878, Compound trans 121 E2 BDBM433635
US10562878, Compound trans 121 E2 BDBM433635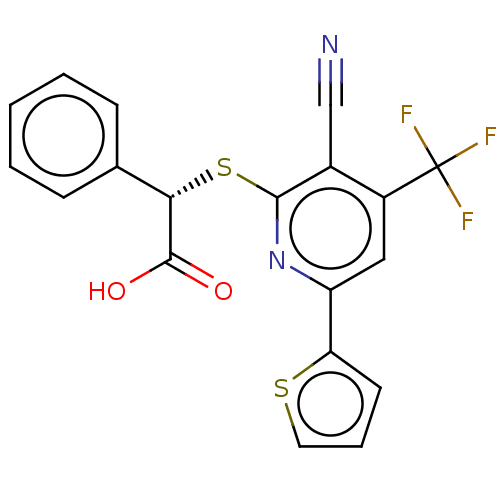 US11375716, Formula Ia-ii-e2 BDBM559874
US11375716, Formula Ia-ii-e2 BDBM559874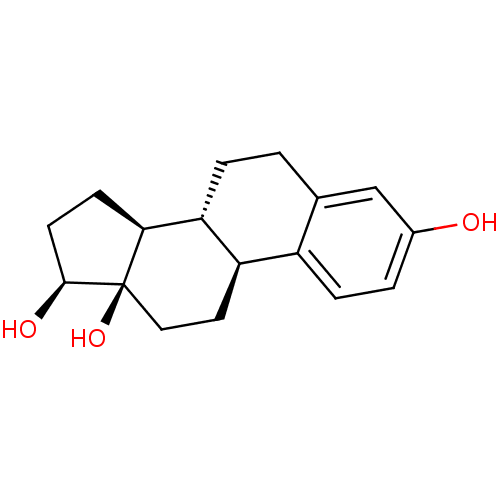 13-beta-hydroxyestradiol Estradiol BDBM50250613 CHEMBL499812
13-beta-hydroxyestradiol Estradiol BDBM50250613 CHEMBL499812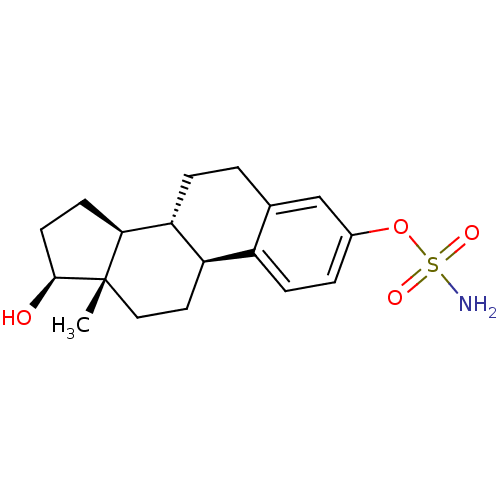 BDBM50200937 CHEMBL219321 estradiol 3-O-sulfamate
BDBM50200937 CHEMBL219321 estradiol 3-O-sulfamate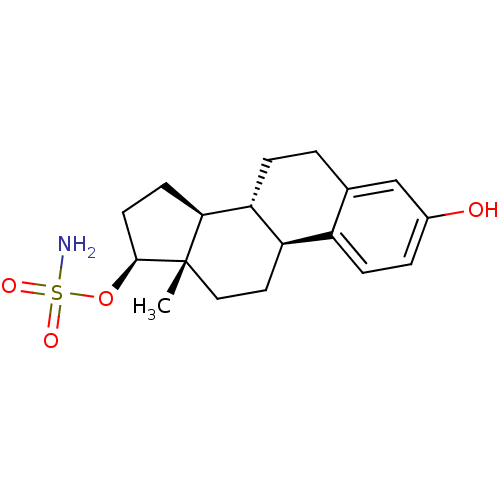 BDBM50200938 CHEMBL220493 estradiol 17-O-sulfamate
BDBM50200938 CHEMBL220493 estradiol 17-O-sulfamate (E)-N-(2-aminophenyl)-3-(2-cinnamylthiazol-4-yl)acrylamide BDBM375766 US10301323, Compound E2 US9908899, Compound E2
(E)-N-(2-aminophenyl)-3-(2-cinnamylthiazol-4-yl)acrylamide BDBM375766 US10301323, Compound E2 US9908899, Compound E2 BDBM433771 US10562878, Compound 140 E2 US10562878, Compound 139 E1 US10562878, Compound 140 E1 US10562878, Compound 139 E2
BDBM433771 US10562878, Compound 140 E2 US10562878, Compound 139 E1 US10562878, Compound 140 E1 US10562878, Compound 139 E2 BDBM433892 US10562878, Compound 146 E1 US10562878, Compound 145 E1 US10562878, Compound 146 E2 US10562878, Compound 145 E2
BDBM433892 US10562878, Compound 146 E1 US10562878, Compound 145 E1 US10562878, Compound 146 E2 US10562878, Compound 145 E2 US10562878, Compound 141 E1 US10562878, Compound 142 E2 US10562878, Compound 141 E2 BDBM433878 US10562878, Compound 142 E1
US10562878, Compound 141 E1 US10562878, Compound 142 E2 US10562878, Compound 141 E2 BDBM433878 US10562878, Compound 142 E1 US10562878, Compound 156 E1 BDBM433785 US10562878, Compound 155 E1 US10562878, Compound 156 E2 US10562878, Compound 155 E2
US10562878, Compound 156 E1 BDBM433785 US10562878, Compound 155 E1 US10562878, Compound 156 E2 US10562878, Compound 155 E2 US10562878, Compound 157 E2 US10562878, Compound 157 E1 US10562878, Compound 158 E2 US10562878, Compound 158 E1 BDBM433888
US10562878, Compound 157 E2 US10562878, Compound 157 E1 US10562878, Compound 158 E2 US10562878, Compound 158 E1 BDBM433888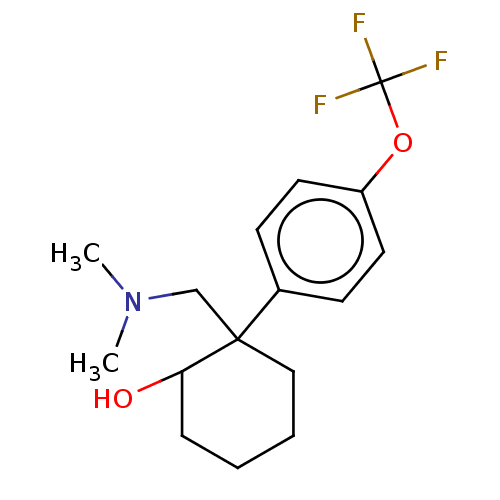 US10562878, Compound 162 E1 BDBM433905 US10562878, Compound 161 E1 US10562878, Compound 161 E2 US10562878, Compound 162 E2
US10562878, Compound 162 E1 BDBM433905 US10562878, Compound 161 E1 US10562878, Compound 161 E2 US10562878, Compound 162 E2 US10562878, Compound 166 E1 BDBM433618 US10562878, Compound 165 E1 US10562878, Compound 166 E2 US10562878, Compound 165 E2
US10562878, Compound 166 E1 BDBM433618 US10562878, Compound 165 E1 US10562878, Compound 166 E2 US10562878, Compound 165 E2 US10562878, Compound 185 E1 US10562878, Compound 184 E1 US10562878, Compound 185 E2 US10562878, Compound 184 E2 BDBM433648
US10562878, Compound 185 E1 US10562878, Compound 184 E1 US10562878, Compound 185 E2 US10562878, Compound 184 E2 BDBM433648 BDBM218873 US9303033, E2, Table 6A, Compound 12
BDBM218873 US9303033, E2, Table 6A, Compound 12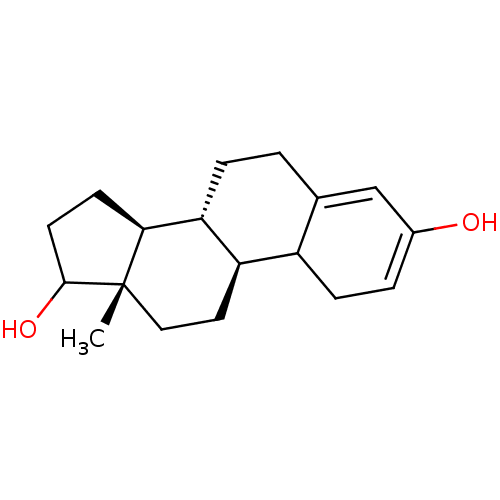 BDBM235683 US9688816, A Estradiol-17β (3)
BDBM235683 US9688816, A Estradiol-17β (3) BDBM50423526 CHEMBL121458 17Beta-Dihydroequillin 7-Dehydro-Estradiol
BDBM50423526 CHEMBL121458 17Beta-Dihydroequillin 7-Dehydro-Estradiol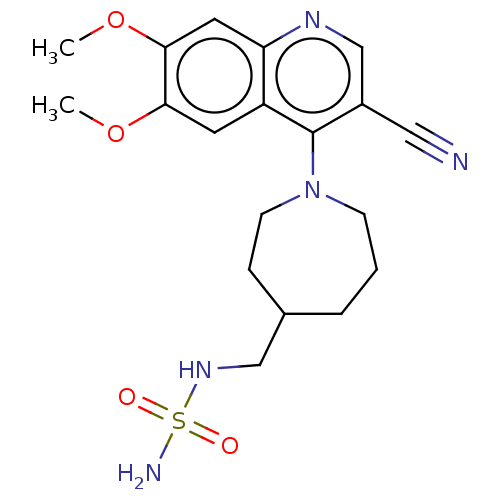 US11591313, Compound 039 BDBM595471 US11591313, Compound 039-E2
US11591313, Compound 039 BDBM595471 US11591313, Compound 039-E2 US10562878, Compound 202 US10562878, Compound 188 E1 BDBM433650 US10562878, Compound 187 E2 US10562878, Compound 187 E1 US10562878, Compound 188 E2
US10562878, Compound 202 US10562878, Compound 188 E1 BDBM433650 US10562878, Compound 187 E2 US10562878, Compound 187 E1 US10562878, Compound 188 E2 US10562878, Compound trans 121 E1 US10562878, Compound trans 121 E2 BDBM433632 US10562878, Compound cis 121 E2 US10562878, Compound cis 121 E1
US10562878, Compound trans 121 E1 US10562878, Compound trans 121 E2 BDBM433632 US10562878, Compound cis 121 E2 US10562878, Compound cis 121 E1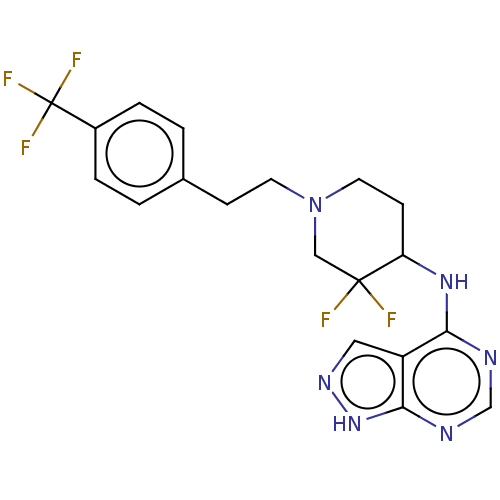 BDBM361982 US10221182, Compound E2-1.5 US10221182, Compound E1-1.5
BDBM361982 US10221182, Compound E2-1.5 US10221182, Compound E1-1.5 BDBM361992 US10221182, Compound E2-1.4 US10221182, Compound E1-1.4
BDBM361992 US10221182, Compound E2-1.4 US10221182, Compound E1-1.4 BDBM362003 US10221182, Compound E1-1.16 US10221182, Compound E2-1.16
BDBM362003 US10221182, Compound E1-1.16 US10221182, Compound E2-1.16 BDBM433561 US10562878, Compound 170 E1 US10562878, Compound 170 E2
BDBM433561 US10562878, Compound 170 E1 US10562878, Compound 170 E2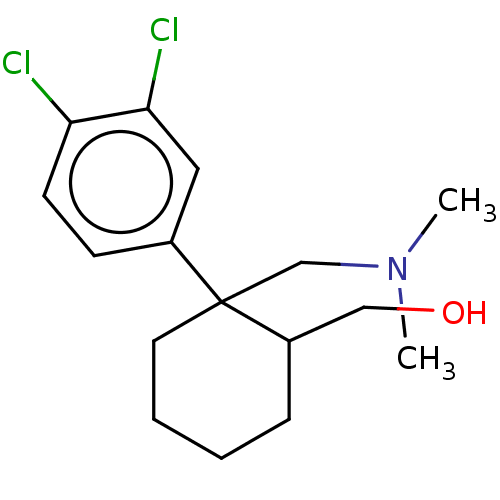 BDBM433566 US10562878, Compound 172 E2 US10562878, Compound 172 E1
BDBM433566 US10562878, Compound 172 E2 US10562878, Compound 172 E1 BDBM433787 US10562878, Compound 136 E1 US10562878, Compound 136 E2
BDBM433787 US10562878, Compound 136 E1 US10562878, Compound 136 E2 BDBM433814 US10562878, Compound 154 E2 US10562878, Compound 154 E1
BDBM433814 US10562878, Compound 154 E2 US10562878, Compound 154 E1 BDBM433820 US10562878, Compound 231 E2 US10562878, Compound 231 E1
BDBM433820 US10562878, Compound 231 E2 US10562878, Compound 231 E1 BDBM433830 US10562878, Compound 59 E2 US10562878, Compound 59 E1
BDBM433830 US10562878, Compound 59 E2 US10562878, Compound 59 E1 BDBM433840 US10562878, Compound 234 E2 US10562878, Compound 234 E1
BDBM433840 US10562878, Compound 234 E2 US10562878, Compound 234 E1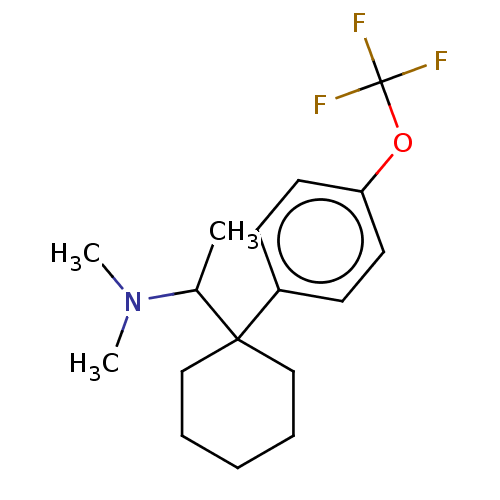 BDBM433842 US10562878, Compound 63 E2 US10562878, Compound 63 E1
BDBM433842 US10562878, Compound 63 E2 US10562878, Compound 63 E1 BDBM433918 US10562878, Compound 160 E2 US10562878, Compound 160 E1
BDBM433918 US10562878, Compound 160 E2 US10562878, Compound 160 E1 US10221182, Compound E1-1.3 US10221182, Compound E2-1.3 BDBM361989
US10221182, Compound E1-1.3 US10221182, Compound E2-1.3 BDBM361989 US10221182, Compound E2-1.6 BDBM361999 US10221182, Compound E1-1.6
US10221182, Compound E2-1.6 BDBM361999 US10221182, Compound E1-1.6 US10221182, Compound E2-1.7 US10221182, Compound E1-1.7 BDBM362001
US10221182, Compound E2-1.7 US10221182, Compound E1-1.7 BDBM362001 US10562878, Compound 133 E2 BDBM433611 US10562878, Compound 133 E1
US10562878, Compound 133 E2 BDBM433611 US10562878, Compound 133 E1 US10562878, Compound 138 E2 US10562878, Compound 138 E1 BDBM433789
US10562878, Compound 138 E2 US10562878, Compound 138 E1 BDBM433789 US10562878, Compound 169 E1 US10562878, Compound 169 E2 BDBM433625
US10562878, Compound 169 E1 US10562878, Compound 169 E2 BDBM433625 US10562878, Compound 193 E1 US10562878, Compound 193 E2 BDBM433793
US10562878, Compound 193 E1 US10562878, Compound 193 E2 BDBM433793 US10562878, Compound 205 E1 US10562878, Compound 205 E2 BDBM433729
US10562878, Compound 205 E1 US10562878, Compound 205 E2 BDBM433729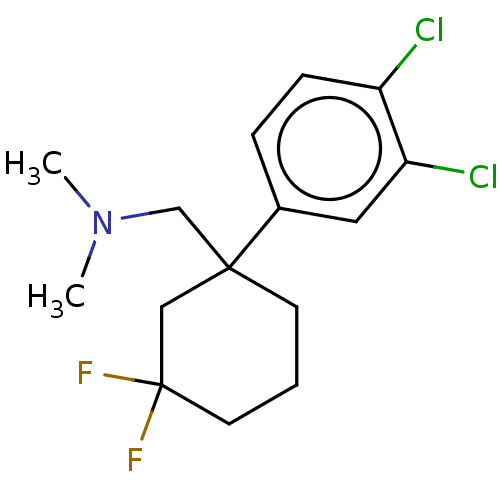 US10562878, Compound 206 E2 US10562878, Compound 206 E1 BDBM433734
US10562878, Compound 206 E2 US10562878, Compound 206 E1 BDBM433734 US10562878, Compound 60 E2 US10562878, Compound 60 E1 BDBM433827
US10562878, Compound 60 E2 US10562878, Compound 60 E1 BDBM433827 US10562878, Compound 61 E2 US10562878, Compound 61 E1 BDBM433829
US10562878, Compound 61 E2 US10562878, Compound 61 E1 BDBM433829 US10562878, Compound 62 E1 US10562878, Compound 62 E2 BDBM433836
US10562878, Compound 62 E1 US10562878, Compound 62 E2 BDBM433836 US10562878, Compound 64 E2 US10562878, Compound 64 E1 BDBM433843
US10562878, Compound 64 E2 US10562878, Compound 64 E1 BDBM433843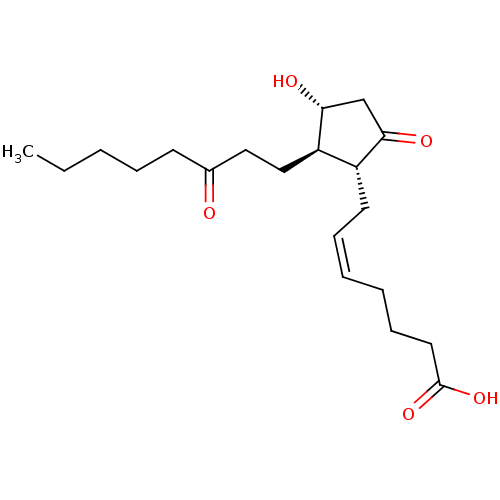 BDBM82093 PGE2 13,14-dihydro CAS_363-23-5 13,14-DIHYDRO-15-KETO PROSTAGLANDIN E2 13,14-dihydro-15-oxo-prostaglandin E2 PGE2, 13,14-dihydro15-oxo
BDBM82093 PGE2 13,14-dihydro CAS_363-23-5 13,14-DIHYDRO-15-KETO PROSTAGLANDIN E2 13,14-dihydro-15-oxo-prostaglandin E2 PGE2, 13,14-dihydro15-oxo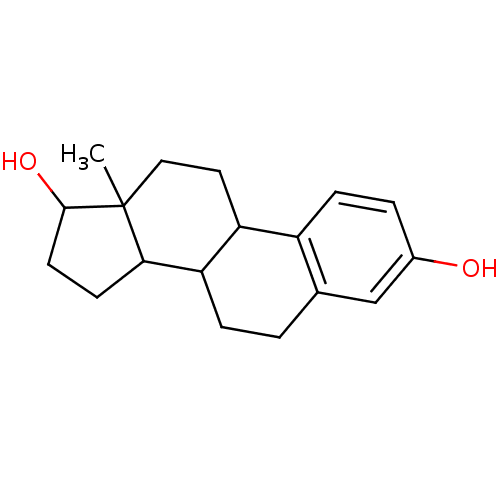 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol(17beta-estradiol) (estradiol)13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol([6,7-3H]-estradiol) 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol(estradiol) CHEMBL135 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol(17alpha-estradiol) 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol 17beta-Estradiol 1,5-Dimethyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-pyrazol-3-one BDBM50005414 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol (estradiol) ESTRADIOL 15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.02,7.011,15]heptadeca-2,4,6-triene-5,14-diol Estradiol13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol( Estradiol)
13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol(17beta-estradiol) (estradiol)13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol([6,7-3H]-estradiol) 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol(estradiol) CHEMBL135 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol(17alpha-estradiol) 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol 17beta-Estradiol 1,5-Dimethyl-2-phenyl-1,2-dihydro-pyrazol-3-one BDBM50005414 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol (estradiol) ESTRADIOL 15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.02,7.011,15]heptadeca-2,4,6-triene-5,14-diol Estradiol13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol 13-Methyl-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol( Estradiol) BDBM50309556 Per-6-(estradiol-17-ethynylbenzylamino)-6-deoxy-betacyclodextrin CHEMBL604989
BDBM50309556 Per-6-(estradiol-17-ethynylbenzylamino)-6-deoxy-betacyclodextrin CHEMBL604989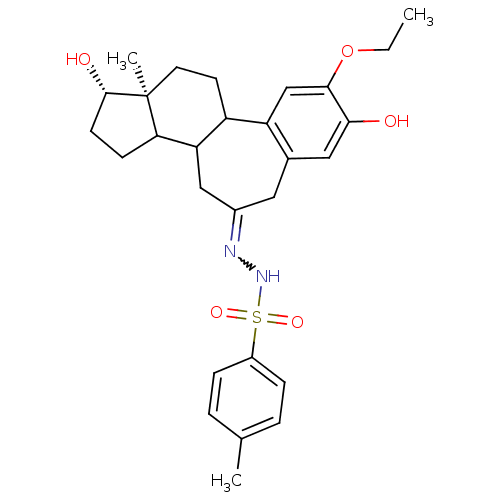 CHEMBL78389 B-Homo-2-ethoxy-3,17beta-estradiol-7-tosylhydrazone BDBM50089345
CHEMBL78389 B-Homo-2-ethoxy-3,17beta-estradiol-7-tosylhydrazone BDBM50089345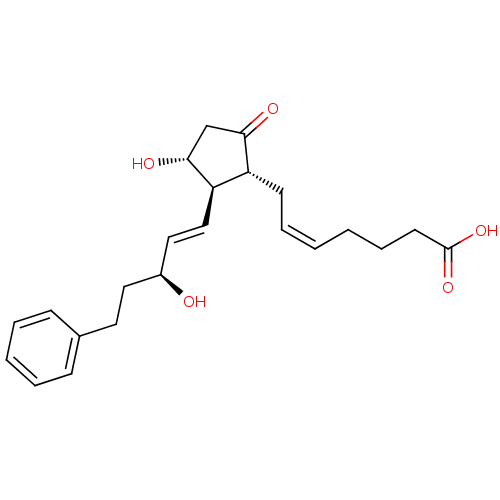 17-PHENYL TRINOR PROSTAGLANDIN E2 PGE2,17-Phenyl BDBM82094 CAS_38315-43-4
17-PHENYL TRINOR PROSTAGLANDIN E2 PGE2,17-Phenyl BDBM82094 CAS_38315-43-4 BDBM433775 US10562878, Compound 20 US10562878, Compound 20 E2 US10562878, Compound 20 E1
BDBM433775 US10562878, Compound 20 US10562878, Compound 20 E2 US10562878, Compound 20 E1 BDBM433784 US10562878, Compound 22 US10562878, Compound 22 E1 US10562878, Compound 22 E2
BDBM433784 US10562878, Compound 22 US10562878, Compound 22 E1 US10562878, Compound 22 E2 US10562878, Compound 173 E1 US10562878, Compound 173 US10562878, Compound 173 E2 BDBM433615
US10562878, Compound 173 E1 US10562878, Compound 173 US10562878, Compound 173 E2 BDBM433615 US10562878, Compound 21 E1 BDBM433778 US10562878, Compound 21 US10562878, Compound 21 E2
US10562878, Compound 21 E1 BDBM433778 US10562878, Compound 21 US10562878, Compound 21 E2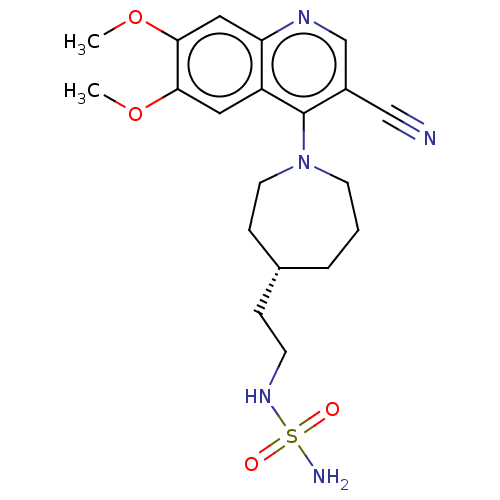 US11591313, Compound 038-E1 BDBM595468 US11591313, Compound 038 US11591313, Compound 038-E2
US11591313, Compound 038-E1 BDBM595468 US11591313, Compound 038 US11591313, Compound 038-E2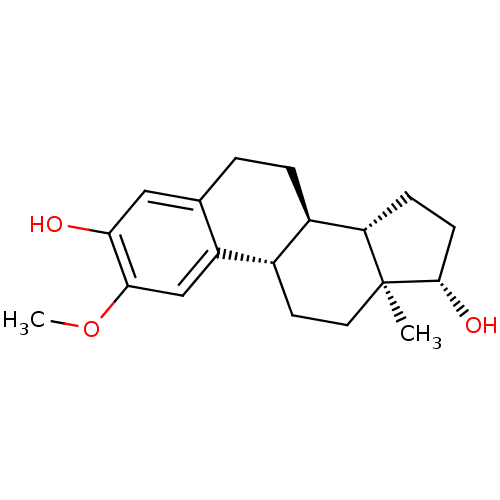 2-methoxy-17beta-estradiol CHEMBL299613 BDBM50060957 Panzem 2-Hydroxyestradol 2-methyl ether
2-methoxy-17beta-estradiol CHEMBL299613 BDBM50060957 Panzem 2-Hydroxyestradol 2-methyl ether BDBM50337905 CHEMBL1684051 US10562878, Compound 19 E2 1-(1-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine
BDBM50337905 CHEMBL1684051 US10562878, Compound 19 E2 1-(1-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine CHEMBL1684049 BDBM50337903 1-(1-(naphthalen-1-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine US10562878, Compound 16 E2
CHEMBL1684049 BDBM50337903 1-(1-(naphthalen-1-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine US10562878, Compound 16 E2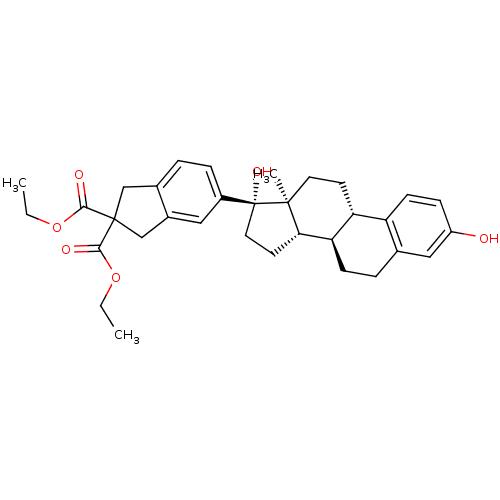 BDBM50318292 CHEMBL1096975 17alpha-[2,2-Bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-5-yl]-estradiol
BDBM50318292 CHEMBL1096975 17alpha-[2,2-Bis(ethoxycarbonyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-5-yl]-estradiol BDBM50337914 CHEMBL1684043 US10562878, Compound 17 E2 (+/-)-1-(1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclohexyl)propan-1-amine
BDBM50337914 CHEMBL1684043 US10562878, Compound 17 E2 (+/-)-1-(1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclohexyl)propan-1-amine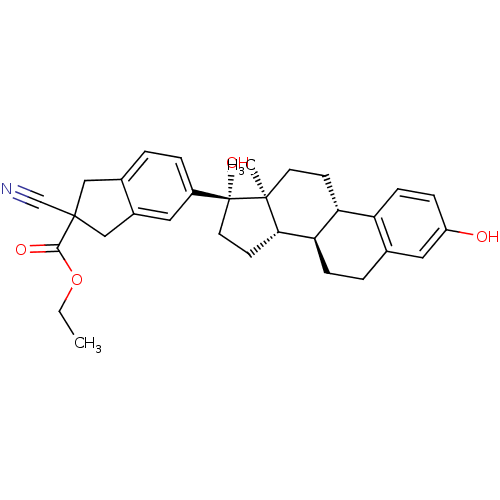 CHEMBL1098710 BDBM50318293 17alpha-[2-Cyano-2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-5-yl]-estradiol
CHEMBL1098710 BDBM50318293 17alpha-[2-Cyano-2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-inden-5-yl]-estradiol Carboxylic acid deriv. E2 BDBM11794 2-{[(3-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl][(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]amino}propanoic acid
Carboxylic acid deriv. E2 BDBM11794 2-{[(3-chlorophenyl)carbamoyl][(2-chlorophenyl)methyl]amino}propanoic acid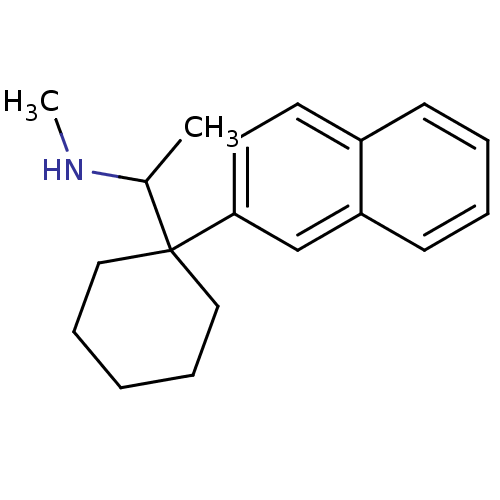 N-methyl-1-(1-(naphthalen-2-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine BDBM50337912 US10562878, Compound 58 E2 CHEMBL1684056
N-methyl-1-(1-(naphthalen-2-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine BDBM50337912 US10562878, Compound 58 E2 CHEMBL1684056 US10562878, Compound cis 124 BDBM433706 US10562878, Compound trans 124 E1 US10562878, Compound trans 124 E2
US10562878, Compound cis 124 BDBM433706 US10562878, Compound trans 124 E1 US10562878, Compound trans 124 E2 US10562878, Compound cis 125 BDBM433715 US10562878, Compound trans 125 E1 US10562878, Compound trans 125 E2
US10562878, Compound cis 125 BDBM433715 US10562878, Compound trans 125 E1 US10562878, Compound trans 125 E2 CHEMBL605828 Per-6-(estradiol-17-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl))-6-deoxy-beta cyclodextrin BDBM50309553
CHEMBL605828 Per-6-(estradiol-17-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl))-6-deoxy-beta cyclodextrin BDBM50309553 Mono-6-(17-estradiol-17-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl))-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin CHEMBL605714 BDBM50309552
Mono-6-(17-estradiol-17-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl))-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin CHEMBL605714 BDBM50309552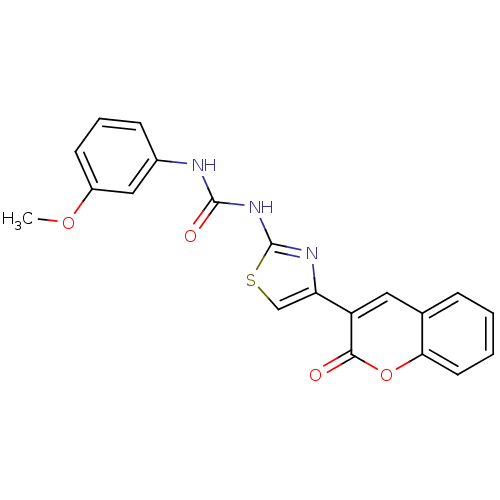 BDBM152438 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)urea (e2)
BDBM152438 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-(2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)thiazol-2-yl)urea (e2)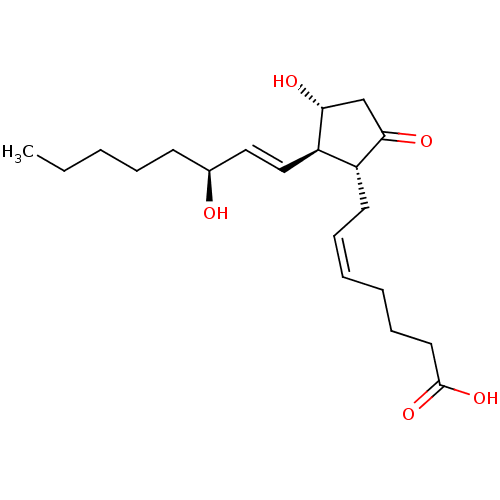 BDBM35847 [3H]Prostaglandin E2 PGE2 CHEMBL548 DINOPROSTONE (15S)-prostaglandin E2 prostaglandin E2 [3H]PGE2 (E,Z)-(1R,2R,3R)-7-(3-Hydroxy-2-((3S)-(3-hydroxy-1-octenyl))-5-oxocyclopentyl)-5-heptenoic acid [3H]Dinoprostone (5Z,11alpha,13E,15S)-11,15-dihydroxy-9-oxoprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid (5Z,13E,15S)-11alpha,15-dihydroxy-9-oxoprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid
BDBM35847 [3H]Prostaglandin E2 PGE2 CHEMBL548 DINOPROSTONE (15S)-prostaglandin E2 prostaglandin E2 [3H]PGE2 (E,Z)-(1R,2R,3R)-7-(3-Hydroxy-2-((3S)-(3-hydroxy-1-octenyl))-5-oxocyclopentyl)-5-heptenoic acid [3H]Dinoprostone (5Z,11alpha,13E,15S)-11,15-dihydroxy-9-oxoprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid (5Z,13E,15S)-11alpha,15-dihydroxy-9-oxoprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid BDBM387142 US9938276, E2 2-((3aR, 7aR)-6-(2- propylbenzoyl)octahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3- c]pyridin-1-yl)isonicotinonitrile
BDBM387142 US9938276, E2 2-((3aR, 7aR)-6-(2- propylbenzoyl)octahydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3- c]pyridin-1-yl)isonicotinonitrile US10457675, Example 88 US10065948, 88 BDBM272152 E2-(abs)-N-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indene- 1-carboxamide
US10457675, Example 88 US10065948, 88 BDBM272152 E2-(abs)-N-hydroxy-1-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-indene- 1-carboxamide US10562878, Compound 2 E2 (+/-)-1-(1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine CHEMBL1684042 1-(1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine BDBM50337909
US10562878, Compound 2 E2 (+/-)-1-(1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine CHEMBL1684042 1-(1-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine BDBM50337909 US11447505, Example E2 5-methyl-4-(1-piperidyl)- 3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine BDBM572413
US11447505, Example E2 5-methyl-4-(1-piperidyl)- 3-(1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H- pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine BDBM572413 (+/-)-1-(1-(naphthalen-2-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine 1-(1-(naphthalen-2-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine BDBM50337904 CHEMBL1684050 US10562878, Compound 13 E2
(+/-)-1-(1-(naphthalen-2-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine 1-(1-(naphthalen-2-yl)cyclohexyl)ethanamine BDBM50337904 CHEMBL1684050 US10562878, Compound 13 E2 US10065948, 32 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-1- phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-indazole-5-carboxamide BDBM272096
US10065948, 32 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-1- phenyl-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-indazole-5-carboxamide BDBM272096 1-[4-(3-fluorophenoxy)-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-2-yl]-4-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)piperidin-4-ol (E2) US9920053, Example 2 BDBM376872
1-[4-(3-fluorophenoxy)-6-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidin-2-yl]-4-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)piperidin-4-ol (E2) US9920053, Example 2 BDBM376872 BDBM272098 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(2- fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2H- indazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 34
BDBM272098 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(2- fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-2H- indazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 34 US10065948, 38 BDBM272102 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-1- (o-tolyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-indazole-5- carboxamide
US10065948, 38 BDBM272102 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-1- (o-tolyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-indazole-5- carboxamide US10065948, 85 E2-(abs)-6-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-2- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2,4,5,6,7,8- hexahydrocyclohepta[c]pyrazole-6-carboxamide BDBM272149
US10065948, 85 E2-(abs)-6-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-2- (2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2,4,5,6,7,8- hexahydrocyclohepta[c]pyrazole-6-carboxamide BDBM272149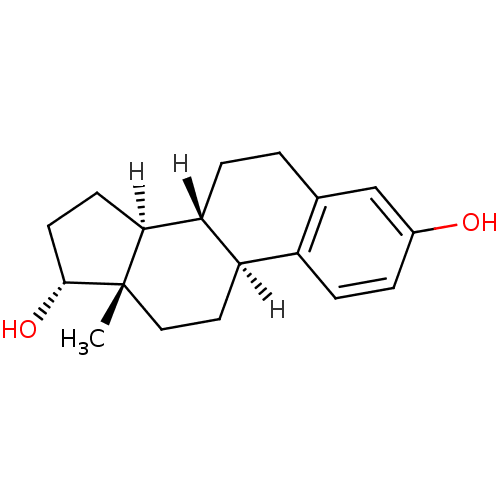 BDBM20624 (1S,10R,11S,14R,15S)-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-triene-5,14-diol 17alpha-estradiol
BDBM20624 (1S,10R,11S,14R,15S)-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2(7),3,5-triene-5,14-diol 17alpha-estradiol Compound 11 16beta-alkyl-E2 BDBM17294 (13S,14S,15S)-15-methyl-13-nonyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-triene-5,14-diol
Compound 11 16beta-alkyl-E2 BDBM17294 (13S,14S,15S)-15-methyl-13-nonyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-triene-5,14-diol BDBM272129 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(3- fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 65
BDBM272129 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(3- fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 65 BDBM751305 US20250195530, Example E2 8-(2-chloro-4- (2-(4- methylpiperazin-1- yl)ethoxy)phenyl)- 9-(3- chlorobenzyl)- 6-(1- methylcyclopropoxy)- 9H- purine
BDBM751305 US20250195530, Example E2 8-(2-chloro-4- (2-(4- methylpiperazin-1- yl)ethoxy)phenyl)- 9-(3- chlorobenzyl)- 6-(1- methylcyclopropoxy)- 9H- purine E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(2- fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 62 BDBM272126
E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(2- fluorophenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 62 BDBM272126 BDBM556745 1-(3-((2-tert-Butyl-4-chloro-5-methylphenoxy)methyl)-6,7-dihydro-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)ethanone US11352330, Example E2
BDBM556745 1-(3-((2-tert-Butyl-4-chloro-5-methylphenoxy)methyl)-6,7-dihydro-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-5(4H)-yl)ethanone US11352330, Example E2 US10065948, 75 BDBM272139 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2- methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide
US10065948, 75 BDBM272139 E2-(abs)-5-(3-Fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-2-(4-fluoro-2- methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide US10065948, 81 BDBM272145 E2-(abs)-5-(3-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-3- phenyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-cyclopenta[d]isothiazole-5- carboxamide US10457675, Example 81
US10065948, 81 BDBM272145 E2-(abs)-5-(3-fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-3- phenyl-5,6-dihydro-4H-cyclopenta[d]isothiazole-5- carboxamide US10457675, Example 81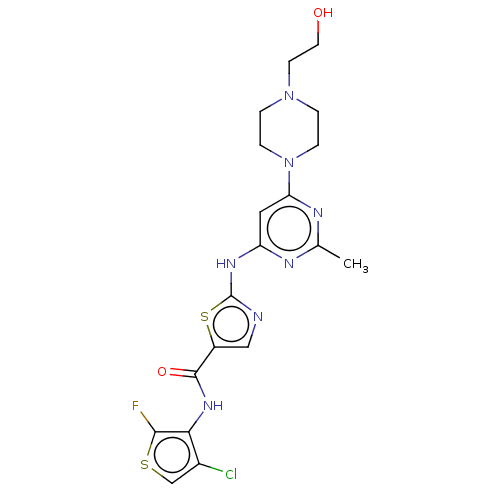 BDBM632967 N-(4-chloro-2-fluorothiophen-3-yl)-2- ((6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl)- 2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl)amino)thiazole- 5-carboxamide US20230348453, Compound E2
BDBM632967 N-(4-chloro-2-fluorothiophen-3-yl)-2- ((6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl)- 2-methylpyrimidin-4-yl)amino)thiazole- 5-carboxamide US20230348453, Compound E2 US10065948, 77 BDBM272141 E2-(abs)-2-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(3- fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide
US10065948, 77 BDBM272141 E2-(abs)-2-(1,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-(3- fluoro-2-methylphenyl)-N-hydroxy-5,6-dihydro-4H- cyclopenta[d]thiazole-5-carboxamide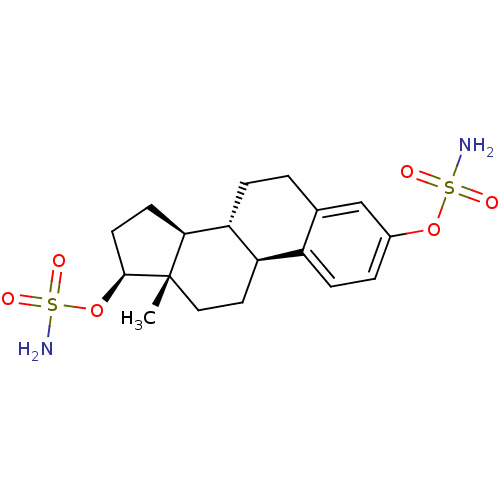 BDBM50159804 CHEMBL221802 estradiol 3,17-O,O-bis-sulfamate sulfamic acid (8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-3-sulfamoyloxy-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl ester
BDBM50159804 CHEMBL221802 estradiol 3,17-O,O-bis-sulfamate sulfamic acid (8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-3-sulfamoyloxy-7,8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-decahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl ester 2-((4-(7-(((2S,5R)-5-(Ethylsulfonamido)tetrahydro- 2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl)-2,7-diazaspiro[3.5]nonan-2- yl)pyrimidin-5-yl)oxy)-5-fluoro-N-((E2)-2- hydroxycyclobutyl)-N-isopropylbenzamide US11919901, Compound 257 BDBM656860
2-((4-(7-(((2S,5R)-5-(Ethylsulfonamido)tetrahydro- 2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl)-2,7-diazaspiro[3.5]nonan-2- yl)pyrimidin-5-yl)oxy)-5-fluoro-N-((E2)-2- hydroxycyclobutyl)-N-isopropylbenzamide US11919901, Compound 257 BDBM656860 [5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl 10-[(1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-5,14-dihydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-13-yl]decanoate BDBM17291 E2-adenosine hybrid compound, 9
[5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl 10-[(1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-5,14-dihydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-13-yl]decanoate BDBM17291 E2-adenosine hybrid compound, 9 [5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl 8-[(1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-5,14-dihydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-13-yl]octanoate E2-adenosine hybrid compound, 7 BDBM17288
[5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl 8-[(1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-5,14-dihydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-13-yl]octanoate E2-adenosine hybrid compound, 7 BDBM17288 [5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl 9-[(1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-5,14-dihydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-13-yl]nonanoate BDBM17290 EM-1745 E2-adenosine hybrid compound, 8 EM1745
[5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl 9-[(1S,10R,11S,14S,15S)-5,14-dihydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadeca-2,4,6-trien-13-yl]nonanoate BDBM17290 EM-1745 E2-adenosine hybrid compound, 8 EM1745 [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] acetate acetic acid [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] ester [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-3-oxidanyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] ethanoate BDBM62878 cid_6852404 MLS000069774 SMR000058696 17BETA-ESTRADIOL 17-ACETATE
[(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] acetate acetic acid [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-3-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] ester [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-3-oxidanyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl] ethanoate BDBM62878 cid_6852404 MLS000069774 SMR000058696 17BETA-ESTRADIOL 17-ACETATE cid_222757 MLS000028477 ESTRADIOL BENZOATE [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-17-oxidanyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] benzoate BDBM56905 SMR000058343 benzoic acid [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] ester [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] benzoate
cid_222757 MLS000028477 ESTRADIOL BENZOATE [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-methyl-17-oxidanyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] benzoate BDBM56905 SMR000058343 benzoic acid [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] ester [(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-13-methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] benzoate BDBM713106 US20250019387, Example 43 (Method 3-E2): 1-((1R,6S,7R)-3-(7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-3-azabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-7-yl)prop-2-en-1-one and 1-((1S,6R,7S)-3-(7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-3-azabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-7-yl)prop-2-en-1-one
BDBM713106 US20250019387, Example 43 (Method 3-E2): 1-((1R,6S,7R)-3-(7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-3-azabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-7-yl)prop-2-en-1-one and 1-((1S,6R,7S)-3-(7-(8-chloronaphthalen-1-yl)-2-(((S)-1-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methoxy)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-3-azabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-7-yl)prop-2-en-1-one